Solution: Since the charges have opposite signs, the force is one of attraction. Its magnitude is ( )
|
|
|
- Charles Collins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Poblm 1. A C chag is locatd 3. m fom a C chag. Find th lctostatic foc xtd by on chag on th oth. Solution: Sinc th chags hav opposit signs, th foc is on of attaction. Its magnitud is N 9 9 ( C)(.8 10 C ) k qq 1 9 N m F = = C = 3. m Poblm. Two nighboing clls a ionizd (chagd) by x-adiation. (a) If th chag on ach cll is qual to C and th clls a.5 μm apat, what is th foc xtd by ach cll? (b) If th distanc btwn th clls is doubld, what happns to th foc btwn thm? Solution: (a) Th foc is 14 ( C ) kq 9 N m F = = C =.5 10 m N pulsion (b) With two tims lag, is fou tims lag and th foc is ducd to on fouth ofits pvious valu. Poblm 3. An lcton is acclatd by a constant lctic fild of magnitud 300 N/C. (a) Find th acclation of th lcton. (b) Us th quations of motion with constant acclation to find th lcton s spd aft s, assuming it stats fom st. Solution: (a) Th magnitud of th foc on th lcton is F = qe= E, and th acclation is ( C ) ( 300 N C ) F E a= = = = m m kg 13 8 (b) v vi at 0 ( m s )( s) = + = + = m s m s
2 Poblm 4. Two idntical conducting sphs a placd with thi cnts 0.30 m apat. On is givn a chag of 1 x 10 9 C and th oth a chag of C. (a) Find th lctostatic foc xtd by on sph on th oth. (b) Th sphs a connctd by a conducting wi. Aft quilibium has occud, find th lctostatic foc btwn th two. Solution: (a) Th sphically symmtic chag distibutions bhav as if all chag was locatd at th cnts of th sphs. Thfo, th magnitud of th attactiv foc is 9 9 ( 1 10 C)( C ) kq 1 q 9 N m F = = C = 0.30 m N (b) Whn th sphs a connctd by a conducting wi, th nt chag 9 qnt = q1+ q =.0 10 C will divid qually btwn th two idntical sphs. Thus, th foc is now 9 N m.0 10 C nt k q 9 F = = C m o F = N (pulsion)
3 Poblm 5. Calculat th magnitud and diction of th Coulomb foc on ach of th th chags in th following figu. Solution: Th focs a as shown in th sktch at th ight μc F 1 F F 1 F μc -.00 μc F 3 F cm.00 cm ( C)( C ) kqq 1 9 N m F1 = = N - 1 = C m ( C)( C ) kq 1 q3 9 N m F = = N - 13 = C m ( C)( C ) kq q3 9 N m F3 = = N - 3 = C m Th nt foc on th μ C chag is F = F1 F = 4.7 N (to th lft). Th nt foc on th 1.5μ C chag is F1.5 = F1+ F3 = 157 N (to th ight). Th nt foc on th μc chag is F = F+ F3 = 111 N (to th lft).
4 Poblm. Two small mtallic sphs, ach of mass 0.0 g, a suspndd as pndulums by light stings fom a common point as shown in th figu. Th sphs a givn th sam lctic chag, and it is found that th two com to quilibium whn ach sting is at an angl of 5.0 with th vtical. If ach sting is 30.0 cm long, what is th magnitud of th chag on ach sph? Solution: Consid th f-body diagam of on of th sphs givn at th ight. H, T is th tnsion in th sting and F is th pulsiv lctical foc xtd by th oth sph. +y 5.0 T Σ F = 0 Tcos5.0 = mg, o y m g T = cos5.0 F +x Σ F = 0 F = Tsin 5.0 = mgtan 5.0 x mg At quilibium, th distanc spaating th two sphs is = Lsin5.0. Thus, F mgtan 5.0 kq = bcoms ( Lsin5.0 ) = mgtan 5.0 and yilds ( Lsin5.0 ) q= mgtan 5.0 k kg 9.80 m s tan 5.0 = ( m ) sin5.0 = N m C 7. nc
5 Poblm 7. A pic of aluminum foil of mass kg is suspndd by a sting in an lctic fild dictd vtically upwad. If th chag on th foil is 3.00 μc, find th stngth of th fild that will duc th tnsion in th sting to zo. Solution: If th is zo tnsion in th sting, th lctical foc suppots th nti wight of th foil. Thus, F= qe= mg, so ( kg)( 9.80 m s ) mg E = = = q C N C Poblm 8. A poton acclats fom st in a unifom lctic fild of 40 N/C. At som lat tim, its spd is m/s. (a) Find th magnitud of th acclation of th poton. (b) How long dos it tak th poton to ach this spd? (c) How fa has it movd in this intval? (d) What is its kintic ngy at th lat tim? Solution: (a) p ( C) ( 40 N C) F qe a= = = = m m kg m s (b) m s Δv 5 t= = = s= a m s 19. μ s (c) ( ) 10 ( ) vf vi m s 0 Δ x = = = a.1 10 m s 11.8 m 1 1 KEf = m pvf = kg m s = 7 (d) J
6 Poblm 9. In th following figu, dtmin th point (oth than infinity) at which th total lctic fild is zo. Solution: If th sultant fild is zo, th +y contibutions fom th two chags must b in opposit dictions and also hav 1 = d 1.0 m +x qual magnituds. Choos th lin E E 1 q 1 =.5 μc q =.0 μc conncting th chags as th x-axis, with th oigin at th.5 μc chag. Thn, th = 1.0 m + d two contibutions will hav opposit dictions only in th gions x< 0 and x > 1.0 m. Fo th magnituds to b qual, th point must b na th small chag. Thus, th point of zo sultant fild is on th x-axis at x< 0. Rquiing qual magnituds givs Thus, ( 1.0 m d) Solving fo d yilds.5 + = d.0 k q k q = o μc.0 μc = d ( 1.0 m + d). d = 1.8 m, o 1.8 m to th lftofth.5 μc chag Poblm 10. In th Boh thoy of th hydogn atom, an lcton movs in a cicula obit about a poton, wh th adius of th obit is m. (a) Find th lctostatic foc acting on ach paticl. (b) If this foc causs th cntiptal acclation of th lcton, what is th spd of th lcton? k q1 q k Solution: (a) F = = 9 19 ( N m C )( C ) 10 ( m ) = = (b) c F= m a = m v, so ( m )( N ) F v = = = -31 m kg N. 10 m s
7 Poblm 11. A small.00-g plastic ball is suspndd by a 0.0-cm-long sting in a unifom lctic fild, as shown in th figu. If th ball is in quilibium whn th sting maks a 15.0 angl with th vtical as indicatd, what is th nt chag on th ball? Solution: Consid th f-body diagam shown at th ight. T θ y m g Σ Fy = 0 Tcos θ = mg o T = cosθ Σ F = 0 F = Tsinθ = mgtanθ x F x Sinc F = qe, w hav mg qe = m gtanθ, o mgtanθ q= E kg 9.80 m s tan15.0 q= = C = N C 5.5 μ C
8 Poblm 1. Two point chags lik thos in following figu a calld an lctic dipol. Show that th lctic fild at a distant point along th x axis is givn by th xpssion E x = 4k qa/x 3. Solution: As shown in th sktch, th lctic fild at any point on th x-axis consists of two pats, on du to ach of th chags in th dipol. k q k q E= E E = + + q a y a +q x + E E + k q k q ( x+ a) ( xa) 4ax E= = k q = kq ( x a) ( x+ a) x a x+ a x a 4ax Thus, if x >> a, this givs E kq = x 4 4k qa 3 x Poblm 13. A poton movs.00 cm paalll to a unifom lctic fild with E = 00 N/C. (a) How much wok is don by th fild on th poton? (b) What chang occus in th potntial ngy of th poton? (c) Though what potntial diffnc did th poton mov? Solution: (a) Th wok don is cosθ W = F s = qe scosθ, o 19 W = C 00 N C m cos0 = J (b) Th chang in th lctical potntial ngy is Δ PE = W = J (c) Th chang in th lctical potntial is 19 ΔPE J Δ V = = = -19 q C 4.00 V
