Chapter 2 Michelson Morley Experiment and Velocity of Light
|
|
|
- Julie Greene
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
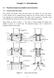
1 Chapter 2 Mihelson Morley Experiment and Veloity of Light 2. Attempts to Loate Speial Privileged Frame Sientists tried to determine relative veloity of light with respet to earth. For this purpose, the veloity of earth relative to ether frame of speial privileged frame was essential. Therefore, sientists performed various experiments involving eletromagneti waves. In this regard, the best and most important experiment was first performed by Mihelson in 88 and repeated the experiment more arefully in ollaboration with Morley in 887 and also reiterated many times thereafter. Atually, Mihelson and Morley experiments laid the experimental foundations of speial relativity. Mihelson was awarded the Nobel prize for his experiment in The Mihelson Morley Experiment (M M The experiment of M M was an attempt to measure the veloity of earth through the ether. The experiment failed in the sense that it showed onlusively that ether does not exist. More generally, it demonstrated that there are no privileged observer that the veloity of light is irrespetively of the state of motion of the observer who measures it. The apparatus of the experiment are: Monohromati soure S of light, Interferometer A, one semi-silvered plate B, two mirrors, M, M 2 (see Fig. 2.. The light from a soure at S falls on a semi-silvered plate B inlined at 45 to the diretion of propagation. The plate B, due to semi-silvered, divides the beam of light into two parts namely refleted and transmitted beams. The two beams, after refleting at mirrors M and M 2 are brought together at A, where interferene fringes are formed due to the small differene between the path lengths of two beams. Let us assume that earth (arrying the apparatus is moving with veloity v along BM = l relative to the privileged frame. The time (t required for the transmitted light ray Springer India 204 F. Rahaman, The Speial Theory of Relativity, DOI 0.007/ _2
2 2 2 Mihelson Morley Experiment and Veloity of Light Fig. 2. Experimental set-up of Mihelson Morley Experiment A v B l S M 2 l 2 2 M to traverse the length l both ways, i.e. along BM B is t = l ( v + l ( + v = ( 2l (2. [ is the veloity of light in the ether. So, downstream speed is ( + v and upstream speed is ( v] Now, onsider the path of the refleted light ray, i.e. the path BM 2 B: As the light travels from B to M 2 ( BM 2 = l 2, the whole apparatus has moved a distane x along BM. The light has therefore travelled a distane (l2 2 + x2. We have seen that earth moves some distane during the same time. Aording to Fig. 2.2, the mirror moves the distane x = vt in time t and light moves in time t is t = (l2 2 + x2. Fig. 2.2 Mirror moves some distane in time t t=0 t= 2 t 2 M2 t=t 2 l 2 B vt 2 B
3 2.2 The Mihelson Morley Experiment (M M 3 Hene, Or, t = x v = (l x2 = (l x2 l 2 ( v2 (2.2 On the bak, it travels an equal distane, so the time for to and fro travel of the light beam ( i.e. the path BM 2 B is t 2 = ( 2l 2 (2.3 Interferene fringes are reated by the differene between t and t 2. The whole apparatus is now swung through 90, so the roles of the two arms are interhanged. Therefore, l takes the plae of l 2 and vie versa. We have, t = ( 2l t 2 = ( 2l 2 ( v2 (2.4 (2.5 The time differenes between the two paths, before and after the apparatus is swung round, are t = t t 2 = ( 2 l l 2 (2.6 t = t t 2 = ( 2 l The hange in t brought about by rotating the apparatus is t t = ( 2 (l + l 2 l 2 ( v2 (2.7 (2.8
4 4 2 Mihelson Morley Experiment and Veloity of Light We expand the right-hand side in a Binomial series, retaining terms up to the seond power of (v/ to yield t t (l + l 2 v2 (2.9 Hene, the shift in the number of fringes is N = t t T = γ (l + l 2 v2 (2.0 [Period of one vibration is T = ( γ = ( λ, where γ and λ are frequeny and wave length of the light] Earth s veloity is presumed to be 30 km/s = m/s, ( v 2 = 0 8 and ( γ 0 4 m for visible light, so N 2(l + l (2. Sine l and l 2 were several metres, suh a shift would be easily detetable and measurable. However, no fringe shift was observed. This experiment was repeated with multiple mirrors to inrease the lengths l and l 2, however, the experimental onlusion was that there was no fringe shift at all. In the year 904, Trouton and Noble done again the experiment using eletromagneti waves instead of visible light, however, no fringe shift was observed. Sine the veloity of earth relative to ether annot always be zero, therefore experiment does not depend solely on an absolute veloity of earth through an ether, but also depends on hanging veloity of earth with respet to ether. Suh a hanging motion through the ether would be easily deteted and measured by the preision of experiments, if there was an ether frame. The null result seems to rule out an ether (absolute frame. Thus, no preferred inertial frame exists. Also, one way to interpret the null result of M M experiment is to onlude simply that the measured speed of light is the same, i.e. for all diretions in every inertial system. In the experiment, the downstream speed and upstream speed being rather than + v or v in any frame. Note : In 882, Fitzgerald and Lorentz independently proposed a hypothesis to explain null results of Mihelson Morley experiment. Their hypothesis is Every body moving with a veloity v through the ether has its length in the diretion of motion ontrated by a fator v2, while the dimensions in diretions perpendiular to motion remain unhanged. Let us onsider in Mihelson Morley experiment, the arms are equal, i.e. l = l 2 = l at rest relative to ether and aording to Fitzgerald and Lorentz hypothesis its length l when it is in motion with veloity v relative to ether will be l ( v2.
