Chapter 2 The Art of the Ancient Near East
|
|
|
- Russell Harrington
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 The Art of the Ancient Near East
2 Bronze Age in the Ancient Near East BCE Iron Age in the Ancient Near East 1200 BCE 600 BCE
3
4 The Ancient Near East Mesopotamia: a Greek word meaning 'between the rivers'. An ancient region of southwest Asia between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in modern-day Iraq.
5 The delta could only be made habitable by large-scale irrigation and flood control, which was managed first by a priestly class and then by godlike kings. Consequently the plentiful supply of food permitted the growth of large urban population. Irrigation in Ancient Mesopotamia Advances in the design of the plough boosted the productivity of the Sumerian peasant. By 3000 BC, the original wooden ploughshare, had given way in Sumer to a much sturdier bronze blade. Cylinder Seal Showing God of Agriculture and Two Others Plowing
6 Sumerian Art: 3 rd millennium BCE (31-20th. c. BCE) Ancient Sumer was not a unified nation but made up of independent city-states. Rulers and priests directed the communal activities including canal construction, crop collection, and food distribution. Development of agriculture made it possible for some members to specialize in other activities such as manufacturing, trade and administration.
7 Sumerian Clay Tokens 4 th mill BCE
8 Comparison of tokens and Sumerian characters Sumerian pictographic tablet. c BCE
9 Stylus Cuneiform (Latin - Wedge Shaped ) Writing Used by the Sumerians, Akkadians Assyrians Babylonians and Persians.
10 Tablet & Envelope with Cuneiform
11 Cella: (Also called Holy of Holies ) the inner room of the temple, in which the statue of the god was situated Cella Plan of thewhite Temple, Uruk, Iraq, ca BCE. 40 high. White Temple and Ziggurat, Uruk, Iraq, ca BCE. 40 high.
12 Inanna: The chief Sumerian goddess, associated with fertility, the natural world, and war. Later equated with the Babylonian Ishtar. Female head (Inanna?), from Uruk, Iraq, ca BCE. Marble, approx. 8 high. Iraq Museum, Baghdad
13 Female head (Inanna?), from Uruk, Iraq, ca BCE. Marble, approx. 8 high. Iraq Museum, Baghdad
14 Register: One of a series of superimposed bands in a pictorial narrative, or the particular levels on which motifs are placed. Warka Vase Presentation of offerings to Inanna from Uruk, Iraq, ca BCE. Alabaster, 3 1/4 high. Iraq Museum, Baghdad
15 Warka Vase
16 Warka Vase. Detail. Innana and the Priest-King
17 Warka Vase Detail.
18 Warka Vase Detail. Comparison: Hunter. Çatal Höyük, Turkey. c.5750 BCE
19 Detail Warka Vase
20 Warka Vase Detail. Presentation of offerings to Inanna
21 Warka Vase Stolen in April 2003, returned to Iraq Museum: June 2003.
22 Egyptian wall painting. Oxen pulling a plow. Tomb of Sennedjem The Courtship of Inanna & Dumuzi ( Circa 3000 BCE ) Inanna spoke: "What I tell you Let the singer weave into song. What I tell you, Let it flow from ear to mouth, Let it pass from old to young: My vulva, the horn, The Boat of Heaven, Is full of eagerness like the young moon. My untilled land lies fallow. As for me, Inanna, Who will plow my vulva! Who will plow my high field! Who will plow my wet ground! As for me, the young woman, Who will plow my vulva! Who will station the ox there! Who will plow my vulva!" Dumuzi replied: "Great Lady, the king will plow your vulva. I, Dumuzi the King, will plow your vulva."
23 I will sing the song of the man of battle, the man of battle. I will sing the song of lord Gilgamesh, the man of battle, I will sing the song of the lord with the very black beard, the man of battle. I will sing the song of him with the wellproportioned limbs, the man of battle From the Epic of Gilgamesh Gilgamesh kills the heavenly bull 3rd millennium BCE Sumerian ceramic relief
24 Votive offering is an object left in a sacred place for ritual purposes. Statuettes of two worshipers Votive figureds from temple at Eshnunna, Iraq, ca BCE. Gypsum inlaid with shell and black limestone, tallest figure approx. 2 6 high.
25 Votive figures from the temple at Eshnunna, Iraq, ca BCE.
26 Votive figures from the temple at Eshnunna, Iraq, ca BCE.
27 Leonard Woolley (right) and T. E. Lawrence at the Excavations at Carchemish, Syria, 1913 Sir Leonard Woolley, , British archaeologist who directed the joint British Museum and Univ. of Pennsylvania expedition at Ur in Mesopotamia ( ). Woolley oversaw the excavation of the cemetery at Ur, which included 16 royal tombs with treasures of gold and lapis lazuli and evidence of large-scale human sacrifice.
28 Standard of Ur, Peace side Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE Wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli (semiprecious blue stone from Afghanistan), red limestone, approx. 8 x 1 7. British Museum. London
29 Hierarchical Scale: The representation of more important figures as larger than less important figures. Standard of Ur, War side, Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE Wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and red limestone, approx. 8 x 1 7.
30
31 Standard of Ur, Peace side, Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE Wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and red limestone, approx. 8 x 1 7.
32 Standard of Ur Detail: lyre player
33 Sir Leonard Woolley with the triangular frame of an excavated Sumerian harp, 1920s. (Plaster cast.) Such a frame is an archetype for the more developed mediaeval and modern framed harps. Bull-headed lyre (restored), Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE. Gold leaf and lapis lazuli over a wooden core, approx. 5 5 high University of Pennsylvania.
34 Bull-headed lyre (restored), Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE. Gold leaf and lapis lazuli over a wooden core, approx. 5 5 high University of Pennsylvania..
35 Heraldic composition: a composition that is symmetrical on either side of a central figure Soundbox of a lyre from the Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE. Wood with inlaid gold, lapis lazuli, and shell, approx. 1 7 high.
36 Ram Caught in a Thicket, From Ur, southern Iraq, about BCE. Gold, silver, lapis lazuli, copper, shell, red limestone, and bitumen H cm. Penn Museum
37 Ram (or Goat) in a Thicket From Ur, southern Iraq, about BCE. British Museum
38 Sacred tree on Sumerian seals L.- c BCE B.-c BCE
39 Cylinder Seal: A small stone cylinder incised with reversed designs so that when it was rolled over a soft surface the design appeared in relief. These seals were used to mark property and to legalize documents. Banquet scene, cylinder seal (left) and its modern impression (right), from the from tomb of Puabi, Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE. Lapis lazuli, approx. 2 high.
40 Cylinder seal with Banquet Scene, from tomb of Puabi, Royal Cemetery, Ur 2600BCE. Lapis Lazuli, 2 high. British Museum, London
41 Akkadian Art: 3 rd millennium BCE (Bronze Age)
42 A map of the Akkadian Empire, its dependent territories, and conquests.
43 Stele - a carved stone slab used to mark graves or to commemorate historical events Victory Stele of Naram-Sin, From Susa, Iran (probably came originally from Sippar, an Akkadian city and brought by the Elamites to Susa), BCE Pink sandstone, approx. 6 7 high. Louvre, Paris.
