Cervix. Case 1 On January 29, 1951, Henrietta Lacks went to Johns Hopkins Hospital. She went there 09/08/2011. all what you need to know as a PhD
|
|
|
- April Bailey
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Female Reproductive Pathology all what you need to know as a PhD scientist Ie-Ming Shih, MD, PhD 09/08/2011 Cervix Cervicitis Cervical stenosis/incompenence Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia Cervical carcinoma Review of anatomy Histology Case 1 On January 29, 1951, Henrietta Lacks went to Johns Hopkins Hospital. She went there because she felt a lump inside her. It all started when she asked her cousins to feel her belly, asking if they felt the lump that she did. Her cousins assumed correctly that she was pregnant. But, after giving birth to her fifth child, Henrietta started bleeding and it wasn't menstrual. She told Day, was then taken to the local doctor, tested for syphilis, which came back negative, and then referred to Johns Hopkins Hospital. B D O Born Died Henrietta Lacks Loretta Pleasant August 1, 1920( ) Roanoke, Virginia October 4, 1951( ) (aged 31) Baltimore, Maryland Occupation Tobacco farmer Spouse David Lacks ( ) Children Parents Lawrence Lacks Elsie Lacks David "Sonny" Lacks, Jr. Deborah (Lacks) Pullum Zakariyya Bari Abdul Rahman (born Joseph Lacks) Eliza ( ) and John Randall Pleasant I ( ) Johns Hopkins was their only choice for a hospital, since it was the only one in a close proximity to them that treated black patients. Howard Jones, her new doctor, examined Henrietta and the lump in her cervix. It was nothing he had ever seen before. He cut off a small part of the tumor and sent it to the pathology lab. Soon after, Jones discovered she had a cervical cancer Stage 1. Lacks was treated with radium tube inserts, which were sewn in place. After several days in place, the tubes were removed and she was released from Johns Hopkins with instructions to return for X-ray treatments as a follow up. During her radiation treatments for the tumor, a small part of Henrietta's cervix was taken off a healthy part and a cancerous part without her permission. The cells from her cervix were given to Dr. George Otto Gey. These cells would eventually become the HeLa immortal cell line In significant pain and without improvement, Lacks returned to Hopkins demanding to be admitted on August 8 and remained until her death. Though she received treatment and blood transfusions, she died of uremic poisoning on October 4, 1951, at the age of thirtyone. A subsequent partial autopsy showed that the cancer had metastasized throughout her body.
2 Low-grade lesion High-grade lesion HPV is the cause of cervical cancer The human papillomaviruses (HPV) are small viruses with double stranded d DNA that t have a particular tropism for the epithelium inducing its proliferation. io It is believed that the HPV enters the body after slight trauma to the epithelium and needs terminally differentiated fe entiated epithelial cells for replication. HPV causes epithelial lesions of varying severity. Over 100 different fe HPV types have been identified and each is associated with a different type of lesion. HPV type 1 causes verrucas, HPV type 2 causes common warts and HPV11 causes genital warts. Certain HPV types, such as HPV16 and HPV18 infect cervical epithelium e and cause lesions that can progress through different e grades of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia to cancer. ce These viruses are known as high-risk papillomaviruses. iru Most high-risk risk HP HPV Vin infections ions are successfully ull ly resolved by the host immune system and do not tb become e life-threatening. t In a small number of cases however, lesions caused by high-risk HPV types can persist and can develop into cancer. Myometrium Leiomyoma Leiomyosarcoma Adenomyosis. r
3 Case 2 Ms. Smith is a 42 years old school teacher and suffered from pelvic pain which is aggravated during menstruation (sick days off). Attempts to become pregnant have failed. Pelvic examination revealed a pelvic mass which was confirmed by imaging. Endometrium Endometritis Atrophy endometrium (cause postmenopausal bleeding) Endometrial hyperplasia (precursor of carcinoma) Endometrial carcinoma (endometrioid and serous type) Leiomyoma, the most common benign uterine tumor in women Leiomyosarcoma Endometriosis Atrophy endometrium Hyperplastic endometrium
