Prostate Cancer. Michael Lock MD CCFP FRCPC Glenn Bauman MD FRCPC Michael Sanatani MD FRCPC Last updated: July 2010
|
|
|
- Kathleen Garrett
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prostate Cancer Michael Lock MD CCFP FRCPC Glenn Bauman MD FRCPC Michael Sanatani MD FRCPC Last updated: July 2010 What is the chance of a male developing prostate cancer? What is the chance of dying of prostate cancer? Most common serious cancer diagnosed and second most common cause of cancer death in males. The chance of developing prostate cancer is 1 in 9, but only 1 in 30 die from the disease. What is the currently recommended screening regimen for prostate cancer? Currently, screening PSA not recommended for asymptomatic males with a normal digital rectal examination at the time of annual physical examination. Males age >50 or with a positive family history or who request the test may be offered PSA screening after appropriate counselling regarding the limitations of the test and the uncertainties regarding intervention versus observation in patients with early prostate cancer. Describe your approach to patients in clinic (i.e. what does your staff person want you to tell him/her after your assessment)? 1. First, determine the TNM stage of the patient. Staging T1 Not palpable/visible T1a <5% of TUR T1b >5% of TUR T1c needle biopsy T2 Confined to prostate (must be palpable or seen on imaging) T2a One half of one lobe or less T2b More than one lobe, but not both lobes T2c Both lobes T3 Extraprostatic extension T3a Extracapsular T3b Seminal vesicle T4 Invades adjacent structures (Bladder neck, external sphincter, rectum, levator muscles or pelvic wall) Nx N0 N1 Not assessed Node negative Node positive
2 Mx M0 M1 Not assessed No evidence distant metastasis Distant metastasis Stage I T1a, G1 (well differentiated) II T1a >G1 or T1b-T2 III T3 IV T4 or N1 or M1 2. Review the pathology The vast majority of neoplasms of the prostate are adenocarcinomas. Occasionally, other histologies (sarcoma, small cell tumors) may be seen. Prostate adenocarcinomas are graded by the Gleason score. This is the sum of two numbers, which represent the 2 most dominant patterns of differentiation scored from 1-5. Tumors may also be divided as well differentiated (Gleason 2-6), moderately differentiated (Gleason 7), and poorly differentiated (Gleason 8-10). Tumor grade is a strong prognostic factor in both treated (surgery or radiation) patients as well as patients where observation is elected. Your staff person will also want to know certain factors from the pathology report that provide prognostic information: The presence or absence of perineural/lymphatic/vascular invasion Extension beyond the prostatic capsule into fat Number of cores involved/percentage of cores involved Which lobes were involved The presence of PIN (prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia) If the pathology is from a prostatectomy specimen: The status of the surgical margins (involved versus clear) Seminal vesicle invasion or extracapsular extension The presence or absence of nodal involvement (if sampled) 3. Review blood and radiological assessments Serum PSA Transrectal ultrasound done as part of biopsy confirmation will determine the size of the prostate and presence of nodules Bone scan (usually performed only if pre-treatment PSA > 20 or Gleason grade >8 or T3)
3 Not recommended: Abdominal ultrasound or CT or MRI of the abdomen or pelvis (low sensitivity and specificity, 50-70%, for both nodal disease and extraprostatic extension). 4. With this information, most patients can be separated into 1. low risk, 2. intermediate risk, 3. high risk, 4. biochemical failure and 5.metastatic disease. See definitions below. Treatment Overview Low risk patients have a high chance of disease control with single modality therapy or observation; intermediate risk patients generally require combined modality therapy for optimal disease control (various combinations of surgery, radiotherapy and hormonal therapy); high risk patients have a high chance of systemic failure with localized treatment modalities and should be considered for adjuvant hormone therapy. 1. Low Risk Prostate Cancer T1, T2 (organ confined) and low PSA (<10) and low Gleason grade (<6) Generally high chance of long term control/cure with single modality therapy Overview of Options Active surveillance Radioactive seed implant (T1 or T2a) * Radical prostatectomy Radical external beam radiotherapy Experimental therapies (cryosurgery, hyperthermia) as part of a clinical trial Detailed Review of Options Observation/Deferred Treatment/Deferred Treatment/Deferred Treatment Active Surveillance: An Active surveillance approach recognizes that many men with low risk prostate have indolent disease with a low rate of cancer related mortality. Monitoring with PSA (every 6-12 months) and periodic biopsy (every 1-3 years) can identify men with more aggressive disease who require treatment with surgery or radiotherapy. Currently this approach is being studied in randomized trials comparing active surveillance with deferred intervention versus early treatment. Radioactive Seed Implant, also known as brachytherapy * What are the inclusion criteria for brachytherapy? Gleason <6 PSA <10 No prior TUR Technically feasible (smaller prostate size and favorable pelvic anatomy) What are the possible side-effects of brachytherapy?