44 Comparison: Ishtar (Queen of heaven/morning and evening star) and Shamash (sun god). Akkadian cylinder seal Victory Stele of Naram-Sin. Detail
45 Victory Stele of Naram-Sin. Detail
46 Victory Stele of Naram-Sin. Detail
47 Victory Stele of Naram-Sin, From Susa, Iran, BCE Pink sandstone, approx. 6 7 high. Louvre, Paris. Discussion Question 5: Compare the Sumerian style with the Akkadian style. Notice the themes; organization of the space; proportions of figures; order vs. chaos; level of realism etc. Standard of Ur, War side, Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE Wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and red limestone, approx. 8 x 1 7.
48 Head of an Akkadian ruler, from Nineveh, Iraq, ca BCE. Copper, 1 2 3/8 high.
49 Neo Sumerian Art: Lagash & Third Dynasty of Ur 3 rd millennium BCE (Bronze Age)
50 Seated statue of Gudea holding temple plan, Iraq, ca BCE. Diorite, approx. 2 5 high. Louvre, Paris.
51 Gudea of Lagash c BCE, Diorite
52 Gudea of Lagash. c BCE, Diorite cm. (29 inches) tall. Louvre, Paris. Comparison: Statuettes of two worshipers Votive figureds, Iraq, ca BCE. Gypsum inlaid with shell and black limestone, tallest figure approx. 2 6 high.
53 Ziggurat: a monumental platform for a temple. The ziggurat was a pyramidal structure, built in receding tiers upon a rectangular or square platform, with a shrine at the summit. Nanna (the moon god) Ziggurat, Ur (present day Muqaiyir) Iraq, ca BCE. Mud bricks. 50 high. (Restored by the Neo-Babylonians, 6 th BCE)
54 Model of the Ziggurat at Ur. Aerial view of the ziggurat
55 Ziggurat, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE. Mud bricks. 50 high. (Restored by the Neo-Babylonians, 6th BCE)
56 Babylonian Art: 2 nd millennium BCE (Bronze Age)
57 Stele of Hammurabi, from Susa, Iran, ca BCE. Basalt, approx. 7 4 high. Louvre, Paris.
58 Comparison: Shamashs rises from Mount Mashu to bring the dawn. Babylonian cylinder seal. Stele of Hammurabi from Susa, Iran, ca BCE. Basalt, approx. 7 4 high.
59 Compare the Victory Stele of Naram Sin with the stele depicting the Code of Hammurabi. Consider the type of stone used, the compositional format, relative size of figures, and treatment of divine figures or sacred ground. How do these images reinforce the authority of the leaders who are depicted?
60 Hittite Art: 2nd millennium BCE (Bronze Age)
61 Lion Gate, Boghazköy, Turkey, ca BCE. Limestone, lions approx. 7 high.
62 Amulet Depicting Enthroned Hittite Sun Goddess. Gold. 2. Late Bronze Age ( B.C.E.)
63 Assyrian Art: 9-7th c. BCE (Iron Age)
64
65 The city's fortification walls form an almost perfect square, covering a surface of about 3 sq km The Palace The citadel with palaces and temples towers above the lower town on an artificially erected platform. The length of the walls was Assyrian units, which corresponded to the numerical value of Sargon's name. Plan of Dur-Sharruken by the French excavator Victor Place Sargon, King of the World, has built a city, Dur Sharukin (citadel of Sargon) he had named it
66 Reconstruction drawing of the citadel of Sargon II Khorsabad, Iraq, ca BCE. 25 acres; more than 200 courtyards and rooms; the length of the walls was Assyrian units, which corresponded to the numerical value of Sargon's name. Sargon, King of the World, has built a city, Dur Sharukin (citadel of Sargon) he had named it
67 Throne Room Reconstruction drawing of the citadel of Sargon II Khorsabad, Iraq, ca BCE. Fortified walls enclose this complex, access to which came by a twisting path through a sequence of courtyards and smaller chambers. The seven stage ziggurat representing the cosmic order of the seven planets
68 Lamassu (winged, human-headed bull), from the citadel of Sargon II, Khorsabad, Iraq, ca BCE. Limestone, approx high. Louvre, Paris.
69 Side view. Lamassu from the citadel of Sargon II, Khorsabad, Iraq, ca BCE.
70 Detail. Lamassu from the citadel of Sargon II, Khorsabad, Iraq, ca BCE.
71 Detail. Lamassu from the citadel of Sargon II, Khorsabad, Iraq, ca BCE.
72 Hero (Izdubar/Gilgamesh?) Overpowering a Lion Citadel of Sargon II BC Alabaster with traces of paint. H m Paris, Louvre Comparison: Gilgamesh kills the heavenly bull 3rd millennium BCE Sumerian ceramic relief
73 Ashurbanipal hunting lions, relief from the North Palace of Ashurbanipal, Nineveh, Iraq, ca BCE. Gypsum, 5 4 high.
74 Ashurbanipal hunting lions, Detail. relief from the North Palace of Ashurbanipal, Nineveh, Iraq, ca BCE. Gypsum, 5 4 high.
75 Detail. Ashurbanipal hunting lions, relief from the Palace of Ashurbanipal, Nineveh, Iraq
76 Ashurbanipal hunting lions. Detail. relief from the Palace of Ashurbanipal, Nineveh, Iraq
77 Ashurbanipal hunting lions. Detail. Relief from the Palace of Ashurbanipal, Nineveh, Iraq
78 Comparison: Standard of Ur, War side Royal Cemetery, Ur, Iraq, ca BCE Wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and red limestone, approx. 8 x 1 7. Ashurbanipal hunting lions, relief from the North Palace of Ashurbanipal, Nineveh, Iraq, ca BCE. Gypsum, 5 4 high.
79 Assyrian archers pursuing enemies, relief from the Northwest Palace of Ashurnasirpal II, Nimrud, Iraq, ca BCE. Gypsum, /8 high. British Museum, London.
80 Traces of black, white, red, and blue paint were visible when the reliefs were first uncovered. Hair, beards, sandals painted black Eyes - white with black pupils; Daggers, bows, tongues of birdheaded divinities red. The mud-brick walls above the reliefs were plastered and painted with floral, geometric, and figural designs in the same four colors. Reconstruction of Ashurnasirpal's throne room at Nimrud., published by Layard Plaster fragment found in debris of the Throne Room of the Northwest Palace.
81 Eagle Headed Spirits by Sacred Tree c BCE. Palace of Ashurnasirpal II. Nimrud. Iraq
82 Two carved figures of Ashurnasirpal II, facing a stylized sacred tree, from Northwest palace at Nimrud.
83 Comparison: Sacred tree on Sumerian seals L.- c BCE B.-c BCE
84 Isis video shows complete destruction of ancient city of Nimrud in Iraq
85 Neo-Babylonian: 7-6th c. BCE (Iron Age)
86 Crenellation: a parapet (short wall) with open spaces that surmounts a wall and is used for defense or decoration. Ishtar Gate, Processional Way, Hanging Gardens and Murduk Ziggurat. Reconstruction drawing of Babylon.
87 Ishtar Gate & Processional Way (also called May the Enemy not Have Victory. )
88 Model of Ishtar Gate. Staatliche Museen, Berlin.
89 Ishtar Gate (restored), Babylon, Iraq, ca. 575 BCE. Glazed brick. 47 high 32 wide Staatliche Museen, Berlin.
90 Marduk: The chief god of the Babylonians. The creator of mankind and the god of light and life. Dragon (Associated with the chief god Marduk) from Ishtar Gate Babylon, Iraq, ca. 575 BCE. Glazed brick.
