Cyanotic a bluish or purplish discoloration (as of skin) due to deficient oxygenation of the blood
|
|
|
- Melina Mitchell
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Newborn Physical Examination Assessment of a Newborn with Joan Richardson Joan Richardson's Assessment of a Newborn What follows is a demonstration of the physical examination of a newborn baby as well as the determination of the gestational age of the baby using the Dubowitz examination. Dubowitz examination From L.M. Dubowitz et al, Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant. Journal of Pediatrics 77-1, 1970, with permission Skin Color When examining a newborn baby, start by closely observing the baby. Observe the color. Is the baby pink or cyanotic? The best place to observe is the lips or tongue. If those are nice and pink then baby does not have cyanosis. The most unreliable places to observe for cyanosis are the fingers and toes because babies frequently have poor blood circulation to the extremities and this results in acrocyanosis.(see video below of baby with cyanotic feet) Also observe the baby for any obvious congenital malformations or any obvious congenital anomalies. Be sure to count the number of fingers and toes. Cyanotic Feet The most unreliable places to observe for cyanosis are the fingers and toes because babies frequently have poor blood circulation to the extremities and this results in a condition called acrocyanosis. Cyanotic a bluish or purplish discoloration (as of skin) due to deficient oxygenation of the blood create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 1 of 12
2 acrocyanosis Blueness or pallor of extremities, normal sign of vasomotor instability characterized by color change limited to the peripheral circulation. Occurs in healthy newborns and will eventually resolve. congenital 1. Existing at or dating from birth 2. Acquired during development in the uterus and not through heredity Respiration Watch the baby breathe. Is the baby breathing easily or is she having problems. Time the respiratory rate. Normal babies breathe about 40 to 60 times a minute. Does the baby have intercostal, subcostal or sternal retraction? Is the baby demonstrating an expiratory grunting respiration, stridor or gasping. grunting forced expiration against a partially closed glottis stridor a harsh vibrating sound heard during respiration in cases of obstruction of the air passages. gasping slow and laborious breaths Movement Look at the baby's movement. Is the baby moving all extremities equally and symmetrically? And does the baby appear to have good muscle tone? If the baby is asleep, does the baby easily arouse, wake up, and cry when disturbed? Generally, babies will start crying when disturbed, so start the examination by looking at those areas that are more easily examined if the baby remains quiet. Start be examining the heart, lungs and abdomen. Save the examination of the head and neck until last because that tends to irritate the baby and cause them to cry more Cardiovascular - PMI Start with the examination of the heart. Palpate the PMI that is the point of maximal impulse. The PMI should be at about the 3rd of4th intercostal space at about the midclavicular line. If the PMI is shifted dramatically either to the right or to the left, you must be concerned about a pneumothorax. If the PMI is shifted remarkable to the right, then you have to consider the possibility of dextrocardia. create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 2 of 12
3 Cardiovascular - Pulses Palpate the pulses. The pulses should be equal and of good intensity. Start by palpating the axillary pulse, then the brachial pulse, and then the radial pulse. Then move down to the palpate the femoral pulses and then the dorsalis pedis and the posterior tibial pulses. axillary pulse The part of the main artery of the arm that lies in the axilla and that is continuous with the subclavian artery above and the brachial artery below brachial pulse Chief artery of the upper arm that is a direct continuation of the axillary artery and divides into the radial and ulnar arteries just below the elbow. radial pulse The smaller of the two branches into which the brachial artery divides just below the bend of the elbow and which passes along the radial side of the forearm to the wrist then winds backward around the outer side of the carpus and enters the palm between the first and second metacarpal bones to form the deep palmer arch. femoral pulse The chief artery of the thigh that lies in the anterior part of the thigh and is undivided until a point about two inches (5 centimeters) below the inguinal ligament where it divides into a large deep branch and a smaller superficial branch. dorsalis pedis An artery of the upper surface of the foot that is a direct continuation of the anterior tibial artery. posterior tibial pulse An artery located just posterior to the medial malleolus. Cardiovascular - Auscultation Auscultate the heart. Concentrate on evaluating four key elements. First, determine the heart rate (normal heart rate for newborn is about 140 beats per minute.) Then determine if heartbeat is of normal rhythm. Third, listen for the 2nd heart sound and make sure that it is split. A split second sound indicates the presence of two valves, aortic and pulmonic. The aortic valve closes slightly before the pulmonic valve, resulting in a biphasic, or split second sound. Murmurs - fourth, listen carefully for heart murmurs. About 25% of all babies have murmurs at the time they are delivered. These usually go away in the first few hours of life. Most of the murmurs are systolic ejection type murmurs. It's very rare to hear a diastolic murmur in a newborn baby. create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 3 of 12
