The Prostate Owner s Manual
|
|
|
- Imogene Florence Taylor
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Prostate Owner s Manual F A C T S H E E T What you Should Know about the Prostate Only men have a prostate. A part of the male reproductive system, the prostate is located just below the bladder. It surrounds the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder and semen through the penis and out of the body). The prostate s main job is to help create semen by generating ejaculatory fluid. Semen is the fluid that helps protect and energize the sperm when a man ejaculates. The seminal vesicles are located next to the prostate. They also add fluid to semen. The prostate gland is in front of the rectum. The prostate gland may be a source of health problems in men. The most common problems are enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH), an inflammatory disease (prostatitis) and prostate cancer. Because the prostate is located inside the pelvis, there are no simple self-exams for a man to check his own prostate. There are two main tests doctors use to monitor prostate health for men: the digital rectal examination (DRE) and a blood test called a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. The AUA recommends men over the age of 40 should have a baseline prostate examination with a PSA test and DRE to screen for cancer and other diseases. What is the DRE? The doctor inserts a lubricated gloved finger into the rectum. He or she feels for abnormal size, shape or consistency in the prostate. The DRE can help the doctor decide if a man has an enlarged prostate. However, the DRE by itself is not the best way to detect early prostate cancer. A man should also have a PSA test. BLADDER PROSTATE URETHRA PENIS RECTUM What is the PSA test? This blood test measures the level of prostatespecific antigen in the blood. Very little PSA is found in the blood of a man with a healthy prostate. Some conditions can cause larger amounts of PSA to leak into the blood. One possible cause of a high PSA level is enlargement of the prostate. Inflammation of the prostate, called prostatitis is another common cause of PSA elevation. Prostate cancer is the most serious possible cause of an increased PSA level. Enlarged Prostate The prostate may become larger and may start to cause problems as a man ages. Enlarged prostate is also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The prostate of a 50-year-old man is about grams or about the size of a walnut. It may grow to or grams or more with BPH. As the prostate enlarges, it can squeeze the urethra. This can cause some men to have lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) when their prostate grows. For more information call the National Urology Health Line at or visit Corporate Boulevard Linthicum, MD 21090
2 Men with an enlarged prostate may have some or all of these symptoms: a frequent urge to urinate a strong, sudden urge to urinate gets up to urinate two or more times a night difficulty emptying his bladder a weak urine stream that may start and stop trouble starting to urinate only urinates a little bit each time he goes to the bathroom leaks or dribbles urine after going to the bathroom feels like he still has to urinate, even after he has gone to the bathroom Bladder Prostate Urethra How do they diagnose an enlarged prostate? The American Urological Association (AUA) designed a series of questions that ask how often symptoms occur. The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) Index helps doctors measure the problems caused by enlarge prostate, ranging from mild to severe. Incomplete emptying Over the past month, how often have you had a sensation of not emptying your bladder completely? Frequency Over the past month, how often have you had to urinate again less than two hours after you finished urinating? Intermittency Over the past month, how often have you found you stopped and started again several times when you urinated? Urgency Over the last month, how difficult have you found it to postpone urination? Weak stream Over the past month, how often have you had a weak urinary stream? Straining Over the past month, how often have you had to push or strain to begin urination? Not at all Less than one time in 5 Less than half the time About half the time More than half the time Almost always Your score Nocturia Over the past month, many times did you most typically get up to urinate from the time you went to bed until the time you got up in the morning? Quality of life due to urinary symptoms Delighted Pleased Mostly satisfied None 1 time 2 times 3 times 4 times 5 times or more Your score Mixed about equally satisfied and dissatisfied Mostly dissatisfied Total IPSS score Unhappy Terrible If you were to spend the rest of your life with your urinary condition the way it is now, how would you feel about that? 6 Total score: 0-7 mildly symptomatic; 8-19 moderately symptomatic; severely symptomatic.
