Pediatric CIMT Evidence Table April 8, 2012
|
|
|
- Ruth Gray
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Group Design Facchin et al. 1 Boyd et al. 2011a 2011b 2011c (multicenter) (single blind matched pairs) Same as Same as Secondary analysis of study To compare the effects of an mcimt program, bimanual training program, and standard treatment To determine if CIMT is more effective than bimanual training to improve UL function, participation & QoL N= 105 Hemiplegic C.P. Age: 2-8 years N= 52 Age: 5-16 years Same as N=63 Age= 5-16 years To determine if CIMT is more effective than bimanual training to improve occupational performance & participation To determine the characteristics of best responders in an comparing CIMT to bimanual training () Group 1: mcimt (volar glove) + intensive rehab program (3h/day) x 7d/week x10 weeks Group 2; Bimanual+intensive rehabx7d/weekx10 weeks Group 3: Traditional Rehab (1 hr/1-2x/week) x10 weeks Group 1: CIMT (mitt) worn 6h/day during group therapy x 5d/week x 2 weeks at camp Group 2: 6h/day bimanual therapy in a group x 2 weeks at camp (Used Circus training theme) Both the mcimt and bimanual groups significantly improved paretic hand function on QUEST & Besta Scale. Standard treatment group did not. Grasp improved in mcimt more than bimanual training (p<.01) Bimanual spontaneous use in play (p=.0005), ADLs in children aged 2-6 years (p<.0001), and unaffected limb (p=.02) improved more in bimanual than mcimt group Methods paper. See Sakzewski et al. 2011(a,b.c) below for results Same as CIMT group had greater outcomes at 26 weeks (p<.001) Both groups had significant improvement in bimanual performance at 3 weeks, and gains were maintained by the bimanual group at 26 weeks (p=.008) There were minimal differences between the two training approaches N=64 Same as Both groups made significant changes on occupational performance and participation Age: 5-16 years outcomes at 3 weeks on COPM (p<.001) and LIFE-H for the CIMT group (p=01) & bimanual group (p=.06) and results were maintained at 26 weeks There were minimal differences between the two training approaches Same as Same as Immediately after intervention, poorer baseline hand function predicted a best response for unimanual capacity on the MUUL At 26 weeks, the CIMT group were 21 times more likely to have a favorable outcome than the bimanual group on the MUUL Children with left hemiplegia achieved a best response on the COPM 3.9 times more than those with right hemiplegia I 7/7 1
2 Hoare et al. 11 De Brito et al. 2 Aarts et al. 3 Psychouli et al 8 Smania et al. 4 Saczews ki et al. 6 Kuhnke et al. 15 Eliasson et al. 7 (study protocol) Randomized Crossover Design Randomized Crossover Design Cross sectional cohort study with Design with To describe an comparing mcimt to bimanual therapy on improving bimanual UE function following Botox To evaluate effects of mcimt followed by bimanual functional training on ADLs To investigate if 6 week mcimt followed by 2 week bimanual (mcimt- BiT) improves affected limb use To identify most appropriate splint from children s and parent s perspectives To compare the effects of mcimt with conventional physiotherapy To explore relationship between unimanual and bimanual performance for children with CP To determine whether the type of corticospinal organization or reorganization influences the efficacy of CIMT To investigate if 2 week day camp model of CIMT is feasible post Botox & to investigate replicability of previous study N=40 Age:18 mo-6 years 6 Age: 4-8 y N=50 Right sided hemiplegic CP Age: years N= 9 Age: 5-11 years 1 Age: 1-9 years N= 85 (total) =70 Age:5-16 years 6 Congenital Age:10-30 y 6 (total) Age: 8-17 years Not described Study not completed Intervention Phase 1: 2 weeks mcimt(elbow & shoulder sling & resting hand splint) x 3h/day (constraint worn 10 h/day) Intervention Phase 2: 1 week functional bimanual training 3 x 45 min/day Control: 3 weeks conventional OT 1 x 45 min/week Intervention: mcimt-bit group (re-movable hand & arm sling) worn 3h/day for 3d/week x 6 weeks, followed by bimanual for 2 weeks. Control: OT/PT usual therapy 1.5h/week x 8 weeks + encouragement to use affected hand 7.5h/week Intervention: Participants wore 1 of 3 splint styles for minimum 1h/day for 4 days and moved on to trialing remaining 2 styles for 12 day intervention Splint 1:CIMT using hand splint (mitt) Splint 2:CIMT using hand splint up to level of elbow Splint 3: Long arm splint from fingertips to shoulder Intervention: mcimt (cotton mitt) worn 8h/day for 5 weeks with 1 hour therapy 2x/week Control: no restraint, regular therapy 2x/week for 5 weeks Compared sensation, grip strength, and movement efficiency between CP sample and 15 typically developing children matched by age and sex Group 1: Ipsi-periventricular lesions Group 2: Cortico-subcortical lesions Intervention(both groups): Constraint (Mitt and sling) worn10h/day for 12 days + group and individual therapy for ~ 9 h/day for days/ week Intervention Group (CIMT + Botox): Restraining mitt (allowing gross hand movements for stabilization & bimanual tasks)worn ~7h/day x 9 days (over 2 weeks of camp) Control (CIMT only-no Botox): Same treatment as Both and intervention groups improved with significant differences in PEDI functional skills (P=0.0027) and independence (p=0.0492) Both and intervention group improved on JTTHF (not statistically significant) Significant improvement in AHA, ABL, COPM, & GAS scores for intervention group Improvement in MUUL scores for intervention group (not statistically significant) Affected limb movement improved with all splints, Greatest movement in effected limb elicted with mid-arm splint (as measured by actomometer) Parents preferred mid arm splint to others & had most negative attitude toward long arm splint mcimt program caused significant improvement of paretic arm use and function. Trend shown toward improvement of bimanual function. Effects maintained at 4 week follow up. Strong relationship between unimanual and bimanual performance (MUUL) Directionality remains unknown therefore cannot assume improvement in unimanual performance will lead to gains in bimanual Both groups significantly improved on WMFT Post-treatment speed to execute tasks was statistically different & clinically relevant between groups (those with ipsi-perventricular lesions were slower to execute movements than those with cortico-subcortical lesions) Significant improvement in JTHFT in CIMT group Immediate improvement in MUUL in Botox + CIMT group, not sustained 6 months post; no improvement in CIMT only No change in AHA for either group Significant improvement in grip strength, in hand manipulation (IHM), task specific performance in CIMT only, improvement in Botox + CIMT 2/7 I I I 3/7 2