9 Poblm 14. A potntial diffnc of 90 mv xists btwn th inn and out sufacs of a cll mmban. Th inn sufac is ngativ lativ to th out sufac. How much wok is quid to jct a positiv sodium ion (Na + ) fom th intio of th cll? Solution: Th wok don by th agnt moving th chag out of th cll is input fild W = W = Δ PE =+ q Δ V = C = C 19 3 J J Poblm 15. Th diffnc in potntial btwn th acclating plats of a TV st is about 5 kv. If th distanc btwn ths plats is 1.5 cm, find th magnitud of th unifom lctic fild in this gion. ΔV J C Solution: E = = = d m N C Poblm 1. Suppos an lcton is lasd fom st in a unifom lctic fild whos stngth is V/m. (a) Though what potntial diffnc will it hav passd aft moving 1.00 cm? (b) How fast will th lcton b moving aft it has tavld 1.00 cm? 3 Solution: (a) V Ed ( V m )( m ) Δ = = = 59.0 V 1 (b) mv 0 KE W PE q( V ) =Δ = =Δ = Δ, so ( ΔV ) 1.0 ( C) ( 59.0 J C ) q v = = = m kg m s Poblm 17. (a) Find th potntial 1.00 cm fom a poton. (b) What is th potntial diffnc btwn two points that a 1.00 cm and.00 cm fom a poton? Solution: (a) V kq ( N m C )( C ) = = = m kq kq 1 1 Δ V = V V = = kq (b) 1 ( ) V = ( N m C )( C ) m m = V
10 Poblm 18. Find th potntial at point P fo th ctangula gouping of chags shown in th figu. Solution: Calling q 3 th chag at th con opposit P, q q q = + + = V V1 V V3 k N m C C C = C m m ( 0.00 ) + ( ) m = V Poblm 19. (a) Find th lctic potntial, taking zo at infinity, at th upp-ight con (th con without a chag) of th ctangl in th following figu. (b) Rpat if th.00- μc chag is placd with a chag of.00 μc. Solution: (a) Calling th.00 μ C chag q 3, V kq q q q k i 1 3 = = + + i i N m C C C = C m m ( 0.000) ( ) + m V =.7 10 V (b) Rplacing C by C in pat (a) yilds V = V
11 Poblm 0. (a) How much chag is on ach plat of a 4.00-μF capacito whn it is connctd to a 1.0-V batty? (b) If this sam capacito is connctd to a 1.50-V batty, what chag is stod? = Δ = F 1.0 V = C = 48.0 μ C Solution: (a) Q C( V) = Δ = = =.00 μ C (b) Q C( V) F 1.50 V C Poblm 1. Consid Eath and a cloud lay 800 m abov Eath to b th plats of a paalll-plat capacito. (a) If th cloud lay has an aa of 1.0 km = m, what is th capacitanc? (b) If an lctic fild stngth gat than N/C causs th ai to bak down and conduct chag (lightning), what is th maximum chag th cloud can hold? A ( m 1 C ) 8 Solution: (a) C = 0 = = N m d F 800 m (b) Q = C( Δ V) = C( E d) max max max 8 ( F)( N C ) ( 800 m ) = = 7 C Poblm. Th potntial diffnc btwn a pai of oppositly chagd paalll plats is 400 V. (a) If th spacing btwn th plats is doubld without alting th chag on th plats, what is th nw potntial diffnc btwn th plats? (b) If th plat spacing is doubld whil th potntial diffnc btwn th plats is kpt constant, what is th atio of th final chag on on of th plats to th oiginal chag? Solution: Fo a paalll plat capacito, Q Q Q d Δ V = = = C Ad A. 0 0 (a) Doubling d whil holding Q and A constant doubls Δ V to 800 V. (b) ( ) 0 A ΔV Q = Thus, doubling d whil holding Δ V and A constant will d cut th chag in half, o Q = Q f i Poblm 3. Th plats of a paalll-plat capacito a spaatd by mm. If th matial btwn th plats is ai, what plat aa is quid to povid a capacitanc of.00 pf? 0 0 A 1 C d F m Solution: C =, so A = = =. 10 m 1 d C N m 5
12 Poblm 4.An ai-filld capacito consists of two paalll plats, ach with an aa of 7.0 cm, spaatd by a distanc of 1.80 mm. If a 0.0-V potntial diffnc is applid to ths plats, calculat (a) th lctic fild btwn th plats, (b) th capacitanc, and (c) th chag on ach plat. ΔV 0.0 V 4 Solution: (a) E = = = V m = 11.1 kv m dictd towad -3 d m th ngativ plat (b) C A d 0 = = ( C N m )( m ) m 1 = F = 3.74 pf (c) Q C( V ) 1 11 = Δ = F 0.0 V = C = 74.7 pc on on plat and 74.7 pc on th oth plat. Poblm 5. A paalll-plat capacito has.00-cm plats that a spaatd by 5.00 mm with ai btwn thm. If a 1.0-V batty is connctd to this capacito, how much ngy dos it sto? Solution: Th capacitanc is C A ( C N m )( m ) 0 13 = = = F -3 d and th stod ngy is m, 1 1 ( W = C Δ V = F ) ( 1.0 V ) = J
13 Poblm. Consid th paalll-plat capacito fomd by Eath and a cloud lay. Assum this capacito will dischag (that is, lightning occus) whn th lctic fild stngth btwn th plats achs N/C. What is th ngy lasd if th capacito dischags compltly duing a lightning stik? Solution: Th capacitanc of this paalll plat capacito is A 1 C 0 ( m ) 8 C = = d = N m F 800 m With an lctic fild stngth of d = 800 m, th potntial diffnc btwn plats is Δ V = Ed= = E = N C and a plat spaation of V m 800 m.4 10 V Thus, th ngy availabl fo las in a lightning stik is 1 1 ( W = C Δ V = F )(.4 10 V ) = J
Problem Solving Session 1: Electric Dipoles and Torque
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Dpatmnt of Physics 8.02 Poblm Solving Sssion 1: Elctic Dipols and Toqu Sction Tabl (if applicabl) Goup Mmbs Intoduction: In th fist poblm you will lan to apply Coulomb
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Dpatmnt of Physics 8.02 Poblm Solving Sssion 1: Elctic Dipols and Toqu Sction Tabl (if applicabl) Goup Mmbs Intoduction: In th fist poblm you will lan to apply Coulomb
Chapter 3. Electric Potential
 Chapt 3 Elctic Potntial 3.1 Potntial and Potntial Engy...3-3. Elctic Potntial in a Unifom Fild...3-5 3.3 Elctic Potntial du to Point Chags...3-6 3.3.1 Potntial Engy in a Systm of Chags...3-8 3.4 Continuous
Chapt 3 Elctic Potntial 3.1 Potntial and Potntial Engy...3-3. Elctic Potntial in a Unifom Fild...3-5 3.3 Elctic Potntial du to Point Chags...3-6 3.3.1 Potntial Engy in a Systm of Chags...3-8 3.4 Continuous
Handout 3. Free Electron Gas in 2D and 1D
 Handout 3 F lcton Gas in D and D In this lctu ou will lan: F lcton gas in two dinsions and in on dinsion Dnsit o Stats in -spac and in ng in low dinsions C 47 Sping 9 Fahan Rana Conll Univsit lcton Gass
Handout 3 F lcton Gas in D and D In this lctu ou will lan: F lcton gas in two dinsions and in on dinsion Dnsit o Stats in -spac and in ng in low dinsions C 47 Sping 9 Fahan Rana Conll Univsit lcton Gass
Physics. Lesson Plan #9 Energy, Work and Simple Machines David V. Fansler Beddingfield High School
 Physics Lsson Plan #9 Engy, Wok an Simpl Machins Davi V. Fansl Bingfil High School Engy an Wok Objctivs: Dscib th lationship btwn wok an ngy; Display an ability to calculat wok on by a foc; Intify th foc
Physics Lsson Plan #9 Engy, Wok an Simpl Machins Davi V. Fansl Bingfil High School Engy an Wok Objctivs: Dscib th lationship btwn wok an ngy; Display an ability to calculat wok on by a foc; Intify th foc
HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS OF LNG TRANSFER LINE
 Scintific Jounal of Impact Facto(SJIF): 3.34 Intnational Jounal of Advanc Engining and sach Dvlopmnt Volum,Issu, Fbuay -05 HEAT TANSFE ANALYSIS OF LNG TANSFE LINE J.D. Jani -ISSN(O): 348-4470 p-issn(p):
Scintific Jounal of Impact Facto(SJIF): 3.34 Intnational Jounal of Advanc Engining and sach Dvlopmnt Volum,Issu, Fbuay -05 HEAT TANSFE ANALYSIS OF LNG TANSFE LINE J.D. Jani -ISSN(O): 348-4470 p-issn(p):
Chapter 22. Outside a uniformly charged sphere, the field looks like that of a point charge at the center of the sphere.
