Syagrus cearensis, a Twin-Stemmed New Palm from Brazil
|
|
|
- Tyler Marshall
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Syagrus cearensis, a Twin-Stemmed New Palm from Brazil LARRY R. NOBLICK Montgomery Botanical Center Old Cutler Road Miami, Florida USA noblick@fiu.edu 1. Syagrus cearensis showing its common habit of growing as paired or twinned trunks. Syagrus cearensis, a striking Brazilian palm with twinned stems (Fig. 1), is described for the first time. It is already widely dispersed in cultivation. 70 PALMS 48(2): 70 76
2 2. Syagrus cearensis habitat near Pacatuba, Brazil; note palms on left. During my early wanderings at Fairchild Tropical Garden, I encountered a two-stemmed palm that had one stem identified as Syagrus comosa (Mart.) Mart. and the other as S. flexuosa (Mart.) Becc. The palm was first received at Fairchild identified as Syagrus comosa, which is a non-clustering palm, but later re-identified as the clustering Syagrus flexuosa. However, there were some important attributes that differed from S. flexuosa the leaflets were larger, broader, and more leathery, the fruits larger, rounder, and more flattened at the tip instead of elongated and pointed, and the primary branches were evenly arranged around the rachis of the inflorescence, not turned to one side as in S. flexuosa. So, other than the clustering habit, there was very little that this palm had in common with S. flexuosa. The fruit of the mystery palm resembled a short Syagrus oleracea fruit, and so I suspected that perhaps the palm might be a hybrid. However, my hybrid theory died when I learned that the palm was both fertile and produced true from seed. I saw the palm again in other gardens, such as Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil, but since I only knew the plant from cultivation, I was still unwilling to commit to publishing a new species. Finally in 1993, Luiz Antonio F. Matthes sent me a dried specimen to identify. He had collected it from a cultivated palm in Forteleza, Ceará, identified as S. comosa. He was convinced that it could not be that species and had the opportunity to observe the species in its natural habitat in the Municipio of Maranguape at the base of a mountain range near Forteleza. He noted that the palm grew solitarily, in twos, and in clusters. The records at Fairchild Tropical Garden revealed that some of the collections originated from the Brazilian state of Ceará, collected by E. D. Kitzke from the Ratosa Plantation near Forteleza in 1959, and was received as S. comosa. My friend s dried collection matched perfectly the living material we had growing at both Montgomery Botanical Center and Fairchild Tropical Garden. As in a good detective novel, the pieces of the puzzle came together. In August 1994 I went in search of this Syagrus and was pleased to find natural populations near the towns of Maranguape, Pacatuba, Baturité, and Araçoiaba, Ceará. The Serra de Maranguape and the Serra de Aratanha (Pacatuba) had especially large populations. We encountered the palm on the lower slopes of the mountains from about 450 to 700 m above sea level (Fig. 2). Later, Don Evans of Fairchild Tropical Garden joined me, and we explored the interior of the state of Pernambuco, which lies to the south of Ceará. Don and I encountered the same species at Brejos dos Cavalos near Caruaru. The palms were growing in open pastures and sprouting from their bases in the same way as they did in Ceará. South of Garanhuns near the border with the state of Alagoas, we saw still more multiple-stemmed palms of the same species. Close to Garanhuns, Don and I visited the village of Neves, which is the type locality for the natural hybrid Syagrus costae Glassman (1970), a supposed cross between S. coronata and S. oleracea. We now know that S. oleracea of this region has been misidentified and that the hybrid is really a 71
3 B A H C E D G F I J 3. Syagrus cearensis. A Habit; B Section of leaf rachis showing inserted leaflets; C Leaf; D Inflorescence; E Primary branch; F Basal portion of primary branch showing staminate flowers with pedicels along side the larger pistillate flowers; G Receptive pistillate flower; H Staminate flower showing the narrowly lanceolate sepals; I Fruit covered with lepidote tomentum; J Cross-section of mature fruit showing a distinct central seed cavity. Habit, leaf and fruit drawn from MBC accession number 94654*E and inflorescence and flowers drawn fresh from 94654*Q. All scales are in 1 cm units except as marked. Drawn by Wes Jurgens. 72
4 4. Map showing distribution of Syagrus cearensis. cross between S. coronata and this new clustering species, S. cearensis. While there were many similarities with S. oleracea that led botanists to identify it as such, it is sufficiently distinct (see Table 1) to distinguish it as its own species rather than a simple clustering form of S. oleracea or even another similar species, Syagrus picrophylla Barb. Rodr., which has also been confused with S. oleracea. Syagrus cearensis Noblick, sp. nov. Palma caespitosa vel solitaria trunco conspicue articulato, foliis m irregulariter pinnatis, foliolis centralibus ad 1 m longis cm latis concoloribus. Inflorescentia ad ca. 1.2 m longa, rachillis ca , floribus masculis ca mm, femineis mm. Fructus lepidotus longior quam latus ca. 4 cm longus, endocarpio ad 5 mm crasso. Semen cavitatem ferens. Typus: Brazil, Ceará, Municipio de Pacatuba, Noblick et al (Holotypus EAC; isotypi FTG, IPA, NY). Unarmed, solitary or clustering palm in clusters of usually 2 4 stems growing in one plane, to multistemmed clusters. Trunk to 4 10 m tall and cm diam., internodes 9 16 cm long at the base and shortening to 2 7 cm long towards the apex, producing a rough trunk with slightly stepped nodes. Leaves in crown, leaf sheath together with petiole ca cm long, sheathing leaf base 18 cm long or more, ca. 18 cm wide at the base, fibrous with papery membrane disintegrating between the fine principal warp fibers, persisting along the margins of the pseudopetiole (apparent petiole); true petiole absent or to 2 cm long and 4 cm wide by 2 cm thick, but often smaller, channeled adaxially, often with a raised central ridge, rounded abaxially, pseudopetiole (true petiole plus part of the sheath) ca cm long; rachis m long, a fine light brown to grayish indument covering the abaxial side of the sheath, continuing up the abaxial side of the petiole and sometimes onto the lower portion of the leaf rachis, the upper parts of the leaf rachis becoming glabrous with age; leaflets medium green color becoming lighter when dried, concolorous, adaxial surface with prominently raised transverse veins when dried, leaflets ca along one side, irregularly distributed in loose clusters of 2 5 along rachis and inserted in divergent planes, ramenta absent, tomentum absent at leaflet insertion and along the abaxial midvein; basal leaflets cm long by cm wide, middle leaflets cm long and 3 4 cm wide, apical leaflets 31 cm long and 0.4 cm wide, usually one lobe of the asymmetric tip attenuate, the other rounded, occasionally both rounded. Androgynous 73
