Jaundice. Dorota Mańkowska. -Wierzbicka,, MD, PhD
|
|
|
- John Hawkins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jaundice Dorota Mańkowska -Wierzbicka,, MD, PhD
2 Jaundice Definition Accumulation of yellow pigment in the skin and other tissues (Bilirubin)
3 Jaundice definition It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin in body tissues, which occurs when the serum bilirubin level exceeds 3 mg/dl or 50 umol/l. 1 Excess bilirubin causes a yellow tinting to the skin, sclera, and mucous membranes.
4 Jaundice The presence of jaundice can indicate a transient hepatitis, biliary obstruction, or progressive deterioration in a patient awaiting liver transplantation. Thus, the appropriate management of the patient with jaundice depends on localizing the site and nature of the problem.
5 Jaundice Hyperbilirubinemia is defined as a total bilirubin level greater than 1.5 mg/dl dl,, an unconjugated level greater than 1 mg/dl dl,, or a conjugated bilirubin level greater than 0.3 mg/dl dl.
6 Jaundice
7 Jaundice- Causes Of Hyperbilirubinemia- unconjugated Hemolysis Ineffective erythropoesis Neonatal causes Uridine diphosphate glucuronoyltransferase deficiencies Gilbert syndrome Crigler-Najjar syndromes Miscellaneous causes (drugs, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis,, pulmonary infarct, fasting)
8 Gilbert Syndom Defective UDPG Transferase Uridine diphosphate glucuronoyltransferase Usually asymptomatic Serum BR < 3 mg% BR-monoglucuronide Benign
9 Crigler Najjar Syndrome Type I No UDPGT No BR conjugation Neonatal kernicterus, death Autosomal recessive
10 Crigler Najjar Syndrom Type II Reduced UDPGT activity Jaundice, 2d-3d decade of life Mostly monoglucuronide in bile Usually benign Treatment: Phenobarbital, induces more UDPGT
11 Jaundice- Causes Of Hyperbilirubinemia- conjugated Congenital causes Rotor syndrome Impaired biliary excretion of conjugated BR. Jaundice appearing in childhood. Autosomal recessive. Uncommon.Benign Dubin-Johnson syndrome Defective transporter for conjugated BR. Uncommon. Benign. Conjugated BR in blood & urine Choledochal cysts Familial disorders Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis Cholestasis of pregnancy
12 Jaundice- Causes Of Hyperbilirubinemia- conjugated Hepatocellular defects Alcohol abuse Viral infection Cholestatic Primary biliary cirrhosis Primary sclerosing cholangitis Biliary obstruction Pancreatic disease
13
14 Jaundice- Causes Of Hyperbilirubinemia- conjugated Systemic disease Infiltrative disorders Postoperative complications Renal disease Sepsis Drugs
15 Jaundice Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia exists if more than 80% to 85% of the total bilirubin is unconjugated.. Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia exists if greater than 30% of the total bilirubin level is conjugated. Overproduction of bilirubin results in unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.. Mild hyperbilirubinemia may require blood or urine tests for detection, as jaundice usually does not become apparent until the bilirubin level exceeds 3 mg/dl dl.
16 Pathophysiologic classification of Jaundice Hemolytic Jaundice Hepatic Jaundice Obstructive Jaundice
17 Hemolytic Jaundice Pathogenesis Overproduction Hemolysis (intra and extra vascular) inherited or genetic disorders acquired immune hemolytic anemia (Autoimmune hemolytic anemia) nonimmune hemolytic anemia (paroxysmal nocturna Hemoglobinruia) Ineffective erythropoesis Overproduction may overload the liver with UB
18 Hemolytic Jaundice Symptoms weakness, Dark urine, anemia, Icterus, splenomegaly Lab UB without bilirubinuria fecal and urine urobilinogen hemolytic anemia hemoglobinuria (in acute intravascular hemolysis) Reticulocyte counts
19 Hepatic Jaundice Due to a disease affective hepatic tissue either congenital or acquired diffuse hepatocellular injury
20 Hepatic Jaundice Pathogenesis Impaired or absent hepatic conjugation of bilirubin decreased GT activity (Gilbert s syndrome) hereditary absence or deficiency of UDPGT (Grigler-Najjar Syndrome) Familiar or hereditary disorders Dubin-Johnson Syndrome Rotor syndrome Acquired disorders hepatocellular necrosis intrahepatic cholestasis (Hepatitis, Cirrhosis, Drug-related)
21 Hepatocellular defects Viral hepatitis Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Hepatitis G
22 Hepatocellular defects Alcohol abuse Liver steatose (fatty liver) Hepatitis Cirrhosis of the liver
23 Obstructive Jaundice Pathogenesis it is due to intra- and extra hepatic obstruction of bile ducts intrahepatic Jaundice: Hepatitis, PBC, Drugs Extra Hepatic Biliary Obstruction: Stones, Stricture, Inflammation, Tumors, (Ampulla of Vater)
24 Cholestasis PBC PSC Biliary obstruction Pancreatic disease
25 PBC The clinical features include jaundice, pruritus, steatorrhea, xanthomas, and osteopenia. In advanced disease, signs of portal hypertension will occur with esophageal varices, ascites, and other conditions. Primary biliary cirrhosis is a chronic progressive cholestatic disorder typically, although not exclusively, found in women in the fourth to fifth decade of life.
