IDIOPATHIC OSTEOPOROSIS IN PREMENOPAUSAL WOMEN. Elizabeth Shane, M.D. Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons USA
|
|
|
- Ann Garrison
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IDIOPATHIC OSTEOPOROSIS IN PREMENOPAUSAL WOMEN Elizabeth Shane, M.D. Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons USA SIGNIFICANCE OF THE TOPIC Although idiopathic osteoporosis (IOP) in premenopausal women is rare, such patients often present challenges in diagnosis and management. LEARNING OBJECTIVES To understand the significance and causes of low BMD in premenopausal women To understand the microstructural, remodeling and bone material property characteristics of bone in women with IOP To understand the principles of management of osteoporosis in premenopausal women with secondary osteoporosis and IOP DIAGNOSIS AND ETIOLOGY OF OSTEOPOROSIS IN PREMENOPAUSAL WOMEN In postmenopausal women, osteoporosis is defined as a BMD of the spine, hip, or forearm more than 2.5 SD below the young adult mean (T-score -2.5), with or without the presence of a low trauma fracture; osteopenia refers to T scores between -1.0 and In premenopausal women, T scores should not be used to categorize BMD, the term osteopenia should not be used at all, and the term osteoporosis should be used judiciously. Z scores, which compare a young woman s BMD to the mean of an age-, gender-, and ethnicitymatched reference population, should be used instead of T scores to categorize BMD measurements. Based on the definition of a Z-score, which encompasses 95% of the normal population, 2.5% of premenopausal women will have a Z-score < 2.0. A Z score that is -2.0 should be designated low bone density or below expected for age. The term osteoporosis should be avoided in premenopausal women with isolated low BMD measurements, because the degree to which isolated low BMD measurements predict shortterm (5-10 year) fracture incidence in young women is unknown. In addition, the clinical significance of isolated low BMD measurements is uncertain. Some premenopausal women with small skeletons may appear to have low BMD, because DXA scanners cannot distinguish between small bones and less dense bones. Thin premenopausal women may have low BMD because their skeletons are adapted to carrying lower loads. They may also have low BMD because they have genetically determined low peak bone mass. It is generally assumed that such women have normal bone quality (normal trabecular and cortical volumetric BMD and microarchitecture and stiffness or strength), although there are no data to support this assumption. On the other hand, during adolescence, certain life style choices (excessive alcohol, tobacco exposure, low calcium intake, physical inactivity) or an underlying illness or exposure to certain medications (glucocorticoids, Depo-Provera) may interfere with peak bone mass acquisition. Such secondary causes of osteoporosis, which may also cause excessive bone loss after adolescence, may be associated with abnormal bone quality, although again there are few data. Lactation is associated with losses of 3-10% at the spine and hip over the first 3-6 months with recovery after weaning over the next months. Therefore, BMD measurements should not 1
2 performed for at least a year after pregnancy or lactation, during this period of transient loss and recovery. Routine BMD screening of premenopausal or perimenopausal women is not recommended unless there is a history of fragility fracture(s), or conditions or medications associated with low bone mass or bone loss (estrogen deficiency, glucocorticoids, etc). Premenopausal women with a low trauma fracture or Z score -2.0 should have a thorough history, physical examination and laboratory evaluation to identify potential secondary causes of bone loss, such as renal or liver disease, hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, Cushing s syndrome, early menopause, other disorders associated with estrogen deficiency, such as anorexia, celiac disease and other forms of malabsorption, idiopathic hypercalciuria, or connective tissue disorders. Table 1: Secondary causes of osteoporosis in premenopausal women Anorexia nervosa Gastrointestinal malabsorption (eg. celiac disease, postoperative states) Vitamin D and/or calcium deficiency Hyperthyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Cushing s syndrome Hypogonadism Hypercalciuria Rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions Alcoholism Renal Disease Liver disease Osteogenesis imperfecta Marfan s syndrome Homocystinuria Medications Glucocorticoids Immunosuppressants (cyclosporine) Antiseizure medications (particularly phenobarbital and phenytoin) GnRH agonists (when used to suppress ovulation) Heparin Cancer chemotherapy Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate Excess thyroid hormone Table 2. Guidelines for BMD Testing in Premenopausal Women History of fragility fracture Diseases or conditions associated with low bone mass or bone loss o Premenopausal estrogen deficiency (e.g., anorexia nervosa, hyperprolactinemia, prolonged amenorrhea) o Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease o Cystic fibrosis o Hyperparathyroidism o Rheumatoid arthritis o Inflammatory bowel disease 2
3 o Celiac disease Medications that cause bone loss o Glucocorticoids o Depot progesterone o GnRH agonists o Aromatase inhibitors o Antiepileptic drugs (phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate) If pharmacologic therapy of osteoporosis is being considered Being monitored for effectiveness of pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis IDIOPATHIC OSTEOPOROSIS IN PREMENOPAUSAL WOMEN Premenopausal women with no identifiable etiology after extensive evaluation for secondary causes are said to have idiopathic osteoporosis (IOP). Idiopathic osteoporosis primarily affects Caucasians, men and women equally. Presentation may occur during pregnancy or lactation. The mean age at diagnosis is in the mid-thirties. Fractures are usually multiple, occurring over a 5 to 10 year period. Abnormalities of osteoblast function and decreased IGF-1 have been found in some studies, but not others. In a recent bone biopsy study of women with IOP, both those with fractures and those with Z scores 2.0 but no fractures had evidence of low volumetric BMD of the hip and spine (by central QCT), distal radius and tibia (by high resolution peripheral QCT or HR-pQCT) and iliac crest bone biopsies (by microct). In addition, both groups had comparable microarchitectural disruption and reduced estimated strength (by finite element analysis or FEA). In