Using GFP, Virtual Concatenation, LCAS and GMPLS for Ethernet Transport over SONET/SDH Networks. By James D. Jones Student ID
|
|
|
- Barrie Stevens
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using GFP, Virtual Concatenation, LCAS and GMPLS for Transport over SONET/SDH Networks By James D. Jones Student ID EETS-8391 Summer 2002
2 Abstract As the bandwidth demand of continues to grow, the influence of is migrating into the transport world. While is the dominant technology in data networking environments, SONET and SDH dominate the MAN/WAN transport world. Pressure is increasing to offer low cost, long reach connectivity between remote nodes or networks using SONET/SDH transport. Several key technologies are enabling this trend, including: - Generic Framing Procedure (GFP): a method to encapsulate any data type into a format suitable for optical transport. - Virtual Concatenation: a technique to assign payload areas of arbitrary size within a SONET/SDH signal. It can be used to transport payloads that do not fit efficiently in the standard STS-Nc SPE sizes that are typically supported by existing SONET/SDH network elements (NEs). - Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme (LCAS): a signaling mechanism to dynamically adjust the size of a container transported in a SONET/SDH Network with Virtual Concatenation. - Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) and Generalized MPLS (GMPLS): efficient data forwarding techniques, originally designed for packet-oriented networks, later extended by GMPLS to support any transport type. GFP, VC and LCAS have been developed in parallel and their main benefits are realized when they are used in combination. These elements combined with the discovery, routing, signaling capabilities of GMPLS enable powerful dynamic bandwidth control applications. This report will explore the role played by each of these technologies in enabling efficient transport of over SONET and SDH. (For simplicity, this article from here on will refer to SONET, although it is meant to include both SONET and SDH). Motivation for GMPLS-Controlled over SONET The case for GMPLS-Controlled over SONET (EoS) is primarily one of economics. The low cost and wide range of equipment and applications supported by continues to expand. As the bit rate and number of users grow, so does the need to provide higher bandwidth and longer reach transport systems to interconnect nodes and networks. The broad base of SONET equipment is the mainstay of carriers MAN and WAN transport, but was originally architected for voice/tdm traffic. Given these factors, there is significant interest in providing a - 1
3 more cost-effective, flexible method of transporting over SONET. At the same time, carriers need to reduce the operating costs of provisioning these services, while offering them in a reduced set up time. GMPLS has been developed to enable automated rapid provisioning of high bandwidth connections over SONET networks. Existing methods of providing long-distance connectivity include Packet-over-SONET (PoS) and X.86 using LAPS framing. These techniques utilize flag word delineation in combination with byte stuffing to map packets or MAC frames into SONET SPEs. The primary limitation of such techniques is the complex termination and adaptation processes that take place at the ingress and egress of the networks. The byte stuffing process required for transparency also causes a variation in the bit rate required of the transport network. The aim of EoS using GFP, VC and LCAS is to deliver the MAC layer simply and in a native format using standards-based techniques between the DTEs or networks. In essence, the end-users would view the transport network as a simple switch providing local connectivity. Further, the elimination of byte stuffing by GFP removes variations in bandwidth needed to transport. The delivery of over SONET networks requires co-existence of data and TDM signals within the SONET payload. The key to this migration is a hybrid network element at the edge of the SONET network that could multiplex either data or TDM traffic into the same SPE. Sample applications enabled by such hybrid nodes include [1]: - private lines (EPLs), providing simple point-to-point connectivity between remote nodes by using SONET transport networks to emulate transport. EPLs could either use dedicated TDM channels for each user or statistically multiplex frames from multiple users within a TDM channel. - Transparent LAN services, providing multipoint connectivity to extend learning and bridging functions over the SONET network. Over the last 3 years, considerable effort has gone into definition and development of GFP, VC and LCAS to deliver this capability. The following sections will discuss each of these, along with GMPLS, then show how they may be used in combination to provide effective EoS. - 2
4 Generic Framing Procedure In 1999, the ITU-T and ANSI chartered an effort on data over SONET to promote vendor equipment and carrier interworking [2]. This was origin of Generic Framing Procedure (GFP), which is being defined in ITU-T Draft Recommendation G.7041/Y.1303 [3]. GFP is a lightweight adaptation protocol to provide flexible mapping of different bitstream types into a single bytesynchronous channel. It provides efficient encapsulation with fixed, but small overhead per packet. Other techniques can map data into SONET payloads, but as discussed, they exhibit nondeterministic bandwidth expansion due to byte-stuffed transparency processing. GFP has two different mapping techniques, transparent and frame-based. Transparent-mapped GFP provides minimum latency by transporting block-coded signals (presently only 8B/10B) for applications such as SAN. Frame-mapped GFP provides more flexibility and simplicity, and is preferred for most packet data types. Frame-mapped GFP stores and forwards entire client frames in a single GFP frame, thus increasing latency over transparent GFP. When mapping using frame-mapped GFP, the preamble and SFD are discarded and the remainder of the frame is mapped into the GFP payload. If both the transport and bridging capabilities of are integrated into transport NEs, the frame-mapped mode is preferable since the layer 1 aspects of both SONET and interfaces are segregated from layer 2 aspects [1]. Virtual Concatenation Virtual Concatenation is an inverse-multiplexing technique that combines an arbitrary number of SONET channels to create a single byte-synchronous stream. It is defined in ITU-T Recommendation G.707 [4] and ANSI T [5]. Virtual Concatenation is intended to solve the problem of coarse bandwidth granularity of the existing containers in a SONET signal. Two methods for concatenation are defined, contiguous and virtual concatenation. Both methods provide concatenated bandwidth of X times Container-N at the path termination. Contiguous concatenation maintains the contiguous bandwidth through out the whole transport, transported through the same physical resources. Virtual concatenation breaks the contiguous bandwidth into individual virtual containers (VCs), transports the individual VCs and recombines these VCs to a contiguous bandwidth at the end point of the transmission. Virtual concatenation requires concatenation functionality only at the path termination equipment, while contiguous concatenation requires concatenation functionality at each network element [4]. Virtual concatenation does not require a single pipe of the required bandwidth through the network, as continuous concatenation does; it can use smaller increments of available bandwidth to build a larger bandwidth end-to-end pipe. - 3