26 PBC laboratory abnormalities: a characteristic isolated alkaline phosphatase elevation out of proportion to other liver function tests, Elevated serum IgM, cholesterol, antimitochondrial antibody (AMA).
27 PBC laboratory abnormalities: a characteristic isolated alkaline phosphatase elevation out of proportion to other liver function tests, Elevated serum IgM, cholesterol, antimitochondrial antibody (AMA).
28 PSC Progressive cholestatic liver disease, which is found mostly in men of middle age. Inflammation of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts Clinically, patients present with recurrent abdominal pain, fever, and intermittent jaundice and later with symptoms of portal hypertension. Characteristic narrowing or "beading" occurs in the hepatic ducts, as demonstrated by cholangiogram.
29 PSC vs. UC Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn, are associated in 30% to 75% of primary sclerosing cholangitis patients Of all patients with ulcerative colitis, 5% to 10% will have primary sclerosing cholangitis.
30 Obstructive Jaundice symptoms Pruritus Jaundice may vary in intensity Chill+fever+gall bladder enlargement stone+cholangitis
31 Obstructive Jaundice Serum Bilirubin Lab Findings Feceal urobilinogen (incomplete obstruction) Feceal urobilinogen absence (complete obstruction) urobilinogenuria is absent in complete obstructive jaundice bilirubinuria ALP, GGTP cholesterol
32 Evaluation to the patient with jaundice The investigation of a patient with jaundice begins with a thorough review of the history of presentation, medication use, past medical history, physical examination, and evaluation of liver function tests.
33 Evaluation to the patient with jaundice Several questions must be answered initially: 1. Is the elevated bilirubin conjugated or unconjugated? In general, most jaundiced patients will not have an isolated unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. 2. If the hyperbilirubinemia is unconjugated, is it caused by increased production, decreased uptake, or impaired conjugation? 3. If the hyperbilirubinemia is conjugated, is the problem intrahepatic or extrahepatic? 4. Is the process acute or chronic?
34 Evaluation to the patient with jaundice Patients with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia usually have acquired disease- identify an intrahepatic or an obstructive cause. Acute disease usually can be differentiated from chronic disease by the patient's history, physical examination (xanthelasma( xanthelasma,, spider angioma, ascites,, or hepatosplenomegaly), and laboratory tests (hypoalbuminemia( hypoalbuminemia, thrombocytopenia,, and an uncorrectable prolongation of the prothrombin time).
35 Evaluation to the patient with jaundice Chronic cholestasis may arise from such diseases as cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis,, primary biliary cirrhosis, secondary biliary cirrhosis, or carcinoma or from drugs. Patients with chronic cholestasis usually do not have hepatitis or gallstones.
36 Evaluation to the patient with jaundice The presence of fever, right upper quadrant pain, tenderness, hepatomegaly,, and new- onset bilirubinuria usually indicates acute disease. Patients older than 50 years of age with asymptomatic cholestasis and mild hepatomegaly may have carcinoma of the pancreas or biliary tree.
37 Evaluation to the patient with jaundice Women aged over 30 years of age are more likely to have choledocholithiasis.
38 Gallstones cholelithiasis the formation or presence of stones in the gallbladder or common bile duct. chole = bile, lith = stone, iasis = condition
39 Gallstones biliary colic: pain associated with gallstones that have entered the common bile duct. choledocholithiasis the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct. cholecystitis inflammation of the gallbladder. cholangitis inflammation of the bile ducts. cholecystectomy : surgical removal of the gallbladder.
40 Gallbladder Disorders Risk factors for cholelithiasis a. Age b. Family history, also Native Americans and persons of northern European heritage c. Obesity, hyperlipidemia d. Females, use of oral contraceptives e. Conditions which lead to biliary stasis: pregnancy, fasting, prolonged parenteral nutrition f. Diseases including cirrhosis, ileal disease or resection, sickle-cell anemia, glucose intolerance
41 Gallbladder Disorders Manifestations of cholelithiasis a. Many persons are asymptomatic b. Early symptoms are epigastic fullness after meals or mild distress after eating a fatty meal c. Biliary colic (if stone is blocking cystic or common bile duct): steady pain in epigastric or RUQ of abdomen lasting up to 5 hours with nausea and vomiting d. Jaundice may occur if there is obstruction of common bile duct
42 Gallbladder Disorders Manifestations of acute cholecystitis a. Episode of biliary colic involving RUQ pain radiating to back, right scapula, or shoulder; the pain may be aggravated by movement, or deep breathing and may last hours b. Anorexia, nausea, and vomiting c. Fever with chills
43 Evaluation to the patient with jaundice An adult with asymptomatic,, isolated unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia who is not taking any drugs and has no evidence of hemolysis probably has Gilbert syndrome and can be monitored with bilirubin determinations for 12 months. If no abnormality develops, no further evaluation is needed.