 Chapte.3 What is the magnitude of a point chage whose electic field 5 cm away has the magnitude of.n/c. E E 5.56 1 11 C.5 An atom of plutonium-39 has a nuclea adius of 6.64 fm and atomic numbe Z94. Assuming
Chapte.3 What is the magnitude of a point chage whose electic field 5 cm away has the magnitude of.n/c. E E 5.56 1 11 C.5 An atom of plutonium-39 has a nuclea adius of 6.64 fm and atomic numbe Z94. Assuming
The force between electric charges. Comparing gravity and the interaction between charges. Coulomb s Law. Forces between two charges
 The foce between electic chages Coulomb s Law Two chaged objects, of chage q and Q, sepaated by a distance, exet a foce on one anothe. The magnitude of this foce is given by: kqq Coulomb s Law: F whee
The foce between electic chages Coulomb s Law Two chaged objects, of chage q and Q, sepaated by a distance, exet a foce on one anothe. The magnitude of this foce is given by: kqq Coulomb s Law: F whee
Voltage ( = Electric Potential )
 V-1 of 9 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
V-1 of 9 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
PHYSICS 206a HOMEWORK #11 SOLUTIONS
 PHYSICS 0a HOEWORK # SOLUTIONS. Using Nwton s law of gavitation, div th acclation du to gavity xpincd by an objct of ass at th sufac of th Eath. Show that this acclation is indpndnt of th ass of th objct.
PHYSICS 0a HOEWORK # SOLUTIONS. Using Nwton s law of gavitation, div th acclation du to gavity xpincd by an objct of ass at th sufac of th Eath. Show that this acclation is indpndnt of th ass of th objct.
Chapter 19: Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields ( ) ( 6 )( 6
 Chapte 9 lectic Chages, Foces, an Fiels 6 9. One in a million (0 ) ogen molecules in a containe has lost an electon. We assume that the lost electons have been emove fom the gas altogethe. Fin the numbe
Chapte 9 lectic Chages, Foces, an Fiels 6 9. One in a million (0 ) ogen molecules in a containe has lost an electon. We assume that the lost electons have been emove fom the gas altogethe. Fin the numbe
Voltage ( = Electric Potential )
 V-1 Voltage ( = Electic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage is
V-1 Voltage ( = Electic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage is
fiziks Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF (JUNE-2011)
 Institut fo NET/JRF, GTE, IIT JM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICL SCIENCES Had offic fiziks, H.No., G.F, Jia Saai, Na IIT, Hauz Khas, Nw Dlhi 6 Phon: 6865455/9 98745498 NUCLER ND PRTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF
Institut fo NET/JRF, GTE, IIT JM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICL SCIENCES Had offic fiziks, H.No., G.F, Jia Saai, Na IIT, Hauz Khas, Nw Dlhi 6 Phon: 6865455/9 98745498 NUCLER ND PRTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF
Exam 3: Equation Summary
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Depatment of Physics Physics 8.1 TEAL Fall Tem 4 Momentum: p = mv, F t = p, Fext ave t= t f t= Exam 3: Equation Summay total = Impulse: I F( t ) = p Toque: τ = S S,P
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Depatment of Physics Physics 8.1 TEAL Fall Tem 4 Momentum: p = mv, F t = p, Fext ave t= t f t= Exam 3: Equation Summay total = Impulse: I F( t ) = p Toque: τ = S S,P
High Voltage Cables. Figure 5.1 - Layout of three, single-core cables
 High oltag Cabls 5.0 High oltag Cabls High oltag Cabls a usd whn undgound tansmission is quid. Ths cabls a laid in ducts o may b buid in th gound. Unlik in ovhad lins, ai dos not fom pat of th insulation,
High oltag Cabls 5.0 High oltag Cabls High oltag Cabls a usd whn undgound tansmission is quid. Ths cabls a laid in ducts o may b buid in th gound. Unlik in ovhad lins, ai dos not fom pat of th insulation,
(a) The centripetal acceleration of a point on the equator of the Earth is given by v2. The velocity of the earth can be found by taking the ratio of
 Homewok VI Ch. 7 - Poblems 15, 19, 22, 25, 35, 43, 51. Poblem 15 (a) The centipetal acceleation of a point on the equato of the Eath is given by v2. The velocity of the eath can be found by taking the
Homewok VI Ch. 7 - Poblems 15, 19, 22, 25, 35, 43, 51. Poblem 15 (a) The centipetal acceleation of a point on the equato of the Eath is given by v2. The velocity of the eath can be found by taking the
Gravity and the Earth Newtonian Gravity and Earth Rotation Effects
 Gavity and th Eath Nwtonian Gavity and Eath Rotation Effcts Jams R. Clynch, 003 I. Nwtonian Gavity A. Nwtonian Gavitational Foc B. Nwtonian Gavitational Fild C. Nwtonian Gavitational Potntial D. Gavity
Gavity and th Eath Nwtonian Gavity and Eath Rotation Effcts Jams R. Clynch, 003 I. Nwtonian Gavity A. Nwtonian Gavitational Foc B. Nwtonian Gavitational Fild C. Nwtonian Gavitational Potntial D. Gavity
PY1052 Problem Set 8 Autumn 2004 Solutions
 PY052 Poblem Set 8 Autumn 2004 Solutions H h () A solid ball stats fom est at the uppe end of the tack shown and olls without slipping until it olls off the ight-hand end. If H 6.0 m and h 2.0 m, what
PY052 Poblem Set 8 Autumn 2004 Solutions H h () A solid ball stats fom est at the uppe end of the tack shown and olls without slipping until it olls off the ight-hand end. If H 6.0 m and h 2.0 m, what
10. Collisions. Before During After
 10. Collisions Use conseation of momentum and enegy and the cente of mass to undestand collisions between two objects. Duing a collision, two o moe objects exet a foce on one anothe fo a shot time: -F(t)
10. Collisions Use conseation of momentum and enegy and the cente of mass to undestand collisions between two objects. Duing a collision, two o moe objects exet a foce on one anothe fo a shot time: -F(t)
Episode 401: Newton s law of universal gravitation
 Episode 401: Newton s law of univesal gavitation This episode intoduces Newton s law of univesal gavitation fo point masses, and fo spheical masses, and gets students pactising calculations of the foce
Episode 401: Newton s law of univesal gavitation This episode intoduces Newton s law of univesal gavitation fo point masses, and fo spheical masses, and gets students pactising calculations of the foce
Question 3: How do you find the relative extrema of a function?
 ustion 3: How do you find th rlativ trma of a function? Th stratgy for tracking th sign of th drivativ is usful for mor than dtrmining whr a function is incrasing or dcrasing. It is also usful for locating
ustion 3: How do you find th rlativ trma of a function? Th stratgy for tracking th sign of th drivativ is usful for mor than dtrmining whr a function is incrasing or dcrasing. It is also usful for locating
Newton s Law of Gravitation
 Physics 106 Lctu 9 Nwton s Law of Gavitation SJ 7 th Ed.: Chap 1.1 to, 1.4 to 5 Histoical ovviw Nwton s invs-squa law of avitation i oc Gavitational acclation Supposition Gavitation na th Eath s sufac
Physics 106 Lctu 9 Nwton s Law of Gavitation SJ 7 th Ed.: Chap 1.1 to, 1.4 to 5 Histoical ovviw Nwton s invs-squa law of avitation i oc Gavitational acclation Supposition Gavitation na th Eath s sufac
7 Circular Motion. 7-1 Centripetal Acceleration and Force. Period, Frequency, and Speed. Vocabulary
 7 Cicula Motion 7-1 Centipetal Acceleation and Foce Peiod, Fequency, and Speed Vocabulay Vocabulay Peiod: he time it takes fo one full otation o evolution of an object. Fequency: he numbe of otations o
7 Cicula Motion 7-1 Centipetal Acceleation and Foce Peiod, Fequency, and Speed Vocabulay Vocabulay Peiod: he time it takes fo one full otation o evolution of an object. Fequency: he numbe of otations o
Solution Derivations for Capa #8
 Solution Deivations fo Capa #8 1) A ass spectoete applies a voltage of 2.00 kv to acceleate a singly chaged ion (+e). A 0.400 T field then bends the ion into a cicula path of adius 0.305. What is the ass
Solution Deivations fo Capa #8 1) A ass spectoete applies a voltage of 2.00 kv to acceleate a singly chaged ion (+e). A 0.400 T field then bends the ion into a cicula path of adius 0.305. What is the ass
12. Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
 12. olling, Toque, and Angula Momentum 1 olling Motion: A motion that is a combination of otational and tanslational motion, e.g. a wheel olling down the oad. Will only conside olling with out slipping.
