5.6 - How to Test for Chirality: Planes of Symmetry - A molecule will not be chiral if it possess a plane of symmetry
|
|
|
- Dominic Parks
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Andrew Rosen Chapter 5 - Stereochemistry Chirality and Stereochemistry - Chiral objects are those that can exist in right and left handed forms - If the mirror image of an object can be superposed onto itself then it is considered achiral Isomerism: Constitutional Isomers and Stereoisomers - Isomers are dierent compounds that have the same molecular formula - Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but dierent connectivity - Stereoisomers have their atoms connected in the same sequence, but they dier in the arrangement of their atoms in space (eg: cis and trans isomers) - Enantiomers are stereoisomers whose molecules are nonsuperposable mirror images of each other (optical isomers) - Diastereomers are stereoisomers whose molecules are not mirror images of each other. - To create a diastereomer given the structure of one molecule simply change a dashed wedge to a solid wedge 1, or vice versa without it creating a mirror image or do a cis-trans swap Enantiomers and Chiral Molecules - A chiral molecule is one that is not superposable on its mirror image (therefore, all enantiomers are pairs of chiral molecules) A Single Chirality Center Causes a Molecule to be Chiral - Even though tetrahedral molecules cannot have geometric isomers, they can, however, be chiral if all four atoms attached to the tetrahedron are dierent. Such molecules are said to have chirality centers - The presence of a single chirality center makes a molecule chiral, but having more than one (or zero) chirality centers does not guarantee this - Interchanging any two groups of the chirality center of an enantiometer converts it into the other - Any atom at which an interchange of groups produces a stereoisomer is called a stereogenic center - Enantiomers do not interconvert spontaneously (need large amounts of energy) - A chirality center is a type of stereogenic center, but not all stereogenic centers are chirality centers - MIT 5.512: A stereogenic center is an element where the interchange of two substituents will lead to a stereoisomer. A chiral center is a specic type of stereogenic center where reection of the molecule results in a non-superposable mirror image More about the Biological Importance of Chirality - Some binding sites are specic for specic enantiomers and not both How to Test for Chirality: Planes of Symmetry - A molecule will not be chiral if it possess a plane of symmetry 1 Remember solid and dashed wedges are drawn on the same side of the carbon atom 1
2 5.7 - Naming Enantiomers: The R, S-System priority or preference of a, b, c, or atomic number of the atom that is directly attached to the - Each of the four groups attached to the chirality center is assigned a d. Priority is assigned rst on the basis of the chirality center. The group with the highest atomic number gets the highest priority and vice versa - When a priority cannot be assigned on the basis of atomic number of the atoms, then the next set of atoms in the unassigned groups is examined. This process is continued until a decision can be made at the rst point of di erence Step 2: Step 1: - We now rotate the structure so that the group with the lowest priority is directed away from the viewer. That is, priority number 4 should be made into a dashed wedge if it's not already - Next, trace a path from a to b to c. If, as we do this, the direction of the path is clockwise, the enantiomer is designated with an R. If the direction is counterclockwise, the enantiomer is designated with an S Example: - For compounds containing at least one π bond, another rule is needed. Groups containing double or triple bonds are assigned priorities as if both atoms were duplicated or triplicated, which a ects the priority: Note: There is a trick. The trick is this: If the 4th atom is a dash, then just analyze if it's clockwise or counterclockwise. If the 4th atom is not a dash, then interchange the dashed atom with the 4th atom. Now analyze this intermediate molecule to see if it's clockwise or counterclockwise to see if it's R or S. When doing this, if the intermediate is R then the original is S and vice versa Properties of Enantiomers: Optical Activity - Enantiomers have identical properties for many physical traits such as boiling point, solubility, infrared spectra, etc. when comparing the S enantiomer with the R enantiomer - Mixtures of enantiomers have di erent physical properties when compared to a solution of just an isolated sample - When a beam of plane-polarized light passes through an enantiomer, the plane of polarization rotates - Separate enantiomers rotate the plane of polarized light in equal amounts but in opposite directions and are optically active compounds - Chiral molecules are optically active (not the same as having a chirality center) 2
3 - A polarizer makes light waves oscillate in only one plane, which is known as plane-polarized light - A substance that rotates plane-polarized light in the clockwise (+) direction is said to be dextrorotatory - A substance that rotates plane-polarized light in the counterclockwise (-) directions is said to be levorotatory - Specic rotation is the number of degrees that the plane of polarization is rotated as the light passes through a solution of an enantiomer - The specic rotation, [α], is given by [α] = α, where [α] is the specic rotation, α is the observed rotation, c l c is the concentration of the solution in g/ml, and l is the length of the cell in decimeters - Specic rotation is dependent on temperature and wavelength - There is no correlation between R and S enantiomers and + or - specic rotation - Enantiomers swap R with S congurations and vice versa The Origin of Optical Activity - Two counterrotating circularly-polarized beams travel with dierent velocities through chiral medium - A racemic mixture is one that has an equimolar mixture of two enantiomers - A racemic mixture, indicated with a ±, causes no net rotation of plane-polarized light - An enantiomerically pure sample is one that consists of a single enantiomer (also said to have an enantiomeric excess of 100%) moles of one enantiomer moles of other enantiomer - Equation: % Enantiomeric Excess = 100% total moles of both enantiomers observed specic rotation - Equation: % Enantiomeric Excess = specic rotation of pure enantiomer 100% The Synthesis of Chiral Molecules - Reactions carried out with achiral reactants can create a chiral molecule, but the resultant mixture is racemic. This is not the case if there is/are chiral molecule(s) and/or chiral inuences like chiral enzymes/catalysts or chiral solvent - Stereoselective reactions are reactions that lead to a preferential formation of one stereoisomer over other stereoisomers - If a reaction produces one enantiomer over its mirror image, the reaction is said to be enantioselective - If a reaction leads to one diastereomer over others that are possible, it is said to be diastereoselective - A kinetic resolution is where the rate of a reaction with one enantiomer is dierent than with the other Molecules with More than One Chirality Center - In compounds whose stereoisomerism is due to chirality centers, the total number of stereoisomers will not exceed 2 n, where n is the number of chirality centers - Diastereoisomers have dierent physical properties, unlike enantiomers - A meso compound is an achiral molecule that contains chirality centers and are not optically active since they are not chiral - To quickly determine if a molecule is a meso compound, check to see if it has a plane of symmetry and/or if its mirror image is identical to the original. A meso compound can also exist if it has a center of inversion 2 - If a molecule has two chirality centers, make all wedges planar. Then, if there is internal symmetry it is achiral and meso - To name a molecule with more than one chirality centers, locants must be used to describe whether each chirality center is R or S (eg: (2R,3R)-2,3-dibromobutane) 2 A center of inversion can be seen if everything can be inverted around the center to regenerate the same thing 3
4 Chiral Drugs - Medicinal drugs can be given as racemic mixtures or as pure, isolated, individual enantiomers - A drug's eect will be stronger if it has just one of the enantiomers Stereoisomerism of Cyclic Compounds 3 - A cyclic molecule can have an enantiomer that is apparent after a ring ip, but they might not be able to be separated because of rapid interconversion. Therefore, they represent dierent conformations of the same compound known as conformational stereoisomers (conformers) Relating Congurations through Reactions in which No Bonds to the Chirality Center Are Broken - If a reaction takes place in a way so that no bonds to the chirality center are broken, the product will have the same general conguration of groups (same relative position) around the chirality center as the reactant. This is a reaction that proceeds with retention of conguration - Chirality centers in dierent molecules have the same relative conguration if they share three groups in common and if these groups with the central carbon can be superposed - The absolute conguration of a chirality center is its R or S designation Separation of Enantiomers: Resolution - Louis Pasteur found that an organic compound gave chiral crystals of + and - optical activity. He physically separated the chiral crystals using a magnifying glass. This is the Pasteur method, but it is not used frequently because not all organic compounds give chiral crystals - When a racemic mixture reacts with a single enantiomer of another compound, a mixture of diastereoisomers results, and diastereoisomers, because they have dierent physical properties, can be separated by conventional means (eg: diastereomeric recrystallization) - Resolution by enzymes, whereby an enzyme selectively converts one enantiomer in a racemic mixture to another compound, after which the unreacted enantiomer and the new compoud are separated is another method Compounds with Chirality Centers other than Carbon - Elements in the same group as carbon can form tetrahedral compounds and thus can have chirality centers if all four groups connected to the central atom are dierent Chiral Molecules that do not Possess a Chirality Center - Conformational isomers that are stable, isolable compounds are known as atropisomers (from such large rotational barriers between conformers) - Allenes are compounds that exhibit stereoisomerism due to the geometry of the π bond (not cis-trans but still chiral with dierent substituents on the end of the carbon atom) General Allene: 3 Note: Fischer Projections are skipped 4
5 Confusion Managed: - The main thing is to recognize that there is a dierence between rotation around an axis and reection over an axis. Reection over an x or y axis isn't going to change the solid or dashed wedge nature of that atoms in 3-space, but a rotation around that axis will! - Sometimes it might be necessary to check to see if a pair of potential enantiomers are the same by rotating one of them over the y axis and then the x axis (double rotation) - When given a chair structure, draw out the planar hexagon form, but make sure the orientation is correct - The conguration (R or S) is unique to each individual molecule, hence the 2 n formula for permutations - With rings, cis and trans describe the solid/dashed wedges of atoms, but this is dierent with regular double bonded hydrocarbons! Double bonded hydrocarbons do not have tetrahedral geometries for the carbon atoms attached to the double bond; it is (trigonal) planar. As a result, Understand these Examples: 4 4 Credit to Stony Brook University CHE 327 PowerPoint slides 5
Isomers Have same molecular formula, but different structures
 Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Molecule Projections
 Key Definitions ü Stereochemistry refers to the chemistry in 3 dimensions (greek stereos = solid). This science was created by Pasteur (1860), van Hoff et LeBel (1874). ü Stereisomers are isomeric molecules
Key Definitions ü Stereochemistry refers to the chemistry in 3 dimensions (greek stereos = solid). This science was created by Pasteur (1860), van Hoff et LeBel (1874). ü Stereisomers are isomeric molecules
IR Applied to Isomer Analysis
 DiscovIR-LC TM Application Note 025 April 2008 Deposition and Detection System IR Applied to Isomer Analysis Infrared spectra provide valuable information about local configurations of atoms in molecules.