addition, both groups of affected women had increased marrow fat (independent of bone volume fraction), reduced bone mineralization density distribution (BMDD by quantitative backscattered electron imaging) and abnormal bone matrix (by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy). Bone turnover was heterogeneous, but those in the lowest tertile of bone turnover had the most marked deficits in volumetric BMD, microarchitecture and strength. Serum IGF-1 was higher in the women in the lowest tertile of bone formation rate, suggesting that they may have IGF-1 resistance at the osteoblast level. There were virtually no differences between premenopausal women with IOP who had fractures and those with only low BMD. However, whether these women reflect the larger population of premenopausal women with low BMD is unknown and the lack of detectable differences may represent ascertainment bias, as women with a family history of osteoporosis or some other reason to suspect poor bone health may have been more likely to participate. MANAGEMENT There are no official guidelines for management of premenopausal women with low bone mass or osteoporosis. Lifestyle modifications should be encouraged for all women with low bone mass since peak bone mass may improve well into the fourth decade. The following should be encouraged: adequate calcium intake ( mg elemental calcium daily); adequate vitamin D intake ( IU vitamin D3 daily) or sufficient to maintain serum 25-OHD levels above ng/ml; regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercise; cessation of smoking; avoid excessive dieting and maintain normal body weight; avoid excess alcohol, caffeine and phosphorus containing drinks. A recent study of 16 premenopausal women with IOP treated only with increased dietary calcium and physical activity revealed small but significant increases in lumbar spine and femoral neck BMD after 2 or 3 years and no new fractures. When a secondary cause of osteoporosis is detected in premenopausal women, treatment should be targeted to that disease or abnormality. Examples of specific approaches that have been shown to lead to increases in BMD include: 3
4 Institution of a gluten-free diet in celiac disease Parathyroidectomy in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism Discontinuation of medroxyprogesterone acetate Oral contraceptives for women with oligo- or amenorrhea, on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) therapy with perimenopausal bone loss Pharmacologic therapy should be avoided unless the patient is losing bone or fracturing. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) such as raloxifene should not be used in menstruating women as they block estrogen action on bone, leading to further bone loss. Bisphosphonates carry a Category C rating for safety in pregnancy as they cross the placenta and accumulate in fetal bones in an experimental rat model. While they are probably safe, their long half-life in bone makes their use in reproductive age women a concern. In premenopausal women without fractures or known secondary causes for fractures, bisphosphonates are generally not indicated. Teriparatide has been shown to prevent bone loss in premenopausal women on GnRH agonists for endometriosis, to increase BMD in premenopausal women with GIOP, and with IOP. Teriparatide has the advantage of not being retained in the skeleton but whether its effects dissipate after cessation, as is seen in postmenopausal women or men, is unknown. Aggressive therapy with anti-osteoporosis agents may be necessary for women with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. However, the 2010 American College of Rheumatology guidelines do not recommend pharmacologic therapy for prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis patients under age 50, unless they have a history of spine or hip fracture and have taken or will be taking at least 7.5 mg of prednisone or equivalent daily for 90 days. Premenopausal women receiving chemotherapy for breast cancer represent another group at risk for rapid bone loss, primarily related to induction of premature menopause. Prospective studies demonstrate bone loss at 1 year of 4 8% in the spine and 2 4% at the hip in premenopausal women who become menopausal after receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Intravenous bisphosphonates prevent bone loss in premenopausal women with chemotherapyinduced amenorrhea. Premenopausal women with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) can be treated with either oral alendronate or intravenous pamidronate. In our recent pilot study of teriparatide in 21 premenopausal women with IOP, there were large and highly significant increases (~10%) in lumbar spine BMD, with smaller but also significant increases at the femoral neck and total hip, and no change at the radius. Teriparatide was also associated with marked improvements in trabecular volumetric BMD and microarchitecture and cortical thickness on iliac crest bone biopsies. About 20% of the women, however, did not respond (no change in BMD at any site). The nonresponsive women had markedly lower bone turnover at baseline, based on serum bone turnover markers and lower bone formation rate on iliac crest bone biopsies. They also had significantly These women also had smaller and delayed rises in serum P1NP and C-telopeptide during teriparatide therapy. We are currently beginning a new federally funded study of teriparatide in premenopausal women with IOP to confirm these preliminary observations and assess the mechanisms for the 4
5 lack of responsiveness in premenopausal women with low turnover IOP. We would welcome referrals to this study. To refer patients, please contact: Elizabeth Shane, MD at Adi Cohen, MD at Polly Young, MPH at SUGGESTED REFERENCES 1. Peris P, Guanabens N, Martinez de Osaba MJ, Monegal A, Alvarez L, Pons F, Ros I, Cerda D, Munoz-Gomez J 2002 Clinical characteristics and etiologic factors of premenopausal osteoporosis in a group of Spanish women. Semin Arthritis Rheum 32(1): Peris P, Monegal A, Martinez MA, Moll C, Pons F, Guanabens N 2007 Bone mineral density evolution in young premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis. Clin Rheumatol 26(6): Cohen A, Fleischer J, Freeby MJ, McMahon DJ, Irani D, Shane E. Clinical characteristics and medication use among premenopausal women with osteoporosis and low BMD: the experience of an osteoporosis referral center. J Womens Health (Larchmt), Jan-Feb; 18(1):79-84, 2009 PMID Cohen A, Liu XS, Stein EM, McMahon DJ, Rogers HF, LeMaster J, Recker RR, Lappe JM, Guo XE, Shane E. Bone Microarchitecture and stiffness in premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Nov; 94(11): , PMID: Cohen A, Recker RR, Lappe J, Dempster DW, Cremers S, McMahon DJ, Stein EM, Fleischer J, Rosen CJ, Rogers HF, Staron RB, LeMaster J, Shane E. Premenopausal women with idiopathic low trauma fractures and/or low bone mineral density. Osteoporos Int Mar 2. [Epub ahead of print] 6. Cohen A, Dempster DW, Recker RR, Zhou H, Wirth AJ, van Lenthe, GH, Kohler T, Müller R, Stein EM, Rosen CJ, Nickolas TL, Rogers HF, Staron RB, LeMaster J, Shane E. Abnormal bone microarchitecture and evidence of osteoblast dysfunction in premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab Oct;96(10): Epub 2011 Aug 10 5
Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment
 Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment Osteoporosis is a condition of decreased bone mass, leading to bone fragility and an increased susceptibility to fractures. While osteoporosis
Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment Osteoporosis is a condition of decreased bone mass, leading to bone fragility and an increased susceptibility to fractures. While osteoporosis
BULLETIN. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health
 BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis. Disclosure and Conflicts of Interest Steven T Harris MD 2014-2015
 Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis Steven T Harris MD FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco steve.harris@ucsf.edu Disclosure
Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis Steven T Harris MD FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco steve.harris@ucsf.edu Disclosure
Bone Basics National Osteoporosis Foundation 2013
 When you have osteoporosis, your bones become weak and are more likely to break (fracture). You can have osteoporosis without any symptoms. Because it can be prevented and treated, an early diagnosis is
When you have osteoporosis, your bones become weak and are more likely to break (fracture). You can have osteoporosis without any symptoms. Because it can be prevented and treated, an early diagnosis is
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES
 PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES Patients newly diagnosed as osteopenic or osteoporotic on a radiology report or patients receiving abnormal lab values on the following lab tests
PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES Patients newly diagnosed as osteopenic or osteoporotic on a radiology report or patients receiving abnormal lab values on the following lab tests
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis
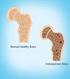 Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Bone Basics National Osteoporosis Foundation 2013
 Certain people are more likely to develop osteoporosis than others. While you have no control over some risk factors for osteoporosis, there are others you can change. By making healthier choices you can
Certain people are more likely to develop osteoporosis than others. While you have no control over some risk factors for osteoporosis, there are others you can change. By making healthier choices you can
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment. William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC
 Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment. Working Together For A Healthier Community
 Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment Working Together For A Healthier Community Osteoporosis The Silent Thief The Facts About Osteoporosis 1 in 2 women will develop osteoporosis
Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment Working Together For A Healthier Community Osteoporosis The Silent Thief The Facts About Osteoporosis 1 in 2 women will develop osteoporosis
Osteoporosis has been identified by the US Surgeon General
 New Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis E. Michael Lewiecki, MD, and Nelson B. Watts, MD Abstract: The World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX ) and the National
New Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis E. Michael Lewiecki, MD, and Nelson B. Watts, MD Abstract: The World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX ) and the National
Cystic fibrosis and bone health
 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Factsheet March 2013 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Introduction As we get older our bones become thinner and weaker, and may become more susceptible to fracture. However
Cystic fibrosis and bone health Factsheet March 2013 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Introduction As we get older our bones become thinner and weaker, and may become more susceptible to fracture. However
Scans and tests and osteoporosis
 Scans and tests and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Scans and tests and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
How To Choose A Biologic Drug
 North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
 BISPHOSPHONATE RELATED OSTEONECROSIS OF THE JAW (BRONJ) BISPHOSPHONATES AND WHAT HAPPENS TO BONE VINCENT E. DIFABIO, DDS, MS MEMBER OF THE COMMITTEE ON HEALTHCARE AND ADVOCACY FROM THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION
BISPHOSPHONATE RELATED OSTEONECROSIS OF THE JAW (BRONJ) BISPHOSPHONATES AND WHAT HAPPENS TO BONE VINCENT E. DIFABIO, DDS, MS MEMBER OF THE COMMITTEE ON HEALTHCARE AND ADVOCACY FROM THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION
Osteoporosis/Bone Health in Adults as a National Public Health Priority
 Position Statement Osteoporosis/Bone Health in Adults as a National Public Health Priority This Position Statement was developed as an educational tool based on the opinion of the authors. It is not a
Position Statement Osteoporosis/Bone Health in Adults as a National Public Health Priority This Position Statement was developed as an educational tool based on the opinion of the authors. It is not a
Osteoporosis. The inside looks like honeycomb, with blood vessels and bone marrow in the spaces between bone.
 Osteoporosis The bones in our skeleton are made of a thick outer shell and a strong inner mesh filled with collagen (protein), calcium salts and other minerals. Osteoporosis The inside looks like honeycomb,
Osteoporosis The bones in our skeleton are made of a thick outer shell and a strong inner mesh filled with collagen (protein), calcium salts and other minerals. Osteoporosis The inside looks like honeycomb,
Bone Densitometry. What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)?
 Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Osteoporosis. Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist. Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013
 Osteoporosis Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013 Plan What is osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Risk factors
Osteoporosis Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013 Plan What is osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Risk factors
DEFINITION OF OSTEOPOROSIS
 CHAPTER 27 OSTEOPOROSIS AND OSTEOMALACIA DEFINITION OF OSTEOPOROSIS THE EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CONSEQUENCES OF OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEW OF BONE REMODELING BONE LOSS PATHOGENESIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS
CHAPTER 27 OSTEOPOROSIS AND OSTEOMALACIA DEFINITION OF OSTEOPOROSIS THE EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CONSEQUENCES OF OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEW OF BONE REMODELING BONE LOSS PATHOGENESIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS
Osteoporosis and Arthritis: Two Common but Different Conditions
 and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health
 What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis The female athlete triad secondary osteoporosis Chronic Conditions Chronic digestive tract conditions
 Spring 2009 Newsletter # 23 Biannual Newsletter The Creighton University Osteoporosis Research Center Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis (Much of this content has been adapted from materials provided by
Spring 2009 Newsletter # 23 Biannual Newsletter The Creighton University Osteoporosis Research Center Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis (Much of this content has been adapted from materials provided by
Clinical Policy Guideline
 Clinical Policy Guideline Policy Title: Bone Density Testing Policy No: B0215A.00 Effective Date: 01/01/15 Date Reviewed: 03/25/15 I. DEFINITION/BACKGROUND Bone density testing is used to estimate the
Clinical Policy Guideline Policy Title: Bone Density Testing Policy No: B0215A.00 Effective Date: 01/01/15 Date Reviewed: 03/25/15 I. DEFINITION/BACKGROUND Bone density testing is used to estimate the
Osteoporosis. Am I at Risk?
 Osteoporosis Am I at Risk? TABLE OF CONTENTS What is osteoporosis?...1 Who gets osteoporosis?...2 How can I prevent osteoporosis?...3 How do I know if I have osteoporosis?...4 What is a bone mineral density
Osteoporosis Am I at Risk? TABLE OF CONTENTS What is osteoporosis?...1 Who gets osteoporosis?...2 How can I prevent osteoporosis?...3 How do I know if I have osteoporosis?...4 What is a bone mineral density
Osteoporosis Treatment Guide
 Osteoporosis Treatment Guide An estimated 10 million Americans have osteoporosis. Another 34 million have low bone mass. If left untreated, osteoporosis can be both debilitating and painful. Fortunately,
Osteoporosis Treatment Guide An estimated 10 million Americans have osteoporosis. Another 34 million have low bone mass. If left untreated, osteoporosis can be both debilitating and painful. Fortunately,
BONE HEALTH AND DISEASE. Bone Health and Disease Goals & Objectives
 Bone Health and Disease Goals & Objectives Course Description Bone Health and Disease is an online continuing education course for physical therapists and physical therapist assistants. This course presents
Bone Health and Disease Goals & Objectives Course Description Bone Health and Disease is an online continuing education course for physical therapists and physical therapist assistants. This course presents
Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis
 1 Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a disease where the strength of bones is less than normal, making them more susceptible to fracture, or breaking, than normal
1 Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a disease where the strength of bones is less than normal, making them more susceptible to fracture, or breaking, than normal
Consumer and Family Sciences
 Purdue Extension Consumer and Family Sciences Department of Foods and Nutrition CFS-150-W Osteoporosis: What You Should Know April C. Mason, Ph.D. William D. Evers, Ph.D., RD Erin E. Hanley, RD Osteoporosis,
Purdue Extension Consumer and Family Sciences Department of Foods and Nutrition CFS-150-W Osteoporosis: What You Should Know April C. Mason, Ph.D. William D. Evers, Ph.D., RD Erin E. Hanley, RD Osteoporosis,
OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM Tricia Orme, R.N. BSc(N) Mary Pack Arthritis Program Victoria i Arthritis i Centre Objectives Participants will gain an understanding of what Osteoporosis is and how
OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM Tricia Orme, R.N. BSc(N) Mary Pack Arthritis Program Victoria i Arthritis i Centre Objectives Participants will gain an understanding of what Osteoporosis is and how
Osteoporosis: key concepts. Azeez Farooki, MD Endocrinologist
 Osteoporosis: key concepts Azeez Farooki, MD Endocrinologist Outline I) Composition of bone II) Definition & pathophysiology of osteoporosis III) Peak bone mass IV) Secondary osteoporosis V) Vitamin D
Osteoporosis: key concepts Azeez Farooki, MD Endocrinologist Outline I) Composition of bone II) Definition & pathophysiology of osteoporosis III) Peak bone mass IV) Secondary osteoporosis V) Vitamin D
Osteoporosis. Drugs to prevent bone fractures in people with: Contents. 2: Our Recommendations. 3: Welcome. 6: Who Needs Drugs to Prevent Fractures?
 Drugs to prevent bone fractures in people with: Osteoporosis Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Contents 2: Our Recommendations 3: Welcome 6: Who Needs Drugs to Prevent Fractures? 8: Choosing a
Drugs to prevent bone fractures in people with: Osteoporosis Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Contents 2: Our Recommendations 3: Welcome 6: Who Needs Drugs to Prevent Fractures? 8: Choosing a
Clinician s Guide. to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Developed by the National Osteoporosis Foundation
 Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Developed by the National Osteoporosis Foundation Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Developed by the National Osteoporosis
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Developed by the National Osteoporosis Foundation Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Developed by the National Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis Medications
 Osteoporosis Medications When does a doctor prescribe osteoporosis medications? Healthcare providers look at several pieces of information before prescribing a bone- preserving or bone- building medication.
Osteoporosis Medications When does a doctor prescribe osteoporosis medications? Healthcare providers look at several pieces of information before prescribing a bone- preserving or bone- building medication.
Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis
 Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
PRACTICAL DENSITOMETRY
 PRACTICAL DENSITOMETRY The Challenge of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a silent disease that develops over decades Goal: identify patients with osteoporosis before fractures occur Means: measure bone density
PRACTICAL DENSITOMETRY The Challenge of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a silent disease that develops over decades Goal: identify patients with osteoporosis before fractures occur Means: measure bone density
Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
 BONE HEALTH FOR LIFE Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and
BONE HEALTH FOR LIFE Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and
A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis
 Indian Medical Gazette FEBRUARY 2012 67 Symposia Update A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis Shailendra Mohan Lakhotia, Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon, Kolkata 700 045. Prashant
Indian Medical Gazette FEBRUARY 2012 67 Symposia Update A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis Shailendra Mohan Lakhotia, Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon, Kolkata 700 045. Prashant
Bone Markers in Osteoporosis: Prediction of Fractures & Treatment Monitoring
 Bone Markers in Osteoporosis: Prediction of Fractures & Treatment Monitoring Richard Eastell, MD FRCP FRCPath FMedSci, Professor of Bone Metabolism, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK Usefulness of
Bone Markers in Osteoporosis: Prediction of Fractures & Treatment Monitoring Richard Eastell, MD FRCP FRCPath FMedSci, Professor of Bone Metabolism, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK Usefulness of
Treatment of osteoporosis in fragility fractures
 Orthogeriatrics Clinical Summary Document Treatment of osteoporosis in fragility fractures Fragility fractures are extremely prevalent in older adults with a staggering cost of treatment. As the population
Orthogeriatrics Clinical Summary Document Treatment of osteoporosis in fragility fractures Fragility fractures are extremely prevalent in older adults with a staggering cost of treatment. As the population
THE BURDEN OF OSTEOPOROSIS IN WEST VIRGINIA
 THE BURDEN OF OSTEOPOROSIS IN WEST VIRGINIA Bob Wise Governor Paul L. Nusbaum, Secretary Department of Health and Human Resources Chris Curtis, M.P.H. Acting Commissioner, Bureau for Public Health Catherine
THE BURDEN OF OSTEOPOROSIS IN WEST VIRGINIA Bob Wise Governor Paul L. Nusbaum, Secretary Department of Health and Human Resources Chris Curtis, M.P.H. Acting Commissioner, Bureau for Public Health Catherine
Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee
 Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee Guideline on Prescribing of Gonadorelin (GnRH) Analogues and Progesterone Receptor Modulators in treatment of Endometriosis or prior to Endometrial Ablation, or
Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee Guideline on Prescribing of Gonadorelin (GnRH) Analogues and Progesterone Receptor Modulators in treatment of Endometriosis or prior to Endometrial Ablation, or
Osteoporosis and you. Find out about the implications of osteoporosis and what you can do for your bone health
 Osteoporosis and you Find out about the implications of osteoporosis and what you can do for your bone health 2 What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis, which literally means porous bone, is a disease in which
Osteoporosis and you Find out about the implications of osteoporosis and what you can do for your bone health 2 What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis, which literally means porous bone, is a disease in which
Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones. A Guide for Women After Menopause
 Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones A Guide for Women After Menopause June 2008 fast facts Medicines for osteoporosis (OSS-tee-oh-puh-ROW-sis) can lower your chance of breaking a bone.
Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones A Guide for Women After Menopause June 2008 fast facts Medicines for osteoporosis (OSS-tee-oh-puh-ROW-sis) can lower your chance of breaking a bone.
Objectives. Osteoporosis a major public health threat. Bone-Up on Osteoporosis Update 2011
 Bone-Up on Osteoporosis Update 2011 3/30/11 Kristine Olson, MS, APN, FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner Mercer Bucks Hematology Oncology 1 Objectives Review risk factors and screening for osteoporosis. Describe
Bone-Up on Osteoporosis Update 2011 3/30/11 Kristine Olson, MS, APN, FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner Mercer Bucks Hematology Oncology 1 Objectives Review risk factors and screening for osteoporosis. Describe
AACE Guidelines. Copyright 2010 AACE.
 AACE Guidelines Nelson B. Watts, MD, FACP, MACE; John P. Bilezikian, MD, MACE; Pauline M. Camacho, MD, FACE; Susan L. Greenspan, MD, FACP, FACE; Steven T. Harris, MD, FACE; Stephen F. Hodgson, MD, FACP,
AACE Guidelines Nelson B. Watts, MD, FACP, MACE; John P. Bilezikian, MD, MACE; Pauline M. Camacho, MD, FACE; Susan L. Greenspan, MD, FACP, FACE; Steven T. Harris, MD, FACE; Stephen F. Hodgson, MD, FACP,
Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis
 Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily
Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily
Steroid-Induced Osteoporosis: First, Do No Harm. Karen E. Hansen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Rheumatology Section University of WI
 Steroid-Induced Osteoporosis: First, Do No Harm Karen E. Hansen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Rheumatology Section University of WI This CME program is sponsored by an unrestricted educational
Steroid-Induced Osteoporosis: First, Do No Harm Karen E. Hansen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Rheumatology Section University of WI This CME program is sponsored by an unrestricted educational
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT OF PRIMARY OSTEOPOROSIS
 European Medicines Agency London, 16 November 2006 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/552/95 Rev. 2 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT
European Medicines Agency London, 16 November 2006 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/552/95 Rev. 2 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT
2-1. Osteoporose. Dr. P. Van Wettere Radiologie en medische beeldvorming
 2-1 Osteoporose Dr. P. Van Wettere Radiologie en medische beeldvorming 2-2 Osteoporose Definitie Incidentie, mortaliteit, morbiditeit, kost Diagnose Radiologie Botdensitometrie FRAX FractureCascade History
2-1 Osteoporose Dr. P. Van Wettere Radiologie en medische beeldvorming 2-2 Osteoporose Definitie Incidentie, mortaliteit, morbiditeit, kost Diagnose Radiologie Botdensitometrie FRAX FractureCascade History
CPT 76977, 77078, 77079, 77080, 77081, 77083, or HCPCS G0130:
 Bone Mass Measurements Coverage Information Noridian Administrative Services (NAS), LLC, is providing coverage information regarding Bone Mass Measurements (BMM) in response to multiple provider inquiries.
