[a] The 5 kω and 7 kω resistors are in series. The simplified circuit is shown below:
|
|
|
- Derick Chase
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 P 3.3 [a] The 5 kω and 7 kω resistors are in series. The simplified circuit is shown below: [b] The 800Ω and 1200Ω resistors are in series, as are the 300Ω and 200Ω resistors. The simplified circuit is shown below:
2 [c] The 35 Ω, 15 Ω, and 25 Ω resistors are in series. as are the 10 Ω and 40 Ω resistors. The simplified circuit is shown below: [d] The 50Ω and 90Ω resistors are in series, as are the 80Ω and 70Ω resistors. The simplified circuit is shown below: P 3.4 [a] The 36 Ω and 18 Ω resistors are in parallel. The simplified circuit is shown below: [b] The 200Ω and 120Ω resistors are in parallel, as are the 210Ω and 280Ω resistors. The simplified circuit is shown below: [c] The 100 kω, 150 kω, and 60 kω resistors are in parallel, as are the 75 kω and 50 kω resistors. The simplified circuit is shown below:
3 [d] The 750Ω and 500Ω resistors are in parallel, as are the 1.5 kω and 3 kω resistors. The simplified circuit is shown below:
4 P 3.7 [a] Circuit in Fig. P3.7(a): R eq = ([(15 60) + (30 45) + 20] 50) = [( ) 50] = (50 50) = = 60Ω Circuit in Fig. P3.7(b) begin by simplifying the 75Ω resistor and all resistors to its right: [( ) ] 75 = ( ) 75 = ( ) 75 = = 30Ω Now simplify the remainder of the circuit: R eq = ([( ) 50] + (20 60)) 40 = [(50 50) + 15] 40 = ( ) 40 = = 20Ω Circuit in Fig. P3.7(c) begin by simplifying the left and right sides of the circuit: R left = [( ) 2000] = ( ) = = 1500Ω R right = [( ) 1000] = ( ) = = 1500Ω Now find the equivalent resistance seen by the source: R eq = (R left R right ) = ( ) = = 4000 = 4 kω Circuit in Fig. P3.7(d): R eq = ([( ) 1000] + 100) ([( ) 500] + 300) = [( ) + 100] [( ) + 300] = ( ) ( ) = = 300Ω [b] Note that in every case, the power delivered by the source must equal the power absorbed by the equivalent resistance in the circuit. For the circuit in Fig. P3.7(a): P = V s 2 = 302 R eq 60 = 15 W For the circuit in Fig. P3.7(b): P = I 2 s (R eq) = (0.08) 2 (20) = = 128 mw For the circuit in Fig. P3.7(c): P = V s 2 = 202 R eq 4000 = 0.1 = 100 mw For the circuit in Fig. P3.7(d): P = I 2 s(r eq ) = (0.05) 2 (300) = 0.75 = 750 mw
5 P 3.12 [a] v o = 160(3300) ( ) = 66 V [b] i = 160/8000 = 20 ma P R1 = ( )( ) = 1.88 W P R2 = ( )( ) = 1.32 W [c] Since R 1 and R 2 carry the same current and R 1 > R 2 to satisfy the voltage requirement, first pick R 1 to meet the 0.5 W specification ( ) i R1 =, Therefore, R R 1 Thus, R R 1 or R 1 17,672Ω Now use the voltage specification: R 2 (160) = 66 R ,672 Thus, R 2 = 12,408Ω P = 20R 2 R so R 2 = 10Ω 3 = 20R e 40 + R e so R e = Ω Thus, = 10R L 10 + R L so R L = 24Ω
6 P 3.16 R eq = 10 [6 + 5 (8 + 12)] = 10 ( ) = 10 (6 + 4) = 5Ω v 10A = v 10Ω = (10 A)(5Ω) = 50 V Using voltage division: v 5Ω = 5 (8 + 12) (8 + 12) (50) = 4 (50) = 20 V Thus, p 5Ω = v2 5Ω 5 = = 80 W
7 P 3.20 [a] 20 kω + 40 kω = 60 kω 30 kω 60 kω = 20 kω v o1 = 20,000 (180) = 120 V (10, ,000) v o = 40,000 60,000 (v o1) = 80 V
8 [b] i = ,000 30,000i = 135 V = 4.5 ma v o = 40,000 (135) = 90 V 60,000 [c] It removes the loading effect of the second voltage divider on the first voltage divider. Observe that the open circuit voltage of the first divider is v o1 = 30,000 (180) = 135 V 40,000 Now note this is the input voltage to the second voltage divider when the current-controlled voltage source is used.
