Triple therapy with clarithromycin, omeprazole, and amoxicillin for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in duodenal ulcer patients in Asia and Africa
|
|
|
- Douglas Harris
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: 1529±1535. Triple therapy with clarithromycin, omeprazole, and amoxicillin for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in duodenal ulcer patients in Asia and Africa B. C. Y. WONG a,f.y.chang b,s.abid c,z.abbas d,b.r.lin e,c.vanrensburg f,p.c.chen g, H. SCHNEIDER h,a.e.simjee i,s.s.hamid j, A SEEBARAN k, J. ZHANG l, M. DESTEFANO l &S.K.LAM a a Department of Medicine, University of Hong Kong, Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong; b Division of Gastroenterology, Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Republic of China; c K.V. Site Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan; d Medical Unit III, Jinnah Post Graduate Medical Center, Karachi, Pakistan; e Department of Internal Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital, Republic of China; f Gastroenterology Unit, Tygerberg Hospital, Cape Town, South Africa; g Digestive Endoscopy Unit, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Republic of China; h Milpark Hospital, Johannesburg, South Africa; i Gastrointestinal Unit, King Edward VIII Hospital, University of Natal, Durban, South Africa; j Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan; k Entabeni Hospital, Durban, South Africa; and l Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, Illinois, Chicago, USA Accepted for publication 25 July 2000 SUMMARY Background: Studies assessing the ef cacy of triple therapy containing clarithromycin and amoxicillin for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection and healing of duodenal ulcers in Asian and African countries are limited. Aim: To determine the ef cacy and safety of 1-week triple therapy with omeprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin for eradicating H. pylori infection in patients with active duodenal ulcer living in Asian and African regions. Methods: This was an open-label, multicentre study in 11 centres in Asia and Africa. Patients with endoscopyproven duodenal ulcer and who were H. pylori-positive were treated with clarithromycin 500 mg, omeprazole 20 mg, and amoxicillin 1000 mg, all given twice daily for 7 days. Upper endoscopy was repeated at week 6 to check for ulcer healing and H. pylori status. Results: A total of 117 patients were recruited. H. pylori eradication rates were 85% by per protocol analysis and 80% by intention-to-treat analysis. Ulcer healing was found in 94% of subjects (per protocol analysis). Clinical success, measured by change of pre-treatment ulcer symptoms, was strongly supported by complete resolution or improvement in 100% of the evaluable patients (per protocol analysis). Since treatment-related adverse events, when present, were largely mild or moderate, the triple therapy regimen was considered safe. Conclusion: Seven-day triple therapy with omeprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin was ef cacious for treating Asian and African patients with duodenal ulcer disease associated with H. pylori infection, and the treatment regimen was well-tolerated. INTRODUCTION Correspondence to: Dr B. C. Y. Wong, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Hong Kong, Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong. bcywong@hku.hk Helicobacter pylori infection is recognized as a causative factor for development of duodenal ulcers. H. pylori eradication results in ulcer healing, prevention of ulcer recurrence, and decreased overall use of health care Ó 2000 Blackwell Science Ltd 1529
2 1530 B. C. Y. WONG et al. resources. 1±8 For H. pylori eradication, the use of various antibioticsðincluding tetracycline, amoxicillin, metronidazole, and clarithromycinðhas been studied. Numerous clinical trials have been conducted to de ne the best drug combinations and duration of treatment. In general, short-term treatment regimens improve patient compliance, whilst triple drug treatment combinations are highly ef cacious, especially against strains that are resistant to certain antibiotics. 9±13 Prevalence of H. pylori infection is high in regions of Africa and Asia, and therapy can be complicated by various factors including drug costs and availability, treatment side-effects, and the presence of bacterial strains that are antibiotic resistant. 14 Some treatment regimens recommended elsewhere in the world are considered too expensive or may be unavailable in these regions. Standard bismuth triple therapy is available, but patients may not comply due to the common occurrences of side-effects. 15 Metronidazole-containing regimens have limited effectiveness because of increasing prevalence of resistance to this drug; resistance rates as high as 74% have been reported in some areas in our region. 16±20 Thus, non-metronidazole containing regimens are currently considered more suitable for eradicating H. pylori infection in Asia and Africa. 14 Elsewhere in the world, clarithromycin-containing regimens which combine a proton pump inhibitor with amoxicillin have shown considerable success. When used for 7±10 days, these therapeutic regimens have achieved H. pylori eradication rates and ulcer healing rates greater than 90%. Furthermore, such therapy afforded a good safety pro le and credible patient compliance. 7, 9, 11±13, 21±23 However, the experience on the overall ef cacy of these regimes in the Asian and African population is limited. Most of the results came from single centre studies in Hong Kong, Taiwan or Japan; data from Southeast Asia and Africa are lacking. The purpose of the present study was therefore to evaluate the ef cacy and safety of 7-day triple therapy with omeprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin for eradicating Helicobacter pylori and healing duodenal ulcers in a multicentre design in Asia and Africa. PATIENTS AND METHODS Patients This was a multicentre study including 11 major hospitals in Hong Kong, Pakistan, South Africa, and Taiwan. Patients who met speci c inclusion criteria were enrolled in the study. To be included, patients had to be aged between 18 and 80 years with an active duodenal ulcer of at least 5 mm in diameter. H. pylori infection was de ned by a positive CLO test (Delta West, Bentley, West Australia) on endoscopic biopsy specimens from the antrum which was con rmed by at least one of two tests: histological examination of antral and body biopsy with Giemsa stain or 13 C-urea breath test ( 13 C-UBT). All patients gave written, informed consent according to the Declaration of Helsinki and applicable local laws. Patients were excluded from enrolment if they: had taken bismuth preparations or antibiotics within 4 weeks prior to the study; had endoscopy-based evidence of gastric ulcer, gastric malignancy, pyloric obstruction, oesophageal stricture requiring dilation, fresh clot, active bleeding, or perforated ulcers; had a history of previous gastric or duodenal surgery, underlying malignant conditions, allergy to proton-pump inhibitors, amoxicillin or clarithromycin; or if they had clinically signi cant cardiovascular, pulmonary, renal, hepatic, metabolic, gastrointestinal, neurological, endocrine, or psychiatric disease. Female patients were nonlactating and had a negative pregnancy test. Study design Patients enrolled in this open-label investigation were treated with clarithromycin 500 mg, omeprazole 20 mg, and amoxicillin 1000 mg, all given twice daily for 7 days. Antacid tablets were provided to each patient for the relief of pain or discomfort, as needed, and patients were instructed to report the usage. Symptoms were recorded at the initial visit, the endtreatment visit (day 8, 9, or 10), and at the follow-up visit (4±6 weeks post-treatment). 13 C-urea breath test and endoscopy with biopsy for histology were performed at the follow-up visit. Samples for urea breath test and histology were sent and analysed by central reference laboratories. Global eradication was de ned as negative results on both tests. The endoscopic examination also assessed ulcer healing. Compliance was assessed by count of returned tablets, and side-effects were determined by direct questioning on the end-treatment visit. Patients who underwent therapeutic procedures that interfered with subsequent evaluation were excluded from ef cacy evaluation, as were those who failed to take at least 70% of the tablets for each study medication.
