BPC TASK FORCE (DOMENICI-RIVLIN) PLAN
|
|
|
- Andrea Wiggins
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SIDE-BY-SIDE COMPARISON COMMISSION, BPC DOMENICI-RIVLIN TASK FORCE, OBAMA, AND CHAIRMAN RYAN POLICY OBAMA S Debt-to-GDP in % 59% Unspecified. Claims $4 trillion in savings over 12 years. 70% Domestic Discretionary 12-yr savings $860 billion Freezes spending for 2012, then cuts back to 2008 levels in 2013, followed by seven years held to half the rate of inflation Assumes both domestic and defense discretionary spending never grow faster than inflation and includes no enforcement mechanism to achieve this after 2020 (historically, discretionary spending has grown approximately with the economy). Therefore, discretionary spending will continuously decrease as a percentage of the economy 12-yr savings $440 billion Freezes domestic discretionary spending for four years, then caps growth at GDP 12-yr savings $770 billion (non-security) Details of the path are unspecified 12-yr savings $2 tillion (nonsecurity) Cuts domestic discretionary spending back to below 2008 levels, then freezes for five years, then caps at inflation Assumes both domestic and defense discretionary spending never grow faster than inflation and includes no enforcement mechanism to achieve this after 2020 (historically, discretionary spending has grown approximately with the economy). Therefore, discretionary spending will continuously decrease as a percentage of the economy 12-yr savings $1.1 trillion 12-yr savings $580 billion 12-yr savings $400 billion $78 billion over 10 years Defense Freezes spending for 2012, then cuts back to 2008 levels in 2013, followed by seven years held to half the rate of inflation Reduces weapon systems, reforms compensation, cuts force structure cuts, and applies Secretary Gates savings Freezes defense discretionary spending for five years, then caps spending at growth of GDP Reduces weapon systems, reforms compensation, cuts force structure, and applies Secretary Gates savings Charges Secretary Gates to eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and conduct a fundamental review of America s missions, capabilities, and our role in a changing world Implements Secretary Gates savings in defense spending
2 Health Reforms Medicare cost-sharing rules Uses Medicare s purchasing power to increase rebates from Caps and phases out tax exclusion of employer-provided health Strengthens IPAB Converts FEHB program from defined benefit to defined contribution with support growing at GDP+1% Medicaid: Expands managed care for dual eligibles Starting in 2020, establishes a global cap on all federal healthcare spending (including Medicare, Medicaid, CHIP, FEHB, and TRICARE) to limit growth to GDP+1% (overall not per beneficiary a more stringent cap than GDP+1% per capita) without specific policies Accommodates a permanent fix to the SGR mechanism that currently requires unrealistic automatic cuts in physician payments ( doc fix ) Reforms Medicare cost-sharing rules Uses Medicare s purchasing power to increase rebates from Caps and phases out tax exclusion of employer-provided health Starting in 2018, transforms Medicare to a premium-support model, but maintains traditional Medicare as default option, and annually grows support level at GDP+1% Medicaid: Expands managed care for dual eligibles Medicaid: Limits program growth starting in 2018: One option would end federal matching payments in Medicaid by decoupling the system, while maintaining strong maintence of effort requirements Accommodates a permanent fix to the SGR mechanism that currently requires unrealistic automatic cuts in physician payments ( doc fix ) OBAMA S Speeds up availability of generic drugs and prohibits brand-name companies from entering into pay-for-delay deals with generic companies Uses Medicare s purchasing power to increase rebates from Stregthens IPAB and sets a new target for annual Medicare spending growth per beneficiary of GDP+0.5% Gives IPAB additional enforcement mechanisms such as an automatic sequester Medicaid: Replaces the complicated current Federal matching formulas with a single matching rate for all program spending that automatically increases if a recession forces enrollment and State costs to rise Medicaid: Closes loopholes that allow states to increase their effective matching rate Establishes upper limits on Mediaid payments for durable medical equipment Does not account for a doc fix in the budget Raises the Medicare eligibility age from 65 to 67 by 2033 Repeals most provisions in the Affordable Care Act (except for the Medicare cost controls), including: health exchanges and subsidies, expansion of Medicaid coverage, IPAB, and the individual mandate Starting in 2022, transforms Medicare to a premium-support model, eventually eliminating traditional Medicare. Annually grows support at rate of inflation significantly slower than projected growth of healthcare costs Medicaid: Block grants payments to states that would grow at rate of inflation plus population growth significantly slower than projected growth in healthcare costs Medicaid: Removes coverage of dual eligibles and acute care from the program and instead creates medical savings accounts for those with income below 150% of poverty Does not account for a doc fix in the budget
