Kelly McDonald, Ph.D. 1/09. Activity 1 Build Your Own Protein Adapted from 3-D Molecular Designs Student Handout 1
|
|
|
- Daniel Johns
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction: Activity 1 Build Your Own Protein Adapted from 3-D Molecular Designs Student Handout 1 Amino Acids the Building Blocks of Proteins Amino acids are small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. They are often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins. The sequence of amino acids in a protein, and hence the protein function, are determined by the genetic code, defined by the sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA determines the amino acid sequence of a protein (definition adapted from National Human Genome Research Institute.). There are 20 amino acids and each one consists of two parts a backbone and a sidechain. The backbone, shown in the figure to the left, is the same in all 20 amino acids, and the sidechain is different in each one. Each sidechain consists of a unique combination of atoms, which determine the side chain s 3-D shape and its chemical properties. Figure (above) from Campbell and Reece, 8 th ed, 2008 When different amino acids join together to make a protein, the unique properties of each amino acid determine how the protein folds into its final 3-D shape. The shape of the protein allows it to perform a specific function in our cells. There are four levels of structure that describe a protein as it folds, as shown in the diagram below: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Figure (right) from
2 Learning Objectives: You will explore how the unique chemical properties of the 20 amino acids determine the final shape of a protein. Specifically, You will be able to identify amino acids according to their chemical properties and create a short polypeptide of 15 amino acids (the primary structure). You will be able to fold your polypeptide into a 3-D shape (the tertiary structure) while satisfying the chemical properties of all of the amino acid sidechains. **Note: A protein generally folds into its secondary structure (of alpha helices and betasheets) prior to assuming its tertiary structure. For the purpose of this activity, you will skip the secondary structure folding. Activity Instructions: 1. Check the kit to make sure that you have each of the following: a. Chemical properties circle b. Amino acid chart c. Mini-toober (foam covered wire) with a blue capped end and red capped end and 15 U-shaped metal clips spaced 3 in apart d. 21 foam amino acid sidechain models with magnets and blue, red, yellow and green dots e. Hydrogen bond connectors 2. Place each foam amino acid sidechain on the magnetic Chemical Properties Circle according to its chemical properties. You will need to consult the Amino Acid Sidechain List. Be sure to look at the colored dots (which represent different atoms) to help you distinguish between similar sidechains) see step #3 below a. Hydrophobic sidechains are yellow b. Hydrophilic sidechains are white c. Acidic sidechains are red d. Basic sidechains are blue e. Cysteine sidechains are green 3. Note the colored dots on the grey side of the amino acid sidechains. These represent different atoms. a. Carbon is gray b. Oxygen is red c. Nitrogen is blue d. Hydrogen is white e. Sulfur is yellow
3 Observations: A. Hydrophobic sidechains are composed primarily of which atoms? What does the term hydrophobic tell you about the chemical properties of these side chains and their respective amino acids? B. Acidic sidechains contain two atoms. This is called a carboxylic acid functional group. Draw a carboxylic acid functional group in the space below. C. Basic sidechains contain atoms. This is called an amino functional group. Draw an amino functional group in the space below. D. Hydrophilic sidechains have various combinations of which atoms? What does the term hydrophilic tell you about the chemical properties of these side chains and their respective amino acids? Predictions: What causes proteins to fold into their 3-D shapes? A. Which sidechains (e.g., hydrophobic, hydrophilic, acidic, basic) might position themselves on the interior of a protein, where they are shielded from water? B. Which sidechains (e.g., hydrophobic, hydrophilic, acidic, basic) might be attracted to one another? Give and example of two amino acids that might form an ionic bond. C. Would the final shape of a protein be a high energy or low energy state for the atoms in the structure? Why?