44 Evaluation to the patient with jaundice Fever, leukocytosis,, and hypotension point to ascending cholangitis Asterixis,, confusion, or stupor may indicate severe hepatocellular dysfunction or fulminant hepatocellular failure
45 Clinical symptoms Fever Chills Weight loss Flu like symptoms Abdominal pain Anorexia Nausea, and vomiting Pruritus
46 Physical examination General appearance cachexia, muscle wasting, palmar erythema, Dupuytren contracture, abnormal nails, parotid enlargement, or xanthelasmas, gynecomastia, spider nevi, or dilated veins.
47
48 Physical examination The size and consistency of the liver shrunken, nodular liver - cirrhosis, a palpable mass - an abscess or malignancy. If the liver span is greater than 15 cm- fatty infiltration, congestion, other infiltrative diseases, or malignancy. Liver tenderness may denote acute disease but is generally not helpful. The presence of a friction rub or bruit suggests malignancy.
49 Clinical examination Spider angioma, palmar erythema, and distended abdominal veins Ascites in the presence of jaundice (cirrhosis, malignancy and severe acute disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis) Splenomegaly (infections, infiltrative diseases, viral hepatitis, or cirrhosis) A palpable, distended gallbladder suggests malignant biliary obstruction. Asterixis in fulminant hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease. Patients with biliary colic or infection may have fever.
50 Laboratory tests TB (conjugated, unconjugated) AspAT, AlAT GGTP AP TP + (albumin, gammaglobulin) Prothrombin
51 Laboratory tests TCh AMA 5 -NT LAP Alfa1-antitrypsin antitrypsin Iron levels Ceruloplasmin Alfa-fetoprotein fetoprotein (AFP) Antinuclear antibody
52 Noninvasive tests US CT Radionuclide imaging is an excellent means of detecting cystic duct obstruction. It is the test of choice if acute cholecystitis is suspected, but it has little value in differentiating intrahepatic from extrahepatic causes of cholestasis.
53 Invasive tests ERCP - endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography PTC - percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography liver biopsy
54 ERCP ERCP is 90% successful regardless of the presence or absence of ductal dilation and can localize the site of obstruction in more than 90% of patients. It is particularly helpful in diagnosing patients with common duct stones. Because it has therapeutic capabilities, it allows some patients to avoid surgery. ERCP is also helpful if a stricture due to chronic pancreatitis is suspected.
55 PTC PTC visualizes the biliary tree in 90% to 100% of patients with dilated ducts and localizes the site of obstruction in 90% of cases. It locates the obstruction in 50% to 90% of patients without dilated ducts, as determined by ultrasound. PTC is less expensive than ERCP and often is easier to perform. The patient must have a prothrombin time of less than 16 seconds, a platelet count greater than 50,000, and no ascites. Minor complications occur in 30% of patients. Major complications, including sepsis, bleeding, biliary leak, pneumothorax, arteriovenous fistula, hematoma, abscess, and peritonitis, occur in 1% to 10% of patients who undergo PTC.
Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases. Premed 2 Pathophysiology
 Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases Premed 2 Pathophysiology Pancreas Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Autodigestion of the pancreas due to activation of the enzymes Hemorrhagic fat necrosis, calcium
Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases Premed 2 Pathophysiology Pancreas Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Autodigestion of the pancreas due to activation of the enzymes Hemorrhagic fat necrosis, calcium
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon
 What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
Service Definition with all Clinical Terms Service: Laprascopic Cholecystectomy Clinic (No Gallstones in bile duct)
 Service Definition with all Clinical Terms Service: Laprascopic Cholecystectomy Clinic (No Gallstones in bile duct) Section 1 Service Details Service ID: 7540540 Service Comments: Referrer Alert: Service
Service Definition with all Clinical Terms Service: Laprascopic Cholecystectomy Clinic (No Gallstones in bile duct) Section 1 Service Details Service ID: 7540540 Service Comments: Referrer Alert: Service
Differential diagnosis of icterus. Katalin Keltai,, MD
 Differential diagnosis of icterus Katalin Keltai,, MD What is icterus? Icterus nigrogularis = ORIOLE DEFINITION: Bile or liver problem causing yellowness A yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes,
Differential diagnosis of icterus Katalin Keltai,, MD What is icterus? Icterus nigrogularis = ORIOLE DEFINITION: Bile or liver problem causing yellowness A yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes,
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Indiana University School
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Indiana University School
Fast Facts. Fast Facts: Liver Disorders. Thomas Mahl and John O Grady. 2006 Health Press Ltd. www.fastfacts.com
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Liver Disorders Thomas Mahl and John O Grady 2006 Health Press Ltd. www.fastfacts.com Fast Facts Fast Facts: Liver Disorders Thomas Mahl MD University at Buffalo School of Medicine
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Liver Disorders Thomas Mahl and John O Grady 2006 Health Press Ltd. www.fastfacts.com Fast Facts Fast Facts: Liver Disorders Thomas Mahl MD University at Buffalo School of Medicine
Biliary Stone Disease
 Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
New Development in Treating Liver Disorders: Approaches to liver function test from mild to fulminant disorders
 Research and Reviews New Development in Treating Liver Disorders: Approaches to liver function test from mild to fulminant disorders JMAJ 53(4): 218 223, 2010 Hirohito TSUBOUCHI,* 1 Akio IDO,* 2 Seiichi
Research and Reviews New Development in Treating Liver Disorders: Approaches to liver function test from mild to fulminant disorders JMAJ 53(4): 218 223, 2010 Hirohito TSUBOUCHI,* 1 Akio IDO,* 2 Seiichi
Mrs. J.S. Your patient in the ER is a 55 year-old female with a short history of upper abdominal discomfort and chills. Her family noticed she was jau
 Jaundice Hilary Sanfey, MD University of Virginia Mrs. J.S. Your patient in the ER is a 55 year-old female with a short history of upper abdominal discomfort and chills. Her family noticed she was jaundiced.