12. olling, Toque, and Angula Momentum 1 olling Motion: A motion that is a combination of otational and tanslational motion, e.g. a wheel olling down the oad. Will only conside olling with out slipping.
PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION #13. May 1, 2013
 PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION #13 May 1, 2013 0.1 In intoductoy physics laboatoies, a typical Cavendish balance fo measuing the gavitational constant G uses lead sphees with masses of 2.10 kg and 21.0
PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION #13 May 1, 2013 0.1 In intoductoy physics laboatoies, a typical Cavendish balance fo measuing the gavitational constant G uses lead sphees with masses of 2.10 kg and 21.0
Experiment 6: Centripetal Force
 Name Section Date Intoduction Expeiment 6: Centipetal oce This expeiment is concened with the foce necessay to keep an object moving in a constant cicula path. Accoding to Newton s fist law of motion thee
Name Section Date Intoduction Expeiment 6: Centipetal oce This expeiment is concened with the foce necessay to keep an object moving in a constant cicula path. Accoding to Newton s fist law of motion thee
FXA 2008. Candidates should be able to : Describe how a mass creates a gravitational field in the space around it.
 Candidates should be able to : Descibe how a mass ceates a gavitational field in the space aound it. Define gavitational field stength as foce pe unit mass. Define and use the peiod of an object descibing
Candidates should be able to : Descibe how a mass ceates a gavitational field in the space aound it. Define gavitational field stength as foce pe unit mass. Define and use the peiod of an object descibing
Phys 2101 Gabriela González. cos. sin. sin
 1 Phys 101 Gabiela González a m t t ma ma m m T α φ ω φ sin cos α τ α φ τ sin m m α τ I We know all of that aleady!! 3 The figue shows the massive shield doo at a neuton test facility at Lawence Livemoe
1 Phys 101 Gabiela González a m t t ma ma m m T α φ ω φ sin cos α τ α φ τ sin m m α τ I We know all of that aleady!! 3 The figue shows the massive shield doo at a neuton test facility at Lawence Livemoe
A Model for Antenna-Plasma Wave Coupling towards Control of Uniformity in Slot-Excited Microwave Discharges
 J. Plasa Fusion Rs. SERIES, Vol. 9 () A Modl fo Antnna-Plasa Wav Couling towads Contol of Unifoity in Slot-Excitd Micowav Dischags Daichi SAWADA, Akihio TSUJI, Takanoi KITSUDO, Yasuyoshi YASAKA, and Hioasa
J. Plasa Fusion Rs. SERIES, Vol. 9 () A Modl fo Antnna-Plasa Wav Couling towads Contol of Unifoity in Slot-Excitd Micowav Dischags Daichi SAWADA, Akihio TSUJI, Takanoi KITSUDO, Yasuyoshi YASAKA, and Hioasa
Multiple choice questions [70 points]
![Multiple choice questions [70 points] Multiple choice questions [70 points]](/thumbs/27/9758213.jpg) Multiple choice questions [70 points] Answe all of the following questions. Read each question caefull. Fill the coect bubble on ou scanton sheet. Each question has exactl one coect answe. All questions
Multiple choice questions [70 points] Answe all of the following questions. Read each question caefull. Fill the coect bubble on ou scanton sheet. Each question has exactl one coect answe. All questions
ME 612 Metal Forming and Theory of Plasticity. 6. Strain
 Mtal Forming and Thory of Plasticity -mail: azsnalp@gyt.du.tr Makin Mühndisliği Bölümü Gbz Yüksk Tknoloji Enstitüsü 6.1. Uniaxial Strain Figur 6.1 Dfinition of th uniaxial strain (a) Tnsil and (b) Comprssiv.
Mtal Forming and Thory of Plasticity -mail: azsnalp@gyt.du.tr Makin Mühndisliği Bölümü Gbz Yüksk Tknoloji Enstitüsü 6.1. Uniaxial Strain Figur 6.1 Dfinition of th uniaxial strain (a) Tnsil and (b) Comprssiv.
Agilent Basics of Measuring the Dielectric Properties of Materials. Application Note
 Agilnt Basics of Masuing th Dilctic Poptis of Matials Application Not Contnts Intoduction...3 Dilctic thoy...4 Dilctic Constant...4 Pmability...7 Elctomagntic popagation...8 Dilctic mchanisms...10 Ointation
Agilnt Basics of Masuing th Dilctic Poptis of Matials Application Not Contnts Intoduction...3 Dilctic thoy...4 Dilctic Constant...4 Pmability...7 Elctomagntic popagation...8 Dilctic mchanisms...10 Ointation
The Role of Gravity in Orbital Motion
 ! The Role of Gavity in Obital Motion Pat of: Inquiy Science with Datmouth Developed by: Chistophe Caoll, Depatment of Physics & Astonomy, Datmouth College Adapted fom: How Gavity Affects Obits (Ohio State
! The Role of Gavity in Obital Motion Pat of: Inquiy Science with Datmouth Developed by: Chistophe Caoll, Depatment of Physics & Astonomy, Datmouth College Adapted fom: How Gavity Affects Obits (Ohio State
HOMEWORK FOR UNIT 5-1: FORCE AND MOTION
 Nam Dat Partnrs HOMEWORK FOR UNIT 51: FORCE AND MOTION 1. You ar givn tn idntial springs. Dsrib how you would dvlop a sal of for (i., a mans of produing rpatabl fors of a varity of sizs) using ths springs.
Nam Dat Partnrs HOMEWORK FOR UNIT 51: FORCE AND MOTION 1. You ar givn tn idntial springs. Dsrib how you would dvlop a sal of for (i., a mans of produing rpatabl fors of a varity of sizs) using ths springs.