5 2.2 The Mihelson Morley Experiment (M M 5 By this, they interpreted the null result of Mihelson Morley experiment as follows: From, Eqs. (2. and (2.3, we have t = ( 2l ( v2 ( 2l ( + v2 ( 2l, t 2 = ( 2l ( + v2 Using Fitzgerald and Lorentz hypothesis, we get by replaing l by l, t = ( 2l ( + v2 = ( 2l v2 Expanding binomially and negleting v4 4, we get, t = ( 2l ( + v2 = t 2 ( + v2 Therefore, aording to Fitzgerald and Lorentz hypothesis, the times taken by refleted and transmitted beams are the same and hene no shift of fringe is observed. However, Fitzgerald and Lorentz hypothesis fails to give orret explanation of null results of Mihelson Morley experiment when the two ears of the interferometer are not equal. Note 2: If some instant, the veloity of earth were zero with respet to ether, no fringe shift would be expeted. From, Eqs. (2. and (2.3, we have, by putting v = 0, t = ( 2l = t 2 Then, there is no relative veloity between earth and the ether, i.e. earth drags the ether with the same veloity as earth during its motion. However, this explanation is in ontradition with various experiments like Bradley s result of aberration, et. 2.3 Phenomena of Aberration: Bradley s Observation In the year 727, Bradley observed that the star, γ Draonis revolves in nearly irular orbit. He found that angular diameter of this irular orbit is about 4 s of ar and other stars appeared to move in elliptial orbit have almost same period. This phenomena of apparent displaement is known as aberration. This an be explained as follows. Let a light ray omes from a star at zenith. An observer together with earth has a veloity v will see the diretion of light ray will not be vertial. This is
6 6 2 Mihelson Morley Experiment and Veloity of Light Fig. 2.3 Telesope will have to tilt to see the star A Atual Diretion A B Apparent Diretion t A vt B A vt B due to relative motion of the observer and light ray. To see the star, the telesope will have to tilt, i.e. diretion slightly away from the vertial as shown in the Fig The angle α between the atual and apparent diretions of the star is alled aberration. Let v be the veloity of earth in the diretion AB. The light ray enters the telesope tube at A and reahes the observer s eye at B in time t. As the light reahes from A to B in the mean time eyepiee moves from A to B. Hene, A B = t, AB = v t. The tilt of the telesope α is given by (see Fig. 2.3 or tan α = v α = tan v Using the veloities of earth and light as 30 km/s and km/s, respetively, one gets, α = tan v = tan = tan (0 4 = 20.5 ars Sine earth s motion is nearly irular, therefore every six months, the diretion of aberration will reverse and telesope axis is traing out a one of aberration during the year. Hene the angular diameter of the one would be 2α = 4 ar s. In 727, Bradley observed this motion and found the angular diameter was 4 ar s for the star γ Draonis. This experiment apparently showed the absolute veloity of earth is 30 km/s. The outome of this experiment is that ether is not dragged around with earth. If it were, then the phenomena of aberration would not be happened.