5 Virtual concatenation can significantly improve the bandwidth utilization of signals mapped into SONET. Table 1 shows examples of bandwidth utilization for both Contiguous and Virtual Concatenation [1, 2]. Table 1: Bandwidth Efficiency Comparison of Contiguous and Virtual Concatenation Data Signal 10 Mbit/s 100 Mbit/s Fast 1 Gbit/s SONET/SDH Payload Mapping and Bandwidth Utilization Contiguous Concatenation STS-1: 20% VC-3: 20% STS-3c: 67% VC-4: 67% STS-48c: 42% VC-4-16c: 42% SONET/SDH Payload Mapping and Bandwidth Utilization Virtual Concatenation VT-1.5-7v: 89% VT-12-5v: 92% STS-1-2v: 100% VC-3-2v: 100% STS-1-21v: 98% VC-3-21v: 98% Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme A companion technology to Virtual Concatenation is the Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme (LCAS), being defined in ITU-T Draft Recommendation G.7042/Y.1305 [6]. LCAS is an extension to Virtual Concatenation that allows dynamic changes to the number of SONET channels in use. LCAS signaling is carried in-band on Path overhead bytes. LCAS bandwidth adjustment is done by the edge NEs to achieve hitless performance of Virtual Concatenation Groups (VCGs). As the bandwidth required by the signals varies, LCAS can be used to signal changes needed to the VCGs, providing elastic bandwidth through the SONET network. LCAS does not signal and set up intermediate resources needed to change the bandwidth from end to end. It is concerned only with coordinating the bandwidth adjustment on the end-points, once the physical resources in between have been provisioned. These intermediate resources can be provisioned through the management plane on an EMS/NMS or dynamically provisioned using a distributed control plane protocol suite such as GMPLS. Generalized MPLS Distributed control plane protocols like GMPLS are intended to provide real-time provisioning, dynamic bandwidth allocation and fast restoration. GMPLS attempts to leverage the Traffic Engineering benefits of MPLS for the control of non-packet switched interfaces such as optical cross-connects (OXCs). Since OXCs generally switch individual wavelengths, this initiative was originally called Multiprotocol Lambda Switching (MPλS). As MPλS progressed, a more general - 4
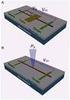
6 need was defined to extend MPLS techniques not just to wavelength switching, but to other entities, such as TDM channels or fibers carrying multiple wavelengths. Consequently, MPλS was redirected into a more universal form called Generalized MPLS (GMPLS). GMPLS is also intended to support a wide variety of NEs with different interface switching types (such as packet-, TDM-, wavelength- and fiber-switched types). Architecture of over SONET with GFP, VC, LCAS and GMPLS This section describes the interworking of the major building blocks of a GMPLS-controlled over SONET network. It begins with the desired behavioral view of such a network, then describe the architectural and protocol aspects. Finally, the architecture of the hybrid edge NEs is discussed to show how SONET networks can accommodate both TDM and data traffic. Figure 1 shows the desired behavioral view of such a network from perspective of the end user systems. The intent is for the SONET transport network to emulate the behavior of a switched network through appropriate adaptation and control. The end users transmit MAC frames to the SONET network, which behaves the same as if it was switched. Figure 1: Behavioral View of over SONET Network (to end users) User A MAC Frames (Virtual) Switched Network MAC Frames User Z Since SONET networks currently handle large volumes of voice/tdm traffic, both data and TDM must gracefully co-exist in the SONET network. The key to this objective is a hybrid edge NE that can aggregate both TDM and data flows to best utilize the available capacity of the SONET network. Figure 2 shows an architectural view of the network with these hybrid NEs originating and terminating both TDM and data flows. The MAC frames, along with other data and TDM traffic are mapped into SONET payloads and transported through the network. By incorporating these features into edge NEs that originate and terminate path layer signals, no other changes are required in intermediate nodes in the SONET network. - 5
7 Figure 2: Architectural View of over SONET Network TDM Traffic MAC Frames SONET Network MAC Frames TDM Traffic User A Other Data Traffic SONET Path Layer Signals (TDM + Data) Hybrid TDM/Data Nodes Other Data Traffic User Z Figure 3 expands on the protocols and functions performed by the edge NEs and the SONET network. To initiate the connection, the end user may signal a connection request to the network over the User-Network Interface (UNI). The UNI, as defined by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) uses GMPLS signaling protocols based on RSVP-TE and CR-LDP to accomplish this. (Alternatively, the connection between end users and the network could be provisioned through an EMS/NMS.) Within the network a routing protocol like OSPF-TE or IS-IS is used to select specific resources that will be used to complete the connection. These resources are set up via signaling protocols. The hybrid NEs on the edge of the SONET network also perform the adaptation and control functions using GFP, Virtual Concatenation and LCAS. The ingress NE encapsulates the MAC frames into GFP frames. It also performs the inverse multiplexing needed to map the GFP frames into VCGs and performs the LCAS signaling to coordinate end-to-end bandwidth changes. LCAS must interwork with the GMPLS protocols on the edge NE. If LCAS needs to increase the bandwidth and an existing Label Switched Path (LSP a GMPLS connection) is available for use, LCAS can signal the bandwidth adjustment. If an existing LSP is not available for LCAS, the GMPLS protocols must establish a new LSP for LCAS to use. - 6
8 UNI Signaling (optional) RSVP-TE CR-LDP Figure 3:Protocol/Functional View GMPLS Signaling and Routing RSVP-TE/CR-LDP OSPF-TE/IS-IS UNI Signaling (optional) RSVP-TE CR-LDP User A User Z Adaptation and Control: GFP Mapping Virtual Concatenation (inverse mux) LCAS Control Adaptation and Control: GFP De-mapping Virtual Concatenation (mux, reassembly) LCAS Control The hybrid NEs at the network edge are critical to this architecture. An expansion of the functionality of a hybrid NE is given in figure 4 (based on [1], [7] and [8]). For simplicity the flow is only shown for signals coming into the NE. (In the figure, the abbreviation Eth represents either 10/100 M or Gb.) Native signals are received and the MAC frames are extracted. The System Packet Interface (SPI) is a standard electrical interface defined by the OIF to separate the synchronous PHY layer from asynchronous packet-based processing. SPI supports transmit and receive data transfers at clock rates independent of the actual line bit rate for the efficient transfer of both variable-sized packet and fixed-sized cell data. In OIF terminology, SPI-3 supports OC-48 rates and SPI-4 supports OC-192 [9]. The MAC Frame is encapsulated in a GFP frame and assigned to a VCG. The LCAS function coordinates the end-end adjustments in bandwidth for each virtual container. - 7
9 Figure 4: Signal Flow, Hardware and Simplified Stack Model for Hybrid NE Native Interface Signals (G)MII System Packet Interface GFP Mapped Frames Virtual Concatenation Groups SONET STS-N Signal Hardware PHY layer Termination Switch Fabric GFP Encapsulation L C A S... ADM Switch Fabric Simplified Stack Models Eth MAC Eth MAC SPI-n PHY Eth MAC GFP frame Eth (G)MII Eth (G)MII SPI-n Elec GFP Frame SONET PHY Eth PHY SONET optics Eth optics Conclusion This paper has described some of the key elements for efficient transport of over SONET. Using GFP in this application makes SONET both versatile and flexible, while the combination of LCAS and Virtual Concatenation make it elastic. Applying GMPLS control to such a network adds rapid provisioning and traffic engineering features. All the techniques described GFP, Virtual Concatenation, LCAS and GMPLS are still emerging technologies. Silicon implementations of GFP are becoming available and should be well-supported by multiple vendors. Virtual Concatenation has been standardized, but the LCAS control to fully exploit it is still completing the standardization process and LCAS software developments are not mature. GMPLS signaling is relatively mature across the UNI, but standardized signaling and routing within the networks (NNI Network-Node Interfaces) is still being defined by both ITU-T and OIF. All these technologies should quickly mature and become available in the near future. The critical factor, however is the demand for such products from network operators. Since the main motivation of GFP, LCAS, Virtual Concatenation and GMPLS is to reduce operating costs and maximize network utilization, over SONET networks based on these technologies can be expected to emerge and grow rapidly. - 8
10 References [1] E. Hernandez-Valencia, Hybrid Transport Solutions for TDM/Data Networking Services, IEEE Communications Magazine, May 2002, p [2] P. Bonenfant and A. Rodriguez-Moral, Generic Framing Procedure (GFP): The Catalyst for Efficient Data over Transport, IEEE Communications Magazine, May 2002, p [3] ITU-T Draft Rec. G.7041/Y.1303, Generic Framing Procedure (GFP), October [4] ITU-T Rec. G.707, Network Node Interface for the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH), October [5] ANSI T , American National Standard for Telecommunications Synchronous Optical Network (SONET): Physical Interfaces Specification, [6] ITU-T Draft Rec. G.7042/Y.1305, Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme (LCAS), [7] D. Cavendish et al, New Transport Services for Next-Generation SONET/SDH Systems, IEEE Communications Magazine, May 2002, p [8] M. Scholten, et al, Data Transport Applications Using GFP, IEEE Communications Magazine, May 2002, p [9] OIF White Paper, OIF Electrical Interfaces,