9 P 3.23 [a] The equivalent resistance of the 6 kω resistor and the resistors to its right is 6 k (5 k + 7 k) = 6 k 12 k = 4 kω
10 Using voltage division, v 6k = [b] v 5k = (18) = 6 V 5000 (6) = 2.5 V P 3.24 [a] The equivalent resistance of the 100Ω resistor and the resistors to its right is 100 ( ) = = 60Ω Using current division, i 50 = [b] v 70 = ( ) (0.03) = 120 (0.03) = = 18 ma 200 ( ) 100 (0.018) = 60 (0.018) = = 7.2 ma
11 P 3.28 [a] v 6k = 6 (18) = 13.5 V v 3k = 3 (18) = 4.5 V v x = v 6k v 3k = = 9 V [b] v 6k = 6 8 (V s) = 0.75V s v 3k = 3 12 (V s) = 0.25V s v x = (0.75V s ) (0.25V s ) = 0.5V s
12 P 3.32 Use current division to find the current in the 8Ω resistor. Begin by finding the equivalent resistance of the 8Ω resistor and all resistors to its right: R eq = ([(20 80) + 4] 30) + 8 = 20Ω i 8 = 60 R eq (0.25) = (0.25) = = ma R eq 20 Use current division to find i 1 from i 8 : i 1 = 30 [4 + (80 20)] 30 (i 8 ) = (0.1875) = = 75 ma 30
13 Use current division to find i 4Ω from i 8 : i 4Ω = 30 [4 + (80 20)] 4 + (80 20) (i 8 ) = (0.1875) = = ma 20 Finally, use current division to find i 2 from i 4Ω : i 2 = (i 4Ω) = (0.1125) = 0.09 = 90 ma 20
14 P 3.58 [a] Use the figure below to transform the Y to an equivalent : R a = R b = R c = (25)(30) + (25)(50) + (30)(50) 30 (25)(30) + (25)(50) + (30)(50) 50 (25)(30) + (25)(50) + (30)(50) 25 = = Ω = = 70Ω = = 140Ω
15 Replace the Y with its equivalent in the circuit to get the figure below: Find the equivalent resistance to the right of the 13Ω and 7Ω resistors: 70 [( ) + (20 140)] = 30Ω Thus, the equivalent resistance seen from the terminals a-b is: R ab = = 50Ω [b] Use the figure below to transform the to an equivalent Y: R 1 = (50)(20) = 10Ω R 2 = (50)(30) = 15Ω R 3 = (20)(30) = 6Ω
16 Replace the with its equivalent Y in the circuit to get the figure below: Find the equivalent resistance to the right of the 13Ω and 7Ω resistors: ( ) ( ) + 6 = 30Ω Thus, the equivalent resistance seen from the terminals a-b is: R ab = = 50Ω [c] Convert the delta connection R 1 R 2 R 3 to its equivalent wye. Convert the wye connection R 1 R 3 R 4 to its equivalent delta.
17 P 3.61 [a] After the 20 Ω 100 Ω 50 Ω wye is replaced by its equivalent delta, the circuit reduces to
18 Now the circuit can be reduced to i = 96 (1000) = 240 ma 400 i o = 400 (240) = 96 ma 1000 [b] i 1 = 80 (240) = 48 ma 400 [c] Now that i o and i 1 are known return to the original circuit v 2 = (50)(0.048) + (600)(0.096) = 60 V i 2 = v = = 600 ma [d] v g = v ( ) = = V p g = (v g )(1) = W Thus the current source delivers W.
19 P 3.67 [a] After making the Y-to- transformation, the circuit reduces to
20 Combining the parallel resistors reduces the circuit to Now note: 0.75R + 3RR L = 2.25R RR L 3R + R L 3R + R L Therefore ( 2.25R 2 ) RR L 3R 3R + R L R ab = ( 2.25R 2 ) = 3R(3R + 5R L) RR L 15R + 9R L 3R + 3R + R L If R = R L, we have R ab = 3R L(8R L ) 24R L Therefore R ab = R L = R L [b] When R = R L, the circuit reduces to i o = i i(3r L ) = 1 4.5R L 1.5 i i = v i R L, v o = 0.75R L i o = 1 2 v i, Therefore v o v i = 0.5
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Series and Parallel Circuits Components in a circuit can be connected in series or parallel. A series arrangement of components is where they are inline with each other, i.e. connected end-to-end. A parallel
Series and Parallel Circuits Components in a circuit can be connected in series or parallel. A series arrangement of components is where they are inline with each other, i.e. connected end-to-end. A parallel
Method 1: 30x50 30 50 18.75 15 18.75 0.8. 80 Method 2: 15
 The University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications ELEC Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Tutorial Solutions Q. In the figure below a voltage source and
The University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications ELEC Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Tutorial Solutions Q. In the figure below a voltage source and
= (0.400 A) (4.80 V) = 1.92 W = (0.400 A) (7.20 V) = 2.88 W
 Physics 2220 Module 06 Homework 0. What are the magnitude and direction of the current in the 8 Ω resister in the figure? Assume the current is moving clockwise. Then use Kirchhoff's second rule: 3.00
Physics 2220 Module 06 Homework 0. What are the magnitude and direction of the current in the 8 Ω resister in the figure? Assume the current is moving clockwise. Then use Kirchhoff's second rule: 3.00
Tristan s Guide to: Solving Series Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006. Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com
 Tristan s Guide to: Solving Series Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006 Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com Series Circuits. A Series circuit, in my opinion, is the simplest circuit
Tristan s Guide to: Solving Series Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006 Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com Series Circuits. A Series circuit, in my opinion, is the simplest circuit
CHAPTER 28 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 8 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 1. Sketch a circuit diagram for a circuit that includes a resistor R 1 connected to the positive terminal of a battery, a pair of parallel resistors R and R connected to the
CHAPTER 8 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 1. Sketch a circuit diagram for a circuit that includes a resistor R 1 connected to the positive terminal of a battery, a pair of parallel resistors R and R connected to the
Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection
 Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection Object To study the properties of series and parallel connection. Apparatus 1. DC circuit training system 2. Set of wires. 3. DC Power supply 4. Digital A.V.O.
Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection Object To study the properties of series and parallel connection. Apparatus 1. DC circuit training system 2. Set of wires. 3. DC Power supply 4. Digital A.V.O.