DiscovIR-LC TM Application Note 025 April 2008 Deposition and Detection System IR Applied to Isomer Analysis Infrared spectra provide valuable information about local configurations of atoms in molecules.
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 (adapted from Blackburn et al., Laboratory Manual to Accompany World of hemistry, 2 nd ed., (1996) Saunders ollege Publishing: Fort Worth) Purpose: To become familiar with organic molecules in three dimensions
(adapted from Blackburn et al., Laboratory Manual to Accompany World of hemistry, 2 nd ed., (1996) Saunders ollege Publishing: Fort Worth) Purpose: To become familiar with organic molecules in three dimensions
Alkanes. Chapter 1.1
 Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Stereochemistry Tutorial: Drawing Enantiomers and Diastereomers
 tereochemistry Tutorial: Drawing Enantiomers and Diastereomers Definitions for vocabulary words can be found in the Illustrated Glossary of rganic Chemistry, available on the course web site. A. Discussion
tereochemistry Tutorial: Drawing Enantiomers and Diastereomers Definitions for vocabulary words can be found in the Illustrated Glossary of rganic Chemistry, available on the course web site. A. Discussion
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
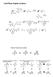 Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fischer Projections revisited C C C Remember that group rotations are always allowed C C 80 rotations of entire molecule are allowed C 80 C 90 rotations of entire molecule
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fischer Projections revisited C C C Remember that group rotations are always allowed C C 80 rotations of entire molecule are allowed C 80 C 90 rotations of entire molecule
Conjugation is broken completely by the introduction of saturated (sp3) carbon:
 Chapter 16 Conjugation, resonance, and dienes Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. A common conjugated system involves 1,3-dienes, such as 1,3-butadiene.
Chapter 16 Conjugation, resonance, and dienes Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. A common conjugated system involves 1,3-dienes, such as 1,3-butadiene.
The Synthesis of trans-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) Chloride
 CHEM 122L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 The Synthesis of trans-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) Chloride To learn about Coordination Compounds and Complex Ions. To learn about Isomerism.
CHEM 122L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 The Synthesis of trans-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) Chloride To learn about Coordination Compounds and Complex Ions. To learn about Isomerism.
CHEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) Page 1
 CEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) B) C) D) Page 1 2. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide? A) B) C) D)
CEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) B) C) D) Page 1 2. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide? A) B) C) D)
On Factoring Chirality and Stereoisomerism
 Topics in Stereochemisty, Volume 14 Edited by Ernest L. Eliel, Norman L. Allinger, Samuel H. Wilen Copyright 1983 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. On Factoring Chirality and Stereoisomerism HANS HIRSCHMANN Department
Topics in Stereochemisty, Volume 14 Edited by Ernest L. Eliel, Norman L. Allinger, Samuel H. Wilen Copyright 1983 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. On Factoring Chirality and Stereoisomerism HANS HIRSCHMANN Department
Dr.B.R.AMBEDKAR OPEN UNVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE M.Sc. I year -CHEMISTRY (2013-14) Course I: Inorganic Chemistry
 M.Sc. I year -CHEMISTRY (2013-14) Course I: Inorganic Chemistry Maximum Marks 15 Minimum Marks - 06 Section A 1X10=10 Answer any One question from the following Two questions a. What is symmetry operation?
M.Sc. I year -CHEMISTRY (2013-14) Course I: Inorganic Chemistry Maximum Marks 15 Minimum Marks - 06 Section A 1X10=10 Answer any One question from the following Two questions a. What is symmetry operation?
Absolute Structure Absolute Configuration
 Absolute Structure Absolute Configuration Some definitions Absolute Configuration -> spatial arrangement of the atoms for a chiral molecule (R/S, P/M or D/L assignment). Absolute Structure -> spatial arrangement
Absolute Structure Absolute Configuration Some definitions Absolute Configuration -> spatial arrangement of the atoms for a chiral molecule (R/S, P/M or D/L assignment). Absolute Structure -> spatial arrangement
Chemistry 1110 Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
 hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations
 Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations SHORT ANSWER Exhibit 11-1 Circle your response in each set below. 1. Circle the least
Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations SHORT ANSWER Exhibit 11-1 Circle your response in each set below. 1. Circle the least
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display
 Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Determination of Molecular Structure by MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY
 Determination of Molecular Structure by MOLEULAR SPETROSOPY hemistry 3 B.Z. Shakhashiri Fall 29 Much of what we know about molecular structure has been learned by observing and analyzing how electromagnetic
Determination of Molecular Structure by MOLEULAR SPETROSOPY hemistry 3 B.Z. Shakhashiri Fall 29 Much of what we know about molecular structure has been learned by observing and analyzing how electromagnetic
Sugar Identification using Polarimetry
 Sugar Identification using Polarimetry Safety Concerns: No special safety precautions need to be implemented. Standard organic laboratory safety measures need to be in place. Purpose The purpose of this
Sugar Identification using Polarimetry Safety Concerns: No special safety precautions need to be implemented. Standard organic laboratory safety measures need to be in place. Purpose The purpose of this
Chapter 15 Radical Reactions. Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by
 Chapter 15 Radical Reactions Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond; a radical contains an atom that does not have an octet of electrons,
Chapter 15 Radical Reactions Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond; a radical contains an atom that does not have an octet of electrons,
Molecular Geometry and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland Community College for the use of this experiment.