4 systolic ejection Murmur occurring after contraction of heart while the cavities are falling with blood diastolic Murmur occurring after contraction of heart while the cavities are filling with blood Lungs Once you have auscultated the heart, then listen to the lungs. Compare each side of the chest with the other side. Try to determine whether the breath sounds are of normal quality and are equal in intensity as you compare one side of the chest with the other. Umbilicus Once the chest has been examined, begin your examination of the abdomen. Start by looking at the umbilical cord. Determine that there are two arteries and one vein. The umbilical arteries are generally small white muscular structures that look like small worms. The umbilical vein is generally larger, less muscular and more patulous. Abdomen Palpate the liver and the spleen. The technique that I use is to start low in the abdomen and gradually move upward until you feel the edge of the liver, and the edge of the spleen. In palpating, be sure to use the tips of your fingers. They are much more sensitive. Normally, the liver is about 1-2 cms below the right costal margin. You can sometimes feel a spleen tip in a newborn but most of the time the spleen is not palpable. A very important part of the abdominal examination is the examination of the kidney. The kidneys are generally about 2 finger breadths in length. They lie very close to the midline. The method of examining the kidneys uses a bimanual palpation method. One hand is placed behind the baby's back, the other hand is placed on the abdomen next to the umbilicus. Then, press down, palpating the kidney between the two hands. create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 4 of 12
5 costal margin edge of the last rib Female Genitalia Next examine the genitalia. In female babies, there is often a hymenal skin tag. The labia majora generally cover the labia minora. Often there are vaginal secretions present which are secondary to maternal hormonal stimulation. Male Genitalia In male babies, examine the penis. The foreskin is never easily retracted in the newborn male. Generally the penis is around 2 to 2-1/2 cms in length. Palpate the testes in the scrotum to make sure they are descended and palpable bilaterally. It is not uncommon to find hydrocoeles bilaterally. hydrocoeles an accumulation of serous fluid in a sacculated cavity (as the scrotum) Hips For examination of the hips, use a modified ortolani maneuver to check for laxity of ligaments or for hip dislocation. In the newborn, the femoral head fits into the acetabular fossa. If the hip is dislocated, it is generally dislocated posteriorly. Therefore when the hips are abducted, the femoral head slides into the acetabular fossa. This causes a click or a crunch and represents the sound of cartilage sliding over cartilage. This can either be felt with the fingers or sometimes even heard. In order to examine for dislocated hips, place the baby in the supine position. Position your hands such that your first two fingers overlie the hip joint. Place the thumbs on the medial side of the baby's thigh. Then abduct the hips slowly, feeling for any click, crunch, or clunk or any resistance to abduction. Ortolani maneuver Abducting the flexed hips while the examiner pushes upward on the posterior proximal femur. create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 5 of 12
6 Back Check the baby's back for midline defects and check for sacral dimple. Head and Neck Now move on to examination of the head and neck. Palpate the clavicles to make sure there are no clavicular fractures. Palpate the neck and the thyroid gland. Examine the ears to make sure the ear canals are patent. It s not necessary to do an otoscopic examination on the newborn at the time of birth. Examine the nares to make sure they are patent. Examine the mouth to make sure there is no cleft palate and the baby has a good suck. Examine the anterior fontanelle, and the posterior fontanelle. Run your fingers over the sagittal suture, the coronal sutures and the lambdoid sutures to make sure they are not prematurely synostosed. sagittal the deeply serrated articulation between the two parietal bones in the median plane of the top of the head coronal a suture extending across the skull between the parietal and frontal bones called also frontoparietal suture lambdoid a suture extending across the skull between the parietal and frontal lobes Eyes This generally requires someone to help open the eyes using q-tips. Sometimes you can get the eyes to open just by turning out the lights. You may see small sub conjunctival hemorrhages. Look for the red reflex bilaterally. This is the reflection of the light coming off the retina. Sometimes the reflex is orange or gray. If not present, this could mean that the baby has a cataract or a retinal tumor. Red Reflex create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 6 of 12
7 Neurological Check the neurological exam including the Moro Reflex. Assess the baby's tone. Check for ankle clonus. Check the baby's reflexes. Determine whether the baby responds normally and has good tone. Moro Reflex The startle reflex, baby flings hands out and appears startled. Dubowitz Exam At this point perform a Dubowitz Examination. This is the method used at our institution to determine the baby's gestational age. This examination evaluates both physical characteristics and neurological characteristics and in the aggregate, estimates the baby's gestational age within 1-2 weeks of the true gestational age. External Criteria Start by examining the baby's physical criteria. The first external sign is edema. Palpate the anterior tibia. If there is no edema, then mark that appropriate score on the Dubowitz examination sheet. Check for skin texture, and then check for skin color. Also check for skin opacity looking for blood vessels and how distinctly they are seen over the abdomen. Look at the baby's back to determine how much lanugo is present. Check the plantar creases. Evaluate nipple formation, breast size, ear formation and ear firmness and examine the genetalia. In this baby, the labia majora essentially completely cover the labia minora. This is the method used at our institution to determine the baby's gestational age. This examination evaluates both physical characteristics and neurological characteristics and in the aggregate, estimates the baby's gestational age within 1-2 weeks of the true gestational age. create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 7 of 12