Gravitation. AP Physics C
 Gavitation AP Physics C Newton s Law of Gavitation What causes YOU to be pulled down? THE EARTH.o moe specifically the EARTH S MASS. Anything that has MASS has a gavitational pull towads it. F α Mm g What
Gavitation AP Physics C Newton s Law of Gavitation What causes YOU to be pulled down? THE EARTH.o moe specifically the EARTH S MASS. Anything that has MASS has a gavitational pull towads it. F α Mm g What
Current and Resistance
 Chaptr 6 Currnt and Rsistanc 6.1 Elctric Currnt...6-6.1.1 Currnt Dnsity...6-6. Ohm s Law...6-4 6.3 Elctrical Enrgy and Powr...6-7 6.4 Summary...6-8 6.5 Solvd Problms...6-9 6.5.1 Rsistivity of a Cabl...6-9
Chaptr 6 Currnt and Rsistanc 6.1 Elctric Currnt...6-6.1.1 Currnt Dnsity...6-6. Ohm s Law...6-4 6.3 Elctrical Enrgy and Powr...6-7 6.4 Summary...6-8 6.5 Solvd Problms...6-9 6.5.1 Rsistivity of a Cabl...6-9
Fluids Lecture 15 Notes
 Fluids Lectue 15 Notes 1. Unifom flow, Souces, Sinks, Doublets Reading: Andeson 3.9 3.12 Unifom Flow Definition A unifom flow consists of a velocit field whee V = uî + vĵ is a constant. In 2-D, this velocit
Fluids Lectue 15 Notes 1. Unifom flow, Souces, Sinks, Doublets Reading: Andeson 3.9 3.12 Unifom Flow Definition A unifom flow consists of a velocit field whee V = uî + vĵ is a constant. In 2-D, this velocit
New Basis Functions. Section 8. Complex Fourier Series
 Nw Basis Functions Sction 8 Complx Fourir Sris Th complx Fourir sris is prsntd first with priod 2, thn with gnral priod. Th connction with th ral-valud Fourir sris is xplaind and formula ar givn for convrting
Nw Basis Functions Sction 8 Complx Fourir Sris Th complx Fourir sris is prsntd first with priod 2, thn with gnral priod. Th connction with th ral-valud Fourir sris is xplaind and formula ar givn for convrting
Charges, Coulomb s Law, and Electric Fields
 Q&E -1 Chages, Coulomb s Law, and Electic ields Some expeimental facts: Expeimental fact 1: Electic chage comes in two types, which we call (+) and ( ). An atom consists of a heavy (+) chaged nucleus suounded
Q&E -1 Chages, Coulomb s Law, and Electic ields Some expeimental facts: Expeimental fact 1: Electic chage comes in two types, which we call (+) and ( ). An atom consists of a heavy (+) chaged nucleus suounded
1240 ev nm 2.5 ev. (4) r 2 or mv 2 = ke2
 Chapte 5 Example The helium atom has 2 electonic enegy levels: E 3p = 23.1 ev and E 2s = 20.6 ev whee the gound state is E = 0. If an electon makes a tansition fom 3p to 2s, what is the wavelength of the
Chapte 5 Example The helium atom has 2 electonic enegy levels: E 3p = 23.1 ev and E 2s = 20.6 ev whee the gound state is E = 0. If an electon makes a tansition fom 3p to 2s, what is the wavelength of the
Incorporating Statistical Process Control and Statistical Quality Control Techniques into a Quality Assurance Program
 Incooating Statistical Pocss Contol and Statistical Quality Contol Tchniqus into a Quality Assuanc Pogam Robyn Sikis U.S. Cnsus Buau Puos Incooat SPC and SQC mthods into quality assuanc ogam Monito and
Incooating Statistical Pocss Contol and Statistical Quality Contol Tchniqus into a Quality Assuanc Pogam Robyn Sikis U.S. Cnsus Buau Puos Incooat SPC and SQC mthods into quality assuanc ogam Monito and
AP Calculus AB 2008 Scoring Guidelines
 AP Calculus AB 8 Scoring Guidlins Th Collg Board: Conncting Studnts to Collg Succss Th Collg Board is a not-for-profit mmbrship association whos mission is to connct studnts to collg succss and opportunity.
AP Calculus AB 8 Scoring Guidlins Th Collg Board: Conncting Studnts to Collg Succss Th Collg Board is a not-for-profit mmbrship association whos mission is to connct studnts to collg succss and opportunity.
Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces. Young and Freedman Chapter 27
 Magnetic Field and Magnetic Foces Young and Feedman Chapte 27 Intoduction Reiew - electic fields 1) A chage (o collection of chages) poduces an electic field in the space aound it. 2) The electic field
Magnetic Field and Magnetic Foces Young and Feedman Chapte 27 Intoduction Reiew - electic fields 1) A chage (o collection of chages) poduces an electic field in the space aound it. 2) The electic field
Before attempting to connect or operate this product, please read these instructions carefully and save this manual for future use.
 Modl No. RAID Boad Instuctions WJ-NDB301 Bfo attmpting to connct o opat this poduct, plas ad ths instuctions cafully and sav this manual fo futu us. Waning: All ok latd to th installation of this poduct
Modl No. RAID Boad Instuctions WJ-NDB301 Bfo attmpting to connct o opat this poduct, plas ad ths instuctions cafully and sav this manual fo futu us. Waning: All ok latd to th installation of this poduct
http://www.wwnorton.com/chemistry/tutorials/ch14.htm Repulsive Force
 ctivation nrgis http://www.wwnorton.com/chmistry/tutorials/ch14.htm (back to collision thory...) Potntial and Kintic nrgy during a collision + + ngativly chargd lctron cloud Rpulsiv Forc ngativly chargd
ctivation nrgis http://www.wwnorton.com/chmistry/tutorials/ch14.htm (back to collision thory...) Potntial and Kintic nrgy during a collision + + ngativly chargd lctron cloud Rpulsiv Forc ngativly chargd
2 r2 θ = r2 t. (3.59) The equal area law is the statement that the term in parentheses,
 3.4. KEPLER S LAWS 145 3.4 Keple s laws You ae familia with the idea that one can solve some mechanics poblems using only consevation of enegy and (linea) momentum. Thus, some of what we see as objects
3.4. KEPLER S LAWS 145 3.4 Keple s laws You ae familia with the idea that one can solve some mechanics poblems using only consevation of enegy and (linea) momentum. Thus, some of what we see as objects
The Electric Potential, Electric Potential Energy and Energy Conservation. V = U/q 0. V = U/q 0 = -W/q 0 1V [Volt] =1 Nm/C
![The Electric Potential, Electric Potential Energy and Energy Conservation. V = U/q 0. V = U/q 0 = -W/q 0 1V [Volt] =1 Nm/C The Electric Potential, Electric Potential Energy and Energy Conservation. V = U/q 0. V = U/q 0 = -W/q 0 1V [Volt] =1 Nm/C](/thumbs/40/21051327.jpg) Geneal Physics - PH Winte 6 Bjoen Seipel The Electic Potential, Electic Potential Enegy and Enegy Consevation Electic Potential Enegy U is the enegy of a chaged object in an extenal electic field (Unit
Geneal Physics - PH Winte 6 Bjoen Seipel The Electic Potential, Electic Potential Enegy and Enegy Consevation Electic Potential Enegy U is the enegy of a chaged object in an extenal electic field (Unit
Reach Versus Competition in Channels with Internet and Traditional Retailers
 Rach Vsus Comptition in Channls with Intnt and Taditional Rtails Bai R Nault Haskayn School of Businss, Univsity of Calgay, Calgay, Albta, Canada, nault@ucalgayca Mohammad S Rahman Haskayn School of Businss,
Rach Vsus Comptition in Channls with Intnt and Taditional Rtails Bai R Nault Haskayn School of Businss, Univsity of Calgay, Calgay, Albta, Canada, nault@ucalgayca Mohammad S Rahman Haskayn School of Businss,
Gravity. A. Law of Gravity. Gravity. Physics: Mechanics. A. The Law of Gravity. Dr. Bill Pezzaglia. B. Gravitational Field. C.
 Physics: Mechanics 1 Gavity D. Bill Pezzaglia A. The Law of Gavity Gavity B. Gavitational Field C. Tides Updated: 01Jul09 A. Law of Gavity 3 1a. Invese Squae Law 4 1. Invese Squae Law. Newton s 4 th law
Physics: Mechanics 1 Gavity D. Bill Pezzaglia A. The Law of Gavity Gavity B. Gavitational Field C. Tides Updated: 01Jul09 A. Law of Gavity 3 1a. Invese Squae Law 4 1. Invese Squae Law. Newton s 4 th law
Load Balancing Algorithm Based on QoS Awareness Applied in Wireless Networks
 , pp.191-195 http://x.oi.og/10.14257/astl.2015.111.37 Loa Balancing Algoithm Bas on QoS Awanss Appli in Wilss Ntwoks CHEN Xiangqian, MA Shaohui Dpatmnt of Comput Scinc an Tchnology, Hnan Mchanic an Elctical
, pp.191-195 http://x.oi.og/10.14257/astl.2015.111.37 Loa Balancing Algoithm Bas on QoS Awanss Appli in Wilss Ntwoks CHEN Xiangqian, MA Shaohui Dpatmnt of Comput Scinc an Tchnology, Hnan Mchanic an Elctical
Electric Field Examples. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 6B lectric Field amples For ampus Learning Assistance Services at USB 7. Two point charges are located on the -ais as follows: charge q +4 n at position 0.m and charge q +5 n at position -0.3m.
Physics 6B lectric Field amples For ampus Learning Assistance Services at USB 7. Two point charges are located on the -ais as follows: charge q +4 n at position 0.m and charge q +5 n at position -0.3m.