3 OBAMA S Social Security Raises retirement ages slowly over time Switches to Chained CPI Includes state and local workers Raises the minimum benefit and creates old-age bump Raises the cap on payroll taxes to the 90% level Makes a significant benefit adjustment, protecting the bottom 50% of beneficiaries Adjusts benefit formula to account for increases in longevity (but does not raise the retirement ages) Switches to Chained CPI Includes state and local workers Raises the minimum benefit and creates old-age bump Raises the cap on payroll taxes to the 90% level Makes a more modest benefit adjustment, protecting the bottom 75% of beneficiaries Benefits from health policy that caps and phases out the employer-provided healthbenefit exclusion (producing more payroll tax revenue), which allows smaller reductions in benefit growth Acknowledges the long-term imbalance, and that it is better addressed sooner than later Supports bipartisan efforts to strengthen Social Security Calls for a bipartisan process to make Social Security solvent
4 OBAMA S Other Mandatory Spending Reforms farm programs Reforms military retirement Reforms civilian retirement Imposes COLA change across governmen Reforms farm programs Reforms military retirement Reforms civilian retirement Imposes COLA change across government Targets $360 billion in savings over 12 years from other mandatory programs Includes unspecified reforms to farm programs, civilian retirement, and unemployment Targets $715 billion in savings over 10 years from other mandatory programs, and then continues to shrink this category of spending relative to the economy, but does not specify policies to do so Decreases funding for food stamps and Pell grants, reforms civilian retirement, winds down (and eventually privatizes) Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, and includes unspecified reforms to farm programs and unemployment Individual Tax Reform Cuts individual income tax rates; creates three brackets of 12%, 22%, and 28% Eliminates almost all deductions and Converts charitable, mortgage, and retirement savings deductions into refundable Raises federal gas tax by 15 cents Cuts individual income tax rates; creates just two brackets of 15% and 27% Eliminates almost all deductions and Converts charitable, mortgage, and retirement savings deductions into refundable Introduces a Debt Reduction Sales Tax of 6.5% Endorses framework used by both Simpson-Bowles and Domenici-Rivlin to eliminate most tax deductions and in order to both lower rates and reduce the deficit Does not specify which expenditures would be curtailed Allows the Bush tax cuts for high earners to expire Cuts top individual tax rate to 25%, and aims to pay for this by eliminating deductions and Does not specify which expenditures would be curtailed Calls for revenue-neutral tax reform Proposes to limit revenues to 21% of GDP New tax system will be more progressive than today s Ensures that half of American households will no longer have to file tax returns New tax system will be more progressive than today s
5 Corporate Tax Reform Cuts corporate rate to 28% Eliminates almost all deductions and Moves to territorial system Cuts corporate rate to 27% Eliminates almost all deductions and OBAMA S Re-issues call for Congress to work on deficit-neutral corporate tax reform to lower rates and broaden the base Cuts the corporate rate to 25%, and aims to pay for this by eliminating deductions and Budget Process Calls for an accelerated legislative process for debt stabilization proposals should the budget not be in primary balance by 2015 or stabilized with regard to the debt-to-gdp ratio thereafter. The president would have to submit policies in his budget to hit targets and they would be fast-tracked for consideration by Congress Changes discretionary spending pots from defense and nondefense to security and non-security Puts in place automatic triggers for extended unemployment benefits Calls for a strong budget enforcement mechanism, SAVEGO*, which would mandate specific amounts of annual deficit reduction from different parts of the budget (three categories: discretionary, healthcare, and other mandatory/revenues) Changes discretionary spending pots from defense and nondefense to security and nonsecurity Moves to a biennial budgeting system Calls for a Debt Failsafe trigger beginning in 2014 