8 From L.M. Dubowitz et al. Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant, Journal of Pediatrics 77:1, 1970 with permission. Neurological Criteria Now assess the neurological criteria. Using the stick figures that are on the Dubowitz form, determine which posture most appropriately characterizes this baby. Check for the square window that is the angle that the hand makes with the wrist. Check for ankle dorsilexion that is the angle that the foot makes with the ankle. The baby who is mature has more flexion and their tone is increased compared to a premature baby. Check for arm recoil, leg recoil, check the popliteal angle. This is done by placing the baby on the back, flexing at the hips and then extending at the knee until you meet resistance. Check for heel to ear. This is done by again placing the baby on his back and pulling the leg towards the ear to determine how closely the heel can come to the ear. Check the scarf sign. This checks the create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 8 of 12
9 resistance the baby has in terms of moving the arm across the chest. Check for head lag and then also for ventral suspension. Posture Observe with infant quiet and in supine position. Score 0 - arms and legs extended, 1 - beginning of flexion of hips and knees, 2 - stronger flexion of legs, arms extended, 3 - arms slightly flexed, legs flexed and abducted, 4 - full flexion of arms and legs Square window The hand is flexed on the forearm between the thumb and index finger of the examiner. Enough pressure is applied to get as full a flexion as possible, and the angle between the hypothenar eminence and the ventral aspect of the forearm is measured and graded according to diagram. [Care is taken not to rotate the infant's wrist while doing this maneuver.] Ankle dorsiflexion The foot is dorsiflexed onto the anterior aspect of the leg, with the examiner's thumb on the sole of foot and other fingers behind the leg. Enough pressure is applied to get as full flexion as possible, and the angle between the dorsum of the foot and the anterior aspect of the leg is measured. Arm recoil With the infant in the supine position, the forearms are first flexed for 5 seconds, then fully extended by pulling on the hands and then released. The sign is fully positive if the arms return briskly to full flexion (Score 2). If the arms return to incomplete flexion or the response is sluggish, it is graded as Score 1. If they remain extended or are only followed by random movements, the Score is 0. Leg recoil With the infant supine, the hips and knees are fully flexed for 5 seconds, then extended by traction on the feet, and released. A maximal response is one of full flexion of the hips and knees (Score 2). A partial flexion scores 1, and minimal or no movement score 0. Popliteal angle With the infant supine and his pelvis flat on the examining couch, the thigh is held in the kneechest position by the examiner's left index finger and thumb supporting the knee. The leg is then extended by gentle pressure from the examiner's right index finger behind the ankle and the popliteal angle is measured. Heel to ear With the baby supine, draw the baby' foot as near to the head as it will go with forcing. Observe the distance between the foot and the head as well as the degree of extension at the knee. Grade according to diagram. Note that the knee is left free and may draw down along side the abdomen. Scarf sign With the baby supine, take the infant's hand and try to put it around the neck and as far posteriorly as possible around the opposite shoulder. Assist this maneuver by lifting the elbow across the body. See how far the elbow will go aross the grade according to the illustrations. Score 0 - Elbow reaches axillary line 1 - Elbow between midline and opposite axillary, 2 - Elbow reaches midline, 3 - Elbow will not reach midline. Head lag create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/2015 Page 9 of 12
10 With the baby lying supine, grasp the hands (or the arms if a very small infant) and pull him slowly towards the sitting position. Observe the position of the head in relation to the trunk and grade accordingly. In a small infant, the head may initially be supported by one hand. Score 0 - Complete lag, 1 - Partial head control, 2 - Able to maintain head in line with body, 3 - Brings head anterior to body. Ventral suspension The infant is suspended in the prone position, with examiner's hand under the infant's chest (one hand in a small infant, two in a large infant). Observe the degree of extension of the back and the amount of flexion of the arms and legs. Also note the relation of the head to the trunk. Grade according to diagrams. Record the Data After each of these examinations, record the data on the Dubowitz form, add it up and then turn the form over to use the graph for reading the gestational age from the total score, the total score for the physical examination and the neurological examination, when plotted on the graph determine the baby's gestational age. create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/ Page 10 of
11 Final Score Score External Criteria 33 Neurological Criteria 25 Total Dubowitz Score 58 which is 40 weeks gestation create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/ Page 11 of
12 Head Circumference We examine the head last because this generally upsets the baby. Complete the physical examination by measuring the head circumference, chest circumference, and length. The head circumference should be measured by determining the largest occipito-frontal circumference. Measure the circumference until you obtain a reproducible measurement. The head circumference is 34.5 centimeters Chest Size Measure the chest circumference. This is done by measuring at the level of the nipples. The chest circumference and the head circumference should be within one to two centimeters of each other. The chest circumference is centimeters Length Then measure the baby's length. This is crown to heel length. The length is 52 centimeters CDC growth charts and/or data tables create 6/24/2015; last modified date 11/23/ Page 12 of
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
stretches and exercises
 stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS. Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain. Assessment & Treatment of. Low Back Pain. Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D.
 THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
General Guidelines. Neck Stretch: Side. Neck Stretch: Forward. Shoulder Rolls. Side Stretch
 Stretching Exercises General Guidelines Perform stretching exercises at least 2 3 days per week and preferably more Hold each stretch for 15 20 seconds Relax and breathe normally Stretching is most effective
Stretching Exercises General Guidelines Perform stretching exercises at least 2 3 days per week and preferably more Hold each stretch for 15 20 seconds Relax and breathe normally Stretching is most effective
Once you have determined that the baby is stable from an airway, breathing and circulation perspective, you can begin your systemic exam.
 Newborn Examination Learnpediatrics.com Narration Written by Dr. V. Leung and Dr. J. Bishop Introduction We do this examination just after birth, prior to discharge from hospital and at regular intervals
Newborn Examination Learnpediatrics.com Narration Written by Dr. V. Leung and Dr. J. Bishop Introduction We do this examination just after birth, prior to discharge from hospital and at regular intervals
Body cavities. Body Planes
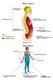 Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and
 A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
Exercise 1: Knee to Chest. Exercise 2: Pelvic Tilt. Exercise 3: Hip Rolling. Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface.
 Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite leg flat on the surface
Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite leg flat on the surface
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
Range of Motion. A guide for you after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program
 Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Sheet 1A. Treating short/tight muscles using MET. Pectorals. Upper trapezius. Levator scapula
 Sheet 1A Treating short/tight muscles using MET Pectorals Once daily lie at edge of bed holding a half-kilo can, arm out sideways. Raise arm and hold for 10 seconds, then allow arm to hang down, stretching
Sheet 1A Treating short/tight muscles using MET Pectorals Once daily lie at edge of bed holding a half-kilo can, arm out sideways. Raise arm and hold for 10 seconds, then allow arm to hang down, stretching
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca
 www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
Range of Motion Exercises
 Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
Obstetrical Emergencies
 Date: July 18, 2014 Page 1 of 5 Obstetrical Emergencies Purpose: To provide the process for the assessment and management of the patient with an obstetrical related emergency. Pre-Medical Control 1. Follow
Date: July 18, 2014 Page 1 of 5 Obstetrical Emergencies Purpose: To provide the process for the assessment and management of the patient with an obstetrical related emergency. Pre-Medical Control 1. Follow
DATA BASE SAMPLE: PHYSICAL EXAMINATION WITH ALL NORMAL FINDINGS
 DATA BASE SAMPLE: PHYSICAL EXAMINATION WITH ALL NORMAL FINDINGS GENERAL APPEARANCE: (include general mental status) 45 y/o female who is awake and alert and who appears healthy and looks her stated age
DATA BASE SAMPLE: PHYSICAL EXAMINATION WITH ALL NORMAL FINDINGS GENERAL APPEARANCE: (include general mental status) 45 y/o female who is awake and alert and who appears healthy and looks her stated age
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
SPINE. Postural Malalignments 4/9/2015. Cervical Spine Evaluation. Thoracic Spine Evaluation. Observations. Assess position of head and neck
 SPINE Observations Body type Postural alignments and asymmetries should be observed from all views Assess height differences between anatomical landmarks Figure 25-9 Figure 25-10 Figure 25-11 & 12 Postural
SPINE Observations Body type Postural alignments and asymmetries should be observed from all views Assess height differences between anatomical landmarks Figure 25-9 Figure 25-10 Figure 25-11 & 12 Postural
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins
 Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins Below is a description of a Core Stability Program, designed to improve the strength and coordination
Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins Below is a description of a Core Stability Program, designed to improve the strength and coordination
SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DOCTORING SCREENING HEAD TO TOE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION 2011 2012
 SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DOCTORING SCREENING HEAD TO TOE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION 2011 2012 The following checklist will be used for evaluating your physical examination skills at Southern
SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DOCTORING SCREENING HEAD TO TOE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION 2011 2012 The following checklist will be used for evaluating your physical examination skills at Southern
Stretching in the Office
 Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder. Chapter 14. Copyright 2008 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Changes to Your Baby and Your Body During Pregnancy
 Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation
 Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation Flexibility refers to the amount of movement possible around a joint and is necessary for normal activities of daily living such as stretching,
Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation Flexibility refers to the amount of movement possible around a joint and is necessary for normal activities of daily living such as stretching,
12 Week Do-it-Yourself Fitness Program
 12 Week Do-it-Yourself Fitness Program Created by Brad Awalt, MS, ACSM Assistant Manager, Health Plus brad.awalt@vanderbilt.edu January 2011 Do you have a goal to begin an exercise routine, but not sure
12 Week Do-it-Yourself Fitness Program Created by Brad Awalt, MS, ACSM Assistant Manager, Health Plus brad.awalt@vanderbilt.edu January 2011 Do you have a goal to begin an exercise routine, but not sure