91
92 Bull (Associated with the storm god Adad) from Ishtar Gate Babylon, Iraq, ca. 575 BCE. Glazed brick.
93 Throne Room Wall (restored). Babylon ca. 575 BCE. Glazed brick. Staatliche Museum, Berlin.
94 Lion from the Processional Way (Associated with the goddess Ishtar). c. 575 BCE. Molded and glazed brick. Babylon. Iraq.
95 Ishtar. 300 BCE -100 BCE. Alabaster Comparison: Woman holding a bison horn from Laussel, Dordogne, France, ca. 25,000 20,000 BCE. Painted limestone 1 6 high
96 Persian: Achaemenid Period 6-4th c. BCE (Iron Age)
97 The Persians are an Iranian people who speak the Persian language and share a common culture and history. Cyrus the Great (ca. 576 or 590 BCE 529 BCE): The founder of the Persian Empire under the Achaemenid dynasty. As leader of the Persian people, he conquered the Medes and unified the two separate Iranian kingdoms. Darius the Great (ca. 549 BCE 486/485 BCE): Divided the Persian Empire into twenty provinces, each under the supervision of a governor or satrap. The satrap position was autonomous, allowing each province its own distinct laws, traditions, and elite class. Every province, however, was responsible for paying a gold or silver tribute to the emperor. Many building projects were initiated during the reign of Darius, with the largest being the building of the new capital of Persepolis.
98 The Persian Empire I am Darius, great King, King of Kings, King of countries, King of this earth.
99 Persepolis (royal audience hall in the background), Iran, ca BCE.
100 This great complex was created by at least three Persian monarchs as one of the capitals of the Persian empire. Its ruins reveal architectural influences from other cultures in Mesopotamia, notably the Hittites and Assyrians, as well as the Egyptians. Plan of the palace at Persepolis, begun ca. 518 B.C.E.
101 The Apadana had seventy-two columns, each is 19 m high. They carried the weight of the vast and heavy ceiling. Capital: Decorative element at the upper part of a column or pier. The capitals were made from animal sculptures such as two headed bulls, lions and eagles. The columns were joined to each other with the help of oak and cedar beams, which were brought from Lebanon. Double griffin (lion and eagle together) Capital of a column of the Audience hall (Apadana) at Louvre, Paris
102 Processional frieze. Detail. On the terrace of the royal audience hall (apadana), Persepolis, Iran, ca BCE.
103
104 Processional frieze. Detail. On the terrace of the royal audience hall (apadana), Persepolis, Iran, ca BCE. Comparison: Kore, from the Acropolis, Athens, Greece, ca BCE. Marble, approx /2 high. Acropolis Museum, Athens.
105
106 Darius celebrating victory over enemies BCE. Persepolis. Iran.
107 Ahura Mazda ( Wise Lord ): The chief deity of Zoroastrianism, the creator of the world, the source of light, and the embodiment of good. Ahura Mazda is not omnipotent, but will utimately prevail. Until then, the role of mankind is to maintain the order - by resisting chaos - through good thoughts, words and actions. Ahriman (Angra Mainyu): Ahura Mazda's adversary, the chief spirit of darkness and evil in Zoroastrianism. Ahura Mazda. Reliefs from Persepolis. Iran BCE.
108 Comparison: Two carved figures of Ashurnasirpal II, facing a stylized sacred tree, from Northwest palace at Nimrud. Darius celebrating victory over enemies BCE. Persepolis. Iran. Comparison: Victory Stele of Naram-Sin, From Susa, Iran (probably came originally from Sippar, an Akkadian city and brought by the Elamites to Susa), BCE Pink sandstone, approx. 6 7 high. Louvre, Paris.
109 Scene from Persian mythology in Apadana Hall: Angra Mainyu (Ahriman) kills the primeval bull, whose seed is rescued by Mah, the moon, as the source for all other animals.
110 Lamassi from Persepolis
111
112 Comparison: Lamassu from the citadel of Sargon II, Khorsabad, Iraq, ca BCE. Alabaster. Louvre, Paris
113 Winged sphinx from the palace of Darius at Susa.
114 Royal Guard. Detail. East gate of the palace of Darius at Susa. 6 th c. BCE London, British Museum Marduk s Dragon. Ishtar Gate, Babylon, Iraq, ca. 575 BCE. Glazed brick.
115 Persian: Sassanian
116 Head of a Sasanian king (Shapur II?), ca. 350 CE. Silver with mercury gilding, 1 3 3/4 high. Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
117 Shapur I Triumphing Over the Emperors Philippus the Arab and Valerian rock-cut relief, Bishapur, Iran, ca. 260 CE.
118
119 Akkadian: Victory Stele of Naram-Sin, BCE Sumerian: Standard of Ur, War side, ca BCE Discussion Question 6: Rulers used art for propaganda since the early days of civilization. Examine the depictions of rulers in the art of the Ancient Near East. Notice the messages that are being conveyed and the relationships between rulers and gods. Discuss Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian, Assyrian and Persian art and give specific examples. Babylonian: Stele of Hammurabi. ca BCE. Basalt, approx. 7 4 high. Persian: Darius celebrating victory over enemies BCE. Persepolis. Iran. Assyrian: Ashurbanipal hunting lions, relief, ca BCE. Gypsum, 5 4 high. Assyrian: Two figures of Ashurnasirpal II with sacred tree
Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and
 Mesopotamia Review Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This curving strip
Mesopotamia Review Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This curving strip
MESOPOTAMIAN ARCHITECTURE The land between two rivers
 MESOPOTAMIAN ARCHITECTURE The land between two rivers (Gk mesos = middle + potamos = river) The Two (2) Rivers: 1. Euphrates 2. Tigris The river comprises the land of Sumer, Akkad and occupied successively
MESOPOTAMIAN ARCHITECTURE The land between two rivers (Gk mesos = middle + potamos = river) The Two (2) Rivers: 1. Euphrates 2. Tigris The river comprises the land of Sumer, Akkad and occupied successively
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia
 Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period of almost 1800 years. This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period of almost 1800 years. This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period
CUNEIFORM INSCRIPTIONS IN THE LOOTED IRAQ MUSEUM
 Originally Printed in: Iraq Double Issue: Volume 6, Nos. 1 & 2 Art Loss In Iraq CUNEIFORM INSCRIPTIONS IN THE LOOTED IRAQ MUSEUM by ROBERT BIGGS Robert Biggs, Ph. D., is Professor of Assyriology at the
Originally Printed in: Iraq Double Issue: Volume 6, Nos. 1 & 2 Art Loss In Iraq CUNEIFORM INSCRIPTIONS IN THE LOOTED IRAQ MUSEUM by ROBERT BIGGS Robert Biggs, Ph. D., is Professor of Assyriology at the
Mesopotamia. The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC. Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2
 The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities
The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L
 7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the soil was rich and easy to farm. It is there that the world
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the soil was rich and easy to farm. It is there that the world
Ancient Greece: the Nereid Tomb
 Ancient Greece: the Nereid Tomb Relief from the Nereid Tomb showing warriors storming a city Lycia, Turkey 390-380 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information
Ancient Greece: the Nereid Tomb Relief from the Nereid Tomb showing warriors storming a city Lycia, Turkey 390-380 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information
download instant at http://testbankinstant.com TEST ITEM FILE Amy Millicent Morris University of Nebraska at Omaha ART HISTORY 5 th EDITION
 TEST ITEM FILE Amy Millicent Morris University of Nebraska at Omaha ART HISTORY 5 th EDITION Marilyn Stokstad Judith Harris Murphy Distinguished Professor of Art History Emerita The University of Kansas
TEST ITEM FILE Amy Millicent Morris University of Nebraska at Omaha ART HISTORY 5 th EDITION Marilyn Stokstad Judith Harris Murphy Distinguished Professor of Art History Emerita The University of Kansas
Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture
 Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture Ancient Greek Architecture The earliest buildings built in Greece in the New Stone Age are small houses or huts with wooden walls around them for protection. Later bigger
Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture Ancient Greek Architecture The earliest buildings built in Greece in the New Stone Age are small houses or huts with wooden walls around them for protection. Later bigger
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Lighthouse of Alexandria. The Colossus of Rhodes. Hanging Gardens of Babylon. www.montessoriforeveryone.