Bone Mass Measurements Coverage Information Noridian Administrative Services (NAS), LLC, is providing coverage information regarding Bone Mass Measurements (BMM) in response to multiple provider inquiries.
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS
 16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
Drug-Induced Osteoporosis
 Drug-Induced Osteoporosis By Susan K. Bowles, Pharm.D., MSc, FCCP Reviewed by Mary Beth O Connell, Pharm.D., FCCP, FASHP, BCPS; and Michelle M. Richardson, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS Learning Objectives 1. Apply
Drug-Induced Osteoporosis By Susan K. Bowles, Pharm.D., MSc, FCCP Reviewed by Mary Beth O Connell, Pharm.D., FCCP, FASHP, BCPS; and Michelle M. Richardson, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS Learning Objectives 1. Apply
CMAJ JAMC. 2002 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada
 CANADIAN M EDICAL A SSOCIATION J OURNAL J OURNAL DE L ASSOCIATION MÉDICALE CANADIENNE CMAJ JAMC 2002 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada CMAJ 2002;167(10
CANADIAN M EDICAL A SSOCIATION J OURNAL J OURNAL DE L ASSOCIATION MÉDICALE CANADIENNE CMAJ JAMC 2002 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada CMAJ 2002;167(10
Vitamin D. Sources of vitamin D
 1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
Recent Topics in Treatment of Osteoporosis
 Review Article Recent Topics in Treatment of Osteoporosis JMAJ 49(9 10): 309 314, 2006 Satoshi Soen* 1 Abstract It has come to light that osteoporosis-related fractures are more critical than previously
Review Article Recent Topics in Treatment of Osteoporosis JMAJ 49(9 10): 309 314, 2006 Satoshi Soen* 1 Abstract It has come to light that osteoporosis-related fractures are more critical than previously
Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis
 Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
The Diagnosis and Workup of Patients for Osteoporosis or Osteopenia (Low Bone Mass)
 The Diagnosis and Workup of Patients for Osteoporosis or Osteopenia (Low Bone Mass) 6 Frank Bonura St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Smithtown, NY USA 1. Introduction The rate of screening and treatment
The Diagnosis and Workup of Patients for Osteoporosis or Osteopenia (Low Bone Mass) 6 Frank Bonura St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Smithtown, NY USA 1. Introduction The rate of screening and treatment
Margaret French, Specialist Nurse, Fracture Liaison Service Glasgow Royal Infirmary Rachel Lewis Rheumatology Specialist Physiotherapist, North
 Margaret French, Specialist Nurse, Fracture Liaison Service Glasgow Royal Infirmary Rachel Lewis Rheumatology Specialist Physiotherapist, North Bristol NHS Trust Very informal workshop to facilitate discussion
Margaret French, Specialist Nurse, Fracture Liaison Service Glasgow Royal Infirmary Rachel Lewis Rheumatology Specialist Physiotherapist, North Bristol NHS Trust Very informal workshop to facilitate discussion
POSITION STATEMENT Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: 2006 position statement of The North American Menopause Society
 Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 340-367 DOI: 10.1097/01.gme.0000222475.93345.b3 * 2006 by The North American Menopause Society 5 Text printed on acid-free
Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 340-367 DOI: 10.1097/01.gme.0000222475.93345.b3 * 2006 by The North American Menopause Society 5 Text printed on acid-free
Healthy Aging Lab: Current Research Abstracts
 Healthy Aging Lab: Current Research Abstracts Arsenic Exposure and Women s Health Environmental exposure to inorganic arsenic is an indisputable source of increased risk of several human cancers and chronic
Healthy Aging Lab: Current Research Abstracts Arsenic Exposure and Women s Health Environmental exposure to inorganic arsenic is an indisputable source of increased risk of several human cancers and chronic
Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
 Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women Version 1.0 Ratified by: East Sussex HEMC Date ratified: 26.01.2011 Job title of originator/author Gillian Ells, East Sussex HEMC Pharmacist
Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women Version 1.0 Ratified by: East Sussex HEMC Date ratified: 26.01.2011 Job title of originator/author Gillian Ells, East Sussex HEMC Pharmacist
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Professor Department of Medicine & Therapeutics The Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Understanding osteoporosis in rheumatic diseases beyond bone density - bone quality and strength Lai-Shan Tam, MD Professor Department of Medicine & Therapeutics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Objective
Understanding osteoporosis in rheumatic diseases beyond bone density - bone quality and strength Lai-Shan Tam, MD Professor Department of Medicine & Therapeutics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Objective
Osteoporosis Clinical guideline for prevention and treatment
 Osteoporosis Clinical guideline for prevention and treatment Executive Summary Updated November 2014 National Osteoporosis Guideline Group on behalf of the Bone Research Society, British Geriatrics Society,
Osteoporosis Clinical guideline for prevention and treatment Executive Summary Updated November 2014 National Osteoporosis Guideline Group on behalf of the Bone Research Society, British Geriatrics Society,
Osteoporosis Overview
 Osteoporosis Overview National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Phone: 202 223 0344 Toll free: 800 624 BONE TTY:
Osteoporosis Overview National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Phone: 202 223 0344 Toll free: 800 624 BONE TTY:
Bone Mineral Density Studies