4 Activity Instructions, Continued: 4. Select the following sidechains from your chemical properties circle (15 total): a. 1 Methionine b. 6 hydrophobic (non-polar) sidechains c. 2 acidic sidechains d. 2 basic sidechains e. 2 Cysteine sidechains f. 2 additional hydrophilic (polar) sidechains 5. Place the Methionine on the metal clip of your mini-toober closest to the Blue End Cap (called the N-terminus). Mix the other sidechains together and place them in any order (randomly) on the 14 remaining metal clips of your minitoober. The sequence of your amino acid sidechains on the mini-toober is called the Primary Structure of your protein. As a general rule, the final shape of a protein is determined by its primary structure. a. What amino acids define the primary structure of your protein (give the single letter abbreviation of your protein from the N-terminal to the C- terminal)? b. Why do we call the beginning of the protein the N-terminus and the end of the protein the C-terminus (hint: look at the functional groups on the backbone of each amino acid)? 6. Now you will fold your 15-amino acid protein according to the chemical properties of the sidechains. Remember that all of the chemical properties affect the protein at the same time. a. Start by folding your protein so that all of the hydrophobic, nonpolar sidechains are buried on the inside of your protein, where they will be hidden from polar water molecules. b. Next, fold your proteins so the acidic and basic (charged) sidechains are on the outside surface of the protein and pair one negative sidechain with one positive sidechain so that they come within one inch, thereby neutralizing each other. c. Continue to fold your protein making sure that your hydrophilic, polar sidechains are also on the outside surface of your protein where they can hydrogen bond with water. d. Last, fold your protein so that the two Cysteine sidechains are positioned opposite each other on the inside of the protein where they can form a
5 disulfide bond that helps stabilize your protein. Disulfide bonds are covalent bonds that form between the sulfur groups of cysteines, thus stabilizing the tertiary shape. Note: As you continue to fold your protein, applying each new property on the list, you will probably find that some of the sidechains you previously positioned are no longer in place. Keep folding until you have a shape in which all properties above apply. The final shape of your protein is called the Tertiary Structure. Post Activity Questions: A. Why should Methionine be next to the Blue End Cap, which represents the N- terminus of the protein? B. Were you able to fold your protein so that all of the chemical properties were in effect at the same time? If not, why do you think this was the case? C. Did your protein look like the proteins that other students folded? Should it have? Why or why not? D. How many different proteins, 15 amino acids long, could you make given an unlimited number of each of the 20 amino acids? E. How many nucleotides would be required to generate a polypeptide that is 15 amino acids long? This requires knowing how many nucleotides of DNA code for one amino acid. F. Assuming that there are between 20,000-25,000 genes in the human genome, do you think there are 1) fewer, 2) approximately the same number, or 3) more proteins in the human genome? Explain your answer.
6 Homework: What causes Sickle-Cell Anemia? Objective: At the end of this activity you will be able to describe the effect that a missense mutation has on a protein s function. Part I: Introduction to Sickle-Cell Anemia Description: Sickle cell anemia is a disease in which red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body assume a rigid, abnormal ( sickle ) shape that restricts their movement through blood vessels. This, in turn, reduces the oxygen that is delivered to the tissues of the body. Under normal conditions, the hemoglobin molecule is composed of 2 alpha-globin and 2-beta globin polypeptides (an example of a quaternary structure). In individuals with sickle-cell anemia, the beta-globin gene has a mutation at the 17 th nucleotide of DNA, which leads to a substitution in the 6 th amino acid (not counting the initial Methionine, which is removed during processing). A missense mutation is one in which a change in the DNA sequence results in a change in the amino acid sequence. Sometimes, this can result in a change in protein folding and/or activity. Sequence Details: Nucleotide #17 - Adenine (A) is replaced by Thymine (T) The codon, GAG, which codes for Glutamic Acid (Glu or E) is changed to GTG, which codes for Valine (Val or V) in the 6 th position of the beta-hemoglobin protein. Questions - To be answered before proceeding to Part II. 1. Draw the side chains of glutamic acid and valine below. 2. Describe the difference in the chemical properties of the side chains of glutamic acid and valine (look at their structures, think to which group of amino acids they belong, and discuss how they would behave as part of a protein). 3. How do you think this mutation (from a glutamic acid to a valine) affects the structure and function of the hemoglobin protein?