3 Who is at risk for an enlarged prostate? Prostate enlargement is common as men age. Experts are still learning what causes an enlarged prostate. Scientists have found that a hormone (dihydrotestosterone, or DHT) may cause the prostate to grow larger. Men who have close relatives with an enlarged prostate are more likely to have it. Being overweight may also increase a man s risk. Aging is the biggest risk factor for enlarged prostate. When a doctor checks a man for enlarged prostate, he or she takes a thorough medical history. The doctor performs a physical exam (including a DRE) and he or she may also ask questions about his symptoms. The doctor will often do a urine test called a urinalysis. They may offer other medical tests to a man who may have enlarged prostate. These include: 1. prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a blood test to screen for prostate cancer 2. urinary cytology, a urine test to screen for bladder cancer 3. measuring the amount of urine left in the bladder after urinating (the post-void residual volume or PVR) 4. a urine flow study (uroflowmetry), to measure of how fast urine flows when a man urinates 5. cystoscopy, a direct look in the urethra and/or bladder using a small flexible scope 6. urodynamic pressure-flow study that tests the pressures inside the bladder during urination 7. ultrasound or other imaging of the kidneys, bladder or prostate When should a man see a doctor about enlarged prostate? A man should see a doctor if he has any of the symptoms that are bothersome. In addition, he should see a doctor immediately if he has blood in his urine, pain with urination, burning with urination or is unable to urinate. Are there treatments for enlarged prostate problems? A urologist will examine a man with enlarged prostate to determine the best treatment option for him. There are medications to treat enlarged prostates. For some men, a combination of drugs may work best. If the medications do not help, some minimally invasive procedures and surgical procedures can help with the lower urinary tract symptoms. If the symptoms do not improve after treatment, men should report back to their doctor to see if there might be a different cause for their symptoms. Are there risks in not seeking treatment for an enlarged prostate? In many men, enlarged prostate can get worse over time. It can lead to bladder damage, infection and even kidney damage. A health care provider should monitor a man with enlarged prostate. Prostatitis Prostatitis is a common and painful disease of the prostate gland and its surrounding structures. Prostate What are the different types of prostatitis and their causes? Acute bacterial prostatitis is the least common type of prostatitis. Bacterial infections are always the cause. In acute bacterial prostatitis, the symptoms are severe and sudden and may cause the patient to seek emergency medical care. Chills, fever, severe burning during urination and being unable empty the bladder completely are common symptoms. A visit to a doctor or hospital is required. Acute bacterial prostatitis can affect any age group but commonly occurs in older and middle-aged men. Bacterial infections also cause chronic bacterial prostatitis. In this condition, a man has urinary tract infections that keep coming back. This condition is most common in young and middle-aged men. In chronic bacterial prostatitis, the symptoms include burning during urination; urinary frequency, especially at night; perineal, testicular, bladder and low back pain; and painful ejaculation. However, it does not cause a fever. Nonbacterial prostatitis and prostatodynia are now called chronic pelvic pain syndrome. These are the most common types of prostatitis. The symptoms of chronic pelvic pain syndrome include difficult and sometimes painful urination, discomfort or pain in the perineum, bladder, testicles and penis as well as difficult and painful ejaculation. In some cases, these symptoms can be hard to tell apart from those of chronic bacterial prostatitis. The exact cause of these non-bacterial
4 prostatitis conditions is unknown. They may be due to persistent infection, inflammation and/or pelvic muscle spasm. Inflammation in the prostate can also occur without symptoms. What causes prostatitis? The bacteria that cause acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis get into the prostate from the urethra by backward flow of infected urine into the prostate ducts. You cannot catch bacterial prostatitis from someone else. It is not a sexually transmitted disease. A sexual partner cannot catch this infection. Certain conditions or medical procedures increase the risk of having bacterial prostatitis. There is a higher risk if the man has recently had a catheter or other instrument inserted into his urethra. The risk may also be higher if a man has an abnormality of his urinary tract or a recent bladder infection. Unusual organisms such as chlamydia, mycoplasma (which may be transmitted by sexual contact) and ureaplasma may cause chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. It may also be due to a chemical or immunologic reaction to an injury. The nerves and muscles in the pelvis may cause pain in the area, either as a response to the prostate infection or inflammation or as an isolated problem itself. How do they diagnose prostatitis? The treatment is different for the