5 Table 1. A comparison between Syagrus cearensis and two other closely related species, S. oleracea and S. picrophylla. Character Syagrus oleracea Syagrus picrophylla Syagrus cearensis Habit Solitary Solitary Solitary, but more frequently clusters, usually 2 4 or more Petiole cross-section Channeled Channeled Channeled but often with a raised mid- ridge on adult leaves Leaflet margin (as seen Inconspicuous Inconspicuous Conspicuous in cross-section) submarginal vein submarginal vein adjacent submarginal vein Leaf margin (as seen Neither notched Neither notched Notched or in cross-section) nor swollen nor swollen swollen adaxially Peduncular bract Glabrous Glabrous Often with a indument fine waxy lepidote Primary branch Laterally broadened, Laterally broadened, Deltoid or subtending bract truncate truncate sometimes absent Basal staminate flowers Sessile Sessile to rarely short Often short pedicellate pedicellate Staminate sepal shape Short deltoid Short deltoid Linear to lanceolate Pistillate sepal and Glabrous Glabrous Basal portion often petal indument with waxy lepidote, especially on petals Pistil shape Cone-like Cone-like Ovoid Staminode length (mm) >3 Staminode shape Irregular Irregular 6-dentate Fruit indument Apically lepidote Apically to upper half Usually entire fruit densely lepidote densely lepidote Cupule ring length (mm) or more Central seed cavity None None Large, distinct inflorescences interfoliar, cm from the first basal primary branch to the apex; prophyll ca cm long; peduncular bract woody, sulcate, exterior covered with a thin indumentum, ca cm or more long including a beak 4 11 cm long, expanded or inflated portion cm long, cm diam. and a cm perimeter and 1 3 mm thickness; peduncle ca cm long, somewhat flattened in cross-section, cm diam., sparsely lepidote; rachis cm long, primary branches 35 45, glabrous, 9 17 cm long at the apex, ( 106) cm at the base, mm diam. at the base and 2 3 mm diameter at the tip, each primary branch, especially the lower ones, subtended by a deltoid rachis bract ca. 5 mm long, pistillate portion cm long with pistillate flowers or fruits per primary branch, staminate portion cm long. Staminate flowers yellow, arranged in triads with pistillate flowers on the lower portion or in dyads or singly on the upper portion of the primary facing page 5. Syagrus cearensis in its natural habitat in the mountains near Pacatuba, Ceará. 74
6 75
7 branch, mm, sepals and petals 3; sepals (3 ) mm, strongly keeled and slightly connate at the base; petals valvate, mm with acute tips, nerves indistinct; stamens 6, 6 8 mm long, anthers 4 6 mm long, filaments 2 mm long; pistillode trifid and less than 0.5 mm long. Pistillate flowers oblong and pyramidal, usually slightly lepidote on the basal portion, mm; sepals 3, imbricate, mm wide; petals 3, unnerved to slightly nerved, imbricate at the base but (upper 5 7 mm) valvate at the tips, mm; staminodal ring about 3 mm high, 6-dentate; pistil lepidote on upper portion, glabrous on lower behind the staminodal ring, 10 6 mm, stigmas 3, 2 mm long. Fruit light orange when mature, color often obscured by a thin dark brown indument, about as long as wide, ( 5) cm long and 3 4 cm diam. with a 7 10 mm thick mesocarp and 3 5 mm thick endocarp, endocarp ca cm. Seed ellipsoid, ca cm, and with a substantial central cavity ca. 6 mm diam. (Fig. 3). COMMON NAME: catolé or coco babão (babão translates as mucus or slobber and refers to the slimy juices of the mesocarp). ETYMOLOGY: The specific epithet honors one of the states to which the palm is native, Ceará, Brazil. DISTRIBUTION AND ECOLOGY: Brazil, locally common in mountainous areas and seasonal forests in the states of Ceará, Pernambuco, Paraíba, and Alagoas. Growing at the base of the mountains or in pastures at an altitude of about m above sea level (Fig. 4). PHENOLOGY: Flowering and fruiting probably throughout the year, but collected in flower and fruit during the months of July to September. SPECIMENS EXAMINED: BRAZIL. Alagoas. União dos Palmares, 19 Nov 1985, R. P. Lyra-Lemos & A. I. L. Pinhero 1049 (PEUFR); 19 Nov 1985, R. P. Lyra- Lemos & A. I. L. Pinhero 1050 (PEUFR); São José da Lage, near AL-110, 17 Oct 1986, R. P. Lyra-Lemos & G.L. Esteves 1240 (PEUFR). Ceará. 1929, Dahlgren s.n. (F ); Forteleza region, near Mejecana, 1935, Dahlgren s.n. (F a); Maranguape, 1940 Dahlgren s.n. (F ); Maraguape, Serra da Pacatuba (close to Forteleza), top and bottom of the Serra, Luiz Antonio F. Matthes s.n (FTG); Pacatuba, Serra de Aratanha, 29 km S. of Forteleza, 3º58 S, 38º32 W, m, 12 Aug 1994, Noblick et al (Holotype, EAC; isotypes IPA, FTG, NY); Araçoiaba, Olho d Agua, 8 km N of Araçoiaba, 4º15 S, 39º00 W, 13 Aug 1994, Noblick et al (FTG, IPA). Paraíba. Santa Rita, 20 Aug 1962, Sérgio Tavares 960 (UFP); Conde, 22 km N of Goiana, Pernambuco on BR-101, 14 km N of the Paraíba/Pernambuco state border, 7º S, 34º W, 1 Jul 1997 L. R. Noblick & J. T. de Medeiros-Costa 5132 (IPA). Pernambuco. Tapera, 1929, B. Pickel 1208 (IPA); Pombos, 1966, Medeiros- Costa (IPA); Goiana, 1966, Medeiros-Costa (IPA); Triunfo, 27 Mar 1970, Medeiros- Costa 133 (IPA); Pombos, 1969, Glassman & Costa 8701 (F); 2 km W of Neves, associated with S. coronata and S. x costae, 1969, Glassman & Costa 8706 (F). USES: This palm has great ornamental potential. The especially attractive character is its tendency to grow in pairs or as twins (Fig. 1 & 5). In summary, Syagrus cearensis merits recognition. Some of the distinct attributes of this species are the common clustering habit with the strong tendency towards twins, fruit nearly as long as wide, evenly covered with a fine dark brown lepidote indument, presence of deltoid rachis bracts, sepals of staminate flowers usually narrowly linear and strongly keeled and a rather large distinct interior seed cavity. I am unaware of any other species of Syagrus with such a large seed cavity. Because of its predisposition to form twins, this species is a great ornamental. Acknowledgments Montgomery Botanical Center funded both the field work and my post-doctorate position at Fairchild Tropical Garden. Thanks to the Federal University of Ceará, Department of Botany for help with transportation in the field in Sincere thanks to Fairchild Tropical Garden where I am a research associate and especially to their volunteer, Wes Jurgens, who furnished the diagnostic plate. The impetus for publishing this species was provided by the National Science Foundation Grant # LITERATURE CITED GLASSMAN, S.F A new hybrid in the palm genus Syagrus. Fieldiana Bot. 32:
