Chapter 2 The Systems Unit: Processing and Memory
|
|
|
- Loreen Sharp
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 15 th Edition Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive Chapter 2 The Systems Unit: Processing and Memory Deborah Morley Charles S. Parker Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning
2 Learning Objectives 1. Understand how data and programs are represented to a computer and be able to identify a few of the coding systems used to accomplish this. 2. Explain the functions of the hardware components commonly found inside the system unit, such as the CPU, GPU, memory, buses, and expansion cards. 3. Describe how peripheral devices or other hardware can be added to a computer. 4. Understand how a computer s CPU and memory components process program instructions and data. Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 2
3 Learning Objectives 5. Name and evaluate several strategies that can be used today for speeding up the operations of a computer. 6. List some processing technologies that may be used in future computers. Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 3
4 Overview Explain how computers represent data and program instructions. Explain how the CPU and memory are arranged with other components inside the system unit. Explain how a CPU performs processing tasks. Identify strategies that can be used today to create faster and better computers in the future. Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 4
5 Data and Program Representation Digital Data Representation Coding Systems Used to represent data and programs in a manner understood by the computer Digital Computers Can only understand two states, off and on (0 and 1) Digital Data Representation The process of representing data in digital form so it can be understood by a computer Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 5
6 Digital Data Representation Bit The smallest unit of data that a binary computer can recognize (a single 1 or 0) Byte = 8 bits Byte terminology used to express the size of documents and other files, programs, etc. Prefixes are often used to express larger quantities of bytes: kilobyte (KB), megabyte (MB), gigabyte (GB), terabyte (TB), petabyte (PB), exabyte (EB), zettabyte (ZB), yottabyte (YB). Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 6
7 Representing Numerical Data The Binary Numbering System Numbering system A way of representing numbers Decimal numbering system Uses 10 symbols (0-9) Binary numbering system Uses only two symbols (1 and 0) to represent all possible numbers In both systems, the position of the digits determines the power to which the base number (such as 10 or 2) is raised Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 7
8 Representing Numerical Data Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 8
9 Coding Systems for Text-Based Data ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) Coding system traditionally used with personal computers EBCDIC (Extended Binary-Coded Decimal Interchange Code) Developed by IBM, primarily for mainframes Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 9
10 Coding Systems for Text-Based Data Unicode Newer code (32 bits per character is common) Universal coding standard designed to represent textbased data written in any ancient or modern language Replacing ASCII as the primary text-coding system Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 10
11 Coding Systems for Other Types of Data Graphics Data (still images such as photos or drawings) Bitmapped images Image made of up of a grid of small dots called pixels Monochrome graphic can only be one of two colors Requires just one bit for color storage Images with more than two colors Can use 4, 8, or 24 bits to store the color data for each pixel More bits = more colors Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 11
12 Coding Systems for Other Types of Data Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 12
13 Coding Systems for Other Types of Data Audio Data Must be in digital form in order to be stored on or processed by a computer Often compressed when sent over the Internet MP3 files are 10 times smaller than their uncompressed digital versions Download more quickly and take up less storage space Video Data Displayed using a collection of frames, each frame contains a still image Amount of data can be substantial, but can be compressed Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 13
14 Representing Software Programs Machine language Binary-based language for representing computer programs the computer can execute directly Early programs were written in machine language Today s programs still need to be translated into machine language in order to be understood by the computer Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 14
15 Quick Quiz 1. Another way to say one million bytes is a. one kilobyte b. one gigabyte c. one megabyte 2. True or False: MP3 files are stored using 0s and 1s. 3. The numbering system is used by computers to perform mathematical computations. Answers: 1) c; 2) True; 3) binary Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 15
16 Inside the System Unit System Unit The main case of a computer Houses the processing hardware for a computer Also contains storage devices, the power supply, and cooling fans Houses processor, memory, interfaces to connect to peripheral devices (printers, etc), and other components With a desktop computer, usually looks like a rectangular box Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 16
17 Inside the System Unit Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 17
18 Inside the System Unit The Motherboard Computer Chip Very small pieces of silicon or other semi-conducting material onto which integrated circuits are embedded Circuit Board A thin board containing computer chips and other electronic components System Board The main circuit board inside the system unit to which all devices must connect Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 18
19 Inside the System Unit External devices (monitors, keyboards, mice, printers) Wireless devices (e.g., Bluetooth) Power Supply Connects to the motherboard to deliver electricity (personal computer) Portable computers use rechargeable battery pack Nonremovable batteries more difficult and expensive to replace Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 19
20 Inside the System Unit Drive Bays Rectangular metal racks inside the system unit that house storage devices Hard drive, CD/DVD drive, flash memory card reader Connected to the motherboard with a cable Processors The CPU (Central Processing Unit) Circuitry and components packaged together and connected directly to the motherboard Does the vast majority of processing for a computer Also called a processor; called a microprocessor when talking about personal computers Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 20
21 Inside the System Unit Dual-core CPU Contains the processing components (cores) of two separate processors on a single CPU Quad-core CPU Contains four cores Multi-core processors allow computers to work on more than one task at a time Typically different CPUs for desktop computers, portable computers, servers, mobile devices, consumer devices, etc. Personal computer CPU often made by Intel or AMD Media tablets and mobile phones use processors made by other companies such as ARM Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 21