4 Hyperplasia Carcinoma in situ Invasive carcinoma Metastatic carcinoma Case 3 Ms. Smith with BMI 38 is a 64 years old presented with heavy vaginal bleeding. No other symptoms were noted. Endometrial biopsy was performed. Imaging study was followed to determine the extent of the disease. Endometrioid carcinoma of the uterus Courtesy of Dr. Russell Vang
5 Fallopian tube Chronic salpingitis and hydrosalpinx Acute pelvic inflammatory disease (pyosalpinx) Tubal pregnancy Tubal serous carcinoma Ectopic Pregnancy Epidemiology: ~20 per 1000 pregnancies Strongly associated with PID 98% occur in fallopian tube Symptoms: Abdominal pain Vaginal bleeding Exam findings: Adnexal mass on bimanual exam Imaging Findings: No evidence of intrauterine pregnancy Presence of pregnancy outside of uterus Diagnosis: Ultrasound Serial beta-hcg tests Treatment: Surgery or methotrexate Case 4 Ms. Smith is a 19 y/o college student. She present with acute abdominal pain, admitted to ER in the early morning. She did not show signs of infection. BP drops and HR increases in ER. B- hcg test is positive. She was operated. Acute and chronic salpingitis Epidemiology: Caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) Pathogens include Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, bacteria that comprise the vaginal flora (e.g. anaerobes, G. vaginalis, H. influenzae, enteric gram negative rods, S. agalactiae) Symptoms: Abdominal/pelvic pain, worse with coitus, shortly following menses Vaginal discharge Abnormal vaginal bleeding Fever Exam findings: Diffuse abdominal tenderness Cervical motion/uterine/adnexal tenderness Purulent endocervical discharge Imaging Findings: Thickened, fluid-filled fallopian tubes on ultrasound Diagnosis: Based on physical exam findings Blood tests: pregnancy test, CBC, urinalysis, gonorrhea and Chlamydia gene probes, wet prep Treatment: Antibiotics for patient and her sexual partner The Fallopian Tube: Physiology Fimbriated end catches oocyte Ciliated columnar epithelium and muscularis sweep oocyte to ampulla In ampulla, fertilization of oocyte typically occurs Cilia and muscularis sweep fertilized oocyte (zygote) to uterus Action of hormones on tube: Estrogen stimulates cilia production Estrogen enhances secretory activity of Peg cells Progesterone stimulates Peg cell production Pyosalpinx Hydrosalpinx
6 Tubal serous carcinoma Ovarian endometriosis Ovary Endometriotic cyst Benign cysts (corpus luteum cyst, serous cyst, etc.) Ovarian neoplasm Case 5 Ms. Smith is a 48 y/o house wife. She has been healthy in the past. Routine Gyn annual check-up reveals a possible adnexal mass, which appears benign by sonogram and CA125 is not elevated. She decides to be operated. Outwater E K et al. Radiographics 2001;21: Ovarian cancers include: Mature Cystic Teratoma Epidemiology: Also known as a dermoid cyst Most common germ cell tumor Accounts for 95% of teratomas and is benign Most common ovarian tumor in the 2 nd and 3 rd decades of life Contains mature tissue of ectodermal, mesodermal, and endodermal origin Symptoms: Usually asymptomatic, but can cause pain if torsion or rupture Exam findings: Adnexal mass on bimanual exam Imaging Findings: Characteristic ultrasound appearance Ultrasound = % sensitive Diagnosis: Based on ultrasound Treatment: Surgery to remove cyst (ovarian cystectomy)
7 The fact of ovarian cancer Ovarian carcinoma is the major disease of cancer mortality in women (22,430 new cases 15,280 new deaths in 2007) Molecular etiology is poorly understood Patients are usually on death roll if tumors recur A peritoneal disease, ideal for i.p. therapy Issues of borderline tumors Prediction of outcome in SBT, invasive vs non-invasive implants Pathogenesis of high-grade serous carcinoma Target-based therapy in recurrent tumors Several others Adnexal Masses: Differential Diagnosis Variables to consider Age Medical history Symptoms Physical exam Objective findings Adnexal Masses Ovarian masses Physiologic cysts (also known as functional