Two new species of Mahonia (Berberidaceae) from Yunnan, China
 Ann. Bot. Fennici 46: 469 473 ISSN 0003-3847 (print) ISSN 1797-2442 (online) Helsinki 30 October 2009 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 2009 Two new species of Mahonia (Berberidaceae) from
Ann. Bot. Fennici 46: 469 473 ISSN 0003-3847 (print) ISSN 1797-2442 (online) Helsinki 30 October 2009 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 2009 Two new species of Mahonia (Berberidaceae) from
New Syagrus Species from Brazil
 New Syagrus Species from razil LRRY R. NOLIK Montgomery otanical enter 11901 Old utler Road Miami, Florida 33156 US N HRRI LORENZI Instituto Plantarum de Estudos da Flora v. rasil, 2000 Nova Odessa Sao
New Syagrus Species from razil LRRY R. NOLIK Montgomery otanical enter 11901 Old utler Road Miami, Florida 33156 US N HRRI LORENZI Instituto Plantarum de Estudos da Flora v. rasil, 2000 Nova Odessa Sao
Geraniaceae geranium family
 Geraniaceae geranium family Long-known for the prized ornamentals and house plants obtained from South African species. Nova Scotia hosts two genera and a half-dozen species. Most are herbs with lobed
Geraniaceae geranium family Long-known for the prized ornamentals and house plants obtained from South African species. Nova Scotia hosts two genera and a half-dozen species. Most are herbs with lobed
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions Sepals Anther Stamens (male) Filament Stigma Pistil Style (female) Ovary Petals sepals petals stamens pistil
 Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey)
 Araştırma Makalesi/Research Article A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey) Ömer KILIÇ 1 Abstract- In this study morphological characters of Malabaila
Araştırma Makalesi/Research Article A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey) Ömer KILIÇ 1 Abstract- In this study morphological characters of Malabaila
What's in a Flower. Ages: 8 to 12. Contributor: Susan Jaquette, Cornell Plantations volunteer
 Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY. Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller. Other Commonly Used Names: none. Previously Used Scientific Names: none
 Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Berberidaceae (barberry) Rarity Ranks: G3/S1 State
Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Berberidaceae (barberry) Rarity Ranks: G3/S1 State
Table 3. List of descritors for maize
 Table 3. List of descritors for maize Descriptor Descriptor Descriptor state Recording stage Remarks number 1 Accession number 2 Total no. of leaves Record the total number of At flowering leaves per plant
Table 3. List of descritors for maize Descriptor Descriptor Descriptor state Recording stage Remarks number 1 Accession number 2 Total no. of leaves Record the total number of At flowering leaves per plant
Systematics of hardy Theaceae and genus Stewartia. Koen Camelbeke Arboretum Wespelaar
 Systematics of hardy Theaceae and genus Stewartia Koen Camelbeke Arboretum Wespelaar Angiosperm Phylogeny Website Angiosperm Phylogeny Website Ericales Systematics Theaceae Family name Theaceae s.s. (versus
Systematics of hardy Theaceae and genus Stewartia Koen Camelbeke Arboretum Wespelaar Angiosperm Phylogeny Website Angiosperm Phylogeny Website Ericales Systematics Theaceae Family name Theaceae s.s. (versus
DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to
 Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification
 1 Tips for Identifying Broadleaf Weeds Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification The cotyledon is an important identifying characteristic for broadleaf weeds. Shape and position of leaves, presence of pubescence
1 Tips for Identifying Broadleaf Weeds Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification The cotyledon is an important identifying characteristic for broadleaf weeds. Shape and position of leaves, presence of pubescence
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development. Chapter 35
 Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Bombax ceiba. Family: Malvaceae Red Silk-Cotton; Red Cotton Tree; Kapok; Flower Display: A+ Silk Cotton
 Stephen H. Brown, Horticulture Agent Lee County Extension, Fort Myers, Florida (239) 533-7513 brownsh@ufl.edu http://lee.ifas.ufl.edu/hort/gardenhome.shtml Bombax ceiba Family: Malvaceae Red Silk-Cotton;
Stephen H. Brown, Horticulture Agent Lee County Extension, Fort Myers, Florida (239) 533-7513 brownsh@ufl.edu http://lee.ifas.ufl.edu/hort/gardenhome.shtml Bombax ceiba Family: Malvaceae Red Silk-Cotton;
Strawberry Leaf Spot
 Strawberry Leaf Spot Cathy Heidenreich and Bill Turechek Introduction - Leaf spot is one of the most common and widespread diseases of strawberry. Mycosphaerella fragariae is also the cause of black seed
Strawberry Leaf Spot Cathy Heidenreich and Bill Turechek Introduction - Leaf spot is one of the most common and widespread diseases of strawberry. Mycosphaerella fragariae is also the cause of black seed
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview Objectives bold Part I Floral Anatomy . calyx sepals corolla, petals, stamens, filament
 Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Hapaline appendiculata (Araceae: Caladieae) Rediscovered
 Gardens' Bulletin Singapore 57 (2005) 13 18 13 Hapaline appendiculata (Araceae: Caladieae) Rediscovered PETER C. BOYCE, JELEND AK KISAI AND JEPOM AK TISAI Malesiana Tropicals, Suite 9-04, Tun Jugah Tower,
Gardens' Bulletin Singapore 57 (2005) 13 18 13 Hapaline appendiculata (Araceae: Caladieae) Rediscovered PETER C. BOYCE, JELEND AK KISAI AND JEPOM AK TISAI Malesiana Tropicals, Suite 9-04, Tun Jugah Tower,
A new species of Mahonia Nutt. (Berberidaceae) from China
 Botanical Studies (2009) 50: 487-492. SYSTEMATICS A new species of Mahonia Nutt. (Berberidaceae) from China Jian-Yong WU 1, Mikinori OGISU 2, Hai-Ning QIN 3, *, and Shi-Nian LU 4 1 Nanjing Institute of
Botanical Studies (2009) 50: 487-492. SYSTEMATICS A new species of Mahonia Nutt. (Berberidaceae) from China Jian-Yong WU 1, Mikinori OGISU 2, Hai-Ning QIN 3, *, and Shi-Nian LU 4 1 Nanjing Institute of
Invasive Tree Species
 Invasive Tree Species A Contents Invasive Tree Species................. 1 Removal Permit Process.............. 2 Mitigation......................... 3 Identification Guide: Norway maple - Acer platanoides............
