Page 1
|
|
|
- Elvin Lang
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOLVED QUESTION BANK CLASS-X (TERM-II) CHAPTER: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE 1. Mention the common mode of reproduction found in (i) Amoeba (ii) Planaria. [2009] Ans. Amoeba Binary fission in any plane. Planaria Transverse binary fission. 2. Name any two types of asexual reproduction. [2009] Ans. (i) Binary fission (ii) Budding 3. State the methods used for growing rose plants. [2009] Ans. (i) Stem cutting (ii) Bud grafting 4. State what type of method is used for growing jasmine plant. [2009] Ans. Layering 5. Name the hormone, secretion of which is responsible for dramatic changes in appearance in girls when they approach years of age. [2008] Ans. Estrogen. 6. What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate on the reproduction process? [2008] Ans. During the process of DNA copying, some mutations are produced which give rise to useful, harmful or neutral variations in the offspring. Other Important Questions 1. Define reproduction. Ans. The process of producing new individuals of the same species by existing organisms, i.e., parents, is known as reproduction. 2. Name two organisms that show asexual reproduction. Ans. Amoeba and yeast show asexual reproduction. 3. How does Hydra reproduce? Name another organism that reproduces by a similar method. Ans. Hydra reproduces by budding. Another organism that reproduces through budding is yeast. 4. What is a spore? Ans. Spores are special cells formed within special structures called sporangia, that disseminate and can form an entire plant under favourable conditions. 5. Name two plants which reproduce through spores. Ans. Mushroom and fern are reproduced by spores. 6. Why is regeneration considered a method of reproduction? Ans. Regeneration is considered a method of reproduction as sometimes an entire organism developed from its fragmented body. 7. Which vegetative part is used in the propagation of Bryophyllum and mint? Ans. For the propagation of Bryophyllum, leaf is used, while for mint the root is used. 8. Name two types of layering. Ans. The two types of layering are air layering and soil layering. 9. Name some plants where layering is used. Ans. Layering is used in lemon, guava, Hibiscus, bougainvillia, jasmine and several other ornamental plants. 10. Which technique would you use for propagating improved varieties of mango and rose? Ans. For mango grafting, a type of artificial vegetative propagation is used. For rose stem cutting, another type of artificial vegetative propagation is used. 11. Name various types of asexual reproduction. Ans. Fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation, regeneration, parthenogenesis, tissue culture, etc. are different types of asexual reproduction Page 1
2 12. Mention the reproductive parts of a flower. Ans. The reproductive parts of a flower are stamens and carpel. 13. Define fertilisation. Ans. The process of fusion of two haploid gametes, usually a male and a female gamete leading to the formation of diploid zygote is known as fertilisation. 14. What is self-pollination? Ans. If the transfer of pollen grain occurs in the same flower, or between two flowers of the same plant it is referred to as self-pollination. 15. What is cross pollination? Ans. If the pollen is transferred from one flower to another flower of different plant of the same species it is known as cross pollination. 16. What are the agents of pollination? Ans. The agents of pollination are wind, water and animals especially insects. 17. Which process results in formation of zygote? Ans. The fusion of germ cells during fertilisation results in formation of zygote. 18. What grows to form a fruit? Ans. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit. 19. What is carpel? Ans. Carpel is present at the centre of a flower and is the female reproductive part. 20. Which parts of the flower transform into the seed and fruit? Ans. The fertilised ovule develops into the seed and the fertilised ovary into the fruit. 21. What are gonads? Ans. The reproductive organs in animals are called gonads. 22. What is puberty? Ans. Puberty is the age or period, when the reproductive organs of a child start functioning and the child attains sexual maturity. 23. When is ovum released in human female? Ans. After attaining sexual maturity, ovum is released from the ovary after every 28 days. 24. What is endometrium? Ans. Uterus lining is called endometrium. 25. What is implantation? Ans. The process of fixation of zygote on the wall of the uterus is called implantation. 26. What is parturition? Ans. The birth of the fully developed foetus is called parturition. 27. What is ovulation? Ans. The release of ovum from the ovary is called ovulation. 28. Where are the ova produced in woman? Ans. In ovaries. 29. Name two sex hormones. Ans. Testosterone and estrogen. 30. What is the normal reproductive life in human female? Ans. The period between menarche and menopause (12 to 50 years) is the normal reproductive life in human female. 31. What are oral contraceptives? Ans. The oral contraceptives (OCs) are purely hormonal preparations that inhibit the production of gametes by the action on hypothalamus, pituitary and the ovaries. Page 2