22 Inside the System Unit Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 22
23 Inside the System Unit The GPU (graphics processing unit) Takes care of the processing needed to display images (including still images, animations) on the screen Can be located on the motherboard, on a video graphics board, on in the CPU package Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 23
24 How It Works Box GPUs and Transformers: The Ride 3D at Universal Studios Uses a 2,000 foot-long track, 14 huge screens, and 34 projectors Motion is synchronized with the action Images are 3D, 4K Used GPUs to see 3D animations in real time as they were being developed Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 24
25 Inside the System Unit Processing Speed CPU clock speed is one measurement of processing speed Rated in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz) Higher CPU clock speed = more instructions processed per second Alternate measure of processing speed is the number of instructions a CPU can process per second Megaflops (millions), gigaflops (billions), teraflops (trillions) Benchmark tests can be used to evaluate overall processing speed Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 25
26 Inside the System Unit Word Size The amount of data that a CPU can manipulate at one time Typically 32 or 64 bits Cache Memory Special group of very fast memory chips located on or close to the CPU Level 1 is fastest, then Level 2, then Level 3 More cache memory typically means faster processing Usually internal cache (built into the CPU) Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 26
27 Inside the System Unit Bus Width, Bus Speed, and Bandwidth A bus is an electronic path over which data can travel Found inside the CPU and on the motherboard Bus width is the number of wires in the bus over which data can travel A wider bus allows more data to be transferred at one time Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 27
28 Inside the System Unit Bus width and speed determine the throughput or bandwidth of the bus The amount of data that can be transferred by the bus in a given time period Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 28
29 Memory Memory Refers to chip-based storage located inside the system unit Storage refers to the amount of long-term storage available to a computer Random Access Memory (RAM) Computer s main memory Consists of chips arranged on a circuit board called a memory module which are plugged into the motherboard Stores essential parts of operating system, programs, and data the computer is currently using Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 29
30 Memory Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 30
31 Memory Volatile RAM content lost when the computer is shut off ROM and flash memory are non-volatile Measured in bytes Amount installed depends on the CPU and operating system being used Most personal computers use SD-RAM MRAM and PRAM - non-volatile RAM under development Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 31
32 Memory Each location in memory has an address Each location typically holds one byte Computer system sets up and maintains directory tables to facilitate retrieval of the data Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 32
33 Memory Registers High-speed memory built into the CPU Used to store data and intermediary results during processing Fastest type of memory ROM (read-only memory) Non-volatile chips located on the motherboard into which data or programs have been permanently stored Retrieved by the computer when needed Being replaced with flash memory Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 33
34 Memory Flash Memory Nonvolatile memory chips that can be used for storage Have begun to replace ROM for storing system information Now stores firmware for personal computers and other devices Built into many types of devices (media tablets, mobile phones, and digital cameras) for user storage Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 34
35 Cooling Components Fans Fans used on most personal computers to help cool the CPU and system unit Heat is an ongoing problem for CPU and computer manufacturers Heat Sinks Can damage components Cooler chips run faster Small components typically made out of aluminum with fins that help to dissipate heat Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 35
36 Cooling Components Cooling Systems Liquid cooling systems Cool the computer with liquid-filled tubes Immersion cooling Hardware is actually submerged into units filled with a liquid cooling solution Notebook cooling stand Cools the underside of a notebook computer Other cooling methods, such as ion pump cooling systems, are under development Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 36
37 Cooling Components Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 37
38 Expansion Expansion Slots, Expansion Cards, and ExpressCard Modules Expansion Slot A location on the motherboard into which expansion cards are inserted Expansion Card A circuit board inserted into an expansion slot Used to add additional functionality or to attach a peripheral device ExpressCard Modules Designed to add additional functionality to notebooks Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 38
39 Expansion Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 39
40 Buses Bus An electronic path within a computer over which data travels Located within the CPU and etched onto the motherboard Expansion Bus Connects the CPU to peripheral (typically input and output) devices Memory Bus Connects CPU directly to RAM Frontside Bus (FSB) Connects CPU to the chipset that connects the CPU to the rest of the bus architecture Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 40
41 Buses PCI and PCI Express (PCIe) Bus PCI has been one of the most common types Today, PCI Express bus, which is extremely fast, has replaced the PCI bus Universal Serial Bus (USB) Extremely versatile Allows 127 different devices to connect to a computer via a single USB port FireWire Bus Developed by Apple to connect multimedia devices to a computer Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 41
42 Ports and Connectors Port A connector on the exterior of a computer s system unit to which a device may be attached Typical desktop computer ports include: Power connector, Firewire, VGA monitor, Network, USB, Audio, and HDMI Others include IrDA and Bluetooth ports, esata ports, Thunderbolt ports (Apple devices) Most computers support the Plug and Play standard Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 42
43 Ports and Connectors Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 43
44 Ports and Connectors Portable computers have ports similar to desktop computers, but often not as many Smartphones and mobile devices have more limited expansion capabilities Usually have a USB port, HDMI port, and/or flash memory card slot Flash memory cards often use the Secure Digital (SD) format MiniSD and microsd cars are smaller than regular SD cards Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 44
45 Ports and Connectors Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 45
46 Trend Box Tablet Docks Used to help with tablet productivity Some are just a stand Many include a keyboard Some include ports (USB, monitor, etc.) to connect peripherals Some contain a battery Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 46