7 Part II: Computer Model of Hemoglobin 1. Open your web browser (e.g., Internet Explorer) and go to the website: 2. Click on Explore the Molecules under the BME3D Contents and select Hemoglobin under Quick Links. 3. Click on Hemoglobin Guided tour (the top Hemoglobin link) and explore the links under the Hemoglobin heading. #7 will show you the hemoglobin molecule in Sickle Cell Anemia. Questions: 1. Briefly describe the affect of the glutamic acid to valine mutation on the Hemoglobin protein as it relates to Sickle Cell Anemia. 2. Is your prediction (from question 3 in Part I) consistent with the description of the cause of the sickle-cell anemia disease (from the BME3D computer tutorial)? Explain.
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids
 Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Pipe Cleaner Proteins. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their function in the cell?
 Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
A disaccharide is formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides. This covalent bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
 CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Structures of Proteins. Primary structure - amino acid sequence
 Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
How To Understand The Chemistry Of Organic Molecules
 CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
 Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon. V. Polypeptides and Proteins
 IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
4. Which carbohydrate would you find as part of a molecule of RNA? a. Galactose b. Deoxyribose c. Ribose d. Glucose
 1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia
 Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia Introduction to Genome Browsing with Ensembl Ensembl The vast amount of information in biological databases today demands a way of organising and accessing
Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia Introduction to Genome Browsing with Ensembl Ensembl The vast amount of information in biological databases today demands a way of organising and accessing
CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006. Lecture 16 March 10
 CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006 Lecture 16 March 10 Lecturer: Michael Brudno Scribe: Jim Huang 16.1 Overview of proteins Proteins are long chains of amino acids (AA) which are produced
CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006 Lecture 16 March 10 Lecturer: Michael Brudno Scribe: Jim Huang 16.1 Overview of proteins Proteins are long chains of amino acids (AA) which are produced
Chapter 12 - Proteins
 Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 Certain human genetic conditions, such as sickle cell anemia, result from single base-pair mutations in DNA. (a) Explain how a single base-pair mutation
AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 Certain human genetic conditions, such as sickle cell anemia, result from single base-pair mutations in DNA. (a) Explain how a single base-pair mutation
Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw
 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?)
 ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
 Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY
 2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
The Molecules of Cells
 The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
 Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2
 Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Proteins. Proteins. Amino Acids. Most diverse and most important molecule in. Functions: Functions (cont d)
 Proteins Proteins Most diverse and most important molecule in living i organisms Functions: 1. Structural (keratin in hair, collagen in ligaments) 2. Storage (casein in mother s milk) 3. Transport (HAEMOGLOBIN!)
Proteins Proteins Most diverse and most important molecule in living i organisms Functions: 1. Structural (keratin in hair, collagen in ligaments) 2. Storage (casein in mother s milk) 3. Transport (HAEMOGLOBIN!)
Chapter 5. The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s
 Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells
 Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE
 AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
Elements in Biological Molecules
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK
 Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are
 This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS
 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS B 1. One of the functions of DNA is to A. secrete vacuoles. B. make copies of itself. C. join amino acids to each other.
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS B 1. One of the functions of DNA is to A. secrete vacuoles. B. make copies of itself. C. join amino acids to each other.
Recap. Lecture 2. Protein conformation. Proteins. 8 types of protein function 10/21/10. Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell
 Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Molecular Genetics. RNA, Transcription, & Protein Synthesis
 Molecular Genetics RNA, Transcription, & Protein Synthesis Section 1 RNA AND TRANSCRIPTION Objectives Describe the primary functions of RNA Identify how RNA differs from DNA Describe the structure and
Molecular Genetics RNA, Transcription, & Protein Synthesis Section 1 RNA AND TRANSCRIPTION Objectives Describe the primary functions of RNA Identify how RNA differs from DNA Describe the structure and
Molecular Models in Biology
 Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes. Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation
 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E.
 Name Student # Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E. 1. A sequence of three nitrogenous bases in a messenger-rna molecule is known as a 1) codon 2) gene 3) polypeptide 4) nucleotide
Name Student # Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E. 1. A sequence of three nitrogenous bases in a messenger-rna molecule is known as a 1) codon 2) gene 3) polypeptide 4) nucleotide
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide monomers covalently linked by a glycosidic bond. They function in sugar transport.