different types of prostatitis syndromes. It is important to make sure other conditions such as urethritis, cystitis, an enlarged prostate or cancer are not causing the symptoms. To help make an accurate diagnosis, several types of examinations are useful. To examine the prostate gland, the doctor will perform a DRE. He or she will be able to feel if the prostate is enlarged or tender. Lumps or firm areas can suggest the presence of prostate cancer. He or she will also ask about the level of pain or discomfort that the man may feel as the doctor presses the muscles and ligaments of the pelvic floor and perineum. If a man has prostatitis, he may have some pain or discomfort with the DRE exam. The urologist may use cystoscopy, where he or she passes a small telescope through the urethra into the bladder. This allows the urologist to see the urethra, prostate and bladder. The urologist may also order urine flow studies, which help measure the strength of your urine flow and any blockage caused by the prostate, urethra or pelvic muscles. How do they treat prostatitis? There is no scientifically proven medication to cure prostatitis. The treatment recommended often depends on the type of prostatitis a man has. For many men with prostatitis, the urologist may give antibiotics. Depending on his symptoms, a man may receive other treatments. These may include alpha-blockers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, plant extracts and repeat prostatic massage (to drain the prostate ducts). Heat therapies, biofeedback and relaxation exercises may help relieve some symptoms. A man may be advised to stay away from some foods (e.g., spicy) and drinks (e.g., caffeinated, acidic) and avoid doing things (e.g., bicycle riding) that make the problem worse. Once he has a correct diagnosis, one of the best therapies may be that of reassurance that the man does not have a life threatening condition. How will prostatitis affect a patient? Prostatitis is frustrating for both the man and his doctor. It can seriously affect a man s quality of life. The correct diagnosis of the prostatitis problem is difficult. Prostatitis can be treated. A man can usually get relief from major symptoms by following the recommended treatment. A cure for prostatitis is not always possible. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a major healthcare problem in the United States. It is the most common non-skin cancer. Each year more than 200,000 American men learn they have prostate cancer. Sometimes this cancer can be small and slow growing, with a limited risk to the patient. Other prostate cancers may threaten his well-being or life. If the doctor wants a closer look at the prostate gland, a transrectal ultrasound uses sound waves to show an image of the prostate gland. If you are at risk for cancer, your physician may order a PSA test. During a prostate infection however, the PSA can be falsely high. The doctor may analyze the urine and prostatic fluid for signs of inflammation and infection. If the doctor thinks that a man has prostatitis or other prostate problems, he may refer him to a urologist. The urologist is a doctor who specializes in diseases of the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Prostate Cancer
5 What are the causes and risks of prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is rare before age 40 and the risk increases as a man ages. One in six men faces a diagnosis of prostate cancer in his lifetime. Researchers are still studying what causes prostate cancer. It is likely that prostate cancer occurs due to many reasons; some have to do with your family history or genetics, others with diet and lifestyle. Men with a close family member (father, brother or uncle) diagnosed with prostate cancer are at greater risk of getting prostate cancer. Prostate cancer also appears to be more common in men with a high intake of fat in their diets. Talk to your doctor about what you can do to reduce the risk of prostate cancer. Most doctors agree if you do things that are heart healthy, that you will also help keep your prostate healthy. Eating right, exercising and not smoking can help improve men s health. What are the symptoms of prostate cancer? In its early stages, prostate cancer often causes no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may include any of the following: dull pain in the lower pelvic area; frequent urination; problems with urination such as the inability, pain, burning, weakened urine flow; blood in the urine or semen; painful ejaculation; general pain in the lower back, hips or upper thighs; loss of appetite and/or weight; and persistent bone pain. The symptoms can be similar to those of BPH so it is very important to have the PSA and DRE when you have such symptoms. How do they diagnose prostate cancer? The DRE and PSA are the main methods to screen for prostate cancer. If the DRE and or PSA suggest further testing, a prostate biopsy is the next step to diagnose prostate cancer. The biopsy removes small pieces of prostate tissue. A pathologist (a physician who examines human tissue to see whether it is normal or diseased) will confirm if cancer is present in the biopsy tissue. If there is cancer, the pathologist will also grade the tumor. The grade indicates the tumor's degree of aggressiveness how quickly it is likely to grow and spread. The Gleason grading system is the