7 2.4 Fizeau s Experiment Fizeau s Experiment In 87, Fresnel proposed that light would be partially dragged along by a moving medium. Using ether hypothesis, he provided the formula for the effet of moving medium on the veloity of light. In 95, Fizeau onfirmed this effet experimentally. Figure 2.4 shows the Fizeau s experimental arrangement. Fizeau used water as the medium inside the tubes. Water flows through the tubes with veloity u. The S is the soure of light. The light ray from S falls on a semi-silver plate inlined 45 from the horizontal is divided into two parts. One is refleted in the diretion M M 2 and other part is transmitted in the diretion M D. Here, one beam of light is entering towards the veloity of water and other opposite to the motion of water. One an note that refleted beam travels the path M M 2 CDM in the diretion of motion of water and the transmitted beam travels the path M EDCM 2 M opposite to the motion of water. Both beams finally enter the telesope. Differene in time taken by both the beams travel equal distane d due to the motion of the water and veloity v of earth. It was assumed that spae is filled uniformly with the ether and ether to be partially dragged. Now, the time differene is t = d μ + ( μ 2 v + u ( μ 2 d μ + ( μ 2 v u ( μ 2 It was assumed that ( ether to be partially dragged and as a result omponent of the veloity in the tube v. It follows also that if a material body is moving with μ 2 ( μ 2. Here, veloity u through ether, the veloity of ether will be u onstant. Negleting higher order terms, we get the time differene as t = 2udμ2 ( μ 2 ( μ 2 = Fig. 2.4 Experimental set-up of Fizeau s experiment B C M2 S M E D F T
8 8 2 Mihelson Morley Experiment and Veloity of Light The phase differene is given by f = 2udμ 2 ( μ 2 T = 2udnμ2 ( μ 2 where, n be the frequeny of the osillation and T is time period of one osillation (nt =. Fizeau observed the shift in the fringes and found exatly the same as given by the above equation. This result also onfirms the result that ( the veloity of the light in any medium of refrative index μ is not simply μ but μ ±, u is μ 2 the veloity of the medium. The fator ( μ is alled Fresnel s ether dragging 2 oeffiient. Thus, Fresnel s formula for ether drag was verified by Fizeau. 2.5 The Relativisti Conept of Spae and Time The null results of Mihelson Morley Experiment ruled out the absolute onept of spae and laid Einstein to formulate the new onept of spae and time. Consider the following two ontraditory statements: [] In lassial mehanis, the veloity of any motion has different values for observers moving relative to eah other. [2] The null results of Mihelson Morley experiment onludes that the veloity of light is not affeted by the motion of the frame of referene. The genius Einstein applied his intuition and realized that this ontradition omes from the imperfetion of the lassial ideas about measuring spae and time. He ruled out the Newton s onept of absolute time by ritiizing our preoneived ideas about simultaneity. He ommented time is indeed doubtful. His intuition may be supported as follows: X O Y Suppose an observer sitting at O where O is the middle point of the straight line XY. Suppose that two events ourring at X and Y whih are fixed in an inertial frame S and the two loks giving absolute time are kept at X and Y. In the inertial frame S, the events ourring at X and Y are said to be simultaneous, if the loks plaed at X and Y indiate the same time when the events our. Let a light signal is giving at X and Y simultaneously. Suppose XOY is moving with v veloity in the diretion XY. Then, one an show that these light signals will not reah simultaneously the observer at O whih is moving with veloity v. Here, the moving O seems to lie in OY ( v another inertial frame. The light signal takes t time to reah from Y to O as and the time t 2 taken by the light signal from X to O is (+v OX. [ is the veloity of light in all diretion. So, aording to Newtonian mehanis, downstream speed is ( + v and upstream speed is ( v]
9 2.5 The Relativisti Conept of Spae and Time 9 One an note that t = OY OX = ( v ( + v = t 2, as + v = v, OX = OY Therefore, time is not absolute. It varies from one inertial frame to another inertial frame, i.e. t = t 2. In other words, every referene frame has its own partiular time. Therefore, onept of absolute time was ruled out by Einstein. The spae oordinate is transformed due to Galilean Transformation as x = x vt. Sine, time depends on frame of referene, therefore, distane between two points will also depend on the frame of referene. In other words, distane between two points is not absolute. Hene, Einstein also ruled out the onept of absolute spae. Einstein proposed his new relativisti onepts of spae and time based on the fat that observers who are moving relative to eah other measure the speed of light to be the same. This new onept of spae and time is not only valid for mehanial phenomenon but also for all optial and eletromagneti phenomenon and known as theory of relativity. To develop these new onepts of spae and time, Einstein replaed Galilean Transformation equations by a new type of transformation equations alled Lorentz transformation, whih was based on the invariant harater of the speed of light. The theory of relativity having new onept of spae and time is divided into two parts. [] Speial theory of relativity (STR [2] General theory of relativity (GTR. The STR deals with inertial systems, i.e. the systems whih move in uniform retilinear motion relative to one another. GTR deals with non-inertial system, i.e. it is an extension of inertial system to aelerated systems, i.e. the systems moving with aelerated veloity relative to one another. The GTR is applied to the area of gravitational field and based on whih laws of gravitation an be explained in a more perfet manner than given by Newton.