4 Acute side effects: Infection or bleeding (rarely) Lower urinary tract symptoms Urinary Retention (uncommon) Late side effects Incontinence (rare) Impotence (approximately 50%) Erectile dysfunction External Beam Radiotherapy Describe the logistics of this treatment A simulation lasting less than an hour is required where a CT is used to obtain three-dimensional anatomical data. Tattoo marks on the skin will be made that are permanent. These help in positioning the patient for daily treatment. Treatments are daily, Monday to Friday, excluding holidays and weekends. Each treatment takes 10 to 15 minutes each day and a course of treatments lasts approximately 7 weeks. What are the possible side-effects of external beam radiotherapy? Acute side effects: Fatigue Lower urinary tract symptoms Late side effects: Chronic cystitis and/or proctitis (usually mild, self limited) Hematuria, hematochezia (rarely severe, rule out other concurrent pathology) Bowel obstruction; urethral stricture; severe proctitis or cystitis (rare) Erectile dysfunction Radical Prostatectomy What happens if the patient undergoes prostatectomy? Inpatient, 3-5 days, general anaesthetic generally indicated for younger patients; no/few medical comorbidities. Open and minimally invasive (laparoscopic or robot assisted laparascopic approaches. What are the possible side-effects of surgery? Acute side effects/complications infection/bleeding/dvt/infarct (rarely) indwelling catheter (1-2 weeks) urinary leak (rare) lymphocele/edema (rare) Late side effects/consequences erectile dysfunction (common) stress incontinence 10-30% total incontinence 2-3%
5 When would you consider radiation after surgery? Post prostatectomy radiotherapy considered for: pathologic evidence of extraprostatic extension (pt3) or positive margins persistent or rising PSA after prostatectomy with no evidence of metastatic disease 2. Intermediate Risk Prostate Cancer: T1/2 and PSA and/or Gleason 7. Usually requires more intensified or combination of treatment. Overview of Treatment Options Dose escalated external beam radiotherapy +/- hormonal therapy Prostatectomy+ node dissection +/-postop radiotherapy Investigational: brachytherapy and external beam radiotherapy Detailed Review of Options External Beam Radiotherapy See above Radical Prostatectomy See above Hormonal Therapy Can be given for 3-8 months prior to radiotherapy to reduce tumor burden and prostate bulk prior to definitive therapy, but the effect on long term survival is subject of ongoing clinical trials. May also be given after radiation for up to 3 years for men with higher risk disease. LHRH agonist (leuprolide/buserelin/goserelin) Antiandrogen (bicalutamide) often given for 1 st six weeks of LHRH agonist to prevent tumor flare. What are the possible side-effects of hormonal therapy? Acute/early side effects: Fatigue (common) Sweats, hot flashes (common) Hepatitis or liver dysfunction, DVT/pulmonary embolus (rare) Loss of libido; erectile dysfunction while on hormones Side effects with long term use (>6 months): Loss of muscle mass Osteoporosis Anemia Gynecomastia 3. High Risk Prostate Cancer T3, T4 (extraprostatic spread or seminal vesicle involvement) or T1, T2 (organ
6 confined) with higher PSA (>20) or higher Gleason grade (8-10) or prostate cancer metastatic to pelvic lymph nodes (biopsy confirmed). High risk of both systemic and/or local failure with surgery or radiation alone Protracted hormonal therapy (>2-3 years) may be associated with a survival benefit when compared to radiotherapy alone in randomized controlled trials. Overview of Treatment Options Radical external beam radiotherapy + adjuvant hormonal therapy x 2-3 years Prostatectomy generally not recommended Experimental therapy as part of a clinical trial Detailed Review of Options External Beam Radiotherapy See above Hormonal Therapy Long term (2-3 years) LHRH agonist (leuprolide/buserelin/goserelin). Orchiectomy is an alternative to medical androgen suppression for permanent hormone suppression. Several trials have shown a survival benefit to combine hormones and radiation compared to radiation or hormone treatment alone. Side effects: What Follow-up Regimen after Radical Therapy would you offer? Men should be followed with PSA every 6-12 months until year 5 after treatment, then annually thereafter. A digital rectal exam should be done at least annually for surveillance. Monitoring should be coordinated