Chapter 7: Skeletal System. I. Bone Structure A. Bone Classification 1. The four classes of bone according to shape are. 2. Examples of long bones are
|
|
|
- Dana Todd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 7: Skeletal System Chapter 7: Skeletal System I. Bone Structure A. Bone Classification 1. The four classes of bone according to shape are 2. Examples of long bones are 3. Short bones are shaped like 4. Examples of short bones are 5. Flat bones are structures. 6. Examples of flat bones are 7. Irregular bones have a variety of 8. Examples of irregular bones are 9. Round bones are also called 10. Sesamoid bones are and and embedded in 11. An example of a sesamoid bone is the B. Parts of a Long Bone 1. An expanded end of a long bone is an 2. An epiphysis articulates with 3. Articular cartilage is located 4. The shaft of a long bone is called a 5. Periosteum is 6. Periosteum functions to 7. Processes provide sites for 8. The wall of the diaphysis is composed of bone. 9. Compact bone has 10. The epiphyses are largely composed of bone. 11. Spongy bone consists of bony plates called 13. A canal called runs through the diaphysis. 14. Endosteum lines 17. The two forms of marrow are 7-1
2 C. Microscopic Structure 1. Introduction a. Bone cells are called d. Osteoctyes transport e. Cellular processes of osteocytes pass through f. The intercellular matrix of bone is composed of 2. Compact Bones a. An osteon is b. The substance of compact bone is formed from c. Each central canal contains d. Perforating canals connect e. Perforating canals contain 3. Spongy Bone a. Spongy bone is also composed of and b. Unlike compact bone, the bone cells do not c. Instead the cells lie within d. Osteocytes get nutrients from II. Bone Development and Growth 1. Parts of the skeleton begin to form 2. Bony structures continue to grow until 3. Bones form by replacing 4. Intramembranous bones originate within 5. Endochondral bones originate within B. Intramembranous Bones 1. Examples of intramembranous bones are 3. During their development, appear at the sites of their future bones. 4. supply the connective tissue layers. 7-2
3 5. Osteoblasts are 6. Osteoblasts deposit 7. Spongy bone can become 8. As development continues, osteoblasts may become surrounded by 9. Matrix surrounding the processes of osteoblasts give rise to 10. Once isolated, osteoblasts become 11. Periosteum comes from 12. Compact bone is formed by 13. Intramembranous ossification is C. Endochondral Bones 1. Most of the bones of the skeleton are 2. Endochondral bones develop as 3. Eventually the cartilage 4. As the cartilage decomposes, forms from 5. invade the disintegrating tissue. 6. Some of the cells differentiate into 7. Osteoblasts form 8. Endochondral ossification is 9. The primary ossification center is 10. Secondary ossification centers appear 11. The epiphyseal plate is E. Homeostasis of Bone Tissue 1. Throughout life, osteoclasts and osteoblasts 2. About of bone calcium is exchanged each year. F. Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair 1. Factors that affect bone development, growth and repair include 2. Vitamin D is necessary for 3. Lack of vitamin D can lead to the diseases 4. Vitamin A is necessary for 7-3
4 5. Vitamin C is required for 6. Growth hormone stimulates 7. In children, the absence of growth hormone leads to 10. Thyroid hormone can halt by causing 11. Deficiency of thyroid hormone may stunt 12. Parathyroid hormone stimulates 13. Androgens are 14. Androgens promote 15. Sex hormones also stimulate 16. Females typically reach their maximum heights earlier than males because 17. Physical stress stimulates III. Bone Function A. Support and Protection 2. The bones of support the body s weight. 3. The bones of the skull protect 4. The bones of the protect the heart and lungs. 5. Bones of the pelvic girdle protect B. Body Movement 1. Bones and muscles interact as 2. The four basic components of a lever system are C. Blood Cell Formation 1. Hematopoiesis is 2. Blood cell formation begins 3. Later in development, blood cells are made 4. Marrow is within 5. Red marrow functions in 6. Red marrow occupies 7. With increasing age, replaces red marrow. 8. Yellow marrow stores D. Inorganic Salt Storage 7-4