10
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Relativity in the Global Positioning System
 Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: ashby@boulder.nist.gov July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: ashby@boulder.nist.gov July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Physics 43 HW 3 Serway Chapter 39 & Knight Chapter 37
 Physis 43 HW 3 Serway Chapter 39 & Knight Chapter 37 Serway 7 th Edition Chapter 39 Problems: 15, 1, 5, 57, 60, 65 15. Review problem. An alien ivilization oupies a brown dwarf, nearly stationary relative
Physis 43 HW 3 Serway Chapter 39 & Knight Chapter 37 Serway 7 th Edition Chapter 39 Problems: 15, 1, 5, 57, 60, 65 15. Review problem. An alien ivilization oupies a brown dwarf, nearly stationary relative
Physical and mathematical postulates behind relativity
 Physial and mathematial postulates behind relativity Tuomo Suntola Physis Foundations Soiety, Finland, www.physisfoundations.org In this presentation we look for answers to questions: What was the problem
Physial and mathematial postulates behind relativity Tuomo Suntola Physis Foundations Soiety, Finland, www.physisfoundations.org In this presentation we look for answers to questions: What was the problem
Relativistic Kinematics -a project in Analytical mechanics Karlstad University
 Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = mc 2, from the Classical Force Laws
 Apeiron, Vol. 14, No. 4, Otober 7 435 Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = m, from the Classial Fore Laws N. Hamdan, A.K. Hariri Department of Physis, University of Aleppo, Syria nhamdan59@hotmail.om,
Apeiron, Vol. 14, No. 4, Otober 7 435 Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = m, from the Classial Fore Laws N. Hamdan, A.K. Hariri Department of Physis, University of Aleppo, Syria nhamdan59@hotmail.om,
On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Special Relativity Theory
 www.senet.org/apr Applied Physis Researh Vol. 4, No. ; 1 On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Speial Relativity Theory Sergey A. Vasiliev 1 1 Sientifi Researh Institute of Exploration Geophysis
www.senet.org/apr Applied Physis Researh Vol. 4, No. ; 1 On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Speial Relativity Theory Sergey A. Vasiliev 1 1 Sientifi Researh Institute of Exploration Geophysis
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES
 ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. EINSTEIN June 30, 905 It is known that Maxwell s eletrodynamis as usually understood at the present time when applied to moing bodies, leads to asymmetries
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. EINSTEIN June 30, 905 It is known that Maxwell s eletrodynamis as usually understood at the present time when applied to moing bodies, leads to asymmetries
Dispersion in Optical Fibres
 Introdution Optial Communiations Systems Dispersion in Optial Fibre (I) Dispersion limits available bandwidth As bit rates are inreasing, dispersion is beoming a ritial aspet of most systems Dispersion
Introdution Optial Communiations Systems Dispersion in Optial Fibre (I) Dispersion limits available bandwidth As bit rates are inreasing, dispersion is beoming a ritial aspet of most systems Dispersion
EXPERIMENT O-6. Michelson Interferometer. Abstract. References. Pre-Lab
 EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units
 Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units or, Why CGS Units Make You Cool Prashanth S. Venkataram February 24, 202 Abstrat In this paper, I ompare the merits of Gaussian CGS and SI units in a variety of different
Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units or, Why CGS Units Make You Cool Prashanth S. Venkataram February 24, 202 Abstrat In this paper, I ompare the merits of Gaussian CGS and SI units in a variety of different
1.3 Complex Numbers; Quadratic Equations in the Complex Number System*
 04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES
 ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. EINSTEIN June 30, 905 It is known that Maxwell s eletrodynamis as usually understood at the present time when applied to moing bodies, leads to asymmetries
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. EINSTEIN June 30, 905 It is known that Maxwell s eletrodynamis as usually understood at the present time when applied to moing bodies, leads to asymmetries
CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS
 J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
Isaac Newton. Translated into English by
 THE MATHEMATICAL PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL PHILOSOPHY (BOOK 1, SECTION 1) By Isaa Newton Translated into English by Andrew Motte Edited by David R. Wilkins 2002 NOTE ON THE TEXT Setion I in Book I of Isaa
THE MATHEMATICAL PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL PHILOSOPHY (BOOK 1, SECTION 1) By Isaa Newton Translated into English by Andrew Motte Edited by David R. Wilkins 2002 NOTE ON THE TEXT Setion I in Book I of Isaa
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL
 BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
Part I Special Relativity