3 Park et al. 12 with To investigate mcimt following Botox on UE function N=32 Age: 1-9 years Intervention: Botox + CIMT CIMT (long arm cast) worn all waking hours for 3 weeks ( days of the week) + direct therapy 2h/day Control: Botox only No CIMT, direct therapy (OT & PT) 2h/day Significant improvements in MTS, MAS, ROM, and PRS for both groups Significant improvement in PMAL in CIMT group I 2/7 Cope et al. 9 Stearns et al. 13 Wallen et al. 16 Juenger et al. 17 Sutcliffe et al. 18 Charlets et al. 19 concurrent Before-after design (A-B-A-A) study group study group concurrent Before-After design (A-B- A-B-A) To investigate effectiveness of CIMT and examine use of fmri to describe changes in the brain To determine if improvements in hand function and changes in muscle activation are associated with functional gains after 2 week CIMT To determine feasibility of family focused mcimt model & to collect preliminary data for an To assess neuromodulative effects of CIMT in congenital To demonstrate change in cortical activity patterns after mcimt & explore baseline predictors of change To investigate long term effects of CIMT & effect of a second course on involved limb function 0 Age: 7- years N=6 Age: 5-8 years 0 Age: 2-8 years (eligible from 6 mos onwards) N= 10 Congenital Age: years N=5 Age: 7-13 years N=8 Age: 5-11 years CIMT (short arm bi-valved cast) worn 90% of waking hours + therapy 4h/day x 5d/week (40h total) Intervention: Bi-valve cast worn 8-12h/day + therapy 4h/day for 5d/week for 2 weeks. Phase A: 2 weeks baseline assessment Phase B: 2 weeks of OT intervention Phase A-2: 2 weeks post intervention assessment Phase A-3: 3 months after intervention Constraint (mitt with solid volar insert) worn 2h/day targeting specific movements during child s daily activities 7d/week for 8 weeks. Weekly therapy 1 time/week to support individualized home program. CIMT (tailored glove inhibiting finger flexion and an elbow sling) worn 9h/day for 12 day training camp, consisting of 2 h/ day of individual therapy + 7 h/day group therapy. Continuous (24h) cast from elbow to fingertips for 3 weeks with therapy 1x/week. Weekly therapy 1 time/week to support home program. Arm and hand sling worn 6h/day with structured practice for 10/12 consecutive days in group setting Positive functional changes reported in parent questionnaire, not statistically significant Improvements in ROM (not significant), MUUL (weak significance with small effect size) Sig. improvement in kinematic analysis of UE 2/7 children showed greater activation in 1 motor area of contralateral side on fmri post CIMT Significant improvement in grip strength from baseline to all phases except at 3 month follow up Pinch gauge, Modified 9-hole peg, & Box and Block test showed significant improvement EMG was inconclusive Statistically significant improvement in COPM, GAS, AHA scores & MUUL improved but were not statistically significant 8/10 participants PMAL s improved (statistically significant) No statistically significant change in MTS Improvement in time & quality of movement and increased passive and active movement of paretic hand on WMFT Significantly increased cortical activation after CIMT for 4 patients on fmri. All participants showed contra lateral activation post intervention on fmri Significant improvement shown on PMAL Inconsistent changes on QUEST and AHA Significant improvement on limb disregard index Significant improvement on JTTHF, BOT-2, & caregiver functional use survey after first intervention were retained at 6 and 12 months There were further improvements after second intervention but were not statistically significant 3
4 de Bode et al. Buesc h et al 20 Fergus at al Boll ea Case Series (Feasibility Study) Single Case Series Case Report Case Study Qualitative Study Design Gilmore et al. 10 Qualitative To evaluate if shortened CIMT protocol results in improvements in UE function & changes in brain imaging (sensorimotor cortex) To examine if CIMT is feasible for community settings and improves function To describe qualitative and quantitative changes in UE function after CIMT To describe functional recovery post CIMT To explore the experiences of children participating in mcimt within a circus themed day-camp Single Subject Research Design () Dicker son et al 26 Coker et al. 21 Martin et al. 22 (ABA) (A-B-A-B) (A-B-A-A) To describe effects of CIMT for a 24 month old in the home environment To evaluate effectiveness of mcimt for a child <1 y To explore changes associated with a CIMT trial on a child s function at all ICF levels. N=4 Hemiplegia post cerebral hemipherectomy Age: years N=2 Obstetric brachial plexus palsy Age: 12 years Stroke at 11 months ABI Age:13 months Neonatal stroke Age: 7 months N=32 Age:9-11 years Hemiparesis post prenatal stroke Age:24 months Neonatal Stroke Age: 9 months Spastic CP Age: 3 years, male Hand splint worn 90% of waking hours for 11 days + therapy 3h/day x 3d/week (total stimulation time 30h). Forearm and hand splint worn 4-6 hours per day for 7d/week with structured therapy for weeks of intervention. CIMT (soft-removable mitt) Phase 1:Splint worn 6 h/day during daily activities Weaning: Decreased constraint time by 1h/wk x 5 weeks Phase 2: 9 weeks of CIMT + home exercise program 1h/day + less structured play Immediate improvements on AAUT and BBT No improvements in FM fmri did not show increased activation, but subtle shifts in location of activation were seen fmri is a useful tool to detect re-organization in the remaining hemisphere Slight improvement (not significant) on MUUL & AHA No improvement on the 9 hole peg test Flexion, reach, grasp and release and hand to hand transfers improved on video analysis Improved willingness to use & performance on PMAL Held arm and hand back No contributions for guidelines V Day camp (sample taken from a larger INCITE trial) Semi-structured interviews examined the child s experience. CIMT (removable splint) worn for most of waking hours + 6h/day therapy during 21 day home intervention Cloth mitt worn 1 h/day for 7d/week. Structured practice in home 3d/week & in clinic 4d/week for 30 days with one month off and then another 30 days. CIMT (bi-valved removable cast covering mid-upper arm to fingertips) worn ~7.5h/day with active therapy 4h/day for 6 d/week for 2 week intervention 3 main themes emerged from interview data. Glove experience- discomfort & frustration Doing the camp- effort, travel, fun, group experience, and activity choices Gains- achieved goals and improved function Self determination theory described enhancers & barriers. Enhancers outweighed the barriers Improvement in grasp, release, reach, sustained grasp, push/pull, and finger feeding on video analysis. Improved scores on PDMS-2 & GMFM Improved reaching, weight bearing, and approaching midline as measured on video analysis Improved satisfaction and performance on COPM Increased use of both hands on PEDI Increased grip strength both hands, no change in pinch strength of hemiplegic hand V 9/ 7/ 7/ 4
5 Cope et al. 24 To explore short and long term effects of mcimt on child & family R sided hemiplegia with suspected CP Age:12 months CIMT (non-removable hand and arm cast) + therapy 8h/week for 2 week home intervention No sig. improvement on PDMS, PMAL & TAUT Increase in UE function, gross motor skills and speech and communication on Knox questionnaire support mcimt safe intervention and parents were pleased with the changes. V 6/ Abbreviations AAUT ABIL ADL BBT BOT-2 CAPE COPM CP fmri FM GMFCS JTTHF LIFE-H Actual Amount of Use Test ABILHAND-Kids Activities of daily living Box and Block Test Bruininks Osteretsky Test of Motor Performance-2 Children s Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment Canadian Occupational Performance Measure Cerebral Palsy Fucntional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Fugl Meyer Test of Motor Recovery Gross Motor Functional Classification System Jebsen-Taylor Test of Hand Function Assessment of Life Habits MACS MAS MCIMT MTS MUUL PEDI PMAL PRS QUEST ROM SFA WMFT Manual Ability Classification System Modfied Ashworth Scale Modified Constraint Induced Movement Therapy Modified Tardieu Scale Melbourne Assessment of Unilateral Upper Limb Function Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Pediatric Motor Activity Log Upper Limb Physicians Rating Scale Quality of Upper Extremity Skills Test Range of Motion School Function Assessment Single Subject Research Design Wolf Motor Function Test Note: s for Single Study Research Designs obtained using AACPDM Singe Subject Quality Tool; s for Group Designs obtained using AACPDM adaptation of Sackett s Levels of Evidence () and AACPDM Quality Assessment Scale for studies Levels I,, or 5
Does the use of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT) result in improved upper limb function for children with hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy?