Invasive Tree Species A Contents Invasive Tree Species................. 1 Removal Permit Process.............. 2 Mitigation......................... 3 Identification Guide: Norway maple - Acer platanoides............
Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdcourt
 Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdcourt A guide to Identification, Risk Assessment and Management Jonathan Newman Plant Protection Service, Wageningen, NL Centre for Ecology and Hydrology Wallingford,
Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdcourt A guide to Identification, Risk Assessment and Management Jonathan Newman Plant Protection Service, Wageningen, NL Centre for Ecology and Hydrology Wallingford,
RARE PLANTS AND BOTANICALLY SIGNIFIGANT ASSEMBLAGES
 Guidelines for Rare Plant Surveys Edited by Diana Bizecki Robson INTRODUCTION With the recent protection of some of Saskatchewan s rare plants under The Wildlife Act, industry will be required to conduct
Guidelines for Rare Plant Surveys Edited by Diana Bizecki Robson INTRODUCTION With the recent protection of some of Saskatchewan s rare plants under The Wildlife Act, industry will be required to conduct
A NEW LARGE-FLOWERED ODONTOGLOSSUM (ORCHIDACEAE: ONCIDIINAE) FROM THE CUSCO REGION IN PERU
 LANKESTERIANA 13(3): 395 399. 2014. A NEW LARGE-FLOWERED ODONTOGLOSSUM (ORCHIDACEAE: ONCIDIINAE) FROM THE CUSCO REGION IN PERU Stig Dalström 1,3 & Saul Ruíz Pérez 2 1 2304 Ringling Boulevard, unit 119,
LANKESTERIANA 13(3): 395 399. 2014. A NEW LARGE-FLOWERED ODONTOGLOSSUM (ORCHIDACEAE: ONCIDIINAE) FROM THE CUSCO REGION IN PERU Stig Dalström 1,3 & Saul Ruíz Pérez 2 1 2304 Ringling Boulevard, unit 119,
April s Featured Plants
 Genus: Geum (Avens) Genus of about 50 perennials, mostly with dense clusters of hairy leaves Geum chiloense Species originating from Island of Chiloe, Chile which enjoys a cold, wet climate. These plants
Genus: Geum (Avens) Genus of about 50 perennials, mostly with dense clusters of hairy leaves Geum chiloense Species originating from Island of Chiloe, Chile which enjoys a cold, wet climate. These plants
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers
 Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Making and using keys Teacher Guidance
 Teacher Guidance Activities in earlier sections should have laid foundations that lead children to these more complex activities, in which they apply their observation and sorting skills to the practical
Teacher Guidance Activities in earlier sections should have laid foundations that lead children to these more complex activities, in which they apply their observation and sorting skills to the practical
version if desired, and Teacher Preparation Notes are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/.
 Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Two Main Precautions Before You Begin Working
 Pruning Mango Trees Roy Beckford, Ag/Natural Resources Agent, UF/IFAS Lee County Two Main Precautions Before You Begin Working 1. Mango peel and sap contain urushiol, the chemical in poison ivy and poison
Pruning Mango Trees Roy Beckford, Ag/Natural Resources Agent, UF/IFAS Lee County Two Main Precautions Before You Begin Working 1. Mango peel and sap contain urushiol, the chemical in poison ivy and poison
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds
 Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Strawberry Anthracnose
 Strawberry Anthracnose Bill Turechek and Cathy Heidenreich Introduction - The term anthracnose is a general term used to describe plant diseases. Strawberry anthracnose refers to several diseases of strawberry
Strawberry Anthracnose Bill Turechek and Cathy Heidenreich Introduction - The term anthracnose is a general term used to describe plant diseases. Strawberry anthracnose refers to several diseases of strawberry
Grapefruit Growing and Certification Requirements
 United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Marketing Service Fruit and Vegetable Programs Fresh Products Branch United States Standards for Grades of Grapefruit (Texas and States other than Florida,
United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Marketing Service Fruit and Vegetable Programs Fresh Products Branch United States Standards for Grades of Grapefruit (Texas and States other than Florida,
Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types
 Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Biology 213 Angiosperms. Introduction
 Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Pruning Trees. Center for Landscape and Urban Horticulture. University of California Cooperative Extension Central Coast & South Region
 University of California Cooperative Extension Central Coast & South Region Center for Landscape and Urban Horticulture Pruning Trees Pruning Trees at Planting Landscape trees should not be pruned at planting
University of California Cooperative Extension Central Coast & South Region Center for Landscape and Urban Horticulture Pruning Trees Pruning Trees at Planting Landscape trees should not be pruned at planting
Anatomical study on Vaccinium arctostaphylos L.
 Department of Pharmacognosy 1, School of Pharmacy, Shaheed Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, and Faculty of Pharmacy 2, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Anatomical study on Vaccinium
Department of Pharmacognosy 1, School of Pharmacy, Shaheed Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, and Faculty of Pharmacy 2, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Anatomical study on Vaccinium
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS
 PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
Dissect a Flower. Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Using and Constructing a Dichotomous Key
 Name Class Date Chapter 18 Classification Using and Constructing a Dichotomous Key You may want to refer students to Chapter 18 in the textbook for a discussion of the classification system used in biology.