3 TRIPLE THERAPY FOR H. PYLORI ERADICATION 1531 Bacterial culture and antimicrobial susceptibility tests Culture and antimicrobial susceptibility testing were performed on an antral biopsy specimen collected from each study participant at the pre-treatment visit. Specimens were placed in collection devices containing glycerol broth and frozen at ) 20 C or below, within 1 hour of biopsy. Specimens were transported on dry ice to the central laboratory where they were stored at ) 70 C. Culture was performed using fresh blood-based media, both selective and non-selective, at 37 C in 12% CO 2 in air with 98% humidity. H. pylori was identi ed by Gram stain, typical colony morphology, and biochemical properties (production of oxidase, catalase, and urease). In addition, the minimal inhibitory concentration for each isolate was determined with the epsilometer test and agar dilution. Ulcer and histological assessment Endoscopic examinations were performed to document pre-treatment ulcer size and post-treatment ulcer healing. An ulcer was considered healed if the pre-treatment ulcer was completely healed, and no additional ulcers were present. The ulcer was considered unhealed if at least one ulcer was present or the index ulcer was not completely re-epithelialized. The condition was indeterminate if the ulcer was not reassessed. At a reference laboratory, a pathologist who was blinded to the patients' clinical status performed the histological examination of gastric biopsy specimens. Pre-treatment examinations assessed for evidence of H. pylori infection and for evidence of chronic gastritis, including in ammation, gastric activity and atrophy, and intestinal metaplasia. Post-treatment examinations reassessed these same parameters. Clinical response Symptoms of epigastric pain or burning, belching, daytime abdominal pain, and night-time abdominal pain were assessed. All symptoms were rated as absent, mild, moderate, or severe. Mild symptoms were transient and easily tolerated. Moderate symptoms caused discomfort and disrupted normal activities. Severe symptoms caused considerable interference with usual activities or were incapacitating. The clinical response of each subject was assessed at the follow-up visit. A pre-treatment symptom was considered resolved if the severity changed from mild, moderate, or severe to absent. A symptom was considered improved if it changed from severe to moderate or mild, or moderate to mild. A symptom was unresolved if it stayed the same or worsened. If all symptoms were resolved, the patient was classi ed as cured. Symptom `improvement' was assigned when some pre-treatment duodenal ulcer symptoms were improved, whilst `failure' was assigned when there was no improvement. The condition was indeterminate if the patient was asymptomatic before treatment or if patient symptoms were not reassessed. Evaluation of safety Safety was assessed by recording adverse events, where an adverse event was any undesirable event, such as a sign, symptom, or laboratory nding, that was associated with the drug treatment regimen. The relationship of an adverse event to the study regimen was rated as probable, possible, or improbable. Statistical analysis Primary ef cacy analyses for H. pylori eradication at 4±6 weeks post-treatment were performed for per protocol and intention-to-treat results, and data analyses were reported with 95% exact binomial con dence intervals. Secondary analyses were likewise determined for ulcer healing and symptom changes from pre-treatment to follow-up visits. RESULTS Subject enrolment and evaluation A total of 119 subjects were enrolled in the study at sites in Hong Kong (37), Pakistan (27), South Africa (25), and Taiwan (30). Two subjects (one from Hong Kong and one from Taiwan) were excluded from the intention-to-treat analysis because they did not take the study drugs. For the per protocol analysis, eight subjects were excluded because they either failed to comply with the treatment regimen, or lacked follow-up endoscopy, or their follow-up examination was not timed correctly. At 4±6 weeks post-treatment, patients were assessed for H. pylori status, clinical response, and ulcer healing. Results are summarized (Figure 1, Table 1) according to per protocol analysis and intention-to-treat analysis.
4 1532 B. C. Y. WONG et al. Figure 1. Protocol summary and per protocol analyses of results for patients receiving 7-day triple therapy. H. pylori susceptibility to antibiotics Primary resistance to metronidazole occurred in 54% (39 out of 72) of tested patients, whilst resistance to clarithromycin was less than 2.7% (2 out of 72), and resistance to amoxicillin was not observed. H. pylori eradication The overall eradication rates for the study were 85% (per protocol analysis) and 80% (intention-to-treat analysis; Table 1), although results varied markedly from site to site. Eradication rates ranged from 72% to 94% for per protocol analysis and from 67% to 92% for intention-to-treat analysis, with Hong Kong showing the highest rates, Pakistan the lowest, and South Africa and Taiwan at intermediate levels (Table 2). Based on histology, all evaluable subjects initially had evidence of in ammation, and 97% had gastritis activity present in gastric biopsy samples. Atrophic changes were noted in more than half of the subjects (53%, 57 out of 107), and intestinal metaplasia was observed in some subjects (12% mild, 8% moderate, and 1% severe). Four to six weeks after completion of the 7-day triple therapy, 75%, 91%, 48% and 65% resolution or improvement were found in in ammation, activity, atrophy and intestinal metaplasia, respectively. Clinical response rate The ulcer-related symptoms reported most frequently at the baseline visit were epigastric pain (78%), daytime abdominal pain (67%), night-time abdominal pain (64%), and belching (56%). The majority of symptoms, more than 74% in each symptom category, were of mild or moderate severity. Following treatment, 81% of study patients experienced a cure and 19% experienced an improvement in symptoms by per protocol analysis, thus providing a 100% total clinical response rate. By intention-to-treat analysis analysis, the total clinical response rate was 94%, including cure (76%) and