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC TITLE Does the use of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT) result in improved upper limb function for children with hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy? AUTHOR Prepared by Email
CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC TITLE Does the use of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT) result in improved upper limb function for children with hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy? AUTHOR Prepared by Email
An Evidence Based Occupational Therapy Toolkit for Assessment and Treatment of the Upper Extremity Post Stroke
 An Evidence Based Occupational Therapy Toolkit for Assessment and Treatment of the Upper Extremity Post Stroke Brenda Semenko, Leyda Thalman, Emily Ewert, Renee Delorme, Suzanne Hui, Heather Flett, Nicole
An Evidence Based Occupational Therapy Toolkit for Assessment and Treatment of the Upper Extremity Post Stroke Brenda Semenko, Leyda Thalman, Emily Ewert, Renee Delorme, Suzanne Hui, Heather Flett, Nicole
Clinical Neuropsychology. Recovery & Rehabilitation. Alan Sunderland School of Psychology
 Clinical Neuropsychology. Recovery & Rehabilitation Alan Sunderland School of Psychology 1 The Changing Role of Clinical Neuropsychology HISTORY The Origins of Clinical Neuropsychology Emergence as a profession
Clinical Neuropsychology. Recovery & Rehabilitation Alan Sunderland School of Psychology 1 The Changing Role of Clinical Neuropsychology HISTORY The Origins of Clinical Neuropsychology Emergence as a profession
THE FUTURE OF STROKE REHABILITATION
 Disclosure of Financial Relationships Gary M. Abrams M.D. THE FUTURE OF STROKE REHABILITATION Gary M. Abrams M.D. Professor of Clinical Neurology Director of Neurorehabilitation UCSF Has disclosed the
Disclosure of Financial Relationships Gary M. Abrams M.D. THE FUTURE OF STROKE REHABILITATION Gary M. Abrams M.D. Professor of Clinical Neurology Director of Neurorehabilitation UCSF Has disclosed the
Virtual Environments
 Re-Learning Motor Control Using Virtual Environments Maureen K. Holden, PhD, PT Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA International Neurorehabilitation Symposium 2009 University of Zurich, Switzerland
Re-Learning Motor Control Using Virtual Environments Maureen K. Holden, PhD, PT Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA International Neurorehabilitation Symposium 2009 University of Zurich, Switzerland
STROKE CARE NOW NETWORK CONFERENCE MAY 22, 2014
 STROKE CARE NOW NETWORK CONFERENCE MAY 22, 2014 Rehabilitation Innovations in Post- Stroke Recovery Madhav Bhat, MD Fort Wayne Neurological Center DISCLOSURE Paid speaker for TEVA Neuroscience Program.
STROKE CARE NOW NETWORK CONFERENCE MAY 22, 2014 Rehabilitation Innovations in Post- Stroke Recovery Madhav Bhat, MD Fort Wayne Neurological Center DISCLOSURE Paid speaker for TEVA Neuroscience Program.
Efficacy of a childfriendly. constraint-induced movement therapy in hemiplegic cerebral palsy: a randomized control trial
 Efficacy of a childfriendly form of constraint-induced movement therapy in hemiplegic cerebral palsy: a randomized control trial Jeanne R Charles PhD MSW PT, Department of Biobehavioral Sciences, Teachers
Efficacy of a childfriendly form of constraint-induced movement therapy in hemiplegic cerebral palsy: a randomized control trial Jeanne R Charles PhD MSW PT, Department of Biobehavioral Sciences, Teachers
A randomized controlled trial comparing two rehabilitation interventions for young children with cerebral palsy
 A randomized controlled trial comparing two rehabilitation interventions for young children with cerebral palsy CO-PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS Mary Law and Johanna Darrah RESEARCH TEAM Brenda Wilson Nancy
A randomized controlled trial comparing two rehabilitation interventions for young children with cerebral palsy CO-PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS Mary Law and Johanna Darrah RESEARCH TEAM Brenda Wilson Nancy
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Splinting in Neurology. Jo Tuckey MSc MCSP
 Splinting in Neurology Jo Tuckey MSc MCSP Splinting in Neurology When should splinting be considered? How to choose the most appropriate splint or position for splinting. Practicalities of providing a
Splinting in Neurology Jo Tuckey MSc MCSP Splinting in Neurology When should splinting be considered? How to choose the most appropriate splint or position for splinting. Practicalities of providing a
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure
 The Long-Term Rehabilitation Management of Stroke Patients Robert Teasell MD FRCPC Professor, Dept PM&R Schulich School of Medicine University of Western Ontario CFPC CoI Templates: Slide 1 Faculty/Presenter
The Long-Term Rehabilitation Management of Stroke Patients Robert Teasell MD FRCPC Professor, Dept PM&R Schulich School of Medicine University of Western Ontario CFPC CoI Templates: Slide 1 Faculty/Presenter
Postgraduate Opportunities for 2013 Queensland Cerebral Palsy Research and Rehabilitation Centre School of Medicine, The University of Queensland
 Postgraduate Opportunities for 2013 Queensland Cerebral Palsy Research and Rehabilitation Centre School of Medicine, The University of Queensland Website: www.som.uq.edu.au/cerebralpalsy Our Research Team
Postgraduate Opportunities for 2013 Queensland Cerebral Palsy Research and Rehabilitation Centre School of Medicine, The University of Queensland Website: www.som.uq.edu.au/cerebralpalsy Our Research Team
Brachial Plexus Palsy
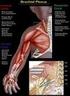 Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
Gait Analysis Laboratory Centro de Rehabilitación Infantil Teletón Estado de México
 Gait Analysis Laboratory Centro de Rehabilitación Infantil Teletón Estado de México Dr. Demetrio Villanueva Ayala Doctorado en Biomecánica, CINVESTAV Dr. Juan Carlos Pérez Moreno Especialista en Medicina
Gait Analysis Laboratory Centro de Rehabilitación Infantil Teletón Estado de México Dr. Demetrio Villanueva Ayala Doctorado en Biomecánica, CINVESTAV Dr. Juan Carlos Pérez Moreno Especialista en Medicina
Mental Practice as a Gateway to Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy: A Promising Combination to Improve Function
 Mental Practice as a Gateway to Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy: A Promising Combination to Improve Function Stephen J. Page, Peter Levine, Valerie Hill KEY WORDS function mental priming modified
Mental Practice as a Gateway to Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy: A Promising Combination to Improve Function Stephen J. Page, Peter Levine, Valerie Hill KEY WORDS function mental priming modified
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY 2012
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY 2012 To study the effectiveness of repetitive task oriented training as Occupational Therapy intervention in upper limb weakness in adult stroke: Systematic
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY 2012 To study the effectiveness of repetitive task oriented training as Occupational Therapy intervention in upper limb weakness in adult stroke: Systematic
Cerebral Palsy. www.teachinngei.org p. 1
 Cerebral Palsy What is cerebral palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disability caused by a static, non-progressive lesion (encephalopathy) in the brain that occurs in early childhood, usually before
Cerebral Palsy What is cerebral palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disability caused by a static, non-progressive lesion (encephalopathy) in the brain that occurs in early childhood, usually before
Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010
 Brief report Hart Walker Reviewer Adrian Purins AHTA Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010 1. Background Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that arise from brain damage
Brief report Hart Walker Reviewer Adrian Purins AHTA Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010 1. Background Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that arise from brain damage
CEREBRAL PALSY (CP) is a neurodevelopmental disorder
 SPECIAL COMMUNICATION Methods of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy for Children With Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: Development of a Child-Friendly Intervention for Improving Upper-Extremity Function Andrew
SPECIAL COMMUNICATION Methods of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy for Children With Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: Development of a Child-Friendly Intervention for Improving Upper-Extremity Function Andrew
Cerebral palsy can be classified according to the type of abnormal muscle tone or movement, and the distribution of these motor impairments.