5 1. Intercellular matrix of bone tissue contains 4. The body requires calcium for IV. Skeletal Organization B. Divisions of the Skeleton 1. Two major portions of the skeleton are 2. The axial skeleton contains 3. The skull is composed of 4. The hyoid bone supports 5. The hyoid bone is located 6. The vertebral column consists of 9. The thoracic cage is composed of 10. The appendicular skeleton consists of 11. The pectoral girdle is formed by 14. Each upper limb consists of 15. The humerus, radius, and ulna articulate 16. The wrist bones are called 18. Bones in the fingers are called 19. The pelvic girdle is formed by 20. The pelvic girdle connects 22. Each lower limb consists of 23. The femur and tibia articulate with each other at 24. The kneecap is called the 25. The ankle bones are 26. The bones of the instep of the foot are called 27. Bones of the toes are called V. Skull B. Cranium 1. The cranium encloses and protects 2. The surface of the cranium provides attachments for 7-5
6 5. The eight bones of the cranium are 6. The frontal bone forms 10. One parietal bone is located 11. Together the parietal bones form 14. The occipital bone joins the parietal bones along the 15. The occipital bone forms the 19. A temporal bone on each side of the skull joins the parietal bone along a 20. The temporal bones form 27. The zygomatic process projects and joins the 28. The sphenoid bone helps form the 31. The ethmoid bone is located C. Facial Skeleton 1. The facial skeleton consists of immovable bones and a movable 3. The forms the upper jaw. 12. The palatine bones are located 18. Lacrimal bones are located 21. The vomer is located D. Infantile Skull 1. At birth, the skull is developed with connecting the cranial bones. VII. Thoracic Cage 1. The thoracic cage includes 2. The thoracic cage supports and protects C. Sternum 7-6
7 1. The sternum is located 2. The three parts of the sternum are VIII. Pectoral Girdle 1. The four parts of the pectoral girdle are 2. The pectoral girdle supports and is an attachment for B. Clavicles 2. Clavicles run between C. Scapulae 2. The spine of a scapula divides IX. Upper Limb 1. The bones of the upper limb form 2. The bones of the upper limbs are C. Radius 1. The radius is located on the side of the forearm D. Ulna 1. The trochlear notch of the ulna is 2. The trochlear notch articulates with E. Wrist and Hand 1. The wrist is at the junction of 2. The bones of the wrist are called 6. The metacarpals form the framework of 12. Each finger has phalanges and the thumb has phalanges. X. Pelvic Girdle 1. The pelvic girdle consists of 3. The pelvic girdle supports 4. The pelvic girdle provides attachments for and protects 7-7
8 XI. Lower Limb 1. The bones of the lower limb form the framework of B. Femur 1. The femur extends from C. Patella 1. The patella is a bone located in D. Tibia 1. The shinbone is 2. The tibia is located on side. E. Fibula 1. The fibula is on the side of the tibia. F. Ankle and Foot 1. The ankle and foot consist of 10. The bones of the toes are called 11. Each toe has phalanges except the great toe because it lacks 7-8
9 Chapter 9: Muscular System I. Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 1. A is an organ of the skeletal system. 2. A skeletal muscle is composed of B. Connective Tissue Coverings 7. A fascicle is C. Skeletal Muscle Fibers 1. A skeletal muscle fiber is a single 2. The sarcolemma is 3. The sarcoplasm is 4. The sarcoplasm contains 5. Myofibrils are and are located in the 6. Myofibrils play a fundamental role in 7. Thick myofilaments are composed of 8. Thin myofilaments are composed of 9. The organization of myofilaments produce 7-9