5 TRIPLE THERAPY FOR H. PYLORI ERADICATION Table 1. Summary of ef cacy results for duodenal ulcer patients receiving 7-day triple therapy Ef cacy result improvement (18%). By symptom, epigastric pain and daytime or night-time abdominal pain were relieved in 98%, 96% and 100% of patients, respectively. Belching remained a problem for just 11% of the patients. Ulcer healing % of subjects (n/n), [95% CI] H. pylori eradication Per protocol 85% (93/109) [77.3%, 91.4%] Intention-to-treat 80% (94/117) [72.0%, 87.1%] Clinical response rate Per protocol TOTAL Cure + 100% (109/109) Improved Cure 81% (88/109) [72.1%, 87.7%] Improvement 19% (21/109) Failure 0% (0/109) Intention-to-treat TOTAL Cure + 94% (110/117) Improved Cure 76% (89/117) [67.3%, 83.5%] Improvement 18% (21/117) Failure 2% (2/117) Indeterminate 4% (5/117) Ulcer healing Per protocol* Healed 94% (99/105) [88.0%, 97.9%] Unhealed 6% (6/105) Indeterminate (4/109) Intention-to-treat Healed 85% (99/117) [76.8%, 90.6%] Unhealed 8% (9/117) Indeterminate 7% (9/117) *For the per protocol analysis, subjects were not included in computation of the ulcer healing rate if the healing status was indeterminate. Healing of the index duodenal ulcer at the posttreatment follow-up visit was observed in 94% (99 out of 105) of the per protocol subjects and in 85% (99 out of 117) of the intention-to-treat subjects (Figure 1, Table 1). For the per protocol analysis, subjects with a status of indeterminate were not included for computation of the healing rate. In the intention-to-treat analysis, however, indeterminate cases were treated as unhealed for computation. Table 2. Strati cation of H. pylori eradication results by country and by test criteria Ef cacy result Overall drug safety and speci c treatment-related adverse events A total of 46% (54 out of 117) of the subjects reported treatment-related adverse events; a majority of these events were considered by the investigator to be mild or moderate in severity. The most commonly reported adverse events were taste perversion (24%), diarrhoea (16%), dizziness (6%), and nausea (5%). The safety of this 7-day triple therapy was indicated by excellent compliance to the treatment regimen, with over 90% of the study subjects taking at least 90% of their prescribed medications. No clinically signi cant changes in haematology or serum chemistry values or in vital signs were observed during the study. DISCUSSION % of subjects (n/n), [95% CI] 13 C-UBT and Histology Hong Kong Per protocol 94% (32/34) [80.3, 99.3] Intention-to-treat 92% (33/36) [77.5, 98.2] Pakistan Per protocol 72% (18/25) [50.6, 87.9] Intention-to-treat 67% (18/27) [46.0, 83.5] South Africa Per protocol 86% (19/22) [65.1, 97.1] Intention-to-treat 76% (19/25) [54.9, 90.6] Taiwan Per protocol 86% (24/29) [64.2, 94.2] Intention-to-treat 83% (24/29) [64.2, 94.2] TOTAL Per protocol 85% (93/109) [77.3,91.4] Intention-to-treat 80% (94/117) [72.0, 87.1] The present study is among the rst in the world to determine the ef cacy and safety of 7-day triple therapy comprising of standard dose omeprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin in a multicentre setting for patients who live in areas of Asia and Africa. The treatment regimen was considered ef cacious because high rates of H. pylori eradication (85%), clinical success (100%), and ulcer healing (94%) were achieved on per protocol analyses of study ndings. Patient compliance was high, and treatment-related adverse events, when present,
6 1534 B. C. Y. WONG et al. were largely mild or moderate. Thus, this triple therapy regimen was also considered safe. In general, our multicentre study yielded results consistent with those reported for similar trials conducted elsewhere in the world. Desired thresholds for H. pylori eradication therapy were established recently as 90% eradication for data analysed on a per protocol basis or 80% eradication for data analysed on an intention-to-treat basis. 14 Our study showed an eradication rate of 85% for per protocol analysis analysis and 80% for intention-to-treat analysis. Recent 7-day triple therapy trials in Europe, Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Taiwan generated eradication rates that ranged from 89% to 98% for per protocol analyses vs. 80% to 91% for intention-to-treat 9±11, 21, 24, 25 analyses (Table 6). Some study-to-study differences may be attributed to different drug combinations in triple therapy, whilst others may be due to differing use of rapid urease testing, 13 C-urea breath test results, and histopathological ndings as criteria for eradication. If the regional prevalence of metronidazole resistance is high, H. pylori eradication rates can be reduced in metronidazole-containing regimens. 26 Reported metronidazole resistance in Asia and Africa has ranged from 20% to 74%, consistent with 54% of metronidazole resistance in this study. 17±20 There are, however, some notable differences in the data from the present study compared to other world studies. In particular, H. pylori eradication rates for the study centre in Pakistan were lower than expected, with 72% per protocol analysis and 67% intention-to-treat analysis. By contrast, eradication rates for Hong Kong were high, with 94% per protocol analysis and 92% intention-to-treat analysis. Although further studies will be necessary to pinpoint reasons for these differences, there are several possible explanations. First, the numbers in individual centres were relatively small to make any meaningful or valid comparisons between countries. Second, differences may be due to variations in conduct of the study; to varying characteristics of the patient populations (nutrition, general health); or to properties of endemic bacterial strains (strain virulence, antibiotic resistance). In addition, Harris et al. raised the issue that not all duodenal ulcers are caused by H. pylori. 24 A third possibility is that 7-day treatment may not be fully effective for all individuals at all sites. Whilst comparisons of identical regimens for 7, 10, and 14 days have generally been lacking, H. pylori eradication rates generally appear to increase directly with the duration of twice-daily triple therapy. 10 Since it has been established that the most cost-effective therapy for H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcers is the treatment that is most effective for eradication, it will be necessary to determine whether longer treatment intervals or altered treatments are needed in speci c sub-populations such as those in Pakistan. 25 It may also be necessary to provide local monitoring for bacterial strains and health conditions that may require additional treatment or alterations in the standard regimen. The stringent protocol design for this study considered subjects who dropped out or had data missing as `treatment failures' for their bacteriological, clinical, and ulcer healing responses, thus contributing to low apparent ef cacy rates at some study sites. For example, of the 25 South African subjects included in the intention-to-treat analysis analyses, ve subjects did not return or were too late for their followup visit, and three subjects were missing biopsy specimens from pre-treatment or follow-up visits. Likewise, of the 27 Pakistan subjects included in the intention-to-treat analysis analyses, one subject experienced a serious adverse event of chest pain and withdrew from the study. Another subject discontinued on their own accord. Furthermore, ve subjects had missing biopsies on follow-up. It is possible that regional conditions which limited protocol adherence may have reduced the apparent successfulness of bacteriological, clinical, and ulcer healing responses in this study. Overall, 7-day triple therapy with omeprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin is ef cacious for treating Asian and African patients who have duodenal ulcers associated with H. pylori infection. The treatment provides good compliance, and produces only mild side-effects. Such treatment thus represents a reasonable choice for clinical practice in regions of Asia and Africa, as is the case elsewhere in the world. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was sponsored by Abbott Laboratories, Chicago, USA. We are grateful to participating endoscopists and nursing staffs in various centres, and investigators in the central reference laboratories for bacterial and pathological diagnosis.