most widely used system for prostate tumors. In this system, the pathologist gives the tumor pattern seen the most in the biopsy sample, a score from 1 to 5. The tumor pattern they see next most often, is also given a score, using the same scale. Both scores are added to give a Gleason score ranging between 2 and 10. Scores of 2 to 4 show low aggressiveness, 5 to 6 mildly aggressive, 7 moderately aggressive and scores of 8 to 10 depict highly aggressive prostate cancers. Why do they stage prostate cancer? The stage of prostate cancer guides a man s treatment options. Has it spread beyond the prostate gland to the nearby tissues? The urologist and other members of the health care team help guide men with prostate cancer as they learn about their treatment options. How do they treat prostate cancer? There are a number of treatment options for men with prostate cancer, the most common being surgery or internal (brachytherapy) or external radiation. The best option for each man depends on many factors, including his age, overall health, stage and grade of the cancer and personal preferences. Once diagnosed, men should discuss prostate cancer treatment options with their health care team. Prostate health is an important men s health issue Prostate health is important for men. Winning the battle against prostate diseases involves a team approach. With a urologist leading a team made up of healthcare workers, family and friends, men can take charge of their prostate health. For more information about prostate health issues, go to or call
6 The American Urological Association Foundation The AUA Foundation is the nation s leading voluntary urological healthcare organization that promotes research, patient/public education and advocacy. Our mission is to improve prevention, detection, treatment and, ultimately, cure urologic diseases. The AUA Foundation provides this information based on current medical and scientific knowledge. This information is not a tool for self-diagnosis or a substitute for professional medical advice. It is not to be used or relied on for that purpose. Please see your urologist or other healthcare provider regarding any health concerns and always consult a healthcare professional before you start or stop any treatments, including medications. For more information about the AUA Foundation, please visit Glossary: Acute bacterial prostatitis: The least common form of prostatitis caused by bacteria traveling up the urethra and the backward flow of infected urine into the prostatic ducts. Alpha-blockers: These drugs work by relaxing the smooth muscle of the prostate and bladder neck to improve urine flow and reduce bladder outlet obstruction. Although alpha-blockers may relieve the symptoms of BPH, they usually do not reduce the size of the prostate. Biopsy: A procedure in which a tiny piece of a body part (tissue sample), such as the prostate or bladder, is removed (with a needle or during surgery) for examination under a microscope to determine if cancer or other abnormal cells are present. Bladder neck: Area of thickened muscle fiber where the bladder joins the urethra. Acting on signals from the brain, bladder neck muscles can either tighten to hold urine in the bladder or relax to allow urine out and into the urethra. These muscles also tighten during ejaculation to prevent backflow of semen into the bladder. Bladder: The balloon-shaped pouch of thin, flexible muscle in which urine is temporarily stored before being discharged through the urethra. Catheter: A thin tube that is inserted through the urethra into the bladder to allow urine to drain or for performance of a procedure or test, such as insertion of a substance during a bladder X-ray. Chronic bacterial prostatitis: An uncommon form of prostatitis caused by bacteria traveling up the urethra and the backward flow of infected urine into the prostatic ducts causing recurrent infections. Cystitis: Also known as bladder infection. Urinary tract infection involving the bladder, which causes inflammation of the bladder and results in pain and a burning feeling in the pelvis or urethra. Cystoscopy: An examination with a narrow, flexible tube-like instrument passed through the urethra to examine the bladder and urinary tract for structural abnormalities or obstructions, such as tumors or stones. Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): Insertion of a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate and check for any abnormalities. Ejaculate: The fluid that is expelled from a man s penis during sexual climax (orgasm). To release semen from the penis during an orgasm. Ejaculation: Release of semen from the penis during sexual climax (orgasm). Immunologic: Relates to the immune system. Nocturia: Excessive urination at night; especially common in older men. Pathologist: A scientist who is skilled in identifying the cause and progress of diseases by examining tissue and fluid from the body, especially one who determines the cause of someone's death by conducting an autopsy. Pelvic: Relating to, involving or located in or near the pelvis. Penis: The male organ used for urination and sex. Perineum: The area between the anus and the scrotum in males. Pernieal: Related to the area between the anus and the scrotum in males and the area between the anus and the vagina in females. Prostate: In men, a walnut-shaped gland that surrounds