between the oncologist, urologist and family doctor. Intent of follow-up: detect recurrence and monitor for side effects 4. Biochemical Failure (rising PSA in an asymptomatic patient) Over time, you will see some patients with a rising PSA. This indicates that the cancer has returned or is persistent. What treatment and when to treat are questions that are still being answered. Possible treatment considerations based on whether the failure is local or distant are listed below. Post Prostatectomy Isolated local failure likely: Nadir PSA after prostatectomy <0.2 Slow rise more than 12 months post prostatectomy PSA <2-3 Risk factors at time of prostatectomy (T3 or positive/close margin)
7 Salvage prostate bed radiotherapy can be considered Isolated local failure unlikely: Nadir PSA after prostatectomy >0.2 Rapid or early (<12 months) rise in PSA post prostatectomy PSA > 2 Salvage with prostate bed radiotherapy alone unlikely Consider hormones +/- radiotherapy Post Radiotherapy Isolated local failure likely: Initial low or intermediate risk prostate cancer Repeat bone scan and CT scan abdomen and pelvis negative Biopsy proven persistent disease within the prostate Lower PSA (<5) at time of salvage therapy Consider for cryotherapy or observation or hormones. Selected patients may be suitable for salvage prostatectomy. Systemic failure likely Initial high risk prostate cancer Positive bone scan Rapid rise in PSA (rising <12 mo. post radiotherapy or doubling time <12 mo.) Negative prostate biopsy and/or higher PSA (>5) at time of salvage therapy Consider for hormones for salvage or observe until symptomatic metastasis develop 5. Metastatic Prostate Cancer Metastatic prostate cancer is not curable but most men have improved symptoms and a period of disease control with hormonal therapy ranging from months on average. Higher PSA, rapidly doubling time of PSA, higher PSA nadir on hormones; extensive bone metastasis or cytopenias generally predict a shorter time to progression on hormones. Hormone refractory disease is usually indicated by increasing symptoms and/or PSA while on hormone therapy. Initial Treatment Hormonal monotherapy (orchidectomy or LHRH agonist such as leuprolide/buserelin/goserelin) is recommended. The benefit of adding an antiandrogen (bicalutamide) to orchidectomy/lhrh agonist has not been proven by recent randomized controlled trials but can be considered for those with incompletely suppressed testosterone on monotherapy and during the first 6-8 weeks of LHRH agonist therapy to prevent tumor flare. Palliative radiotherapy to
8 symptomatic metastatic sites can be considered in addition to hormone therapy. Treatment of Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC) CRPC is defined by rising PSA or worsening symptoms while under hormonal therapy. Castrate testosterone levels should be confirmed and effective gonadal androgen ablation implemented if not the case. Addition of antiandrogen (bicalutamide) to orchiectomy or LHRH agonist may be tried. Discontinuation of long-term antiandrogen (bicalutamide) may produce a withdrawal response in about 20% of men who have been on this medication long term thus antiandrogens should be stopped if there is clear progression while on this medication. Symptom control should be optimized, especially analgesic therapy. Recent randomized trials have suggested a benefit to the prophylactic use of bisphosphonates in reducing adverse skeletal events (fracture, spinal cord compression) in patients with symptomatic bone metastases The use of chemotherapy has been suggested to provide a modest survival advantage over secondary hormonal treatments in men with hormone refractory disease. Hormone refractory prostate cancer does not have a high objective response rate (tumour shrinkage, PSA decline) however clinical trials have indicated the following: Comparing prednisone 5 mg bid alone vs. prednisone plus Mitoxantrone: improved quality of life in the combination arm Comparing Mitoxantrone plus prednisone vs Docetaxel plus prednisone (Tannock et al): improved quality of life, pain control, and a small survival advantage (<8 weeks) in favour of Docetaxel/prednisone. This is now the standard for fit patients with HRPC. Other interventions aimed at improving symptomatology may include: Systemic radionuclide (See below) Local field radiotherapy (helpful if 1 or 2 dominant symptomatic sites) Low dose steroid (i.e., prednisone 5-10 mg/day or decadron 1-2 mg/day) Bisphosphonate therapy