Name Class Date Chapter 18 Classification Using and Constructing a Dichotomous Key You may want to refer students to Chapter 18 in the textbook for a discussion of the classification system used in biology.
Mighty Oaks From Little Acorns
 Science Process: Observe and Measure / Life Science / Math: Measurement (Length), data Analysis (graphing) / reading: Sequencing / Listening / Writing / Visual Arts expression Background Buds are on the
Science Process: Observe and Measure / Life Science / Math: Measurement (Length), data Analysis (graphing) / reading: Sequencing / Listening / Writing / Visual Arts expression Background Buds are on the
Palm Trees for Landscapes in Tulare & Kings Counties Suggested by Nancy Gravender, UC Master Gardener
 Palm Trees for Landscapes in Tulare & Kings Counties Suggested by Nancy Gravender, UC Master Gardener MEDIUM-SIZED PALM TREES (10-25 Ft. Tall) FAN PALMS: Guadalupe Palm (Brahea edulis) Grows to 20 ft.,
Palm Trees for Landscapes in Tulare & Kings Counties Suggested by Nancy Gravender, UC Master Gardener MEDIUM-SIZED PALM TREES (10-25 Ft. Tall) FAN PALMS: Guadalupe Palm (Brahea edulis) Grows to 20 ft.,
CAPPARACEAE. 山 柑 科 shan gan ke
 CAPPARACEAE 山 柑 科 shan gan ke Zhang Mingli ( 张 明 理 ) 1 ; Gordon C. Tucker 2 Shrubs, trees, or woody vines, evergreen (deciduous in some Crateva), with branched or simple trichomes. Stipules spinelike,
CAPPARACEAE 山 柑 科 shan gan ke Zhang Mingli ( 张 明 理 ) 1 ; Gordon C. Tucker 2 Shrubs, trees, or woody vines, evergreen (deciduous in some Crateva), with branched or simple trichomes. Stipules spinelike,
Plant Parts. Background Information
 Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Grade 4 Title: My Name is Magnolia Whittney McCray
 Grade 4 Title: My Name is Magnolia Whittney McCray Student Learning Objective(s): The students will understand why Magnolias are a type of evergreen. The students will create a story based on the information
Grade 4 Title: My Name is Magnolia Whittney McCray Student Learning Objective(s): The students will understand why Magnolias are a type of evergreen. The students will create a story based on the information
Growing Cocoa Beans. Growing Region
 Growing Cocoa Beans All chocolate begins with cocoa beans, the fruit of the cacao tree (also called a cocoa tree). Scientists know that the cacao tree originated somewhere in South or Central America.
Growing Cocoa Beans All chocolate begins with cocoa beans, the fruit of the cacao tree (also called a cocoa tree). Scientists know that the cacao tree originated somewhere in South or Central America.
Plant Reproduction. 2. Evolutionarily, floral parts are modified A. stems B. leaves C. roots D. stolons E. suberins
 Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Brazil s Response to Lower Commodity Prices Will Infrastructure Improvements Support Further Expansion?
 Brazil s Response to Lower Commodity Prices Will Infrastructure Improvements Support Further Expansion? By Dr. Michael Cordonnier www.soybeansandcorn.com soycorn@comcast.net 630-325-0192 (Chicago) Overview
Brazil s Response to Lower Commodity Prices Will Infrastructure Improvements Support Further Expansion? By Dr. Michael Cordonnier www.soybeansandcorn.com soycorn@comcast.net 630-325-0192 (Chicago) Overview
Introducing the parts of a flower
 Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Parts of a Flower and Pollination
 Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Quírico Jiménez-Madrigal, 4 and Laura P. Lagomarsino 5
 Two new species of Freziera (Pentaphylacaceae) from Costa Rica Daniel Santamaría-Aguilar, 1,2 Alex K. Monro, 3 Quírico Jiménez-Madrigal, 4 and Laura P. Lagomarsino 5 Abstract. Two new species of Freziera
Two new species of Freziera (Pentaphylacaceae) from Costa Rica Daniel Santamaría-Aguilar, 1,2 Alex K. Monro, 3 Quírico Jiménez-Madrigal, 4 and Laura P. Lagomarsino 5 Abstract. Two new species of Freziera
Apricot Tree Prunus armeniaca
 Apricot Tree Prunus armeniaca Up to 25-30 tall x 15-20 wide or partial shade 10 degrees F. General: The Apricot Tree is a subspecies of the peach and dates back 3,000 years to northeastern China. Apricots
Apricot Tree Prunus armeniaca Up to 25-30 tall x 15-20 wide or partial shade 10 degrees F. General: The Apricot Tree is a subspecies of the peach and dates back 3,000 years to northeastern China. Apricots
FIELD RECOGNITION OF THE LARVAE OF NATIVE COCCINELLIDAE, COMMON TO THE POTATO FIELDS OF AROOSTOOK COUNTY
 FIELD RECOGNITION OF THE LARVAE OF NATIVE COCCINELLIDAE, COMMON TO THE POTATO FIELDS OF AROOSTOOK COUNTY R. H. Storch Department of Entomolgy, University of Maine TECHNICAL BULLETIN 43 MAINE AGRICULTURAL
FIELD RECOGNITION OF THE LARVAE OF NATIVE COCCINELLIDAE, COMMON TO THE POTATO FIELDS OF AROOSTOOK COUNTY R. H. Storch Department of Entomolgy, University of Maine TECHNICAL BULLETIN 43 MAINE AGRICULTURAL
Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort
 The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Seeds What Is a Seed? A seed is a very young plant that is in the dormant, or resting stage. It is very much alive. There are three
The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Seeds What Is a Seed? A seed is a very young plant that is in the dormant, or resting stage. It is very much alive. There are three
JAPANESE KNOTWEED. What is Japanese Knotweed?