Tutorial 12 Solutions
 PHYS000 Tutorial 2 solutions Tutorial 2 Solutions. Two resistors, of 00 Ω and 200 Ω, are connected in series to a 6.0 V DC power supply. (a) Draw a circuit diagram. 6 V 00 Ω 200 Ω (b) What is the total
PHYS000 Tutorial 2 solutions Tutorial 2 Solutions. Two resistors, of 00 Ω and 200 Ω, are connected in series to a 6.0 V DC power supply. (a) Draw a circuit diagram. 6 V 00 Ω 200 Ω (b) What is the total
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
 Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) I. Charge (current flow) conservation law (the Kirchhoff s Current law) Pipe Pipe Pipe 3 Total volume of water per second flowing through pipe = total volume of water per
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) I. Charge (current flow) conservation law (the Kirchhoff s Current law) Pipe Pipe Pipe 3 Total volume of water per second flowing through pipe = total volume of water per
120 CHAPTER 3 NODAL AND LOOP ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES SUMMARY PROBLEMS SECTION 3.1
 IRWI03_082132v3 8/26/04 9:41 AM Page 120 120 CHAPTER 3 NODAL AND LOOP ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES SUMMARY Nodal analysis for an Nnode circuit Select one node in the Nnode circuit as the reference node. Assume
IRWI03_082132v3 8/26/04 9:41 AM Page 120 120 CHAPTER 3 NODAL AND LOOP ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES SUMMARY Nodal analysis for an Nnode circuit Select one node in the Nnode circuit as the reference node. Assume
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Preamble. Kirchoff Voltage Law (KVL) Series Resistors. In this section of my lectures we will be. resistor arrangements; series and
 Preamble Series and Parallel Circuits Physics, 8th Edition Custom Edition Cutnell & Johnson Chapter 0.6-0.8, 0.0 Pages 60-68, 69-6 n this section of my lectures we will be developing the two common types
Preamble Series and Parallel Circuits Physics, 8th Edition Custom Edition Cutnell & Johnson Chapter 0.6-0.8, 0.0 Pages 60-68, 69-6 n this section of my lectures we will be developing the two common types
Lecture Notes ELE A6
 ecture Notes EE A6 Ramadan El-Shatshat Three Phase circuits 9/12/2006 EE A6 Three-phase Circuits 1 Three-phase Circuits 9/12/2006 EE A6 Three-phase Circuits 2 Advantages of Three-phase Circuits Smooth
ecture Notes EE A6 Ramadan El-Shatshat Three Phase circuits 9/12/2006 EE A6 Three-phase Circuits 1 Three-phase Circuits 9/12/2006 EE A6 Three-phase Circuits 2 Advantages of Three-phase Circuits Smooth
Experiment 8 Series-Parallel Circuits
 Experiment 8 Series-Parallel Circuits EL 111 - DC Fundamentals By: Walter Banzhaf, E.K. Smith, and Winfield Young University of Hartford Ward College of Technology Objectives: 1. For the student to measure
Experiment 8 Series-Parallel Circuits EL 111 - DC Fundamentals By: Walter Banzhaf, E.K. Smith, and Winfield Young University of Hartford Ward College of Technology Objectives: 1. For the student to measure
Circuit Analyses. Laboration 1 how to measure Current and Voltage and Resistance
 Circuit Analyses. Laboration 1 how to measure Current and Voltage and Resistance This booklet, signed by the teacher, serves as a receipt for passing the lab. Each student must have a booklet of his own
Circuit Analyses. Laboration 1 how to measure Current and Voltage and Resistance This booklet, signed by the teacher, serves as a receipt for passing the lab. Each student must have a booklet of his own
13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571
 13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571 Key Concepts: 5. Connecting loads in series and parallel affects the current, potential difference, and total resistance. - Using your knowledge of
13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571 Key Concepts: 5. Connecting loads in series and parallel affects the current, potential difference, and total resistance. - Using your knowledge of
Resistors. Some substances are insulators. A battery will not make detectible current flow through them.
 Resistors Some substances are insulators. A battery will not make detectible current flow through them. Many substances (lead, iron, graphite, etc.) will let current flow. For most substances that are
Resistors Some substances are insulators. A battery will not make detectible current flow through them. Many substances (lead, iron, graphite, etc.) will let current flow. For most substances that are
Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law
 Experiment 2 31 Kuwait University Physics 107 Physics Department Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law Introduction In this experiment the relations among voltages, currents and resistances for
Experiment 2 31 Kuwait University Physics 107 Physics Department Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law Introduction In this experiment the relations among voltages, currents and resistances for
Chapter 19. Electric Circuits
 Chapter 9 Electric Circuits Series Wiring There are many circuits in which more than one device is connected to a voltage source. Series wiring means that the devices are connected in such a way that there
Chapter 9 Electric Circuits Series Wiring There are many circuits in which more than one device is connected to a voltage source. Series wiring means that the devices are connected in such a way that there
Tristan s Guide to: Solving Parallel Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006. Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com
 Tristan s Guide to: Solving Parallel Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006 Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com Parallel Circuits. Parallel Circuits are a little bit more complicated
Tristan s Guide to: Solving Parallel Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006 Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com Parallel Circuits. Parallel Circuits are a little bit more complicated
Chapter 24. Three-Phase Voltage Generation
 Chapter 24 Three-Phase Systems Three-Phase Voltage Generation Three-phase generators Three sets of windings and produce three ac voltages Windings are placed 120 apart Voltages are three identical sinusoidal
Chapter 24 Three-Phase Systems Three-Phase Voltage Generation Three-phase generators Three sets of windings and produce three ac voltages Windings are placed 120 apart Voltages are three identical sinusoidal
Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel
 Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel Objective: In this experiment you will set up three circuits: one with resistors in series, one with resistors in parallel, and one with some of each. You
Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel Objective: In this experiment you will set up three circuits: one with resistors in series, one with resistors in parallel, and one with some of each. You
AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR
 AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR INTRODUCTION This Project "Automatic Night Lamp with Morning Alarm" was developed using Microprocessor. It is the Heart of the system. The sensors
AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR INTRODUCTION This Project "Automatic Night Lamp with Morning Alarm" was developed using Microprocessor. It is the Heart of the system. The sensors
Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems
 c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems This document contains
c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems This document contains
AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules
 Name Period AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules Dr. Campbell 1. Four 240 Ω light bulbs are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? What
Name Period AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules Dr. Campbell 1. Four 240 Ω light bulbs are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? What
Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits
 Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits PREPARED BY IAT Curriculum Unit August 2008 Institute of Applied Technology, 2008 ATE310- Electrical Fundamentals 2 Module 3 Parallel Circuits Module
Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits PREPARED BY IAT Curriculum Unit August 2008 Institute of Applied Technology, 2008 ATE310- Electrical Fundamentals 2 Module 3 Parallel Circuits Module
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 15 Combination Circuits (Series-Parallel Circuits)
 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 15 Combination Circuits (Series-Parallel Circuits) Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz Electricity and Electronics, Chapter 8, Introduction: o
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 15 Combination Circuits (Series-Parallel Circuits) Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz Electricity and Electronics, Chapter 8, Introduction: o
Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods
 Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods We have seen that using Kirchhoff s laws and Ohm s law we can analyze any circuit to determine the operating conditions (the currents and voltages). The
Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods We have seen that using Kirchhoff s laws and Ohm s law we can analyze any circuit to determine the operating conditions (the currents and voltages). The
Chapter 5. Parallel Circuits ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 5 Parallel Circuits Objectives Identify a parallel circuit Determine the voltage across each parallel branch Apply Kirchhoff s current law Determine total parallel resistance Apply Ohm s law in
Chapter 5 Parallel Circuits Objectives Identify a parallel circuit Determine the voltage across each parallel branch Apply Kirchhoff s current law Determine total parallel resistance Apply Ohm s law in
Application for Small Generator Facility Interconnection Tier 2, Tier 3 or Tier 4 Interconnection
 Application for Small Generator Facility Interconnection Tier 2, Tier 3 or Tier 4 Interconnection (See ARSD chapter 20:10:36 for the requirements for a Tier 2, Tier 3, or Tier 4 Interconnection.) Applicant/Interconnection
Application for Small Generator Facility Interconnection Tier 2, Tier 3 or Tier 4 Interconnection (See ARSD chapter 20:10:36 for the requirements for a Tier 2, Tier 3, or Tier 4 Interconnection.) Applicant/Interconnection
Physics 133: tutorial week 4 Ohm s law, electrical power, emf and internal resistance.
 Physics 133: tutorial week 4 Ohm s law, electrical power, emf and internal resistance. 41. The heating element of a clothes drier has a resistance of 11Ïand is connected across a 240V electrical outlet.
Physics 133: tutorial week 4 Ohm s law, electrical power, emf and internal resistance. 41. The heating element of a clothes drier has a resistance of 11Ïand is connected across a 240V electrical outlet.
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits
 Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits The configuration of circuit elements clearly affects the behaviour of a circuit. Resistors connected in series or in parallel are very common in a circuit and act
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits The configuration of circuit elements clearly affects the behaviour of a circuit. Resistors connected in series or in parallel are very common in a circuit and act
HOW TO USE MULTIMETER. COMPILE BY: Dzulautotech
 HOW TO USE MULTIMETER COMPILE BY: Dzulautotech 1. GENERAL Electricity is absolutely necessary for an automobile. It is indispensable when the engine is started, the air fuel mixture is ignited and exploded,
HOW TO USE MULTIMETER COMPILE BY: Dzulautotech 1. GENERAL Electricity is absolutely necessary for an automobile. It is indispensable when the engine is started, the air fuel mixture is ignited and exploded,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 67 - FURTHER ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 TUTORIAL 1 - DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUIT THEOREMS
 EDEXCE NATIONA CERTIFICATE/DIPOMA UNIT 67 - FURTHER EECTRICA PRINCIPES NQF EVE 3 OUTCOME 1 TUTORIA 1 - DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUIT THEOREMS Unit content 1 Be able to apply direct current (DC) circuit analysis
EDEXCE NATIONA CERTIFICATE/DIPOMA UNIT 67 - FURTHER EECTRICA PRINCIPES NQF EVE 3 OUTCOME 1 TUTORIA 1 - DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUIT THEOREMS Unit content 1 Be able to apply direct current (DC) circuit analysis
GE Multilin technical note
 Digital Energy Multilin GE Multilin technical note eutral voltage unbalance function at grounded wye capacitor banks GE publication number: GET-8544 Copyright 00 GE Multilin eutral voltage unbalance function
Digital Energy Multilin GE Multilin technical note eutral voltage unbalance function at grounded wye capacitor banks GE publication number: GET-8544 Copyright 00 GE Multilin eutral voltage unbalance function
THE BREADBOARD; DC POWER SUPPLY; RESISTANCE OF METERS; NODE VOLTAGES AND EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE; THÉVENIN EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
 THE BREADBOARD; DC POWER SUPPLY; RESISTANCE OF METERS; NODE VOLTAGES AND EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE; THÉVENIN EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT YOUR NAME LAB MEETING TIME Reference: C.W. Alexander and M.N.O Sadiku, Fundamentals