Jaundice Hilary Sanfey, MD University of Virginia Mrs. J.S. Your patient in the ER is a 55 year-old female with a short history of upper abdominal discomfort and chills. Her family noticed she was jaundiced.
Bilirubin (serum, plasma)
 Bilirubin (serum, plasma) 1 Analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Bilirubin 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NLMC code 1.4 Description of analyte Bilirubin is a linear tetrapyrrole (MW 585 Da), the final product of
Bilirubin (serum, plasma) 1 Analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Bilirubin 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NLMC code 1.4 Description of analyte Bilirubin is a linear tetrapyrrole (MW 585 Da), the final product of
Interpretation of liver chemistry tests
 Interpretation of liver chemistry tests Fuad A.M. Hasan, Salim Owyed Bulletin of KIMS carries some articles specifically designated as CME/CPD. They provide the opportunity for the reader to obtain credit
Interpretation of liver chemistry tests Fuad A.M. Hasan, Salim Owyed Bulletin of KIMS carries some articles specifically designated as CME/CPD. They provide the opportunity for the reader to obtain credit
CMS Limitations Guide - Laboratory Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Laboratory Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their exisiting medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitattions
CMS Limitations Guide - Laboratory Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their exisiting medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitattions
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015
 Benign liver diseases Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015 1 Agenda Benign focal liver lesions Fatty liver disease
Benign liver diseases Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015 1 Agenda Benign focal liver lesions Fatty liver disease
The child with abnormal liver function tests
 The child with abnormal liver function tests Dr Jane Hartley Consultant Paediatric Hepatologist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK 1 st Global Congress CIP, Paris 2011 Contents Over view of liver anatomy,
The child with abnormal liver function tests Dr Jane Hartley Consultant Paediatric Hepatologist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK 1 st Global Congress CIP, Paris 2011 Contents Over view of liver anatomy,
Disclosures. Interpreting Liver Tests: What Do They Mean? Liver Function Tests. Objectives. Common Tests. Case 1
 Disclosures Interpreting Liver Tests: What Do They Mean? I have no financial disclosures to make. Roman Perri, MD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Objectives Discuss tests commonly used
Disclosures Interpreting Liver Tests: What Do They Mean? I have no financial disclosures to make. Roman Perri, MD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Objectives Discuss tests commonly used
Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies
 Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies Preoperative Labratorey and Diagnostic Studies The concept of standardized testing in all presurgical patients regardless of age or medical condition is no
Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies Preoperative Labratorey and Diagnostic Studies The concept of standardized testing in all presurgical patients regardless of age or medical condition is no
Clinical Approach to the Patient With Abnormal Liver Test Results. ALT =alanine aminotransferase; AST =aspartate aminotransferase;
 Concise Review o rlmary..._.. Physicians Clinical Approach to the Patient With Abnormal Liver Test Results PATRICK S. KAMATH, M.D. Abnormal results of standard biochemical liver tests occur frequently;
Concise Review o rlmary..._.. Physicians Clinical Approach to the Patient With Abnormal Liver Test Results PATRICK S. KAMATH, M.D. Abnormal results of standard biochemical liver tests occur frequently;
Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD
 Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD Biliary Injuries during Cholecystectomy In the 1990s, high rate of biliary injury was due in part to learning
Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD Biliary Injuries during Cholecystectomy In the 1990s, high rate of biliary injury was due in part to learning
Assessment of some biochemical tests in liver diseases
 Assessment of some biochemical tests in liver diseases By Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-Eldin Prof. of Hepatology & Gastroenterology Faculty of Medicine Tanta University, Egypt. Significant liver damage may occur
Assessment of some biochemical tests in liver diseases By Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-Eldin Prof. of Hepatology & Gastroenterology Faculty of Medicine Tanta University, Egypt. Significant liver damage may occur
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND LIVER DISEASES. Prof. Fang Zheng Department of Laboratory Medicine School of Medicine, Wuhan University
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND LIVER DISEASES Prof. Fang Zheng Department of Laboratory Medicine School of Medicine, Wuhan University Content the Anatomy of Liver the Function of Liver Tests of Liver Function
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND LIVER DISEASES Prof. Fang Zheng Department of Laboratory Medicine School of Medicine, Wuhan University Content the Anatomy of Liver the Function of Liver Tests of Liver Function
Evaluation of Liver Function tests in Primary Care. Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies, KCH
 Evaluation of Liver Function tests in Primary Care Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies, KCH Liver Function tests Markers of hepatocellular damage Cholestasis Liver synthetic function Markers of Hepatocellular
Evaluation of Liver Function tests in Primary Care Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies, KCH Liver Function tests Markers of hepatocellular damage Cholestasis Liver synthetic function Markers of Hepatocellular