3 32. What is epididymis? Ans. This is a coiled tube like structure which is firmly attached to the testis. 33. What are the functions of urethra? Ans. Urethra performs two functions : (i) It acts as a passage for urine. (ii) It acts as the passage for sperms. 34. What are the secondary sex characters in human male? Ans. Secondary sex characters in human males are deepening of voice, growth of beard,moustache and pubic hair. 2. (a) Give reason : Regeneration is not the same as Reproduction. (b) State the mode of a asexual reproduction in Plasmodium [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) Regeneration is not the same as reproduction because most organisms would not normally depend on being cut up to be able to reproduce. (b) Plasmodium reproduce through multiple fission. 3. Name the type of asexual reproduction in : (a) Planaria (b) Rhizopus (iii) Spirogyra (iv) Hydra [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) Planaria Regeneration. (b) Rhizopus Spore formation. 35. Why do testes lie outside the abdominal cavity? (c) Spirogyra Fragmentation (d) Hydra Budding Ans. Testes are present inside a fibrous covering called scrotum or scrotal sac. The scrotum helps in maintaining C lower than the body temperature. This is necessary for the development of sperms. 36. When does puberty occur in human male and female? Ans. In males, puberty is attained at the age of years, while in females, it is years. Short Answer Questions - I [2 Marks] Previous Years' Questions 1. What will happen when : (a) A mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length? (b) Planaria gets cut into two pieces? [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) When a mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length it breaks up into smaller pieces (fragments). These fragments grow into new individuals. (b) If Planaria gets cut into two pieces, both pieces grow into separate individuals. 4. (a) Surgical methods can be used to create a block in the reproductive system for contraceptive purposes. Name such parts where blocks are created in : (i) males (ii) females (b) State any two reasons for using contraceptive devices. [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) (i) In males, the vas deferens is blocked. (ii) In females, the fallopian tube is blocked. (b) Reasons for using contraceptive devices : (i) They prevent pregnancies. (ii) They help to prevent transm 5. (a) What is vegetative propagation? (b) Write any two advantages of practising this method. [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) The formation of a new individual from any vegetative part of the plant body is known as vegetative propagation. (b) Advantages of practising vegetative reproduction. Page 3
4 (i) It allows quicker and easy propagation. (ii) Better qualities of the plants can be maintained and the quality can even be enhanced as in seedless oranges. 6. How does the process of budding differ from the process of spore formation? [2011 (T-II)] Ans. In budding a protuberance develops on the mature organism's body, attains full maturity and then detaches. While in spore formation, spores are formed within special structures called sporangia that disseminate and can form the entire plant. 7. (a) Out of the following plants which two plants are reproduced by vegetative propagation? jasmine, wheat, mustard, banana (b) List any one advantage of practising this kind of propagation. [2011 (T-II)] come from two different and sexually distinct individuals. (ii) Sexual reproduction involves meiosis which provides opportunities for new combination of genes. (iii) It plays a prominent role in the origin of new species and lead to variation required for evolution. 10. In a bisexual flower inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Give reasons. (a) Name the parts of the flower which ripens to form fruit and seed? (b) In the following diagram label A and B. Ans. (a) Jasmine and banana. (b) It allows quicker and easy propagation. 