47 Quick Quiz 1. Which type of memory is erased when the power goes out? a. ROM b. RAM c. flash memory 2. True or False: The CPU can also be called the motherboard. 3. A(n) electronic path within a computer over which data travels is called a(n). Answers: 1) b; 2) False; 3) bus Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 47
48 How the CPU Works CPU (Central Processing Unit) Consists of a variety of circuitry and components packaged together Transistor: Key element of the microprocessor Made of semi-conductor material that acts like a switch controlling the flow of electrons inside a chip Today s CPUs contain hundreds of millions of transistors; the number doubles about every 18 months (Moore s Law) Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 48
49 Inside the Industry Box Moore s Law In 1965, Gordon Moore predicted that the number of transistors per square inch on chips had doubled every two years and that trend would continue Moore s Law is still relevant today for processors as well as other computer components Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 49
50 How the CPU Works Typical CPU Components Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU) Performs arithmetic involving integers and logical operations Floating Point Unit (FPU) Performs decimal arithmetic Control Unit Coordinates and controls activities within a CPU core Prefetch Unit Attempts to retrieve data and instructions before they are needed for processing in order to avoid delays Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 50
51 How the CPU Works Decode Unit Translates instructions from the prefetch unit so they are understood by the control unit, ALU, and FPU Registers and Internal Cache Memory Store data and instructions needed by the CPU Bus Interface Unit Allows the core to communicate with other CPU components Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 51
52 How the CPU Works Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 52
53 System Clock The System Clock and the Machine Cycle Small quartz crystal on the motherboard Timing mechanism within the computer system that synchronizes the computer s operations Sends out a signal on a regular basis to all computer components Each signal is a cycle Number of cycles per second is measured in hertz (Hz) One megahertz = one million ticks of the system clock Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 53
54 The System Clock and the Machine Cycle Many PC system clocks run at 200 MHz Computers can run at a multiple or fraction of the system clock speed A CPU clock speed of 2 GHz means the CPU clock ticks 10 times during each system clock tick During each CPU clock tick, one or more pieces of microcode are processed A CPU with a higher clock speed processes more instructions per second than the same CPU with a lower CPU clock speed Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 54
55 Machine Cycle The System Clock and the Machine Cycle The series of operations involved in the execution of a single machine level instruction Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 55
56 Making Computers Faster and Better Now and in the Future Improving the Performance of Your System Today Add more memory Perform system maintenance Uninstall programs properly Remove unnecessary programs from the Startup list Consider placing large files not needed on a regular basis on external storage Delete temporary files Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 56
57 Making Computers Faster and Better Now and in the Future Error check and defrag the hard drive periodically Scan for viruses and spyware continually Clean out dust once or twice a year Buy a larger or second hard drive Upgrade your Internet connection Upgrade your video graphics card Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 57
58 Making Computers Faster and Better Now and in the Future Strategies for Making Faster and Better Computers Improved Architecture Smaller components, faster bus speeds, multiple CPU cores, support for virtualization Improved Materials Flexible electronic components Copper, high-k, graphene chip Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 58
59 Pipelining Making Computers Faster and Better Now and in the Future Allows multiple instructions to be processed at one time Multiprocessing and Parallel Processing Use multiple processors to speed up processing Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 59
60 Making Computers Faster and Better Now and in the Future Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 60
61 Future Trends Nanotechnology The science of creating tiny computers and components less than 100 nanometers in size Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) used in many products today Nanofilters and nanosensors Future applications may be built by working at the individual atomic and molecular levels Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 61
62 Technology and You Box Magic Glass MIT has developed nano-sized conical patterns on the surface of glass to eliminated its reflective properties Glass resists fogging and is self-cleaning Possible uses: Smartphone screens Eyeglasses TVs Car windshieds Building windows Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 62
63 Future Trends Quantum Computing Applies the principles of quantum physics and quantum mechanics to computers Utilizes atoms or nuclei working together as quantum bits (qubits) Qubits function simultaneously as the computer s processor and memory and can represent more than two states Expected to be used for specialized applications, such as encryption and code breaking Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 63
64 Future Trends Optical Computing Uses light, from laser beams or infrared beams, to perform digital computations Opto-electronic computers use both optical and electronic components Silicon Photonics The process of making optical devices using silicon manufacturing techniques Possible low-cost solution to future data-intensive computing applications telemedicine, cloud data centers Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 64
65 Future Trends Tera-Scale Computing The ability to process one trillion floating-point operations per second (teraflops) Terascale research is focusing on creating multi-core processors with tens to hundreds of cores Intel has created a Single-chip Cloud Computer which contains 48 cores on one silicon chip Expected to be needed for future applications Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 65
66 Future Trends 3D Chips Contain transistors that are layered to cut down on the surface area required Created by layering individual silicon wafers on top of one another Being used with memory, flash memory, and CPUs Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 66
67 Quick Quiz 1. Optical computers use which of the following to transmit and process data? a. Liquid b. Light c. Silicon 2. True or False: If your computer is running slowly, adding more memory might speed it up. 3. A quantum bit is known as a(n). Answers: 1) b; 2) True; 3) qubit Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 67
68 Summary Data and Program Representation Inside the System Unit How the CPU Works Making Computers Faster and Better Now and in the Future Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 15th Edition 68
Logical Operations. Control Unit. Contents. Arithmetic Operations. Objectives. The Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic / Logic Unit.
 Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Discovering Computers 2011. Living in a Digital World
 Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
Chapter 6. Inside the System Unit. What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future. What You Will Learn... Describing Hardware Performance
 What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
Chapter 4 System Unit Components. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
The Central Processing Unit:
 The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX
 CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
Lecture 2: Computer Hardware and Ports. y.alharbi@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/y.alharbi/en
 BMTS 242: Computer and Systems Lecture 2: Computer Hardware and Ports Yousef Alharbi Email Website y.alharbi@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/y.alharbi/en The System Unit McGraw-Hill Copyright 2011
BMTS 242: Computer and Systems Lecture 2: Computer Hardware and Ports Yousef Alharbi Email Website y.alharbi@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/y.alharbi/en The System Unit McGraw-Hill Copyright 2011
CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications. Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global
 CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global Chapter 2 Data Storage Concepts System Unit The system unit
CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global Chapter 2 Data Storage Concepts System Unit The system unit
Understanding Digital Components
 Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O
 Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices. A PC in Every Home. Assembling a Computer System
 C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
Management Challenge. Managing Hardware Assets. Central Processing Unit. What is a Computer System?
 Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT)
 Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT) Objectives Define Computer and Identify the Four Basic Computing Functions Identify the Different Types of Computers Describe Hardware Devices and Their Uses
Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT) Objectives Define Computer and Identify the Four Basic Computing Functions Identify the Different Types of Computers Describe Hardware Devices and Their Uses
Computer Hardware HARDWARE. Computer Hardware. Mainboard (Motherboard) Instructor Özgür ZEYDAN
 Computer Hardware HARDWARE Hardware: the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering 1. Case and inside 2. Peripherals
Computer Hardware HARDWARE Hardware: the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering 1. Case and inside 2. Peripherals
Parts of a Computer. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. 1 1999 Micron Technology Foundation, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Unit A451: Computer systems and programming. Section 2: Computing Hardware 1/5: Central Processing Unit
 Unit A451: Computer systems and programming Section 2: Computing Hardware 1/5: Central Processing Unit Section Objectives Candidates should be able to: (a) State the purpose of the CPU (b) Understand the
Unit A451: Computer systems and programming Section 2: Computing Hardware 1/5: Central Processing Unit Section Objectives Candidates should be able to: (a) State the purpose of the CPU (b) Understand the
Computers. Hardware. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer
 Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Figure 1. Front and Back of a Computer Case
 Introduction Almost everyone uses a computer daily, but many don't know how a computer works or all the different individual pieces that make it up. In fact, many people erroneously look at a computer
Introduction Almost everyone uses a computer daily, but many don't know how a computer works or all the different individual pieces that make it up. In fact, many people erroneously look at a computer
Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett
 Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett Page 1 of 11 Table of Contents Technical Product Specifications Model 3 PC Technical Diagrams Front Exterior Specifications
Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett Page 1 of 11 Table of Contents Technical Product Specifications Model 3 PC Technical Diagrams Front Exterior Specifications
Technology in Action. Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy. Tenth Edition. Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Tenth Edition Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers Understanding
Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Tenth Edition Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers Understanding
TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS
 TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Changes that you make in virtual machines do not affect your physical computer. 2. The size of a bus
TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Changes that you make in virtual machines do not affect your physical computer. 2. The size of a bus
Computer Performance. Topic 3. Contents. Prerequisite knowledge Before studying this topic you should be able to:
 55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
1 PERSONAL COMPUTERS
 PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module
 Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System
 essential concepts lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System This lesson includes the following sections: The Computer System Defined Hardware: The Nuts and Bolts of the Machine Software: Bringing the
essential concepts lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System This lesson includes the following sections: The Computer System Defined Hardware: The Nuts and Bolts of the Machine Software: Bringing the
The Motherboard Chapter #5
 The Motherboard Chapter #5 Amy Hissom Key Terms Advanced Transfer Cache (ATC) A type of L2 cache contained within the Pentium processor housing that is embedded on the same core processor die as the CPU
The Motherboard Chapter #5 Amy Hissom Key Terms Advanced Transfer Cache (ATC) A type of L2 cache contained within the Pentium processor housing that is embedded on the same core processor die as the CPU
Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2
 Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2 Definition of a Computer What does IPOS stand for? Input Process Output Storage Other types of Computers Name some examples of other types of computers, other than a typical
Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2 Definition of a Computer What does IPOS stand for? Input Process Output Storage Other types of Computers Name some examples of other types of computers, other than a typical
Primary Memory. Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit)
 Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
New Mexico Broadband Program. Basic Computer Skills. Module 1 Types of Personal Computers Computer Hardware and Software
 New Mexico Broadband Program Basic Computer Skills Module 1 Types of Personal Computers Computer Hardware and Software Basic Computer Skills Learning Objectives Acquire introductory familiarity with basic
New Mexico Broadband Program Basic Computer Skills Module 1 Types of Personal Computers Computer Hardware and Software Basic Computer Skills Learning Objectives Acquire introductory familiarity with basic
Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software
 What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
K Hinds 2015 Kumar1.ajm1@gmail.com www.smsbarbados.wordpress.com Page No. 1. Lecture 3 ASCII
 www.smsbarbados.wordpress.com Page No. 1 ASCII Lecture 3 ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. Computers can only understand numbers, so an ASCII code is the numerical representation
www.smsbarbados.wordpress.com Page No. 1 ASCII Lecture 3 ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. Computers can only understand numbers, so an ASCII code is the numerical representation
Central Processing Unit
 Computer Components c 2015 by David W. Gerbing School of Business Administration Portland State University Computer Components Central Processing Unit CPU Characteristics Other Components of a Computer
Computer Components c 2015 by David W. Gerbing School of Business Administration Portland State University Computer Components Central Processing Unit CPU Characteristics Other Components of a Computer
Fall 2009. Lecture 1. Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345. Introduction to Operating Systems. Mostafa Z. Ali. mzali@just.edu.