7 TRIPLE THERAPY FOR H. PYLORI ERADICATION 1535 REFERENCES 1 Forbes G, Glaser M, Cullen D, et al. Duodenal ulcer treated with with Helicobacter pylori eradication: seven year follow-up. Lancet 1994; 343: 258±60. 2 Graham D, Lew G, Klein P, et al. Effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infction on the long-term recurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcer. Ann Intern Med 1992; 116: 705±8. 3 Lam SK, Ching CK, Lai KC. Does treatment of Helicobacter pylori with antibiotics alone heal duodenal ulcer? A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study. Gut 1997; 41: 43±8. 4 Hopkins R, Girardi L, Turney E. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori eradication and reduced duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer recurrence: a review. Gastroenterology 1996; 110: 1244±52. 5 Shirotani T, Okada M, Murayama H, et al. Effect of the eradication of Helicobacter pylori on duodenal ulcer healing and ulcer relapse; randomized controlled study in Japan. J Gastroenterol 1996; 31: 175± Wong BC, Lam SK, Lai KC, et al. Triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication is more effective than long-term maintenance anti-secretory treatment in the prevention of recurrence of duodenal ulcer: a prospective long-term follow-up study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1999; 13: 303±9. 7 Porro G, Lazzaroni M, Bargiggia S, et al. Omeprazole coupled with two antibiotics for Helicobacter pylori eradication and prevention of ulcer recurrence. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91: 675± Cottril M, McKinnon C, Mason I, et al. Two omeprazole-based Helicobacter pylori eradication regimens for the treatment of duodenal ulcer disease in general practice. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 5: 919±27. 9 Lind T, van Veldhuyzen Zanten S, Unge P, et al. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori using one-week triple therapies combining omeprazole with two antimicrobials: The MACH 1 study. Helicobacter 1996; 1: 138± Laine L, Estrada R, Truillo M, et al. Randomized comparison of differing periods of twice-a-day triple therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1996; 10: 1029± Forne M, Viver J, Esteve M, et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing two one-week triple-therapy regimens for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection and duodenal ulcer healing. Am J Gastroenterol 1998; 93: 35±8. 12 Labenz J, Stolte M, Ruhl G, et al. One-week low-dose triple therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1994; 7: 9± Bazzoli F, Zagari R, Fossi S, et al. Short-term low-dose triple therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Eur J Hepatol 1994; 6: 773±7. 14 Lam S, Talley N. Report of the 1997 Asia Paci c Consensus Conference on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998; 13: 1± van der Hulst R, Keller J, Rauws E, Tytgat G. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: a review of the world literature. Helicobacter 1996; 1: 6± Megraud F, Lehn N, Lind T, et al. Helicobacter pylori resistance to antimicrobial agents and its in uence on clinical outcome. Gastroenterology 1997; 112: A138(Abstract). 17 Ching C, Leung K, Yung R, Lam S, et al. Prevalence of metronidazole resistant Helicobacter pylori strains among Chinese peptic ulcer disease patients and normal controls in Hong Kong. Gut 1996; 38: 675±8. 18 Greig A, Hanslo D, Lastovica A, Louw J. In vitro antibiotic sensitivity of H. pylori. S Afr Med J 1993; 83: Han D, Cho Y, Sohn J, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Korean duodenal ulcer patients. Gastroenterology 1997; 112: A138(Abstract). 20 Harries A, Stewart M, Deegan K, et al. Helicobacter pylori in Malawi, central Africa. J Infect 1992; 24: 269± Pieramico O, Zanetti M, Innerhofer M, Malfertheiner P. Omeprazole-based dual and triple therapy for treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in peptic ulcer disease: a randomized trial. Helicobacter 1997; 2: 92±7. 22 Schultze K, Hentschl E. Duodenal ulcer healing after 7-day treatment: a pilot study with lansoprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin. Z Gastroenterol 1995; 33: 651±3. 23 Misiewicz J, Harris A, Bardhan K, et al. One week low-dose triple therapy for eradication of H. pylori: a large multicentre comparative study. Gut 1997; 41: 735±9. 24 Sharma S, Prasad K, Chamoli D, Ayyagari A. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern and biotyping of Helicobacter pylori isolates from patients with peptic ulcer disease. Indian J Med Res 1995; 102: 261±6. 25 Goh KL, Cutler A, Chua A, et al. Optimal treatment for duodenal ulcer disease: a cost decision anaylsis in Malaysian patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1999; 14: 32±8.
A rapid-release 50-mg tablet-based 13 C-urea breath test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17: 253 257. doi: 10.1046/j.0269-2813.2003.01417.x A rapid-release 50-mg tablet-based 13 C-urea breath test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection W.M.WONG*,S.K.LAM*,K.C.LAI*,K.M.CHU,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17: 253 257. doi: 10.1046/j.0269-2813.2003.01417.x A rapid-release 50-mg tablet-based 13 C-urea breath test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection W.M.WONG*,S.K.LAM*,K.C.LAI*,K.M.CHU,
A rapid, low-dose, 13 C-urea tablet for the detection of Helicobacter pylori infection before and after treatment
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17: 793 798. doi: 10.1046/j.0269-2813.2003.01490.x A rapid, low-dose, 13 C-urea tablet for the detection of Helicobacter pylori infection before and after treatment L. GATTA*,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17: 793 798. doi: 10.1046/j.0269-2813.2003.01490.x A rapid, low-dose, 13 C-urea tablet for the detection of Helicobacter pylori infection before and after treatment L. GATTA*,
Gloucestershire Hospitals
 TRUST GUIDELINE In the case of hard copies of this policy the content can only be assured to be accurate on the date of issue marked on the document. The Policy framework requires that the policy is fully
TRUST GUIDELINE In the case of hard copies of this policy the content can only be assured to be accurate on the date of issue marked on the document. The Policy framework requires that the policy is fully
H. pylori Eradication Regimens
 H. pylori Eradication Regimens 1-2-3 Cured March 1999 Highlights H. pylori eradication drastically reduces ulcer recurrence in patients with duodenal or gastric ulcers. 7-day triple therapies with a proton
H. pylori Eradication Regimens 1-2-3 Cured March 1999 Highlights H. pylori eradication drastically reduces ulcer recurrence in patients with duodenal or gastric ulcers. 7-day triple therapies with a proton
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
A. Ketorolac*** B. Naproxen C. Ibuprofen D. Celecoxib
 1. A man, 66 years of age, with a history of knee osteoarthritis (OA) is experiencing increasing pain at rest and with physical activity. He also has a history of depression and coronary artery disease.