Indications in Hepatology and Liver Diseases
 exclusively working in Health Care sananet GmbH Tilo Stolzke Breite Str. 6-8 23562 Lübeck Germany Telefon : +49 451 400 8301 Telefax : +49 451 400 8302 E-Mail : stolzke@sananet.com Internet : www.sananet.com
exclusively working in Health Care sananet GmbH Tilo Stolzke Breite Str. 6-8 23562 Lübeck Germany Telefon : +49 451 400 8301 Telefax : +49 451 400 8302 E-Mail : stolzke@sananet.com Internet : www.sananet.com
Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery
 Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery Summary Gallstones are small stones made from cholesterol, bile pigment and calcium salts, which form in a person s gall bladder. Medical treatment isn t necessary
Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery Summary Gallstones are small stones made from cholesterol, bile pigment and calcium salts, which form in a person s gall bladder. Medical treatment isn t necessary
LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests
 LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests Applicable CPT Code(s): 86692 Antibody; Hepatitis, Delta Agent 86704 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); Total 86705 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); IgM Antibody
LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests Applicable CPT Code(s): 86692 Antibody; Hepatitis, Delta Agent 86704 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); Total 86705 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); IgM Antibody
Assessment of Liver Function and Diagnostic Studies. Disclosures
 Assessment of Liver Function and Diagnostic Studies 2011 Joseph Ahn, M.D., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Liver Transplantation v.3 Disclosures Absolute Autopsy Key Points 1. Review
Assessment of Liver Function and Diagnostic Studies 2011 Joseph Ahn, M.D., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Liver Transplantation v.3 Disclosures Absolute Autopsy Key Points 1. Review
Laboratory Monitoring of Adult Hospital Patients Receiving Parenteral Nutrition
 Laboratory Monitoring of Adult Hospital Patients Receiving Parenteral Nutrition Copy 1 Location of copies Web based only The following guideline is for use by medical staff caring for the patient and members
Laboratory Monitoring of Adult Hospital Patients Receiving Parenteral Nutrition Copy 1 Location of copies Web based only The following guideline is for use by medical staff caring for the patient and members
Pathway for the Management of Acute Gallstone Diseases
 Pathway for the Management of Acute Gallstone Diseases What s in this document? Pathways to encourage safer, faster and more cost effective management of acute gallstone (GS) disease by stratification
Pathway for the Management of Acute Gallstone Diseases What s in this document? Pathways to encourage safer, faster and more cost effective management of acute gallstone (GS) disease by stratification
Albumin. Prothrombin time. Total protein
 Hepatitis C Fact Sheet February 2016 www.hepatitis.va.gov Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to about learn more about your individual hepatitis
Hepatitis C Fact Sheet February 2016 www.hepatitis.va.gov Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to about learn more about your individual hepatitis
Amylase and Lipase Tests
 Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Prof. of Tropical Medicine Faculty of Medicine Alexandria University
 prof. Dr. Ali El-Kady (MD) Prof. of Tropical Medicine Faculty of Medicine Alexandria University DRUGS THAT MAY CAUSE LIVER DYSFUNCTION DAMAGE The liver is the principal organ that is capable of converting
prof. Dr. Ali El-Kady (MD) Prof. of Tropical Medicine Faculty of Medicine Alexandria University DRUGS THAT MAY CAUSE LIVER DYSFUNCTION DAMAGE The liver is the principal organ that is capable of converting
Liver Function Tests. Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB
 Liver Function Tests Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB Introduction Case presentation What is the liver? Overview of tests used to measure liver function RJ 10 month old European girl
Liver Function Tests Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB Introduction Case presentation What is the liver? Overview of tests used to measure liver function RJ 10 month old European girl
GUIDELINES & PROTOCOLS
 GUIDELINES & PROTOCOLS ADVISORY COMMITTEE Effective Date: August 1, 2011 Scope This guideline provides recommendations for the evaluation and interpretation of abnormal liver test results in adults ( 19
GUIDELINES & PROTOCOLS ADVISORY COMMITTEE Effective Date: August 1, 2011 Scope This guideline provides recommendations for the evaluation and interpretation of abnormal liver test results in adults ( 19
NP/PA Clinical Hepatology Fellowship Summary of Year-Long Curriculum
 OVERVIEW OF THE FELLOWSHIP The goal of the AASLD NP/PA Fellowship is to provide a 1-year postgraduate hepatology training program for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in a clinical outpatient
OVERVIEW OF THE FELLOWSHIP The goal of the AASLD NP/PA Fellowship is to provide a 1-year postgraduate hepatology training program for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in a clinical outpatient
Liver, biliary, and pancreatic needs
 Liver, biliary, and pancreatic needs Therapeutic nursing interventions NSG 4037: Adult Nursing III 2006 Acute pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas Autodigestion of pancreas Fat necrosis Hemorrhage
Liver, biliary, and pancreatic needs Therapeutic nursing interventions NSG 4037: Adult Nursing III 2006 Acute pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas Autodigestion of pancreas Fat necrosis Hemorrhage
Evaluation of suspected liver disease requires an understanding of the diverse tests of liver
 Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Chemistry Values Differential Diagnosis Evaluation of suspected liver disease requires an understanding of the diverse tests of liver function and serum markers
Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Chemistry Values Differential Diagnosis Evaluation of suspected liver disease requires an understanding of the diverse tests of liver function and serum markers
The word jaundice comes
 COVER ARTICLE PROBLEM-ORIENTED DIAGNOSIS Jaundice in the Adult Patient SEAN P. ROCHE, M.D., Albany Medical College, Albany, New York REBECCA KOBOS, M.D., University of Nevada School of Medicine, Reno,
COVER ARTICLE PROBLEM-ORIENTED DIAGNOSIS Jaundice in the Adult Patient SEAN P. ROCHE, M.D., Albany Medical College, Albany, New York REBECCA KOBOS, M.D., University of Nevada School of Medicine, Reno,
HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP
 College of Osteopathic Medicine HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP Office for Clinical Affairs 515-271-1629 FAX 515-271-1727 Elective Rotation General Description This elective rotation is a four (4) week introductory,
College of Osteopathic Medicine HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP Office for Clinical Affairs 515-271-1629 FAX 515-271-1727 Elective Rotation General Description This elective rotation is a four (4) week introductory,
Interpretation of abnormal liver function tests. Dr Rania Bakry, MD
 Interpretation of abnormal liver function tests Dr Rania Bakry, MD Liver function tests Noninvasive method of screening for the presence of liver dysfunction Pattern of lab test abnormality allows recognition
Interpretation of abnormal liver function tests Dr Rania Bakry, MD Liver function tests Noninvasive method of screening for the presence of liver dysfunction Pattern of lab test abnormality allows recognition
Evaluation of a Child with Elevated Transaminases. Linda V. Muir, M.D. April 11, 2008 Northwest Pediatric Liver Disease Symposium
 Evaluation of a Child with Elevated Transaminases Linda V. Muir, M.D. April 11, 2008 Northwest Pediatric Liver Disease Symposium Disclosures I do not have a financial interest, arrangement or affiliation
Evaluation of a Child with Elevated Transaminases Linda V. Muir, M.D. April 11, 2008 Northwest Pediatric Liver Disease Symposium Disclosures I do not have a financial interest, arrangement or affiliation
Alcoholic Hepatitis (Teacher s Guide)
 Thomas Ormiston, M.D. Updated 5/5/15 2007-2015, SCVMC Alcoholic Hepatitis (Teacher s Guide) (30 minutes) I. Objectives Recognize the signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis Understand the treatment options
Thomas Ormiston, M.D. Updated 5/5/15 2007-2015, SCVMC Alcoholic Hepatitis (Teacher s Guide) (30 minutes) I. Objectives Recognize the signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis Understand the treatment options
Steven B. Goldin, MD, PhD University of South Florida Dimitrios Stefanidis, MD, PhD
 RUQ Abdominal Pain Steven B. Goldin, MD, PhD University of South Florida Dimitrios Stefanidis, MD, PhD Mrs. Stone 41 year-old woman in the ER presenting with 12 hours duration of progressively worsening
RUQ Abdominal Pain Steven B. Goldin, MD, PhD University of South Florida Dimitrios Stefanidis, MD, PhD Mrs. Stone 41 year-old woman in the ER presenting with 12 hours duration of progressively worsening
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder)
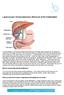 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder) The gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ that lies in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen under your liver (under your ribs). The liver
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder) The gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ that lies in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen under your liver (under your ribs). The liver
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1047385/ Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals Description: Liver disease is a rapidly growing
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1047385/ Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals Description: Liver disease is a rapidly growing
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Summary liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Summary liver function / liver function
Abnormal Liver Tests. Dr David Scott Gastroenterologist
 Abnormal Liver Tests Dr David Scott Gastroenterologist Talk Outline Understanding Liver Tests Examples of Liver Diseases Case Studies Blood Tests for the Liver LFTs = Liver Function tests Hepatocyte damage
Abnormal Liver Tests Dr David Scott Gastroenterologist Talk Outline Understanding Liver Tests Examples of Liver Diseases Case Studies Blood Tests for the Liver LFTs = Liver Function tests Hepatocyte damage
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
Asymptomatic Elevated Liver Function Tests: Physiology, Chemistry, and Workup
 Asymptomatic Elevated Liver Function Tests: Physiology, Chemistry, and Workup James T. Sing, Jr., D.O., FACG, AGAF Scott & White Clinic Assistant Professor Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology
Asymptomatic Elevated Liver Function Tests: Physiology, Chemistry, and Workup James T. Sing, Jr., D.O., FACG, AGAF Scott & White Clinic Assistant Professor Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein
 Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal Impairment
 Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Canadian Association of Gastroenterology (CAG) Practice Guidelines: Evaluation of abnormal liver enzyme tests
 CAG PRACTICE GUIDELINES Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Practice Guidelines: Evaluation of abnormal liver enzyme tests Approximately one in 10 Canadians has at least one abnormal liver biochemical
CAG PRACTICE GUIDELINES Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Practice Guidelines: Evaluation of abnormal liver enzyme tests Approximately one in 10 Canadians has at least one abnormal liver biochemical
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations
 Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 24 January 2012 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 24 January 2012 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