cysts) Simple vs. complex Simple cysts: follicular cyst Complex cysts: hemorrhagic cyst, corpus luteum cyst, theca lutein cyst Neoplasms Benign: endometrioma, cystadenoma, teratoma Borderline Malignant: epithelial ovarian cancer, germ cell tumors, sex cord stromal tumors Metastatic: from cancer of breast, colon, endometrium Adnexal Masses: Age <15 years old high percentage of ovarian masses are malignant Premenopausal women 6-11% risk of ovarian malignancy Postmenopausal women 29-35% risk of ovarian malignancy Adnexal Masses cont d Tubal masses Paratubal cyst Ectopic pregnancy Hydrosalpinx Tuboovarian abscess (TOA) Fallopian tube cancer Adnexal masses not involving the ovary or fallopian tube Peritoneal inclusion cyst Pedunculated fibroid Diverticular abscess Appendiceal abscess or tumor Inflammatory or malignant bowel disease Pelvic kidney Adnexal Masses: History Personal history of breast cancer Increased risk for an ovarian malignancy Family history of breast, ovarian, colon cancer Increased risk of ovarian malignancy
8 Adnexal Masses: Symptoms Mid-cycle pain in premenopausal women physiologic cyst Pain immediately following intercourse ruptured cyst Pain, fever, purulent cervical discharge TOA Dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia endometrioma Chronic abdominopelvic pain, bloating ovarian neoplasm or fibroid Pain, postmenopausal bleeding, watery vaginal discharge fallopian tube cancer Adnexal Masses: Imaging Pelvic ultrasound Most valuable imaging test to evaluate the adnexa Performed using transducer transabdominally and/or transvaginally Ultrasound findings: Malignancy Solid component Nodular or papillary excrescences Thick septations Blood flow in the solid component Presence of ascites Peritoneal masses, enlarged nodes, or matted bowel Functional cysts: solitary, thin walled, unilocular, < 8 to 10 cm in diameter Dermoid cysts: varying densities due to the presence of sebaceous material, bone, adipose tissue, and/or hair Endometriomas: homogeneous low to medium level echoes, thick walled Serous cysts: anechoic Mucinous cysts: echogenic Pelvic MRI Can be useful when ultrasound does not provide adequate information Adnexal Masses: Physical Exam Pelvic exam Look at cervix Perform Pap if needed Consider endometrial biopsy if abnormal bleeding Bimanual exam: assess uterus, assess adnexa for size, location, consistency, mobility, and tenderness Rectal exam Assess posterior uterus, assess for stool in rectum and uterosacral nodularity Abdominal exam Assess for fluid shift consistent with ascites Breast exam Assess for masses Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Definition: Menstrual irregularity + signs of hyperandrogenism Menstrual irregularity = oligo or amenorrhea Hyperandrogenism = hirsutism, severe acne, and/or pattern alopecia Associated with: Infertility Type 2 diabetes mellitus Obesity Cardiovascular disease Endometrial carcinoma Imaging finding: 12 or more follicles in each ovary measuring 2-9 mm in diameter and/or increased ovarian volume on ultrasound Treatment: Oral contraceptives or cyclic progesterone Adnexal masses: Blood tests Pregnancy test Positive: ectopic pregnancy, theca lutein cyst Complete blood count Elevated white blood cell count : TOA, appendicitis, diverticulitis Tumor Markers CA 125: serum glycoprotein that is elevated in ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, pancreatic cancers, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, pelvic inflammatory disease, heart failure, liver and renal disease, and in 1% of healthy women Sensitivity for predicting ovarian malignancy» Premenopausal women: 50-74%» Postmenopausal: 69-87% Specificity for predicting ovarian malignancy» Premenopausal: 26-92%,» Postmenopausal: % Positive predictive value for ovarian malignancy» Premenopausal: 5-67%» Postmenopausal: % HE4: protein expressed in ovarian cancer tissue Not elevated in women with endometriosis Approved by FDA in 2008 for monitoring patients with ovarian cancer for disease progession or recurrence Not approved for use to differentiate benign from malignant adnexal masses AFP, LDH, hcg: measured when germ cell tumor is suspected CA19-9, CEA: measured to assess for GI malignancy involving the adnexa Serous Borderline Tumor Epidemiology: Account for 10-20% of epithelial ovarian tumors Average age at diagnosis = years Symptoms: Usually asymptomatic, but may cause pain Exam findings: Adnexal mass on bimanual exam Imaging Findings: No sonographic features highly suggestive of a borderline tumor Diagnosis: Diagnosis made based on histology once ovary removed Treatment: Surgery to remove ovary (oophorectomy)