THE BREADBOARD; DC POWER SUPPLY; RESISTANCE OF METERS; NODE VOLTAGES AND EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE; THÉVENIN EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT YOUR NAME LAB MEETING TIME Reference: C.W. Alexander and M.N.O Sadiku, Fundamentals
Application Note 82 Using the Dallas Trickle Charge Timekeeper
 www.maxim-ic.com Application Note 82 Using the Dallas Trickle Charge Timekeeper DESCRIPTION The Dallas Semiconductor/Maxim real-time clock (RTC) family contains a number of parts within an integrated trickle-charging
www.maxim-ic.com Application Note 82 Using the Dallas Trickle Charge Timekeeper DESCRIPTION The Dallas Semiconductor/Maxim real-time clock (RTC) family contains a number of parts within an integrated trickle-charging
Measuring Temperature withthermistors a Tutorial David Potter
 NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS The Software is the Instrument Application Note 065 Measuring Temperature withthermistors a Tutorial David Potter Introduction Thermistors are thermally sensitive resistors used in
NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS The Software is the Instrument Application Note 065 Measuring Temperature withthermistors a Tutorial David Potter Introduction Thermistors are thermally sensitive resistors used in
Thevenin Equivalent Circuits
 hevenin Equivalent Circuits Introduction In each of these problems, we are shown a circuit and its hevenin or Norton equivalent circuit. he hevenin and Norton equivalent circuits are described using three
hevenin Equivalent Circuits Introduction In each of these problems, we are shown a circuit and its hevenin or Norton equivalent circuit. he hevenin and Norton equivalent circuits are described using three
Student Exploration: Circuits
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Circuits Vocabulary: ammeter, circuit, current, ohmmeter, Ohm s law, parallel circuit, resistance, resistor, series circuit, voltage Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Circuits Vocabulary: ammeter, circuit, current, ohmmeter, Ohm s law, parallel circuit, resistance, resistor, series circuit, voltage Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these
Experiment: Series and Parallel Circuits
 Phy203: General Physics Lab page 1 of 6 Experiment: Series and Parallel Circuits OBJECTVES MATERALS To study current flow and voltages in series and parallel circuits. To use Ohm s law to calculate equivalent
Phy203: General Physics Lab page 1 of 6 Experiment: Series and Parallel Circuits OBJECTVES MATERALS To study current flow and voltages in series and parallel circuits. To use Ohm s law to calculate equivalent
Section 3. Sensor to ADC Design Example
 Section 3 Sensor to ADC Design Example 3-1 This section describes the design of a sensor to ADC system. The sensor measures temperature, and the measurement is interfaced into an ADC selected by the systems
Section 3 Sensor to ADC Design Example 3-1 This section describes the design of a sensor to ADC system. The sensor measures temperature, and the measurement is interfaced into an ADC selected by the systems
Experiment #5, Series and Parallel Circuits, Kirchhoff s Laws
 Physics 182 Summer 2013 Experiment #5 1 Experiment #5, Series and Parallel Circuits, Kirchhoff s Laws 1 Purpose Our purpose is to explore and validate Kirchhoff s laws as a way to better understanding
Physics 182 Summer 2013 Experiment #5 1 Experiment #5, Series and Parallel Circuits, Kirchhoff s Laws 1 Purpose Our purpose is to explore and validate Kirchhoff s laws as a way to better understanding
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
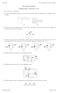 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Example: Determine the power supplied by each of the sources, independent and dependent, in this circuit:
 Example: Determine the power supplied by each of the sources, independent and dependent, in this circuit: Solution: We ll begin by choosing the bottom node to be the reference node. Next we ll label the
Example: Determine the power supplied by each of the sources, independent and dependent, in this circuit: Solution: We ll begin by choosing the bottom node to be the reference node. Next we ll label the
Lab #4 Thevenin s Theorem
 In this experiment you will become familiar with one of the most important theorems in circuit analysis, Thevenin s Theorem. Thevenin s Theorem can be used for two purposes: 1. To calculate the current
In this experiment you will become familiar with one of the most important theorems in circuit analysis, Thevenin s Theorem. Thevenin s Theorem can be used for two purposes: 1. To calculate the current
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents. Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49
 Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Solutions to Bulb questions
 Solutions to Bulb questions Note: We did some basic circuits with bulbs in fact three main ones I can think of I have summarized our results below. For the final exam, you must have an understanding of
Solutions to Bulb questions Note: We did some basic circuits with bulbs in fact three main ones I can think of I have summarized our results below. For the final exam, you must have an understanding of
100% Stator Ground Fault Detection Implementation at Hibbard Renewable Energy Center. 598 N. Buth Rd 3215 Arrowhead Rd
 100% Stator Ground Fault Detection Implementation at Hibbard Renewable Energy Center Introduction Roger Hedding Steven Schoenherr, P.E. ABB Inc. Minnesota Power 598 N. Buth Rd 3215 Arrowhead Rd Dousman,
100% Stator Ground Fault Detection Implementation at Hibbard Renewable Energy Center Introduction Roger Hedding Steven Schoenherr, P.E. ABB Inc. Minnesota Power 598 N. Buth Rd 3215 Arrowhead Rd Dousman,
How To Find The Current Of A Circuit
 The node voltage method Equivalent resistance Voltage / current dividers Source transformations Node voltages Mesh currents Superposition Not every circuit lends itself to short-cut methods. Sometimes
The node voltage method Equivalent resistance Voltage / current dividers Source transformations Node voltages Mesh currents Superposition Not every circuit lends itself to short-cut methods. Sometimes
The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure
 The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I
 Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I Objectives The objective of this lab is to study operational amplifier (op amp) and its applications. We will be simulating and building some basic op amp circuits,
Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I Objectives The objective of this lab is to study operational amplifier (op amp) and its applications. We will be simulating and building some basic op amp circuits,
THE PER-UNIT SYSTEM. (2) The per-unit values for various components lie within a narrow range regardless of the equipment rating.