 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
DNA Worksheet BIOL 1107L DNA
 Worksheet BIOL 1107L Name Day/Time Refer to Chapter 5 and Chapter 16 (Figs. 16.5, 16.7, 16.8 and figure embedded in text on p. 310) in your textbook, Biology, 9th Ed, for information on and its structure
Worksheet BIOL 1107L Name Day/Time Refer to Chapter 5 and Chapter 16 (Figs. 16.5, 16.7, 16.8 and figure embedded in text on p. 310) in your textbook, Biology, 9th Ed, for information on and its structure
Biological Molecules
 Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Name Date Period. 2. When a molecule of double-stranded DNA undergoes replication, it results in
 DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis Keystone 1. During the process shown above, the two strands of one DNA molecule are unwound. Then, DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides to each strand which results
DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis Keystone 1. During the process shown above, the two strands of one DNA molecule are unwound. Then, DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides to each strand which results
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE C A R B O H Y D R A T E S, L I P I D S, P R O T E I N S, A N D N U C L E I C A C I D S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 115, Page 1 of 29) Carbon
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE C A R B O H Y D R A T E S, L I P I D S, P R O T E I N S, A N D N U C L E I C A C I D S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 115, Page 1 of 29) Carbon
DNA is found in all organisms from the smallest bacteria to humans. DNA has the same composition and structure in all organisms!
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI DNA omponents and Structure Introduction Nucleic acids are molecules that are essential to, and characteristic of, life on Earth. There are two basic types of nucleic
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI DNA omponents and Structure Introduction Nucleic acids are molecules that are essential to, and characteristic of, life on Earth. There are two basic types of nucleic
a. Ribosomal RNA rrna a type ofrna that combines with proteins to form Ribosomes on which polypeptide chains of proteins are assembled
 Biology 101 Chapter 14 Name: Fill-in-the-Blanks Which base follows the next in a strand of DNA is referred to. as the base (1) Sequence. The region of DNA that calls for the assembly of specific amino
Biology 101 Chapter 14 Name: Fill-in-the-Blanks Which base follows the next in a strand of DNA is referred to. as the base (1) Sequence. The region of DNA that calls for the assembly of specific amino
Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance
 Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Date: Per: Table # Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Name: Date: Per: Table # Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
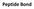 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
PROTEINS THE PEPTIDE BOND. The peptide bond, shown above enclosed in the blue curves, generates the basic structural unit for proteins.
 Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys
 Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds
Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri
 http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
Concluding lesson. Student manual. What kind of protein are you? (Basic)
 Concluding lesson Student manual What kind of protein are you? (Basic) Part 1 The hereditary material of an organism is stored in a coded way on the DNA. This code consists of four different nucleotides:
Concluding lesson Student manual What kind of protein are you? (Basic) Part 1 The hereditary material of an organism is stored in a coded way on the DNA. This code consists of four different nucleotides:
Helices From Readily in Biological Structures
 The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
Preliminary MFM Quiz
 Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Structure and Function of DNA
 Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four
Name Period Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7. 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0?
 Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon
 Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon Three Alpha Helices Stabilized By Disulfide Bonds! In order for hair to grow 6 inches in one year, 9 1/2 turns of α helix must be produced every second!!! In some proteins,
Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon Three Alpha Helices Stabilized By Disulfide Bonds! In order for hair to grow 6 inches in one year, 9 1/2 turns of α helix must be produced every second!!! In some proteins,
Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool
 Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool Jmol is a free open source molecular visualization program used by students, teachers, professors, and scientists to explore protein structures. Section
Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool Jmol is a free open source molecular visualization program used by students, teachers, professors, and scientists to explore protein structures. Section
HEMOGLOBIN AND MYOGLOBIN
 HEMOGLOBIN AND MYOGLOBIN I. OXYGEN CARRIERS A. Why do we need oxygen carriers? i. Cannot carry enough in blood to meet metabolic demand ii. Oxygen is very reactive oxidizes iii. Oxygen cannot diffuse very
HEMOGLOBIN AND MYOGLOBIN I. OXYGEN CARRIERS A. Why do we need oxygen carriers? i. Cannot carry enough in blood to meet metabolic demand ii. Oxygen is very reactive oxidizes iii. Oxygen cannot diffuse very
NO CALCULATORS OR CELL PHONES ALLOWED
 Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE
 Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Amino Acids and Proteins
 Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Academic Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Test
 Academic Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Each organism has a unique combination
Academic Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Each organism has a unique combination
8/20/2012 H C OH H R. Proteins
 Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Sickle cell anemia: Altered beta chain Single AA change (#6 Glu to Val) Consequence: Protein polymerizes Change in RBC shape ---> phenotypes
 Protein Structure Polypeptide: Protein: Therefore: Example: Single chain of amino acids 1 or more polypeptide chains All polypeptides are proteins Some proteins contain >1 polypeptide Hemoglobin (O 2 binding
Protein Structure Polypeptide: Protein: Therefore: Example: Single chain of amino acids 1 or more polypeptide chains All polypeptides are proteins Some proteins contain >1 polypeptide Hemoglobin (O 2 binding
13.2 Ribosomes & Protein Synthesis
 13.2 Ribosomes & Protein Synthesis Introduction: *A specific sequence of bases in DNA carries the directions for forming a polypeptide, a chain of amino acids (there are 20 different types of amino acid).
13.2 Ribosomes & Protein Synthesis Introduction: *A specific sequence of bases in DNA carries the directions for forming a polypeptide, a chain of amino acids (there are 20 different types of amino acid).
From DNA to Protein. Proteins. Chapter 13. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. The Path From Genes to Proteins. All proteins consist of polypeptide chains
 Proteins From DNA to Protein Chapter 13 All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequence of a gene The Path From Genes
Proteins From DNA to Protein Chapter 13 All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequence of a gene The Path From Genes
Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture
 CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
Biological molecules:
 Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
H H N - C - C 2 R. Three possible forms (not counting R group) depending on ph
 Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Protein Physics. A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1
 Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
K'NEX DNA Models. Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical Sciences Mount Sinai School of Medicine
 KNEX DNA Models Introduction Page 1 of 11 All photos by Kevin Kelliher. To download an Acrobat pdf version of this website Click here. K'NEX DNA Models Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical
KNEX DNA Models Introduction Page 1 of 11 All photos by Kevin Kelliher. To download an Acrobat pdf version of this website Click here. K'NEX DNA Models Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models
 EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
Transcription and Translation of DNA
 Transcription and Translation of DNA Genotype our genetic constitution ( makeup) is determined (controlled) by the sequence of bases in its genes Phenotype determined by the proteins synthesised when genes
Transcription and Translation of DNA Genotype our genetic constitution ( makeup) is determined (controlled) by the sequence of bases in its genes Phenotype determined by the proteins synthesised when genes
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations. Chapters 12-13.3
 DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations Chapters 12-13.3 1A)Identify the components of DNA and explain its role in heredity. DNA s Role in heredity: Contains the genetic information of a cell that can
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations Chapters 12-13.3 1A)Identify the components of DNA and explain its role in heredity. DNA s Role in heredity: Contains the genetic information of a cell that can
Translation Study Guide
 Translation Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. In translation, the cell uses the genetic information contained in mrna to
Translation Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. In translation, the cell uses the genetic information contained in mrna to
Section Activity #1: Fill out the following table for biology s most common elements assuming that each atom is neutrally charged.