Capacitance and Dielectrics
 Chaptr 5 Capacitanc and Dilctrics 5.1 Introduction...5-3 5. Calculation of Capacitanc...5-4 Exampl 5.1: Paralll-Plat Capacitor...5-4 Intractiv Simulation 5.1: Paralll-Plat Capacitor...5-6 Exampl 5.: Cylindrical
Chaptr 5 Capacitanc and Dilctrics 5.1 Introduction...5-3 5. Calculation of Capacitanc...5-4 Exampl 5.1: Paralll-Plat Capacitor...5-4 Intractiv Simulation 5.1: Paralll-Plat Capacitor...5-6 Exampl 5.: Cylindrical
Econ 371: Answer Key for Problem Set 1 (Chapter 12-13)
 con 37: Answr Ky for Problm St (Chaptr 2-3) Instructor: Kanda Naknoi Sptmbr 4, 2005. (2 points) Is it possibl for a country to hav a currnt account dficit at th sam tim and has a surplus in its balanc
con 37: Answr Ky for Problm St (Chaptr 2-3) Instructor: Kanda Naknoi Sptmbr 4, 2005. (2 points) Is it possibl for a country to hav a currnt account dficit at th sam tim and has a surplus in its balanc
Determining solar characteristics using planetary data
 Detemining sola chaacteistics using planetay data Intoduction The Sun is a G type main sequence sta at the cente of the Sola System aound which the planets, including ou Eath, obit. In this inestigation
Detemining sola chaacteistics using planetay data Intoduction The Sun is a G type main sequence sta at the cente of the Sola System aound which the planets, including ou Eath, obit. In this inestigation
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Factors that Influence Memory
 Ovlaning Factos that Influnc Mmoy Continu to study somthing aft you can call it pfctly. Psychology 390 Psychology of Laning Stvn E. Mi, Ph.D. Listn to th audio lctu whil viwing ths slids 1 2 Oganization
Ovlaning Factos that Influnc Mmoy Continu to study somthing aft you can call it pfctly. Psychology 390 Psychology of Laning Stvn E. Mi, Ph.D. Listn to th audio lctu whil viwing ths slids 1 2 Oganization
Vector Calculus: Are you ready? Vectors in 2D and 3D Space: Review
 Vecto Calculus: Ae you eady? Vectos in D and 3D Space: Review Pupose: Make cetain that you can define, and use in context, vecto tems, concepts and fomulas listed below: Section 7.-7. find the vecto defined
Vecto Calculus: Ae you eady? Vectos in D and 3D Space: Review Pupose: Make cetain that you can define, and use in context, vecto tems, concepts and fomulas listed below: Section 7.-7. find the vecto defined
Forces & Magnetic Dipoles. r r τ = μ B r
 Foces & Magnetic Dipoles x θ F θ F. = AI τ = U = Fist electic moto invented by Faaday, 1821 Wie with cuent flow (in cup of Hg) otates aound a a magnet Faaday s moto Wie with cuent otates aound a Pemanent
Foces & Magnetic Dipoles x θ F θ F. = AI τ = U = Fist electic moto invented by Faaday, 1821 Wie with cuent flow (in cup of Hg) otates aound a a magnet Faaday s moto Wie with cuent otates aound a Pemanent
Chapter 7 Homework solutions
 Chapter 7 Homework solutions 8 Strategy Use the component form of the definition of center of mass Solution Find the location of the center of mass Find x and y ma xa + mbxb (50 g)(0) + (10 g)(5 cm) x
Chapter 7 Homework solutions 8 Strategy Use the component form of the definition of center of mass Solution Find the location of the center of mass Find x and y ma xa + mbxb (50 g)(0) + (10 g)(5 cm) x
Lecture 3: Diffusion: Fick s first law
 Lctur 3: Diffusion: Fick s first law Today s topics What is diffusion? What drivs diffusion to occur? Undrstand why diffusion can surprisingly occur against th concntration gradint? Larn how to dduc th
Lctur 3: Diffusion: Fick s first law Today s topics What is diffusion? What drivs diffusion to occur? Undrstand why diffusion can surprisingly occur against th concntration gradint? Larn how to dduc th
Physics 112 Homework 5 (solutions) (2004 Fall) Solutions to Homework Questions 5
 Solutions to Homework Questions 5 Chapt19, Problem-2: (a) Find the direction of the force on a proton (a positively charged particle) moving through the magnetic fields in Figure P19.2, as shown. (b) Repeat
Solutions to Homework Questions 5 Chapt19, Problem-2: (a) Find the direction of the force on a proton (a positively charged particle) moving through the magnetic fields in Figure P19.2, as shown. (b) Repeat
Instruction: Solving Exponential Equations without Logarithms. This lecture uses a four-step process to solve exponential equations:
 49 Instuction: Solving Eponntil Equtions without Logithms This lctu uss fou-stp pocss to solv ponntil qutions: Isolt th bs. Wit both sids of th qution s ponntil pssions with lik bss. St th ponnts qul to
49 Instuction: Solving Eponntil Equtions without Logithms This lctu uss fou-stp pocss to solv ponntil qutions: Isolt th bs. Wit both sids of th qution s ponntil pssions with lik bss. St th ponnts qul to
Deflection of Electrons by Electric and Magnetic Fields
 Physics 233 Expeiment 42 Deflection of Electons by Electic and Magnetic Fields Refeences Loain, P. and D.R. Coson, Electomagnetism, Pinciples and Applications, 2nd ed., W.H. Feeman, 199. Intoduction An
Physics 233 Expeiment 42 Deflection of Electons by Electic and Magnetic Fields Refeences Loain, P. and D.R. Coson, Electomagnetism, Pinciples and Applications, 2nd ed., W.H. Feeman, 199. Intoduction An
Chapter 22: The Electric Field. Read Chapter 22 Do Ch. 22 Questions 3, 5, 7, 9 Do Ch. 22 Problems 5, 19, 24
 Chapter : The Electric Field Read Chapter Do Ch. Questions 3, 5, 7, 9 Do Ch. Problems 5, 19, 4 The Electric Field Replaces action-at-a-distance Instead of Q 1 exerting a force directly on Q at a distance,
Chapter : The Electric Field Read Chapter Do Ch. Questions 3, 5, 7, 9 Do Ch. Problems 5, 19, 4 The Electric Field Replaces action-at-a-distance Instead of Q 1 exerting a force directly on Q at a distance,
Section 7.4: Exponential Growth and Decay
 1 Sction 7.4: Exponntial Growth and Dcay Practic HW from Stwart Txtbook (not to hand in) p. 532 # 1-17 odd In th nxt two ction, w xamin how population growth can b modld uing diffrntial quation. W tart
1 Sction 7.4: Exponntial Growth and Dcay Practic HW from Stwart Txtbook (not to hand in) p. 532 # 1-17 odd In th nxt two ction, w xamin how population growth can b modld uing diffrntial quation. W tart
AP Physics Electromagnetic Wrap Up
 AP Physics Electomagnetic Wap Up Hee ae the gloious equations fo this wondeful section. F qsin This is the equation fo the magnetic foce acting on a moing chaged paticle in a magnetic field. The angle
AP Physics Electomagnetic Wap Up Hee ae the gloious equations fo this wondeful section. F qsin This is the equation fo the magnetic foce acting on a moing chaged paticle in a magnetic field. The angle
Basis risk. When speaking about forward or futures contracts, basis risk is the market
 Basis risk Whn spaking about forward or futurs contracts, basis risk is th markt risk mismatch btwn a position in th spot asst and th corrsponding futurs contract. Mor broadly spaking, basis risk (also
Basis risk Whn spaking about forward or futurs contracts, basis risk is th markt risk mismatch btwn a position in th spot asst and th corrsponding futurs contract. Mor broadly spaking, basis risk (also
Solution. Problem. Solution. Problem. Solution