 JAPANESE KNOTWEED What is Japanese Knotweed? Japanese Knotweed (botanical name Fallopia japonica) was introduced into Britain from Japan in the early 1800 s. It was originally grown as an ornamental plant,
JAPANESE KNOTWEED What is Japanese Knotweed? Japanese Knotweed (botanical name Fallopia japonica) was introduced into Britain from Japan in the early 1800 s. It was originally grown as an ornamental plant,
(12) United States Plant Patent Cho
 USO0PP24596P2 (12) United States Plant Patent Cho (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COLOCASIA PLANT NAMED HAWAIIAN PUNCH (50) Latin Name: Colocasia esculenta Varietal Denomination: HAWAIIAN PUNCH
USO0PP24596P2 (12) United States Plant Patent Cho (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COLOCASIA PLANT NAMED HAWAIIAN PUNCH (50) Latin Name: Colocasia esculenta Varietal Denomination: HAWAIIAN PUNCH
A new species of Symplocos (Symplocaceae) from Mont Panié (New Caledonia)
 A new species of Symplocos (Symplocaceae) from Mont Panié (New Caledonia) Yohan PILLON Institut de Recherche pour le Développement, Laboratoire de Botanique, BP A5, 98848 Nouméa cedex (New Caledonia) and
A new species of Symplocos (Symplocaceae) from Mont Panié (New Caledonia) Yohan PILLON Institut de Recherche pour le Développement, Laboratoire de Botanique, BP A5, 98848 Nouméa cedex (New Caledonia) and
Different wing in pitchers of the myrmecophagous species
 Different wing in pitchers of the myrmecophagous species Sarracenia minor and S. rubra Miloslav Studnička Liberec Botanic Gardens Purkyňova 630/1 CZ-460 01 Liberec Czech Republic botangarden@volny.cz Keywords:
Different wing in pitchers of the myrmecophagous species Sarracenia minor and S. rubra Miloslav Studnička Liberec Botanic Gardens Purkyňova 630/1 CZ-460 01 Liberec Czech Republic botangarden@volny.cz Keywords:
A NEW SPECIES OF ZIZIPHUS (RHAMNACEAE) FROM NEPAL HIMALAYAS
 A NEW SPECIES OF ZIZIPHUS (RHAMNACEAE) FROM NEPAL HIMALAYAS *Khem Raj Bhattarai and Mitra Lal Pathak National Herbarium and Plant Laboratories, Department of Plant Resources, Godawari, Lalitpur, G.P.O.
A NEW SPECIES OF ZIZIPHUS (RHAMNACEAE) FROM NEPAL HIMALAYAS *Khem Raj Bhattarai and Mitra Lal Pathak National Herbarium and Plant Laboratories, Department of Plant Resources, Godawari, Lalitpur, G.P.O.
A preliminary study of the genus Hornstedtia (Zingiberaceae) in Thailand
 THAI FOR. BULL. (BOT.), SPECIAL ISSUE : 138 142. 2009. A preliminary study of the genus Hornstedtia (Zingiberaceae) in Thailand Charun Maknoi 1 ABSTRACT. The taxonomy of the genus Hornstedtia Retz. in
THAI FOR. BULL. (BOT.), SPECIAL ISSUE : 138 142. 2009. A preliminary study of the genus Hornstedtia (Zingiberaceae) in Thailand Charun Maknoi 1 ABSTRACT. The taxonomy of the genus Hornstedtia Retz. in
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice
 10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
A new Campanula (Campanulaceae) from east Anatolia, Turkey
 Nordic Journal of Botany 25: 5357, 2007 doi: 10.1111/j.2007.0107-055X.00091.x, # The Authors. Journal compilation # Nordic Journal of Botany 2007 Subject Editor: Torbjörn Tyler. Accepted 10 September 2007
Nordic Journal of Botany 25: 5357, 2007 doi: 10.1111/j.2007.0107-055X.00091.x, # The Authors. Journal compilation # Nordic Journal of Botany 2007 Subject Editor: Torbjörn Tyler. Accepted 10 September 2007
Trees help us experience connections with our natural heritage and with our most deeply held spiritual and cultural values.
 REASONS FOR PLANTING TREES Shade from trees cools hot streets and parking lots and drive ways. Cities are "heat islands" that are 5-9 degrees hotter than surrounding areas. Trees and shrubs add beauty
REASONS FOR PLANTING TREES Shade from trees cools hot streets and parking lots and drive ways. Cities are "heat islands" that are 5-9 degrees hotter than surrounding areas. Trees and shrubs add beauty
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
 Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth?
 1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1. VIBURNUM Linnaeus, Sp. Pl. 1: 267. 1753.
 Fl. China 19: 570 611. 2011. 1. VIBURNUM Linnaeus, Sp. Pl. 1: 267. 1753. 荚 蒾 属 jia mi shu Yang Qiner ( 杨 亲 二 ); Valéry Malécot Actinotinus Oliver, p.p. Shrubs or small trees, deciduous or sometimes evergreen.
Fl. China 19: 570 611. 2011. 1. VIBURNUM Linnaeus, Sp. Pl. 1: 267. 1753. 荚 蒾 属 jia mi shu Yang Qiner ( 杨 亲 二 ); Valéry Malécot Actinotinus Oliver, p.p. Shrubs or small trees, deciduous or sometimes evergreen.