to ensure that debt is on a declining path Although details are unspecified, this would call for a cut in spending (exempting Social Security, Medicare, and lowincome programs) and tax expenditures if certain targets were not met Under this trigger, calls for debt to average no more than 2.8% of GDP in the second half of the decade Calls for discretionary spending caps Also calls for caps on total spending as a percentage of GDP consistent with the levels in the budget resolution Caps would be enforced by across-the-board sequester of spending Requires a regular congressional review of mandatory spending programs *SAVEGO is a mechanism developed by the Bipartisan Policy Center in collaboration with Sen. Pete Domenici, Dr. Alice Rivlin, Dr. Joe Minarik, Dr. Bill Hoagland, Steve Bell, and Charles Konigsberg. For more information, please see
A BIPARTISAN PLAN TO REDUCE OUR NATION S DEFICITS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 A BIPARTISAN PLAN TO REDUCE OUR NATION S DEFICITS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This bipartisan, comprehensive, and balanced plan consistent with the recommendations of the Bowles-Simpson fiscal commission that will:
A BIPARTISAN PLAN TO REDUCE OUR NATION S DEFICITS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This bipartisan, comprehensive, and balanced plan consistent with the recommendations of the Bowles-Simpson fiscal commission that will:
Uh Oh!! You failed to reduce the debt to a sustainable level. Without further changes, a fiscal crisis is likely to occur.
 Uh Oh!! You failed to reduce the debt to a sustainable level. Without further changes, a fiscal crisis is likely to occur. Savings Relative to Current Law in Billions $ Savings Relative to Current Policy
Uh Oh!! You failed to reduce the debt to a sustainable level. Without further changes, a fiscal crisis is likely to occur. Savings Relative to Current Law in Billions $ Savings Relative to Current Policy
Congratulations! You reduced the debt to below 60% of GDP in 2018, and kept it at a sustainable level through 2030.
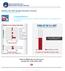 Congratulations! You reduced the debt to below 60% of GDP in 2018, and kept it at a sustainable level through 2030. Dollars in Billions that you need to cut to get under 60% of the GDP by 2018. $0 See
Congratulations! You reduced the debt to below 60% of GDP in 2018, and kept it at a sustainable level through 2030. Dollars in Billions that you need to cut to get under 60% of the GDP by 2018. $0 See
Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force. Restoring America s Future. Released November 17, 2010
 Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force Restoring America s Future Released November 17, 2010 1 Debt Held By The Public 300% 250% 200% Percent of GDP 150% 100% 50% 0% 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2030
Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force Restoring America s Future Released November 17, 2010 1 Debt Held By The Public 300% 250% 200% Percent of GDP 150% 100% 50% 0% 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2030
Bipartisan Policy Center Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force Plan 2.0 Senator Pete Domenici and Dr. Alice Rivlin
 INTRODUCTION Bipartisan Policy Center Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force Plan 2.0 Senator Pete Domenici and Dr. Alice Rivlin In 2010, the Bipartisan Policy Center (BPC) convened a Debt Reduction
INTRODUCTION Bipartisan Policy Center Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force Plan 2.0 Senator Pete Domenici and Dr. Alice Rivlin In 2010, the Bipartisan Policy Center (BPC) convened a Debt Reduction
Overview of Policy Options to Sustain Medicare for the Future
 Overview of Policy Options to Sustain Medicare for the Future Juliette Cubanski, Ph.D. Associate Director, Program on Medicare Policy Kaiser Family Foundation [email protected] Medicare NewsGroup Journalism
Overview of Policy Options to Sustain Medicare for the Future Juliette Cubanski, Ph.D. Associate Director, Program on Medicare Policy Kaiser Family Foundation [email protected] Medicare NewsGroup Journalism
Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force Plan 2.0 Senator Pete Domenici and Dr. Alice Rivlin
 Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force Plan 2.0 Senator Pete Domenici and Dr. Alice Rivlin In 2010, the Bipartisan Policy Center (BPC) convened a Debt Reduction Task Force (DRTF) of 19 former elected
Domenici-Rivlin Debt Reduction Task Force Plan 2.0 Senator Pete Domenici and Dr. Alice Rivlin In 2010, the Bipartisan Policy Center (BPC) convened a Debt Reduction Task Force (DRTF) of 19 former elected
CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE CBO. An Update to the Budget and Economic Outlook: 2015 to 2025. Defense 2.7 3.3 2.2 2.
 CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE An Update to the Budget and Economic Outlook: 2015 to 2025 Percentage of GDP Major Health Care Programs Mandatory Spending Social Security Other
CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE An Update to the Budget and Economic Outlook: 2015 to 2025 Percentage of GDP Major Health Care Programs Mandatory Spending Social Security Other
The Estimated Effect of the Affordable Care Act on Medicare and Medicaid Outlays and Total National Health Care Expenditures
 The Estimated Effect of the Affordable Care Act on Medicare and Medicaid Outlays and Total National Health Care Expenditures Testimony before the House Committee on the Budget January 26, 2011 by Richard
The Estimated Effect of the Affordable Care Act on Medicare and Medicaid Outlays and Total National Health Care Expenditures Testimony before the House Committee on the Budget January 26, 2011 by Richard
Health Care Implementation Timeline
 Health Care Implementation Timeline The massive healthcare (H.R. 3590) and its companion reconciliation bill (H.R. 4872) passed by the Senate and House in early 2010 will go into effect over several years.
Health Care Implementation Timeline The massive healthcare (H.R. 3590) and its companion reconciliation bill (H.R. 4872) passed by the Senate and House in early 2010 will go into effect over several years.
Macroeconomics Instructor Miller Fiscal Policy Practice Problems
 Macroeconomics Instructor Miller Fiscal Policy Practice Problems 1. Fiscal policy refers to changes in A) state and local taxes and purchases that are intended to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives.
Macroeconomics Instructor Miller Fiscal Policy Practice Problems 1. Fiscal policy refers to changes in A) state and local taxes and purchases that are intended to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives.
A Bipartisan Approach to America s Fiscal Future
 A Bipartisan Approach to America s Fiscal Future Bipartisan Policy Center Bill Hoagland, Steve Bell, Shai Akabas, and Brian Collins INTRODUCTION The Bipartisan Policy Center (BPC) has long been concerned
A Bipartisan Approach to America s Fiscal Future Bipartisan Policy Center Bill Hoagland, Steve Bell, Shai Akabas, and Brian Collins INTRODUCTION The Bipartisan Policy Center (BPC) has long been concerned
Mandatory Spending Since 1962
 Mindy R. Levit Specialist in Public Finance D. Andrew Austin Analyst in Economic Policy Jeffrey M. Stupak Research Assistant March 18, 2015 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL33074 Summary
Mindy R. Levit Specialist in Public Finance D. Andrew Austin Analyst in Economic Policy Jeffrey M. Stupak Research Assistant March 18, 2015 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL33074 Summary
How To Compare The Health Care Reform Plan To The Health Insurance Reform Plan From The Health Plan Of A Medicare Plan
 A Comparison of Medicare Proposals: The Affordable Care Act and the Romney/ October 2012 Prepared by: Area Agency on Aging 1-B A Comparison of Medicare Proposals: Affordable Care Act and the Romney/ Background
A Comparison of Medicare Proposals: The Affordable Care Act and the Romney/ October 2012 Prepared by: Area Agency on Aging 1-B A Comparison of Medicare Proposals: Affordable Care Act and the Romney/ Background
GAO PATIENT PROTECTION AND AFFORDABLE CARE ACT. Effect on Long-Term Federal Budget Outlook Largely Depends on Whether Cost Containment Sustained
 GAO United States Government Accountability Office Report to the Ranking Member, Committee on the Budget, U.S. Senate January 2013 PATIENT PROTECTION AND AFFORDABLE CARE ACT Effect on Long-Term Federal
GAO United States Government Accountability Office Report to the Ranking Member, Committee on the Budget, U.S. Senate January 2013 PATIENT PROTECTION AND AFFORDABLE CARE ACT Effect on Long-Term Federal
Composition of Federal Spending
 The Honorable David M. Walker Comptroller General of the United States U.S. Government Accountability Office February 10, 2005 2 Composition of Federal Spending 1964 1984 2004* Defense Net interest *Current
The Honorable David M. Walker Comptroller General of the United States U.S. Government Accountability Office February 10, 2005 2 Composition of Federal Spending 1964 1984 2004* Defense Net interest *Current
April 5, 2011. Honorable Paul Ryan Chairman Committee on the Budget U.S. House of Representatives Washington, DC 20515. Dear Mr.
 CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE U.S. Congress Washington, DC 20515 Douglas W. Elmendorf, Director April 5, 2011 Honorable Paul Ryan Chairman Committee on the Budget U.S. House of Representatives Washington,
CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE U.S. Congress Washington, DC 20515 Douglas W. Elmendorf, Director April 5, 2011 Honorable Paul Ryan Chairman Committee on the Budget U.S. House of Representatives Washington,
Draft Workstate Stimulus For Housing Projects
 DRAFT WORKING GROUP STIMULUS PLAN UPDATED 02-02-09 MODERNIZING U.S. TAX CODE TO CREATE JOBS: Cost or CBO Score Description of Tax Provisions $330 Billion Eliminate the 3.1% payroll tax for all American
DRAFT WORKING GROUP STIMULUS PLAN UPDATED 02-02-09 MODERNIZING U.S. TAX CODE TO CREATE JOBS: Cost or CBO Score Description of Tax Provisions $330 Billion Eliminate the 3.1% payroll tax for all American
Summary of Federal SCHIP Reauthorization, Economic Stimulus, and Health Care Reform Bills and Proposals
 Summary of Federal SCHIP Reauthorization, Economic Stimulus, and Health Care Reform Bills and Proposals I. Children s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) Reauthorization Act of 2009 A. Funding for CHIP. The
Summary of Federal SCHIP Reauthorization, Economic Stimulus, and Health Care Reform Bills and Proposals I. Children s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) Reauthorization Act of 2009 A. Funding for CHIP. The
THE SOLUTIONS INITIATIVE III MAY 2015
 THE SOLUTIONS INITIATIVE III MAY 2015 The mission of the Peter G. Peterson Foundation is to increase public awareness of the nature and urgency of key fiscal challenges threatening America s future and
THE SOLUTIONS INITIATIVE III MAY 2015 The mission of the Peter G. Peterson Foundation is to increase public awareness of the nature and urgency of key fiscal challenges threatening America s future and
Timeline of New Health Care Law and Its Impact on American Businesses
 Timeline of New Health Care Law and Its Impact on American Businesses Summaries of the Patient Protection and Affordable Health Care Act (Public Law 111-148) Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act
Timeline of New Health Care Law and Its Impact on American Businesses Summaries of the Patient Protection and Affordable Health Care Act (Public Law 111-148) Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act
This glossary provides simple and straightforward definitions of key terms that are part of the health reform law.
 This glossary provides simple and straightforward definitions of key terms that are part of the health reform law. A Affordable Care Act Also known as the ACA. A law that creates new options for people
This glossary provides simple and straightforward definitions of key terms that are part of the health reform law. A Affordable Care Act Also known as the ACA. A law that creates new options for people
United States Government Required Supplementary Information (Unaudited) For the Years Ended September 30, 2014, and 2013
 REQUIRED SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (UNAUDITED) 151 United States Government Required Supplementary Information (Unaudited) For the Years Ended September 30, 2014, and 2013 Fiscal Projections for the U.S.
REQUIRED SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (UNAUDITED) 151 United States Government Required Supplementary Information (Unaudited) For the Years Ended September 30, 2014, and 2013 Fiscal Projections for the U.S.