11 Internet Addresses of Standards Bodies and Forums International Telecommunications Union: Internet Engineering Task Force: Optical Internetworking Forum: Acronyms ANSI American National Standard Institute NMS Network Management System CR-LDP Constraint-based Label Distribution Protocol NNI Network-Network Interface, or Network Node Interface DTE Data Terminating Equipment OC Optical Carrier EoS over SONET OIF Optical Internetworking Forum EMS Element Management System OSPF-TE Open Shortest Path First - Traffic Engineering EPL Private Line OXC Optical Cross-Connect GFP Generic Framing Procedure PHY Physical Layer GMII Gigabit Medium Independent PoS Packet over SONET Interface GMPLS Generalized Multiprotocol Label RSVP-TE Resource Reservation Protocol - Traffic Switching Engineering IETF Internet Engineering Task Force SAN Storage Area Network IS-IS Intermediate System - Intermediate SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy System ITU-T SFD Start of Frame Delimiter International Telecommunications Union - Telecommunications Standardization Sector LAN Local Area Network SONET Synchronous Optical NETwork LAPS Link Access Procedure - SONET SPE Synchronous Payload Envelope LCAS Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme SPI System Packet Interface LSP Label Switched Path STS Synchronous Transport Signal MAC Medium Access Control TDM Time Division Multiplexing MAN Metropolitan Area Network UNI User-Network Interface MII Medium Independent Interface VC Virtual Container MPLS Multiprotocol Label Switching VCG Virtual Container Group MPλS Multiprotocol Lambda Switching VLAN Virtual Local Area Network NE Network Element WAN Wide Area Network - 10
Making Ethernet Over SONET Fit a Transport Network Operations Model
 Making Over SONET Fit a Transport Network Operations Model Introduction Many carriers deploy or evaluate deployment of EoS as a private line offering to enhance existing service offerings. Service definitions
Making Over SONET Fit a Transport Network Operations Model Introduction Many carriers deploy or evaluate deployment of EoS as a private line offering to enhance existing service offerings. Service definitions
Next Generation SONET/SDH Technologies and Applications
 White Paper Next Generation SONET/SDH Technologies and Applications By Werner Habisreitinger Executive summary Innovation, the lifeline to survival in the telecommunications market, has spurred the telecommunications
White Paper Next Generation SONET/SDH Technologies and Applications By Werner Habisreitinger Executive summary Innovation, the lifeline to survival in the telecommunications market, has spurred the telecommunications
Relationship between SMP, ASON, GMPLS and SDN
 Relationship between SMP, ASON, GMPLS and SDN With the introduction of a control plane in optical networks, this white paper describes the relationships between different protocols and architectures. Introduction
Relationship between SMP, ASON, GMPLS and SDN With the introduction of a control plane in optical networks, this white paper describes the relationships between different protocols and architectures. Introduction
Deploying Multiservice Applications Using RPR Over the Existing SONET Infrastructure
 Deploying Multiservice Applications Using RPR Over the Existing SONET Infrastructure Introduction The migration of Ethernet technology from the LAN to metro networks, driven by increasing demand in VoIP,
Deploying Multiservice Applications Using RPR Over the Existing SONET Infrastructure Introduction The migration of Ethernet technology from the LAN to metro networks, driven by increasing demand in VoIP,
SDH and WDM A look at the physical layer
 SDH and WDM A look at the physical Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network management and QoS provisioning - 1 Copyright This
SDH and WDM A look at the physical Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network management and QoS provisioning - 1 Copyright This
SDH and WDM: a look at the physical layer
 SDH and WDM: a look at the physical SDH and WDM A look at the physical Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network management and
SDH and WDM: a look at the physical SDH and WDM A look at the physical Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network management and
Delivering Ethernet services in the Metro
 Delivering Ethernet services in the Metro MICHAEL S. BERGER Research Center COM Technical University of Denmark DTU Building 33, 800 Kgs. Lyngby DENMARK Abstract: - Today, Ethernet is widely deployed in
Delivering Ethernet services in the Metro MICHAEL S. BERGER Research Center COM Technical University of Denmark DTU Building 33, 800 Kgs. Lyngby DENMARK Abstract: - Today, Ethernet is widely deployed in
Introduction. Background
 Introduction By far, the most widely used networking technology in Wide Area Networks (WANs) is SONET/SDH. With the growth of Ethernet now into Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) there is a growing need
Introduction By far, the most widely used networking technology in Wide Area Networks (WANs) is SONET/SDH. With the growth of Ethernet now into Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) there is a growing need
Broadband Networks. Prof. Abhay Karandikar. Electrical Engineering Department. Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbai.
 Broadband Networks Prof. Abhay Karandikar Electrical Engineering Department Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbai Lecture - 32 Metro Ethernet Access Networks So, in today s lecture we will talk about
Broadband Networks Prof. Abhay Karandikar Electrical Engineering Department Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbai Lecture - 32 Metro Ethernet Access Networks So, in today s lecture we will talk about
Ethernet Over SONET. Technology White Paper. Mimi Dannhardt Technical Advisor
 Mimi Dannhardt Technical Advisor Issue 1: February, 2002 PMC-2020296 Abstract This White Paper describes the use of the new ITU G.7041 GFP and ITU G.7042 LCAS standards to provide Ethernet leased line
Mimi Dannhardt Technical Advisor Issue 1: February, 2002 PMC-2020296 Abstract This White Paper describes the use of the new ITU G.7041 GFP and ITU G.7042 LCAS standards to provide Ethernet leased line
GMPLS Network Management: Challenges and Solutions
 GMPLS Network Management: Challenges and Solutions Thomas D. Nadeau Technical Leader 1 Fundamental Question Why is network management so important to the success of GMPLS/UCP? 2 Agenda Motivations and
GMPLS Network Management: Challenges and Solutions Thomas D. Nadeau Technical Leader 1 Fundamental Question Why is network management so important to the success of GMPLS/UCP? 2 Agenda Motivations and
GPON - EPON Comparison
 White Paper GPON - EPON Comparison CommScope Solutions Marketing October 2013 Contents Introduction 3 Protocol fundamentals 4 Framing/service adaption 4 Basic operation 5 Service hierarchy 7 Bandwidth
White Paper GPON - EPON Comparison CommScope Solutions Marketing October 2013 Contents Introduction 3 Protocol fundamentals 4 Framing/service adaption 4 Basic operation 5 Service hierarchy 7 Bandwidth
Master Course Computer Networks IN2097
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department for Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Chair for
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department for Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Chair for
Building a Bigger Pipe: Inverse Multiplexing for Transparent Ethernet Bridging over Bonded T1/E1s
 Building a Bigger Pipe: Inverse Multiplexing for Transparent Ethernet Bridging over Bonded T1/E1s The fast path to increased bandwidth for carriers, service providers, and enterprises Printed in the USA.
Building a Bigger Pipe: Inverse Multiplexing for Transparent Ethernet Bridging over Bonded T1/E1s The fast path to increased bandwidth for carriers, service providers, and enterprises Printed in the USA.
Connection-Oriented Ethernet On-Ramp Aggregation for Next-Generation Networks
 Connection-Oriented Ethernet On-Ramp Aggregation for Next-Generation Networks Introduction The GIG and its component networks, including the DISN, form the state-of-the-art network foundation for DoD communications.
Connection-Oriented Ethernet On-Ramp Aggregation for Next-Generation Networks Introduction The GIG and its component networks, including the DISN, form the state-of-the-art network foundation for DoD communications.