8. (a) Why do testes located in scrotum outside the abdominal cavity? (b) What will happen to ovary and ovule after fertilization in angiospermic plants.] Ans. (a) Testes located in scrotum outside the abdominal cavity since the production of spermatozoa is feasible at a temperature of 2 C lower than the body temperature. (b) After fertilization, the ovary enlarges considerably and becomes the fruit and the ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into seed. Ans. A bisexual flower also contains ovary. The ovary enlarges considerable and becomes the fruit. (a) Ovary ripens to form fruit and ovule develops into seed. 11. With the help of a diagram only show regeneration in Planaria. Regeneration is not possible in all types of animals. Why? [2011 (T-II)] 9. The organisms formed by asexual reproduction are considered as clones. Why? State the advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction. [2011 (T-II)] Ans. In asexual reproduction, the young ones formed are genetically identical to the parents and are considered as clones. Sexual reproduction has following advantages : (i) The offsprings produced by sexual reproduction exhibit diversity of characters because fusing gametes Ans. Regeneration is not possible in all types of animals because all organisms will not depend upon being cut or broken for its reproduction. 12. How does the process of seed germination take place in plants? Describe in brief. Page 4
5 [2011 (T-II)] Ans. Germination starts with the rapid uptake of water by the seed through its micropyle. The first visible indication of germination is the swelling of the seed with a resultant increase in weight. It is also accompanied by the softening of the seed coat. Absorption of water causes a number of physiological changes in the seed. Germinating seeds exhibit increased respiratory activity. The embryo produces enzymes which convert the food material stored in the cotyledons or endosperm into soluble form usable by the growing embryo. Once the food is made available, cell division activity starts in the growing embryo, i.e., radical and plumule. The growth of the embryonic tissue ruptures the seed coat. The radicle is the first to come out of the seed coat and forms the root system. It soon grows towards the soil. The plumule after coming out of the ruptured seed forms the shoot. 13. Name the sex hormones secreted by male and female sex organs in human beings. State one function of each. Ans. Testosterone is produced by the testical (male sex organs) and estrogen and progesterone are produced by ovary (female sex organ). Function of testosterone It brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. Function of estrogen It helps in the development of secondary sex characters like breast development. 15. State in brief any two functions of copper-t used by some women. [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) It prevents pregnancy. (b) It kills the germs. 16. In what respect is the human male gamete different from the female gamete?[2011 (T-II)] Ans. Male gametes (sperms) are mobile and smaller in size while female gamete (ovum) is immobile and bigger in size. 17. What is reproduction? What are its two types? Which one of the two confers new characteristics on the offsprings and how? [2009] Ans. Reproduction is the process of formation of new young individuals of the similar type of mature living being. Reproduction is of two types : (i) Asexual reproduction (ii) Sexual reproduction Only sexual reproduction confers new characteristics on the offspring because the process of DNA replication occurs in sexual reproduction. Mutations occur during DNA replication which give rise to variation, thus confers new characteristics on the offspring. 18. What is binary fission? Draw a diagram to show binary fission in Amoeba. [2009] Ans. Binary fission is a mode of asexual reproduction in many bacteria and protozoans. In it organism simply splits into two equal halves during cell division. 14. State the mode of reproduction in following organisms : Earthworm, Frog, Rhizopus, Plasmodium. [2011 (T-II)] Ans. Earthworm Sexual reproduction Frog Sexual reproduction Rhizopus Spore formation Plasmodium Multiple fission 19. What is regeneration? State a reason why a more complex organism cannot give rise to new individuals through this method. [2009] Page 5
6 Ans. Many organisms like Hydra, Planaria, etc. have the ability to give rise to new organisms from their body parts. This process is called regeneration. Regeneration does not occur in complex organisms. The ability to degenerate in fully differentiated organism is due to specialised cells. In complex organisms, these specialized cells can form lost tissues and organs but not the complete individual as the highly differentiated tissues and organs do not allow this. In complex organisms, regeneration is under neurohormonal control. Fragments do not have nervous or hormonal stimulus to grow into complete organisms. 20. Name the male and female gametes in animals. What is fertilisation and where does it take place in human females? [2009] Ans. Male gamete Sperm Female gamete Ovum Fertilisation is the fusion of male and female gametes to form diploid zygote during sexual reproduction. In human females fertilisation occurs in fallopian tubes. 