 Molecular and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland ommunity ollege for the use of this experiment. Objectives To construct molecular models for covalently bonded atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions
Molecular and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland ommunity ollege for the use of this experiment. Objectives To construct molecular models for covalently bonded atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions
Properties of a molecule. Absolute configuration, Cahn-Ingold Prelog. Planar, axial, topological chirality and chirality at atoms other than carbon
 Key stereochemical terminology Stereochemical terminology in organic chemistry can refer to structure of a molecule or to properties of a physical sample of the molecule. It is very important to recognize
Key stereochemical terminology Stereochemical terminology in organic chemistry can refer to structure of a molecule or to properties of a physical sample of the molecule. It is very important to recognize
Part B 2. Allow a total of 15 credits for this part. The student must answer all questions in this part.
 Part B 2 Allow a total of 15 credits for this part. The student must answer all questions in this part. 51 [1] Allow 1 credit for 3 Mg(s) N 2 (g) Mg 3 N 2 (s). Allow credit even if the coefficient 1 is
Part B 2 Allow a total of 15 credits for this part. The student must answer all questions in this part. 51 [1] Allow 1 credit for 3 Mg(s) N 2 (g) Mg 3 N 2 (s). Allow credit even if the coefficient 1 is
PRACTICE PROBLEMS, CHAPTERS 1-3
 PRATIE PRBLEMS, APTERS 1-3 (overed from h. 3: Alkane and Alkyl alide nomenclature only) 1. The atomic number of boron is 5. The correct electronic configuration of boron is: A. 1s 2 2s 3 B. 1s 2 2p 3.
PRATIE PRBLEMS, APTERS 1-3 (overed from h. 3: Alkane and Alkyl alide nomenclature only) 1. The atomic number of boron is 5. The correct electronic configuration of boron is: A. 1s 2 2s 3 B. 1s 2 2p 3.
A pure covalent bond is an equal sharing of shared electron pair(s) in a bond. A polar covalent bond is an unequal sharing.
 CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
Current Staff Course Unit/ Length. Basic Outline/ Structure. Unit Objectives/ Big Ideas. Properties of Waves A simple wave has a PH: Sound and Light
 Current Staff Course Unit/ Length August August September September October Unit Objectives/ Big Ideas Basic Outline/ Structure PS4- Types of Waves Because light can travel through space, it cannot be
Current Staff Course Unit/ Length August August September September October Unit Objectives/ Big Ideas Basic Outline/ Structure PS4- Types of Waves Because light can travel through space, it cannot be
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson
 Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
Chem 11 Oa-Section 2. Exam #2. 1 October 2004
 " Chem 11 Oa-Section 2 Exam #2 1 October 2004 Name: K~ Instructions Please read each question carefully and answer it completely and clearly. Do the problems in the order that is easiest for you. Point
" Chem 11 Oa-Section 2 Exam #2 1 October 2004 Name: K~ Instructions Please read each question carefully and answer it completely and clearly. Do the problems in the order that is easiest for you. Point
2.4 Enantiomeric Isomers
 2.4 Enantiomeric Isomers There is an additional type of isomer that can exist when we have an atom with 4 different groups attached to that atom in tetrahedral geometry. Consider a methane molecule with
2.4 Enantiomeric Isomers There is an additional type of isomer that can exist when we have an atom with 4 different groups attached to that atom in tetrahedral geometry. Consider a methane molecule with
Chemical reactions allow living things to grow, develop, reproduce, and adapt.
 Section 2: Chemical reactions allow living things to grow, develop, reproduce, and adapt. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the parts of a chemical reaction?
Section 2: Chemical reactions allow living things to grow, develop, reproduce, and adapt. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the parts of a chemical reaction?
VSEPR Model. The Valence-Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model. Predicting Molecular Geometry
 VSEPR Model The structure around a given atom is determined principally by minimizing electron pair repulsions. The Valence-Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model The valence-shell electron pair repulsion
VSEPR Model The structure around a given atom is determined principally by minimizing electron pair repulsions. The Valence-Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model The valence-shell electron pair repulsion
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
CHAPTER 10 THE SHAPES OF MOLECULES
 ATER 10 TE AE MLEULE 10.1 To be the central atom in a compound, the atom must be able to simultaneously bond to at least two other atoms. e,, and cannot serve as central atoms in a Lewis structure. elium
ATER 10 TE AE MLEULE 10.1 To be the central atom in a compound, the atom must be able to simultaneously bond to at least two other atoms. e,, and cannot serve as central atoms in a Lewis structure. elium
experiment5 Understanding and applying the concept of limiting reagents. Learning how to perform a vacuum filtration.
 81 experiment5 LECTURE AND LAB SKILLS EMPHASIZED Synthesizing an organic substance. Understanding and applying the concept of limiting reagents. Determining percent yield. Learning how to perform a vacuum
81 experiment5 LECTURE AND LAB SKILLS EMPHASIZED Synthesizing an organic substance. Understanding and applying the concept of limiting reagents. Determining percent yield. Learning how to perform a vacuum
C has 4 valence electrons, O has six electrons. The total number of electrons is 4 + 2(6) = 16.
 129 Lewis Structures G. N. Lewis hypothesized that electron pair bonds between unlike elements in the second (and sometimes the third) row occurred in a way that electrons were shared such that each element
129 Lewis Structures G. N. Lewis hypothesized that electron pair bonds between unlike elements in the second (and sometimes the third) row occurred in a way that electrons were shared such that each element
CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami. Tel: (618)545-3361. Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu. Web: www.kc.cc.il.
 CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami Tel: (618)545-3361 Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu Web: www.kc.cc.il.us/ngoswami CHEM 208 COURSE SYLLABUS KASKASKIA COLLEGE NAME TERM YEAR TEXT:
CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami Tel: (618)545-3361 Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu Web: www.kc.cc.il.us/ngoswami CHEM 208 COURSE SYLLABUS KASKASKIA COLLEGE NAME TERM YEAR TEXT:
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols
 F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Concept Check 10.1 An atom in a molecule is surrounded by four pairs of electrons, one lone pair and three bonding pairs. Describe how the four
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Concept Check 10.1 An atom in a molecule is surrounded by four pairs of electrons, one lone pair and three bonding pairs. Describe how the four
AP CHEMISTRY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP CHEMISTRY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 6 6. Answer each of the following in terms of principles of molecular behavior and chemical concepts. (a) The structures for glucose, C 6 H 12 O 6, and cyclohexane,
AP CHEMISTRY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 6 6. Answer each of the following in terms of principles of molecular behavior and chemical concepts. (a) The structures for glucose, C 6 H 12 O 6, and cyclohexane,
Draft agreed by the QWP February 2015. Draft adopted by the CHMP for release for consultation March 2015. Draft endorsed by the CMD(h) March 2015
 1 2 3 26 March 2015 EMA/CHMP/QWP/104223/2015 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) 4 5 6 7 Reflection paper on the chemical structure and properties criteria to be considered for the evaluation
1 2 3 26 March 2015 EMA/CHMP/QWP/104223/2015 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) 4 5 6 7 Reflection paper on the chemical structure and properties criteria to be considered for the evaluation
LMB Crystallography Course, 2013. Crystals, Symmetry and Space Groups Andrew Leslie
 LMB Crystallography Course, 2013 Crystals, Symmetry and Space Groups Andrew Leslie Many of the slides were kindly provided by Erhard Hohenester (Imperial College), several other illustrations are from
LMB Crystallography Course, 2013 Crystals, Symmetry and Space Groups Andrew Leslie Many of the slides were kindly provided by Erhard Hohenester (Imperial College), several other illustrations are from
Introduction to Chemistry. Course Description
 CHM 1025 & CHM 1025L Introduction to Chemistry Course Description CHM 1025 Introduction to Chemistry (3) P CHM 1025L Introduction to Chemistry Laboratory (1) P This introductory course is intended to introduce
CHM 1025 & CHM 1025L Introduction to Chemistry Course Description CHM 1025 Introduction to Chemistry (3) P CHM 1025L Introduction to Chemistry Laboratory (1) P This introductory course is intended to introduce
the double or triple bond. If the multiple bond is CH 3 C CCHCCH 3
 Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic ompounds Alkenes and Alkynes Unsaturated contain carbon-carbon double and triple bond to which more hydrogen atoms can be added. Alkenes: carbon-carbon double bonds Alkynes:
Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic ompounds Alkenes and Alkynes Unsaturated contain carbon-carbon double and triple bond to which more hydrogen atoms can be added. Alkenes: carbon-carbon double bonds Alkynes:
Final Examination, Organic Chemistry 1 (CHEM 2210) December 2000 Version *A* A. B. C. D.
 Final Examination, rganic hemistry 1 (EM 2210) December 2000 Version *A* 1. What are the hybridization of, and the geometrical shape around, the nitrogen atom in the following molecule? N 3 3 A. sp, linear
Final Examination, rganic hemistry 1 (EM 2210) December 2000 Version *A* 1. What are the hybridization of, and the geometrical shape around, the nitrogen atom in the following molecule? N 3 3 A. sp, linear
17.2 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS
 17. REACTINS INVLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS 793 As Eq. 17. shows, the products derived from the reaction of water at the ring carbons are not formed. The reason is that these products are not aromatic
17. REACTINS INVLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS 793 As Eq. 17. shows, the products derived from the reaction of water at the ring carbons are not formed. The reason is that these products are not aromatic
Draft agreed by the QWP February 2015. Draft adopted by the CHMP for release for consultation March 2015. Draft endorsed by the CMD(h) March 2015
 17 December 2015 EMA/CHMP/QWP/104223/2015 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Reflection paper on the chemical structure and properties criteria to be considered for the evaluation of
17 December 2015 EMA/CHMP/QWP/104223/2015 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Reflection paper on the chemical structure and properties criteria to be considered for the evaluation of
cyclohexane cyclopentane Nomenclature Follows same rules as for stright-chain alkanes. Examples: name the following
 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Reading: Wade chapter 3, sections 3-10- 3-16 Study Problems: 3-43, 3-44, 3-45, 3-46 Key oncepts and Skills: ompare the energies of cycloalkanes, and explain ring
Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Reading: Wade chapter 3, sections 3-10- 3-16 Study Problems: 3-43, 3-44, 3-45, 3-46 Key oncepts and Skills: ompare the energies of cycloalkanes, and explain ring
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2
 Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
 Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
2/10/2011. Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain. Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain. 4.3 Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain
 4.3 Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain Angle strain The strain induced in a molecule when bond angles are forced to deviate from the ideal 109º tetrahedral value (Adolf von Baeyer 1885) Stability of
4.3 Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain Angle strain The strain induced in a molecule when bond angles are forced to deviate from the ideal 109º tetrahedral value (Adolf von Baeyer 1885) Stability of