FLORA DA RESERVA DUCKE, AMAZONAS, BRASIL: ANNONACEAE
 FLORA DA RESERVA DUCKE, AMAZONAS, BRASIL: ANNONACEAE Paul J. M. Maas 1, Hiltje Maas 1 & J. M. S. Miralha 2 with bark descriptions by Leo Junikka 3 Annonaceae Juss., Gen. Pl. 283. 4. 1789, nom. cons. Chatrou,
FLORA DA RESERVA DUCKE, AMAZONAS, BRASIL: ANNONACEAE Paul J. M. Maas 1, Hiltje Maas 1 & J. M. S. Miralha 2 with bark descriptions by Leo Junikka 3 Annonaceae Juss., Gen. Pl. 283. 4. 1789, nom. cons. Chatrou,
Article. Vochysia microphylla (Vochysiaceae), a new species from Serra do Cipó, Minas Gerais, Brazil
 Phytotaxa 56: 10 14 (2012) www.mapress.com/phytotaxa/ Copyright 2012 Magnolia Press Article ISSN 1179-3155 (print edition) PHYTOTAXA ISSN 1179-3163 (online edition) Vochysia microphylla (Vochysiaceae),
Phytotaxa 56: 10 14 (2012) www.mapress.com/phytotaxa/ Copyright 2012 Magnolia Press Article ISSN 1179-3155 (print edition) PHYTOTAXA ISSN 1179-3163 (online edition) Vochysia microphylla (Vochysiaceae),
PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES
 PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES Compiled by HOLLY BROWN and MARTIN WILKINSON, School of Life Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland Although
PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES Compiled by HOLLY BROWN and MARTIN WILKINSON, School of Life Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland Although
Plant Parts and Their Function
 Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Tree factsheet images at pages 3, 4, 5
 Forest Ecology and Forest Management Group Tree factsheet images at pages 3, 4, 5 Prunus serotina Ehrh. taxonomy author, year Ehrhart 1783 synonym - Family Rosaceae Eng. Name Black Cherry, Wild Cherry
Forest Ecology and Forest Management Group Tree factsheet images at pages 3, 4, 5 Prunus serotina Ehrh. taxonomy author, year Ehrhart 1783 synonym - Family Rosaceae Eng. Name Black Cherry, Wild Cherry
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Hair & Fiber. (Unit 5)
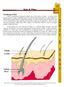 37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
2.75 6.525 Problem Set 1 Solutions to ME problems Fall 2013
 2.75 6.525 Problem Set 1 Solutions to ME problems Fall 2013 2. Pinned Joint problem Jacob Bayless a) Draw a free-body diagram for the pin. How is it loaded? Does the loading depend on whether the pin is
2.75 6.525 Problem Set 1 Solutions to ME problems Fall 2013 2. Pinned Joint problem Jacob Bayless a) Draw a free-body diagram for the pin. How is it loaded? Does the loading depend on whether the pin is
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Glass & Soil (Unit 3)
 13 Glass & Soil (Unit 3) Glass Fractures Glass bends in response to any force that is exerted on any one of its surfaces. When the limit of its elasticity is reached, the glass will fracture. Frequently,
13 Glass & Soil (Unit 3) Glass Fractures Glass bends in response to any force that is exerted on any one of its surfaces. When the limit of its elasticity is reached, the glass will fracture. Frequently,
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator
 Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
FORMATIVE PRUNING OF BUSH TREES WINTER PRUNING OF ESTABLISHED BUSH TREES AIMS SPUR BEARERS & TIP BEARERS PRUNING OF SPUR BEARERS
 FORMATIVE PRUNING OF BUSH TREES Formative pruning is essential and should be carried out in the dormant season, November- March. Its purpose is to produce a well-balanced tree with a strong branch framework
FORMATIVE PRUNING OF BUSH TREES Formative pruning is essential and should be carried out in the dormant season, November- March. Its purpose is to produce a well-balanced tree with a strong branch framework
GARDEN FACTS. When are apples ripe?
 A3743-E GARDEN FACTS U n i v e r s i t y o f W i s c o n s i n E x t e n s i o n When are apples ripe? Teryl R. Roper DIFFERENT APPLE CULTIVARS RIPEN over a long season. In Wisconsin, apples ripen from
A3743-E GARDEN FACTS U n i v e r s i t y o f W i s c o n s i n E x t e n s i o n When are apples ripe? Teryl R. Roper DIFFERENT APPLE CULTIVARS RIPEN over a long season. In Wisconsin, apples ripen from
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function. I. Background
 Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Phoenix roebelenii (pygmy date palm)
 Australia/New Zealand Weed Risk Assessment adapted for Florida. Data used for analysis published in: Gordon, D.R., D.A. Onderdonk, A.M. Fox, R.K. Stocker, and C. Gantz. 28. Predicting Invasive Plants in
Australia/New Zealand Weed Risk Assessment adapted for Florida. Data used for analysis published in: Gordon, D.R., D.A. Onderdonk, A.M. Fox, R.K. Stocker, and C. Gantz. 28. Predicting Invasive Plants in
Chapter 39: Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals
 Name Period Concept 39.1 Signal transduction pathways link signal reception to response This concept brings together the general ideas on cell communication from Chapter 11 with specific examples of signal
Name Period Concept 39.1 Signal transduction pathways link signal reception to response This concept brings together the general ideas on cell communication from Chapter 11 with specific examples of signal
Cercis Ruby Falls. www.planthaven.com. Origin: Redbud breeding program at NCSU Species: Cercis canadensis Protection Status: US PPAF
 Cercis Ruby Falls Origin: Redbud breeding program at NCSU Protection Status: US PPAF Key Features Unique weeping habit. Full crown of foliage at the top. Large heart shaped purple leaves. Attractive reddish-purple
Cercis Ruby Falls Origin: Redbud breeding program at NCSU Protection Status: US PPAF Key Features Unique weeping habit. Full crown of foliage at the top. Large heart shaped purple leaves. Attractive reddish-purple
KINGMAN IS GROWING! COLUMN
 KINGMAN IS GROWING! COLUMN THE INTRIGUING AGAVE BY LINDA REDDICK, KINGMAN AREA MASTER GARDENER An Agave is a tough, easy-care succulent that can add style to your garden, tolerate less than ideal conditions
KINGMAN IS GROWING! COLUMN THE INTRIGUING AGAVE BY LINDA REDDICK, KINGMAN AREA MASTER GARDENER An Agave is a tough, easy-care succulent that can add style to your garden, tolerate less than ideal conditions
The Parts of a Flower
 The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
Algological Investigations of Hungarian Forest Soils III. Soil Algal Surface Communities in Mts. Mátra
 ANNALES HISTORICO-NATURALES MUSEI NATIONALIS HUNGARICI Tomus 67. Budapest 1975. Algological Investigations of Hungarian Forest Soils III. Soil Algal Surface Communities in Mts. Mátra by Zs. P.-KOMÁROMY,
ANNALES HISTORICO-NATURALES MUSEI NATIONALIS HUNGARICI Tomus 67. Budapest 1975. Algological Investigations of Hungarian Forest Soils III. Soil Algal Surface Communities in Mts. Mátra by Zs. P.-KOMÁROMY,
The Basics of Tree Pruning
 The Basics of Tree Pruning By John Ball, Forest Health Specialist and Aaron Kiesz, Urban and Community Forestry Specialist Until the end of the 19 th century, trees were not a common sight in many parts
The Basics of Tree Pruning By John Ball, Forest Health Specialist and Aaron Kiesz, Urban and Community Forestry Specialist Until the end of the 19 th century, trees were not a common sight in many parts