 THE PER-UNIT SYSTEM An interconnected power system typically consists of many different voltage levels given a system containing several transformers and/or rotating machines. The per-unit system simplifies
THE PER-UNIT SYSTEM An interconnected power system typically consists of many different voltage levels given a system containing several transformers and/or rotating machines. The per-unit system simplifies
BJT AC Analysis. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
Constant Voltage and Constant Current Controller for Adaptors and Battery Chargers
 TECHNICAL DATA Constant Voltage and Constant Current Controller for Adaptors and Battery Chargers IK3051 Description IK3051 is a highly integrated solution for SMPS applications requiring constant voltage
TECHNICAL DATA Constant Voltage and Constant Current Controller for Adaptors and Battery Chargers IK3051 Description IK3051 is a highly integrated solution for SMPS applications requiring constant voltage
www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LF411 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LF411 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description
Unit 33 Three-Phase Motors
 Unit 33 Three-Phase Motors Objectives: Discuss the operation of wound rotor motors. Discuss the operation of selsyn motors. Discuss the operation of synchronous motors. Determine the direction of rotation
Unit 33 Three-Phase Motors Objectives: Discuss the operation of wound rotor motors. Discuss the operation of selsyn motors. Discuss the operation of synchronous motors. Determine the direction of rotation
1Meg. 11.A. Resistive Circuit Nodal Analysis
 11. Creating and Using Netlists PART 11 Creating and Using Netlists For this entire text, we have created circuits schematically and then run simulations. Behind the scenes, Capture generates a netlist
11. Creating and Using Netlists PART 11 Creating and Using Netlists For this entire text, we have created circuits schematically and then run simulations. Behind the scenes, Capture generates a netlist
PHOTOTRANSISTOR OPTOCOUPLERS
 MCT2 MCT2E MCT20 MCT27 WHITE PACKAGE (-M SUFFIX) BLACK PACKAGE (NO -M SUFFIX) DESCRIPTION The MCT2XXX series optoisolators consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode driving a silicon phototransistor
MCT2 MCT2E MCT20 MCT27 WHITE PACKAGE (-M SUFFIX) BLACK PACKAGE (NO -M SUFFIX) DESCRIPTION The MCT2XXX series optoisolators consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode driving a silicon phototransistor
STF201-22 & STF201-30
 Description The STF201 is a combination EMI filter and line termination device with integrated TVS diodes for use on downstream USB ports. It is constructed using a proprietary technology that allows passive
Description The STF201 is a combination EMI filter and line termination device with integrated TVS diodes for use on downstream USB ports. It is constructed using a proprietary technology that allows passive
POWER SUPPLY MODEL XP-15. Instruction Manual ELENCO
 POWER SUPPLY MODEL XP-15 Instruction Manual ELENCO Copyright 2013 by Elenco Electronics, Inc. REV-A 753020 All rights reserved. No part of this book shall be reproduced by any means; electronic, photocopying,
POWER SUPPLY MODEL XP-15 Instruction Manual ELENCO Copyright 2013 by Elenco Electronics, Inc. REV-A 753020 All rights reserved. No part of this book shall be reproduced by any means; electronic, photocopying,
Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models
 EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Current, Voltage, Impedance Ohm
EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Current, Voltage, Impedance Ohm
Physical Address: City: State: Zip Code:
 Application for Small Generator Facility Interconnection Tier 2, Tier 3 or Tier 4 Interconnection (For Small Generator Facilities with Electric Nameplate Capacities of 10 MW and less) Applicant Contact
Application for Small Generator Facility Interconnection Tier 2, Tier 3 or Tier 4 Interconnection (For Small Generator Facilities with Electric Nameplate Capacities of 10 MW and less) Applicant Contact
Transformer circuit calculations
 Transformer circuit calculations This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Transformer circuit calculations This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
How To Control A Power Supply On A Powerline With A.F.F Amplifier
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Sound I.F. amplifier/demodulator for TV File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 March 1986 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is an i.f. amplifier with a symmetrical FM demodulator and
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Sound I.F. amplifier/demodulator for TV File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 March 1986 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is an i.f. amplifier with a symmetrical FM demodulator and
Module 2. DC Circuit. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module DC Circuit Lesson 4 Loop Analysis of resistive circuit in the context of dc voltages and currents Objectives Meaning of circuit analysis; distinguish between the terms mesh and loop. To provide
Module DC Circuit Lesson 4 Loop Analysis of resistive circuit in the context of dc voltages and currents Objectives Meaning of circuit analysis; distinguish between the terms mesh and loop. To provide
Circuits. The light bulbs in the circuits below are identical. Which configuration produces more light? (a) circuit I (b) circuit II (c) both the same
 Circuits The light bulbs in the circuits below are identical. Which configuration produces more light? (a) circuit I (b) circuit II (c) both the same Circuit II has ½ current of each branch of circuit
Circuits The light bulbs in the circuits below are identical. Which configuration produces more light? (a) circuit I (b) circuit II (c) both the same Circuit II has ½ current of each branch of circuit
Development of a Single Phase Automatic Change-Over Switch
 Development of a Single Phase Automatic Change-Over Switch M.S. Ahmed, A.S. Mohammed and O.. Agusiobo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Federal University of Technology Minna, Nigeria
Development of a Single Phase Automatic Change-Over Switch M.S. Ahmed, A.S. Mohammed and O.. Agusiobo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Federal University of Technology Minna, Nigeria
See Horenstein 4.3 and 4.4
 EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes by Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (2/14/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated
EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes by Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (2/14/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