Ethernet over SONET. Dr. John S. Graham University of London Computer Centre
 Ethernet over SONET Dr. John S. Graham University of London Computer Centre Ethernet vs SONET Feature Ethernet SONET Guaranteed Delivery No (Packet Switched) Yes (Circuit Switched) Guaranteed BW No Yes
Ethernet over SONET Dr. John S. Graham University of London Computer Centre Ethernet vs SONET Feature Ethernet SONET Guaranteed Delivery No (Packet Switched) Yes (Circuit Switched) Guaranteed BW No Yes
Lecture 12 Transport Networks (SONET) and circuit-switched networks
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 1 Transport Networks (SONET) and circuit-switched networks Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 005 Transport Networks and SONET/SDH In most cases
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 1 Transport Networks (SONET) and circuit-switched networks Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 005 Transport Networks and SONET/SDH In most cases
Lecture Computer Networks
 Lecture Computer Networks Prof. Dr. Hans Peter Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Asynchronous
Lecture Computer Networks Prof. Dr. Hans Peter Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Asynchronous
New WAN PHY Approach Proposals
 New WAN Approach Proposals Feed Forward Rate Control (FFRC) & 10Gigabit Ethernet Network Interface Extension (10GENIE) IEEE P802.3ae 6-10 March, 2000 Albuquerque, NM Osamu ISHIDA and Haruhiko ICHINO NTT
New WAN Approach Proposals Feed Forward Rate Control (FFRC) & 10Gigabit Ethernet Network Interface Extension (10GENIE) IEEE P802.3ae 6-10 March, 2000 Albuquerque, NM Osamu ISHIDA and Haruhiko ICHINO NTT
DigiPoints Volume 1. Student Workbook. Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology
 Growing Capacity Through Technology Page 5. 1 DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology Summary This module covers the North American Digital Hierarchy (NADH), the European Digital
Growing Capacity Through Technology Page 5. 1 DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology Summary This module covers the North American Digital Hierarchy (NADH), the European Digital
Enhancing Converged MPLS Data Networks with ATM, Frame Relay and Ethernet Interworking
 TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPER Enhancing Converged Data Networks with, Frame Relay and Ethernet Interworking Virtual Private Networks (VPN) are a popular way for enterprises to interconnect remote sites. Traditionally,
TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPER Enhancing Converged Data Networks with, Frame Relay and Ethernet Interworking Virtual Private Networks (VPN) are a popular way for enterprises to interconnect remote sites. Traditionally,
It explains the differences between the Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy and the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy.
 TECHNICAL TUTORIAL Subject: SDH Date: October, 00 Prepared by: John Rumsey SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy. Introduction. The Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH). The Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
TECHNICAL TUTORIAL Subject: SDH Date: October, 00 Prepared by: John Rumsey SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy. Introduction. The Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH). The Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
Migrating to MPLS Technology and Applications
 Migrating to MPLS Technology and Applications Serge-Paul Carrasco June 2003 asiliconvalleyinsider.com Table Of Content Why to migrate to MPLS? Congestion on the Internet Traffic Engineering MPLS Fundamentals
Migrating to MPLS Technology and Applications Serge-Paul Carrasco June 2003 asiliconvalleyinsider.com Table Of Content Why to migrate to MPLS? Congestion on the Internet Traffic Engineering MPLS Fundamentals
Understanding PBB-TE for Carrier Ethernet
 Understanding PBB-TE for Carrier Ethernet Introduction Ethernet is evolving from an enterprise LAN technology to a much more robust, carrier-grade transport technology for metropolitan service networks.
Understanding PBB-TE for Carrier Ethernet Introduction Ethernet is evolving from an enterprise LAN technology to a much more robust, carrier-grade transport technology for metropolitan service networks.
Communication Networks. MAP-TELE 2011/12 José Ruela
 Communication Networks MAP-TELE 2011/12 José Ruela Network basic mechanisms Introduction to Communications Networks Communications networks Communications networks are used to transport information (data)
Communication Networks MAP-TELE 2011/12 José Ruela Network basic mechanisms Introduction to Communications Networks Communications networks Communications networks are used to transport information (data)
Metro Ethernet Networks (MEN)
 185 Metro Ethernet Networks (MEN) Luis Velasco, Jordi Perelló, Gabriel Junyent Optical Communication Group - Universitat Politècnica de Cataluya (UPC) E-mail: luis.velasco@tsc.upc.edu, jper7775@alu-etsetb.upc.edu,
185 Metro Ethernet Networks (MEN) Luis Velasco, Jordi Perelló, Gabriel Junyent Optical Communication Group - Universitat Politècnica de Cataluya (UPC) E-mail: luis.velasco@tsc.upc.edu, jper7775@alu-etsetb.upc.edu,
Module 4. Switched Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 Switched Communication Networks Lesson 6 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Switching (ATM) Specific Instructional Objectives On completion on this lesson, the student will be able to: State the need
Module 4 Switched Communication Networks Lesson 6 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Switching (ATM) Specific Instructional Objectives On completion on this lesson, the student will be able to: State the need
FURTHER READING: As a preview for further reading, the following reference has been provided from the pages of the book below:
 FURTHER READING: As a preview for further reading, the following reference has been provided from the pages of the book below: Title: Broadband Telecommunications Handbook Author: Regis J. Bud Bates Publisher:
FURTHER READING: As a preview for further reading, the following reference has been provided from the pages of the book below: Title: Broadband Telecommunications Handbook Author: Regis J. Bud Bates Publisher:
A Brief Overview of SONET Technology
 A Brief Overview of SONET Technology Document ID: 13567 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions SONET Basics SONET Transport Hierarchy Configuration Example SONET Framing
A Brief Overview of SONET Technology Document ID: 13567 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions SONET Basics SONET Transport Hierarchy Configuration Example SONET Framing
Network Working Group (PPP)
 Network Working Group W. Simpson Request for Comments: 1619 Daydreamer Category: Standards Track May 1994 PPP over SONET/SDH Status of this Memo This document specifies an Internet standards track protocol
Network Working Group W. Simpson Request for Comments: 1619 Daydreamer Category: Standards Track May 1994 PPP over SONET/SDH Status of this Memo This document specifies an Internet standards track protocol
Carrier Ethernet Defined
 Carrier Ethernet Defined A comparison of the key WAN transport methods now available for delivering high-value Ethernet services Describing each method s capabilities and how they support the end-user
Carrier Ethernet Defined A comparison of the key WAN transport methods now available for delivering high-value Ethernet services Describing each method s capabilities and how they support the end-user
IP Over WDM Integration Mechanisms
 5 IP Over WDM Integration Mechanisms 5.1 Introduction Different approaches have been proposed for the smooth, fast, and reliable provisioning and management of Internet services over the optical layer.
5 IP Over WDM Integration Mechanisms 5.1 Introduction Different approaches have been proposed for the smooth, fast, and reliable provisioning and management of Internet services over the optical layer.