 Fall 2009 Lecture 1 Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345 Introduction to Operating Systems Mostafa Z. Ali mzali@just.edu.jo 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems An Overview of Microcomputers
Fall 2009 Lecture 1 Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345 Introduction to Operating Systems Mostafa Z. Ali mzali@just.edu.jo 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems An Overview of Microcomputers
Definition of Computers. INTRODUCTION to COMPUTERS. Historical Development ENIAC
 Definition of Computers INTRODUCTION to COMPUTERS Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering A general-purpose machine that processes data according to a set of instructions that
Definition of Computers INTRODUCTION to COMPUTERS Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering A general-purpose machine that processes data according to a set of instructions that
Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware. Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA
 Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA 1 Information System Layers Learning Objectives Task Statements
Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA 1 Information System Layers Learning Objectives Task Statements
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory
 CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
Communicating with devices
 Introduction to I/O Where does the data for our CPU and memory come from or go to? Computers communicate with the outside world via I/O devices. Input devices supply computers with data to operate on.
Introduction to I/O Where does the data for our CPU and memory come from or go to? Computers communicate with the outside world via I/O devices. Input devices supply computers with data to operate on.
The Bus (PCI and PCI-Express)
 4 Jan, 2008 The Bus (PCI and PCI-Express) The CPU, memory, disks, and all the other devices in a computer have to be able to communicate and exchange data. The technology that connects them is called the
4 Jan, 2008 The Bus (PCI and PCI-Express) The CPU, memory, disks, and all the other devices in a computer have to be able to communicate and exchange data. The technology that connects them is called the
Revised: November 2013. GCSE Computer Science
 Revised: November 2013 GCSE Computer Science 2013 Geraint D. Jones Mark D. Thomas Disclaimer This resource is provided to support the teaching and learning of GCSE Computer Science. The materials provide
Revised: November 2013 GCSE Computer Science 2013 Geraint D. Jones Mark D. Thomas Disclaimer This resource is provided to support the teaching and learning of GCSE Computer Science. The materials provide
Discovering Computers 2008. Chapter 7 Storage
 Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 7 Storage Chapter 7 Objectives Differentiate between storage devices and storage media Describe the characteristics of magnetic disks Describe the characteristics of
Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 7 Storage Chapter 7 Objectives Differentiate between storage devices and storage media Describe the characteristics of magnetic disks Describe the characteristics of
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Like millions of other computer users, you have probably used your
 435487389_ch0_CTP.qxd 7/6/09 9:00 PM Page CHAPTER Introducing Hardware In this chapter, you will learn: That a computer requires both hardware and software to work About the many different hardware components
435487389_ch0_CTP.qxd 7/6/09 9:00 PM Page CHAPTER Introducing Hardware In this chapter, you will learn: That a computer requires both hardware and software to work About the many different hardware components
Chapter One Introduction to Computer
 Chapter One Introduction to Computer Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according
Chapter One Introduction to Computer Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according
How PCI Express Works (by Tracy V. Wilson)
 1 How PCI Express Works (by Tracy V. Wilson) http://computer.howstuffworks.com/pci-express.htm Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slots are such an integral part of a computer's architecture that
1 How PCI Express Works (by Tracy V. Wilson) http://computer.howstuffworks.com/pci-express.htm Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slots are such an integral part of a computer's architecture that
Main Memory & Backing Store. Main memory backing storage devices
 Main Memory & Backing Store Main memory backing storage devices 1 Introduction computers store programs & data in two different ways: nmain memory ntemporarily stores programs & data that are being processed
Main Memory & Backing Store Main memory backing storage devices 1 Introduction computers store programs & data in two different ways: nmain memory ntemporarily stores programs & data that are being processed
Introduction to Computer Applications CISY 1225. Dr. Zahoor Khan
 Introduction to Computer Applications CISY 1225 Dr. Zahoor Khan Last updated: May 2014 Why Computer is Important HOME COMPUTING COMMERCE NOT THIS EDUCATION ENGINEERING Medical THE FUTURE? Computer-literate
Introduction to Computer Applications CISY 1225 Dr. Zahoor Khan Last updated: May 2014 Why Computer is Important HOME COMPUTING COMMERCE NOT THIS EDUCATION ENGINEERING Medical THE FUTURE? Computer-literate
Overview. CPU Manufacturers. Current Intel and AMD Offerings
 Central Processor Units (CPUs) Overview... 1 CPU Manufacturers... 1 Current Intel and AMD Offerings... 1 Evolution of Intel Processors... 3 S-Spec Code... 5 Basic Components of a CPU... 6 The CPU Die and
Central Processor Units (CPUs) Overview... 1 CPU Manufacturers... 1 Current Intel and AMD Offerings... 1 Evolution of Intel Processors... 3 S-Spec Code... 5 Basic Components of a CPU... 6 The CPU Die and
EUCIP - IT Administrator. Module 1 - PC Hardware. Version 2.0
 EUCIP - IT Administrator Module 1 - PC Hardware Version 2.0 Module 1 Goals Module 1 The PC Hardware module requires the candidate to know and recognise the basic physical make-up of a personal computer
EUCIP - IT Administrator Module 1 - PC Hardware Version 2.0 Module 1 Goals Module 1 The PC Hardware module requires the candidate to know and recognise the basic physical make-up of a personal computer
Chapter 8 Memory Units
 Chapter 8 Memory Units Contents: I. Introduction Basic units of Measurement II. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Storage versus Memory III. Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk IV.Optical
Chapter 8 Memory Units Contents: I. Introduction Basic units of Measurement II. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Storage versus Memory III. Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk IV.Optical
ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT IMAGING
 AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