9 Serous carcinoma Epidemiology: Serous carcinoma of the ovary is an epithelial ovarian cancer 90% of cancer arising from ovary is epithelial in origin Epithelial ovarian cancer = 2 nd most common gyn malignancy Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common cause of death among women with gyn malignancy ~ 21,500 cases/year ~14,600 deaths/year Average age of diagnosis = 45-6O years Symptoms: Vague and ill-defined: bloating, early satiety, increased abdominal size, pelvic/abdominal pain, urinary urgency/frequency Exam findings: Solid, fixed, irregular mass noted on bimanual exam Ascites noted on abdominal exam Imaging Findings: Solid component Nodular or papillary excrescences Thick septations Blood flow in the solid component Presence of ascites Peritoneal masses, enlarged nodes, or matted bowel Diagnosis: Ultrasound CA 125 CT scan Surgery Treatment: Gyn oncologist: removal of uterus and cervix (total abdominal hysterectomy), removal of tubes and ovaries (bilateral salpingooophorectomy), staging cystadenoma inclusion cyst TP53 LG SBT CCC HG EM/CC borderline tumor endometriosis HG LG CCEM MU TP53 BRCA1/2 KRAS BRAF PIK3CA PTEN CTNNB1 ARID1A PPP2R1A? Mutation > 90% 45%-90% 30%-45% 10%-30% 3%-10% < 3% cadherin ERRB -catenin Mut TK Mut KRAS PI3K PTEN cyclin E -catenin -catenin LEF/TCF BRAF AKT mtor MEK MAPK (ERK) cyclin D1 Endometrioid TP53 progression survival proliferation Ovarian cancer- not a single disease ARID1A PI3K/AKT ZNF217 PP2A ARID1A Wnt/ -cat PI3K/PTEN PP2A Clear cell Endometrioid KRAS/E RK Mucinous High-grade serous HR/BRCA P53 Rb CIN Notch3 PI3K/AKT/KRAS FOXM1 Ovarian endometrioid carcinoma (Type I) PTEN CTNNB1 ( -catenin) PIK3CA TP53 (in high-grade CA) Endometriosis Endometrioid borderline tumor Endometrioid carcinoma Apc flox/flox Pten flox/flox Ad-cre Cancer Cell 2007,11:321; Annual Rev Pathol, 2009, 4:287
10 Case 6 Ms. Smith is a 65 y/o retired pharmacist. She never gave a birth and has been healthy in the past until recently she complains for abdominal fullness. She had an ovarian benign simple cyst but it appears to have solid component and her CA125 is 213 one year later. She was referred to a gynecologic oncologist. July 1998 Stage III HG serous CA July 1999 Screening for ovarian cancer does not work JAMA, 305:2295, 2011 (June 8) 78,216 women undergo annual screening with TVU and CA-125 testing Screening did not result in fewer deaths from the disease False-positive results (5%) often led to unnecessary surgeries and other serious complications Many of the positive screening results from TVU and CA-125 turned out not to be cancer Only 1.6 out of every 100 women who test positive actually have cancer Ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma serous High-grade ovarian serous carcinoma is difficult for early detection (Type II tumors) July 1998 Not curable stage Metastatic disease Pre-neoplastic stage high-grade serous low-grade serous clear cell endometrioid mucinous others Tumor load Detection point Biomarker/imaging Time Stage III HG serous CA July 1999 Early stage Late stage
11 fallopian tube fimbriated end Why from fallopian tube? H&E H2AX Ki-67 Hypothesis Tubal intraepithelial carcinoma (TIC) * * * * Ovarian cancer is a heterogeneous group of diseases with different clinicopathological and molecular features Ovarian carcinoma is theoretically an imported disease Ovary itself is innocent to develop carcinoma. Type I tumors: ancestor is endometriosis then CA develops Type II tumors: ancestor is TIC widespread disease Potential paradigm shift in managing ovarian cancer patients prophylaxis- detection- therapy- salpingectomy instead of salpingectomy+oophorectomy detection of low-volume Dx rather then serum markers targeted therapy for Type I Dx p53 Ki-67 p16 Tubal origin of ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma Ovarian serous carcinoma originates from fallopian tube epithelium Ovarian cancer progresses from STIC then spreads from the tube to ovary, pelvis, abdomen/pelvic soft tissues and distant sites Ovary is only secondly involved v