 The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
Translating the Move and PLAY Study: Thoughts for Families and Practitioners
 Translating the Move and PLAY Study: Thoughts for Families and Practitioners Lisa Chiarello, PT, PhD, PCS, Drexel University Lynn Jeffries, PT, PhD, PCS, Langston University Move and PLAY Movement & Participation
Translating the Move and PLAY Study: Thoughts for Families and Practitioners Lisa Chiarello, PT, PhD, PCS, Drexel University Lynn Jeffries, PT, PhD, PCS, Langston University Move and PLAY Movement & Participation
Occupational Therapy Sample Reports 2009
 Sample Reports 2009 Includes: Clinical Reports Progress/ Treatment Note Plan of Care Initial Evaluation Periodic Re-Evaluation Discharge Summary Missed Visit Report Physician s Communication The Rehab
Sample Reports 2009 Includes: Clinical Reports Progress/ Treatment Note Plan of Care Initial Evaluation Periodic Re-Evaluation Discharge Summary Missed Visit Report Physician s Communication The Rehab
Potential for new technologies in clinical practice
 Potential for new technologies in clinical practice International Neurorehabilitation Symposium University of Zurich Feb 12-13th 2009 Prof Jane Burridge Jane Burridge Feb 2009 Introduction Societal drivers
Potential for new technologies in clinical practice International Neurorehabilitation Symposium University of Zurich Feb 12-13th 2009 Prof Jane Burridge Jane Burridge Feb 2009 Introduction Societal drivers
Neuro-rehabilitation in Stroke. Amit Kumar Neuro-Occupational Therapist
 Neuro-rehabilitation in Stroke Amit Kumar Neuro-Occupational Therapist Neuro-rehabilitation A process whereby patients who suffer from impairment following neurologic diseases regain their former abilities
Neuro-rehabilitation in Stroke Amit Kumar Neuro-Occupational Therapist Neuro-rehabilitation A process whereby patients who suffer from impairment following neurologic diseases regain their former abilities
Functional Treatment Ideas
 I n t e r n a t i o n a l C l i n i c a l E d u c a t o r s, i n c. Functional Treatment Ideas and Strategies In Adult Hemiplegia s e c o n d e d i t i o n By Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L Video Registration No.
I n t e r n a t i o n a l C l i n i c a l E d u c a t o r s, i n c. Functional Treatment Ideas and Strategies In Adult Hemiplegia s e c o n d e d i t i o n By Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L Video Registration No.
Dr. Enas Elsayed. Brunnstrom Approach
 Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Surgery of the Upper Extremity in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy
 Article submitted, at the request of CHASA, by Robert Bunata, M.D., Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon. Dr. Bunata has a special interest in upper extremity surgery in children who have hemiplegia. He
Article submitted, at the request of CHASA, by Robert Bunata, M.D., Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon. Dr. Bunata has a special interest in upper extremity surgery in children who have hemiplegia. He
How To Control A Prosthetic Leg
 OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY OUTCOMES WITH TARGETED HYPER- REINNERVATION NERVE TRANSFER SURGERY : TWO CASE STUDIES Stubblefield, K.A., 1,2 Milller, L.A., 1,3 Lipschutz, R.D., 1,3 Phillips, M.E., 1,2 Heckathorne,
OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY OUTCOMES WITH TARGETED HYPER- REINNERVATION NERVE TRANSFER SURGERY : TWO CASE STUDIES Stubblefield, K.A., 1,2 Milller, L.A., 1,3 Lipschutz, R.D., 1,3 Phillips, M.E., 1,2 Heckathorne,
William E. Janes. Date: May 2013. 1. Personal Information: a. Sex Male b. Place of Birth St. Louis, MO. 2. Citizenship:
 William E. Janes Date: May 2013 1. Personal Information: a. Sex Male b. Place of Birth St. Louis, MO 2. Citizenship: USA Other 3. Address and Telephone Numbers: a. Office Program in Occupational Therapy
William E. Janes Date: May 2013 1. Personal Information: a. Sex Male b. Place of Birth St. Louis, MO 2. Citizenship: USA Other 3. Address and Telephone Numbers: a. Office Program in Occupational Therapy
Brad Steinle, M.D. Medical Director, Rehabilitation Services Saint Luke s Hospital of Kansas City Medical Director, Adult Rehabilitation Services,
 Brad Steinle, M.D. Medical Director, Rehabilitation Services Saint Luke s Hospital of Kansas City Medical Director, Adult Rehabilitation Services, Rehabilitation Institute of Kansas City Presenter Disclosure
Brad Steinle, M.D. Medical Director, Rehabilitation Services Saint Luke s Hospital of Kansas City Medical Director, Adult Rehabilitation Services, Rehabilitation Institute of Kansas City Presenter Disclosure
PROGRAM SERVICES GUIDE 2015 FALL / 2016 WINTER
 PROGRAM SERVICES GUIDE 2015 FALL / 2016 WINTER Welcome to Easter Seals Easter Seals is the champion for abilities, opening new pathways to opportunities, so that every child can reach for and realize their
PROGRAM SERVICES GUIDE 2015 FALL / 2016 WINTER Welcome to Easter Seals Easter Seals is the champion for abilities, opening new pathways to opportunities, so that every child can reach for and realize their
Critical Review: Sarah Rentz M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
 Critical Review: In children with cerebral palsy and a diagnosis of dysarthria, what is the effectiveness of speech interventions on improving speech intelligibility? Sarah Rentz M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate
Critical Review: In children with cerebral palsy and a diagnosis of dysarthria, what is the effectiveness of speech interventions on improving speech intelligibility? Sarah Rentz M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate
Intensive Pediatric Constraint-Induced Therapy for Children With Cerebral Palsy: Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial
 Lobar Asymmetries in Dyslexics / Zadina et al 931 Original Article Intensive Pediatric Constraint-Induced Therapy for Children With Cerebral Palsy: Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial Stephanie C.