MPLS Environment. To allow more complex routing capabilities, MPLS permits attaching a
 MPLS Environment Introduction to MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a highly efficient and flexible routing approach for forwarding packets over packet-switched networks, irrespective of the
MPLS Environment Introduction to MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a highly efficient and flexible routing approach for forwarding packets over packet-switched networks, irrespective of the
10G LAN PHY over G.709 OTN: A Service Provider Prospective
 10G LAN PHY over G.709 OTN: A Service Provider Prospective Nee Ben Gee, Bert E.E. Basch, Steven Gringeri Verizon, 40 Sylvan Road, Waltham, MA 02451 781 466 2860, nee-ben.gee@verizon.com Abstract: This
10G LAN PHY over G.709 OTN: A Service Provider Prospective Nee Ben Gee, Bert E.E. Basch, Steven Gringeri Verizon, 40 Sylvan Road, Waltham, MA 02451 781 466 2860, nee-ben.gee@verizon.com Abstract: This
Broadband Networks. Prof. Karandikar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture - 26
 Broadband Networks Prof. Karandikar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 26 Optical Network &MPLS So, as you were discussing in the previous lectures, next
Broadband Networks Prof. Karandikar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 26 Optical Network &MPLS So, as you were discussing in the previous lectures, next
Course 12 Synchronous transmission multiplexing systems used in digital telephone networks
 Course 12 Synchronous transmission multiplexing systems used in digital telephone networks o Disadvantages of the PDH transmission multiplexing system PDH: no unitary international standardization of the
Course 12 Synchronous transmission multiplexing systems used in digital telephone networks o Disadvantages of the PDH transmission multiplexing system PDH: no unitary international standardization of the
LECTURE 5: Wide Area Networks (WANs) CIS484. Communications Systems. Summer 2015 Instructor: Dr. Song Xing
 LECTURE 5: Wide Area Networks (WANs) CIS484 Summer 2015 Instructor: Dr. Song Xing Department of Information Systems California State University, Los Angeles Outlines Introduction to WAN Point-to-point
LECTURE 5: Wide Area Networks (WANs) CIS484 Summer 2015 Instructor: Dr. Song Xing Department of Information Systems California State University, Los Angeles Outlines Introduction to WAN Point-to-point
TDM services over IP networks
 Keyur Parikh Junius Kim TDM services over IP networks 1. ABSTRACT Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) circuits have been the backbone of communications over the past several decades. These circuits which
Keyur Parikh Junius Kim TDM services over IP networks 1. ABSTRACT Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) circuits have been the backbone of communications over the past several decades. These circuits which
MPLS and IPSec A Misunderstood Relationship
 # 129 TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPER Page: 1 of 5 MPLS and IPSec A Misunderstood Relationship Jon Ranger, Riverstone Networks ABSTRACT A large quantity of misinformation and misunderstanding exists about the place
# 129 TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPER Page: 1 of 5 MPLS and IPSec A Misunderstood Relationship Jon Ranger, Riverstone Networks ABSTRACT A large quantity of misinformation and misunderstanding exists about the place
Protocol Architecture. ATM architecture
 Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Asynchronous Transfer Mode: ATM 1990 s/00 standard for high-speed (155Mbps to 622 Mbps and higher) Broadband Integrated Service Digital Network architecture Goal: integrated,
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Asynchronous Transfer Mode: ATM 1990 s/00 standard for high-speed (155Mbps to 622 Mbps and higher) Broadband Integrated Service Digital Network architecture Goal: integrated,
A review of Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)
 677 A review of Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) Olabenjo Babatunde 1, Salim Mbarouk 2 1 (Department of Information Systems Engineering, Cyprus International
677 A review of Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) Olabenjo Babatunde 1, Salim Mbarouk 2 1 (Department of Information Systems Engineering, Cyprus International
Transport for Enterprise VoIP Services
 Transport for Enterprise VoIP Services Introduction Many carriers are looking to advanced packet services as an opportunity to generate new revenue or lower costs. These services, which include VoIP, IP
Transport for Enterprise VoIP Services Introduction Many carriers are looking to advanced packet services as an opportunity to generate new revenue or lower costs. These services, which include VoIP, IP
Computer Networks. Definition of LAN. Connection of Network. Key Points of LAN. Lecture 06 Connecting Networks
 Computer Networks Lecture 06 Connecting Networks Kuang-hua Chen Department of Library and Information Science National Taiwan University Local Area Networks (LAN) 5 kilometer IEEE 802.3 Ethernet IEEE 802.4
Computer Networks Lecture 06 Connecting Networks Kuang-hua Chen Department of Library and Information Science National Taiwan University Local Area Networks (LAN) 5 kilometer IEEE 802.3 Ethernet IEEE 802.4
10 Gigabit Ethernet: Scaling across LAN, MAN, WAN
 Arasan Chip Systems Inc. White Paper 10 Gigabit Ethernet: Scaling across LAN, MAN, WAN By Dennis McCarty March 2011 Overview Ethernet is one of the few protocols that has increased its bandwidth, while
Arasan Chip Systems Inc. White Paper 10 Gigabit Ethernet: Scaling across LAN, MAN, WAN By Dennis McCarty March 2011 Overview Ethernet is one of the few protocols that has increased its bandwidth, while
MPLS is the enabling technology for the New Broadband (IP) Public Network
 From the MPLS Forum Multi-Protocol Switching (MPLS) An Overview Mario BALI Turin Polytechnic Mario.Baldi@polito.it www.polito.it/~baldi MPLS is the enabling technology for the New Broadband (IP) Public
From the MPLS Forum Multi-Protocol Switching (MPLS) An Overview Mario BALI Turin Polytechnic Mario.Baldi@polito.it www.polito.it/~baldi MPLS is the enabling technology for the New Broadband (IP) Public
MPLS VPN Services. PW, VPLS and BGP MPLS/IP VPNs
 A Silicon Valley Insider MPLS VPN Services PW, VPLS and BGP MPLS/IP VPNs Technology White Paper Serge-Paul Carrasco Abstract Organizations have been demanding virtual private networks (VPNs) instead of
A Silicon Valley Insider MPLS VPN Services PW, VPLS and BGP MPLS/IP VPNs Technology White Paper Serge-Paul Carrasco Abstract Organizations have been demanding virtual private networks (VPNs) instead of
Performance Management and Fault Management. 1 Dept. of ECE, SRM University
 Performance Management and Fault Management 1 Dept. of ECE, SRM University Performance Management Performance management requires monitoring of the performance parameters for all the connections supported
Performance Management and Fault Management 1 Dept. of ECE, SRM University Performance Management Performance management requires monitoring of the performance parameters for all the connections supported
Bandwidth Profiles for Ethernet Services Ralph Santitoro
 Ralph Santitoro Abstract This paper provides a comprehensive technical overview of bandwidth profiles for Ethernet services, based on the work (as of October 2003) of the Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) Technical
Ralph Santitoro Abstract This paper provides a comprehensive technical overview of bandwidth profiles for Ethernet services, based on the work (as of October 2003) of the Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) Technical
Bandwidth Profiles for Ethernet Services Ralph Santitoro
 Ralph Santitoro Abstract This paper provides a comprehensive technical overview of bandwidth profiles for Ethernet services, based on the work of the Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) Technical Committee. The
Ralph Santitoro Abstract This paper provides a comprehensive technical overview of bandwidth profiles for Ethernet services, based on the work of the Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) Technical Committee. The