No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe
 No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe Introduction Program designed to be performed in a circuit. Perform exercises in sequence without rest 2-3 times. Increase
No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe Introduction Program designed to be performed in a circuit. Perform exercises in sequence without rest 2-3 times. Increase
CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD
 1 CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD Doctor of Oriental Medicine MORNING ROUTINE SUMMATION 1. Joint Opening Exercises 2. Meridian Stretching Exercises 3. Qi Circulation Exercises
1 CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD Doctor of Oriental Medicine MORNING ROUTINE SUMMATION 1. Joint Opening Exercises 2. Meridian Stretching Exercises 3. Qi Circulation Exercises
Exercises for the Hip
 Exercises for the Hip Gluteal Sets: Lie on your back, tighten buttocks and hold for 3-5 seconds. Repeat 20 times. Supine Hip ER/IR: Lie on your back with legs straight. Gently rotate knees out and in limited
Exercises for the Hip Gluteal Sets: Lie on your back, tighten buttocks and hold for 3-5 seconds. Repeat 20 times. Supine Hip ER/IR: Lie on your back with legs straight. Gently rotate knees out and in limited
Exercises for older people
 Exercise for older people Exercises for older people Sitting Getting started If you ve not done much physical activity for a while, you may want to get the all-clear from a GP before starting. For the
Exercise for older people Exercises for older people Sitting Getting started If you ve not done much physical activity for a while, you may want to get the all-clear from a GP before starting. For the
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Living Room Bodyweight Workout Week 1 March or jog in place for 1 min to increase heart rate and lubricate joints.
 Warm Up- Living Room Bodyweight Workout Week 1 March or jog in place for 1 min to increase heart rate and lubricate joints. Protocol- All exercises will be done for 2 sets of 10 repetitions. After the
Warm Up- Living Room Bodyweight Workout Week 1 March or jog in place for 1 min to increase heart rate and lubricate joints. Protocol- All exercises will be done for 2 sets of 10 repetitions. After the
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Shoulders (free weights)
 Dumbbell Shoulder Raise Dumbbell Shoulder Raise 1) Lie back onto an incline bench (45 or less) with a DB in each hand. (You may rest each DB on the corresponding thigh.) 2) Start position: Bring the DB
Dumbbell Shoulder Raise Dumbbell Shoulder Raise 1) Lie back onto an incline bench (45 or less) with a DB in each hand. (You may rest each DB on the corresponding thigh.) 2) Start position: Bring the DB
This document fully describes the 30 Day Flexibility Challenge and allows you to keep a record of your improvements in flexibility.
 Welcome to the StretchTowel 30 Day Flexibility Challenge! You can Be More Flexible in 30 days by following our stretching program for 10 minutes a day. The best part is that you can stretch using the StretchTowel
Welcome to the StretchTowel 30 Day Flexibility Challenge! You can Be More Flexible in 30 days by following our stretching program for 10 minutes a day. The best part is that you can stretch using the StretchTowel
Specific massage movements.
 Specific massage movements. Exclusive Body Digi-Esth Esthétique movements Awakening Prelude 5 min + Specific movements Relaxing 30 min Aromatic bags 30 min Plantar 20 min Hands 10 min = Position of the
Specific massage movements. Exclusive Body Digi-Esth Esthétique movements Awakening Prelude 5 min + Specific movements Relaxing 30 min Aromatic bags 30 min Plantar 20 min Hands 10 min = Position of the
Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises
 Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises Walk around the room, step side to side, ride a bike or walk on a treadmill for at least 5 minutes to warm up before doing these stretches. Stretch warm muscles
Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises Walk around the room, step side to side, ride a bike or walk on a treadmill for at least 5 minutes to warm up before doing these stretches. Stretch warm muscles
Lower Body Strength/Balance Exercises
 Compliments of (Medical Group Name & Phone # to be inserted here) Lower Body Strength/Balance Exercises Hip Flexion Strengthens thigh and hip muscles. Use ankle weights, if you are ready to. Stand to the
Compliments of (Medical Group Name & Phone # to be inserted here) Lower Body Strength/Balance Exercises Hip Flexion Strengthens thigh and hip muscles. Use ankle weights, if you are ready to. Stand to the
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
The Thorax - Anterior and Lateral Chest Wall
 The Thorax - Anterior and Lateral Chest Wall by Marc Heller,DC When we think of the thorax, most of us think of the thoracic vertebrae and the posterior ribs. When examining for thoracic restrictions,
The Thorax - Anterior and Lateral Chest Wall by Marc Heller,DC When we think of the thorax, most of us think of the thoracic vertebrae and the posterior ribs. When examining for thoracic restrictions,
Infant CPR. What You Need to Know. How to Do Infant CPR
 Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema
 Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema Patient Education Improving health through education The lymphatic system is part of our circulatory system. It helps balance the fluids of our
Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema Patient Education Improving health through education The lymphatic system is part of our circulatory system. It helps balance the fluids of our
Vital and Diagnostic Signs
 GENERAL The four vital signs and the five diagnostic signs evaluated during patient assessment provide valuable information to the care provider, and when recorded properly, to the receiving facility/personnel.