12 Gynaecologic cancer New cases Deaths poly(adp-ribose) polymerase (PARP) synthetic lethality PARP x x BRCA Normal DNA DNA damage Single strand break DNA damage Double strand break Nature, on line version June 30 Lancet Oncology Vol 12 September 2011 TCGA- major pathway analysis PARP inhibitor + CDK1 inhibitor
13 mutation deletion amplification translocation Nanopore sequencing-towards the 15-minute genome Genetics: Pulling strands of DNA through nanopores could dramatically speed up the sequencing of human genomes Mar 10th 2011 Nanopore -hemolysin) Gross anatomy of female genital organs Leiomyoma Leiomyosarcoma Ovarian cancer: Primary carcinoma Metastatic carcinoma Stromal tumor Germ cell tumor? mole Choriocarcinoma Endometrial hyperplasia Endometrioid carcinoma estrogen Squamous intraepithelial lesion HPV Squamous carcinoma
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries. Simple Cystic Masses
 Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management
 Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
ProSono Copyright 2006. Ovarian Pathology
 Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Benign Ovarian Masses
 Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
POSTMENOPAUSAL ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO
 POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
What are the differences between fibroid and ovarian cyst?
 DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
Ovarian cancer. A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment
 Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East. Oxford Clinic
 Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East Oxford Clinic Objectives of this talk To understand risk of malignancy and thus not fear it Practical advice for follow up of asymptomatic cysts Practical advice
Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East Oxford Clinic Objectives of this talk To understand risk of malignancy and thus not fear it Practical advice for follow up of asymptomatic cysts Practical advice
良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介. Benign adnexal mass
 良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介 Benign adnexal mass Prepubertal Age Group Adolescent Age Group Reproductive Age Group Postmenopausal Age Group Prepubertal Age Group Differential Diagnosis Diagnosis and Management Prepubertal
良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介 Benign adnexal mass Prepubertal Age Group Adolescent Age Group Reproductive Age Group Postmenopausal Age Group Prepubertal Age Group Differential Diagnosis Diagnosis and Management Prepubertal
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
The Adnexal Mass and Early Ovarian Cancer
 The Adnexal Mass and Early Ovarian Cancer Fred Ueland, MD University of Kentucky Gynecologic Oncology Never give in. Never give in. Never, never, never, never- in nothing great or small, large or petty-
The Adnexal Mass and Early Ovarian Cancer Fred Ueland, MD University of Kentucky Gynecologic Oncology Never give in. Never give in. Never, never, never, never- in nothing great or small, large or petty-
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report
 Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report Abstract Ovarian cancer is a very common cancer among women. It is an extremely diverse disease requiring several treatment options. Occasionally ovarian cancer is diagnosed
Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report Abstract Ovarian cancer is a very common cancer among women. It is an extremely diverse disease requiring several treatment options. Occasionally ovarian cancer is diagnosed
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Guideline on the management of ovarian masses. Gynaecologists, radiologists, sonographers, nurses. Ovarian masses, ovarian cysts, management