1. A man, 66 years of age, with a history of knee osteoarthritis (OA) is experiencing increasing pain at rest and with physical activity. He also has a history of depression and coronary artery disease.
Digestive System (continued) Digestive System. Stomach. Peptic Ulcer Disease
 Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
NSAIDs and Peptic Ulcers
 NSAIDs and Peptic Ulcers National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a peptic ulcer? A peptic ulcer is a sore
NSAIDs and Peptic Ulcers National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a peptic ulcer? A peptic ulcer is a sore
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis
 Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia. John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital
 Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
American College of Gastroenterology Guideline on the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2007 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01393.x Published by Blackwell Publishing American College of Gastroenterology
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2007 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01393.x Published by Blackwell Publishing American College of Gastroenterology
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery
 Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Review of the evidence for H. Pylori treatment regimens. Dr Lennita Wannmacher
 18th Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines (21 to 25 March 2011) Review Section 17.1 (Antacids and other antiulcer medicines) -- Adults and children Review of the evidence for
18th Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines (21 to 25 March 2011) Review Section 17.1 (Antacids and other antiulcer medicines) -- Adults and children Review of the evidence for
Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Peptic Ulcer Disease and H. pylori
 Peptic Ulcer Disease and H. pylori National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is a peptic ulcer? A peptic ulcer is a sore on the inner lining of the stomach or duodenum the first part of
Peptic Ulcer Disease and H. pylori National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is a peptic ulcer? A peptic ulcer is a sore on the inner lining of the stomach or duodenum the first part of
understanding GI bleeding
 understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
What are peptic ulcers?
 Information about Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are the symptoms? What are the causes? What are peptic ulcers? When should I consult a doctor? What will the doctor do? How should I treat peptic
Information about Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are the symptoms? What are the causes? What are peptic ulcers? When should I consult a doctor? What will the doctor do? How should I treat peptic
What is Barrett s esophagus? How does Barrett s esophagus develop?
 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H. pylori even be good for us?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Helicobacter pylori? What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H.
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Helicobacter pylori? What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H.
What can I eat? Peptic ulcers. What are peptic ulcers? What tests are needed? Will the ulcer come back? What causes a peptic ulcer?
 In association with: INFORMATION ABOUT Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are peptic ulcers? What causes a peptic ulcer? How are NSAIDs and aspirin involved? How do I know if I ve got an ulcer?
In association with: INFORMATION ABOUT Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are peptic ulcers? What causes a peptic ulcer? How are NSAIDs and aspirin involved? How do I know if I ve got an ulcer?
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal Impairment
 Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Omeprazol XXX 40 mg powder for solution for infusion omeprazole
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Omeprazol XXX 40 mg powder for solution for infusion omeprazole Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. - Keep this leaflet. You
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Omeprazol XXX 40 mg powder for solution for infusion omeprazole Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. - Keep this leaflet. You
Public Assessment Report. Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification. Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets.
 Public Assessment Report Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets (Esomeprazole) EMA Agency number: Pfizer Consumer Healthcare Ltd TABLE OF CONTENTS
Public Assessment Report Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets (Esomeprazole) EMA Agency number: Pfizer Consumer Healthcare Ltd TABLE OF CONTENTS
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
What is Helicobacter pylori? The Life Cycle (Pathogenesis) of Helicobacter pylori
 Helicobacter pylori Source: http://www.medicaltribune.net/put/default.htm Source: http://www.shef.ac.uk/mbb/academic/staff/djk010.gif What is Helicobacter pylori? Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) are a
Helicobacter pylori Source: http://www.medicaltribune.net/put/default.htm Source: http://www.shef.ac.uk/mbb/academic/staff/djk010.gif What is Helicobacter pylori? Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) are a
Is H. pylori infection...
 Is H. pylori infection... the culprit behind your stomach symptoms? What s really going on in your stomach? You may often have stomach symptoms that you blame on certain foods or stress. You may take over-the-counter
Is H. pylori infection... the culprit behind your stomach symptoms? What s really going on in your stomach? You may often have stomach symptoms that you blame on certain foods or stress. You may take over-the-counter
PATIENTS AND METHODS
 symptoms 5. Heartburn is also common and the sufferers attribute symptoms to various lifestyle events, including diet and stress. In all these cases antacid usage is the commonest mode of therapy 6. Antacid
symptoms 5. Heartburn is also common and the sufferers attribute symptoms to various lifestyle events, including diet and stress. In all these cases antacid usage is the commonest mode of therapy 6. Antacid
Phase: IV. Study Period: 20 Jan. 2006-17 Sep. 2008
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for use of high dose Intravenous Esomeprazole in Adults (Previously called the Hong Kong Protocol)
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for use of high dose Intravenous Esomeprazole in Adults (Previously called the Hong Kong Protocol) Date of First Issue 10/05/2010 Approved 16/06/2010 Current Issue Date 18/11/2015
NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for use of high dose Intravenous Esomeprazole in Adults (Previously called the Hong Kong Protocol) Date of First Issue 10/05/2010 Approved 16/06/2010 Current Issue Date 18/11/2015
Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin
 Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 1 patient with chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of n-esophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat
Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 1 patient with chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of n-esophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat
SYNOPSIS. Risperidone: Clinical Study Report CR003274
 SYNOPSIS Protocol No: CR003274 Title of Study: An Open-Label, Long-Term Trial of Risperidone Long-Acting Microspheres in the Treatment of Subjects Diagnosed with Schizophrenia Coordinating Investigator:
SYNOPSIS Protocol No: CR003274 Title of Study: An Open-Label, Long-Term Trial of Risperidone Long-Acting Microspheres in the Treatment of Subjects Diagnosed with Schizophrenia Coordinating Investigator:
The background behind Matula Herbal Formula
 (Available in Packs of 60 Sachets equivalent to a full 30 day treatment) The background behind Matula Herbal Formula Matula Herbal Formula was discovered in 1998 and has successfully served the global
(Available in Packs of 60 Sachets equivalent to a full 30 day treatment) The background behind Matula Herbal Formula Matula Herbal Formula was discovered in 1998 and has successfully served the global
Articles Presented. Journal Presentation. Dr Albert Lo. Dr Albert Lo
 * This presentation is prepared by the author in one s personal capacity for the purpose of academic exchange and does not represent the views of his/her organisations on the topic discussed. Journal Presentation
* This presentation is prepared by the author in one s personal capacity for the purpose of academic exchange and does not represent the views of his/her organisations on the topic discussed. Journal Presentation
WGO Practice Guideline: Helicobacter pylori in Developing Countries
 WGO Practice Guideline: Helicobacter pylori in Developing Countries Hp in Developing Countries 2 Review team Prof. R.H. Hunt, Chair (Canada) Prof. S.D. Xiao (China) Prof. F. Megraud (France) Prof. R. Leon-Barua
WGO Practice Guideline: Helicobacter pylori in Developing Countries Hp in Developing Countries 2 Review team Prof. R.H. Hunt, Chair (Canada) Prof. S.D. Xiao (China) Prof. F. Megraud (France) Prof. R. Leon-Barua
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders. By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc.
 Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Sponsor Novartis. Generic Drug Name Secukinumab. Therapeutic Area of Trial Psoriasis. Approved Indication investigational
 Clinical Trial Results Database Page 2 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Secukinumab Therapeutic Area of Trial Psoriasis Approved Indication investigational Clinical Trial Results Database Page 3 Study
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 2 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Secukinumab Therapeutic Area of Trial Psoriasis Approved Indication investigational Clinical Trial Results Database Page 3 Study
Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia
 Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia Version: 3.0 Ratified by: Medicines Committee Date ratified: 16 th November 2011 Name of originator/author: James
Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia Version: 3.0 Ratified by: Medicines Committee Date ratified: 16 th November 2011 Name of originator/author: James
Series 1 Case Studies Adverse Events that Represent Unanticipated Problems: Reporting Required
 Welcome! This document contains three (3) series of Case Study examples that will demonstrate all four OHSU reporting categories (#1 4) as well as examples of events that are considered not reportable.
Welcome! This document contains three (3) series of Case Study examples that will demonstrate all four OHSU reporting categories (#1 4) as well as examples of events that are considered not reportable.
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Version History. Previous Versions. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fingolimod Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fingolimod Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fingolimod Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA
 GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA 2010 1 TB prophylaxis GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS Background
GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA 2010 1 TB prophylaxis GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS Background
Lung Pathway Group Nintedanib (Vargatef) in advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
 Lung Pathway Group Nintedanib (Vargatef) in advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Indication: In combination with docetaxel in locally advanced, metastatic or locally recurrent NSCLC of adenocarcinoma
Lung Pathway Group Nintedanib (Vargatef) in advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Indication: In combination with docetaxel in locally advanced, metastatic or locally recurrent NSCLC of adenocarcinoma
Breath Test Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in Peptic Ulcer Disease: A Noninvasive Primary Care Option
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Breath Test Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in Peptic Ulcer Disease: A Noninvasive Primary Care Option Michael W Felz, MD, George] Burke, MD, and Bernard M. Schuman, MD Background: Hellcobacter
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Breath Test Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in Peptic Ulcer Disease: A Noninvasive Primary Care Option Michael W Felz, MD, George] Burke, MD, and Bernard M. Schuman, MD Background: Hellcobacter
10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis
 10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) The use of
10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) The use of
Figure 3: Dysphagia. 14 meets. esophageal. esophageal manometry +/- +/- impedance measurement. structural lesion? no. 19 yes
 Figure 3: Dysphagia 1 patient with dysphagia 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of nesophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat as as indicated 4 upper GI GI endoscopy with biopsies 15 achalasia, absent
Figure 3: Dysphagia 1 patient with dysphagia 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of nesophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat as as indicated 4 upper GI GI endoscopy with biopsies 15 achalasia, absent
Summary 1. Comparative-effectiveness
 Cost-effectiveness of Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol (Sativex ) as add-on treatment, for symptom improvement in patients with moderate to severe spasticity due to MS who have not responded adequately
Cost-effectiveness of Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol (Sativex ) as add-on treatment, for symptom improvement in patients with moderate to severe spasticity due to MS who have not responded adequately
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Version History. Previous Versions. Policy Title. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields
The submission positioned dimethyl fumarate as a first-line treatment option.
 Product: Dimethyl Fumarate, capsules, 120 mg and 240 mg, Tecfidera Sponsor: Biogen Idec Australia Pty Ltd Date of PBAC Consideration: July 2013 1. Purpose of Application The major submission sought an
Product: Dimethyl Fumarate, capsules, 120 mg and 240 mg, Tecfidera Sponsor: Biogen Idec Australia Pty Ltd Date of PBAC Consideration: July 2013 1. Purpose of Application The major submission sought an