21. What is reproduction? Mention the importance of DNA copying in reproduction. [2008] Ans. Reproduction is a process by which the living organisms produce the new organisms of their own kinds. The process of copying the DNA may have some variations. These variations are the basis for evolution. 22. Mention the information source of making proteins in the cell. What is the basic event in reproduction? [2008] Ans. Ribosome is the information source of making protein in the cell. The basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy. 23. Name one sexually transmitted disease each caused due to bacterial infection and viral infection. How can these be prevented? [2008] Ans. Sexually transmitted diseases : (a) Bacterial disease Gonorrhoea (b) Viral disease HIV-AIDS These diseases can be prevented by using a covering by the males called condom. 24. Describe briefly four ways in which individuals with a particular trait may increase in a population. [2008] Ans. The individuals with a particular trait may increase in a population by : (A) Simply break up into smaller pieces and grow into new individuals, i.e., fragmentation. (B) Developing a bud which becomes new individual, i.e., budding. (C) Giving rise to new individuals from their body parts, i.e., regeneration. (D) Using some plant parts (stem, root, leaf, etc.) to develop new individuals, i.e., vegetative propagation. 25. Why is it said that sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in the offspring? Ans. It is because sexual reproduction results from the fusion of two gametes coming from two different and sexually distinct individuals. This leads to variation which is necessary for evolution. 26. Why cannot fertilisation take place in flowers if pollination does not occur? Ans. Pollination is essential for transfer of pollen grain to stigma. In the absence of pollination, there will be no male gamete (pollen grain) for fertilisation. Hence, fertilisation cannot take place in flowers if pollination does not occur 27. Why does bread mould grow profusely on a moist slice of bread rather than on a dry slice of bread? (Imp.) Ans. Bread mould requires nutrient and moisture for growth. A dry slice of bread has nutrients but it does Page 6
7 not have water. A moist bread slice contains both nutrients and water hence bread mould grows on it. 28. Leaves of Bryophyllum fallen on the ground produce new plants whereas the leaves of Jasmine do not, why? (V. Imp.) Ans. In Bryophyllum, vegetative propagation occurs through leaves. Buds occur in notches of Bryophyllum leaf. However, when the leaf falls down and comes in contact with the soil, the buds spout and produce plantlets. Leaves of rose do not contain buds and cannot give rise to plantlets What is clone? Why do offspring formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity? (Imp.) Ans. Clone is an exact genetic replica of another individual. In asexual reproduction, offspring are produced by a single parent without fertilisation or fusion of gametes. In asexual reproduction, the younger ones are genetically identical to the parents and another young ones as they posses exact copies of DNA. Hence, offspring formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity 30. Write one disadvantage of asexual reproduction. When and how does multiple fission take place? Ans. Asexual reproduction produces identical organisms generation after generation. New organisms, therefore, carry the defects of their parents. Under unfavourable conditions, multiple fission which results in the formation of many new organisms from a single parent takes place. Multiple fission occurs by the formation of a cyst. 1. State in brief the function of the following organs in the human female reproductive system. (a) Ovary (b) Fallopian tube (c) Uterus [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) Ovary Ovary produces ova or eggs. Ovary also secrete a hormone estrogen which helps in the development of secondary sexual characters like breast development. (b) Fallopian tube Fallopian tube conveys the egg from the ovary to the uterus and provides the appropriate environment for its fertilisation. (c) Uterus After fertilisation, the embryo develops in uterus. 2. (a) Identify the asexual method of reproduction in each of the following organisms : (i) rose (ii) yeast (iii) planaria (b) What is fragmentation? Name a multicellular organism which reproduces by this method. Ans. (a) (i) Rose Propagates through stem (ii) Yeast Budding (iii) Planaria Regeneration (b) Fragmentation Some multicellular organisms with relatively simple body organisation reproduce by breaking their bodies into small pieces. Each of these pieces is called a fragment. These fragments grow into new individuals and the mode of reproduction is called fragmentation. Spirogyra reproduces by fragmentation. 3. Differentiate between : (a) Asexual and sexual reproduction. (b) Plumule and Radicle (c) Pollination and Fertilisation Answer: Nucleus divides followed by the distribution of cytoplasm around the daughter nuclei. On the return of favourable conditions, daughter cells are released by breaking the cell wall. Short Answer Questions - II [3 Marks] Asexual Reproduction (i) New individual is produced from a single parent. (ii) It involves the union of gametes. (iii) The young ones are genetically identical to the parents. (b) Plumule (i) Plumule is future shoot. Sexual Reproduction (i) New individual is produced from two parents. (ii) It does not involve the union of gametes. (iii) The young ones are not genetically identical to the parents. Radicle (i) Radicle is future root. Page 7