 Part I Speial Relativity G. W. Gibbons D.A.M.T.P., Cambridge University, Wilberfore Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, U.K. February 14, 2008 The views of spae and time whih I wish to lay before you have sprung
Part I Speial Relativity G. W. Gibbons D.A.M.T.P., Cambridge University, Wilberfore Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, U.K. February 14, 2008 The views of spae and time whih I wish to lay before you have sprung
Conversion of short optical pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsica, vol. 21, no. 4, Dezembro, 1999 469. Surface Charges and Electric Field in a Two-Wire
 Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
3 Game Theory: Basic Concepts
 3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
The Special Theory of Relativity
 Chapter 1 The Special Theory of Relativity 1.1 Pre-History of concepts about light It is interesting to note that so much of our understanding of the physical universe is based on our interpretations of
Chapter 1 The Special Theory of Relativity 1.1 Pre-History of concepts about light It is interesting to note that so much of our understanding of the physical universe is based on our interpretations of
FORCE ON A CURRENT IN A MAGNETIC FIELD
 7/16 Force current 1/8 FORCE ON A CURRENT IN A MAGNETIC FIELD PURPOSE: To study the force exerted on an electric current by a magnetic field. BACKGROUND: When an electric charge moves with a velocity v
7/16 Force current 1/8 FORCE ON A CURRENT IN A MAGNETIC FIELD PURPOSE: To study the force exerted on an electric current by a magnetic field. BACKGROUND: When an electric charge moves with a velocity v
Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismic Code IS 1893 (Part I)
 Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY
 P THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY 4 Referene Tables for Physial Setting/PHYSICS 006 Edition List of Physial Constants Name Symbol Value Universal gravitational
P THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY 4 Referene Tables for Physial Setting/PHYSICS 006 Edition List of Physial Constants Name Symbol Value Universal gravitational
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I
 DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
PHY1020 BASIC CONCEPTS IN PHYSICS I
 PHY1020 BASIC CONCEPTS IN PHYSICS I Jackson Levi Said 14 lectures/tutorials/past paper session Project on one of the interesting fields in physics (30%) Exam in January/February (70%) 1 The Course RECOMMENDED
PHY1020 BASIC CONCEPTS IN PHYSICS I Jackson Levi Said 14 lectures/tutorials/past paper session Project on one of the interesting fields in physics (30%) Exam in January/February (70%) 1 The Course RECOMMENDED
Dynamic Model of the Spacecraft Position and Attitude
 Dnami Model of the Spaeraft Position and Attitude Basilio BNA, nrio CANUT Dipartimento di Automatia e Informatia, Politenio di Torino Corso Dua degli Abruzzi 4 9 Torino, Ital tel. 564 76, fa 564 799 bona@polito.it
Dnami Model of the Spaeraft Position and Attitude Basilio BNA, nrio CANUT Dipartimento di Automatia e Informatia, Politenio di Torino Corso Dua degli Abruzzi 4 9 Torino, Ital tel. 564 76, fa 564 799 bona@polito.it
Gravity and the quantum vacuum inertia hypothesis
 Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 14, No. 8, 479 498 (2005) / DOI 10.1002/andp.200510147 Gravity and the quantum vauum inertia hypothesis Alfonso Rueda 1, and Bernard Haish 2, 1 Department of Eletrial Engineering,
Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 14, No. 8, 479 498 (2005) / DOI 10.1002/andp.200510147 Gravity and the quantum vauum inertia hypothesis Alfonso Rueda 1, and Bernard Haish 2, 1 Department of Eletrial Engineering,
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Equipment: Ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale. Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Equipment: Ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale. Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Magnetic Force and Current Balance. Your name Lab section
 Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Magnetic Force and Current Balance Your name Lab section 1. What do you investigate in this lab? 2. Two straight wires are in parallel and carry electric currents in opposite directions
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Magnetic Force and Current Balance Your name Lab section 1. What do you investigate in this lab? 2. Two straight wires are in parallel and carry electric currents in opposite directions
Comay s Paradox: Do Magnetic Charges Conserve Energy?
 Comay s Paradox: Do Magneti Charges Conserve Energy? 1 Problem Kirk T. MDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Prineton University, Prineton, NJ 08544 (June 1, 2015; updated July 16, 2015) The interation energy
Comay s Paradox: Do Magneti Charges Conserve Energy? 1 Problem Kirk T. MDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Prineton University, Prineton, NJ 08544 (June 1, 2015; updated July 16, 2015) The interation energy
Chapter 5 Using Newton s Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Using Newton s Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces Units of Chapter 5 Applications of Newton s Laws Involving Friction Uniform Circular Motion Kinematics Dynamics of Uniform Circular