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma
 A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
PROSTATE CANCER. Get the facts, know your options. Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology
 PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
Prostate Cancer In-Depth
 Prostate Cancer In-Depth Introduction Prostate cancer is the most common visceral malignancy among American men. In the year 2003, there are expected to be 220,000 new cases and nearly 29,000 deaths in
Prostate Cancer In-Depth Introduction Prostate cancer is the most common visceral malignancy among American men. In the year 2003, there are expected to be 220,000 new cases and nearly 29,000 deaths in
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 2005 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology
 Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk
 Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk When the urologist calls with the life-changing news that your prostate biopsy is positive for prostate cancer, an office appointment is made to
Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk When the urologist calls with the life-changing news that your prostate biopsy is positive for prostate cancer, an office appointment is made to
一 本 共 識 依 下 列 參 考 資 料 修 改 版 本 : 1. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology- Prostate cancer V.2.2014
 一 本 共 識 依 下 列 參 考 資 料 修 改 版 本 : 1. NCCN Clinical Practice in Oncology- Prostate cancer V.2.2014 二 制 訂 人 員 : 泌 尿 外 科 : 鍾 旭 東 醫 師 蔡 宗 佑 醫 師 洪 順 發 醫 師 腫 瘤 內 科 : 蕭 吉 晃 醫 師 放 射 腫 瘤 : 熊 佩 韋 醫 師 解 剖 病 理 : 蔡 建
一 本 共 識 依 下 列 參 考 資 料 修 改 版 本 : 1. NCCN Clinical Practice in Oncology- Prostate cancer V.2.2014 二 制 訂 人 員 : 泌 尿 外 科 : 鍾 旭 東 醫 師 蔡 宗 佑 醫 師 洪 順 發 醫 師 腫 瘤 內 科 : 蕭 吉 晃 醫 師 放 射 腫 瘤 : 熊 佩 韋 醫 師 解 剖 病 理 : 蔡 建
For further information on screening and early detection of prostate cancer, see the Section entitled Screening for Prostate Cancer.
 Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you
 Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment. Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Prostate Cancer. An overview of. Treatment. Prolapse. Information and Answers
 Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute
 Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute None 240,000 new diagnosis per year, and an estimated 28,100 deaths (2012) 2 nd leading cause of death from cancer in U.S.A. Approximately 1 in 6 men
Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute None 240,000 new diagnosis per year, and an estimated 28,100 deaths (2012) 2 nd leading cause of death from cancer in U.S.A. Approximately 1 in 6 men
PROSTATE CANCER. Diagnosis and Treatment
 Diagnosis and Treatment Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Patient and Coach Information... 1 About Your Prostate... 1 What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer... 2 Screening and Diagnosis... 2 Digital
Diagnosis and Treatment Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Patient and Coach Information... 1 About Your Prostate... 1 What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer... 2 Screening and Diagnosis... 2 Digital
Issues Concerning Development of Products for Treatment of Non-Metastatic Castration- Resistant Prostate Cancer (NM-CRPC)
 Issues Concerning Development of Products for Treatment of Non-Metastatic Castration- Resistant Prostate Cancer (NM-CRPC) FDA Presentation ODAC Meeting September 14, 2011 1 Review Team Paul G. Kluetz,
Issues Concerning Development of Products for Treatment of Non-Metastatic Castration- Resistant Prostate Cancer (NM-CRPC) FDA Presentation ODAC Meeting September 14, 2011 1 Review Team Paul G. Kluetz,
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT
 MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT KEYWORDS: Prostate cancer, PSA, Screening, Radical Prostatectomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to:
MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT KEYWORDS: Prostate cancer, PSA, Screening, Radical Prostatectomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to:
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer
 Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer SECTION 1: TREATMENTS This pamphlet provides information about different treatments for prostate cancer including what to expect and any risks and side-effects.
Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer SECTION 1: TREATMENTS This pamphlet provides information about different treatments for prostate cancer including what to expect and any risks and side-effects.
Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You?
 Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You? Prostate Cancer: Radiation Therapy Approaches I. Choices There is really a variety of options in prostate cancer management overall and in radiation therapy.
Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You? Prostate Cancer: Radiation Therapy Approaches I. Choices There is really a variety of options in prostate cancer management overall and in radiation therapy.
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment. Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto
 Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto What I will cover.. A little about radiation treatment The clinical trials
Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto What I will cover.. A little about radiation treatment The clinical trials
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER
 2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER Humboldt County is located on the Redwood Coast of Northern California. U.S census data for 2010 reports county population at 134,623, an increase of
2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER Humboldt County is located on the Redwood Coast of Northern California. U.S census data for 2010 reports county population at 134,623, an increase of
Prostate Cancer. Patient Information
 Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Roswell Park scientists and clinicians:
 The Prostate Cancer Center at Roswell Park Connects You to Nationally Recognized Experts for State-of-the-Art Treatment Options and Compassionate, Evidence-based Care Founded in 1898, Roswell Park Cancer
The Prostate Cancer Center at Roswell Park Connects You to Nationally Recognized Experts for State-of-the-Art Treatment Options and Compassionate, Evidence-based Care Founded in 1898, Roswell Park Cancer
Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC
 Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC Clinician-Scientist and Professor, Radiation Oncology and Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto and Ontario Cancer Institute/ (UHN) Head, PMH-CFCRI Prostate Cancer Research
Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC Clinician-Scientist and Professor, Radiation Oncology and Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto and Ontario Cancer Institute/ (UHN) Head, PMH-CFCRI Prostate Cancer Research
Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer
 Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it
Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Carcinoma of the vagina is a relatively uncommon disease, affecting only about 2,000 women in
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
Prostate Cancer Information and Facts
 Prostate Cancer Information and Facts Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnutsized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system.
Prostate Cancer Information and Facts Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnutsized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system.
Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection
 Prostatic Diseases Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection JMAJ 47(12): 555 560, 2004 Yoichi ARAI Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
Prostatic Diseases Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection JMAJ 47(12): 555 560, 2004 Yoichi ARAI Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
SRO Tutorial: Prostate Cancer Treatment Options
 SRO Tutorial: Prostate Cancer Treatment Options May 7th, 2010 Daniel M. Aebersold Klinik und Poliklinik für Radio-Onkologie Universität Bern, Inselspital Is cure necessary in those in whom it may be possible,
SRO Tutorial: Prostate Cancer Treatment Options May 7th, 2010 Daniel M. Aebersold Klinik und Poliklinik für Radio-Onkologie Universität Bern, Inselspital Is cure necessary in those in whom it may be possible,
Understanding Prostate Cancer. The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients. Advanced Care. Improving Lives.