 Bone Mineral Density Studies Policy Number: 6.01.01 Last Review: 5/2015 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 5/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for bone
Bone Mineral Density Studies Policy Number: 6.01.01 Last Review: 5/2015 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 5/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for bone
American College of Rheumatology 2010 Recommendations for the Prevention and Treatment of
 merican ollege of Rheumatology 2 Recommendations for the Prevention and Treatment of G L U O O R T I O I D - I N D U E D O S T E O P O R O S I S L I N I I N S G U I D E The objective of this guide is to
merican ollege of Rheumatology 2 Recommendations for the Prevention and Treatment of G L U O O R T I O I D - I N D U E D O S T E O P O R O S I S L I N I I N S G U I D E The objective of this guide is to
Hormones and Healthy Bones
 Hormones and Healthy Bones Helping Midlife Women Make Better Choices for a Healthy Future 1 Hormones and Healthy Bones helps midlife women make better choices for a healthy future. Midlife women are the
Hormones and Healthy Bones Helping Midlife Women Make Better Choices for a Healthy Future 1 Hormones and Healthy Bones helps midlife women make better choices for a healthy future. Midlife women are the
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis in Canada: Background and Technical Report
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis in Canada: Background and Technical Report Authors: Alexandra Papaioannou MD MSc 1, Suzanne Morin MD MSc 2, Angela M. Cheung
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis in Canada: Background and Technical Report Authors: Alexandra Papaioannou MD MSc 1, Suzanne Morin MD MSc 2, Angela M. Cheung
SIGN 142 Management of osteoporosis and the prevention of fragility fractures. A national clinical guideline March 2015. Evidence
 SIGN 142 Management of osteoporosis and the prevention of fragility fractures A national clinical guideline March 2015 Evidence KEY TO EVIDENCE STATEMENTS AND ECOMMENDATIONS LEVELS OF EVIDENCE High-quality
SIGN 142 Management of osteoporosis and the prevention of fragility fractures A national clinical guideline March 2015 Evidence KEY TO EVIDENCE STATEMENTS AND ECOMMENDATIONS LEVELS OF EVIDENCE High-quality
Facts About Aging and Bone Health
 Facts About Aging and Bone Health A Guide to Better Understanding and Well Being with the compliments of Division of Health Services Diocese of Camden Exercise as treatment Along with medication, proper
Facts About Aging and Bone Health A Guide to Better Understanding and Well Being with the compliments of Division of Health Services Diocese of Camden Exercise as treatment Along with medication, proper
Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and older men
 Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and older men February 2010 Approved by NHMRC on 5 February 2010 The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners,
Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and older men February 2010 Approved by NHMRC on 5 February 2010 The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners,
Go to Table of Contents. The Man s Guide. to Osteoporosis. National Osteoporosis Foundation
 Go to Table of Contents The Man s Guide to Osteoporosis National Osteoporosis Foundation Contents Introduction... 2 Chapter 1: Start with bone healthy behaviors... 3 Get the calcium and vitamin D you need
Go to Table of Contents The Man s Guide to Osteoporosis National Osteoporosis Foundation Contents Introduction... 2 Chapter 1: Start with bone healthy behaviors... 3 Get the calcium and vitamin D you need
Improving and Measuring Osteoporosis Management
 Improving and Measuring Osteoporosis Management Normal Bone Bone with Osteoporosis National Pharmaceutical Council 2008 by The Joint Commission. All rights reserved. This monograph may be reproduced in
Improving and Measuring Osteoporosis Management Normal Bone Bone with Osteoporosis National Pharmaceutical Council 2008 by The Joint Commission. All rights reserved. This monograph may be reproduced in
Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER
 Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER 80% of children and adults with FA have an endocrine abnormality Endocrine cells make a hormone (message) Carried in bloodstream
Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER 80% of children and adults with FA have an endocrine abnormality Endocrine cells make a hormone (message) Carried in bloodstream
Calcium. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nuf40101 Last reviewed: 02/19/2013 1
 Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Prevention of Osteoporosis
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: osteoporosis Prevention of Osteoporosis Key reviewers: Professor Ian Reid, Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, University of Auckland Dr Rebecca Grainger, Rheumatologist and
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: osteoporosis Prevention of Osteoporosis Key reviewers: Professor Ian Reid, Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, University of Auckland Dr Rebecca Grainger, Rheumatologist and
SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product)
 PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis
 Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bones. It occurs when the struts which make up the mesh like structure within bones become thin, causing bones
Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bones. It occurs when the struts which make up the mesh like structure within bones become thin, causing bones
The menopausal transition usually has three parts:
 The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
Smoking and Age of Menopause. Women who smoke experience menopause an average of 2 years earlier than women who do not smoke.