 Seven Wonders of the Ancient World Lighthouse of Alexandria The Colossus of Rhodes Hanging Gardens of Babylon Please note: this PDF is copyrighted by Montessori for Everyone and is free for personal use
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World Lighthouse of Alexandria The Colossus of Rhodes Hanging Gardens of Babylon Please note: this PDF is copyrighted by Montessori for Everyone and is free for personal use
Ancient Greece: The Parthenon
 Ancient Greece: The Parthenon Figure of a river-god from the Parthenon Greece, 438-432 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information
Ancient Greece: The Parthenon Figure of a river-god from the Parthenon Greece, 438-432 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information
Natural Advantages 2/21/2012. Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt
 Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt HIST 213 Spring 2012 750 miles long Natural Advantages Transportation (both ways) rich soil (450/sq. mi.) annual flooding (silt) simple irrigation systems relatively unified
Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt HIST 213 Spring 2012 750 miles long Natural Advantages Transportation (both ways) rich soil (450/sq. mi.) annual flooding (silt) simple irrigation systems relatively unified
The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire
 The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire The origin of the Persian Empire can be attributed to the leadership of one man Cyrus the Great. A brilliant and powerful Persian king, Cyrus strategy for
The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire The origin of the Persian Empire can be attributed to the leadership of one man Cyrus the Great. A brilliant and powerful Persian king, Cyrus strategy for
AP World History Class Notes, Bentley Brief Edition Ch 1 The Foundations of Complex Societies September 14, 2010
 This first chapter of Traditions and Encounters sets the stage for the drama of world history by tracing the development of humans from their earliest appearance on earth through the rise of important
This first chapter of Traditions and Encounters sets the stage for the drama of world history by tracing the development of humans from their earliest appearance on earth through the rise of important
Eleanor Guralnick. oi.uchicago.edu. khorsabad Relief fragment project. Figure 2. Falling warrior. Room 13 or 14. OIM A70605
 KHORSABAD Relief Fragment PROJECT Eleanor Guralnick For more than three summers progress has been made on uncrating, cleaning, conserving, photographing, registering, and cataloging the hundreds of fragment
KHORSABAD Relief Fragment PROJECT Eleanor Guralnick For more than three summers progress has been made on uncrating, cleaning, conserving, photographing, registering, and cataloging the hundreds of fragment
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao
 Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET
 ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET 1. Case 11 The Royal Graves of Ur What animal is mounted on the top of the rein ring? How old are the Royal Cemetery burials? Why do you think the excavator believed these
ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET 1. Case 11 The Royal Graves of Ur What animal is mounted on the top of the rein ring? How old are the Royal Cemetery burials? Why do you think the excavator believed these
Timeline of Egyptian History. Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script)
 Timeline of Egyptian History 1 Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script) Timeline of Egyptian History 2 Early Dynastic Period 3100 2686 BCE 1 st & 2 nd Dynasty Narmer
Timeline of Egyptian History 1 Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script) Timeline of Egyptian History 2 Early Dynastic Period 3100 2686 BCE 1 st & 2 nd Dynasty Narmer
Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet
 Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet Your group will research Ancient Egyptian culture focusing on the Government of Ancient Egypt. Assign jobs to group members. Everyone must have a job. Research
Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet Your group will research Ancient Egyptian culture focusing on the Government of Ancient Egypt. Assign jobs to group members. Everyone must have a job. Research
In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
 Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
PERSIAN WARRIORS DEFEATED
 PERSIAN WARRIORS DEFEATED Questions to ask before reading the story: What is a counter offensive move? How is it different from a defensive move? What is the meaning of the statement The surest defense
PERSIAN WARRIORS DEFEATED Questions to ask before reading the story: What is a counter offensive move? How is it different from a defensive move? What is the meaning of the statement The surest defense
Cy8, the second register, inscription 美 國 紐 約 大 都 會 博 物 館
 20140904 回 目 錄 Cy8, the second register, inscription 美 國 紐 約 大 都 會 博 物 館 收 藏 Cy3, Cy6, Cy7, Cy8, Cy9, Cy10, Cy11, Cy12, Cy13, Cy16, Cy17, Cy18 參 考 Phoenician Bronze and Silver Bowls from Cyprus and the
20140904 回 目 錄 Cy8, the second register, inscription 美 國 紐 約 大 都 會 博 物 館 收 藏 Cy3, Cy6, Cy7, Cy8, Cy9, Cy10, Cy11, Cy12, Cy13, Cy16, Cy17, Cy18 參 考 Phoenician Bronze and Silver Bowls from Cyprus and the
The Rise of Civilizations
 Page 1 of 6 The Rise of Civilizations Thousands of years ago, several societies in different parts of the world changed from hunting and gathering to farming. Some began to produce surpluses of food. Those
Page 1 of 6 The Rise of Civilizations Thousands of years ago, several societies in different parts of the world changed from hunting and gathering to farming. Some began to produce surpluses of food. Those
Pre-reading class discussion about Islamic Culture and Islamic Art 1
 Contents: PRE-VISIT ACTIVITIES Pre-reading class discussion about Islamic Culture and Islamic Art 1 Reading Islamic Art in Egypt / Arabic Calligraphy 2 Arabesques / Geometrical designs 3 VISIT ACTIVITIES
Contents: PRE-VISIT ACTIVITIES Pre-reading class discussion about Islamic Culture and Islamic Art 1 Reading Islamic Art in Egypt / Arabic Calligraphy 2 Arabesques / Geometrical designs 3 VISIT ACTIVITIES
KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES
 KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES 612 B.C. Nineveh falls to neo-babylonian army (Nebuchadnezzar) 608 Pharaoh Necho II marched to Carchemesh to halt expansion of neo-babylonian
KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES 612 B.C. Nineveh falls to neo-babylonian army (Nebuchadnezzar) 608 Pharaoh Necho II marched to Carchemesh to halt expansion of neo-babylonian
Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt
 Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt MAIN IDEAS Economics Egyptians developed a complex society with many different jobs and social roles. Science and Technology Egyptians made advances in calendars, geometry,
Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt MAIN IDEAS Economics Egyptians developed a complex society with many different jobs and social roles. Science and Technology Egyptians made advances in calendars, geometry,
Sumerian Civilization
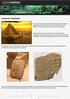 Sumerian Civilization In the south eastern region of Mesopotamia between the mighty Euphrates and Tigris Rivers lay the ruins of the Sumerian City- States. The history of the Sumerians is shrouded in mystery.
Sumerian Civilization In the south eastern region of Mesopotamia between the mighty Euphrates and Tigris Rivers lay the ruins of the Sumerian City- States. The history of the Sumerians is shrouded in mystery.