 Understanding Prostate Cancer The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients Advanced Care. Improving Lives. UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CANCER The Urology Group has created this publication to provide
Understanding Prostate Cancer The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients Advanced Care. Improving Lives. UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CANCER The Urology Group has created this publication to provide
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer
 Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
Prostate Cancer. Treatments as unique as you are
 Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men
 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
DOCTOr. Doctor to HIGHLIGHTS. issue NO. 3 VOLuMe NO. 1
 Doctor to DOCTOr issue NO. 3 VOLuMe NO. 1 PROSTATE CANCER is the most common cancer in men, with 233,000 new cases diagnosed per year. Although prostate cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer
Doctor to DOCTOr issue NO. 3 VOLuMe NO. 1 PROSTATE CANCER is the most common cancer in men, with 233,000 new cases diagnosed per year. Although prostate cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
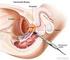 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Clinical guideline Published: 8 January 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg175
 Prostate cancer: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 8 January 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg175 NICE 2014. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction... 4 Drug recommendations... 5 Patient-centred
Prostate cancer: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 8 January 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg175 NICE 2014. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction... 4 Drug recommendations... 5 Patient-centred
ACTION PLAN. Choosing the treatment that s right for you. Endorsed by Kaiser Permanente Inter-regional Chiefs of Urology
 Prostate Cancer ACTION PLAN Choosing the treatment that s right for you Video Series Guidebook View videos at kpactionplans.org Endorsed by Kaiser Permanente Inter-regional Chiefs of Urology 2015 Kaiser
Prostate Cancer ACTION PLAN Choosing the treatment that s right for you Video Series Guidebook View videos at kpactionplans.org Endorsed by Kaiser Permanente Inter-regional Chiefs of Urology 2015 Kaiser
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER?
 PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
Prostate Cancer: National Collaborating Centre for Cancer. diagnosis and treatment. Clinical Guideline. January 2014. Prostate Cancer.
 National Collaborating Centre for Cancer Prostate Cancer Prostate Cancer: diagnosis and treatment Clinical Guideline Full Guideline January 2014 Final version Commissioned by the National Institute for
National Collaborating Centre for Cancer Prostate Cancer Prostate Cancer: diagnosis and treatment Clinical Guideline Full Guideline January 2014 Final version Commissioned by the National Institute for
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
A to Z of medical words
 Notes Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 A to Z of medical words 1 This fact sheet explains some of the medical words you might come across when you are finding out about prostate problems and prostate cancer.
Notes Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 A to Z of medical words 1 This fact sheet explains some of the medical words you might come across when you are finding out about prostate problems and prostate cancer.
Questions to Ask My Doctor About Prostate Cancer
 Questions to Ask My Doctor Being told you have prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it s treated, and how this
Questions to Ask My Doctor Being told you have prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it s treated, and how this
PROSTATE CANCER CONTENTS. December 2013 MICA (P) 035/05/2012
 December 2013 MICA (P) 035/05/2012 PROSTATE CANCER What is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer generally affects men over 50 and is rare in younger men. It is the uncontrolled spread or malignant growth of
December 2013 MICA (P) 035/05/2012 PROSTATE CANCER What is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer generally affects men over 50 and is rare in younger men. It is the uncontrolled spread or malignant growth of
Your Health Matters. Localized Prostate Cancer and Its Treatment
 Your Health Matters Localized Prostate Cancer and Its Treatment Greetings! Understanding prostate cancer and choosing among the various treatment options can be a difficult and anxiety-arousing process.
Your Health Matters Localized Prostate Cancer and Its Treatment Greetings! Understanding prostate cancer and choosing among the various treatment options can be a difficult and anxiety-arousing process.
Report with statistical data from 2007
 2008 Cancer Program Annual Report with statistical data from 2007 Lake Cumberland Regional Hospital 305 Langdon Streett Somerset, KY 42503 Telephone: 606-679-7441 Fax: 606-678-9919 Cancer Committee Mullai,
2008 Cancer Program Annual Report with statistical data from 2007 Lake Cumberland Regional Hospital 305 Langdon Streett Somerset, KY 42503 Telephone: 606-679-7441 Fax: 606-678-9919 Cancer Committee Mullai,
prostate cancer: A Success Story
 prostate cancer: A Success Story Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in human beings. That is, even though prostate cancer occurs only in men, the number of men with prostate cancer exceeds the combined
prostate cancer: A Success Story Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in human beings. That is, even though prostate cancer occurs only in men, the number of men with prostate cancer exceeds the combined
Secondary Cancer and Relapse Rates Following Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate-Confined Cancer
 Copyright E 2007 Journal of Insurance Medicine J Insur Med 2007;39:242 250 MORTALITY Secondary Cancer and Relapse Rates Following Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate-Confined Cancer David Wesley, MD; Hugh
Copyright E 2007 Journal of Insurance Medicine J Insur Med 2007;39:242 250 MORTALITY Secondary Cancer and Relapse Rates Following Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate-Confined Cancer David Wesley, MD; Hugh
LIvING WITH Prostate Cancer
 Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions David Weksberg, M.D., Ph.D. PinnacleHealth Cancer Institute September 12, 2015 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions David Weksberg, M.D., Ph.D. PinnacleHealth Cancer Institute September 12, 2015 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment
What is prostate cancer?