Medi-Growth Medicaid, Medicare Poised to Expand
 C H A P T E R 7 Medi-Growth Medicaid, Medicare Poised to Expand More than 100 million Americans rely upon Medicaid and Medicare for insurance coverage. Medicaid, the government s insurance program for
C H A P T E R 7 Medi-Growth Medicaid, Medicare Poised to Expand More than 100 million Americans rely upon Medicaid and Medicare for insurance coverage. Medicaid, the government s insurance program for
ACA Implementation Timeline
 ACA Implementation Timeline Published: March 5, 2013 Updated: July 5, 2013 Producer: Sophie Novack Director: Jessica Guzik National Journal Presentation Credits Most ACA Reforms Implemented 2013-2014 Jan.
ACA Implementation Timeline Published: March 5, 2013 Updated: July 5, 2013 Producer: Sophie Novack Director: Jessica Guzik National Journal Presentation Credits Most ACA Reforms Implemented 2013-2014 Jan.
May 2012 HEALTH CARE COSTS
 HEALTH CARE COSTS A Primer May 2012 KEY INFORMATION ON HEALTH CARE COSTS AND THEIR IMPACT HEALTH CARE COSTS: A Primer KEY INFORMATION ON HEALTH CARE COSTS AND THEIR IMPACT May 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS
HEALTH CARE COSTS A Primer May 2012 KEY INFORMATION ON HEALTH CARE COSTS AND THEIR IMPACT HEALTH CARE COSTS: A Primer KEY INFORMATION ON HEALTH CARE COSTS AND THEIR IMPACT May 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Affordable Care Act at 3: Strengthening Medicare
 Affordable Care Act at 3: Strengthening Medicare ISSUE BRIEF Fifth in a series May 22, 2013 Kyle Brown Senior Health Policy Analyst 789 Sherman St. Suite 300 Denver, CO 80203 www.cclponline.org 303-573-5669
Affordable Care Act at 3: Strengthening Medicare ISSUE BRIEF Fifth in a series May 22, 2013 Kyle Brown Senior Health Policy Analyst 789 Sherman St. Suite 300 Denver, CO 80203 www.cclponline.org 303-573-5669
Private Health Insurance: Changes Made by the Reconciliation Act of 2010 to Senate-Passed H.R. 3590
 Private Health Insurance: Changes Made by the Reconciliation Act of 2010 to Senate-Passed H.R. 3590 Hinda Chaikind Specialist in Health Care Financing Bernadette Fernandez Analyst in Health Care Financing
Private Health Insurance: Changes Made by the Reconciliation Act of 2010 to Senate-Passed H.R. 3590 Hinda Chaikind Specialist in Health Care Financing Bernadette Fernandez Analyst in Health Care Financing
The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and presenter and do not necessarily reflect the views and opinions of
 The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and presenter and do not necessarily reflect the views and opinions of the sponsoring companies or their affiliates. Disclosure
The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and presenter and do not necessarily reflect the views and opinions of the sponsoring companies or their affiliates. Disclosure
Key Features of the Affordable Care Act, By Year
 Page 1 of 10 Key Features of the Affordable Care Act, By Year On March 23, 2010, President Obama signed the Affordable Care Act. The law puts in place comprehensive health insurance reforms that will roll
Page 1 of 10 Key Features of the Affordable Care Act, By Year On March 23, 2010, President Obama signed the Affordable Care Act. The law puts in place comprehensive health insurance reforms that will roll
california Health Care Almanac
 california Health Care Almanac : Slow But Steady august 2012 Introduction In 2014, implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) will cause a spike in US health spending; analysts project an increase
california Health Care Almanac : Slow But Steady august 2012 Introduction In 2014, implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) will cause a spike in US health spending; analysts project an increase
How To Calculate Health Care Spending As A Share Of Gdp
 california Health Care Almanac : Slow Growth: A New Trend? September 2013 Introduction The United States continues to spend a greater percentage of its wealth on health care than any other industrialized
california Health Care Almanac : Slow Growth: A New Trend? September 2013 Introduction The United States continues to spend a greater percentage of its wealth on health care than any other industrialized
Medicare Part D. MMA establishes a standard Part D drug benefit, which consists of four components or phases.