VJ 6040 Mobile Digital TV UHF Antenna Evaluation Board
 VISHAY VITRAMON Multilayer Chip Capacitors Application Note GENERAL is a multilayer ceramic chip antenna designed for receiving mobile digital TV transmissions in the UHF band. The target application for
VISHAY VITRAMON Multilayer Chip Capacitors Application Note GENERAL is a multilayer ceramic chip antenna designed for receiving mobile digital TV transmissions in the UHF band. The target application for
Alkaline Manganese (Mercury free) IEC: LR03; JIS: AM-4; ANSI: AAA; MN2400; Micro chemical system: Zn / KOH-H 2 O / MnO 2
 IEC: LR03; JIS: AM-4; ANSI: AAA; MN2400; Micro rated: 1200 mah discharge at 10mA load; 24hours/day 1070 mah discharge at 75ohms load; 24hours/day minimum: 1050 mah discharge at 20mA constant current 300
IEC: LR03; JIS: AM-4; ANSI: AAA; MN2400; Micro rated: 1200 mah discharge at 10mA load; 24hours/day 1070 mah discharge at 75ohms load; 24hours/day minimum: 1050 mah discharge at 20mA constant current 300
3 The TTL NAND Gate. Fig. 3.1 Multiple Input Emitter Structure of TTL
 3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
Reliability Applications (Independence and Bayes Rule)
 Reliability Applications (Independence and Bayes Rule ECE 313 Probability with Engineering Applications Lecture 5 Professor Ravi K. Iyer University of Illinois Today s Topics Review of Physical vs. Stochastic
Reliability Applications (Independence and Bayes Rule ECE 313 Probability with Engineering Applications Lecture 5 Professor Ravi K. Iyer University of Illinois Today s Topics Review of Physical vs. Stochastic
NAME: DATE: (Please Print) RESISTOR NETWORK AND OHMS LAW PRACTICE EXAM (See formulas at the back of this exam) 120 Volts AC 35 Ohms
 NAM: DAT: (lease rint) RSISTOR NTWORK AND OHMS LAW RACTIC XAM (See formulas at the back of this exam) 25 Ohms 120 Volts AC 35 Ohms 1. Based on the drawing above, what is the total circuit resistance? This
NAM: DAT: (lease rint) RSISTOR NTWORK AND OHMS LAW RACTIC XAM (See formulas at the back of this exam) 25 Ohms 120 Volts AC 35 Ohms 1. Based on the drawing above, what is the total circuit resistance? This
LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER. Bridge Rectifier
 LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER Full-wave Rectification: Bridge Rectifier For many electronic circuits, DC supply voltages are required but only AC voltages are available.
LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER Full-wave Rectification: Bridge Rectifier For many electronic circuits, DC supply voltages are required but only AC voltages are available.
CAN-Bus Troubleshooting Guide
 CAN-Bus Troubleshooting Guide CAN-Troubleshooting Guide Rev. 1.1 Seite 1 von 8 esd electronic system design gmbh Vahrenwalder Str. 207 30165 Hannover Germany www.esd-electronics.com Fax: 0511/37 29 8-68
CAN-Bus Troubleshooting Guide CAN-Troubleshooting Guide Rev. 1.1 Seite 1 von 8 esd electronic system design gmbh Vahrenwalder Str. 207 30165 Hannover Germany www.esd-electronics.com Fax: 0511/37 29 8-68
AC Transport constant current vs. low impedance modes
 Application Note 184-42 AC Transport constant current vs. low impedance modes The AC Transport option offers the user the ability to put the current source in a low output impedance mode. This mode is
Application Note 184-42 AC Transport constant current vs. low impedance modes The AC Transport option offers the user the ability to put the current source in a low output impedance mode. This mode is
3. On the top menu bar, click on File > New > Project as shown in Fig. 2 below: Figure 2 Window for Orcad Capture CIS
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of North Texas Denton, TX. 76207 EENG 2920 Quickstart PSpice Tutorial Tutorial Prepared by Oluwayomi Adamo 1. To run the PSpice program, click on Start >
Department of Electrical Engineering University of North Texas Denton, TX. 76207 EENG 2920 Quickstart PSpice Tutorial Tutorial Prepared by Oluwayomi Adamo 1. To run the PSpice program, click on Start >
Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V. Huan Lin
 Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V Huan Lin 4/2/2010 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Objective... Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Implementation...
Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V Huan Lin 4/2/2010 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Objective... Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Implementation...
Equipment: Power Supply, DAI, Variable resistance (8311), Variable inductance (8321)
 Lab 4: 3-phase circuits. Objective: to study voltage-current relationships in 3-phase circuits; to learn to make delta and Y connections; to calculate and measure real, apparent, and reactive powers. Equipment:
Lab 4: 3-phase circuits. Objective: to study voltage-current relationships in 3-phase circuits; to learn to make delta and Y connections; to calculate and measure real, apparent, and reactive powers. Equipment:
Lab 2: Resistance, Current, and Voltage
 2 Lab 2: Resistance, Current, and Voltage I. Before you come to la.. A. Read the following chapters from the text (Giancoli): 1. Chapter 25, sections 1, 2, 3, 5 2. Chapter 26, sections 1, 2, 3 B. Read
2 Lab 2: Resistance, Current, and Voltage I. Before you come to la.. A. Read the following chapters from the text (Giancoli): 1. Chapter 25, sections 1, 2, 3, 5 2. Chapter 26, sections 1, 2, 3 B. Read
First Order Circuits. EENG223 Circuit Theory I
 First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
Resistors in Series and Parallel Circuits
 69 Resistors in Series and Parallel Circuits E&M: Series and parallel circuits Equipment List DataStudio file: Not Required Qty s Part Numbers 1 C/DC Electronics Lab EM-8656 2 D cell 1.5 volt Introduction
69 Resistors in Series and Parallel Circuits E&M: Series and parallel circuits Equipment List DataStudio file: Not Required Qty s Part Numbers 1 C/DC Electronics Lab EM-8656 2 D cell 1.5 volt Introduction
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits Physics Lab VIII
 Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits Physics Lab VIII Objective In the set of experiments, the theoretical expressions used to calculate the total resistance in a combination of resistors will be tested
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits Physics Lab VIII Objective In the set of experiments, the theoretical expressions used to calculate the total resistance in a combination of resistors will be tested
Σ I in = Σ I out E = IR 1 + IR 2 FXA 2008 KIRCHHOFF S LAWS 1. Candidates should be able to : LAW 1 (K1)
 UNT G482 Module 3 2.3.1 Series & Parallel Circuits Candidates should be able to : KRCHHOFF S LAWS 1 LAW 1 (K1) State Kirchhoff s second law and appreciate that it is a consequence of conservation of energy.