10 10. A sarcomere is 11. Myofibrils may be thought of as joined end to end. 13. Z lines are 18. A sarcomere extends from one 19. Each myosin molecule consists of 20. Thin filaments consist of double 21. Actin has a binding site to which can attach. 23. Sarcoplasmic reticulum is II. Skeletal Muscle Contraction A. Neuromuscular Junction 1. Each skeletal muscle is connected to 2. A motor neuron passes out from 3. Normally, a skeletal muscle fiber contracts only upon 4. A neuromuscular junction is 5. A motor end plate is 6. A motor unit is B. Stimulus for Contraction 1. is the neurotrasnmitter that motor neurons use to control skeletal muscle. 2. ACh is synthesized in the cytoplasm of and is stored in 3. When a nerve impulse, acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft. 4. ACh combines with on the motor end plate, and stimulates 5. A muscle impulse is C. Excitation Contraction Coupling 1. The sarcoplasmic reticulum has a high concentration of 2. In response to a muscle impulse, the membranes, and the calcium 3. When a muscle fiber is at rest, block the binding 7-10
11 sites on the actin molecules. 4. Calcium ions bind to, changing its and altering 5. The movement of the tropomyosin molecule exposes, allowing D. The Sliding Filament Theory 1. The functional unit of skeletal muscles is 2. According to the sliding filament theory, when sarcomeres shorten, 3. As contraction occurs, and get narrower and move closer together. E. Cross-bridge Cycling 1. The force that shortens the sarcomeres comes from 2. A myosin cross-bridge attaches to actin in order to 8. When a muscle is stimulated to contract, a attaches to and pulls, shortening the F. Relaxation 1. In order for a muscle fiber to relax, acetylcholine must be decomposed by an enzyme called 2. The action of acetycholinesterase prevents 3. When acetylcholine is broken down, ceases. 5. When calcium is removed from the cytoplasm, the break and rolls back into its groove, preventing 6. ATP is necessary for both muscle and 7. The trigger for contraction is H. Oxygen Supply and Cellular Respiration 1. Glycolysis occurs and is 7-11
12 2. Glycolysis releases a few 3. The complete break down of glucose occurs in and requires 5. Oxygen is carried in the blood stream bound to I. Oxygen Debt 1. Lactic acid threshold is 2. Under anaerobic conditions, glycolysis breaks down glucose into and converts it to 3. Lactic acid is carried by the blood to the 4. Liver cells can convert lactic acid to 5. Oxygen debt reflects J. Muscle Fatigue 1. Fatigue is 2. Fatigue may result from 3. A cramp is 4. Physically fit people make less lactic acid because III. Muscle Responses 1. One way to observe muscle contraction is to 2. An is usually used to produce muscle contraction. B. Threshold Stimulus 1. Threshold stimulus is 2. An impulse in normally releases enough to bring the muscle fibers in its to C. Recording a Muscle Contraction 1. A twitch is 2. A myogram is 3. Three periods of a muscle fiber contraction are 7-12
13 4. During the period of contraction, a muscle fiber is 5. The latent period is 6. The period of relaxation is 8. An all-or-none response is D. Summation 1. Twitches in a muscle can combine to become 2. Summation is 3. Tetanic contractions are E. Recruitment of Motor Units 1. The in the motor units, the more the movements can be produced in a particular muscle. 2. All muscle fibers in a motor unit are stimulated at time. 3. Multiple motor unit summation is 4. Recruitment is 5. As the intensity of stimulation increases, continues until all possible motor units are activated in a muscle. 4. Muscle tone is IV. Smooth Muscles A. Smooth Muscle Fibers 1. Compared to skeletal muscle fibers, smooth muscle fibers 2. Two major types of smooth muscle are 3. Multiunit smooth muscle is located 4. Visceral smooth muscle is located 5. Fibers of visceral smooth muscle are connected by 6. Rhythmicity is 7. Peristalsis is 8. Peristalsis helps force B. Smooth Muscle Contraction 7-13