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts
 AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
3/5/2014. iclicker Participation Question: A. MgS < AlP < NaCl B. MgS < NaCl < AlP C. NaCl < AlP < MgS D. NaCl < MgS < AlP
 Today: Ionic Bonding vs. Covalent Bonding Strengths of Covalent Bonds: Bond Energy Diagrams Bond Polarities: Nonpolar Covalent vs. Polar Covalent vs. Ionic Electronegativity Differences Dipole Moments
Today: Ionic Bonding vs. Covalent Bonding Strengths of Covalent Bonds: Bond Energy Diagrams Bond Polarities: Nonpolar Covalent vs. Polar Covalent vs. Ionic Electronegativity Differences Dipole Moments
5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules
 5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules What you will accomplish in this experiment This experiment will give you an opportunity to draw Lewis structures of covalent compounds, then use those
5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules What you will accomplish in this experiment This experiment will give you an opportunity to draw Lewis structures of covalent compounds, then use those
Organic Chemistry Calculations
 Organic Chemistry Calculations There are three basic units for measurement in the organic laboratory mass, volume, and number, measured in moles. Most of the other types of measurements are combinations
Organic Chemistry Calculations There are three basic units for measurement in the organic laboratory mass, volume, and number, measured in moles. Most of the other types of measurements are combinations
: : Solutions to Additional Bonding Problems
 Solutions to Additional Bonding Problems 1 1. For the following examples, the valence electron count is placed in parentheses after the empirical formula and only the resonance structures that satisfy
Solutions to Additional Bonding Problems 1 1. For the following examples, the valence electron count is placed in parentheses after the empirical formula and only the resonance structures that satisfy
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 81 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e.g. carbonates (CO 3 2- ), carbon dioxide
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 81 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e.g. carbonates (CO 3 2- ), carbon dioxide
Performing Calculatons
 Performing Calculatons There are three basic units for measurement in the organic laboratory mass, volume, and number, measured in moles. Most of the other types of measurements are combinations of them,
Performing Calculatons There are three basic units for measurement in the organic laboratory mass, volume, and number, measured in moles. Most of the other types of measurements are combinations of them,
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
 Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Page 1. 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? (1) 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? (1) (2) (2) (3) (3) (4) (4)
 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391)
 NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
CHAPTER 10 THE SHAPES OF MOLECULES
 ATER 10 TE AE MLEULE EMIAL ETI BED READIG RBLEM B10.1 lan: Examine the Lewis structure, noting the number of regions of electron density around the carbon and nitrogen atoms in the two resonance structures.
ATER 10 TE AE MLEULE EMIAL ETI BED READIG RBLEM B10.1 lan: Examine the Lewis structure, noting the number of regions of electron density around the carbon and nitrogen atoms in the two resonance structures.
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models
 EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3
 DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3 Standard Enthalpy Change Standard Enthalpy Change for a reaction, symbolized as H 0 298, is defined as The enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants
DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3 Standard Enthalpy Change Standard Enthalpy Change for a reaction, symbolized as H 0 298, is defined as The enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants
11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry
 Copyright ç 1996 Richard Hochstim. All rights reserved. Terms of use.» 37 11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the study of heat, and how heat can be interconverted into other energy
Copyright ç 1996 Richard Hochstim. All rights reserved. Terms of use.» 37 11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the study of heat, and how heat can be interconverted into other energy
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Chem 1: Chapter 10 Page 1 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory I) VSEPR Model Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Model A) Model predicts Predicts electron arrangement and molecular
Chem 1: Chapter 10 Page 1 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory I) VSEPR Model Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Model A) Model predicts Predicts electron arrangement and molecular
Enantiomers: Synthesis, characterization, and resolution of tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) chloride Introduction:
 Enantiomers: Synthesis, characterization, and resolution of tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) chloride Introduction: The development of coordination chemistry prior to 1950 involved the synthesis and characterization
Enantiomers: Synthesis, characterization, and resolution of tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) chloride Introduction: The development of coordination chemistry prior to 1950 involved the synthesis and characterization
Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound
 Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound The analysis of the outcome of a reaction requires that we know the full structure of the products as well as the reactants In the 19 th and early 20 th
Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound The analysis of the outcome of a reaction requires that we know the full structure of the products as well as the reactants In the 19 th and early 20 th
STANDARD ANSWERS AND DEFINITIONS
 Evidence for Kekule s model to be wrong: STANDARD ANSWERS AND DEFINITIONS All C-C bond lengths are the same length, between C-C and C=C. Only reacts with Br2 with a halogen carrier Benzene is lower in