CPU. Motherboard RAM. Power Supply. Storage. Optical Drives
 CPU Motherboard RAM Power Supply Storage Optical Drives GPU 2 The CPU is the brain of a computer CPU receives instructions from software programs stored in memory Instructions are read and the tasks performed
CPU Motherboard RAM Power Supply Storage Optical Drives GPU 2 The CPU is the brain of a computer CPU receives instructions from software programs stored in memory Instructions are read and the tasks performed
Acknowledgments. Thanks to the following web site and people for the materials and images used in this presentation:
 Computers Hardware Acknowledgments Thanks to the following web site and people for the materials and images used in this presentation: -Wikipedia -Prof. Patrice Koehl -Prof. Chirs Nitta -Sean Davis -Nick
Computers Hardware Acknowledgments Thanks to the following web site and people for the materials and images used in this presentation: -Wikipedia -Prof. Patrice Koehl -Prof. Chirs Nitta -Sean Davis -Nick
Chapter 7 Types of Storage. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 7 Types of Storage Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate between storage devices and storage media Describe the characteristics
Chapter 7 Types of Storage Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate between storage devices and storage media Describe the characteristics
IBM Europe Announcement ZG08-0232, dated March 11, 2008
 IBM Europe Announcement ZG08-0232, dated March 11, 2008 IBM System x3450 servers feature fast Intel Xeon 2.80 GHz/1600 MHz, 3.0 GHz/1600 MHz, both with 12 MB L2, and 3.4 GHz/1600 MHz, with 6 MB L2 processors,
IBM Europe Announcement ZG08-0232, dated March 11, 2008 IBM System x3450 servers feature fast Intel Xeon 2.80 GHz/1600 MHz, 3.0 GHz/1600 MHz, both with 12 MB L2, and 3.4 GHz/1600 MHz, with 6 MB L2 processors,
EUCIP IT Administrator - Module 1 PC Hardware Syllabus Version 3.0
 EUCIP IT Administrator - Module 1 PC Hardware Syllabus Version 3.0 Copyright 2011 ECDL Foundation All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form except as permitted by ECDL
EUCIP IT Administrator - Module 1 PC Hardware Syllabus Version 3.0 Copyright 2011 ECDL Foundation All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form except as permitted by ECDL
Week One Lecture Note 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER 1.1 WHAT IS COMPUTER?
 Week One Lecture Note 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER 1.1 WHAT IS COMPUTER? A Computer is a device or set of devices that work under the control of a stored program, automatically accepts and processes data
Week One Lecture Note 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER 1.1 WHAT IS COMPUTER? A Computer is a device or set of devices that work under the control of a stored program, automatically accepts and processes data
1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now
 1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now The first electronic computer was built in the late 1930s by Dr.John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State University in USA. They designed their computer to
1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now The first electronic computer was built in the late 1930s by Dr.John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State University in USA. They designed their computer to
Chapter 5 Busses, Ports and Connecting Peripherals
 Chapter 5 Busses, Ports and Connecting Peripherals 1 The Bus bus - groups of wires on a circuit board that carry information (bits - on s and off s) between computer components on a circuit board or within
Chapter 5 Busses, Ports and Connecting Peripherals 1 The Bus bus - groups of wires on a circuit board that carry information (bits - on s and off s) between computer components on a circuit board or within
MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS World ORT Union I n p u t d e v i c e s Where would you find the letters QUERTY? A. Mouse B. Keyboard C.Numeric Keypad How did the computer mouse get its name? A.
MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS World ORT Union I n p u t d e v i c e s Where would you find the letters QUERTY? A. Mouse B. Keyboard C.Numeric Keypad How did the computer mouse get its name? A.
Choosing a Computer for Running SLX, P3D, and P5
 Choosing a Computer for Running SLX, P3D, and P5 This paper is based on my experience purchasing a new laptop in January, 2010. I ll lead you through my selection criteria and point you to some on-line
Choosing a Computer for Running SLX, P3D, and P5 This paper is based on my experience purchasing a new laptop in January, 2010. I ll lead you through my selection criteria and point you to some on-line
Slide Set 8. for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 8 for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2015 ENCM 369 W15 Section
Slide Set 8 for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2015 ENCM 369 W15 Section
Three steps to the best technology: 1. The Assessment 2. The Dialogue 3. The Recommendation
 Technology Assessment Checklist for Small Businesses A quick way to help your small-business customers get the best technology. Today's small-business owners want reliable technology that helps them do
Technology Assessment Checklist for Small Businesses A quick way to help your small-business customers get the best technology. Today's small-business owners want reliable technology that helps them do
TYPES OF COMPUTERS AND THEIR PARTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? a. A programmable electronic device that processes data via instructions to output information for future use. b. Raw facts and figures that has no meaning
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? a. A programmable electronic device that processes data via instructions to output information for future use. b. Raw facts and figures that has no meaning
RAM. Overview DRAM. What RAM means? DRAM
 Overview RAM In this chapter, you will learn how to Identify the different types of RAM packaging Explain the varieties of DRAM Install RAM properly Perform basic RAM troubleshooting Program Execution
Overview RAM In this chapter, you will learn how to Identify the different types of RAM packaging Explain the varieties of DRAM Install RAM properly Perform basic RAM troubleshooting Program Execution
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 1
 STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 1 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Digital technology has made it easy to produce copies of music with no loss of quality from the original. 2. Free source
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 1 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Digital technology has made it easy to produce copies of music with no loss of quality from the original. 2. Free source
Generations of the computer. processors.