14 1. Compared to skeletal muscle fibers, smooth muscle fibers lack and use to bind calcium instead. 2. Two neurotransmitters that affect smooth muscle are 3. Hormones affect smooth muscle by 4. Stretching of smooth muscle can trigger 5. Smooth muscle is to contract and to relax than skeletal muscle. 6. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle fibers can change length without changing V. Cardiac Muscle A. Cardiac muscle appears only in B. Cardiac muscle is composed of cells, forming fibers that are C. Cardiac muscle fibers can contract then skeletal muscle fibers. D. Intercalated discs are E. Intercalated discs allow muscle impulses to F. A syncytium is VI. Skeletal Muscle Actions 1. Skeletal muscles generate 2. The action of each muscle mostly depends upon B. Origin and Insertion 1. The origin of a muscle is 2. The insertion of a muscle is 3. When a muscle contracts, its is pulled toward its 4. The head of a muscle is 5. The origins of the biceps brachii are 6. The insertion of the bicep brachii is 7. When the biceps brachii contracts, the bends. C. Interaction of Skeletal Muscles 7-14
15 1. A prime mover is 2. A synergist is 3. An antagonist is VII. Major Skeletal Muscles 1. The name of a muscle may reflect 2. An example of a muscle named for it size is 3. An example of a muscle named for its shape is 4. An example of a muscle named for its function is 5. An example of a muscle named for its number of origins is 6. An example of a muscle named for its attachments site is 7. An example of a muscle named of the direction of its muscle fibers is B. Muscles of Facial Expression 1. As a group, muscles of facial expression connect 2. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions. Epicranius Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Zygomaticus Platysma 7-15
16 C. Muscles of Mastication 1. Muscles of mastication produce movements. 2. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Masseter Temporalis Medial pterygoid Lateral pterygoid D. Muscles That Move the Head and Vertebral Column 1. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Sternocleidomastoid Splenius capitis Semispinalis capitis Erector spinae E. Muscles That Move the Pectoral Girdle 1. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Trapezius Rhomboideus major Levator spinae Serratus anterior Pectoralis major F. Muscles That Move the Arm 1. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Coracobrachialis Pectoralis major Teres major Latissimus dorsi Supraspinatus Deltoid Subscapularis Infraspinatus Teres minor G. Muscles That Move the Forearm 1. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Biceps brachii 7-16
17 Brachialis Brachioradialis Triceps brachii Supinator Pronator teres Pronator quadratus H. Muscles That Move the Hand 1. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Flexor carpi radialis longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Palmaris longus Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor digitorum superficialis Extensor carpi radialis Extensor carpi radialis brevic Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor digitorum I. Muscles of the Abdominal Wall 1. The linea aspera is 2. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions External oblique Internal oblique Transversus abdominis Rectus abdominis J. Muscles of the Pelvic Outlet 1. The pelvic diaphragm forms 2. The urogenital diaphragm fills 3. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Levator ani Coccygeus Superficial transversus perinea Bulbospongiosus Ischiocavernosus Sphincter urethra 7-17
18 K. Muscles That Move the Thigh 1. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Psoas major Iliacus Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Gluteus minimus Pectineus Adductor longus Adductor magnus Gracilis L. Muscles That Move the Leg 1. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Sartorius Quadriceps femoris group M. Muscle That Move the Foot 1. For the following muscles, list their origins, insertions, and actions Tibialis anterior Fibularis tertius Extensor digitorum longus Gastrocnemius Soleus Flexor digitorum longus Tibialis posterior Fibularis longus VIII. Life-Span Changes A. Signs of aging of the muscular system begin to appear B. At a microscopic level, decline. C. being to replace some muscle tissue. D. can help maintain a healthy muscular system E. According to the National Institute on Aging, exercise should include 7-18
19 7-19
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B.
 Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Chapter 9: Muscular System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 9: Muscular System Chapter 9: Muscular System I. Structure of a Skeletal Muscle A. Introduction 1. A skeletal muscle is
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 9: Muscular System Chapter 9: Muscular System I. Structure of a Skeletal Muscle A. Introduction 1. A skeletal muscle is
Practice Chapter 6. Figure 6.3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
The Muscular System General & Anatomy
 The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Figure 6.1. 2) The A band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 188
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
CHAPTER 9: THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014
 PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Deltoid Trapezius. Identify the muscle pair(s) that work together to produce the movements listed above.
 Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) a function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B)
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) a function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B)
Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory
 Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of 4-20 myofibrils Myofibrils are
Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of 4-20 myofibrils Myofibrils are
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8
 Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscle Organization and Function. Chapter 10: The Muscular System. Parallel (Fusiform) Muscles. Organization of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
 Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen
 I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Function of Bones. Bone Tissue and Bones BONE CLASSIFICATION. Long Bones Gross Anatomy. Lab Activity 1 - Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
 Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Muscular System Teacher s lecture notes, curriculum and guides 2012
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Name the muscle, A: (Action), O: (Origin), and I: (Insertion)
 FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
10/12/2011. Classification of Bones Every adult skeleton contains 206 bones which can be arranged into six broad categories according to shape
 Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM
 EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
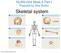 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Anatomy for Sport and Exercise
 Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE. Striations Present or Absent?
 BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
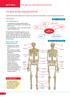 SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Describe the three key functions of muscle. 2. Describe the four special properties of muscle tissue. SKELETAL MUSCLE
Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Describe the three key functions of muscle. 2. Describe the four special properties of muscle tissue. SKELETAL MUSCLE
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
BONES AND BONE TISSUE
 BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
OBJECTIVE: List and describe the functions of the skeletal system. D. Storage depot for minerals and homeostasis
 Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510
 Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE
 ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
The skeletal and muscular systems
 anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle Structure
 VertebrateSkeletalMuscleStructure HumanAnatomy&PhysiologyLab#1 Todaywewillexaminethemuscularsystemoftherat,withparticularemphasison themusclesofthehindlimb.thegoalofthislabistoconsidertherelationship betweenfineandgrossmusclestructureandfunction.byfocusingonrathindlimb
VertebrateSkeletalMuscleStructure HumanAnatomy&PhysiologyLab#1 Todaywewillexaminethemuscularsystemoftherat,withparticularemphasison themusclesofthehindlimb.thegoalofthislabistoconsidertherelationship betweenfineandgrossmusclestructureandfunction.byfocusingonrathindlimb
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE
 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE The muscular system provides for movement of the body and its parts (as muscles shorten), maintains posture, generates heat and stabilizes joints. The various types of muscles
MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE The muscular system provides for movement of the body and its parts (as muscles shorten), maintains posture, generates heat and stabilizes joints. The various types of muscles
Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21
 activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Muscles and Contraction
 Muscles and Contraction Muscle tissue forms the organs called muscle. Three types of muscle tissue are (1) skeletal, (2) cardiac, and (3) smooth. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen
Muscles and Contraction Muscle tissue forms the organs called muscle. Three types of muscle tissue are (1) skeletal, (2) cardiac, and (3) smooth. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen
Teppe Treppe: A staircase increase in tension production after repeated simulation, even though the muscle is allowed to relax between twitches.
 Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
The Muscular System. Appendicular Musculature
 11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
MUSCLES. b. labor in female's uterus at birth I. GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLES. 5. Heart and Blood vessels
 MUSCLES I. GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLES The major function of muscle tissue is contraction(the ability to shorten and thus cause movement in the body), and relaxation(the ability to lengthen again and
MUSCLES I. GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLES The major function of muscle tissue is contraction(the ability to shorten and thus cause movement in the body), and relaxation(the ability to lengthen again and
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME
 EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb
 2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins
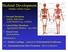 Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE. Chapter 6. Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