 Prostate Cancer What is prostate cancer? Let us explain it to you. www.anticancerfund.org www.esmo.org ESMO/ACF Patient Guide Series based on the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines PROSTATE CANCER: A GUIDE
Prostate Cancer What is prostate cancer? Let us explain it to you. www.anticancerfund.org www.esmo.org ESMO/ACF Patient Guide Series based on the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines PROSTATE CANCER: A GUIDE
Localised prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
First-line Hormone Therapy
 First-line Hormone Therapy Alan Horwich Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden Hospital, London, UK Alan.Horwich@icr.ac.uk MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE CANCER Treatment windows Subclinical Localised
First-line Hormone Therapy Alan Horwich Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden Hospital, London, UK Alan.Horwich@icr.ac.uk MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE CANCER Treatment windows Subclinical Localised
The Prognosis and Survival Rates For Localized Prostate Cancer
 WHITE PAPER Prostate Cancer and Stereotactic Radiosurgery I. Introduction This white paper will focus on carcinoma of the prostate with sections one though six (I-VI) comprising a general review of prostatic
WHITE PAPER Prostate Cancer and Stereotactic Radiosurgery I. Introduction This white paper will focus on carcinoma of the prostate with sections one though six (I-VI) comprising a general review of prostatic
PROSTATE CANCER. Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American
 PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer
 Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer Treatment Plan Stage of prostate cancer: RADIATION THERAPY Radiation Treatments: Date for planning CT: Date to start radiation
Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer Treatment Plan Stage of prostate cancer: RADIATION THERAPY Radiation Treatments: Date for planning CT: Date to start radiation
Prostate Cancer Management Clinical Guidelines
 Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland e-publications@rcsi Surgery (The Colles Institute) Surgical Clinical Guidelines Surgery (The Colles Institute) 1-2-2002 Prostate Cancer Management Clinical Guidelines
Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland e-publications@rcsi Surgery (The Colles Institute) Surgical Clinical Guidelines Surgery (The Colles Institute) 1-2-2002 Prostate Cancer Management Clinical Guidelines
Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report
 Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report The Cancer Committee of CHRISTUS St. Patrick Hospital is proud to present its 2010 Annual Report. The Community Hospital Comprehensive Cancer Program
Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report The Cancer Committee of CHRISTUS St. Patrick Hospital is proud to present its 2010 Annual Report. The Community Hospital Comprehensive Cancer Program
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
to Know About Your Partner s
 What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer www.nshealth.ca Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer What is the prostate? The prostate is one of the male sex glands. It makes seminal fluid
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer www.nshealth.ca Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer What is the prostate? The prostate is one of the male sex glands. It makes seminal fluid
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer. Understanding Your Treatment Options
 After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
Locally advanced prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? How is locally advanced prostate cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? How is locally advanced prostate cancer diagnosed?
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment
 Your Health Matters Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment By the UCSF Medical Center Prostate Cancer Advocates Greetings! From our personal experience in dealing with our own prostate cancers, we UCSF Patient
Your Health Matters Prostate Cancer & Its Treatment By the UCSF Medical Center Prostate Cancer Advocates Greetings! From our personal experience in dealing with our own prostate cancers, we UCSF Patient
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
SCA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR PROSTATE CANCER
 Saskatchewan Cancer Agency A healthy population free from cancer SCA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR PROSTATE CANCER Original Guideline date: March 2002 Update(s): October 2004, October 2008 1. General
Saskatchewan Cancer Agency A healthy population free from cancer SCA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR PROSTATE CANCER Original Guideline date: March 2002 Update(s): October 2004, October 2008 1. General
CONTENTS. What is Cancer?... 2. What Should I Know About Prostate Cancer?... 3. Who's at Risk?... 3 Diagnosis & Staging Tests... 3
 CONTENTS Introduction................................. 1 What is Cancer?.............................. 2 What Should I Know About Prostate Cancer?....... 3 Who's at Risk?................................