 4. A 2-g ping-pong ball rubbed against a wool jacket acquires a net positive charge of 1 µc. Estimate the fraction of the ball s electrons that have been removed. If half the ball s mass is protons, their
4. A 2-g ping-pong ball rubbed against a wool jacket acquires a net positive charge of 1 µc. Estimate the fraction of the ball s electrons that have been removed. If half the ball s mass is protons, their
by John Donald, Lecturer, School of Accounting, Economics and Finance, Deakin University, Australia
 Studnt Nots Cost Volum Profit Analysis by John Donald, Lcturr, School of Accounting, Economics and Financ, Dakin Univrsity, Australia As mntiond in th last st of Studnt Nots, th ability to catgoris costs
Studnt Nots Cost Volum Profit Analysis by John Donald, Lcturr, School of Accounting, Economics and Financ, Dakin Univrsity, Australia As mntiond in th last st of Studnt Nots, th ability to catgoris costs
Mathematics. Mathematics 3. hsn.uk.net. Higher HSN23000
 hsn uknt Highr Mathmatics UNIT Mathmatics HSN000 This documnt was producd spcially for th HSNuknt wbsit, and w rquir that any copis or drivativ works attribut th work to Highr Still Nots For mor dtails
hsn uknt Highr Mathmatics UNIT Mathmatics HSN000 This documnt was producd spcially for th HSNuknt wbsit, and w rquir that any copis or drivativ works attribut th work to Highr Still Nots For mor dtails
Multiple choice questions [60 points]
![Multiple choice questions [60 points] Multiple choice questions [60 points]](/thumbs/40/20623569.jpg) 1 Multiple choice questions [60 points] Answe all o the ollowing questions. Read each question caeully. Fill the coect bubble on you scanton sheet. Each question has exactly one coect answe. All questions
1 Multiple choice questions [60 points] Answe all o the ollowing questions. Read each question caeully. Fill the coect bubble on you scanton sheet. Each question has exactly one coect answe. All questions
Physics 41 HW Set 1 Chapter 15
 Physics 4 HW Set Chapter 5 Serway 8 th OC:, 4, 7 CQ: 4, 8 P: 4, 5, 8, 8, 0, 9,, 4, 9, 4, 5, 5 Discussion Problems:, 57, 59, 67, 74 OC CQ P: 4, 5, 8, 8, 0, 9,, 4, 9, 4, 5, 5 Discussion Problems:, 57, 59,
Physics 4 HW Set Chapter 5 Serway 8 th OC:, 4, 7 CQ: 4, 8 P: 4, 5, 8, 8, 0, 9,, 4, 9, 4, 5, 5 Discussion Problems:, 57, 59, 67, 74 OC CQ P: 4, 5, 8, 8, 0, 9,, 4, 9, 4, 5, 5 Discussion Problems:, 57, 59,
Traffic Flow Analysis (2)
 Traffic Flow Analysis () Statistical Proprtis. Flow rat distributions. Hadway distributions. Spd distributions by Dr. Gang-Ln Chang, Profssor Dirctor of Traffic safty and Oprations Lab. Univrsity of Maryland,
Traffic Flow Analysis () Statistical Proprtis. Flow rat distributions. Hadway distributions. Spd distributions by Dr. Gang-Ln Chang, Profssor Dirctor of Traffic safty and Oprations Lab. Univrsity of Maryland,
F G r. Don't confuse G with g: "Big G" and "little g" are totally different things.
 G-1 Gavity Newton's Univesal Law of Gavitation (fist stated by Newton): any two masses m 1 and m exet an attactive gavitational foce on each othe accoding to m m G 1 This applies to all masses, not just
G-1 Gavity Newton's Univesal Law of Gavitation (fist stated by Newton): any two masses m 1 and m exet an attactive gavitational foce on each othe accoding to m m G 1 This applies to all masses, not just
Design for Cyclic Loading
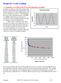 Dsign o Cyclic Loading 1. Compltly vsing cyclic stss and ndanc stngth A ply vsing o cyclic stss mans whn th stss altnats btwn qal positiv and ngativ pak stsss sinsoidally ding ach 300 cycl o opation, as
Dsign o Cyclic Loading 1. Compltly vsing cyclic stss and ndanc stngth A ply vsing o cyclic stss mans whn th stss altnats btwn qal positiv and ngativ pak stsss sinsoidally ding ach 300 cycl o opation, as
Physics 590 Homework, Week 6 Week 6, Homework 1
 Physics 590 Homework, Week 6 Week 6, Homework 1 Prob. 6.1.1 A descent vehicle landing on the moon has a vertical velocity toward the surface of the moon of 35 m/s. At the same time it has a horizontal
Physics 590 Homework, Week 6 Week 6, Homework 1 Prob. 6.1.1 A descent vehicle landing on the moon has a vertical velocity toward the surface of the moon of 35 m/s. At the same time it has a horizontal
Chapter 21. = 26 10 6 C and point charge
 Chapter 21 21.1 What must the distance between point charge 1 26 10 6 C and point charge 2 47 10 6 C for the electrostatic force between them to be 5.70N? The magnitude of the force of attraction is given
Chapter 21 21.1 What must the distance between point charge 1 26 10 6 C and point charge 2 47 10 6 C for the electrostatic force between them to be 5.70N? The magnitude of the force of attraction is given
Chapter 7 Yielding criteria
 Chat 7 Yiling itia. Citia fo yiling What is th maning about yil ition? In this as th stss is un-axial an this oint an aily b tmin. But what if th a sval stss ating at a oint in iffnt ition? Th itia fo
Chat 7 Yiling itia. Citia fo yiling What is th maning about yil ition? In this as th stss is un-axial an this oint an aily b tmin. But what if th a sval stss ating at a oint in iffnt ition? Th itia fo
at 10 knots to avoid the hurricane, what could be the maximum CPA? 59 miles - 54 nm STEP 1 Ship s Speed Radius (e-r) 10 k - 1.0 nm every 6 minutes
 :1 Navigatio :1 Gal 1 1 1 Rf: P, Huica You a udway o cous T ad you axiu spd is 1 kots. Th y of a huica bas 1 T, ils fo you positio. Th huica is ovig towads T at 1 kots. If you auv at 1 kots to avoid th
:1 Navigatio :1 Gal 1 1 1 Rf: P, Huica You a udway o cous T ad you axiu spd is 1 kots. Th y of a huica bas 1 T, ils fo you positio. Th huica is ovig towads T at 1 kots. If you auv at 1 kots to avoid th
The Casino Experience
 Th Casino Expin with Mahi s authnti Indian uisin Lt us nttain you Th Casino Expin 10 Th Staight Flush Expin 20 p ps If you looking fo a gat night out, a Casino Expin patnd This is a gat intoduti to gaing
Th Casino Expin with Mahi s authnti Indian uisin Lt us nttain you Th Casino Expin 10 Th Staight Flush Expin 20 p ps If you looking fo a gat night out, a Casino Expin patnd This is a gat intoduti to gaing
Implied volatility formula of European Power Option Pricing
 Impli volatility fomula of Euopan Pow Option Picing Jingwi Liu * ing hn chool of Mathmatics an ystm cincs, Bihang Univsity, LMIB of th Ministy of Eucation,, Bijing, 009, P.R hina Abstact:W iv th impli
Impli volatility fomula of Euopan Pow Option Picing Jingwi Liu * ing hn chool of Mathmatics an ystm cincs, Bihang Univsity, LMIB of th Ministy of Eucation,, Bijing, 009, P.R hina Abstact:W iv th impli
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
 Chapte 1 1 1.6. Solved Examples Example 1.1 Dimensions and Units A body weighs 1 Ibf when exposed to a standad eath gavity g = 3.174 ft/s. (a) What is its mass in kg? (b) What will the weight of this body
Chapte 1 1 1.6. Solved Examples Example 1.1 Dimensions and Units A body weighs 1 Ibf when exposed to a standad eath gavity g = 3.174 ft/s. (a) What is its mass in kg? (b) What will the weight of this body
(Ch. 22.5) 2. What is the magnitude (in pc) of a point charge whose electric field 50 cm away has a magnitude of 2V/m?