CH10 Practice Test 2015
 Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Four Early River Valley Civilizations. Egyptian Civilization - Nile River
 Four Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River I. GEOGRAPHY A. The Nile Egypt on the Nile 1. Egypt s settlements
Four Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River I. GEOGRAPHY A. The Nile Egypt on the Nile 1. Egypt s settlements
Egypt. The Old Kingdom
 Egypt The Old Kingdom Vocabulary: Narmer (Menes)- King that united Upper and Lower Egypt Old Kingdom Began around 2600BC, rise of Egyptian cities as centers for religion and government Artisans- someone
Egypt The Old Kingdom Vocabulary: Narmer (Menes)- King that united Upper and Lower Egypt Old Kingdom Began around 2600BC, rise of Egyptian cities as centers for religion and government Artisans- someone
Lecture 9 Ancient Near East Cultures: Sumeria, Babylonia, Judea
 1 Lecture 9 Ancient Near East Cultures: Sumeria, Babylonia, Judea The ancient Near East cultures, known as Mesopotamian civilization are largely based on Semitic populations that existed between the Tigris
1 Lecture 9 Ancient Near East Cultures: Sumeria, Babylonia, Judea The ancient Near East cultures, known as Mesopotamian civilization are largely based on Semitic populations that existed between the Tigris
Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK #
 Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK # H0MEWORK # I THE RIVER NILE The river Nile is one of the world's great rivers. It begins its long journey in Africa, as two
Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK # H0MEWORK # I THE RIVER NILE The river Nile is one of the world's great rivers. It begins its long journey in Africa, as two
a. farmers b. merchants c. priests d. warriors a. the Maya b. the Moche c. the Nazca a. making pottery b. making textiles c.
 Ancient America Chapter 9 Test Form A Part 1: Multiple Choice Choose the letter of the best answer. (4 points each) 1. What geographic feature is common in Mesoamerica s tropical lowlands? a. jungles b.
Ancient America Chapter 9 Test Form A Part 1: Multiple Choice Choose the letter of the best answer. (4 points each) 1. What geographic feature is common in Mesoamerica s tropical lowlands? a. jungles b.
In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs.
 Name: Date: Period: Lesson 8 - The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs. In 1922, archaeologists
Name: Date: Period: Lesson 8 - The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs. In 1922, archaeologists
7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR?
 7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR? In this three-part video David Christian explains how the rise of agriculture led to the formation of the world s first large-scale civilizations. Fueled by
7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR? In this three-part video David Christian explains how the rise of agriculture led to the formation of the world s first large-scale civilizations. Fueled by
The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers. What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty.
 1 The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty. 2 3 Predynasty: c.3100 2649 BC Major Events: Unification
1 The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty. 2 3 Predynasty: c.3100 2649 BC Major Events: Unification
Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack
 Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack This pack includes the following lessons: Locating Egypt The River Nile Archeology Hieroglyphics Pharaohs Every effort has been made to seek permission for the
Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack This pack includes the following lessons: Locating Egypt The River Nile Archeology Hieroglyphics Pharaohs Every effort has been made to seek permission for the
Lions and Warriors: Mycenaean Greece Lecture 12
 Lions and Warriors: Mycenaean Greece Lecture 12 Greece Anatolia (Turkey) CYCLADES ISLANDS CRETE Europa and the Bull. According to the Greek myth, Zeus, disguised as a bull, kidnapped the beautiful young
Lions and Warriors: Mycenaean Greece Lecture 12 Greece Anatolia (Turkey) CYCLADES ISLANDS CRETE Europa and the Bull. According to the Greek myth, Zeus, disguised as a bull, kidnapped the beautiful young
Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power
 Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power Understanding kingship is essential when reading the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. Most of its authors knew no other political system and it influenced their work
Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power Understanding kingship is essential when reading the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. Most of its authors knew no other political system and it influenced their work
Period #1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, c. 8,000 B.C.E. - 600 B.C.E. Study Guide by Key Concepts
 Note: the question numbers are my own customization, and do NOT reflect official College Board designation. Ask yourself the question in the left column. Your answer should come close to the middle column.
Note: the question numbers are my own customization, and do NOT reflect official College Board designation. Ask yourself the question in the left column. Your answer should come close to the middle column.
Gilded Wooden Figure of Tutankhamun on a Skiff, Throwing a Harpoon: Figure
 Gilded Wooden Figure of Tutankhamun on a Skiff, Throwing a Harpoon: Figure Catalogue #: JE 60710.1 75.50 cm 5.6 cm 18.50 cm Description: Gilded Wooden Figure of Tutankhamun on a Skiff, Throwing a Harpoon:
Gilded Wooden Figure of Tutankhamun on a Skiff, Throwing a Harpoon: Figure Catalogue #: JE 60710.1 75.50 cm 5.6 cm 18.50 cm Description: Gilded Wooden Figure of Tutankhamun on a Skiff, Throwing a Harpoon:
An Overview of Western Civilization
 The Six Major Periods of Western Civilization (BCE = BC; CE = AD) 1. Mesopotamia, Egypt, & Hebrews (3000-500 BCE) 2. Ancient Greece (1200-200 BCE) 3. Ancient Rome (753 BCE - 476 CE) -----------------------------------------------------------------
The Six Major Periods of Western Civilization (BCE = BC; CE = AD) 1. Mesopotamia, Egypt, & Hebrews (3000-500 BCE) 2. Ancient Greece (1200-200 BCE) 3. Ancient Rome (753 BCE - 476 CE) -----------------------------------------------------------------
Keywords for the study of Junior Cert art
 able abstract acrylic activity aesthetic/aesthetics analyze ancient animation applied arch arches architect architectural architecture art art process artist artistic artists arts artwork artworks assemble
able abstract acrylic activity aesthetic/aesthetics analyze ancient animation applied arch arches architect architectural architecture art art process artist artistic artists arts artwork artworks assemble
30. STATuETTE Of A KNEElING PHARAOH IN A WHITE CROWN
 30. STATuETTE Of A KNEElING PHARAOH IN A WHITE CROWN Bronze 6 7/8 x 2 1/8 x 2 5/16 in. 17.5 x 5.4 x 5.9 cm Dynasty XXVI FGA-ARCH-EG-12 PROVENANCE: Sotheby s London, 28th May 1883, lot no. 46 Lt. Gen. A.
30. STATuETTE Of A KNEElING PHARAOH IN A WHITE CROWN Bronze 6 7/8 x 2 1/8 x 2 5/16 in. 17.5 x 5.4 x 5.9 cm Dynasty XXVI FGA-ARCH-EG-12 PROVENANCE: Sotheby s London, 28th May 1883, lot no. 46 Lt. Gen. A.