 . Piotr Gwizdała 1 Contents 1 st Generation 2 nd Generation 3 rd Generation 4 th Generation 5 th Generation 6 th Generation 7 th Generation 8 th Generation Dual Core generation Improves and actualizations
. Piotr Gwizdała 1 Contents 1 st Generation 2 nd Generation 3 rd Generation 4 th Generation 5 th Generation 6 th Generation 7 th Generation 8 th Generation Dual Core generation Improves and actualizations
Mainframe hardware course: Mainframe s processors
 Mainframe hardware course: Mainframe s processors z/os Basic Skills: The mainframe s processors Mainframe s processors This hardware course introduces you to one model of IBM mainframe computer, the IBM
Mainframe hardware course: Mainframe s processors z/os Basic Skills: The mainframe s processors Mainframe s processors This hardware course introduces you to one model of IBM mainframe computer, the IBM
Chap-02, Hardware and Software. Hardware Model
 Philadelphia University School of Business Administration INFO-101 Information Systems Prof London Chap-02, Hardware and Software Hardware Components Central processing unit (CPU) Arithmetic/logic unit
Philadelphia University School of Business Administration INFO-101 Information Systems Prof London Chap-02, Hardware and Software Hardware Components Central processing unit (CPU) Arithmetic/logic unit
Computer Components Study Guide. The Case or System Box
 Computer Components Study Guide In this lesson, we will briefly explore the basics of identifying the parts and components inside of a computer. This lesson is used to introduce the students to the inside
Computer Components Study Guide In this lesson, we will briefly explore the basics of identifying the parts and components inside of a computer. This lesson is used to introduce the students to the inside
Here are my slides from lecture, along with my notes about each slide.
 Chapter 3: Storage Here are my slides from lecture, along with my notes about each slide. NOTE: You are expected to attend all class meetings. Please be in the room when class begins and be ready to participate
Chapter 3: Storage Here are my slides from lecture, along with my notes about each slide. NOTE: You are expected to attend all class meetings. Please be in the room when class begins and be ready to participate
How To Store Data On A Computer (For A Computer)
 TH3. Data storage http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ A computer uses two types of storage. A main store consisting of ROM and RAM, and backing stores which can be internal, eg hard disk, or
TH3. Data storage http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ A computer uses two types of storage. A main store consisting of ROM and RAM, and backing stores which can be internal, eg hard disk, or
Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 110 Course Title: Computer Literacy
 Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 11 Course Title: Computer Literacy Course Length: 3 credits 3 5-minute meetings per week or equivalent Course Description: An introduction to the
Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 11 Course Title: Computer Literacy Course Length: 3 credits 3 5-minute meetings per week or equivalent Course Description: An introduction to the
Block diagram of typical laptop/desktop
 What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
Microprocessor or Microcontroller?
 Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
Computer System: User s View. Computer System Components: High Level View. Input. Output. Computer. Computer System: Motherboard Level
 System: User s View System Components: High Level View Input Output 1 System: Motherboard Level 2 Components: Interconnection I/O MEMORY 3 4 Organization Registers ALU CU 5 6 1 Input/Output I/O MEMORY
System: User s View System Components: High Level View Input Output 1 System: Motherboard Level 2 Components: Interconnection I/O MEMORY 3 4 Organization Registers ALU CU 5 6 1 Input/Output I/O MEMORY
Determining Your Computer Resources
 Determining Your Computer Resources There are a number of computer components that must meet certain requirements in order for your computer to perform effectively. This document explains how to check
Determining Your Computer Resources There are a number of computer components that must meet certain requirements in order for your computer to perform effectively. This document explains how to check
Concepts and Applications of Information Technology
 Concepts and Applications of Information Technology IFSM201-C806 Midterm Exam Name:_ Exam Directions: The exam is open book and notes are allowed You will have 2 days to complete the exam Select the best
Concepts and Applications of Information Technology IFSM201-C806 Midterm Exam Name:_ Exam Directions: The exam is open book and notes are allowed You will have 2 days to complete the exam Select the best
The computer's internal components
 Computer hardware and types of computer A brief introduction to the insides of a computer and its added hardware. This will help explain what a computer is from a hardware point of view, how we control
Computer hardware and types of computer A brief introduction to the insides of a computer and its added hardware. This will help explain what a computer is from a hardware point of view, how we control
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output
 Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 2
 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 2 1. The microprocessor is the most important component of a computer and usually the most expensive single component. 2.
True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 2 1. The microprocessor is the most important component of a computer and usually the most expensive single component. 2.
CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS
 CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS Multiple Choice: 1. is the early operating system developed by Microsoft A. Monitor B. MS-DOS C. Mouse D. Video games Answer: B Reference: Bill Gates Rides the Digital
CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS Multiple Choice: 1. is the early operating system developed by Microsoft A. Monitor B. MS-DOS C. Mouse D. Video games Answer: B Reference: Bill Gates Rides the Digital
Chapter 3 Storage. 15 th Edition Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive. Deborah Morley Charles S. Parker
 15 th Edition Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive Chapter 3 Storage Deborah Morley Charles S. Parker Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning Learning Objectives 1. Name several general characteristics
15 th Edition Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive Chapter 3 Storage Deborah Morley Charles S. Parker Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning Learning Objectives 1. Name several general characteristics
Tomorrow s Technology and You
 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
IP Video Rendering Basics
 CohuHD offers a broad line of High Definition network based cameras, positioning systems and VMS solutions designed for the performance requirements associated with critical infrastructure applications.
CohuHD offers a broad line of High Definition network based cameras, positioning systems and VMS solutions designed for the performance requirements associated with critical infrastructure applications.
Computer Organization. and Instruction Execution. August 22
 Computer Organization and Instruction Execution August 22 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 The Main Parts of a Computer CSC201 Section Copyright 2000, Douglas Reeves 2 I/O and Storage Devices (lots of devices,
Computer Organization and Instruction Execution August 22 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 The Main Parts of a Computer CSC201 Section Copyright 2000, Douglas Reeves 2 I/O and Storage Devices (lots of devices,
How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7
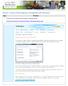 How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7 Enterprise Computing & Service Management 1 Follow this link to download the Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windows-7/get/upgrade-advisor.aspx
How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7 Enterprise Computing & Service Management 1 Follow this link to download the Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windows-7/get/upgrade-advisor.aspx
Programming Logic controllers
 Programming Logic controllers Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a microprocessor based system that uses programmable memory to store instructions and implement functions such as logic, sequencing,
Programming Logic controllers Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a microprocessor based system that uses programmable memory to store instructions and implement functions such as logic, sequencing,
Choosing a computer for ANY-maze
 Choosing a computer for ANY-maze ANY-maze www.anymaze.com Choosing a computer for ANY-maze 1 Introduction... 3 2 Overview... 3 3 Recommended and minimum specifications at a glance... 3 3.1 Recommended
Choosing a computer for ANY-maze ANY-maze www.anymaze.com Choosing a computer for ANY-maze 1 Introduction... 3 2 Overview... 3 3 Recommended and minimum specifications at a glance... 3 3.1 Recommended
COMPUTER BASICS. Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre
 COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
Measuring Cache and Memory Latency and CPU to Memory Bandwidth
 White Paper Joshua Ruggiero Computer Systems Engineer Intel Corporation Measuring Cache and Memory Latency and CPU to Memory Bandwidth For use with Intel Architecture December 2008 1 321074 Executive Summary
White Paper Joshua Ruggiero Computer Systems Engineer Intel Corporation Measuring Cache and Memory Latency and CPU to Memory Bandwidth For use with Intel Architecture December 2008 1 321074 Executive Summary
Introduction To Computer Hardware
 Introduction To Computer Hardware You will learn common technical specifications Slide #2 Technical Specifications As mentioned this version of this course will focus on more practical benefits than previous
Introduction To Computer Hardware You will learn common technical specifications Slide #2 Technical Specifications As mentioned this version of this course will focus on more practical benefits than previous
A+ Practical Applications Solution Key
 A+ Practical Applications Solution Key Module 1 Assignment: Introducing Microsoft Windows - answer the following questions: 1. What attributes are available in the NTFS file system that are not available
A+ Practical Applications Solution Key Module 1 Assignment: Introducing Microsoft Windows - answer the following questions: 1. What attributes are available in the NTFS file system that are not available
Lesson Plan. Preparation
 Lesson Plan Course Title: Computer Maintenance Session Title: Hard Drives Lesson Duration: 90 Minutes Performance Objective: Upon completion of this assignment, the student will be able to recognize a
Lesson Plan Course Title: Computer Maintenance Session Title: Hard Drives Lesson Duration: 90 Minutes Performance Objective: Upon completion of this assignment, the student will be able to recognize a
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING. Chapter 5 Storage Devices
 CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 5 Storage Devices 1 1. Computer Data Storage 2. Types of Storage 3. Storage Device Features 4. Other Examples of Storage Device 2 Storage Devices A storage device
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 5 Storage Devices 1 1. Computer Data Storage 2. Types of Storage 3. Storage Device Features 4. Other Examples of Storage Device 2 Storage Devices A storage device
Chapter 1. The largest computers, used mainly for research, are called a. microcomputers. b. maxicomputers. c. supercomputers. d. mainframe computers.
 Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
A Computer Glossary. For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses
 A Computer Glossary For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses 2006 GLOSSARY This Glossary is primarily applicable to DOS- and Windows-based machines and applications. Address:
A Computer Glossary For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses 2006 GLOSSARY This Glossary is primarily applicable to DOS- and Windows-based machines and applications. Address:
Writing Assignment #2 due Today (5:00pm) - Post on your CSC101 webpage - Ask if you have questions! Lab #2 Today. Quiz #1 Tomorrow (Lectures 1-7)
 Overview of Computer Science CSC 101 Summer 2011 Main Memory vs. Auxiliary Storage Lecture 7 July 14, 2011 Announcements Writing Assignment #2 due Today (5:00pm) - Post on your CSC101 webpage - Ask if
Overview of Computer Science CSC 101 Summer 2011 Main Memory vs. Auxiliary Storage Lecture 7 July 14, 2011 Announcements Writing Assignment #2 due Today (5:00pm) - Post on your CSC101 webpage - Ask if