8 (ii) It grow towards the sun. (c) Pollination (i) It is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a gametes. (ii) It is a physical process. (iii) It occurs only in seed plants. (iv) It carries the male gamete to the (v) It precedes fertilisation. (ii) It grows inside the soil or water Fertilisation (i) It is the fusion of male and female flower. (ii) It is a physio-chemical (biological) process. (iii) It occurs in plants and animals of various types. (iv) It actually brings about fusion of gametes. (v) Fertilisation occurs only after pollination when the pollen grain has germinated and sent the male gametes to the ovule. 4. Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants? (b) Name the different parts of a flower that has germ cells. (c) List any two agents of pollination. [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) Some plants like banana, seedless grapes, rose, which cannot produce viable seeds, can be easily grown by vegetative propagation. To get genetically identical copies and to maintain and preserve a stock of selected varieties, vegetative propagation is the only means. It is an easier less expensive and rapid method of propagation. (b) Style and ovule both have germ cells. (c) Wind and water. 5. What happens to the pollen which falls on a suitable stigma? Explain. [2011 (T-II)] Ans: After the pollen grains are deposited on the suitable stigma, the pollen grains absorb water and sugar from the surface of stigma and swell up. A tube grows out of the pollen grain and travel through the style to reach the ovary. The pollen tube carrying two male gametes which liberated inside the embryo sac. One male gamete fuses with the egg to form zygote. The other male gamete fuses with the secondary nucleus to form the endosperm, which provides nourishment to the growing embryo. 6. (a) How do the oral pills function as contraceptives? (b) The use of these pills may be harmful. Why? [2011 (T-II)] Ans. (a) Oral pills acts by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilisation cannot occur. (b) Since oral pills change hormonal balances, they can cause side effect too. 7. List and describe in brief any three ways devised to avoid pregnancy. [2011 (T-II)] Ans. Foam tablets, jellies, creams and spermicides are common chemicals used by females. These are placed in vagina. Ovulation and fertilisation can be prevented by changing hormonal balance of the body. It can be done by taking oral pills. Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD) such as the loop or the copper-t are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. The drawbacks with these devices are bleeding and discomfort. 8. What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name four such diseases. Which one of them damages the immune system of human body? [2009] Ans. The diseases which are spread by sexual contact from an infected person to a healthy person, are called sexually transmitted diseases or STDs. (i) AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) (ii) Gonorrhoea (iii) Syphilis (iv) Genital herpes AIDS damages the immune system of human body. 9. (a) Explain the terms : (i) implantation (ii) placenta (b) What is the average duration of human pregnancy? [2009] Ans. (a) (i) Implantation : The embedding of a fertilised mammalian egg into the wall of the uterus (womb) where it will continue developing, is called implantation. (ii) Placenta : After implantation, a disc like special tissue develops between uterus wall and the embryo called placenta. The placenta is responsible for exchange of nutrients, oxygen and waste products between the embryo and mother. (b) The average duration of human pregnancy is 280 days or 40 weeks. 10. Define grafting. Suggest any two advantages and disadvantages of grafting. (V.Imp.) Page 8