Laboratory. Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs
 Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
1 SEEDLING QUALITY. Seedling quality
 Seedling quality Quality versus quantity A nursery manager s most important goal is to produce quality trees. Quality is more important than quantity. It is a common mistake in nurseries to concentrate
Seedling quality Quality versus quantity A nursery manager s most important goal is to produce quality trees. Quality is more important than quantity. It is a common mistake in nurseries to concentrate
Dry Bean Types and Development Stages
 Dry Bean Types and Development Stages Two basic plant growth habits are found in dry edible bean: determinate (bush) or indeterminate (vining or trailing). Cultivars may be classified according to plant
Dry Bean Types and Development Stages Two basic plant growth habits are found in dry edible bean: determinate (bush) or indeterminate (vining or trailing). Cultivars may be classified according to plant
New Species and Combinations in Astragalus (Leguminosae) from China and the Himalayas
 New Species and Combinations in Astragalus (Leguminosae) from China and the Himalayas Dietrich Podlech Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, Department Biologie I Systematic Botany, Menzinger Straße 67,
New Species and Combinations in Astragalus (Leguminosae) from China and the Himalayas Dietrich Podlech Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, Department Biologie I Systematic Botany, Menzinger Straße 67,
New species from NE Turkey: Chaerophyllum posofianum (Apiaceae) and Vicia erzurumica (Fabaceae)
 Willdenowia 28-1998 151 SADIK ERIK & NASIP DEMIRKUŞ New species from NE Turkey: Chaerophyllum posofianum (Apiaceae) and Vicia erzurumica (Fabaceae) Abstract Erik, S. & Demirkuş, Ν.: New species from NE
Willdenowia 28-1998 151 SADIK ERIK & NASIP DEMIRKUŞ New species from NE Turkey: Chaerophyllum posofianum (Apiaceae) and Vicia erzurumica (Fabaceae) Abstract Erik, S. & Demirkuş, Ν.: New species from NE
Great Crested Newt Habitat Suitability Index
 Great Crested Newt Habitat Suitability Index Background The Habitat Suitability Index (H) for the great crested newt was developed by Oldham et al. (2000). H scoring systems were originally developed by
Great Crested Newt Habitat Suitability Index Background The Habitat Suitability Index (H) for the great crested newt was developed by Oldham et al. (2000). H scoring systems were originally developed by
There are several consequences of not conducting a regular pruning program. These include:
 Pruning is a double-edged sword, either helping or hurting according to if, where, when, how, and why it is applied. When properly executed, a variety of benefits can occur. Benefits include reducing risk
Pruning is a double-edged sword, either helping or hurting according to if, where, when, how, and why it is applied. When properly executed, a variety of benefits can occur. Benefits include reducing risk
Listing Statement for Caladenia tonellii (robust fingers) robust fingers
 Caladenia tonellii Listing Statement for Caladenia tonellii (robust fingers) robust fingers T A S M A N I A N T H R E A T E N E D S P E C I E S L I S T I N G S T A T E M E N T Image by Mark Wapstra Scientific
Caladenia tonellii Listing Statement for Caladenia tonellii (robust fingers) robust fingers T A S M A N I A N T H R E A T E N E D S P E C I E S L I S T I N G S T A T E M E N T Image by Mark Wapstra Scientific
8. Study the cladogram underline the derived characteristics and circle the organisms that developed from them.
 Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Do Leaves Need Chlorophyll for Growth?
 Do Leaves Need Chlorophyll for Growth? by Kranti Patil, Gurinder Singh and Karen Haydock Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education VN Purav Marg, Mankhurd Mumbai 400088 India haydock@gmail.com Students
Do Leaves Need Chlorophyll for Growth? by Kranti Patil, Gurinder Singh and Karen Haydock Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education VN Purav Marg, Mankhurd Mumbai 400088 India haydock@gmail.com Students
Growth and development of. Trees
 Growth and development of Objectives: Trees 1. To study the morphological and physiological processes that occur for a temperate deciduous tree during the annual cycle, and the whole life cycle. 2. To
Growth and development of Objectives: Trees 1. To study the morphological and physiological processes that occur for a temperate deciduous tree during the annual cycle, and the whole life cycle. 2. To
Pineapples. Ian Hewett Horticultural Marketing Inspectorate United Kingdom. Version - October 2011
 Pineapples Ian Hewett Horticultural Marketing Inspectorate United Kingdom Version - October 2011 1 Definition Of Produce This Standard applies to pineapples of varieties (cultivars) grown from Ananascomosus(L).
Pineapples Ian Hewett Horticultural Marketing Inspectorate United Kingdom Version - October 2011 1 Definition Of Produce This Standard applies to pineapples of varieties (cultivars) grown from Ananascomosus(L).
731. MAHONIA LINDSAYAE CANTAB Berberidaceae. James Cullen
 731. MAHONIA LINDSAYAE CANTAB Berberidaceae James Cullen Summary. Mahonia lindsayae P.F. Yeo Cantab is illustrated, and its history is revealed. This continues a series of articles on plants connected
731. MAHONIA LINDSAYAE CANTAB Berberidaceae James Cullen Summary. Mahonia lindsayae P.F. Yeo Cantab is illustrated, and its history is revealed. This continues a series of articles on plants connected
Rural Flooding: The Potential Role of Forestry
 Rural Flooding: The Potential Role of Forestry Nadeem Shah, Tom Nisbet, & Huw Thomas Centre for Forestry and Climate Change Structure Background Woodland and Flood Alleviation The Theory. Studies on Woodland
Rural Flooding: The Potential Role of Forestry Nadeem Shah, Tom Nisbet, & Huw Thomas Centre for Forestry and Climate Change Structure Background Woodland and Flood Alleviation The Theory. Studies on Woodland
Landscape Plant Recognition Plant Descriptions Field Day #1
 CUPRESSACEAE cypress family Cosmopolitan Mostly scale like foliage or whorled in 3 s Resinous Cones, male & female Cone scales in pairs, peltate or basally attached Cones generally smaller than Pinaceae
CUPRESSACEAE cypress family Cosmopolitan Mostly scale like foliage or whorled in 3 s Resinous Cones, male & female Cone scales in pairs, peltate or basally attached Cones generally smaller than Pinaceae
BULK ROOIBOS PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS AND PACKAGING SPECIFICATIONS
 BULK ROOIBOS PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS AND PACKAGING SPECIFICATIONS The product range is available as conventional or organic certified. Superior Short Cut Rooibos Superior Short Cut is our most popular product.
BULK ROOIBOS PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS AND PACKAGING SPECIFICATIONS The product range is available as conventional or organic certified. Superior Short Cut Rooibos Superior Short Cut is our most popular product.
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