Evaluation of abnormal LFT in the asymptomatic patient. Son Do, M.D. Advanced Gastroenterology Vancouver, WA
 Evaluation of abnormal LFT in the asymptomatic patient Son Do, M.D. Advanced Gastroenterology Vancouver, WA Definition of chronic, abnormally elevated LFT Elevation of one or more of the following for
Evaluation of abnormal LFT in the asymptomatic patient Son Do, M.D. Advanced Gastroenterology Vancouver, WA Definition of chronic, abnormally elevated LFT Elevation of one or more of the following for
CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
 CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA WHAT IS CANCER OF THE LIVER? Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form and it comes from the main type of liver cell, the hepatocyte. About 3 out 4
CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA WHAT IS CANCER OF THE LIVER? Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form and it comes from the main type of liver cell, the hepatocyte. About 3 out 4
Managing LFT s in General Practice
 Managing LFT s in General Practice Sulleman Moreea FRCP(Edin Edin) ) FRCS(Glasg Glasg) Consultant Gastroenterologist/Hepatologist Bradford Hospitals Trust The normal liver Managing LFT s History and examination
Managing LFT s in General Practice Sulleman Moreea FRCP(Edin Edin) ) FRCS(Glasg Glasg) Consultant Gastroenterologist/Hepatologist Bradford Hospitals Trust The normal liver Managing LFT s History and examination
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406
 Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
11/10/2014. I have nothing to Disclose. Covered Stents discussed are NOT FDA approved for the indications covered in my presentation
 I have nothing to Disclose Ramsey Dallal, MD, FACS Vice Chair Department of Surgery Chief Bariatric i and Minimally i Invasive Surgery Einstein Healthcare Network Nemacolin, PA 2014 Covered Stents discussed
I have nothing to Disclose Ramsey Dallal, MD, FACS Vice Chair Department of Surgery Chief Bariatric i and Minimally i Invasive Surgery Einstein Healthcare Network Nemacolin, PA 2014 Covered Stents discussed
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives
 Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent
 A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
ICD-9-CM/ICD-10-CM Codes for MNT
 / Codes for MNT ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are used by physicians and medical coders to assign medical diagnoses to individual patients. It is not within the scope of practice
/ Codes for MNT ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are used by physicians and medical coders to assign medical diagnoses to individual patients. It is not within the scope of practice
HOW TO EVALUATE ELEVATED LIVER ENZYMES
 HOW TO EVALUATE ELEVATED LIVER ENZYMES Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine LABORATORY TESTS OF
HOW TO EVALUATE ELEVATED LIVER ENZYMES Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine LABORATORY TESTS OF
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS University of PNG School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences, Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology VJ Temple 1 What are some of the functions
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS University of PNG School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences, Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology VJ Temple 1 What are some of the functions
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES
 NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
Cirrhosis and Ascites. Thomas S. Foster, Pharm.D. Integrated Therapeutics PHR 961
 Cirrhosis and Ascites Thomas S. Foster, Pharm.D. Integrated Therapeutics PHR 961 Overview Liver weighs about 3 pounds and is the largest organ in the body. It is located in the upper right side of the
Cirrhosis and Ascites Thomas S. Foster, Pharm.D. Integrated Therapeutics PHR 961 Overview Liver weighs about 3 pounds and is the largest organ in the body. It is located in the upper right side of the
Hepatitis C. Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET
 LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET NEOPLASM OF LIVER PRIMARY 1)BENIGN 2)MALIGNANT METASTATIC/SECONDARY LIVER Primary Liver Cancer the Second Killer among tumors high morbidity and mortality(20.40/100,000) etiology
LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET NEOPLASM OF LIVER PRIMARY 1)BENIGN 2)MALIGNANT METASTATIC/SECONDARY LIVER Primary Liver Cancer the Second Killer among tumors high morbidity and mortality(20.40/100,000) etiology
Diseases of peritoneum Lect. Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32
 Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Session 11: The ABCs of LFTs Learning Objectives
 Session 11: The ABCs of LFTs Learning Objectives 1. Define 3 key components of the patient history that should be further evaluated when liver function testing reveals elevated aminotransferases. 2. Identify
Session 11: The ABCs of LFTs Learning Objectives 1. Define 3 key components of the patient history that should be further evaluated when liver function testing reveals elevated aminotransferases. 2. Identify
Gallstones. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gallstones National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Gallstones National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION IN ALAGILLE SYNDROME
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION IN ALAGILLE SYNDROME Ronald J. Sokol, MD Children s Hospital Colorado University of Colorado School of Medicine Treatment of Liver Disease in Improve bile flow ALGS Ursodeoxycholic
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION IN ALAGILLE SYNDROME Ronald J. Sokol, MD Children s Hospital Colorado University of Colorado School of Medicine Treatment of Liver Disease in Improve bile flow ALGS Ursodeoxycholic
OMG my LFT s! How to Interpret and Use Them. OMG my LFT s! OMG my LFT s!