Lobar Asymmetries in Dyslexics / Zadina et al 931 Original Article Intensive Pediatric Constraint-Induced Therapy for Children With Cerebral Palsy: Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial Stephanie C.
GRASP. Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program: A home-work based program to improve arm and hand function in people living with stroke
 GRASP Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program: A home-work based program to improve arm and hand function in people living with stroke GUIDELINES & MANUAL October 2012 The GRASP Program was developed
GRASP Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program: A home-work based program to improve arm and hand function in people living with stroke GUIDELINES & MANUAL October 2012 The GRASP Program was developed
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Rehabilitation for movement difficulties after stroke bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online.
Rehabilitation for movement difficulties after stroke bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online.
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY (OT) POLICY NUMBER: 8.01.17 CATEGORY: Therapy/Rehabilitation
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY (OT) PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY (OT) PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
Integrating Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy for Persons with Chronic Disease: Lessons Learned from Research in Primary Care
 Integrating Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy for Persons with Chronic Disease: Lessons Learned from Research in Primary Care Lori Letts & Julie Richardson School of Rehabilitation Science McMaster
Integrating Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy for Persons with Chronic Disease: Lessons Learned from Research in Primary Care Lori Letts & Julie Richardson School of Rehabilitation Science McMaster
A Pediatric Case Example: Application of the Guide to Physical Therapist Practice
 , SECTION ON Section on Pediatics This case example is written from the point of view of a school-based physical therapist providing therapy services under IDEA Part B. It is assumed that services are
, SECTION ON Section on Pediatics This case example is written from the point of view of a school-based physical therapist providing therapy services under IDEA Part B. It is assumed that services are
Physiotherapy for the severely paretic arm and hand in patients with acquired brain injury - Virtual reality combined with task specific practice
 Physiotherapy for the severely paretic arm and hand in patients with acquired brain injury - Virtual reality combined with task specific practice Christian Gunge Riberholt, PT MR Nakayama et al, 1994 (Copenhagen
Physiotherapy for the severely paretic arm and hand in patients with acquired brain injury - Virtual reality combined with task specific practice Christian Gunge Riberholt, PT MR Nakayama et al, 1994 (Copenhagen
Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors
 1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
EMG Biofeedback & EMG- Triggered Electrical Muscle Stimulation in pediatric rehabilitation. Schedule. Advanced Muscle Stimulators, LLC
 & EMG- Triggered Electrical Muscle in pediatric rehabilitation Creating permanent changes in patient outcomes. Presented by: Pia Stampe, PT, DPT Owner of Advanced Muscle Stimulators, LLC Schedule 10:00-10:20:
& EMG- Triggered Electrical Muscle in pediatric rehabilitation Creating permanent changes in patient outcomes. Presented by: Pia Stampe, PT, DPT Owner of Advanced Muscle Stimulators, LLC Schedule 10:00-10:20:
Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy. Jenny Wilson, MD wilsjen@ohsu.edu OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015
 Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy Jenny Wilson, MD wilsjen@ohsu.edu OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015 Disclosures I am involved in a Dysport sponsored research study Goals Describe
Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy Jenny Wilson, MD wilsjen@ohsu.edu OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015 Disclosures I am involved in a Dysport sponsored research study Goals Describe
Neuro-developmental Treatment of Adults with Hemiplegia. Kathryn R. Shaab, PT, DPT Sheltering Arms Hospital May 2008
 Neuro-developmental Treatment of Adults with Hemiplegia Kathryn R. Shaab, PT, DPT Sheltering Arms Hospital May 2008 History of NDT Developed by Berta Bobath Physiotherapist Gymnast Assisted by her husband,
Neuro-developmental Treatment of Adults with Hemiplegia Kathryn R. Shaab, PT, DPT Sheltering Arms Hospital May 2008 History of NDT Developed by Berta Bobath Physiotherapist Gymnast Assisted by her husband,
UNILATERAL SPATIAL NEGLECT Information for Patients and Families
 UNILATERAL SPATIAL NEGLECT Information for Patients and Families What is unilateral spatial neglect? Unilateral spatial neglect (USN) is the inability to pay attention to things on the side that is affected
UNILATERAL SPATIAL NEGLECT Information for Patients and Families What is unilateral spatial neglect? Unilateral spatial neglect (USN) is the inability to pay attention to things on the side that is affected
LSU Health Sciences Center Occupational Therapy Flexor Tendon Injury Treatment Protocol
 . LSU Health Sciences Center Occupational Therapy Flexor Tendon Injury Treatment Protocol DIP PIP MCP Zone 1 Zone 2 T 1 T 2 Zone 3 T 3 Zone 4 Zone 5 Zone 5 cs Carla M. Saulsbery LOTR, CHT Dr. A. Hollister,
. LSU Health Sciences Center Occupational Therapy Flexor Tendon Injury Treatment Protocol DIP PIP MCP Zone 1 Zone 2 T 1 T 2 Zone 3 T 3 Zone 4 Zone 5 Zone 5 cs Carla M. Saulsbery LOTR, CHT Dr. A. Hollister,
Rehabilitation Programme of Stroke Patients in RC Kladruby
 Rehabilitation Programme of Stroke Patients in RC Kladruby Bc. Zdeněk Váňa Content About rehabilitation centre Rehabilitation team members roles Stroke patients rehabilitation programme Basic Information
Rehabilitation Programme of Stroke Patients in RC Kladruby Bc. Zdeněk Váňa Content About rehabilitation centre Rehabilitation team members roles Stroke patients rehabilitation programme Basic Information
Range of Motion Exercises
 Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Presentation - Rehabilitation Institute Ljubljana, Slovenia. Hermina Damjan
 Presentation - Rehabilitation Institute Ljubljana, Slovenia Hermina Damjan Medical rehabilitation intervention Goal oriented comprehensive therapeutic program provided by rehabilitation team planned on
Presentation - Rehabilitation Institute Ljubljana, Slovenia Hermina Damjan Medical rehabilitation intervention Goal oriented comprehensive therapeutic program provided by rehabilitation team planned on
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY?
 WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy
 MARIANJOY Rehabilitation Hospital Wheaton Franciscan Healthcare The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy Celebrating Even the Smallest Steps, One Step at a Time The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy Celebrating
MARIANJOY Rehabilitation Hospital Wheaton Franciscan Healthcare The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy Celebrating Even the Smallest Steps, One Step at a Time The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy Celebrating
EFFECT OF VIBRATORY PLATFORM THERAPY ON POSTURE IN CHILDREN WITH CEREBRAL PALSY: A PILOT STUDY
 EFFECT OF VIBRATORY PLATFORM THERAPY ON URE IN CHILDREN WITH CEREBRAL PALSY: A PILOT STUDY Pierina MAGNA a, Natalia JERIA a, Carlos ALVAREZ a,b, Chiara RIGOLDI c & Manuela GALLI c a Departamento de Kinesiología
EFFECT OF VIBRATORY PLATFORM THERAPY ON URE IN CHILDREN WITH CEREBRAL PALSY: A PILOT STUDY Pierina MAGNA a, Natalia JERIA a, Carlos ALVAREZ a,b, Chiara RIGOLDI c & Manuela GALLI c a Departamento de Kinesiología
Therapeutic Recreation: Effects of a Riding Protocol on a Child with Cerebral Palsy
 May 2009 Rose Flammang, SPT Katrina Francis, SPT Therapeutic Recreation: Effects of a Riding Protocol on a Child with Cerebral Palsy The purpose of our research project was to Evaluate the effect of a
May 2009 Rose Flammang, SPT Katrina Francis, SPT Therapeutic Recreation: Effects of a Riding Protocol on a Child with Cerebral Palsy The purpose of our research project was to Evaluate the effect of a
Assessment of upperlimb function and movement in children with cerebral palsy wearing lycra garments
 Assessment of upperlimb function and movement in children with cerebral palsy wearing lycra garments J H Nicholson*, Senior Paediatric Occupational Therapist, Ronnie Mac Keith Centre; R E Morton, Consultant
Assessment of upperlimb function and movement in children with cerebral palsy wearing lycra garments J H Nicholson*, Senior Paediatric Occupational Therapist, Ronnie Mac Keith Centre; R E Morton, Consultant
Functional Treatment SAMPLE. Ideas & Strategies. In Adult Hemiplegia. s e c o n d e d i t i o n. By Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L. Video Registration No.
 Functional Treatment Ideas & Strategies In Adult Hemiplegia s e c o n d e d i t i o n By Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L Video Registration No. Table of Contents Introduction.........................................
Functional Treatment Ideas & Strategies In Adult Hemiplegia s e c o n d e d i t i o n By Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L Video Registration No. Table of Contents Introduction.........................................
Stationary (St)--This subtest measures a child's ability to sustain control of the body within its center of gravity and retain equilibrium.
 Peabody Developmental Motor Scales Second Edition (PDMS-2) Summary Report Section I. Identifying Information Name: Jane Doe Date of Testing: 9/13/2006 Date of Birth: 4/8/2003 Prematurity Adjustment: 0
Peabody Developmental Motor Scales Second Edition (PDMS-2) Summary Report Section I. Identifying Information Name: Jane Doe Date of Testing: 9/13/2006 Date of Birth: 4/8/2003 Prematurity Adjustment: 0
Exercise therapy in the management of upper limb dysfunction in people with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Speaker declaration: no conflicts of interest
 Exercise therapy in the management of upper limb dysfunction in people with Rheumatoid Arthritis Speaker declaration: no conflicts of interest Exercise a planned, structured and repetitive bodily movement
Exercise therapy in the management of upper limb dysfunction in people with Rheumatoid Arthritis Speaker declaration: no conflicts of interest Exercise a planned, structured and repetitive bodily movement
Motor rehabilitation and brain plasticity after hemiparetic stroke
 Progress in Neurobiology 73 (2004) 61 72 Motor rehabilitation and brain plasticity after hemiparetic stroke Judith D. Schaechter MGH/MIT/HMS, Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, 13th Street,
Progress in Neurobiology 73 (2004) 61 72 Motor rehabilitation and brain plasticity after hemiparetic stroke Judith D. Schaechter MGH/MIT/HMS, Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, 13th Street,
1. What is Cerebral Palsy?
 1. What is Cerebral Palsy? Introduction Cerebral palsy refers to a group of disorders that affect movement. It is a permanent, but not unchanging, physical disability caused by an injury to the developing
1. What is Cerebral Palsy? Introduction Cerebral palsy refers to a group of disorders that affect movement. It is a permanent, but not unchanging, physical disability caused by an injury to the developing
 SUMMARY This PhD thesis addresses the long term recovery of hemiplegic gait in severely affected stroke patients. It first reviews current rehabilitation research developments in functional recovery after
SUMMARY This PhD thesis addresses the long term recovery of hemiplegic gait in severely affected stroke patients. It first reviews current rehabilitation research developments in functional recovery after
Cerebral Palsy: Intervention Methods for Young Children. Emma Zercher. San Francisco State University
 RUNNING HEAD: Cerebral Palsy & Intervention Methods Cerebral Palsy & Intervention Methods, 1 Cerebral Palsy: Intervention Methods for Young Children Emma Zercher San Francisco State University May 21,
RUNNING HEAD: Cerebral Palsy & Intervention Methods Cerebral Palsy & Intervention Methods, 1 Cerebral Palsy: Intervention Methods for Young Children Emma Zercher San Francisco State University May 21,
Incidence. Upper limb involvement. Manual Ability Classification System. Upper limb involvement 02/03/2015
 Why neuromuscular conditions? The spastic hand Matthew Nixon Consultant orthopaedic hand surgeon Complex decision making MDT approach Often told nothing can be done Variety of surgical treatments Multilevel,
Why neuromuscular conditions? The spastic hand Matthew Nixon Consultant orthopaedic hand surgeon Complex decision making MDT approach Often told nothing can be done Variety of surgical treatments Multilevel,
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
Referral Form & Instructions Questions? Call 1 888 284 5433 and press 7
 Therapist Name: Phone: Referral Form & Instructions Questions? Call 1 888 284 5433 and press 7 1 2 Indicate all products that might be appropriate for your patient. Please check all products that might
Therapist Name: Phone: Referral Form & Instructions Questions? Call 1 888 284 5433 and press 7 1 2 Indicate all products that might be appropriate for your patient. Please check all products that might
HOPE EXERCISE RECOVERY RESOURCES RELATIONSHIPS INFORMATION REHABILITATION PREVENTION SELF ADVOCACY RELATIONSHIPS MOVEMENT. A Stroke Recovery Guide
 INFORMATION REHABILITATION PREVENTION SELF ADVOCACY RECOVERY HOPE A Stroke Recovery Guide RELATIONSHIPS MOVEMENT RESOURCES RELATIONSHIPS EXERCISE www.stroke.org CHAPTER FOUR Movement and Exercise Moving
INFORMATION REHABILITATION PREVENTION SELF ADVOCACY RECOVERY HOPE A Stroke Recovery Guide RELATIONSHIPS MOVEMENT RESOURCES RELATIONSHIPS EXERCISE www.stroke.org CHAPTER FOUR Movement and Exercise Moving
CommonKnowledge. Pacific University. Morgan Williams Pacific University 1-1-2008. Recommended Citation. Notice to Readers
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge Physical Function CATs OT Critically Appraised Topics --2008 What evidence exists (published between 988 and 2008) on the treatment of spinal cord injury related spasticity
Pacific University CommonKnowledge Physical Function CATs OT Critically Appraised Topics --2008 What evidence exists (published between 988 and 2008) on the treatment of spinal cord injury related spasticity
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) may improve the home behavior of children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
 ADHD 4 Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) may improve the home behavior of children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). CITATION: Fehlings, D. L., Roberts, W., Humphries, T., Dawe, G.
ADHD 4 Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) may improve the home behavior of children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). CITATION: Fehlings, D. L., Roberts, W., Humphries, T., Dawe, G.