Dragon Legend in Chinese Art Motifs (Jade, Bronze, Porcelain, and Folk Arts) Chinese Culture and Society Series
 1 Dragon Legend in Chinese Art Motifs (Jade, Bronze, Porcelain, and Folk Arts) Chinese Culture and Society Series Phylis Lan Lin, PhD Associate Vice President for International Partnerships University
1 Dragon Legend in Chinese Art Motifs (Jade, Bronze, Porcelain, and Folk Arts) Chinese Culture and Society Series Phylis Lan Lin, PhD Associate Vice President for International Partnerships University
Ancient China. Vocabulary. 15. Terracotta Army collection of seven thousand life-sized sculptures made from pottery in the tomb of Shi Huangdi
 Ancient China 1. Analects the collected sayings and teachings of Confucius 2. Bronze Age (3300 1200 B.C.) time when people made weapons and tools from bronze 3. calligraphy artistic form of ancient Chinese
Ancient China 1. Analects the collected sayings and teachings of Confucius 2. Bronze Age (3300 1200 B.C.) time when people made weapons and tools from bronze 3. calligraphy artistic form of ancient Chinese
Ancient India Lesson 2
 Name: Date: Ancient India Lesson 2 Early Indian Civilization Over 1,000 miles separate the Indus River valley from Iraq, the region once known as Mesopotamia. This distance did not keep people from traveling
Name: Date: Ancient India Lesson 2 Early Indian Civilization Over 1,000 miles separate the Indus River valley from Iraq, the region once known as Mesopotamia. This distance did not keep people from traveling
Lesson 35. The Tabernacle. Exodus 25 27. God lives among his people
 Gospel Story Curriculum (OT) lower Lower elementary Lesson 35 The Tabernacle Exodus 25 27 Bible Truth God lives among his people l e s s o n snapshot 1. Opening review.... 5 min Use last week s lesson
Gospel Story Curriculum (OT) lower Lower elementary Lesson 35 The Tabernacle Exodus 25 27 Bible Truth God lives among his people l e s s o n snapshot 1. Opening review.... 5 min Use last week s lesson
KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons)
 KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons) Contents Include: An Introduction to Mesopotamia Building Baghdad The House of Wisdom The Mongol Attack on Baghdad in 1258 This pack of lessons has been designed for Key
KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons) Contents Include: An Introduction to Mesopotamia Building Baghdad The House of Wisdom The Mongol Attack on Baghdad in 1258 This pack of lessons has been designed for Key
Arch. 158 Early Humans O Teachers' Curriculum Institute
 Arch Some archeologists believe that the arch was the Sumerians' greatest architectural achievement. Made of bricks, Sumerian arches were inverted U- or V-shaped openings built above doorways. Sumerians
Arch Some archeologists believe that the arch was the Sumerians' greatest architectural achievement. Made of bricks, Sumerian arches were inverted U- or V-shaped openings built above doorways. Sumerians
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009
 Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Naqada III (roughly 3200-3050 BC): the last century of the Predynastic period Contemporary
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Naqada III (roughly 3200-3050 BC): the last century of the Predynastic period Contemporary
ART OF THE AMERICAS AFTER 1300
 ART OF THE AMERICAS AFTER 1300 AZTECS Tenochtitlan and the Codex Mendoza The Great Pyramid Religious Sculpture: iconography and style Featherwork INCAS Masonry techniques Machu Picchu: city-sanctuary Textiles:
ART OF THE AMERICAS AFTER 1300 AZTECS Tenochtitlan and the Codex Mendoza The Great Pyramid Religious Sculpture: iconography and style Featherwork INCAS Masonry techniques Machu Picchu: city-sanctuary Textiles:
Ancient Egypt and Kush. Topic 3 Presentation
 Ancient Egypt and Kush Topic 3 Presentation Egyptian Civilization: The Gift of the Nile The Egyptian Nile surpasses all the rivers of the world in sweetness of taste, in length of course and usefulness.
Ancient Egypt and Kush Topic 3 Presentation Egyptian Civilization: The Gift of the Nile The Egyptian Nile surpasses all the rivers of the world in sweetness of taste, in length of course and usefulness.
Ancient Egypt Handouts
 Ancient Egypt Handouts Map of Egypt Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Ancient Egypt 1 Map of Egypt-Answer Sheet 30ºE 40ºE 50ºN Mediterranean Sea 40ºN Africa Alexandria Rosetta Giza Memphis Sinai Pen. Middle East
Ancient Egypt Handouts Map of Egypt Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Ancient Egypt 1 Map of Egypt-Answer Sheet 30ºE 40ºE 50ºN Mediterranean Sea 40ºN Africa Alexandria Rosetta Giza Memphis Sinai Pen. Middle East
Students will: Explain how ancient Egypt was united. Analyze the workings of government and the importance of religion in Egypt.
 Ancient Egypt Unit Name: Lisa Nash Grade Level: 6 Lesson Topic: The Kingdoms of Egypt Day 02, 03, & 04 of 14 Teacher s Initials: Date: November 10, 11, & 12, 2003 Instructional Goals Students will: Explain
Ancient Egypt Unit Name: Lisa Nash Grade Level: 6 Lesson Topic: The Kingdoms of Egypt Day 02, 03, & 04 of 14 Teacher s Initials: Date: November 10, 11, & 12, 2003 Instructional Goals Students will: Explain
The Neolithic Revolution
 The Neolithic Revolution The archaeologist took out his small brush and carefully removed the remaining dirt from the fragment of human skull. To help him reconstruct the life of the ancient human, he
The Neolithic Revolution The archaeologist took out his small brush and carefully removed the remaining dirt from the fragment of human skull. To help him reconstruct the life of the ancient human, he
WHI.03: Early River Valley Civilizations
 WHI.03: Early River Valley Civilizations In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 18-32. You will be graded on your use of space,
WHI.03: Early River Valley Civilizations In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 18-32. You will be graded on your use of space,
The World of. Mythology. Middle Eastern. By Jim Ollhoff
 The World of Mythology: Middle Eastern Mythology By Jim Ollhoff VISIT US AT WWW.ABDOPUBLISHING.COM Published by ABDO Publishing Company, 8000 West 78th Street, Suite 310, Edina, MN 55439. Copyright 2012
The World of Mythology: Middle Eastern Mythology By Jim Ollhoff VISIT US AT WWW.ABDOPUBLISHING.COM Published by ABDO Publishing Company, 8000 West 78th Street, Suite 310, Edina, MN 55439. Copyright 2012
The Revelation of Jesus Christ: A commentary by John F. Walvoord The Victory of the Lamb and His Followers Chapter 14
 The Revelation of Jesus Christ: A commentary by John F. Walvoord The Victory of the Lamb and His Followers Chapter 14 Vs. 1 We are seeing, through John s eyes, the end of the Tribulation period. The 144,000
The Revelation of Jesus Christ: A commentary by John F. Walvoord The Victory of the Lamb and His Followers Chapter 14 Vs. 1 We are seeing, through John s eyes, the end of the Tribulation period. The 144,000
The Greeks 500 300 BC. Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis
 The Greeks 500 300 BC Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis Greek City-State Political Monarch - ruled by a single person
The Greeks 500 300 BC Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis Greek City-State Political Monarch - ruled by a single person
Ancient Mediterranean
 CONTENT AREA 2 Ancient Mediterranean 3500 B.C.E. 300 C.E. ENDURING UNDERSTANDING 2-1. Artistic traditions of the ancient Near East and dynastic Egypt focused on representing royal figures and divinities
CONTENT AREA 2 Ancient Mediterranean 3500 B.C.E. 300 C.E. ENDURING UNDERSTANDING 2-1. Artistic traditions of the ancient Near East and dynastic Egypt focused on representing royal figures and divinities
West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society
 West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society Bantu Migration Around 1500 BCE farmers of the Niger and Benue River valleys in West Africa began migrating south and east, bringing with them their
West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society Bantu Migration Around 1500 BCE farmers of the Niger and Benue River valleys in West Africa began migrating south and east, bringing with them their
Name Period. The Indus Valley Civilization
 Name Period The Indus Valley Civilization Indus Valley Civilization Daily Life 3000BCE 1500BCE We know very little about the Indus Valley civilization, but what we do know is fascinating! Over 4,000 years
Name Period The Indus Valley Civilization Indus Valley Civilization Daily Life 3000BCE 1500BCE We know very little about the Indus Valley civilization, but what we do know is fascinating! Over 4,000 years
Ancient Egypt. LEVELED BOOK L Ancient Egypt. www.readinga-z.com. Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