 How to Interpret and Use Them René Romero, M.D. Clinical Director, Pediatric Hepatology CPG Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Emory University School of Medicine Objectives Understand the anatomy
How to Interpret and Use Them René Romero, M.D. Clinical Director, Pediatric Hepatology CPG Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Emory University School of Medicine Objectives Understand the anatomy
The most serious symptoms of this stage are:
 The Natural Progression of Hepatitis C The natural history of hepatitis C looks at the likely outcomes for people infected with the virus if there is no medical intervention. However, the process of trying
The Natural Progression of Hepatitis C The natural history of hepatitis C looks at the likely outcomes for people infected with the virus if there is no medical intervention. However, the process of trying
190.33 - Hepatitis Panel/Acute Hepatitis Panel
 190.33 - Hepatitis Panel/Acute Hepatitis Panel This panel consists of the following tests: Hepatitis A antibody (HAAb), IgM antibody; Hepatitis B core antibody (HBcAb), IgM antibody; Hepatitis B surface
190.33 - Hepatitis Panel/Acute Hepatitis Panel This panel consists of the following tests: Hepatitis A antibody (HAAb), IgM antibody; Hepatitis B core antibody (HBcAb), IgM antibody; Hepatitis B surface
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction)
 SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Surgical Treatment of Various GI Tract Cancers
 Surgical Treatment of Various GI Tract Cancers By James Ouellette, DO, FACS, Surgical Oncology, Hepatobiliary Surgery Surgical treatment for most gastrointestinal (GI) cancers requires multidisciplinary
Surgical Treatment of Various GI Tract Cancers By James Ouellette, DO, FACS, Surgical Oncology, Hepatobiliary Surgery Surgical treatment for most gastrointestinal (GI) cancers requires multidisciplinary
Jaundice is not a diagnosis per se but rather a physical manifestation
 Jaundice: An Emergency Department Approach To Diagnosis And Management You re in the middle of a busy Monday afternoon shift. The next chart simply states other complaint, but one look at the patient tells
Jaundice: An Emergency Department Approach To Diagnosis And Management You re in the middle of a busy Monday afternoon shift. The next chart simply states other complaint, but one look at the patient tells
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
understanding CIRRHOSIS of the liver A patient s guide from your doctor and
 understanding CIRRHOSIS of the liver A patient s guide from your doctor and Cirrhosis Basics The liver is one of the most important organs in your body and weighs about 3 pounds. It sits in the upper right
understanding CIRRHOSIS of the liver A patient s guide from your doctor and Cirrhosis Basics The liver is one of the most important organs in your body and weighs about 3 pounds. It sits in the upper right
A.P. Chen, MD Director, Developmental Therapeutics Clinic Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis National Cancer Institute
 A.P. Chen, MD Director, Developmental Therapeutics Clinic Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis National Cancer Institute Click to view Biosketch and Presentation Abstract or page down to review presentation
A.P. Chen, MD Director, Developmental Therapeutics Clinic Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis National Cancer Institute Click to view Biosketch and Presentation Abstract or page down to review presentation
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis
 Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
UCLA Asian Liver Program
 CLA Program Update Program Faculty Myron J. Tong, PhD, MD Professor of Medicine Hepatology Director, Asian Liver Program Surgery Ronald W. Busuttil, MD, PhD Executive Chair Department of Surgery Director,
CLA Program Update Program Faculty Myron J. Tong, PhD, MD Professor of Medicine Hepatology Director, Asian Liver Program Surgery Ronald W. Busuttil, MD, PhD Executive Chair Department of Surgery Director,
Subproject 4: Specification and Documentation of Metabolic and Neoplastic Diseases
 Subproject 4: Specification and Documentation of Metabolic and Neoplastic Diseases M. Trauner, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, MUG Co- Investigator: H. Samonigg,
Subproject 4: Specification and Documentation of Metabolic and Neoplastic Diseases M. Trauner, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, MUG Co- Investigator: H. Samonigg,
Acute Pancreatitis. Questionnaire. if yes: amount (cigarettes/day): since when (year): Drug consumption: yes / no if yes: type of drug:. amount:.
 The physical examination has to be done AT ADMISSION! The blood for laboratory parameters has to be drawn AT ADMISSION! This form has to be filled AT ADMISSION! Questionnaire Country: 1. Patient personal
The physical examination has to be done AT ADMISSION! The blood for laboratory parameters has to be drawn AT ADMISSION! This form has to be filled AT ADMISSION! Questionnaire Country: 1. Patient personal
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) Patient Information Booklet
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
Southern Derbyshire. Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Abnormal Liver Function Tests (LFTs) in Adults
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Abnormal Liver Function Tests (LFTs) in Adults Purpose of Guideline The management of patients with abnormal liver function test results Scope This
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Abnormal Liver Function Tests (LFTs) in Adults Purpose of Guideline The management of patients with abnormal liver function test results Scope This
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric Bypass. Patient Name
 Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric Bypass Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric Bypass Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated 14 September 1999 Pre- Transformed Ig Surface Surface Secreted Myeloma Major malignant counterpart
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol)
 MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol) 1. Hepatotoxicity: In Active TB Disease a. Background: 1. Among the 4 standard anti-tb drugs,
MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol) 1. Hepatotoxicity: In Active TB Disease a. Background: 1. Among the 4 standard anti-tb drugs,
To Whipple or Not to Whipple, that is the Question: Evaluating the Resectability of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
 August 2009 To Whipple or Not to Whipple, that is the Question: Evaluating the Resectability of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Christina Ramirez, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Agenda
August 2009 To Whipple or Not to Whipple, that is the Question: Evaluating the Resectability of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Christina Ramirez, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Agenda
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