General Therapies for Individuals with Autism
 General Therapies for Individuals with Autism Speech and Language Pathology Speech- language therapy entails the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and helping to prevent speech, language, cognitive, communication,
General Therapies for Individuals with Autism Speech and Language Pathology Speech- language therapy entails the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and helping to prevent speech, language, cognitive, communication,
Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
Web-based home rehabilitation gaming system for balance training
 Web-based home rehabilitation gaming system for balance training V I Kozyavkin, O O Kachmar, V E Markelov, V V Melnychuk, B O Kachmar International Clinic of Rehabilitation, 37 Pomiretska str, Truskavets,
Web-based home rehabilitation gaming system for balance training V I Kozyavkin, O O Kachmar, V E Markelov, V V Melnychuk, B O Kachmar International Clinic of Rehabilitation, 37 Pomiretska str, Truskavets,
What is cerebral palsy?
 What is cerebral palsy? This booklet will help you to have a better understanding of the physical and medical aspects of cerebral palsy. We hope it will be a source of information to anyone who wishes
What is cerebral palsy? This booklet will help you to have a better understanding of the physical and medical aspects of cerebral palsy. We hope it will be a source of information to anyone who wishes
By Dr. Mindy Aisen CEO and Director United Cerebral Palsy Research and Educational Foundation www.ucpresearch.org CEREBRAL PALSY RESEARCH
 By Dr. Mindy Aisen CEO and Director United Cerebral Palsy Research and Educational Foundation www.ucpresearch.org CEREBRAL PALSY RESEARCH Main Sources of Federal Funding for Cerebral Palsy and Disability
By Dr. Mindy Aisen CEO and Director United Cerebral Palsy Research and Educational Foundation www.ucpresearch.org CEREBRAL PALSY RESEARCH Main Sources of Federal Funding for Cerebral Palsy and Disability
GUIDELINES AND SERVICES FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY AND PHYSICAL THERAPY
 GUIDELINES AND SERVICES FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY AND PHYSICAL THERAPY Linda Paule, Coordinator San Bernardino City Unified School District Dr. Patty Imbiorski, Director Special Education TABLE OF CONTENTS
GUIDELINES AND SERVICES FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY AND PHYSICAL THERAPY Linda Paule, Coordinator San Bernardino City Unified School District Dr. Patty Imbiorski, Director Special Education TABLE OF CONTENTS
STROKE REHABILITATION INTENSITY:
 STROKE REHABILITATION INTENSITY: Shelley Huffman Stroke Rehabilitation Coordinator Stroke Network of Southeastern Ontario Janine Theben Stroke Rehabilitation Coordinator West GTA Stroke Network Rehab Intensity
STROKE REHABILITATION INTENSITY: Shelley Huffman Stroke Rehabilitation Coordinator Stroke Network of Southeastern Ontario Janine Theben Stroke Rehabilitation Coordinator West GTA Stroke Network Rehab Intensity
OPTIMAL CORE TRAINING FOR FUNCTIONAL GAINS AND PEAK PERFORMANCE: CXWORX
 OPTIMAL CORE TRAINING FOR FUNCTIONAL GAINS AND PEAK PERFORMANCE: CXWORX Jinger S. Gottschall 1, Jackie Mills 2, and Bryce Hastings 2 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, USA 2 Les Mills
OPTIMAL CORE TRAINING FOR FUNCTIONAL GAINS AND PEAK PERFORMANCE: CXWORX Jinger S. Gottschall 1, Jackie Mills 2, and Bryce Hastings 2 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, USA 2 Les Mills
Virtual Reality Technology in Stroke Rehabilitation: Ready for Prime Time
 Virtual Reality Technology in Stroke Rehabilitation: Ready for Prime Time Hillel Finestone, MD CM, FRCPC (Physiatrist/PM&R) Ontario Hospital Association Third Annual Senior Friendly Hospital Care Conference
Virtual Reality Technology in Stroke Rehabilitation: Ready for Prime Time Hillel Finestone, MD CM, FRCPC (Physiatrist/PM&R) Ontario Hospital Association Third Annual Senior Friendly Hospital Care Conference
Effec%ve Evidence- Based Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy Novak, Morgan & Wallen
 Effec%ve Evidence- Based Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy vak, Morgan & Wallen Effec%ve Evidence- Based Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy Prof Iona NOVAK Cathy MORGAN Dr Margaret WALLEN
Effec%ve Evidence- Based Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy vak, Morgan & Wallen Effec%ve Evidence- Based Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy Prof Iona NOVAK Cathy MORGAN Dr Margaret WALLEN
AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES.
 AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES. Sancha Eliot Johannesburg 2010 DECLARATION I SANCHA ELIOT declare that
AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES. Sancha Eliot Johannesburg 2010 DECLARATION I SANCHA ELIOT declare that
SCRIPTA MEDICA (BRNO) 580 (5): 219 224, November 2007
 SCRIPTA MEDICA (BRNO) 580 (5): 219 224, November 2007 children with cerebral palsy after 6-month PHYSIOtherapy Drlíková L. 1, HASHIM M. K. A. 2, AL FADHLIA. K. 2, ANBAIS F. H. 2, ERAJHI A. A. 2, POSPÍŠIL
SCRIPTA MEDICA (BRNO) 580 (5): 219 224, November 2007 children with cerebral palsy after 6-month PHYSIOtherapy Drlíková L. 1, HASHIM M. K. A. 2, AL FADHLIA. K. 2, ANBAIS F. H. 2, ERAJHI A. A. 2, POSPÍŠIL
What is the Spasticity Clinic?
 The Spasticity Clinic This booklet can help you learn about: the Spasticity Clinic at McMaster Children s Hospital spasticity and how it may be treated Your therapist will give you more information and
The Spasticity Clinic This booklet can help you learn about: the Spasticity Clinic at McMaster Children s Hospital spasticity and how it may be treated Your therapist will give you more information and
Routine For: OT - General Guidelines/Energy Conservation (Caregiver)
 GENERAL GUIDELINES - 9 Tips for Exercise: Body Mechanics for Helper - To protect back, stay as upright as possible and keep head in line with trunk. - Always position yourself as close as possible to the
GENERAL GUIDELINES - 9 Tips for Exercise: Body Mechanics for Helper - To protect back, stay as upright as possible and keep head in line with trunk. - Always position yourself as close as possible to the
An Evidence Based Occupational Therapy Toolkit for Assessment and Treatment of the Upper Extremity Post Stroke
 An Evidence Based Occupational Therapy Toolkit for Assessment and Treatment of the Upper Extremity Post Stroke Brenda Semenko, Leyda Thalman, Emily Ewert, Renee Delorme, Suzanne Hui, Heather Flett, Nicole
An Evidence Based Occupational Therapy Toolkit for Assessment and Treatment of the Upper Extremity Post Stroke Brenda Semenko, Leyda Thalman, Emily Ewert, Renee Delorme, Suzanne Hui, Heather Flett, Nicole
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Rotator Cuff Repair
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 3 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Pre-Operative... 3 7.2 Post-Operative...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 3 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Pre-Operative... 3 7.2 Post-Operative...