the urethra at the neck of the bladder. The prostate supplies fluid that goes into semen. Prostatitis: Inflammation or infection of the prostate. Chronic prostatitis means the prostate gets inflamed repeatedly. The most common form of prostatitis is not associated with any known infecting organism. PSA Test: Also referred to as prostate-specific antigen test. A blood test used to help detect prostate cancer. PSA: Also referred to as prostate-specific antigen. A protein made only by the prostate gland. High levels of PSA in the blood may be a sign of prostate cancer. Rectum: The lower part of the large intestine, ending in the anal opening. Semen: Also known as seminal fluid or ejaculate fluid. Thick, whitish fluid produced by glands of the male reproductive system that carries the sperm (reproductive cells) through the penis during ejaculation. Seminal vesicles: Two pouch-like glands behind the bladder. They produce a sugar-rich fluid called fructose that provides sperm with a source of energy that helps sperm move. The fluid of the seminal vesicles makes up most of the volume of a man's ejaculatory fluid, or ejaculate. Sperm: Also referred to as spermatozoa. Male germ cells (gametes or reproductive cells) that are produced by the testicles and that are capable of fertilizing the female partner's eggs. Testicular: Relating to the testicle (testis). Tissue: Group of cells in an organism that are similar in form and function.
7 Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS): A special ultrasound test in which the sound waves are produced by a probe inserted into the rectum. In men, the structures most commonly examined with this test are the prostate, bladder, seminal vesicles and ejaculatory ducts. Tumor: An abnormal mass of tissue or growth of cells. Urethra: In males, this narrow tube carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body and serves as the channel through which semen is ejaculated. Extends from the bladder to the tip of the penis. Urethritis: Inflammation of the urethra. Urinalysis: An examination of the urine to determine the general health of the body. Urinary cytology: Inspection under a microscope of cells found in the urine. Urinary tract: The system that takes wastes from the blood and carries them out of the body in the form of urine. Passageway from the kidneys to the ureters, bladder and urethra. Urinate: To excrete urine. Urine: Liquid waste product filtered from the blood by the kidneys, stored in the bladder and expelled from the body through the urethra by the act of urinating (voiding). This AUA Foundation urologic information was provided to you by: For more information call the National Urology Health Line at or visit Corporate Boulevard Linthicum, MD This product made possible with funding from GlaxoSmithKline.
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER?
 PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
Talking about Prostate Cancer
 Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Prevention Series. Prostate Cancer. How to reduce your risk. Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca
 Prevention Series Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian
Prevention Series Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH
 MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH J E S S I C A E. P A O N E S S A, M. D. A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F U R O L O G Y S U N Y U P S T A T E M E D I C A L U N I V E R
MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH J E S S I C A E. P A O N E S S A, M. D. A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F U R O L O G Y S U N Y U P S T A T E M E D I C A L U N I V E R
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Prostate Cancer Screening
 Prostate Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team June Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Prostate Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team June Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
Testing for Prostate Cancer
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
The PSA Test for Prostate Cancer Screening:
 For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment. Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Prostate Cancer. An overview of. Treatment. Prolapse. Information and Answers
 Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Urinary Incontinence. Types
 Urinary Incontinence Leakage of urine is called urinary incontinence. It is a common problem in women. Some women occasionally leak small amounts of urine. At other times, leakage of urine is frequent
Urinary Incontinence Leakage of urine is called urinary incontinence. It is a common problem in women. Some women occasionally leak small amounts of urine. At other times, leakage of urine is frequent
Getting checked for Prostate Cancer
 Getting checked for Prostate Cancer Quick guide for men and their families and whanau Stay well for your family and whanau. doctor, nurse or health professional about prostate cancer. You should do this
Getting checked for Prostate Cancer Quick guide for men and their families and whanau Stay well for your family and whanau. doctor, nurse or health professional about prostate cancer. You should do this
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Testing for Prostate Cancer. Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me?
