8 th Grade Science. Directed Reading Packet. The Human Body. Name: Teacher: Period:
|
|
|
- Henry Sharp
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 th Grade Science Directed Reading Packet The Human Body Name: Teacher: Period:
2 Homeostasis 1) What is homeostasis? Section 1: Organization of Your Body 2) Circle the examples that you think illustrate your body maintaining homeostasis: shivering in a cold swimming pool getting goosebumps on a cold winter day sleeping at night getting thirsty sweating in gym class getting hungry breathing faster when running thinking hard during a test Homeostasis and Cells 3) The human body has many specialized cells. Specialized cells perform specific functions for the body. Match the type of cell with its function to help the body maintain homeostasis. skin cell red blood cell muscle cell nerve cell white blood cell carries electrical messages form the brain to body fights bacteria in body carries oxygen from lungs to rest of body covers and protects the body from the outside contracts and allows for movement Groups of Cells Form Tissues 4) What is a tissue? 5) Fill in the chart below describing the four types of tissue found in the body: Type of Tissue Description Examples Epithelial Made of layers of tightly packed cells that line the surfaces of the body. skin, lining of mouth and nose, lining of the digestive system
3 Groups of Tissues for Organs 6) What is an organ? 7) Describe the role of each type of tissue in the organ of the heart. o nervous tissue sends messages to control the beating of the heart o epithelial tissue o connective tissue o muscle tissue Groups of Organs Form Organ Systems 8) Fill in the chart below describing the functions of the organ systems. Organ System cardiovascular Function Transport oxygen, hormones and nutrients to the body cells. Moves wastes and carbon dioxide away from cells. lymphatic digestive endocrine integumentary muscular nervous reproductive respiratory skeletal urinary immune
4 Homeostasis and Feedback Regulation: Feedback regulation occurs when the response to a stimulus has an effect of some kind on the original stimulus. The most common in a negative feedback loop. See example below: Try to fill in the empty boxes on the following negative feedback loops: Drop in body temperature. Drop in blood sugar level. Lesson Summary The levels of organization in the human body include:,,, and. A is a group of cells working together. An is made of two or more that work together. Organs that work together make up. There are four types of tissue in the body: tissue, tissue, tissue, and tissue. There are major organ systems in the body. Organs and organ systems work together to maintain.
5 Section 2: The Integumentary System Your Skin and Homeostasis 1) What are the three parts of your body that make your integumentary system? 2) What are three ways your integumentary system helps you maintain homeostasis? Functions of Skin 3) Describe how your skin performs the following functions for your body: My skin provides a barrier by My skin helps control body temperature by My skin helps me gather information from my environment by My skin helps me get rid of some types of waste by My skin acts as a sun block by Structure of Skin 4) What is keratin? Use colored pencils to color the cross section of skin below:
6 The Epidermis 5) Describe the structure and function of the epidermis. 6) What is melanin? The Dermis 7) Where is the dermis located? 8) What structures are located in the dermis? Oil Glands and Sweat Glands 9) Oil glands make sebum. What does sebum do for the body? 10) Sweat glands make sweat. What does sweat do for the body? Nails and Hair 11) Hair and nails are made of the protein. Nails 12) What are the functions of nails? 13) Label and color the picture of a fingernail. Hair 14) What makes hair colors different? 15) What are the functions of hair? 16) Label and color the sketch.
7 Keeping Skin Healthy 17) Why is some sunlight good for you? 18) Why do some people get sunburn more easily than others? 19) What causes 90% of skin cancers? Bathing and Hygiene 20) List things that can accumulate on your skin and encourage the growth of bacteria. 21) What effects does the bacteria on skin have? 22) How can you keep your skin healthy? Injury 23) Describe how the skin heals itself? 24) When is it necessary to get stitches for a cut? Lesson Summary Skin acts as a that keeps particles and water out of the body. The skin helps to the body in hot temperatures, and keeps the body in cool temperatures. Skin is made up of two layers, the and the. Pimples occur when the skin produces too much. Hair and nails are made of, the same protein as skin. Nails grow from nail and hairs grow from hair in the skin. Ski cancer can be caused by excess exposure from light from the or tanning beds. Frequent helps keep the skin clean and healthy. Wearing and a when outdoors can help prevent skin cancer.