 Medicare Part D The Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003 (MMA) added voluntary prescription drug coverage to Medicare, the federal health insurance program for seniors
Medicare Part D The Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003 (MMA) added voluntary prescription drug coverage to Medicare, the federal health insurance program for seniors
COST OF TAX CUT WOULD MORE THAN DOUBLE TO $5 TRILLION IN SECOND TEN YEARS. Tax Cut Would Worsen Deteriorating Long-Term Budget Forecast
 820 First Street, NE, Suite 510, Washington, DC 20002 Tel: 202-408-1080 Fax: 202-408-1056 [email protected] http://www.cbpp.org Revised April 4, 2001 COST OF TAX CUT WOULD MORE THAN DOUBLE TO $5 TRILLION
820 First Street, NE, Suite 510, Washington, DC 20002 Tel: 202-408-1080 Fax: 202-408-1056 [email protected] http://www.cbpp.org Revised April 4, 2001 COST OF TAX CUT WOULD MORE THAN DOUBLE TO $5 TRILLION
The GPO predominantly penalizes women educators in California, while the WEP penalizes many individuals who switch careers into public service.
 Chair Pomeroy and Members, Social Security has met the social insurance promise to ensure workers will not have to live in old age poverty. This promise needs to be guaranteed for current and future workers.
Chair Pomeroy and Members, Social Security has met the social insurance promise to ensure workers will not have to live in old age poverty. This promise needs to be guaranteed for current and future workers.
Strengthening Community Health Centers. Provides funds to build new and expand existing community health centers. Effective Fiscal Year 2011.
 Implementation Timeline Reflecting the Affordable Care Act 2010 Access to Insurance for Uninsured Americans with a Pre-Existing Condition. Provides uninsured Americans with pre-existing conditions access
Implementation Timeline Reflecting the Affordable Care Act 2010 Access to Insurance for Uninsured Americans with a Pre-Existing Condition. Provides uninsured Americans with pre-existing conditions access
Federal Budget in Pictures CUT SPENDING // FIX THE DEBT // REDUCE THE TAX BURDEN$
 2015 Federal Budget in Pictures CUT SPENDING // FIX THE DEBT // REDUCE THE TAX BURDEN$ 2015 Federal Budget in Pictures CUT SPENDING // FIX THE DEBT // REDUCE THE TAX BURDEN Thomas A. Roe Institute for
2015 Federal Budget in Pictures CUT SPENDING // FIX THE DEBT // REDUCE THE TAX BURDEN$ 2015 Federal Budget in Pictures CUT SPENDING // FIX THE DEBT // REDUCE THE TAX BURDEN Thomas A. Roe Institute for
When Reform Will Affect You
 When Reform Will Affect You N AV I G AT I N G T H R O U G H T H E N E W F E D E R A L H E A LT H C A R E L A W Dear Colleague, In March, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) was signed
When Reform Will Affect You N AV I G AT I N G T H R O U G H T H E N E W F E D E R A L H E A LT H C A R E L A W Dear Colleague, In March, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) was signed
Baucus Framework Senate HELP Bill House Tri-Committee Bill President Obama
 SJR 35: HEALTH CARE Comparison of Selected Elements of the Major Federal Health Care Reform Proposals Prepared for the Children, Families, Health, and Human Services Interim Committee Sept. 11, 2009 Baucus
SJR 35: HEALTH CARE Comparison of Selected Elements of the Major Federal Health Care Reform Proposals Prepared for the Children, Families, Health, and Human Services Interim Committee Sept. 11, 2009 Baucus
THE FUTURE OF EMPLOYER BASED HEALTH INSURANCE FOLLOWING HEALTH REFORM
 THE FUTURE OF EMPLOYER BASED HEALTH INSURANCE FOLLOWING HEALTH REFORM National Congress on Health Insurance Reform Washington, D.C., January 20, 2011 Elise Gould, PhD Health Policy Research Director Economic