MPLS VPNs: Layer 2 or Layer 3? Understanding the Choice
 #128 TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPER Page: 1 of 6 MPLS VPNs: Layer 2 or Layer 3? Understanding the Choice Tim Wu, Riverstone Networks ABSTRACT Since there s been data networking, there s been a debate between switched
#128 TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPER Page: 1 of 6 MPLS VPNs: Layer 2 or Layer 3? Understanding the Choice Tim Wu, Riverstone Networks ABSTRACT Since there s been data networking, there s been a debate between switched
MPLS-TP The New Technology for Packet Transport Networks
 MPLS-TP The New Technology for Packet Transport Networks Dieter Beller, Rolf Sperber FS/O/PDL, FS/R/VP Alcatel-Lucent Deutschland AG Lorenzstraße 10 D-70435 Stuttgart Dieter.Beller@alcatel-lucent.com Rolf.Sperber@alcatel-lucent.de
MPLS-TP The New Technology for Packet Transport Networks Dieter Beller, Rolf Sperber FS/O/PDL, FS/R/VP Alcatel-Lucent Deutschland AG Lorenzstraße 10 D-70435 Stuttgart Dieter.Beller@alcatel-lucent.com Rolf.Sperber@alcatel-lucent.de
DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL
 IJVD: 3(1), 2012, pp. 15-20 DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL Suvarna A. Jadhav 1 and U.L. Bombale 2 1,2 Department of Technology Shivaji university, Kolhapur, 1 E-mail: suvarna_jadhav@rediffmail.com
IJVD: 3(1), 2012, pp. 15-20 DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL Suvarna A. Jadhav 1 and U.L. Bombale 2 1,2 Department of Technology Shivaji university, Kolhapur, 1 E-mail: suvarna_jadhav@rediffmail.com
Evaluating Carrier-Class Ethernet Services
 Technical Paper Evaluating Carrier-Class Ethernet Services Demand for Ethernet-based services is on the rise, and the key driving force behind this is continuous growth of data traffic in the metro/access
Technical Paper Evaluating Carrier-Class Ethernet Services Demand for Ethernet-based services is on the rise, and the key driving force behind this is continuous growth of data traffic in the metro/access
Link Layer. 5.6 Hubs and switches 5.7 PPP 5.8 Link Virtualization: ATM and MPLS
 Link Layer 5.1 Introduction and services 5.2 Error detection and correction 5.3Multiple access protocols 5.4 Link-Layer Addressing 5.5 Ethernet 5.6 Hubs and switches 5.7 PPP 5.8 Link Virtualization: and
Link Layer 5.1 Introduction and services 5.2 Error detection and correction 5.3Multiple access protocols 5.4 Link-Layer Addressing 5.5 Ethernet 5.6 Hubs and switches 5.7 PPP 5.8 Link Virtualization: and
Primary Data Center. Remote Data Center Plans (COOP), Business Continuity (BC), Disaster Recovery (DR), and data
 White Paper Storage Extension Network Solutions Between Data Centers Simplified, Low Cost, Networks for Storage Replication, Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery TODAY S OPERATING CLIMATE DEMANDS
White Paper Storage Extension Network Solutions Between Data Centers Simplified, Low Cost, Networks for Storage Replication, Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery TODAY S OPERATING CLIMATE DEMANDS
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
 CHAPTER 15 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Background Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) technology is based on the efforts of the International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector
CHAPTER 15 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Background Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) technology is based on the efforts of the International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector
White Paper Abstract Disclaimer
 White Paper Synopsis of the Data Streaming Logical Specification (Phase I) Based on: RapidIO Specification Part X: Data Streaming Logical Specification Rev. 1.2, 08/2004 Abstract The Data Streaming specification
White Paper Synopsis of the Data Streaming Logical Specification (Phase I) Based on: RapidIO Specification Part X: Data Streaming Logical Specification Rev. 1.2, 08/2004 Abstract The Data Streaming specification
LoopStar 700. Next Generation Ethernet Access and Transport Solutions
 LoopStar 700 Next Generation Ethernet Access and Transport Solutions The LoopStar 700 Product Family The LoopStar 700 product family delivers all efficiently consolidate all services onto a the features
LoopStar 700 Next Generation Ethernet Access and Transport Solutions The LoopStar 700 Product Family The LoopStar 700 product family delivers all efficiently consolidate all services onto a the features
OPTICAL TRANSPORT NETWORKS
 OPTICAL TRANSPORT NETWORKS EVOLUTION, NOT REVOLUTION by Brent Allen and James Rouse Nortel Networks, OPTera Metro Solutions KANATA, Canada This paper describes how the deployment today of an Optical Network
OPTICAL TRANSPORT NETWORKS EVOLUTION, NOT REVOLUTION by Brent Allen and James Rouse Nortel Networks, OPTera Metro Solutions KANATA, Canada This paper describes how the deployment today of an Optical Network
WAN. Introduction. Services used by WAN. Circuit Switched Services. Architecture of Switch Services
 WAN Introduction Wide area networks (WANs) Connect BNs and LANs across longer distances, often hundreds of miles or more Typically built by using leased circuits from common carriers such as AT&T Most
WAN Introduction Wide area networks (WANs) Connect BNs and LANs across longer distances, often hundreds of miles or more Typically built by using leased circuits from common carriers such as AT&T Most
Scalability Analysis of Metro Ethernet
 Scalability Analysis of Metro Ethernet Heikki Mahkonen Helsinki University of Technology Email: heikki.mahkonen@piuha.net Abstract This document gives a scalability analysis of Metro Ethernet architecture.
Scalability Analysis of Metro Ethernet Heikki Mahkonen Helsinki University of Technology Email: heikki.mahkonen@piuha.net Abstract This document gives a scalability analysis of Metro Ethernet architecture.
Carrier Class Transport Network Technologies: Summary of Initial Research
 Carrier Class Transport Network Technologies: Summary of Initial Research This document is a summary of the JRA1 Task 1 Carrier Class Transport Network Technologies deliverable [DJ1.1.1], which presents
Carrier Class Transport Network Technologies: Summary of Initial Research This document is a summary of the JRA1 Task 1 Carrier Class Transport Network Technologies deliverable [DJ1.1.1], which presents
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)
 Definition Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a fiber-optic transmission technique that employs light wavelengths to transmit data parallel-by-bit
Definition Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a fiber-optic transmission technique that employs light wavelengths to transmit data parallel-by-bit
Internet Dagarna 2000
 Internet Dagarna 2000 October 24th 2000 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Dennis Davidsson Director Market Development Public Carrier IP Group 2 What s Driving the Demand? 3 How How How Many Many Many of of
Internet Dagarna 2000 October 24th 2000 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Dennis Davidsson Director Market Development Public Carrier IP Group 2 What s Driving the Demand? 3 How How How Many Many Many of of
Blue 102. IP Service Architecture Futures. Geoff Huston May 2000
 Blue 102 IP Service Architecture Futures Geoff Huston May 2000 Next Wave IP Services Service Requirements Connectivity service for customer-operated routers Service payload is IP packet High peak carriage
Blue 102 IP Service Architecture Futures Geoff Huston May 2000 Next Wave IP Services Service Requirements Connectivity service for customer-operated routers Service payload is IP packet High peak carriage
White Paper. Requirements of Network Virtualization
 White Paper on Requirements of Network Virtualization INDEX 1. Introduction 2. Architecture of Network Virtualization 3. Requirements for Network virtualization 3.1. Isolation 3.2. Network abstraction
White Paper on Requirements of Network Virtualization INDEX 1. Introduction 2. Architecture of Network Virtualization 3. Requirements for Network virtualization 3.1. Isolation 3.2. Network abstraction