8 Section 3: The Skeletal System Your Skeleton 1) The main organs of the skeletal system are the. 2) Humans have a backbone, therefore they are classified as. 3) The adult human skeleton has bones. 4) How does the skeleton of babies and small children compare to the skeleton of an adult? 5) What are the functions of cartilage and ligaments? cartilageligamants- 6) Label the picture of the skeleton with the names of the bones.
9 Functions of Bones 7) Explain how the skeletal system provides the following functions for the body: Support- Protection- Movement- Making blood cells- Storage- Structure of Bones 8) Describe the two main types of bone found in the body. 9) Describe the two types of marrow found in the body. 10) Label and color the picture of the femur. Joints and How They Move Draw lines to match the type of joint on the left with the description on the right. Fixed joint Partly moveable joint Moveable joint Allows for little movement. Found in vertebrae. Allows for movement. Found in limbs. Do not allow for any bone movement. Found in skull
10 Moveable Joints Fill in the chart below to describe the different types of joints. Type of Joint Short Description Locations in Body ball and socket A ball-shaped surface of one bone fits into the cup-like shape of another. Allows for movement in all directions. hip and shoulder hinge pivot gliding Keeping Bones and Joints Healthy Eating Well 11) What two nutrients are important to maintain a healthy skeletal system? 12) List some foods that contain nutrients important to maintaining a healthy skeletal system? 13) How does your skin help you maintain a healthy skeletal system? Lesson Summary Bones, cartilage, and ligaments make up the system. The skeleton supports the body against the pull of. The skeleton provides a that supports and protects soft of the body. Bones work together with to move the body. Blood cells are mostly made inside the bone. There are three types of joints in the body:, partly and. and are the two most important nutrients for a healthy skeletal system. The breakdown of the leads to pain and stiffness in the joint. A is an injury to a ligament. A is a break or crack in a bone.
11 Section 4: The Muscular System Types of Muscles 1) Long, thin cells that are able to contract are called muscle. 2) What is the difference between voluntary muscles and involuntary muscles? 3) Fill in the chart below to describe the three types of muscles. Type of Muscle Voluntary/Involuntary Location in Body Job skeletal involuntary move food through the digestive system heart pump blood through body Below are pictures of muscle cells. Write the type of cells below each picture: Muscles, Bones, and Movement 4) Draw lines to match the term on the left with the description on the right. tendon ligament flexor extensor the muscle that contracts to cause and joint to bend the muscle that contracts to cause a joint to straighten a tough band of connective tissue that connects a muscle to a bone connective tissue that joints bones together
12 Muscles and the Nervous System 5) Draw a sketch in the space to the right, and label it showing how the nervous system controls muscles. Include the following parts in your sketch: brain, nerves, muscle. Muscles and Exercise - Fill in the chart below to describe the three types of exercise Type of Exercise Purpose Examples aerobic increase muscle strength stretching Muscle Injuries 6) How does warming up before exercise reduce the chance of injury? 7) What is a strain? 8) What is tendonitis? Steroids 9) What are some of the negative effects of taking anabolic steroids to increase muscle size? Lesson Summary The body has three types of muscle tissue:,,. Muscles move the body by against the skeleton. Muscles are controlled by the system. Regular improves the health of the muscular system and makes muscles bigger and stronger. Muscular is the ability of a muscle to exert during a contraction. Muscular is the ability of a muscle to continue to contract over a long time without getting tired. A is an injury to a muscle in which the muscle tear because the muscle contracts too much or contracts before the muscle is warmed up. Tiny tears and swelling in a tendon results in.