GENERAL The four vital signs and the five diagnostic signs evaluated during patient assessment provide valuable information to the care provider, and when recorded properly, to the receiving facility/personnel.
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
How To Improve Drainage
 Rehabilitation Home Program Edema Exercises To Improve Drainage You will improve your lymph flow by doing a few exercises each day. These exercises are an important part of your home program. They may
Rehabilitation Home Program Edema Exercises To Improve Drainage You will improve your lymph flow by doing a few exercises each day. These exercises are an important part of your home program. They may
Knee Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Qigong. Ba Duan Jin. The Eight Pieces of Brocade
 Qigong Ba Duan Jin The Eight Pieces of Brocade by Col and g Hamilton Yiheyuan Martial Arts Contents Page Introduction 2 Preparation 2 1. Hold up the Sky 3 2. The Archer 4 3. Join Heaven and Earth 5 4a.
Qigong Ba Duan Jin The Eight Pieces of Brocade by Col and g Hamilton Yiheyuan Martial Arts Contents Page Introduction 2 Preparation 2 1. Hold up the Sky 3 2. The Archer 4 3. Join Heaven and Earth 5 4a.
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28
 The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers
 Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers These exercises will help keep your muscles strong and mobile, and your joints flexible. Other benefits of these exercises include: C
Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers These exercises will help keep your muscles strong and mobile, and your joints flexible. Other benefits of these exercises include: C
Low Back Pain: Exercises
 Low Back Pain: Exercises Your Kaiser Permanente Care Instructions Here are some examples of typical rehabilitation exercises for your condition. Start each exercise slowly. Ease off the exercise if you
Low Back Pain: Exercises Your Kaiser Permanente Care Instructions Here are some examples of typical rehabilitation exercises for your condition. Start each exercise slowly. Ease off the exercise if you
OVERALL PERFORMANCE. Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment
 OVERALL PERFORMANCE Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment Name: University: This resident completed the standardized assessment of history -taking, physical examination
OVERALL PERFORMANCE Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment Name: University: This resident completed the standardized assessment of history -taking, physical examination
Self-mobilization methods
 Self-mobilization methods 5 Muscle energy techniques, as outlined in previous chapters, provide us with an excellent series of methods for relaxation and stretching of specific tight, shortened, contracted
Self-mobilization methods 5 Muscle energy techniques, as outlined in previous chapters, provide us with an excellent series of methods for relaxation and stretching of specific tight, shortened, contracted
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
During the breathing exercises, it is important not to use your neck or shoulder muscles. Generally, ten breath cycles per session is adequate.
 Cool-Down Breathing Exercises Overview Breathing exercises help make use of the entire lung and keep the chest muscles active. They allow for more oxygen with each breath and to breathe with less effort.
Cool-Down Breathing Exercises Overview Breathing exercises help make use of the entire lung and keep the chest muscles active. They allow for more oxygen with each breath and to breathe with less effort.
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery
 Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises
 Athletic Medicine Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises Introduction Low back pain can be the result of many different things. Pain can be triggered by some combination of overuse, muscle strain,
Athletic Medicine Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises Introduction Low back pain can be the result of many different things. Pain can be triggered by some combination of overuse, muscle strain,
Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights
 Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights Why are chair exercises and lifting weights important? Physical activity is one of the most important things you can do to maintain your diabetes control as well as
Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights Why are chair exercises and lifting weights important? Physical activity is one of the most important things you can do to maintain your diabetes control as well as
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin
 by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
Elbow Examination. Haroon Majeed
 Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease.
 Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Guide for therapists/specialists Questions and comments to: info@childmuscleweakness.org Surveillance and Referral
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Guide for therapists/specialists Questions and comments to: info@childmuscleweakness.org Surveillance and Referral
Exercises for Growing Taller
 1 Exercises for Growing Taller A Mini-Guide By Rodney Williams Copyright and Legal Notice 2 Published by: Copyright 2011. All Rights Reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted
1 Exercises for Growing Taller A Mini-Guide By Rodney Williams Copyright and Legal Notice 2 Published by: Copyright 2011. All Rights Reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted
CHAPTER 3: BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES. Standing Quad Stretch Athletic Edge - www.athleticedge.biz - (650) 815-6552
 CHAPTER : BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES Standing Quad Stretch ) Stand and grasp right ankle with same hand, use a wall or chair to Lower maintain Back balance with left hand. Maintain an upright Stretches
CHAPTER : BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES Standing Quad Stretch ) Stand and grasp right ankle with same hand, use a wall or chair to Lower maintain Back balance with left hand. Maintain an upright Stretches
HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK
 HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK 1. Standing and Walking For correct posture, balance your head above your shoulders, eyes straight ahead, everything else falls into place. Try to point toes straight ahead
HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK 1. Standing and Walking For correct posture, balance your head above your shoulders, eyes straight ahead, everything else falls into place. Try to point toes straight ahead
A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain. History
 A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain Hamilton Hall MD FRCSC Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto Medical Director, CBI Health Group Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society
A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain Hamilton Hall MD FRCSC Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto Medical Director, CBI Health Group Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Pendulum Exercise: Wal Walk: Back Scratcher:
 Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Begin these exercises when your pain has decreased about 25% from the time when your injury was most painful. Pendulum Exercise: Lean over with your uninjured
Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Begin these exercises when your pain has decreased about 25% from the time when your injury was most painful. Pendulum Exercise: Lean over with your uninjured
SHOULDER PULL DOWNS. To learn efficient use of the shoulder blades and arms while maintaining a neutral spine position.
 SHOULDER INTRODUCT ION Welcome to your shoulder exercise program The exercises in the program are designed to improve your shoulder mobility, posture and the control of the muscles in your neck and shoulder
SHOULDER INTRODUCT ION Welcome to your shoulder exercise program The exercises in the program are designed to improve your shoulder mobility, posture and the control of the muscles in your neck and shoulder
Keep fit at the workplace! A simple training programme for more exercise at the workplace.
 Keep fit at the workplace! A simple training programme for more exercise at the workplace. INTRODUCTION Dear Readers, Keeping your body in one position, such as sitting or standing for a long time, results
Keep fit at the workplace! A simple training programme for more exercise at the workplace. INTRODUCTION Dear Readers, Keeping your body in one position, such as sitting or standing for a long time, results
are you reaching your full potential...
 T h e r e s n o s u c h t h i n g a s b a d e x e r c i s e - j u s t e x e r c i s e d o n e b a d l y FIT for sport are you reaching your full potential... These tests are a series of exercises designed
T h e r e s n o s u c h t h i n g a s b a d e x e r c i s e - j u s t e x e r c i s e d o n e b a d l y FIT for sport are you reaching your full potential... These tests are a series of exercises designed
Adult Choking and CPR Manual
 Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
Workout Routine - Dumbbells - Full Body Printed on Apr 28 2011
 Workout Routine - Dumbbells - Full Body Printed on Apr 28 2011 Workout Routine Snapshot 2 Workout Days 0 Cardio Exercises 14 Strength Training 0 Stretching Exercises 2 Abs 2 Back 2 Chest 2 Shoulders 2
Workout Routine - Dumbbells - Full Body Printed on Apr 28 2011 Workout Routine Snapshot 2 Workout Days 0 Cardio Exercises 14 Strength Training 0 Stretching Exercises 2 Abs 2 Back 2 Chest 2 Shoulders 2
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Bankart Repair For Shoulder Instability Rehabilitation Guidelines
 Bankart Repair For Shoulder Instability Rehabilitation Guidelines Phase I: The first week after surgery. Goals:!! 1. Control pain and swelling! 2. Protect the repair! 3. Begin early shoulder motion Activities:
Bankart Repair For Shoulder Instability Rehabilitation Guidelines Phase I: The first week after surgery. Goals:!! 1. Control pain and swelling! 2. Protect the repair! 3. Begin early shoulder motion Activities:
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Range of Motion & Positioning
 Range of Motion & Positioning Teaching Guide To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner
Range of Motion & Positioning Teaching Guide To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner
Switch Assessment and Planning Framework for Individuals with Physical Disabilities
 Guidance Notes Pre- assessment: It is important to gather together appropriate information before the assessment to inform on possible starting points for the assessment. The Pre-Assessment Form should
Guidance Notes Pre- assessment: It is important to gather together appropriate information before the assessment to inform on possible starting points for the assessment. The Pre-Assessment Form should
Chair Exercises For Older Adults
 Chair Exercises For Older Adults Many of these exercises were adapted from these sources: National Institute on Aging, Exercise: A Guide from the National Institute on Aging, 2001, http://www.nia.nih.gov/healthinformation/publications/exerciseguide/.