White Paper: Carrier Ethernet
 White Paper: Carrier Ethernet Activity and Task: JRA1 T1 Target Audience: NREN technical networking specialists Document Code: Authors: J. Kloots (SURFnet), V. Olifer (JANET) Acknowledgement: The research
White Paper: Carrier Ethernet Activity and Task: JRA1 T1 Target Audience: NREN technical networking specialists Document Code: Authors: J. Kloots (SURFnet), V. Olifer (JANET) Acknowledgement: The research
Asynchronous Transfer Mode: ATM. ATM architecture. ATM: network or link layer? ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL)
 Asynchrous Transfer Mode: architecture 1980s/1990 s standard for high-speed (155Mbps to 622 Mbps and higher) Broadband Integrated Service Digital Network architecture Goal: integrated, end-end transport
Asynchrous Transfer Mode: architecture 1980s/1990 s standard for high-speed (155Mbps to 622 Mbps and higher) Broadband Integrated Service Digital Network architecture Goal: integrated, end-end transport
An ATM WAN/LAN Gateway Architecture
 An ATM WAN/LAN Gateway Architecture Gary J. Minden, Joseph B. Evans, David W. Petr, Victor S. Frost Telecommunications & Information Sciences Laboratory Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
An ATM WAN/LAN Gateway Architecture Gary J. Minden, Joseph B. Evans, David W. Petr, Victor S. Frost Telecommunications & Information Sciences Laboratory Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Frame Relay and Frame-Based ATM: A Comparison of Technologies
 White Paper and -Based : A Comparison of Technologies Larry Greenstein Nuera Communications VP, Technology, Forum June 1995 June 27, 1995 i TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. PREFACE...1 2. INTRODUCTION...1 3. INTERWORKING
White Paper and -Based : A Comparison of Technologies Larry Greenstein Nuera Communications VP, Technology, Forum June 1995 June 27, 1995 i TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. PREFACE...1 2. INTRODUCTION...1 3. INTERWORKING
Development of the FITELnet-G20 Metro Edge Router
 Development of the Metro Edge Router by Tomoyuki Fukunaga * With the increasing use of broadband Internet, it is to be expected that fiber-tothe-home (FTTH) service will expand as the means of providing
Development of the Metro Edge Router by Tomoyuki Fukunaga * With the increasing use of broadband Internet, it is to be expected that fiber-tothe-home (FTTH) service will expand as the means of providing
Raj Jain. The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@CIS.Ohio-State.Edu These slides are available on-line at:
 IP Over SONET The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@CIS.Ohio-State.Edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/cis788-99/h_bipsn.htm 1 Overview IP over SONET:
IP Over SONET The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@CIS.Ohio-State.Edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/cis788-99/h_bipsn.htm 1 Overview IP over SONET:
Alcatel-Lucent 1850 TSS-3 Transport Service Switch. A versatile network termination unit
 Alcatel-Lucent Transport Service Switch A versatile network termination unit The Alcatel-Lucent 1850 Transport Service Switch (TSS-3) is a carriergrade network termination unit (NTU). Providing a rich
Alcatel-Lucent Transport Service Switch A versatile network termination unit The Alcatel-Lucent 1850 Transport Service Switch (TSS-3) is a carriergrade network termination unit (NTU). Providing a rich
Fibre Channel over Ethernet in the Data Center: An Introduction
 Fibre Channel over Ethernet in the Data Center: An Introduction Introduction Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a newly proposed standard that is being developed by INCITS T11. The FCoE protocol specification
Fibre Channel over Ethernet in the Data Center: An Introduction Introduction Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a newly proposed standard that is being developed by INCITS T11. The FCoE protocol specification
Alcatel-Lucent 1645 AMC Access Mutiplexer Compact. Cost-effective and compact STM-1/4 multiservice metro access
 Alcatel-Lucent 1645 AMC Access Mutiplexer Compact Cost-effective and compact STM-1/4 multiservice metro access The Alcatel-Lucent 1645 Access Multiplexer Compact (AMC) is a Synchronous Transport Module
Alcatel-Lucent 1645 AMC Access Mutiplexer Compact Cost-effective and compact STM-1/4 multiservice metro access The Alcatel-Lucent 1645 Access Multiplexer Compact (AMC) is a Synchronous Transport Module
Switching Technology S38.165
 Switching Technology S38.165 Pertti Raatikainen, research professor VTT Information Technology pertti.raatikainen@vtt.fi L1-1 General Lecturer: Pertti Raatikainen, research professor /VTT email: pertti.raatikainen@vtt.fi
Switching Technology S38.165 Pertti Raatikainen, research professor VTT Information Technology pertti.raatikainen@vtt.fi L1-1 General Lecturer: Pertti Raatikainen, research professor /VTT email: pertti.raatikainen@vtt.fi
Construction of High-speed and High-reliability Optical Networks for Social Infrastructure
 Hitachi Review Vol. 59 (Feb. 2010) 1 Construction of High-speed and High-reliability Optical Networks for Social Infrastructure Ryosuke Nishino Hideaki Tsushima, Dr. Eng. Eisuke Sato Shinsuke Tanaka OVERVIEW:
Hitachi Review Vol. 59 (Feb. 2010) 1 Construction of High-speed and High-reliability Optical Networks for Social Infrastructure Ryosuke Nishino Hideaki Tsushima, Dr. Eng. Eisuke Sato Shinsuke Tanaka OVERVIEW:
Broadband Networks Virgil Dobrota Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, Romania Virgil.Dobrota@com.utcluj.ro
 Broadband Networks Virgil Dobrota Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, Romania Virgil.Dobrota@com.utcluj.ro Copyright Virgil Dobrota 2007-2008, All rights reserved 1 Course 12 - Outline 46. NGN Next Generation
Broadband Networks Virgil Dobrota Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, Romania Virgil.Dobrota@com.utcluj.ro Copyright Virgil Dobrota 2007-2008, All rights reserved 1 Course 12 - Outline 46. NGN Next Generation
SINET3 for Grid Environments (New Japanese Academic Backbone Network)
 SINET3 for Grid Environments (New Japanese Academic Backbone Network) M. Koibuchi, M. Nakao, and NW groupers National Institute of Informatics (NII), JAPAN 1 2 Evolution of Japanese Academic Networks SINET3
SINET3 for Grid Environments (New Japanese Academic Backbone Network) M. Koibuchi, M. Nakao, and NW groupers National Institute of Informatics (NII), JAPAN 1 2 Evolution of Japanese Academic Networks SINET3
TRILL for Data Center Networks
 24.05.13 TRILL for Data Center Networks www.huawei.com enterprise.huawei.com Davis Wu Deputy Director of Switzerland Enterprise Group E-mail: wuhuajun@huawei.com Tel: 0041-798658759 Agenda 1 TRILL Overview
24.05.13 TRILL for Data Center Networks www.huawei.com enterprise.huawei.com Davis Wu Deputy Director of Switzerland Enterprise Group E-mail: wuhuajun@huawei.com Tel: 0041-798658759 Agenda 1 TRILL Overview
MPLS in Optical Networks
 MPLS in Optical Networks An analysis of the features of MPLS and Generalized MPLS and their application to Optical Networks, with reference to the Link Management Protocol and Optical UNI Neil Jerram,
MPLS in Optical Networks An analysis of the features of MPLS and Generalized MPLS and their application to Optical Networks, with reference to the Link Management Protocol and Optical UNI Neil Jerram,
The Key Benefits of OTN Networks
 he Key Benefits of ON Networks Introduction Optical transport networks have been migrating from SO technology to WDM architectures over the past 5 10 years. Deploying WDM systems has allowed carriers to
he Key Benefits of ON Networks Introduction Optical transport networks have been migrating from SO technology to WDM architectures over the past 5 10 years. Deploying WDM systems has allowed carriers to
Ultra High-Speed SONET Fiber-Optic Transmission System
 Ultra High-Speed Fiber-Optic Transmission System Takashi Mori Hirokuni Tsuji Hiroyuki Nakano, D.E. Shigeo Shinada ABSTRACT: Recently, there have been numerous demands not only on voice but also data/image
Ultra High-Speed Fiber-Optic Transmission System Takashi Mori Hirokuni Tsuji Hiroyuki Nakano, D.E. Shigeo Shinada ABSTRACT: Recently, there have been numerous demands not only on voice but also data/image