13 Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1) The four jobs of the cardiovascular system are: 1. a delivery service 2. a 3. a system 4. a against diseases 2) What are the three main parts of the cardiovascular system? The Movement of Gases Section 5: Introduction to the Cardiovascular 3) What body system works closely with the cardiovascular system to move gases around the body? 4) Every cell in your body needs the gas and needs to get rid of the gas. 5) is an important protein found in the blood. It allows oxygen gas to attach to it. Parts of the Cardiovascular System 6) Draw lines to match the term on the left with the description on the right. heart arteries veins capillaries plasma red blood cells white blood cells closed system Two Blood Circulation Systems fight against infection and diseases blood never leaves the blood vessels inside of the body pumps blood through blood vessels carry oxygen thin-walled blood vessels, carry blood to heart, has valves a colorless, watery fluid in which blood cells are suspended thick-walled blood vessels, carry blood away from heart a network of tiny blood vessels, allows for exchange of nutrients and gases between blood and body cells 7) There are two loops of the cardiovascular system. Describe the two loops below: Systemic circulation- Pulmonary circulation- Summary The system includes the, the blood, and the. There are three main types of blood vessels in the body:,, and. circulation is the part of the cardiovascular system that carries oxygen-rich blood away from the, to the body and returns oxygen-poor blood back to the. circulation is the part of the cardiovascular system that carries oxygen-poor blood away from the, to the lungs, and returns oxygen-rich blood back to the.
14 Section 6: Heart and Blood Vessels The Heart 1) How many chambers are in the human heart? 2) How are the atria different from the ventricles? 3) Complete the statements below to describe the job of each chamber of the heart. The right atrium The right ventricle The left atrium The left ventricle Where is the Heart? 4) Describe the heart s location. Explain why it seems like the heart is on the left side of the chest. Blood Flow Through the Heart 5) How does the left side loop and right side loop differ with blood flow through the heart? The Heartbeat 6) What is the function of valves in the heart? What produces the heartbeat sound? Blood Circulation and Blood Vessels 1. Label the following chambers of the heart: right atrium left atrium right ventricle left ventricle 2. Color the heart and surrounding blood vessels: use light/bright red for oxygen-rich blood areas use dark red/maroon for oxygen-poor areas Summary The heart is divided into chambers, the left and right and the left and right. The side of the heart collects oxygen-poor blood from the body and pumps it to the, where it releases and picks up. The side carries the oxygen-rich blood back from the into the of the heart, which then pumps the oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. The in the heart prevent blood from flowing backward into the heart.
15 Section 7: Health of the Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels and Blood Pressure 1) What causes pressure on the walls of blood vessels? 2) What happens to the blood pressure as you move to blood vessels further from the heart? 3) What can be said about the blood pressure in veins? 4) Name and describe the two blood pressure readings Healthy Blood Pressure Ranges 5) What are healthy ranges for blood pressure? 6) Circle the factors below that can affect blood pressure ranges: age gender race exercise emotions sleep stress nutrition drugs disease Cardiovascular Diseases 7) Draw lines to match the term on the left with the description on the right. Hypertension Atherosclerosis Coronary heart disease Heart attack Stroke A loss of brain function due to a blockage of the blood supply to the brain. It can be caused by a blood clot, an object gets caught in a blood vessel, or by a bleeding blood vessel. Occurs when blood cannot reach the heart because of a blood vessel is blocked. If cardiac muscle is starved of oxygen for more than about five minutes, it will die. When a person s blood pressure is always high. Systolic blood pressure is 140 or higher and/or diastolic blood pressure is 90 or higher. Can lead to many other cardiovascular problems. Hardening or inflammation of the arteries that causes swelling and a buildup of material called plaque. Causes the arteries to narrow, making blood flow through the artery difficult. The end result of the buildup of plaque within the walls of coronary arteries. May cause angina (chest pain).
16 Keeping Your Cardiovascular System Healthy 8) What is a risk factor? 9) Give a short description of the following risk factors for CVD that you cannot control: Age: Gender: Genetics: 10) Give a short description of the following risk factors for CVD that you can control: Tobacco smoking: Diabetes: High cholesterol levels: Obesity: High blood pressure: Lack of physical activity: Poor eating habits: Summary Blood is the force put on the walls of blood by circulating blood. The force put on the balls of is called blood pressure. Blood pressure is measured by an instrument called a. In the United States, the healthy ranges for blood pressure is less than 120mm Hg and pressure is 80 mm Hg. occurs when a person s blood pressure is always. A disease (CVD) is any disease that affects the system., heart disease and are examples of CVDs. Cardiovascular diseases are diseases. Having a poor and not getting enough are two major causes of CVD.