 LS1a Fall 2014 Section Week #1 I. Valence Electrons and Bonding The number of valence (outer shell) electrons in an atom determines how many bonds it can form. Knowing the number of valence electrons present
LS1a Fall 2014 Section Week #1 I. Valence Electrons and Bonding The number of valence (outer shell) electrons in an atom determines how many bonds it can form. Knowing the number of valence electrons present
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
 Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012
 Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012 You need to bring a pencil and your ACT card. Chapter 24: Lipids 1. Describe the properties and types of lipids a. All are hydrophobic b. Fatty acid-based typically contain
Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012 You need to bring a pencil and your ACT card. Chapter 24: Lipids 1. Describe the properties and types of lipids a. All are hydrophobic b. Fatty acid-based typically contain
RNA & Protein Synthesis
 RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes send messages to cellular machinery RNA Plays a major role in process Process has three phases (Genetic) Transcription (Genetic) Translation Protein Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes send messages to cellular machinery RNA Plays a major role in process Process has three phases (Genetic) Transcription (Genetic) Translation Protein Synthesis RNA Synthesis
Papers listed: Cell2. This weeks papers. Chapt 4. Protein structure and function
 Papers listed: Cell2 During the semester I will speak of information from several papers. For many of them you will not be required to read these papers, however, you can do so for the fun of it (and it
Papers listed: Cell2 During the semester I will speak of information from several papers. For many of them you will not be required to read these papers, however, you can do so for the fun of it (and it
CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW
 Answer the following questions. CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW 1. What are the three kinds of bonds which can form between atoms? The three types of Bonds are Covalent, Ionic and Metallic. Name Date Block 2.
Answer the following questions. CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW 1. What are the three kinds of bonds which can form between atoms? The three types of Bonds are Covalent, Ionic and Metallic. Name Date Block 2.
The peptide bond is rigid and planar
 Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis. This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!!
 DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!! The Discovery of DNA s Structure Watson and Crick s discovery of DNA s structure was based on almost fifty years of research by other
DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!! The Discovery of DNA s Structure Watson and Crick s discovery of DNA s structure was based on almost fifty years of research by other
Basic Concepts of DNA, Proteins, Genes and Genomes
 Basic Concepts of DNA, Proteins, Genes and Genomes Kun-Mao Chao 1,2,3 1 Graduate Institute of Biomedical Electronics and Bioinformatics 2 Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering 3 Graduate
Basic Concepts of DNA, Proteins, Genes and Genomes Kun-Mao Chao 1,2,3 1 Graduate Institute of Biomedical Electronics and Bioinformatics 2 Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering 3 Graduate
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression What is Gene Expression? Gene expression is the process by which informa9on from a gene is used in the synthesis of a func9onal gene product. What is Gene Expression? Figure
Control of Gene Expression What is Gene Expression? Gene expression is the process by which informa9on from a gene is used in the synthesis of a func9onal gene product. What is Gene Expression? Figure
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity
 12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems
 Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Oxygen is required for oxidative metabolism
Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Oxygen is required for oxidative metabolism
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Genetic information (DNA) determines structure of proteins DNA RNA proteins cell structure 3.11 3.15 enzymes control cell chemistry ( metabolism )
 Biology 1406 Exam 3 Notes Structure of DNA Ch. 10 Genetic information (DNA) determines structure of proteins DNA RNA proteins cell structure 3.11 3.15 enzymes control cell chemistry ( metabolism ) Proteins
Biology 1406 Exam 3 Notes Structure of DNA Ch. 10 Genetic information (DNA) determines structure of proteins DNA RNA proteins cell structure 3.11 3.15 enzymes control cell chemistry ( metabolism ) Proteins
Coding sequence the sequence of nucleotide bases on the DNA that are transcribed into RNA which are in turn translated into protein
 Assignment 3 Michele Owens Vocabulary Gene: A sequence of DNA that instructs a cell to produce a particular protein Promoter a control sequence near the start of a gene Coding sequence the sequence of
Assignment 3 Michele Owens Vocabulary Gene: A sequence of DNA that instructs a cell to produce a particular protein Promoter a control sequence near the start of a gene Coding sequence the sequence of
Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond)
 Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond) Weak bonds are those forces of attraction that, in biological situations, do not take a large amount of energy to break. For example, hydrogen bonds are broken by energies
Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond) Weak bonds are those forces of attraction that, in biological situations, do not take a large amount of energy to break. For example, hydrogen bonds are broken by energies
The Organic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Polar Covalent Bonds and Hydrogen Bonds
 Lesson 6.1: Polar Covalent Bonds and Hydrogen Bonds The last section of code will add hydrogen bonding functionality between molecules. To do so, we have to understand the chemistry of polar covalent bonds
Lesson 6.1: Polar Covalent Bonds and Hydrogen Bonds The last section of code will add hydrogen bonding functionality between molecules. To do so, we have to understand the chemistry of polar covalent bonds
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