2. Background This drug had not previously been considered by the PBAC.
 PUBLIC SUMMARY DOCUMENT Product: Ambrisentan, tablets, 5 mg and 10 mg, Volibris Sponsor: GlaxoSmithKline Australia Pty Ltd Date of PBAC Consideration: July 2009 1. Purpose of Application The submission
PUBLIC SUMMARY DOCUMENT Product: Ambrisentan, tablets, 5 mg and 10 mg, Volibris Sponsor: GlaxoSmithKline Australia Pty Ltd Date of PBAC Consideration: July 2009 1. Purpose of Application The submission
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 19 March 2003 CPMP/EWP/785/97 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) POINTS TO CONSIDER
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 19 March 2003 CPMP/EWP/785/97 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) POINTS TO CONSIDER
Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa )
 Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa ) ESCA: For the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. SECONDARY CARE SECTION TO BE COMPLETED BY INITIATING DOCTOR
Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa ) ESCA: For the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. SECONDARY CARE SECTION TO BE COMPLETED BY INITIATING DOCTOR
2.0 Synopsis. Vicodin CR (ABT-712) M05-765 Clinical Study Report R&D/07/095. (For National Authority Use Only) to Part of Dossier: Volume:
 2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen Extended Release (ABT-712) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen Extended Release (ABT-712) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors
 Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors Final Report Update 5 May 2009 Update 4: May 2006 Update 3: May 2005 Update 2: April 2004 Update 1: April 2003 Original Report: November 2002 The literature on
Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors Final Report Update 5 May 2009 Update 4: May 2006 Update 3: May 2005 Update 2: April 2004 Update 1: April 2003 Original Report: November 2002 The literature on
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial Marcus R. Pereira A. Study Purpose Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication
Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial Marcus R. Pereira A. Study Purpose Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication
Version History. Previous Versions. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Tapered Withdrawal of a Proton Pump Inhibitor to Prevent Rebound Acid-Related Symptoms
 Akin Oyalowo CRC Rotation IRB Proposal August 8, 2012 Tapered Withdrawal of a Proton Pump Inhibitor to Prevent Rebound Acid-Related Symptoms A. Study Purpose and Rationale Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Akin Oyalowo CRC Rotation IRB Proposal August 8, 2012 Tapered Withdrawal of a Proton Pump Inhibitor to Prevent Rebound Acid-Related Symptoms A. Study Purpose and Rationale Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch
 Bass N.M., et. al. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:1071-1081 Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch Faculty Advisor: Dr. Fred
Bass N.M., et. al. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:1071-1081 Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch Faculty Advisor: Dr. Fred
Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2005 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.00225.x Published by Blackwell Publishing PRACTICE GUIDELINES Guidelines for the
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2005 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.00225.x Published by Blackwell Publishing PRACTICE GUIDELINES Guidelines for the
Riociguat Clinical Trial Program
 Riociguat Clinical Trial Program Riociguat (BAY 63-2521) is an oral agent being investigated as a new approach to treat chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) and pulmonary arterial hypertension
Riociguat Clinical Trial Program Riociguat (BAY 63-2521) is an oral agent being investigated as a new approach to treat chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) and pulmonary arterial hypertension
VITAMIN C AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND THE RESULTS OF A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, PROSPECTIVE STUDY OVER 8 YEARS
 39 Chapter 3 VITAMIN C AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND THE RESULTS OF A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, PROSPECTIVE STUDY OVER 8 YEARS Maxine Briggs TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Review of the
39 Chapter 3 VITAMIN C AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND THE RESULTS OF A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, PROSPECTIVE STUDY OVER 8 YEARS Maxine Briggs TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Review of the
Sponsor Novartis Pharmaceuticals
 Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Pharmaceuticals Generic Drug Name Indacaterol Therapeutic Area of Trial Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Indication studied: COPD Study
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Pharmaceuticals Generic Drug Name Indacaterol Therapeutic Area of Trial Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Indication studied: COPD Study
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER)
 Guidance for Industry Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Developing Antimicrobial Drugs for Treatment U.S. Department of Health
Guidance for Industry Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Developing Antimicrobial Drugs for Treatment U.S. Department of Health
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
Re: LUMIGAN 0.03% (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03%) and LUMIGAN 0.01% (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.01%)
 Allergan Ltd, 1st Floor, Marlow International, Parkway, Marlow, Bucks SL7 1YL Tel: (01628) 494444 Facsimile: (01628) 494449 Ref No: UK15-000677 Mandeep Allingham NW Surrey CCG February 18, 2015 Dear Ms
Allergan Ltd, 1st Floor, Marlow International, Parkway, Marlow, Bucks SL7 1YL Tel: (01628) 494444 Facsimile: (01628) 494449 Ref No: UK15-000677 Mandeep Allingham NW Surrey CCG February 18, 2015 Dear Ms
The discovery of Helicobacter pylori as
 Update on Helicobacter pylori Treatment ADRIENNE Z. ABLES, PHARM.D., I. SIMON, M.D., and EMILY R. MELTON, M.D. Spartanburg Family Medicine Residency Program, Spartanburg, South Carolina One half of the
Update on Helicobacter pylori Treatment ADRIENNE Z. ABLES, PHARM.D., I. SIMON, M.D., and EMILY R. MELTON, M.D. Spartanburg Family Medicine Residency Program, Spartanburg, South Carolina One half of the
patient group direction
 DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
CMAJ JAMC. An evidence-based approach to the management of uninvestigated dyspepsia in the era of Helicobacter pylori
 CANADIAN M EDICAL A SSOCIATION J OURNAL J OURNAL DE L ASSOCIATION MÉDICALE CANADIENNE CMAJ JAMC Return to June 13, 2000 Table of Contents An evidence-based approach to the management of uninvestigated
CANADIAN M EDICAL A SSOCIATION J OURNAL J OURNAL DE L ASSOCIATION MÉDICALE CANADIENNE CMAJ JAMC Return to June 13, 2000 Table of Contents An evidence-based approach to the management of uninvestigated
Position Statement from the Irish Thoracic Society on the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 BACKGROUND Position Statement from the Irish Thoracic Society on the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a rare, chronic and fatal disease characterised by
BACKGROUND Position Statement from the Irish Thoracic Society on the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a rare, chronic and fatal disease characterised by
The cost-effectiveness of IVF in the UK: a comparison of three gonadotrophin treatments Sykes D, Out H J, Palmer S J, van Loon J
 The cost-effectiveness of IVF in the UK: a comparison of three gonadotrophin treatments Sykes D, Out H J, Palmer S J, van Loon J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that
The cost-effectiveness of IVF in the UK: a comparison of three gonadotrophin treatments Sykes D, Out H J, Palmer S J, van Loon J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that
placebo-controlledcontrolled double-blind, blind,
 Clinical Potential of Minocycline for Depression with Psychotic Features Tsuyoshi Miyaoka Department of Psychiatry Shimane University School of Medicine Minocycline 1. Second-generation tetracycline which
Clinical Potential of Minocycline for Depression with Psychotic Features Tsuyoshi Miyaoka Department of Psychiatry Shimane University School of Medicine Minocycline 1. Second-generation tetracycline which
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D.
 Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Examination Content Blueprint
 Examination Content Blueprint Overview The material on NCCPA s certification and recertification exams can be organized in two dimensions: (1) organ systems and the diseases, disorders and medical assessments
Examination Content Blueprint Overview The material on NCCPA s certification and recertification exams can be organized in two dimensions: (1) organ systems and the diseases, disorders and medical assessments
The use of text messaging to improve asthma control: a pilot study using the mobile phone short messaging service (SMS)
 RESEARCH Original article... Q The use of text messaging to improve asthma control: a pilot study using the mobile phone short messaging service (SMS) Lathy Prabhakaran*, Wai Yan Chee*, Kia Chong Chua,
RESEARCH Original article... Q The use of text messaging to improve asthma control: a pilot study using the mobile phone short messaging service (SMS) Lathy Prabhakaran*, Wai Yan Chee*, Kia Chong Chua,
Biotie Therapies Oyj Biotie Therapies Corp. Varsinainen yhtiökokous 26.5.2015 Annual General Meeting 26 May 2015
 Biotie Therapies Oyj Biotie Therapies Corp. Varsinainen yhtiökokous 26.5.2015 Annual General Meeting 26 May 2015 1 Timo Veromaa President & CEO 2 Company Highlights 2014 through Q1 2015 Continued advances
Biotie Therapies Oyj Biotie Therapies Corp. Varsinainen yhtiökokous 26.5.2015 Annual General Meeting 26 May 2015 1 Timo Veromaa President & CEO 2 Company Highlights 2014 through Q1 2015 Continued advances
Evidence of Crohn s Disease. Case Presentation
 Witt Wait to Treat tutiled Until Endoscopic Evidence of Crohn s Disease Raymond Cross, MD, MS, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Director, IBD Program University of Maryland School of Medicine Co-Director,
Witt Wait to Treat tutiled Until Endoscopic Evidence of Crohn s Disease Raymond Cross, MD, MS, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Director, IBD Program University of Maryland School of Medicine Co-Director,
A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels. Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD
 A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD The sunshine vitamin Existed over 500 million years. Prehormone, not only a vitamin. Two major sources:
A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD The sunshine vitamin Existed over 500 million years. Prehormone, not only a vitamin. Two major sources:
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty. Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan
 Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
The digestive system. Medicine and technology. Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies
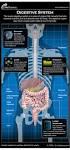 The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
Losec. Omeprazole 10 mg, 20 mg and 40 mg capsules. CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION
 Losec Omeprazole 10 mg, 20 mg and 40 mg capsules. CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some of the common questions people ask about Losec. It does not contain all
Losec Omeprazole 10 mg, 20 mg and 40 mg capsules. CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some of the common questions people ask about Losec. It does not contain all
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Contents
 Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
A Phase 2 Study of Interferon Beta-1a (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis
 A Phase 2 Study of (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis - Study Results - ClinicalTrials.gov A Phase 2 Study of (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis This study has been completed. Sponsor: Biogen Idec Information
A Phase 2 Study of (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis - Study Results - ClinicalTrials.gov A Phase 2 Study of (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis This study has been completed. Sponsor: Biogen Idec Information
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE) Hashem El-Serag, M.D., M.P.H. Dan L. Duncan Professor of Medicine Chief, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE) Hashem El-Serag, M.D., M.P.H. Dan L. Duncan Professor of Medicine Chief, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
1-800-HRT-BURN. understanding gerd. Is it just a little HEARTBURN. or something more serious? NEW
 Do you have GERD? Measure Yourself on the Richter Scale/Acid Test How significant is your heartburn? What are the chances that it is something more serious? If you need a yardstick, here s a simple self-test
Do you have GERD? Measure Yourself on the Richter Scale/Acid Test How significant is your heartburn? What are the chances that it is something more serious? If you need a yardstick, here s a simple self-test
**Form 1: - Consultant Copy** Telephone Number: Fax Number: Email: Author: Dr Bernard Udeze Pharmacist: Claire Ault Date of issue July 2011
 Effective Shared Care Agreement for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease Donepezil tablets / orodispersible tablets (Aricept / Aricept Evess ) These forms (1 and 2) are to be completed by both
Effective Shared Care Agreement for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease Donepezil tablets / orodispersible tablets (Aricept / Aricept Evess ) These forms (1 and 2) are to be completed by both
Harmony Clinical Trial Medical Media Factsheet
 Overview Harmony is the global Phase III clinical trial program for Tanzeum (albiglutide), a product developed by GSK for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The comprehensive program comprised eight individual
Overview Harmony is the global Phase III clinical trial program for Tanzeum (albiglutide), a product developed by GSK for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The comprehensive program comprised eight individual
Cirrhosis and HCV. Jonathan Israel M.D.
 Cirrhosis and HCV Jonathan Israel M.D. Outline Relationship of fibrosis and cirrhosisprevalence and epidemiology. Sequelae of cirrhosis Diagnosis of cirrhosis Effect of cirrhosis on efficacy of treatment
Cirrhosis and HCV Jonathan Israel M.D. Outline Relationship of fibrosis and cirrhosisprevalence and epidemiology. Sequelae of cirrhosis Diagnosis of cirrhosis Effect of cirrhosis on efficacy of treatment
The Anorexic Cat For this reason, any cat that stops eating for any reason is considered an emergency situation.
 The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
Renovascular Hypertension
 Renovascular Hypertension Philip Stockwell, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Warren Alpert School of Medicine Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider September 28, 201 Renovascular Hypertension
Renovascular Hypertension Philip Stockwell, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Warren Alpert School of Medicine Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider September 28, 201 Renovascular Hypertension
PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain
 P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
Human Clinical Study for Free Testosterone & Muscle Mass Boosting
 Human Clinical Study for Free Testosterone & Muscle Mass Boosting GE Nutrients, Inc. 920 E. Orangethorpe Avenue, Suite B Anaheim, California 92801, USA Phone: +1-714-870-8723 Fax: +1-732-875-0306 Contact
Human Clinical Study for Free Testosterone & Muscle Mass Boosting GE Nutrients, Inc. 920 E. Orangethorpe Avenue, Suite B Anaheim, California 92801, USA Phone: +1-714-870-8723 Fax: +1-732-875-0306 Contact
Humulin (LY041001) Page 1 of 1
 (LY041001) These clinical study results are supplied for informational purposes only in the interests of scientific disclosure. They are not intended to substitute for the FDA-approved package insert or
(LY041001) These clinical study results are supplied for informational purposes only in the interests of scientific disclosure. They are not intended to substitute for the FDA-approved package insert or
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Intravenous Methyl Prednisolone in Multiple Sclerosis
 Intravenous Methyl Prednisolone in Multiple Sclerosis Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Relapse management in multiple sclerosis Relapses in multiple sclerosis (MS) are common and caused by
Intravenous Methyl Prednisolone in Multiple Sclerosis Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Relapse management in multiple sclerosis Relapses in multiple sclerosis (MS) are common and caused by
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
Efficacy, safety and preference study of a insulin pen PDS290 vs. a Novo Nordisk marketed insulin pen in diabetics
 Efficacy, safety and preference study of a insulin pen PDS290 vs. a Novo Nordisk marketed insulin pen in diabetics This trial is conducted in the United States of America (USA). The aim of this clinical
Efficacy, safety and preference study of a insulin pen PDS290 vs. a Novo Nordisk marketed insulin pen in diabetics This trial is conducted in the United States of America (USA). The aim of this clinical