THE FUTURE OF EMPLOYER BASED HEALTH INSURANCE FOLLOWING HEALTH REFORM National Congress on Health Insurance Reform Washington, D.C., January 20, 2011 Elise Gould, PhD Health Policy Research Director Economic
Health Insurance Reform at a Glance Implementation Timeline
 Health Insurance Reform at a Glance Implementation Timeline 2010 Access to Insurance for Uninsured Americans with a Pre-Existing Condition. Provides uninsured Americans with pre-existing conditions access
Health Insurance Reform at a Glance Implementation Timeline 2010 Access to Insurance for Uninsured Americans with a Pre-Existing Condition. Provides uninsured Americans with pre-existing conditions access
Timeline: Key Feature Implementations of the Affordable Care Act
 Timeline: Key Feature Implementations of the Affordable Care Act The Affordable Care Act, signed on March 23, 2010, puts in place health insurance reforms that will roll out incrementally over the next
Timeline: Key Feature Implementations of the Affordable Care Act The Affordable Care Act, signed on March 23, 2010, puts in place health insurance reforms that will roll out incrementally over the next
THE MEDICAID PROGRAM AT A GLANCE. Health Insurance Coverage
 on on medicaid and and the the uninsured March 2013 THE MEDICAID PROGRAM AT A GLANCE Medicaid, the nation s main public health insurance program for low-income people, covers over 62 million Americans,
on on medicaid and and the the uninsured March 2013 THE MEDICAID PROGRAM AT A GLANCE Medicaid, the nation s main public health insurance program for low-income people, covers over 62 million Americans,
Affordable Care Act (ACA) Health Insurance Exchanges and Medicaid Expansion
 Affordable Care Act (ACA) Health Insurance Exchanges and Medicaid Expansion Table of Contents Expanded Coverage... 2 Health Insurance Exchanges... 3 Medicaid Expansion... 8 Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
Affordable Care Act (ACA) Health Insurance Exchanges and Medicaid Expansion Table of Contents Expanded Coverage... 2 Health Insurance Exchanges... 3 Medicaid Expansion... 8 Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
2016 ANNUAL REPORT OF THE BOARDS OF TRUSTEES OF THE FEDERAL HOSPITAL INSURANCE AND FEDERAL SUPPLEMENTARY MEDICAL INSURANCE TRUST FUNDS COMMUNICATION
 2016 ANNUAL REPORT OF THE BOARDS OF TRUSTEES OF THE FEDERAL HOSPITAL INSURANCE AND FEDERAL SUPPLEMENTARY MEDICAL INSURANCE TRUST FUNDS COMMUNICATION From THE BOARDS OF TRUSTEES, FEDERAL HOSPITAL INSURANCE
2016 ANNUAL REPORT OF THE BOARDS OF TRUSTEES OF THE FEDERAL HOSPITAL INSURANCE AND FEDERAL SUPPLEMENTARY MEDICAL INSURANCE TRUST FUNDS COMMUNICATION From THE BOARDS OF TRUSTEES, FEDERAL HOSPITAL INSURANCE
Hungary. 1. Economic situation
 2. COUNTRY NOTES: HUNGARY 125 1. Economic situation has faced considerable challenges to regain fiscal credibility. After almost a decade of persistent, high fiscal deficits and the building up of external
2. COUNTRY NOTES: HUNGARY 125 1. Economic situation has faced considerable challenges to regain fiscal credibility. After almost a decade of persistent, high fiscal deficits and the building up of external
Medicare Economics. Part A (Hospital Insurance) Funding
 Medicare Economics Medicare expenditures are a substantial part of the federal budget $556 billion, or 15 percent in 2012. They also comprise 3.7 percent of the country s gross domestic product (GDP),
Medicare Economics Medicare expenditures are a substantial part of the federal budget $556 billion, or 15 percent in 2012. They also comprise 3.7 percent of the country s gross domestic product (GDP),