 Ancient Egypt A Reading A Z Level L Leveled Book Word Count: 482 LEVELED BOOK L Ancient Egypt Written by Kira Freed Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Ancient
Ancient Egypt A Reading A Z Level L Leveled Book Word Count: 482 LEVELED BOOK L Ancient Egypt Written by Kira Freed Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Ancient
Rock Art Calendars from Negev Desert, Israel
 Rock Art Calendars from Negev Desert, Israel Negev Rock Art, Israel www.israelrockart.com The sun, moon and stars were important symbols in early Eastern religions in Egypt and Mesopotamia. Observing the
Rock Art Calendars from Negev Desert, Israel Negev Rock Art, Israel www.israelrockart.com The sun, moon and stars were important symbols in early Eastern religions in Egypt and Mesopotamia. Observing the
www.teachtci.com Sample Lesson
 Sample Lesson Welcome to History Alive! The Ancient World. This document contains everything you need to teach the sample lesson The Rise of Sumerian City-States. We invite you to use this sample lesson
Sample Lesson Welcome to History Alive! The Ancient World. This document contains everything you need to teach the sample lesson The Rise of Sumerian City-States. We invite you to use this sample lesson
Teacher-Directed Tour World History I: Egypt
 Teacher-Directed Tour World History I: Egypt Visit VMFA s Egyptian Gallery to find out more about Ancient Egyptian Art! 1 Get Ready! Please make sure you visit the VMFA Teacher-Directed Tour page at http://vmfaresources.org/teacher-directed-gallery-tour-instructions/
Teacher-Directed Tour World History I: Egypt Visit VMFA s Egyptian Gallery to find out more about Ancient Egyptian Art! 1 Get Ready! Please make sure you visit the VMFA Teacher-Directed Tour page at http://vmfaresources.org/teacher-directed-gallery-tour-instructions/
I. THE FIRST ARMAGEDDON
 Cosmic Controversy Series: Part 2 Study Guide Pastor Michael Oxentenko I. THE FIRST ARMAGEDDON KEY NOTE: The Ark of the Covenant represents God s throne. Revelation 16:16 And they assembled them at the
Cosmic Controversy Series: Part 2 Study Guide Pastor Michael Oxentenko I. THE FIRST ARMAGEDDON KEY NOTE: The Ark of the Covenant represents God s throne. Revelation 16:16 And they assembled them at the
Wall of China Project
 Target Age: K-3 rd Grades Wall of China Project Skills Used Following directions, introduction to fractions, measuring with a ruler using half-inches, 2-D to 3-D concept transfer, creative interpretation,
Target Age: K-3 rd Grades Wall of China Project Skills Used Following directions, introduction to fractions, measuring with a ruler using half-inches, 2-D to 3-D concept transfer, creative interpretation,
YEAR 3: ANCIENT GREECE- UNIT 2 (5 lessons)
 YEAR 3: ANCIENT GREECE- UNIT 2 (5 lessons) Contents Include: Greek Philosophy The Rise of Alexander the Great Alexander s conquests The death and legacy of Alexander Suggested Teacher Resources: A Little
YEAR 3: ANCIENT GREECE- UNIT 2 (5 lessons) Contents Include: Greek Philosophy The Rise of Alexander the Great Alexander s conquests The death and legacy of Alexander Suggested Teacher Resources: A Little
Ancient Egyptian Gods and Symbols
 Ancient Egyptian Gods and Symbols AAH ALABASTER ANKH The lunar god, Aah, was responsible for creating the Egyptian calendar, which is 30 days to a month and 12 months to a year. He is considered the patron
Ancient Egyptian Gods and Symbols AAH ALABASTER ANKH The lunar god, Aah, was responsible for creating the Egyptian calendar, which is 30 days to a month and 12 months to a year. He is considered the patron
Ancient Egypt: Symbols of the pharaoh
 Ancient Egypt: Symbols of the pharaoh Colossal bust of Ramesses II Thebes, Egypt 1250 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information
Ancient Egypt: Symbols of the pharaoh Colossal bust of Ramesses II Thebes, Egypt 1250 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information
Sources for the War of Reunification at the end of the Second Intermediate Period
 Sources for the War of Reunification at the end of the Second Intermediate Period Archaeological: body of Seqenenre-Taa campaign palace (?) at Deir el Ballas remarkably little else destruction layers at
Sources for the War of Reunification at the end of the Second Intermediate Period Archaeological: body of Seqenenre-Taa campaign palace (?) at Deir el Ballas remarkably little else destruction layers at
Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks
 Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
INTERNATIONAL HOUSE OF PRAYER MIKE BICKLE. Appendix: The 30 Descriptions of Jesus in Revelation 1-3
 Appendix: The 30 Descriptions of Jesus in Revelation 1-3 I. INTRODUCTION A. There are 24 distinct descriptions in Revelation 1 (7 descriptions in v. 5-7 plus 17 directly related to Jesus as the Son of
Appendix: The 30 Descriptions of Jesus in Revelation 1-3 I. INTRODUCTION A. There are 24 distinct descriptions in Revelation 1 (7 descriptions in v. 5-7 plus 17 directly related to Jesus as the Son of
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE.
 SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
Ancient Civilizations: Prehistory to Egypt
 Chapter 1 Ancient Civilizations: Prehistory to Egypt 1 1-4 Stonehenge, c. 2000 b.c.e., Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire, England learning objectives Understand the distinctive artistic, literary, and cultural
Chapter 1 Ancient Civilizations: Prehistory to Egypt 1 1-4 Stonehenge, c. 2000 b.c.e., Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire, England learning objectives Understand the distinctive artistic, literary, and cultural
Jesus, the Promised Messiah
 28 Who Jesus Is LESSON 2 Jesus, the Promised Messiah Promises are part of our lives. Parents promise to do things for children. Politicians, business people, and friends make promises. We have all had
28 Who Jesus Is LESSON 2 Jesus, the Promised Messiah Promises are part of our lives. Parents promise to do things for children. Politicians, business people, and friends make promises. We have all had
eb.com/>. eastern Africa, history of. Encyclopaedia Britannica Online. May 27,
 Daily Life in Aksum Aksum was a powerful and wealthy ancient kingdom. Located in East Africa, it was very influential between A.D. 50 and 600. During this time, goods from all over the ancient world were
Daily Life in Aksum Aksum was a powerful and wealthy ancient kingdom. Located in East Africa, it was very influential between A.D. 50 and 600. During this time, goods from all over the ancient world were
Bronze plinth. Quantity: 1
 Item catalogue Bronze plinth A lovely bronze effect plinth perfect for displaying vases or artworks Dimensions: 33 cm x 33 cm top x 100 cm (h) Quantity: 1 Cost to rent: 50 Cost to buy: 250 1 Silver ridged
Item catalogue Bronze plinth A lovely bronze effect plinth perfect for displaying vases or artworks Dimensions: 33 cm x 33 cm top x 100 cm (h) Quantity: 1 Cost to rent: 50 Cost to buy: 250 1 Silver ridged
Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA Focus Question: What factors encouraged the rise of powerful civilizations in Mesoamerica? A. As you read People Settle in the Americas, complete
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA Focus Question: What factors encouraged the rise of powerful civilizations in Mesoamerica? A. As you read People Settle in the Americas, complete
Herodotus and the Persian Wars
 Herodotus is the first true historian known in Western Civilization he lived during the Classical Age of Greece (the fifth century BCE) he is the earliest Western author known to have written a systematic
Herodotus is the first true historian known in Western Civilization he lived during the Classical Age of Greece (the fifth century BCE) he is the earliest Western author known to have written a systematic
PYRAMID CFE 3284V. OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed
 PYRAMID CFE 3284V OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed DESCRIPTION Burial practices and beliefs, such as the building of pyramids, mummification,
PYRAMID CFE 3284V OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed DESCRIPTION Burial practices and beliefs, such as the building of pyramids, mummification,
Intro to Ancient Writing Systems
 Cave painting from Lascaux, c. 15,000 10,000 B.C. Random placement and shifting scale signify prehistoric people s lack of structure and sequence in recording their experiences. Beautifully drawn but not
Cave painting from Lascaux, c. 15,000 10,000 B.C. Random placement and shifting scale signify prehistoric people s lack of structure and sequence in recording their experiences. Beautifully drawn but not
Shapes & Symbols. Shape is an element of art. There are two kinds of shapes, geometric and organic.