By: Mohsen Aminifar Fall 2014
 By: Mohsen Aminifar Fall 2014 Contact Information: E-Mail: m.aminifar@modares.ac.ir admin@parsenet.ir Phone : 021-22919726 09128442885 Website : http://parsenet.ir http://aminifar.ir SMS Center : 5000262175
By: Mohsen Aminifar Fall 2014 Contact Information: E-Mail: m.aminifar@modares.ac.ir admin@parsenet.ir Phone : 021-22919726 09128442885 Website : http://parsenet.ir http://aminifar.ir SMS Center : 5000262175
Rohde & Schwarz R&S SITLine ETH VLAN Encryption Device Functionality & Performance Tests
 Rohde & Schwarz R&S Encryption Device Functionality & Performance Tests Introduction Following to our test of the Rohde & Schwarz ETH encryption device in April 28 the European Advanced Networking Test
Rohde & Schwarz R&S Encryption Device Functionality & Performance Tests Introduction Following to our test of the Rohde & Schwarz ETH encryption device in April 28 the European Advanced Networking Test
Protocol Overhead in IP/ATM Networks
 Protocol Overhead in IP/ATM Networks John David Cavanaugh * Minnesota Supercomputer Center, Inc. This paper discusses the sources of protocol overhead in an IP/ATM protocol stack. It quantifies the amount
Protocol Overhead in IP/ATM Networks John David Cavanaugh * Minnesota Supercomputer Center, Inc. This paper discusses the sources of protocol overhead in an IP/ATM protocol stack. It quantifies the amount
The Keys for Campus Networking: Integration, Integration, and Integration
 The Keys for Campus Networking: Introduction Internet Protocol (IP) is considered the working-horse that the vast majority of current and future applications use as the key technology for information exchange,
The Keys for Campus Networking: Introduction Internet Protocol (IP) is considered the working-horse that the vast majority of current and future applications use as the key technology for information exchange,
How To Make A Multilink Ame Relay Work Faster And More Efficiently
 1/16/01 - ick Franks / Tiara etworks nc. / nanks@tiaranetworks.com / 408-535-1222 Multilink Frame Relay Prior to the advent of the multilink ame relay () protocol, some ame relay users were experiencing
1/16/01 - ick Franks / Tiara etworks nc. / nanks@tiaranetworks.com / 408-535-1222 Multilink Frame Relay Prior to the advent of the multilink ame relay () protocol, some ame relay users were experiencing
Introduction to Wide Area Network Protocols
 1 Introduction to Wide Area Network Protocols Session 2 Agenda Wide Area Network (WAN) Environment Requirements Technologies Interface Signaling Protocols 3 Take-Away Message By selecting the right cache
1 Introduction to Wide Area Network Protocols Session 2 Agenda Wide Area Network (WAN) Environment Requirements Technologies Interface Signaling Protocols 3 Take-Away Message By selecting the right cache
Objectives for Service Provider Shared Transport of 802.3 Higher Speed Ethernet
 Objectives for Service Provider Shared Transport of 802.3 Higher Speed Ethernet George Young AT&T george_young@labs.att.com IEEE 802.3 HSSG - November, 2006 802.3 HSE MAN/WAN Transport Issues 802.3 HSE
Objectives for Service Provider Shared Transport of 802.3 Higher Speed Ethernet George Young AT&T george_young@labs.att.com IEEE 802.3 HSSG - November, 2006 802.3 HSE MAN/WAN Transport Issues 802.3 HSE
Alcatel-Lucent 1665 Data Multiplexer (DMX) for Service Providers
 Alcatel-Lucent 1665 Data Multiplexer (DMX) for Service Providers Bridges the bandwidth gap between LANs and core backbone networks. Offers multiservice growth from traditional voice/private line services
Alcatel-Lucent 1665 Data Multiplexer (DMX) for Service Providers Bridges the bandwidth gap between LANs and core backbone networks. Offers multiservice growth from traditional voice/private line services
In this lecture we will start our discussion on another very important technology, namely, Asynchronous Transfer Mode or ATM.
 Computer networks Prof: Sujoy Ghosh Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. 24 ATM: Asynchronous Transfer Mode In this lecture we will start
Computer networks Prof: Sujoy Ghosh Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. 24 ATM: Asynchronous Transfer Mode In this lecture we will start
MPLS Pseudowire Innovations: The Next Phase Technology for Today s Service Providers
 MPLS Innovations: The Next Phase Technology for Today s Service Providers Introduction MPLS technology enables a smooth evolution of core networks within today s service provider infrastructures. In particular,
MPLS Innovations: The Next Phase Technology for Today s Service Providers Introduction MPLS technology enables a smooth evolution of core networks within today s service provider infrastructures. In particular,
10 Gigabit Ethernet MAC Core for Altera CPLDs. 1 Introduction. Product Brief Version 1.4 - February 2002
 1 Introduction Initially, network managers use 10 Gigabit Ethernet to provide high-speed, local backbone interconnection between large-capacity switches. 10 Gigabit Ethernet enables Internet Service Providers
1 Introduction Initially, network managers use 10 Gigabit Ethernet to provide high-speed, local backbone interconnection between large-capacity switches. 10 Gigabit Ethernet enables Internet Service Providers
Interfaces and Payload Testing
 application note 225 Packet Optical Transport Network Testing: From Commissioning to In-Service Monitoring Mai Abou-Shaban, Product Specialist, Transport and Datacom For network service providers considering
application note 225 Packet Optical Transport Network Testing: From Commissioning to In-Service Monitoring Mai Abou-Shaban, Product Specialist, Transport and Datacom For network service providers considering
Metro Ethernet Services
 CHAPTER 6 Metro Ethernet Service Framework This chapter describes the typical available from service providers (SPs). For the most part, these services are derived from and map to the following Metro Ethernet
CHAPTER 6 Metro Ethernet Service Framework This chapter describes the typical available from service providers (SPs). For the most part, these services are derived from and map to the following Metro Ethernet
Chapter 2 - The TCP/IP and OSI Networking Models
 Chapter 2 - The TCP/IP and OSI Networking Models TCP/IP : Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol OSI : Open System Interconnection RFC Request for Comments TCP/IP Architecture Layers Application
Chapter 2 - The TCP/IP and OSI Networking Models TCP/IP : Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol OSI : Open System Interconnection RFC Request for Comments TCP/IP Architecture Layers Application
RFC 2544 Testing of Ethernet Services in Telecom Networks
 RFC 2544 Testing of Ethernet Services in Telecom Networks White Paper Nigel Burgess Agilent Technologies Introduction The object of this paper is to discuss the use and testing of Ethernet services in
RFC 2544 Testing of Ethernet Services in Telecom Networks White Paper Nigel Burgess Agilent Technologies Introduction The object of this paper is to discuss the use and testing of Ethernet services in
Cox Business. L2 / L3 and Network Topology Overview. February 1, 2011
 Cox Business L2 / L3 and Network Topology Overview February 1, 2011 Layer 3 / Layer 2 Comparo Protocol Architecture Control Change: Adding sites Change: IP changes Faults: Management Faults: Calls Layer
Cox Business L2 / L3 and Network Topology Overview February 1, 2011 Layer 3 / Layer 2 Comparo Protocol Architecture Control Change: Adding sites Change: IP changes Faults: Management Faults: Calls Layer
Overview of Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and MPC860SAR. For More Information On This Product, Go to: www.freescale.com
 Overview of Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and MPC860SAR nc. 2 What is ATM? o Protocol that applies primarily to layer 2 of the OSI protocol stack: Application Presentation Session Transport Network
Overview of Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and MPC860SAR nc. 2 What is ATM? o Protocol that applies primarily to layer 2 of the OSI protocol stack: Application Presentation Session Transport Network