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
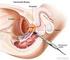 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Urinary Incontinence. Causes of Incontinence. What s Happening?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
A start to help you understand prostate cancer
 A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Understanding the PSA test. A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer
 Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
to Know About Your Partner s
 What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology
 Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence. Patient Information Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Urinary Tract Infections in Children
 Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
LIvING WITH Prostate Cancer
 Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate)
 Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) This leaflet is designed to answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) This leaflet is designed to answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
How to Improve Bladder After Bowler Cancer
 Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer. Understanding Your Treatment Options
 After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female)
 Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female) Definition: Increased urinary frequency > 8 voids / day More than 1 void/night in women 80 years old Diagnosis
Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female) Definition: Increased urinary frequency > 8 voids / day More than 1 void/night in women 80 years old Diagnosis
Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer
 Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer Treatment Plan Stage of prostate cancer: RADIATION THERAPY Radiation Treatments: Date for planning CT: Date to start radiation
Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer Treatment Plan Stage of prostate cancer: RADIATION THERAPY Radiation Treatments: Date for planning CT: Date to start radiation
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
 Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
Kegel Exercises for Men
 Kegel Exercises for Men The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Kegel Exercises for Men The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions
 Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Prostate Cancer. Patient Information
 Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you
 Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
A Physical Therapist s Perspective
 You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
Science Highlights. To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question.
 Science Highlights June 2012 by Ann A. Kiessling, PhD at the To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question. The current raucous debate over the commonly used PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer,
Science Highlights June 2012 by Ann A. Kiessling, PhD at the To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question. The current raucous debate over the commonly used PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer,
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Registered Charity No. 5365
 THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER?
 PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
GreenLight Laser Therapy for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
 GreenLight Laser Therapy for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) To learn about this procedure it helps to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm
GreenLight Laser Therapy for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) To learn about this procedure it helps to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm
PROSTATE CHANGES UNDERSTANDING A HEALTH GUIDE FOR MEN. family EDUCATION PATIENT. National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute
 UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CHANGES A HEALTH GUIDE FOR MEN PATIENT & family EDUCATION U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Table of Contents Introduction
UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CHANGES A HEALTH GUIDE FOR MEN PATIENT & family EDUCATION U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Table of Contents Introduction
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast. September 2012
 Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Answering Your Questions on prostate cancer
 Answering Your Questions on prostate cancer SECTION 1: THE BASICS Understanding prostate cancer may seem overwhelming at first. In this section, we will explain the basics: the who, what, where, when and
Answering Your Questions on prostate cancer SECTION 1: THE BASICS Understanding prostate cancer may seem overwhelming at first. In this section, we will explain the basics: the who, what, where, when and
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
PSA. and beyond. A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer
 PSA and beyond A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer This booklet is for men who are considering having a PSA test or want to know more about PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen). It explains how
PSA and beyond A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer This booklet is for men who are considering having a PSA test or want to know more about PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen). It explains how
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Making the Choice. Deciding What to Do About Early Stage Prostate Cancer
 Making the Choice Deciding What to Do About Early Stage Prostate Cancer We have all faced the same tough choices you face now. We talked with our doctors and others we love and trust. We each made our
Making the Choice Deciding What to Do About Early Stage Prostate Cancer We have all faced the same tough choices you face now. We talked with our doctors and others we love and trust. We each made our
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland
 Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland Information compiled by Daniel J. Faber, Coordinator of the Warriors+one, a Breakout Group of the Prostate Cancer Canada Network- Ottawa,
Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland Information compiled by Daniel J. Faber, Coordinator of the Warriors+one, a Breakout Group of the Prostate Cancer Canada Network- Ottawa,
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
 Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Prostate cancer screening. It s YOUR decision!
 Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