Stroke Rehabilitation - Evidence Based Practice
 Stroke Rehabilitation - Evidence Based Practice Section 1 1) What percent of stroke patients are left with moderate functional impairment? a) 25% b) 40% c) 55% d) 70% 2) Which is not a component of the
Stroke Rehabilitation - Evidence Based Practice Section 1 1) What percent of stroke patients are left with moderate functional impairment? a) 25% b) 40% c) 55% d) 70% 2) Which is not a component of the
Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006. SUBJECT: Changes Conforming to CR3648 for Therapy Services
 CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006 Change
CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006 Change
Executive Summary Relationship of Student Outcomes to School-Based Physical Therapy Service PT COUNTS
 Executive Summary Relationship of Student Outcomes to School-Based Physical Therapy Service PT COUNTS Physical Therapy related Child Outcomes in the Schools (PT COUNTS) was a national study supported by
Executive Summary Relationship of Student Outcomes to School-Based Physical Therapy Service PT COUNTS Physical Therapy related Child Outcomes in the Schools (PT COUNTS) was a national study supported by
Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy
 Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
Cerebral Palsy. Causes
 Cerebral Palsy Cerebral Palsy (sera brul PAUL zee) (CP) is an injury or abnormality of the developing brain that affects movement. This means that something happened to the brain or the brain did not develop
Cerebral Palsy Cerebral Palsy (sera brul PAUL zee) (CP) is an injury or abnormality of the developing brain that affects movement. This means that something happened to the brain or the brain did not develop
www.kennedykrieger.org www.kennedykrieger.org
 Too Early for Mobility? The Benefits of Early Mobility on Pediatric Development Disclosures Julie Cagney, PT, DPT Sarah Murdoch, PT, DPT, ATP Kaitlin MacDonald, MOT, OTR/L Have no financial or non-financial
Too Early for Mobility? The Benefits of Early Mobility on Pediatric Development Disclosures Julie Cagney, PT, DPT Sarah Murdoch, PT, DPT, ATP Kaitlin MacDonald, MOT, OTR/L Have no financial or non-financial
Low-dose/highconcentration. botulinum toxin A improves upper limb movement and function in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy
 Low-dose/highconcentration localized botulinum toxin A improves upper limb movement and function in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy Kevin Lowe* MBBS FRACP FAFRM, Department of Paediatric Rehabilitation,
Low-dose/highconcentration localized botulinum toxin A improves upper limb movement and function in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy Kevin Lowe* MBBS FRACP FAFRM, Department of Paediatric Rehabilitation,
Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Upper and Lower Limb Spasticity Post Stroke
 Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Upper and Lower Limb Spasticity Post Stroke Robert Teasell MD, Norine Foley MSc, Katherine Salter BA, Sanjit Bhogal MSc. Botulinum toxin is significantly associated
Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Upper and Lower Limb Spasticity Post Stroke Robert Teasell MD, Norine Foley MSc, Katherine Salter BA, Sanjit Bhogal MSc. Botulinum toxin is significantly associated
STROKE REHABILITATION RESOURCE GUIDE
 STROKE REHABILITATION RESOURCE GUIDE INTRODUCTION The intent of the Stroke Rehabilitation Resource Guide is to enable stroke care providers seeking information related to the rehabilitation of the stroke
STROKE REHABILITATION RESOURCE GUIDE INTRODUCTION The intent of the Stroke Rehabilitation Resource Guide is to enable stroke care providers seeking information related to the rehabilitation of the stroke
Trauma Center Alcohol Screening. Michael Mello, MD, MPH Injury Prevention Center at Rhode Island Hospital /Hasbro Children s Hospital
 Trauma Center Alcohol Screening and Intervention Michael Mello, MD, MPH Injury Prevention Center at Rhode Island Hospital /Hasbro Children s Hospital Disclosures I have no affiliations, sponsorship, financial
Trauma Center Alcohol Screening and Intervention Michael Mello, MD, MPH Injury Prevention Center at Rhode Island Hospital /Hasbro Children s Hospital Disclosures I have no affiliations, sponsorship, financial
The Use of the Lokomat System in Clinical Research
 International Neurorehabilitation Symposium February 12, 2009 The Use of the Lokomat System in Clinical Research Keith Tansey, MD, PhD Director, Spinal Cord Injury Research Crawford Research Institute,
International Neurorehabilitation Symposium February 12, 2009 The Use of the Lokomat System in Clinical Research Keith Tansey, MD, PhD Director, Spinal Cord Injury Research Crawford Research Institute,
YouGrabber playful therapy for finger, hand and arm rehabilitation
 playful therapy for finger, hand and arm rehabilitation Intensive and motivating training For hospitals, clinics and patients at home Award-winning Swiss therapy system swiss technology Our patients see
playful therapy for finger, hand and arm rehabilitation Intensive and motivating training For hospitals, clinics and patients at home Award-winning Swiss therapy system swiss technology Our patients see
Winter/Spring 2016. Community Therapy Programs
 Winter/Spring 2016 Community Therapy Programs 2015 Martina Magnusson Community Based Therapy Programs compliment our comprehensive center-based therapy services. We ve developed unique programs that target
Winter/Spring 2016 Community Therapy Programs 2015 Martina Magnusson Community Based Therapy Programs compliment our comprehensive center-based therapy services. We ve developed unique programs that target
Rehabilitation of the Elite Athlete After TBI. Suzanne Carr, DPT Margaret Fuller, MA, OT/L February, 2015
 Rehabilitation of the Elite Athlete After TBI Suzanne Carr, DPT Margaret Fuller, MA, OT/L February, 2015 Outline Case study medical history Initial Evaluation Status, Treatment problems Treatment approaches
Rehabilitation of the Elite Athlete After TBI Suzanne Carr, DPT Margaret Fuller, MA, OT/L February, 2015 Outline Case study medical history Initial Evaluation Status, Treatment problems Treatment approaches
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Post-Operative Shoulder Instability Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Post-Operative Shoulder Instability Repair Please note that this is advisory information only. Your experiences may differ from those described. A fully qualified Physiotherapist
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Post-Operative Shoulder Instability Repair Please note that this is advisory information only. Your experiences may differ from those described. A fully qualified Physiotherapist
International Neurorehabilitation Symposium 2009 Rehabilitation of the Upper Limbs: First Experiences with Armor and Amadeo
 International Neurorehabilitation Symposium 2009 Rehabilitation of the Upper Limbs: First Experiences with Armor and Amadeo Leopold Saltuari Hospital Hochzirl, Austria Zurich, 12 14 February 2009 Different
International Neurorehabilitation Symposium 2009 Rehabilitation of the Upper Limbs: First Experiences with Armor and Amadeo Leopold Saltuari Hospital Hochzirl, Austria Zurich, 12 14 February 2009 Different
Physical Therapy and Occupational Therapy Services of Young Children with Cerebral Palsy
 Physical Therapy and Occupational Therapy Services of Young Children with Cerebral Palsy Denise Begnoche, PT, DPT, Lisa Chiarello, PT, PhD, PCS, Doreen Bartlett, PT, PhD, Robert Palisano, PT, ScD Hui-Ju
Physical Therapy and Occupational Therapy Services of Young Children with Cerebral Palsy Denise Begnoche, PT, DPT, Lisa Chiarello, PT, PhD, PCS, Doreen Bartlett, PT, PhD, Robert Palisano, PT, ScD Hui-Ju