 Guideline on the management of ovarian masses. A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Written by: Gynaecology Services Gynaecologists, radiologists, sonographers, nurses Management
Guideline on the management of ovarian masses. A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Written by: Gynaecology Services Gynaecologists, radiologists, sonographers, nurses Management
Progress and Prospects in Ovarian Cancer Screening and Prevention
 Progress and Prospects in Ovarian Cancer Screening and Prevention Rebecca Stone, MD MS Assistant Professor Kelly Gynecologic Oncology Service The Johns Hopkins Hospital 1 No Disclosures 4/12/2016 2 Ovarian
Progress and Prospects in Ovarian Cancer Screening and Prevention Rebecca Stone, MD MS Assistant Professor Kelly Gynecologic Oncology Service The Johns Hopkins Hospital 1 No Disclosures 4/12/2016 2 Ovarian
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013
 Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
K Raja/N Varol FPA 2013. FPA Sydney August 31 2013
 FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination
 Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN. Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY.
 Ovarian Cancer 2 OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN by Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY Ogden, Utah Instructor s Name Date Ovarian Cancer 2 Background
Ovarian Cancer 2 OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN by Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY Ogden, Utah Instructor s Name Date Ovarian Cancer 2 Background
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer?
 Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Cancer Facts for Women
 2006, American Cancer Society, Inc. No.200700-Rev.03/08 The American Cancer Society is the nationwide community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer as a major health problem
2006, American Cancer Society, Inc. No.200700-Rev.03/08 The American Cancer Society is the nationwide community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer as a major health problem
Ovarian Cancer. in Georgia, 1999-2003. Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health
 Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL ABNORMAL PAP SMEAR (ABNORMAL CERVICAL CYTOLOGIC FINDINGS) Kathleen Dor
 1 ABNORMAL PAP SMEAR (ABNORMAL CERVICAL CYTOLOGIC FINDINGS) Kathleen Dor Cervical cytology screening has significantly decreased rates of mortality from cervical cancer; however, 400 women die each year
1 ABNORMAL PAP SMEAR (ABNORMAL CERVICAL CYTOLOGIC FINDINGS) Kathleen Dor Cervical cytology screening has significantly decreased rates of mortality from cervical cancer; however, 400 women die each year
Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer
 A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
Ovarian Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
3 Summary of clinical applications and limitations of measurements
 CA125 (serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cancer Antigen 125 (CA125) 1.2 Alternative names Mucin 16 1.3 NLMC code To follow 1.4 Description of analyte CA125 is an antigenic determinant
CA125 (serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cancer Antigen 125 (CA125) 1.2 Alternative names Mucin 16 1.3 NLMC code To follow 1.4 Description of analyte CA125 is an antigenic determinant
Medical criteria for IUCD s Based on the WHO MEC (2004- Annexure 3) system a woman s eligibility for IUCD insertion falls in 4 categories. These categ
 CLIENT ASSESSMENT Ensure that the woman is not pregnant Determine the length and direction of uterus. Ensure that she does not have gonorrhea and chlamydia, and is not a high risk case of STI s Identify
CLIENT ASSESSMENT Ensure that the woman is not pregnant Determine the length and direction of uterus. Ensure that she does not have gonorrhea and chlamydia, and is not a high risk case of STI s Identify
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
 Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer starts when cells in the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer starts when cells in the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Ovarian Cancer. What is ovarian cancer?
 Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can spread to other areas of the body.
Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can spread to other areas of the body.
Ovarian Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Understanding CA 125 Levels A GUIDE FOR OVARIAN CANCER PATIENTS. foundationforwomenscancer.org
 Understanding CA 125 Levels A GUIDE FOR OVARIAN CANCER PATIENTS foundationforwomenscancer.org Contents Introduction...1 CA 125................................... 1 The CA 125 Test...2 The Use of the CA
Understanding CA 125 Levels A GUIDE FOR OVARIAN CANCER PATIENTS foundationforwomenscancer.org Contents Introduction...1 CA 125................................... 1 The CA 125 Test...2 The Use of the CA
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
All you need to know about Endometriosis. Nordica Fertility Centre, Lagos, Asaba, Abuja
 All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Gynecologic Cancer in Women with Lynch Syndrome
 Gynecologic Cancer in Women with Lynch Syndrome Sarah E. Ferguson, MD FRCSC Division of Gynecologic Oncology, Princess Margaret Hospital, University of Toronto June 11, 2013 Objective 1. To review the
Gynecologic Cancer in Women with Lynch Syndrome Sarah E. Ferguson, MD FRCSC Division of Gynecologic Oncology, Princess Margaret Hospital, University of Toronto June 11, 2013 Objective 1. To review the
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding)
 Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization
 September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
Examples of good screening tests include: mammography for breast cancer screening and Pap smears for cervical cancer screening.
 CANCER SCREENING Dr. Tracy Sexton (updated July 2010) What is screening? Screening is the identification of asymptomatic disease or risk factors by history taking, physical examination, laboratory tests
CANCER SCREENING Dr. Tracy Sexton (updated July 2010) What is screening? Screening is the identification of asymptomatic disease or risk factors by history taking, physical examination, laboratory tests
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
Try out the online ROMA calculator available on the Elecsys HE4 page at cobas.com
 Try out the online calculator available on the Elecsys HE4 page at cobas.com Download the Roche application for the iphone and the ipad from the App Store. Roche References 1 Huhtinen, K. et al. (29).
Try out the online calculator available on the Elecsys HE4 page at cobas.com Download the Roche application for the iphone and the ipad from the App Store. Roche References 1 Huhtinen, K. et al. (29).
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
Carcinoma of the vagina is a relatively uncommon disease, affecting only about 2,000 women in
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
DISCLOSURE OBJECTIVES IN THE INEREST OF TIME LAPAROSCOPY AND AN APPROACH TO THE ADNEXAL MASS
 LAPAROSCOPY AND AN APPROACH TO THE ADNEXAL MASS DISCLOSURE I do not have any financial relationship with commercial interests. Michael Traynor Michael Traynor MD MPH Northwest Permanente, PC KAISER PERMANENTE
LAPAROSCOPY AND AN APPROACH TO THE ADNEXAL MASS DISCLOSURE I do not have any financial relationship with commercial interests. Michael Traynor Michael Traynor MD MPH Northwest Permanente, PC KAISER PERMANENTE
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts
 Image Presentation Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts Kiran A. Jain, MD Objective. To present the spectrum of sonographic findings associated with hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Methods. Experience
Image Presentation Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts Kiran A. Jain, MD Objective. To present the spectrum of sonographic findings associated with hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Methods. Experience
Gynaecology FAQ s. Correspondence address: 204 Fulham Road London SW10 9PJ Email: enquiries@missayida.com Tel: 02077514489
 Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
Uterine Fibroids. More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth.
 Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
HEALTH UPDATE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
Uterus myomatosus. 10-May-15. Clinical presentation. Incidence. Causes? 3 out of 4 women. Growth rate vary. Most common solid pelvic tumor in women
 Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up
 Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up What is a Pap Smear? A Pap smear (also known as the Pap test) is a medical procedure in which a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the
Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up What is a Pap Smear? A Pap smear (also known as the Pap test) is a medical procedure in which a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the
Overview of Gynaecologic Cancer
 Overview of Gynaecologic Cancer Stuart Salfinger Gynaecologic Oncologist St John of God Hospital King Edward Memorial Hospital Cervical Cancer Cervical Cancer Risk HPV Smoking?OCP Cervical Cancer Symptoms
Overview of Gynaecologic Cancer Stuart Salfinger Gynaecologic Oncologist St John of God Hospital King Edward Memorial Hospital Cervical Cancer Cervical Cancer Risk HPV Smoking?OCP Cervical Cancer Symptoms
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Tumour Markers. What are Tumour Markers? How Are Tumour Markers Used?
 Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A.
 Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
PRIMARY SEROUS CARCINOMA OF PERITONEUM: A CASE REPORT
 PRIMARY SEROUS CARCINOMA OF PERITONEUM: A CASE REPORT Dott. Francesco Pontieri (*) U.O. di Anatomia Patologica P.O. di Rossano (CS) Dott. Gian Franco Zannoni Anatomia Patologica Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia
PRIMARY SEROUS CARCINOMA OF PERITONEUM: A CASE REPORT Dott. Francesco Pontieri (*) U.O. di Anatomia Patologica P.O. di Rossano (CS) Dott. Gian Franco Zannoni Anatomia Patologica Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia
2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide
 2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide Effective January 1, 2014 Medicare National Average Rates and Allowables (Not Adjusted For Geography) CPT * HCPCS Code 58150 58152 58180 58200 58210
2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide Effective January 1, 2014 Medicare National Average Rates and Allowables (Not Adjusted For Geography) CPT * HCPCS Code 58150 58152 58180 58200 58210
Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology
 Objectives Cervical Dysplasia and Cancer Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Western Ontario Discuss the incidence and risk factors for cervical dysplasia
Objectives Cervical Dysplasia and Cancer Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Western Ontario Discuss the incidence and risk factors for cervical dysplasia
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group
 Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Common Breast Complaints:
 : Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
: Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
MHRI IUD Protocol. Migraine with aura Current DVT or PE History of or current breast cancer Active viral hepatitis Severe cirrhosis or liver tumors
 Table of Contents A. Indications B. Contraindications C. Prior to Insertion D. Insertion E. Follow-Up Visit F. Removal G. Re-Insertion H. Complications/Side Effects I. Appendices MHRI IUD Protocol A. Indications
Table of Contents A. Indications B. Contraindications C. Prior to Insertion D. Insertion E. Follow-Up Visit F. Removal G. Re-Insertion H. Complications/Side Effects I. Appendices MHRI IUD Protocol A. Indications
Ovarian Cancer 101 Jessica McAlpine, MD
 Ovarian Cancer 101 Jessica McAlpine, MD Different types of ovarian cancer: Outline: Ovarian Cancer Presentation, behavior, site of origin Primary treatment: surgery, chemo, +/-radiation Role of genetics
Ovarian Cancer 101 Jessica McAlpine, MD Different types of ovarian cancer: Outline: Ovarian Cancer Presentation, behavior, site of origin Primary treatment: surgery, chemo, +/-radiation Role of genetics
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court. A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and
 Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Endometriosis: An Overview
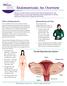 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer
 Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer Cervical Ovarian Uterine Vaginal Vulvar Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer Cervical Ovarian Uterine Vaginal Vulvar Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer What is cancer?
 Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of
What Athletic Trainers Need to Know About Gynecology
 What Athletic Trainers Need to Know About Gynecology Mona M. Shangold,, M.D. Director The Center for Women s Health and Sports Gynecology Philadelphia, PA Main Topics Normal development and function Effects
What Athletic Trainers Need to Know About Gynecology Mona M. Shangold,, M.D. Director The Center for Women s Health and Sports Gynecology Philadelphia, PA Main Topics Normal development and function Effects
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast

 Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE  Additional details >>> HERE
Additional details >>> HERE  Additional information >>> HERE
Additional information >>> HERE