 Em I Solutions PHY049 Summe 0 (Ch..5). Two smll, positively chged sphees hve combined chge of 50 μc. If ech sphee is epelled fom the othe by n electosttic foce of N when the sphees e.0 m pt, wht is the
Em I Solutions PHY049 Summe 0 (Ch..5). Two smll, positively chged sphees hve combined chge of 50 μc. If ech sphee is epelled fom the othe by n electosttic foce of N when the sphees e.0 m pt, wht is the
Displacement, Velocity And Acceleration
 Displacement, Velocity And Acceleation Vectos and Scalas Position Vectos Displacement Speed and Velocity Acceleation Complete Motion Diagams Outline Scala vs. Vecto Scalas vs. vectos Scala : a eal numbe,
Displacement, Velocity And Acceleation Vectos and Scalas Position Vectos Displacement Speed and Velocity Acceleation Complete Motion Diagams Outline Scala vs. Vecto Scalas vs. vectos Scala : a eal numbe,
5.4 Exponential Functions: Differentiation and Integration TOOTLIFTST:
 .4 Eponntial Functions: Diffrntiation an Intgration TOOTLIFTST: Eponntial functions ar of th form f ( ) Ab. W will, in this sction, look at a spcific typ of ponntial function whr th bas, b, is.78.... This
.4 Eponntial Functions: Diffrntiation an Intgration TOOTLIFTST: Eponntial functions ar of th form f ( ) Ab. W will, in this sction, look at a spcific typ of ponntial function whr th bas, b, is.78.... This
Mechanics 1: Work, Power and Kinetic Energy
 Mechanics 1: Wok, Powe and Kinetic Eneg We fist intoduce the ideas of wok and powe. The notion of wok can be viewed as the bidge between Newton s second law, and eneg (which we have et to define and discuss).
Mechanics 1: Wok, Powe and Kinetic Eneg We fist intoduce the ideas of wok and powe. The notion of wok can be viewed as the bidge between Newton s second law, and eneg (which we have et to define and discuss).
[ ] These are the motor parameters that are needed: Motor voltage constant. J total (lb-in-sec^2)
![[ ] These are the motor parameters that are needed: Motor voltage constant. J total (lb-in-sec^2) [ ] These are the motor parameters that are needed: Motor voltage constant. J total (lb-in-sec^2)](/thumbs/40/20779684.jpg) MEASURING MOOR PARAMEERS Fil: Motor paramtrs hs ar th motor paramtrs that ar ndd: Motor voltag constant (volts-sc/rad Motor torqu constant (lb-in/amp Motor rsistanc R a (ohms Motor inductanc L a (Hnris
MEASURING MOOR PARAMEERS Fil: Motor paramtrs hs ar th motor paramtrs that ar ndd: Motor voltag constant (volts-sc/rad Motor torqu constant (lb-in/amp Motor rsistanc R a (ohms Motor inductanc L a (Hnris
Objectives. Capacitors 262 CHAPTER 5 ENERGY
 Objectives Describe a capacitor. Explain how a capacitor stores energy. Define capacitance. Calculate the electrical energy stored in a capacitor. Describe an inductor. Explain how an inductor stores energy.
Objectives Describe a capacitor. Explain how a capacitor stores energy. Define capacitance. Calculate the electrical energy stored in a capacitor. Describe an inductor. Explain how an inductor stores energy.
Carter-Penrose diagrams and black holes
 Cate-Penose diagams and black holes Ewa Felinska The basic intoduction to the method of building Penose diagams has been pesented, stating with obtaining a Penose diagam fom Minkowski space. An example
Cate-Penose diagams and black holes Ewa Felinska The basic intoduction to the method of building Penose diagams has been pesented, stating with obtaining a Penose diagam fom Minkowski space. An example
Gauss Law. Physics 231 Lecture 2-1
 Gauss Law Physics 31 Lectue -1 lectic Field Lines The numbe of field lines, also known as lines of foce, ae elated to stength of the electic field Moe appopiately it is the numbe of field lines cossing
Gauss Law Physics 31 Lectue -1 lectic Field Lines The numbe of field lines, also known as lines of foce, ae elated to stength of the electic field Moe appopiately it is the numbe of field lines cossing
Experiment MF Magnetic Force
 Expeiment MF Magnetic Foce Intoduction The magnetic foce on a cuent-caying conducto is basic to evey electic moto -- tuning the hands of electic watches and clocks, tanspoting tape in Walkmans, stating
Expeiment MF Magnetic Foce Intoduction The magnetic foce on a cuent-caying conducto is basic to evey electic moto -- tuning the hands of electic watches and clocks, tanspoting tape in Walkmans, stating
The example is taken from Sect. 1.2 of Vol. 1 of the CPN book.
 Rsourc Allocation Abstract This is a small toy xampl which is wll-suitd as a first introduction to Cnts. Th CN modl is dscribd in grat dtail, xplaining th basic concpts of C-nts. Hnc, it can b rad by popl
Rsourc Allocation Abstract This is a small toy xampl which is wll-suitd as a first introduction to Cnts. Th CN modl is dscribd in grat dtail, xplaining th basic concpts of C-nts. Hnc, it can b rad by popl
Exam 2 is at 7 pm tomorrow Conflict is at 5:15 pm in 151 Loomis
 * By request, but I m not vouching for these since I didn t write them Exam 2 is at 7 pm tomorrow Conflict is at 5:15 pm in 151 Loomis There are extra office hours today & tomorrow Lots of practice exams
* By request, but I m not vouching for these since I didn t write them Exam 2 is at 7 pm tomorrow Conflict is at 5:15 pm in 151 Loomis There are extra office hours today & tomorrow Lots of practice exams
PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION, week 4, chapter 5, sec 1-7. February 13, 2013
 PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION, week 4, chapter 5, sec 1-7 February 13, 2013 0.1 A 2.00-kg object undergoes an acceleration given by a = (6.00î + 4.00ĵ)m/s 2 a) Find the resultatnt force acting on the object
PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION, week 4, chapter 5, sec 1-7 February 13, 2013 0.1 A 2.00-kg object undergoes an acceleration given by a = (6.00î + 4.00ĵ)m/s 2 a) Find the resultatnt force acting on the object
DEGRADATION MODEL OF BREAST IMAGING BY DISPERSED RADIATION
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Sis A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volum 1, Numb 4/011, pp. 347 35 DEGRADATION MODEL OF BREAST IMAGING BY DISPERSED RADIATION Migul BUSTAMANTE 1, Gastón
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Sis A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volum 1, Numb 4/011, pp. 347 35 DEGRADATION MODEL OF BREAST IMAGING BY DISPERSED RADIATION Migul BUSTAMANTE 1, Gastón
The (Bad?) Timing of Mutual Fund Investors. Oded Braverman,* Shmuel Kandel,** and Avi Wohl*** First version: February 2005 This version: August 2005
 Th (Bad? Timing of Mutual Fund Invstos by Odd Bavman,* Shmul Kandl,** and Avi Wohl*** Fist vsion: Fbuay 2005 This vsion: August 2005 W thank Invstmnt Comany Institut (ICI fo oviding us th mutual fund data
Th (Bad? Timing of Mutual Fund Invstos by Odd Bavman,* Shmul Kandl,** and Avi Wohl*** Fist vsion: Fbuay 2005 This vsion: August 2005 W thank Invstmnt Comany Institut (ICI fo oviding us th mutual fund data
UNIT CIRCLE TRIGONOMETRY
 UNIT CIRCLE TRIGONOMETRY The Unit Cicle is the cicle centeed at the oigin with adius unit (hence, the unit cicle. The equation of this cicle is + =. A diagam of the unit cicle is shown below: + = - - -
UNIT CIRCLE TRIGONOMETRY The Unit Cicle is the cicle centeed at the oigin with adius unit (hence, the unit cicle. The equation of this cicle is + =. A diagam of the unit cicle is shown below: + = - - -
Chapter 6. Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy The concept of forces acting on a mass (one object) is intimately related to the concept of ENERGY production or storage. A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy
Chapter 6 Work and Energy The concept of forces acting on a mass (one object) is intimately related to the concept of ENERGY production or storage. A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy
Lecture 7 Force and Motion. Practice with Free-body Diagrams and Newton s Laws
 Lecture 7 Force and Motion Practice with Free-body Diagrams and Newton s Laws oday we ll just work through as many examples as we can utilizing Newton s Laws and free-body diagrams. Example 1: An eleator
Lecture 7 Force and Motion Practice with Free-body Diagrams and Newton s Laws oday we ll just work through as many examples as we can utilizing Newton s Laws and free-body diagrams. Example 1: An eleator
5 2 index. e e. Prime numbers. Prime factors and factor trees. Powers. worked example 10. base. power
 Prim numbrs W giv spcial nams to numbrs dpnding on how many factors thy hav. A prim numbr has xactly two factors: itslf and 1. A composit numbr has mor than two factors. 1 is a spcial numbr nithr prim
Prim numbrs W giv spcial nams to numbrs dpnding on how many factors thy hav. A prim numbr has xactly two factors: itslf and 1. A composit numbr has mor than two factors. 1 is a spcial numbr nithr prim