Chair Exercises For Older Adults Many of these exercises were adapted from these sources: National Institute on Aging, Exercise: A Guide from the National Institute on Aging, 2001, http://www.nia.nih.gov/healthinformation/publications/exerciseguide/.
Don t. Hamstrings. Calf Muscles. both legs 2-3 times. stretch is felt in the back of the calf. Repeat with both legs 2-3 times.
 Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching (e.g. stretch after walking). Stretch until you feel mild discomfort, not pain. Never bounce or force a stretch. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds
Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching (e.g. stretch after walking). Stretch until you feel mild discomfort, not pain. Never bounce or force a stretch. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds
How To Stretch Your Body
 Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
Strengthening Exercises - Below Knee Amputation
 Strengthening Exercises - Below Knee Amputation These exercises will help you strengthen your muscles to best use your prosthetic leg. Do these exercises as directed by your therapist or doctor. Do the
Strengthening Exercises - Below Knee Amputation These exercises will help you strengthen your muscles to best use your prosthetic leg. Do these exercises as directed by your therapist or doctor. Do the
What is Acupuncture? 1 Summary of Acupoint Indications. 1.1 Head
 What is Acupuncture? Acupuncture dates back over three thousand years, but only recently has it gained recognition as a valid treatment for chronic or long-standing pain. Using the PAIN GONE on acupoints
What is Acupuncture? Acupuncture dates back over three thousand years, but only recently has it gained recognition as a valid treatment for chronic or long-standing pain. Using the PAIN GONE on acupoints
Stretching the Low Back THERAPIST ASSISTED AND CLIENT SELF-CARE STRETCHES FOR THE LUMBOSACRAL SPINE
 EXPERT CONTENT by Joseph E. Muscolino photos by Yanik Chauvin body mechanics THE ESSENCE OF MOST MANUAL THERAPIES, and certainly clinical orthopedic massage therapy, is to loosen taut soft tissues, thereby
EXPERT CONTENT by Joseph E. Muscolino photos by Yanik Chauvin body mechanics THE ESSENCE OF MOST MANUAL THERAPIES, and certainly clinical orthopedic massage therapy, is to loosen taut soft tissues, thereby
Extremity Trauma. William Schecter, MD
 Extremity Trauma William Schecter, MD Approach to the Evaluation of the Patient with an Extremity Injury Blood Supply Skeleton Neurologic Function Risk for Compartment Syndrome? Coverage (Skin and Soft
Extremity Trauma William Schecter, MD Approach to the Evaluation of the Patient with an Extremity Injury Blood Supply Skeleton Neurologic Function Risk for Compartment Syndrome? Coverage (Skin and Soft
Physical Capability Strength Test: One Component of the Selection Process
 Physical Capability Strength Test: One Component of the Selection Process One aspect of the Power Systems Institute selection process is to successfully complete and achieve a passing score on a physical
Physical Capability Strength Test: One Component of the Selection Process One aspect of the Power Systems Institute selection process is to successfully complete and achieve a passing score on a physical
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE
 UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
EGOSCUE CLINIC PAIN/POSTURE STRETCHES 1. Standing Arm Circles: Helps Restore Upper Body Strength
 EGOSCUE CLINIC PAIN/POSTURE STRETCHES 1. Standing Arm Circles: Helps Restore Upper Body Strength Two sets of 40 repetitions each. Stand with your feet pointed straight and hip-width apart. Place your fingertips
EGOSCUE CLINIC PAIN/POSTURE STRETCHES 1. Standing Arm Circles: Helps Restore Upper Body Strength Two sets of 40 repetitions each. Stand with your feet pointed straight and hip-width apart. Place your fingertips
CORRECTIVE CHIROPRACTIC EXERCISES
 CORRECTIVE CHIROPRACTIC EXERCISES J O W E T T & M O U L T O N C h i r o p r a c t o r s introduction This booklet, presented by Jowett and Moulton Chiropractors, is designed to provide you with a general
CORRECTIVE CHIROPRACTIC EXERCISES J O W E T T & M O U L T O N C h i r o p r a c t o r s introduction This booklet, presented by Jowett and Moulton Chiropractors, is designed to provide you with a general
Lower Extremities. Posterior Compartment of Thighs Knee Flexors
 Lower Extremities Lower extremities are adjusted to provide locomotion but, at the same time, carry the full body weight. The lower limb movement is transferred through the hip joint and pelvis onto the
Lower Extremities Lower extremities are adjusted to provide locomotion but, at the same time, carry the full body weight. The lower limb movement is transferred through the hip joint and pelvis onto the