Chapter 5 Using Newton s Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces Units of Chapter 5 Applications of Newton s Laws Involving Friction Uniform Circular Motion Kinematics Dynamics of Uniform Circular
LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES
 55 Name Date Partners LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly Bodies by the attraction
55 Name Date Partners LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly Bodies by the attraction
Deformation of the Bodies by the Result of Length Contraction: A new Approach to the Lorentz Contraction
 1 Deformation of the Bodies by the Result of Length Contraction: A new Approach to the Lorentz Contraction Bayram Akarsu, Ph.D Erciyes University Kayseri/ Turkiye 2 Abstract It has been more than a century
1 Deformation of the Bodies by the Result of Length Contraction: A new Approach to the Lorentz Contraction Bayram Akarsu, Ph.D Erciyes University Kayseri/ Turkiye 2 Abstract It has been more than a century
The Neo-classical Theory of Relativity
 Toronto, Canada December 29, 2013 Second Edition 2013, Revision 2.1 The Neo-classical Theory of Relativity by Valentin T. Danci Introduction to the Neo-classical Theory of Relativity... 3 1. The conceptual
Toronto, Canada December 29, 2013 Second Edition 2013, Revision 2.1 The Neo-classical Theory of Relativity by Valentin T. Danci Introduction to the Neo-classical Theory of Relativity... 3 1. The conceptual
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Economics
 Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Intuitive Guide to Principles of Communications By Charan Langton www.complextoreal.com
 Intuitive Guide to Priniples of Communiations By Charan Langton www.omplextoreal.om Understanding Frequeny Modulation (FM), Frequeny Shift Keying (FSK), Sunde s FSK and MSK and some more The proess of
Intuitive Guide to Priniples of Communiations By Charan Langton www.omplextoreal.om Understanding Frequeny Modulation (FM), Frequeny Shift Keying (FSK), Sunde s FSK and MSK and some more The proess of
Physics 41, Winter 1998 Lab 1 - The Current Balance. Theory
 Physics 41, Winter 1998 Lab 1 - The Current Balance Theory Consider a point at a perpendicular distance d from a long straight wire carrying a current I as shown in figure 1. If the wire is very long compared
Physics 41, Winter 1998 Lab 1 - The Current Balance Theory Consider a point at a perpendicular distance d from a long straight wire carrying a current I as shown in figure 1. If the wire is very long compared
Celestial Sphere. Celestial Coordinates. Lecture 3: Motions of the Sun and Moon. ecliptic (path of Sun) ecliptic (path of Sun)
 Lecture 3: Motions of the and Moon ecliptic (path of ) ecliptic (path of ) The 23.5 degree tilt of Earth s spin axis relative to its orbital axis around the causes the seasons Celestial Sphere Celestial
Lecture 3: Motions of the and Moon ecliptic (path of ) ecliptic (path of ) The 23.5 degree tilt of Earth s spin axis relative to its orbital axis around the causes the seasons Celestial Sphere Celestial
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Diffraction of a Circular Aperture
 Diffraction of a Circular Aperture Diffraction can be understood by considering the wave nature of light. Huygen's principle, illustrated in the image below, states that each point on a propagating wavefront
Diffraction of a Circular Aperture Diffraction can be understood by considering the wave nature of light. Huygen's principle, illustrated in the image below, states that each point on a propagating wavefront
12.1 What is Refraction pg. 515. Light travels in straight lines through air. What happens to light when it travels from one material into another?
 12.1 What is Refraction pg. 515 Light travels in straight lines through air. What happens to light when it travels from one material into another? Bending Light The light traveling from an object in water
12.1 What is Refraction pg. 515 Light travels in straight lines through air. What happens to light when it travels from one material into another? Bending Light The light traveling from an object in water
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
Involute-Evolute Curve Couples in the Euclidean 4-Space
 Int J Open Problem Compt Math Vol o June 9 Involute-volute Curve Couple in the ulidean -Spae min Özyılmaz Süha Yılmaz ge Univerity Faulty of Siene Dept of Math ornova-izmir urkey Dokuz ylül Univerity ua
Int J Open Problem Compt Math Vol o June 9 Involute-volute Curve Couple in the ulidean -Spae min Özyılmaz Süha Yılmaz ge Univerity Faulty of Siene Dept of Math ornova-izmir urkey Dokuz ylül Univerity ua
Physics 112 Homework 5 (solutions) (2004 Fall) Solutions to Homework Questions 5
 Solutions to Homework Questions 5 Chapt19, Problem-2: (a) Find the direction of the force on a proton (a positively charged particle) moving through the magnetic fields in Figure P19.2, as shown. (b) Repeat
Solutions to Homework Questions 5 Chapt19, Problem-2: (a) Find the direction of the force on a proton (a positively charged particle) moving through the magnetic fields in Figure P19.2, as shown. (b) Repeat
Force on Moving Charges in a Magnetic Field
 [ Assignment View ] [ Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 27. Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, February 28, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after