17 Section 8: The Respiratory System Roles of the Respiratory System 1) Label the following parts of the respiratory system on the diagram to the right: nose, mouth, trachea, lungs, diaphragm Parts of the Respiratory System 2) Draw lines to match the term on the left with the description on the right. diaphragm nose/nasal cavity pharynx larynx trachea bronchi epiglottis alveoli the area of the throat the produces your voice small sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place the major breathing muscle a flap of tissue that overs the trachea when you swallow a long tube from the pharynx to the bronchi a pathway in the throat for food and air filters, warms and moistens the air you breath tubes leading from the trachea to the lungs How We Breathe 3) Is breathing mostly a voluntary or involuntary action? 4) Describe inhalation. 5) Describe exhalation. 6) Use colored pencils to highlight the blood vessels in the picture in the picture.
18 The Journey of a Breath of Air 7) Fill in the boxes in the following diagram. Color the blood with colored pencils. Breathing and Cellular Respiration 8) What is cellular respiration? 9) What are the waste products of cellular respiration? Summary Your system is made up of the tissues and organs that allow to enter and to leave your body. Respiratory system organs in include your,,,,, and During, the contracts and moves, and brings air into the lungs. During, the and rib muscles and air is pushed out of the lungs. enters the lungs, then passes through the alveoli and into the. The oxygen is carried around the body in., a waste gas, moves into the blood and is brought to the lungs to be released into the air during. The that arrives from the lungs is used by the during cellular respiration to release the stored in molecules of sugar.
19 Section 9: Health of the Respiratory System Respiratory System Disease 1) What can happen to your respiratory system when homeostasis is thrown out of balance? 2) What is the difference between an acute disease and a chronic disease? 3) List the structures of the respiratory system that a respiratory disease can affect: 4) Circle the causes of respiratory diseases below: bacteria viruses pollutants tobacco smoke genetic causes 5) Draw lines to match the respiratory disease on the left with the description on the right. Bronchitis Asthma Pneumonia Tuberculosis (TB) Lung cancer Emphysema A disease where the cells in the lungs grow out of control. Can form a tumor. There is an increased risk of getting this disease if you smoke. A common and often deadly disease caused by a bacteria. Considered infectious, because it can be spread from person to person. Most commonly attacks the lungs. Considered highly contagious because the bacteria is spread by a cough or sneeze. Inflammation of the bronchi. The bronchi become red and swollen. The acute form of this disease can be caused by bacteria for viruses. The condition may last for several days to several weeks. Chronic forms of this disease can last for months or years. A chronic lung disease caused by the breakdown of lung tissue. The tissues that support the alveoli become hard and stiff, instead of springy and flexible. The efficiency of the alveoli is reduced. People with this disease experience shortness of breath during exercise. A chronic condition in which the bronchioles are inflamed and narrow. The muscles around the bronchioles contract and narrow the airways. Excess mucus is made. Causes a person to have difficulty breathing, their chest feels tight, and they may wheeze. Can be caused by allergens, cold or warm air, most air, exercise or stress. An illness in which the alveoli become inflamed and filled with fluid. Gas exchange cannot properly take place. Caused by infection by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites.
20 Causes of Respiratory Disease 6) Describe briefly how the following can cause respiratory diseases: pathogens pollution lifestyle choices Dangers of Smoking 7) A friend of yours tried cigarettes for the first time. You are afraid they will become a smoker. Write a letter, using information from the Flexbook, as to why they shouldn t smoke. Dear Friend, Keeping Your Respiratory System Healthy 8) Design a billboard about ways to keep your respiratory system healthy. Use information from the Flexbook. Use colored pencils to draw what the billboard will look like below.