CONTENTS Introduction................................. 1 What is Cancer?.............................. 2 What Should I Know About Prostate Cancer?....... 3 Who's at Risk?................................
Before, Frank's immune cells could
 Before, Frank's immune cells could barely recognize a prostate cancer cell. Now, they are focused on it. Stimulate an immune response against advanced prostate cancer Extend median survival beyond 2 years
Before, Frank's immune cells could barely recognize a prostate cancer cell. Now, they are focused on it. Stimulate an immune response against advanced prostate cancer Extend median survival beyond 2 years
Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery?
 Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery? Contact the GenomeDx Patient Care Team at: 1.888.792.1601 (toll-free) or e-mail: client.service@genomedx.com Prostate Cancer Classifier
Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery? Contact the GenomeDx Patient Care Team at: 1.888.792.1601 (toll-free) or e-mail: client.service@genomedx.com Prostate Cancer Classifier
Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatments
 Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatments Guest Expert: Kevin, DO Associate Professor of Medical Oncology, Yale Cancer Center www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with
Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatments Guest Expert: Kevin, DO Associate Professor of Medical Oncology, Yale Cancer Center www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with
GENERAL CODING. When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis.
 GENERAL CODING When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis. Exception: You must review and revise EOD coding for prostate
GENERAL CODING When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis. Exception: You must review and revise EOD coding for prostate
Understanding Treatment Choices for Prostate Cancer
 Know Your Options A Prostate Cancer Education Program Understanding Treatment Choices for Prostate Cancer US TOO International, Inc. National Cancer Institute U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
Know Your Options A Prostate Cancer Education Program Understanding Treatment Choices for Prostate Cancer US TOO International, Inc. National Cancer Institute U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
SIGNPOSTS. Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer. Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer
 SIGNPOSTS Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer Your journey is unique like you. Signposts along the pathway can show you where you
SIGNPOSTS Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer Your journey is unique like you. Signposts along the pathway can show you where you
Running Head: PROSTATE CANCER TREATMENTS AND CASE STUDY 1. Prostate Cancer: Treatments and Case Study
 Running Head: PROSTATE CANCER TREATMENTS AND CASE STUDY 1 Prostate Cancer: Treatments and Case Study November 13, 2012 PROSTATE CANCER 2 Abstract Prostate cancer affected 192,280 men in the United States
Running Head: PROSTATE CANCER TREATMENTS AND CASE STUDY 1 Prostate Cancer: Treatments and Case Study November 13, 2012 PROSTATE CANCER 2 Abstract Prostate cancer affected 192,280 men in the United States
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects
 Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
 Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
Clinical Management Guideline Management of locally advanced or recurrent Renal cell carcinoma. Protocol for Planning and Treatment
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: LOCALLY ADVANCED OR METASTATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Patient information given at each stage following agreed information
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: LOCALLY ADVANCED OR METASTATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Patient information given at each stage following agreed information
Implementation Date: April 2015 Clinical Operations
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guideline PROSTATE CANCER Original Date: March 2011 Page 1 of 5 Radiation Oncology Last Review Date: March 2015 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_124 Last Revised Date:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guideline PROSTATE CANCER Original Date: March 2011 Page 1 of 5 Radiation Oncology Last Review Date: March 2015 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_124 Last Revised Date:
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer HORMONE THERAPY FOR ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer HORMONE THERAPY FOR ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical
Historical Basis for Concern
 Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Making the Choice. Deciding What to Do About Early Stage Prostate Cancer
 Making the Choice Deciding What to Do About Early Stage Prostate Cancer We have all faced the same tough choices you face now. We talked with our doctors and others we love and trust. We each made our
Making the Choice Deciding What to Do About Early Stage Prostate Cancer We have all faced the same tough choices you face now. We talked with our doctors and others we love and trust. We each made our