9 Ans. Grafting is a process in which the two parts of different plants are joined by bandaging them tightly. Advantages : (i) A young scion can be made to flower when it is grafted on a mature tree. (ii) Different varieties can be grafted on the same stock. Disadvantages : (i) Sexual reproduction is a necessity for evolution. (ii) Plants produce very few seeds. 11. Name any two mechanical barriers of pregnancy. What are the benefits of using mechanical barriers during sexual act? (Imp.) Ans. Mechanical barriers of pregnancy : (i) Condoms (ii) Diaphragms Benefits of using mechanical barriers (i) Prevention of pregnancy Mechanical barriers prevent the passage of sperms into the genital tract of the female. Consequently, pregnancy does not occur. (ii) No transmission of infections Mechanical barriers also prevent the transmission of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) from infected partner to the noninfected partner. 12. State in brief the functions of the following parts of the human male reproductive system : (i) Scrotum (ii) Testes (iii) Vas deferens Ans : (i) Scrotum : It contains and supports the testes. It is situated outside the body cavity and allow sperm to develop at the optimum temperature, which is slightly lower than body temperature. (ii) Testes : The formation of male germ cells or sperms take place in it. Leydig cells of testes secrete hormone testosterone which brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. Ans: Ovary produces ova (female gamete) and also produce a hormone estrogen. Fallopian tube conveys the egg from the ovary to the uterus and also provides the appropriate environment for its fertilisation. 14. What could be the possible reason for declining female to male sex ratio in our country. Suggest two measures to achieve 1:1 ratio. Ans: Because of reckless female foeticides, child sex ratio is declining at an alarming rate in our country. Measures to achieve 1:1 ratio (i) Prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law. It should be followed strictly. (ii) Peoples should be literate to understand the importance of girl child. 15. What is the advantage of reproducing through spores? Ans: The spores are covered by thick walls that protect them until they come into contact with another moist surface and can begin to grow. 16. How does variation lead to the survival of species overtime? Ans: If some variations were to be present in a few individuals in these populations, there would be some chance for them to survive. Thus, if there were a population of bacteria living in temperate water and if the water temperature were to be increased by global warming most of these bacteria would die, but the few variants resistant to heat would survive and grow further. Variation is thus useful for the survival of species over time. (iii) Vas deferens : It ascends into the abdomen, passes over the urinary bladder and receives duct from the seminal vesicles behind the urinary bladder to form the ejaculatory duct. 13. State the role of ovary and fallopian tube in human body. Page 9
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout
 PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Plant Reproduction. 2. Evolutionarily, floral parts are modified A. stems B. leaves C. roots D. stolons E. suberins
 Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction
 Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns
 Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions. Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9. Chapter 6 Plant structure and function
 1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth?
 1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
8. Study the cladogram underline the derived characteristics and circle the organisms that developed from them.
 Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice
 10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification
 Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification 1. Who proposed Five Kingdom Classification? Give the bases of classification. Ans. Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification based on :- (i) Cell
Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification 1. Who proposed Five Kingdom Classification? Give the bases of classification. Ans. Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification based on :- (i) Cell
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Biology 213 Angiosperms. Introduction
 Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring
 WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes?
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Fungi and plants practice
 Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
www.njctl.org PSI Biology Mitosis & Meiosis
 Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Sexual Reproduction. The specialized cells that are required for sexual reproduction are known as. And come from the process of: GAMETES
 Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Dissect a Flower. Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination
 Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Chapter 3. Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction. Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview Objectives bold Part I Floral Anatomy . calyx sepals corolla, petals, stamens, filament
 Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
2. Fill in the blank. The of a cell is like a leader, directing and telling the different parts of the cell what to do.
 1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
Introduction to Plant Propagation. Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM
 Introduction to Plant Propagation Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM Purposes for Plant Propagation Multiply the number of a species Perpetuate a species Maintain the youthfulness
Introduction to Plant Propagation Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM Purposes for Plant Propagation Multiply the number of a species Perpetuate a species Maintain the youthfulness
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS
 CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
Asexual Reproduction Grade Six
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark B Describe the characteristics of an organism in terms of a combination of inherited traits and recognize reproduction as a characteristic of living organisms
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark B Describe the characteristics of an organism in terms of a combination of inherited traits and recognize reproduction as a characteristic of living organisms
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
Class Time: 30 minutes. Other activities in the Stem Cells in the Spotlight module can be found at: http://gslc.genetics.utah.edu/teachers/tindex/
 Teacher Guide: Color-Label-Learn: Creating Stem Cells for Research ACTIVITY OVERVIEW Abstract: Students color and label images on a worksheet and answer questions about the on-line content featured in
Teacher Guide: Color-Label-Learn: Creating Stem Cells for Research ACTIVITY OVERVIEW Abstract: Students color and label images on a worksheet and answer questions about the on-line content featured in
1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells
 Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
Germination is the process in which a
 The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS
 PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land,
 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Master Curriculum Topic Study: Human Body Systems
 Master Curriculum Topic Study: Human Body Systems Session C Section I: Culminating Ideas for Adult Literacy 1. The fundamental building block of organisms is cells. a. Cells combine to form tissues, which
Master Curriculum Topic Study: Human Body Systems Session C Section I: Culminating Ideas for Adult Literacy 1. The fundamental building block of organisms is cells. a. Cells combine to form tissues, which
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
 Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
PLANT DIVERSITY. EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae
 PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Stages. Differences in the Developmental Mechanisms of Plants and Animals. Development
 Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Puberty is the name given to the physical changes that happen between childhood and adulthood
 LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
II. III. 2004 Core Knowledge National Conference, Grade Level, (Unit Name Here) 1
 Teaching A Touchy Topic: Life Cycles and Reproduction Grade Level: Fifth Grade Written by: Kimberly Ruckh, Linda Cambra, Dallas Bankston; Challenge Charter School, Glendale, Az. Length of Unit: Five Lessons
Teaching A Touchy Topic: Life Cycles and Reproduction Grade Level: Fifth Grade Written by: Kimberly Ruckh, Linda Cambra, Dallas Bankston; Challenge Charter School, Glendale, Az. Length of Unit: Five Lessons
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida. Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology
 Lesson 251c Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Core Area. Animal Science Unit 250. Genetics and Breeding Topic 251. Fertilization California Academic Standard. Science Grades 9 through 12 Biology/Life
Lesson 251c Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Core Area. Animal Science Unit 250. Genetics and Breeding Topic 251. Fertilization California Academic Standard. Science Grades 9 through 12 Biology/Life
Plant and Soil Science I
 Plant and Soil Science I Levels: Grades 9-12 Units of Credit: 1.00 CIP Code: 02.0411 Core Code: 30-02-00-00-080 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: # 140 COURSE DESCRIPTION Students will develop knowledge and
Plant and Soil Science I Levels: Grades 9-12 Units of Credit: 1.00 CIP Code: 02.0411 Core Code: 30-02-00-00-080 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: # 140 COURSE DESCRIPTION Students will develop knowledge and
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
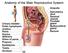 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones
 Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses
 B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 55 Q. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released
B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 55 Q. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released
THE WELL. Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices WOMAN CENTRE
 THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
KENDRIYAVIDYALAYASANGATHAN.CHENNAI REGION CLASS XII COMMONPREBOARD EXAMINATION SUBJECT- BIOLOGY. Section - A
 KENDRIYAVIDYALAYASANGATHAN.CHENNAI REGION CLASS XII COMMONPREBOARD EXAMINATION SUBJECT- BIOLOGY TIMEALLOTED: 3HRS MAX.MARKS:70 General Instructions: All questions are compulsory. This question paper consists
KENDRIYAVIDYALAYASANGATHAN.CHENNAI REGION CLASS XII COMMONPREBOARD EXAMINATION SUBJECT- BIOLOGY TIMEALLOTED: 3HRS MAX.MARKS:70 General Instructions: All questions are compulsory. This question paper consists
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