UNT G482 Module 3 2.3.1 Series & Parallel Circuits Candidates should be able to : KRCHHOFF S LAWS 1 LAW 1 (K1) State Kirchhoff s second law and appreciate that it is a consequence of conservation of energy.
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Pre-Laboratory Assignment Series and Parallel Circuits ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis Laboratory updated 16 May 2011 1. Consider the following series circuit. Derive a formula to calculate voltages V 1, V 2,
Pre-Laboratory Assignment Series and Parallel Circuits ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis Laboratory updated 16 May 2011 1. Consider the following series circuit. Derive a formula to calculate voltages V 1, V 2,
ELECTRONIC POWER SYSTEMS
 ELECTRONIC POWER SYSTEMS TRADEOFFS BETWEEN SINGLE-PHASE & THREE-PHASE POWER WHITE PAPER: TW0057 1 Executive Summary Modern Electronic Systems are quite often powered from a three-phase power source. While
ELECTRONIC POWER SYSTEMS TRADEOFFS BETWEEN SINGLE-PHASE & THREE-PHASE POWER WHITE PAPER: TW0057 1 Executive Summary Modern Electronic Systems are quite often powered from a three-phase power source. While
The Programming Interface
 : In-System Programming Features Program any AVR MCU In-System Reprogram both data Flash and parameter EEPROM memories Eliminate sockets Simple -wire SPI programming interface Introduction In-System programming
: In-System Programming Features Program any AVR MCU In-System Reprogram both data Flash and parameter EEPROM memories Eliminate sockets Simple -wire SPI programming interface Introduction In-System programming
SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS
 Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong SAE 800
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
Series 90 Series 90HV
 Series 90 Series 90HV PC-BASED CONTINUITY TESTERS Cablescan s Series 90 PC-based circuit analyzers provide exceptional speed, versatility, and SERIES 90 accuracy in the testing of wire harnesses and backplanes,
Series 90 Series 90HV PC-BASED CONTINUITY TESTERS Cablescan s Series 90 PC-based circuit analyzers provide exceptional speed, versatility, and SERIES 90 accuracy in the testing of wire harnesses and backplanes,
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier
 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits
 Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
Series-Parallel Circuits. Objectives
 Series-Parallel Circuits Objectives Identify series-parallel configuration Analyze series-parallel circuits Apply KVL and KCL to the series-parallel circuits Analyze loaded voltage dividers Determine the
Series-Parallel Circuits Objectives Identify series-parallel configuration Analyze series-parallel circuits Apply KVL and KCL to the series-parallel circuits Analyze loaded voltage dividers Determine the
Using Ohm s Law to Build a Voltage Divider
 Using Ohm s Law to Build a Voltage Provided by TryEngineering - Lesson Focus Students will design, build, and characterize one of the basic circuits of electrical engineering, the voltage divider. These
Using Ohm s Law to Build a Voltage Provided by TryEngineering - Lesson Focus Students will design, build, and characterize one of the basic circuits of electrical engineering, the voltage divider. These
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY. Fig. 8.1a Fig 8.1b
 DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
12. The current in an inductor is changing at the rate of 100 A/s, and the inductor emf is 40 V. What is its self-inductance?
 12. The current in an inductor is changing at the rate of 100 A/s, and the inductor emf is 40 V. What is its self-inductance? From Equation 32-5, L = -E=(dI =dt) = 40 V=(100 A/s) = 0.4 H. 15. A cardboard
12. The current in an inductor is changing at the rate of 100 A/s, and the inductor emf is 40 V. What is its self-inductance? From Equation 32-5, L = -E=(dI =dt) = 40 V=(100 A/s) = 0.4 H. 15. A cardboard
Automatic Impedance Matching for 13.56 MHz NFC Antennas
 Automatic Impedance Matching for 13.56 MHz NFC Antennas Michael Roland 1, Harald Witschnig 2, Erich Merlin 2, Christian Saminger 1 1 Upper Austria University of Applied Sciences, Hagenberg, Austria 2 NXP
Automatic Impedance Matching for 13.56 MHz NFC Antennas Michael Roland 1, Harald Witschnig 2, Erich Merlin 2, Christian Saminger 1 1 Upper Austria University of Applied Sciences, Hagenberg, Austria 2 NXP
MAS.836 HOW TO BIAS AN OP-AMP
 MAS.836 HOW TO BIAS AN OP-AMP Op-Amp Circuits: Bias, in an electronic circuit, describes the steady state operating characteristics with no signal being applied. In an op-amp circuit, the operating characteristic
MAS.836 HOW TO BIAS AN OP-AMP Op-Amp Circuits: Bias, in an electronic circuit, describes the steady state operating characteristics with no signal being applied. In an op-amp circuit, the operating characteristic
Chapter 28B - EMF and Terminal P.D. A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University
 Chapter 28B - EMF and Terminal P.D. A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University 2007 Objectives: After completin this module, you should be
Chapter 28B - EMF and Terminal P.D. A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University 2007 Objectives: After completin this module, you should be