 Notes 10/6 Name: Period: Date: Shapes & Symbols Shape is an element of art. There are two kinds of shapes, geometric and organic. Geometric Shapes Geometric shapes are shapes that have names. These are
Notes 10/6 Name: Period: Date: Shapes & Symbols Shape is an element of art. There are two kinds of shapes, geometric and organic. Geometric Shapes Geometric shapes are shapes that have names. These are
The Story of the Nile
 1 of 7 1/8/2007 4:06 PM http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/ The Story of the Nile By John Baines Without the Nile, Egypt may never have become one of the most extraordinary civilisations in history. John Baines
1 of 7 1/8/2007 4:06 PM http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/ The Story of the Nile By John Baines Without the Nile, Egypt may never have become one of the most extraordinary civilisations in history. John Baines
Egypt and China. Ancient Worlds: VMFA Resources
 VMFA Resources Ancient Worlds: Pre- and Post-Visit Activities VIRGINIA MUSEUM OF FINE ARTS Egypt and China Grade 2 Based on images of two works of art from VMFA s collection, these activities will provide
VMFA Resources Ancient Worlds: Pre- and Post-Visit Activities VIRGINIA MUSEUM OF FINE ARTS Egypt and China Grade 2 Based on images of two works of art from VMFA s collection, these activities will provide
Chapter 3. Ancient Egypt & Nubia
 Chapter 3 Ancient Egypt & Nubia Section 1 The Geography of the Nile The longest river in the world is - The Nile River - Flows north East Africa to Mediterranean Sea - Over 4,000 miles long (more than
Chapter 3 Ancient Egypt & Nubia Section 1 The Geography of the Nile The longest river in the world is - The Nile River - Flows north East Africa to Mediterranean Sea - Over 4,000 miles long (more than
Painting an Egyptian tomb
 Painting an Egyptian tomb Aims To provide students with visual encounters with the equipment and techniques used to create ancient Egyptian tomb paintings. To provide teachers with an opportunity to build
Painting an Egyptian tomb Aims To provide students with visual encounters with the equipment and techniques used to create ancient Egyptian tomb paintings. To provide teachers with an opportunity to build
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE
 SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE In sixth grade, students are ready to deepen their understanding of the Earth and its peoples through the study of history, geography, politics, culture, and
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE In sixth grade, students are ready to deepen their understanding of the Earth and its peoples through the study of history, geography, politics, culture, and
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS. Christine H. Salcito, Director of Curriculum and Instruction Tiffany Lynch, Program Supervisor of Literacy.
 CURRICULUM FOR SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 6 This curriculum is part of the Educational Program of Studies of the Rahway Public Schools. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Christine H. Salcito, Director of Curriculum and Instruction
CURRICULUM FOR SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 6 This curriculum is part of the Educational Program of Studies of the Rahway Public Schools. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Christine H. Salcito, Director of Curriculum and Instruction
EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS. Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush
 PART I Chapter 2 EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush I. The First and Second Dynasties (3100 2686 B.C.) II. 1. The natural barriers of deserts and sea insulated Egypt from invading armies
PART I Chapter 2 EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush I. The First and Second Dynasties (3100 2686 B.C.) II. 1. The natural barriers of deserts and sea insulated Egypt from invading armies
Figure 10.1 Totally collapsed mosque at Kavakl district of Gölcük
 10 DAMAGE TO DOMES, MINARETS AND HISTORICAL STRUCTURES Most of historical structures existing in the earthquake-affected area are in Istanbul. Istanbul is situated on two continents; Asia and Europe. Istanbul
10 DAMAGE TO DOMES, MINARETS AND HISTORICAL STRUCTURES Most of historical structures existing in the earthquake-affected area are in Istanbul. Istanbul is situated on two continents; Asia and Europe. Istanbul
Hieroglyphs and Community By Grant
 Hieroglyphs and Community By Grant Hieroglyphs were hard to understand in the ancient times and are still hard to understand today. Hieroglyphs are carvings of an object or creature that Egyptians used
Hieroglyphs and Community By Grant Hieroglyphs were hard to understand in the ancient times and are still hard to understand today. Hieroglyphs are carvings of an object or creature that Egyptians used
The Throne Room of God (Message #13) Revelation 4: 2-11
 The Throne Room of God (Message #13) Revelation 4: 2-11 In our last study we found John taken up into heaven to see the things which must be hereafter. Keep in mind that John represents the church being
The Throne Room of God (Message #13) Revelation 4: 2-11 In our last study we found John taken up into heaven to see the things which must be hereafter. Keep in mind that John represents the church being
Webquest: The Dog of Pompeii by Louis Untermeyer
 Name Date Webquest: The Dog of Pompeii by Louis Untermeyer http://www.history.com/topics/ancient history/pompeii Watch the 2 minute video. Pay special attention to where Pompeii is and where Vesuvius is
Name Date Webquest: The Dog of Pompeii by Louis Untermeyer http://www.history.com/topics/ancient history/pompeii Watch the 2 minute video. Pay special attention to where Pompeii is and where Vesuvius is
C-14: God Created the World and People Spoiled It
 Title: GOD CREATED THE WORLD AND PEOPLE SPOILED IT Theme / Bible Basis: Review of Genesis 1-11 Bible Reading: Psalm 148, NLT Introduction: In our recent messages, we have read together from several stories
Title: GOD CREATED THE WORLD AND PEOPLE SPOILED IT Theme / Bible Basis: Review of Genesis 1-11 Bible Reading: Psalm 148, NLT Introduction: In our recent messages, we have read together from several stories
Could Babylon be the Revived Head of the Beast?
 Could Babylon be the Revived Head of the Beast? by Rodrigo Silva 12/20/2008 www.beastfromtheeast.org In Revelation 17 we read one of the most mysterious passages in the entire Bible. It goes as follows:
Could Babylon be the Revived Head of the Beast? by Rodrigo Silva 12/20/2008 www.beastfromtheeast.org In Revelation 17 we read one of the most mysterious passages in the entire Bible. It goes as follows:
 GODS IN COLOUR Painted Sculpture of Classical Antiquity November 13, 2012 - March 17, 2013 Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, Collection of Greek and Roman Antiquities An exhibition by the Kunsthistorisches
GODS IN COLOUR Painted Sculpture of Classical Antiquity November 13, 2012 - March 17, 2013 Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, Collection of Greek and Roman Antiquities An exhibition by the Kunsthistorisches