 Menopause Menopause Feared event To many, it indicates old age - a sign of life coming to a close. Many expect a difficult psychological adjustment to menopause (bad press, bad jokes). Menopause Effect
Menopause Menopause Feared event To many, it indicates old age - a sign of life coming to a close. Many expect a difficult psychological adjustment to menopause (bad press, bad jokes). Menopause Effect
OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis
 Basingstoke, Southampton and Winchester District Prescribing Committee OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis Frail, increased fall risk + housebound
Basingstoke, Southampton and Winchester District Prescribing Committee OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis Frail, increased fall risk + housebound
Vitamin D, Parathyroid Hormone, and Bone Mineral Density Status in Kidney Transplant Recipients
 Transplantation Vitamin D, arathyroid Hormone, and Bone Mineral Density Status in Kidney Transplant Recipients Shokoufeh Savaj, Farinaz J Ghods Firoozgar Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences,
Transplantation Vitamin D, arathyroid Hormone, and Bone Mineral Density Status in Kidney Transplant Recipients Shokoufeh Savaj, Farinaz J Ghods Firoozgar Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences,
How To Take A Bone Marrow Transplant
 Drug treatments to protect your bones This information is an extract from the booklet, Bone health. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Bisphosphonates
Drug treatments to protect your bones This information is an extract from the booklet, Bone health. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Bisphosphonates
Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
Osteoporosis Medicines and Jaw Problems
 Osteoporosis Medicines and Jaw Problems J. Michael Digney, D.D.S. Osteoporosis is a condition that affects over 10 million patients in this country, with the majority of those being post-menopausal women.
Osteoporosis Medicines and Jaw Problems J. Michael Digney, D.D.S. Osteoporosis is a condition that affects over 10 million patients in this country, with the majority of those being post-menopausal women.
Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management
 Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management Disclosures: Although various guidelines and studies were reviewed, this represents my own personal bias and conclusions. What do we know? 1) Fractures
Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management Disclosures: Although various guidelines and studies were reviewed, this represents my own personal bias and conclusions. What do we know? 1) Fractures
OsteOpOrOsis Guidelines
 OsteOpOrOsis Guidelines FOr health professionals [these are not actors] OsteOpOrOsis Guidelines FOr health professionals The Irish Osteoporosis Society wish to acknowledge the support of an unrestricted
OsteOpOrOsis Guidelines FOr health professionals [these are not actors] OsteOpOrOsis Guidelines FOr health professionals The Irish Osteoporosis Society wish to acknowledge the support of an unrestricted
RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS)
 Page 1 Initial REMS Approval: July 2009 Most Recent Modification: August 2013 NDA 21-318 FORTEO (teriparatide) (rdna origin) Injection RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS) Eli Lilly and Company
Page 1 Initial REMS Approval: July 2009 Most Recent Modification: August 2013 NDA 21-318 FORTEO (teriparatide) (rdna origin) Injection RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS) Eli Lilly and Company
European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
 Osteoporos Int (2008) 19:399 428 DOI 10.1007/s00198-008-0560-z POSITION PAPER European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women J. A. Kanis & N. Burlet & C. Cooper
Osteoporos Int (2008) 19:399 428 DOI 10.1007/s00198-008-0560-z POSITION PAPER European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women J. A. Kanis & N. Burlet & C. Cooper
25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker
 DIABETES 25 OH Vitamin D TOTAL Assay 25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Vitamin D Receptors Brain Heart Breast Colon Pancreas Prostate
DIABETES 25 OH Vitamin D TOTAL Assay 25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Vitamin D Receptors Brain Heart Breast Colon Pancreas Prostate
What is the Menopause?
 What is the Menopause? This information is also available on request in other formats by phoning 01387 241053. Information leaflet Produced by Dr H Currie & Sr. K Martin May 2005 Checked 2013 Review 2015
What is the Menopause? This information is also available on request in other formats by phoning 01387 241053. Information leaflet Produced by Dr H Currie & Sr. K Martin May 2005 Checked 2013 Review 2015
European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
 DOI 10.1007/s00198-012-2074-y POSITION PAPER European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women J. A. Kanis & E. V. McCloskey & H. Johansson & C. Cooper & R. Rizzoli
DOI 10.1007/s00198-012-2074-y POSITION PAPER European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women J. A. Kanis & E. V. McCloskey & H. Johansson & C. Cooper & R. Rizzoli
D. Vitamin D. 1. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3
 D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
Female Athlete Triad. Dr. Willa Fornetti, DO, MS Primary Care Sports Medicine The Kennedy Center At Mercy Medical Center Oshkosh, Wisconsin
 Female Athlete Triad Dr. Willa Fornetti, DO, MS Primary Care Sports Medicine The Kennedy Center At Mercy Medical Center Oshkosh, Wisconsin Female Athlete Triad I have no disclosures. I do not have any
Female Athlete Triad Dr. Willa Fornetti, DO, MS Primary Care Sports Medicine The Kennedy Center At Mercy Medical Center Oshkosh, Wisconsin Female Athlete Triad I have no disclosures. I do not have any
BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader. Two years ago, I was working as a bedside nurse. One of my colleagues felt
 Ali A. Kader, S. (2010). Breast cancer awareness for women and men. UCQ Nursing Journal of Academic Writing, Winter 2010, 70 76. BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader Two years
Ali A. Kader, S. (2010). Breast cancer awareness for women and men. UCQ Nursing Journal of Academic Writing, Winter 2010, 70 76. BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader Two years
Presented by: Nicole Nisly, MD
 Presented by: Nicole Nisly, MD About Today s Presentation I will discuss osteoporosis and focus on causes, treatment op;ons and preven;on I will discuss medica;ons and life style choices that can be of
Presented by: Nicole Nisly, MD About Today s Presentation I will discuss osteoporosis and focus on causes, treatment op;ons and preven;on I will discuss medica;ons and life style choices that can be of