[ Assignment View ] [ Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 27. Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, February 28, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Analysis of micro-doppler signatures
 Analysis of miro-doppler signatures V.C. Chen, F. Li, S.-S. Ho and H. Wehsler Abstrat: Mehanial vibration or rotation of a target or strutures on the target may indue additional frequeny modulations on
Analysis of miro-doppler signatures V.C. Chen, F. Li, S.-S. Ho and H. Wehsler Abstrat: Mehanial vibration or rotation of a target or strutures on the target may indue additional frequeny modulations on
Advanced Topics in Physics: Special Relativity Course Syllabus
 Advanced Topics in Physics: Special Relativity Course Syllabus Day Period What How 1. Introduction 2. Course Information 3. Math Pre-Assessment Day 1. Morning 1. Physics Pre-Assessment 2. Coordinate Systems
Advanced Topics in Physics: Special Relativity Course Syllabus Day Period What How 1. Introduction 2. Course Information 3. Math Pre-Assessment Day 1. Morning 1. Physics Pre-Assessment 2. Coordinate Systems
Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
 1 P a g e Motion Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE If an object changes its position with respect to its surroundings with time, then it is called in motion. Rest If an object
1 P a g e Motion Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE If an object changes its position with respect to its surroundings with time, then it is called in motion. Rest If an object
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA
 WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
Fraunhofer Diffraction
 Physics 334 Spring 1 Purpose Fraunhofer Diffraction The experiment will test the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction at a single slit by comparing a careful measurement of the angular dependence of intensity
Physics 334 Spring 1 Purpose Fraunhofer Diffraction The experiment will test the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction at a single slit by comparing a careful measurement of the angular dependence of intensity
DIRECT ORBITAL DYNAMICS: USING INDEPENDENT ORBITAL TERMS TO TREAT BODIES AS ORBITING EACH OTHER DIRECTLY WHILE IN MOTION
 1 DIRECT ORBITAL DYNAMICS: USING INDEPENDENT ORBITAL TERMS TO TREAT BODIES AS ORBITING EACH OTHER DIRECTLY WHILE IN MOTION Daniel S. Orton email: dsorton1@gmail.com Abstract: There are many longstanding
1 DIRECT ORBITAL DYNAMICS: USING INDEPENDENT ORBITAL TERMS TO TREAT BODIES AS ORBITING EACH OTHER DIRECTLY WHILE IN MOTION Daniel S. Orton email: dsorton1@gmail.com Abstract: There are many longstanding
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
The Reduced van der Waals Equation of State
 The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
4/3 Problem for the Gravitational Field
 4/3 Proble for the Gravitational Field Serey G. Fedosin PO bo 6488 Sviazeva str. -79 Per Russia E-ail: intelli@list.ru Abstrat The ravitational field potentials outside and inside a unifor assive ball
4/3 Proble for the Gravitational Field Serey G. Fedosin PO bo 6488 Sviazeva str. -79 Per Russia E-ail: intelli@list.ru Abstrat The ravitational field potentials outside and inside a unifor assive ball
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water
 Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
Comparison of the Phenomena of Light Refraction. and Gravitational Bending
 Comparison of the Phenomena of Light Refraction and Gravitational Bending ROBERT J. BUENKER, BERGISHE UNIVERSITAET WUPPERTAL, Fachbereich C-Theoretische Chemie, Gaussstr. 20, D-42119 Wuppertal, Germany
Comparison of the Phenomena of Light Refraction and Gravitational Bending ROBERT J. BUENKER, BERGISHE UNIVERSITAET WUPPERTAL, Fachbereich C-Theoretische Chemie, Gaussstr. 20, D-42119 Wuppertal, Germany
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
Programming Basics - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physics.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html
 CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
Centripetal Force. This result is independent of the size of r. A full circle has 2π rad, and 360 deg = 2π rad.
 Centripetal Force 1 Introduction In classical mechanics, the dynamics of a point particle are described by Newton s 2nd law, F = m a, where F is the net force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
Centripetal Force 1 Introduction In classical mechanics, the dynamics of a point particle are described by Newton s 2nd law, F = m a, where F is the net force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
Part I. Student Laboratory Manuals
 Part I Student Laboratory Manuals 1 GK 4. The Gravitational Constant G 4.1 Introduction Gravitation, or gravity, is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature 1, giving rise to attractive forces
Part I Student Laboratory Manuals 1 GK 4. The Gravitational Constant G 4.1 Introduction Gravitation, or gravity, is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature 1, giving rise to attractive forces
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynamic Cycles of Reciprocating and Rotary Engines - R.S.
 THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
Experiment #12: The Bohr Atom. Equipment: Spectroscope Hydrogen and Helium Gas Discharge Tubes, Holder, and Variac Flashlight
 Experiment #12: The Bohr Atom Purpose: To observe the visible spectrum of hydrogen and helium and verify the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. Equipment: Spectroscope Hydrogen and Helium Gas Discharge Tubes,
Experiment #12: The Bohr Atom Purpose: To observe the visible spectrum of hydrogen and helium and verify the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. Equipment: Spectroscope Hydrogen and Helium Gas Discharge Tubes,
Physical Principle of Formation and Essence of Radio Waves
 Physical Principle of Formation and Essence of Radio Waves Anatoli Bedritsky Abstract. This article opens physical phenomena which occur at the formation of the radio waves, and opens the essence of the
Physical Principle of Formation and Essence of Radio Waves Anatoli Bedritsky Abstract. This article opens physical phenomena which occur at the formation of the radio waves, and opens the essence of the
Reflection and Refraction
 Equipment Reflection and Refraction Acrylic block set, plane-concave-convex universal mirror, cork board, cork board stand, pins, flashlight, protractor, ruler, mirror worksheet, rectangular block worksheet,
Equipment Reflection and Refraction Acrylic block set, plane-concave-convex universal mirror, cork board, cork board stand, pins, flashlight, protractor, ruler, mirror worksheet, rectangular block worksheet,
cos t sin t sin t cos t
 Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
HEAT EXCHANGERS-2. Associate Professor. IIT Delhi E-mail: prabal@mech.iitd.ac.in. P.Talukdar/ Mech-IITD
 HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
Motions of Earth, Moon, and Sun
 Motions of Earth, Moon, and Sun Apparent Motions of Celestial Objects An apparent motion is a motion that an object appears to make. Apparent motions can be real or illusions. When you see a person spinning
Motions of Earth, Moon, and Sun Apparent Motions of Celestial Objects An apparent motion is a motion that an object appears to make. Apparent motions can be real or illusions. When you see a person spinning
Lab 7: Rotational Motion
 Lab 7: Rotational Motion Equipment: DataStudio, rotary motion sensor mounted on 80 cm rod and heavy duty bench clamp (PASCO ME-9472), string with loop at one end and small white bead at the other end (125
Lab 7: Rotational Motion Equipment: DataStudio, rotary motion sensor mounted on 80 cm rod and heavy duty bench clamp (PASCO ME-9472), string with loop at one end and small white bead at the other end (125
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Chapter 3.8 & 6 Solutions
 Chapter 3.8 & 6 Solutions P3.37. Prepare: We are asked to find period, speed and acceleration. Period and frequency are inverses according to Equation 3.26. To find speed we need to know the distance traveled
Chapter 3.8 & 6 Solutions P3.37. Prepare: We are asked to find period, speed and acceleration. Period and frequency are inverses according to Equation 3.26. To find speed we need to know the distance traveled
Licensed to: ichapters User
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Chapters 39 46, Seventh Edition Raymond A. Serway and John W. Jewett, Jr. Physics Acquisition Editor: Chris Hall Publisher: David Harris Vice President,
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Chapters 39 46, Seventh Edition Raymond A. Serway and John W. Jewett, Jr. Physics Acquisition Editor: Chris Hall Publisher: David Harris Vice President,
Einstein s Theory of Special Relativity Made Relatively Simple!
 Einstein s Theory of Special Relativity Made Relatively Simple! by Christopher P. Benton, PhD Young Einstein Albert Einstein was born in 1879 and died in 1955. He didn't start talking until he was three,
Einstein s Theory of Special Relativity Made Relatively Simple! by Christopher P. Benton, PhD Young Einstein Albert Einstein was born in 1879 and died in 1955. He didn't start talking until he was three,
A Theoretical Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia *
 A Theoretial Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia * by Joshua S. Gans and Stephen P. King Melbourne Business Shool University of Melbourne First Draft: 12 th May, 2001 This Version: 5 th May, 2003
A Theoretial Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia * by Joshua S. Gans and Stephen P. King Melbourne Business Shool University of Melbourne First Draft: 12 th May, 2001 This Version: 5 th May, 2003
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Winners First Place: Kay Gemba (University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, USA)
 Aoustial Soiety of Ameria International Student Challenge Problem in Aousti Signal Proessing 14 Student Entry Evaluation Report by the Tehnial Committee on Signal Proessing in Aoustis Bakground Bakground
Aoustial Soiety of Ameria International Student Challenge Problem in Aousti Signal Proessing 14 Student Entry Evaluation Report by the Tehnial Committee on Signal Proessing in Aoustis Bakground Bakground
VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR. A Thesis by. Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu
 VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR A Thesis by Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu Eletrial Engineer, Polytehni University of HCMC, 1993 Submitted to the College of
VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR A Thesis by Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu Eletrial Engineer, Polytehni University of HCMC, 1993 Submitted to the College of
Introduction to General Relativity
 Chapter 8 Introduction to General Relativity 8.1 The Problem After 1905 and the success of the Special Theory of Relativity, Einstein turned his attention to the problem of making the other known fundamental
Chapter 8 Introduction to General Relativity 8.1 The Problem After 1905 and the success of the Special Theory of Relativity, Einstein turned his attention to the problem of making the other known fundamental
Gravitation and Newton s Synthesis
 Gravitation and Newton s Synthesis Vocabulary law of unviversal Kepler s laws of planetary perturbations casual laws gravitation motion casuality field graviational field inertial mass gravitational mass
Gravitation and Newton s Synthesis Vocabulary law of unviversal Kepler s laws of planetary perturbations casual laws gravitation motion casuality field graviational field inertial mass gravitational mass