Evidence for Kekule s model to be wrong: STANDARD ANSWERS AND DEFINITIONS All C-C bond lengths are the same length, between C-C and C=C. Only reacts with Br2 with a halogen carrier Benzene is lower in
Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil
 Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil Textbook and Materials What you must buy: Organic Chemistry 4 th Ed. Janice G. Smith, McGraw Hill. (Older edition is fine) Chem
Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil Textbook and Materials What you must buy: Organic Chemistry 4 th Ed. Janice G. Smith, McGraw Hill. (Older edition is fine) Chem
Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Stereochemistry of Alkanes and ycloalkanes onformation of ethane: Rotation is possible around - Different arrangements of atoms that can be converted into one another by rotation about single bonds are
Stereochemistry of Alkanes and ycloalkanes onformation of ethane: Rotation is possible around - Different arrangements of atoms that can be converted into one another by rotation about single bonds are
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: States of Matter In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. The kinetic-molecular
Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: States of Matter In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. The kinetic-molecular
The Fundamentals of Infrared Spectroscopy. Joe Van Gompel, PhD
 TN-100 The Fundamentals of Infrared Spectroscopy The Principles of Infrared Spectroscopy Joe Van Gompel, PhD Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter. The electromagnetic
TN-100 The Fundamentals of Infrared Spectroscopy The Principles of Infrared Spectroscopy Joe Van Gompel, PhD Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter. The electromagnetic
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility
 Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
The Mole Concept. The Mole. Masses of molecules
 The Mole Concept Ron Robertson r2 c:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 final slides for web\mole concept.docx The Mole The mole is a unit of measurement equal to 6.022 x 10 23 things (to 4 sf) just like there
The Mole Concept Ron Robertson r2 c:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 final slides for web\mole concept.docx The Mole The mole is a unit of measurement equal to 6.022 x 10 23 things (to 4 sf) just like there
Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics 1
 Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Some Important Topics First Law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy U ( or E) Enthalpy H Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S Third law of Thermodynamics Absolute Entropy
Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Some Important Topics First Law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy U ( or E) Enthalpy H Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S Third law of Thermodynamics Absolute Entropy
Chemistry 151 Final Exam
 Chemistry 151 Final Exam Name: SSN: Exam Rules & Guidelines Show your work. No credit will be given for an answer unless your work is shown. Indicate your answer with a box or a circle. All paperwork must
Chemistry 151 Final Exam Name: SSN: Exam Rules & Guidelines Show your work. No credit will be given for an answer unless your work is shown. Indicate your answer with a box or a circle. All paperwork must
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE C A R B O H Y D R A T E S, L I P I D S, P R O T E I N S, A N D N U C L E I C A C I D S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 115, Page 1 of 29) Carbon
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE C A R B O H Y D R A T E S, L I P I D S, P R O T E I N S, A N D N U C L E I C A C I D S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 115, Page 1 of 29) Carbon
CHAPTER 10: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES: THE UNIQUENESS OF WATER Problems: 10.2, 10.6,10.15-10.33, 10.35-10.40, 10.56-10.60, 10.101-10.
 CHAPTER 10: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES: THE UNIQUENESS OF WATER Problems: 10.2, 10.6,10.15-10.33, 10.35-10.40, 10.56-10.60, 10.101-10.102 10.1 INTERACTIONS BETWEEN IONS Ion-ion Interactions and Lattice Energy
CHAPTER 10: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES: THE UNIQUENESS OF WATER Problems: 10.2, 10.6,10.15-10.33, 10.35-10.40, 10.56-10.60, 10.101-10.102 10.1 INTERACTIONS BETWEEN IONS Ion-ion Interactions and Lattice Energy
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT
 EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
2. Atoms with very similar electronegativity values are expected to form
 AP hemistry Practice Test #6 hapter 8 and 9 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect? a. Ionic bonding results from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. b. Dipole moments result
AP hemistry Practice Test #6 hapter 8 and 9 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect? a. Ionic bonding results from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. b. Dipole moments result
Chemistry 105, Chapter 7 Exercises
 hemistry 15, hapter 7 Exercises Types of Bonds 1. Using the periodic table classify the bonds in the following compounds as ionic or covalent. If covalent, classify the bond as polar or not. Mg2 4 i2 a(3)2
hemistry 15, hapter 7 Exercises Types of Bonds 1. Using the periodic table classify the bonds in the following compounds as ionic or covalent. If covalent, classify the bond as polar or not. Mg2 4 i2 a(3)2
States of Matter CHAPTER 10 REVIEW SECTION 1. Name Date Class. Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 10 REVIEW States of Matter SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. ideal gas
CHAPTER 10 REVIEW States of Matter SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. ideal gas
Experiment 8: Chemical Moles: Converting Baking Soda to Table Salt
 Experiment 8: Chemical Moles: Converting Baking Soda to Table Salt What is the purpose of this lab? We want to develop a model that shows in a simple way the relationship between the amounts of reactants
Experiment 8: Chemical Moles: Converting Baking Soda to Table Salt What is the purpose of this lab? We want to develop a model that shows in a simple way the relationship between the amounts of reactants
1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule?
 Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2210, rganic Chem I 1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule? A. sp 3 B. sp 2 C. sp D. not hybridized 2. Name the functional groups in
Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2210, rganic Chem I 1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule? A. sp 3 B. sp 2 C. sp D. not hybridized 2. Name the functional groups in
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11. PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2
 MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
A. Essentially the order of Pt II affinity for these ligands (their Lewis basicity or nucleophilicity)
 (c) Entering Ligand Effects 284 The second order rate constant k 2 in square planar complexes in the rate law below that we just discussed is strongly dependent on the nature of Y, the entering ligand
(c) Entering Ligand Effects 284 The second order rate constant k 2 in square planar complexes in the rate law below that we just discussed is strongly dependent on the nature of Y, the entering ligand
The Unshifted Atom-A Simpler Method of Deriving Vibrational Modes of Molecular Symmetries
 Est. 1984 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-020 X CODEN: OJCHEG 2012, Vol. 28, No. (1): Pg. 189-202 The Unshifted
Est. 1984 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-020 X CODEN: OJCHEG 2012, Vol. 28, No. (1): Pg. 189-202 The Unshifted
The K value enumeration of hydrocarbons alkanes, alkenes and alkynes
 Oriental Journal of Chemistry Vol. 24(3), 795-800 (2008) The K value enumeration of hydrocarbons alkanes, alkenes and alkynes E.M.R. KIREMIRE Department of Chemistry, University of Namibia, Private Bag
Oriental Journal of Chemistry Vol. 24(3), 795-800 (2008) The K value enumeration of hydrocarbons alkanes, alkenes and alkynes E.M.R. KIREMIRE Department of Chemistry, University of Namibia, Private Bag
Carbon-Carbon bonds: Hybridization
 Carbon-Carbon bonds: Hybridization Abstract: Gina 05/05/11 Molecular binding behavior has a large inuence on the structure of a material and their properties. As a exclusion, carbon bind themself not in
Carbon-Carbon bonds: Hybridization Abstract: Gina 05/05/11 Molecular binding behavior has a large inuence on the structure of a material and their properties. As a exclusion, carbon bind themself not in
Chemical Reactions in Water Ron Robertson
 Chemical Reactions in Water Ron Robertson r2 f:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\waterchemtrans.doc Properties of Compounds in Water Electrolytes and nonelectrolytes Water soluble compounds
Chemical Reactions in Water Ron Robertson r2 f:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\waterchemtrans.doc Properties of Compounds in Water Electrolytes and nonelectrolytes Water soluble compounds
7.14 Linear triatomic: A-----B-----C. Bond angles = 180 degrees. Trigonal planar: Bond angles = 120 degrees. B < B A B = 120
 APTER SEVEN Molecular Geometry 7.13 Molecular geometry may be defined as the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. The study of molecular geometry is important in that a molecule s geometry
APTER SEVEN Molecular Geometry 7.13 Molecular geometry may be defined as the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. The study of molecular geometry is important in that a molecule s geometry
EXPERIMENT 9 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan - Cherif Synthesis of Aspirin - Esterification
 EXPERIMENT 9 (rganic hemistry II) Pahlavan - herif Materials Hot plate 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask Melting point capillaries Melting point apparatus Büchner funnel 400-mL beaker Stirring rod hemicals Salicylic
EXPERIMENT 9 (rganic hemistry II) Pahlavan - herif Materials Hot plate 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask Melting point capillaries Melting point apparatus Büchner funnel 400-mL beaker Stirring rod hemicals Salicylic
Indiana's Academic Standards 2010 ICP Indiana's Academic Standards 2016 ICP. map) that describe the relationship acceleration, velocity and distance.
 .1.1 Measure the motion of objects to understand.1.1 Develop graphical, the relationships among distance, velocity and mathematical, and pictorial acceleration. Develop deeper understanding through representations
.1.1 Measure the motion of objects to understand.1.1 Develop graphical, the relationships among distance, velocity and mathematical, and pictorial acceleration. Develop deeper understanding through representations
Electrophilic Addition Reactions
 Electrophilic Addition Reactions Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reactions that allow the interconversion of C=C and C C into a range of important functional groups. Conceptually,
Electrophilic Addition Reactions Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reactions that allow the interconversion of C=C and C C into a range of important functional groups. Conceptually,
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies
 Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the following ionic compounds in order of increasing lattice energy: NaF, CsI, and CaO. Analyze: From the formulas
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the following ionic compounds in order of increasing lattice energy: NaF, CsI, and CaO. Analyze: From the formulas
Study the following diagrams of the States of Matter. Label the names of the Changes of State between the different states.
 Describe the strength of attractive forces between particles. Describe the amount of space between particles. Can the particles in this state be compressed? Do the particles in this state have a definite
Describe the strength of attractive forces between particles. Describe the amount of space between particles. Can the particles in this state be compressed? Do the particles in this state have a definite
Chemical Bonds. Chemical Bonds. The Nature of Molecules. Energy and Metabolism < < Covalent bonds form when atoms share 2 or more valence electrons.
 The Nature of Molecules Chapter 2 Energy and Metabolism Chapter 6 Chemical Bonds Molecules are groups of atoms held together in a stable association. Compounds are molecules containing more than one type
The Nature of Molecules Chapter 2 Energy and Metabolism Chapter 6 Chemical Bonds Molecules are groups of atoms held together in a stable association. Compounds are molecules containing more than one type
Chapter 13 Spectroscopy NMR, IR, MS, UV-Vis
 Chapter 13 Spectroscopy NMR, IR, MS, UV-Vis Main points of the chapter 1. Hydrogen Nuclear Magnetic Resonance a. Splitting or coupling (what s next to what) b. Chemical shifts (what type is it) c. Integration
Chapter 13 Spectroscopy NMR, IR, MS, UV-Vis Main points of the chapter 1. Hydrogen Nuclear Magnetic Resonance a. Splitting or coupling (what s next to what) b. Chemical shifts (what type is it) c. Integration