21 What Does the Digestive System Do? Section 10: The Digestive System 1) What are the main jobs of the digestive system? 2) What is the difference between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion? 3) Describe the process of absorption. 4) Color and label the diagram of the digestive system. Include the following parts: pancreas, esophagus, mouth, tongue, anus, rectum, liver, epiglottis, stomach, salivary glands, large intestine, small intestine, appendix The Role of Enzymes in Digestion 5) How do enzymes help with digestion? 6) Draw lines to match the enzyme with its function. amylase pepsin trypsin lipase bile produced in the pancreas, used to break down fats produced in the liver,secreted into intestines,breaks down fat produced in they salivary glands, helps break down starches produced in the pancrease, breaks down proteins produced in the stomach, breaks down protien Digestive Organs and Their Roles 7) How long is the adult human digestive system? 8) Why do you think digestive organs are lined with sticky, slippery mucus? 9) Use colored pencils to draw a sketch to show your understanding of how peristalsis moves food through the digestive system.
22 10) Describe how each part listed below contributes to the process of digestion. mouth esophagus stomach small intestine villi large intestine liver Bacteria in the Digestive System 11) List the ways bacteria in the large intestine is helpful: Keeping Your Digestive System Healthy 12) What are some suggestions for the best ways to keep your digestive system healthy? Summary The digestive system food, nutrients, and of food wastes. Digestive speed up the reactions of digestion. The main organs of the digestive system are the,,,, and. in the large intestine produce and have other roles in the body.
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST
 REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Pre-requisites: Successful completion of 4th grade science and the 4th grade science assessment.
 Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES
 ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES TIME 50 minutes, computer lab REQUIRED RESOURCES Activity Computer lab with internet access for student research Notepaper and pencil for research Poster board
ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES TIME 50 minutes, computer lab REQUIRED RESOURCES Activity Computer lab with internet access for student research Notepaper and pencil for research Poster board
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100
 Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network of connected that bring
 The Respiratory System Webquest http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/health-and-human-body/human-body/lungs-article/ The Breath of Life-National Geographic 1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network
The Respiratory System Webquest http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/health-and-human-body/human-body/lungs-article/ The Breath of Life-National Geographic 1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
First Grade The Human Body Assessment
 First Grade The Human Body Assessment 1a. When we talk about the skeletal system we are talking about what part of our body? a. stomach b. bones 1b. How many bones in your skeleton? a. more than two hundred
First Grade The Human Body Assessment 1a. When we talk about the skeletal system we are talking about what part of our body? a. stomach b. bones 1b. How many bones in your skeleton? a. more than two hundred
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems
 Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology
 Version 01 Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology 2012 by Open School BC This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. To view
Version 01 Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology 2012 by Open School BC This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. To view
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Emphysema. Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
What You Should Know About ASTHMA
 What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource
 CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
tissues are made of cells that work together, organs are )
 Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST. Part I: Cells. 1. The cell grows to its mature size during. a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d.
 7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST Part I: Cells 1. The cell grows to its mature size during a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d. interphase 2. The final stage of the cell cycle is called a. interphase
7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST Part I: Cells 1. The cell grows to its mature size during a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d. interphase 2. The final stage of the cell cycle is called a. interphase
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
In 2009, Canadian astronaut Robert Thirsk began a six-month stay
 Topic 1.4 How do systems work together in the human body? Key Concepts The respiratory system carries oxygen to and removes carbon dioxide from the blood. The circulatory system transports dissolved gases
Topic 1.4 How do systems work together in the human body? Key Concepts The respiratory system carries oxygen to and removes carbon dioxide from the blood. The circulatory system transports dissolved gases
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
HEALTH EFFECTS. Inhalation
 Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test
 Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test Student Name Class 1. Characteristics of living organisms include all of the following, EXCEPT... A. they need energy and produce wastes B. they reproduce and grow C. they
Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test Student Name Class 1. Characteristics of living organisms include all of the following, EXCEPT... A. they need energy and produce wastes B. they reproduce and grow C. they
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision
 National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
About lung cancer. Contents. The lungs
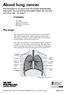 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
Gas Exchange. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the alveoli
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the alveoli
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
High Blood Pressure (Essential Hypertension)
 Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM"
 CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM" You have read how the blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and carries carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. It is the function of the respiratory
CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM" You have read how the blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and carries carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. It is the function of the respiratory
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
