CURRICULUM OBJECTIVES
|
|
|
- Harvey McDaniel
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CURRICULUM OBJECTIVES NUMBER RECOGNITION Arabic Numbers 1 understand and use correctly the word digit 2 recognize Arabic numbers: 0 1,000 3 recognize Arabic numbers: 1, Roman Numerals 4 recognize Roman numerals: I XXXIX (1 39) 5 recognize Roman numerals: XL M (40 1,000) 6 read dates in Roman numerals (i.e. MCMLXXI 1971) NUMBER/WORD RECOGNITION Number Words 1 write the number words for write the number words for 10 1,000 3 write the number words for 1,000 1,000,000 Conventions 4 use of comma to separate thousands, (i.e. 1,000, etc.) 5 use of hyphen to separate number words (e.g. forty-one) 6 use of zero as a place holder PLACE VALUE Place Value 1 identify place value in numbers 0 1,000 2 demonstrate an understanding of place value 3 identify place value in numbers 1,000 1,000,000 4 place value in whole numbers is found from right to left 5 explain expanded notation 6 value of expanded notation for identifying numbers Rounding Off 7 round off whole numbers (to the nearest one, ten, hundred, thousand, million) COUNTING Counting 1 orally from 0 1,000, starting any place in between 2 drill and practice counting by 1 s, 2 s, 5 s, and 10 s (0 100) 3 orally from 1,000 1,000,000, starting any place between 4 drill and practice counting by 1 s, 2 s, 5 s, 10 s (1,000 1,000,000) Other 5 recognize < and > signs 6 compare numbers with, and. signs 7 explain even and odd numbers 8 order numbers from least to greatest and greatest to least ADDITION Terms 1 use the terms addend and sum 2 explain relationship between adding and counting 3 recognize and use + sign and the = sign
2 4 explain whole number Addition 5 demonstrate an understanding of addition 6 master addition facts up to and including 18 7 find sum of four whole numbers up to 3 digits 8 find sum of four whole numbers up to 6 digits 9 add numbers in columns 10 add numbers written in equation form 11 regroup ones, tens, hundreds, thousands 12 insert zero in blank spaces to make addition easier 13 the order in which numbers are added doesn t change the sum SUBTRACTION Terms 1 use find the difference between to signify subtraction 2 know the meaning of the subtraction sign - Subtraction 3 demonstrate an understanding of subtraction 4 master subtraction facts up to and including 18 5 find the difference in 2 whole numbers up to 3 digits 6 find the difference in 2 whole numbers up to 6 digits 7 subtract numbers written in columns 8 borrow numbers 9 regroup ones, tens, hundreds, thousands, etc. 10 subtract numbers written in equation format 11 insert zeros in blank spaces to make subtraction easier 12 explain the relation between addition and subtraction 13 solve addition/subtraction equations (37 -? = 14) MULTIPLICATION Terms 1 understand and use the term factor 2 understand and use the term multiple 3 understand and use the term product 4 recognize and use the multiplication sign x Multiplication 5 demonstrate an understanding of multiplication 6 relation between addition and multiplication 7 memorize times table to 12 x 12; use a chart showing relation between numbers 8 carry numbers 9 regroup ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands 10 multiply by zero 11 multiply numbers in columns 12 multiply numbers written in equation format 13 importance of accuracy 14 double checking for computational errors 15 neatness in recording columns 16 printing legibly 17 order in which numbers are multiplied doesn t affect the answer
3 DIVISION Terms 1 understand and use the term dividend 2 understand and use the term divisor 3 understand and use the term quotient 4 understand and use the term remainder 5 understand and use the term prime number 6 understand and use the term average (mean) 7 use the division signs, -, and / 8 divide using horizontal format Division 9 demonstrate an understanding of division 10 carrying numbers 11 dividing numbers in horizontal format 12 dividing numbers in equation format 13 dividing with zero 14 expressing remainders using r 15 explain relation between multiplication and division Factoring 16 explain factoring 17 find the factors of a given list of products 18 identify prime numbers from a given list Average 19 how to calculate average 20 when to use averages WORD PROBLEMS WITH WHOLE NUMBERS Problems 1 demonstrate ability to solve word problems with whole numbers Strategies 2 develop good work habits 3 read all parts of question carefully 4 determine what is asked for or required 5 separate information given from question being asked 6 record information given and solution required separately 7 decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem 8 work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible 9 label the answer in terms of values given in question 10 estimate an answer 11 check every step 12 compare estimated answer with answer found 13 use clue words to solve word problems (e.g. total, sum, how much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer, more, difference, left, remains, times, at) UNDERSTANDING AND COMPARING FRACTIONS Terms 1 explain fraction
4 2 explain numerator and denominator 3 explain proper and improper fraction 4 explain equivalent fractions 5 explain mixed number 6 lowest common denominator (LCM) Fractions 7 demonstrate an understanding of fractions 8 visualize fractions: divide circle or line into correct number of segments to represent a given fraction 9 compare fractions: order list of fractions from greatest to least 10 compare fractions: order list of fractions from least to greatest 11 compare 2 fractions using < and > (like denominators) 12 read < and > left to right and right to left 13 provide equivalent fractions for each fraction in a given list 14 identify fractions in their lowest terms 15 reduce fractions to their lowest terms 16 express improper fractions as mixed numbers 17 express mixed numbers as improper fractions 18 find lowest common denominator for group of 2 or 3 fractions 19 express these fractions using lowest common denominator ADDITION OF FRACTIONS Adding Fractions 1 add fractions with like denominators 2 reduce fractions to lowest terms 3 change improper fractions to mixed numbers 4 report answers as mixed numbers 5 add fractions with unlike denominators 6 find common denominators 7 fractions that equal 1 8 add mixed numbers 9 change mixed numbers to improper fractions SUBTRACTION OF FRACTIONS Subtracting Fractions 1 subtract fractions with like denominators 2 reduce fractions to lowest terms 3 change improper fractions to mixed numbers 4 report answers as mixed numbers 5 subtract fractions with unlike denominators 6 find common denominators 7 fractions that equal one 8 subtract mixed numbers 9 borrowing
5 10 change mixed numbers to improper fractions 11 subtract fractions from whole numbers 12 change whole numbers to fractions MULTIPLICATION OF FRACTIONS Terms 1 explain greatest common factor (GCF) 2 explain lowest common multiple (LCM) Multiplying Fractions 3 explain cancelling 4 demonstrate an understanding of cancelling 5 find GCF and LCM 6 find factors for each number 7 find greatest factor common to both 8 find multiples of two numbers 9 find LCM common to both 10 reduce fractions and/or cancel before multiplying 11 multiplication of numerator and denominator by same number 12 multiply fractions by whole numbers 13 multiply mixed numbers 14 reduce answers to lowest common denominator 15 change improper fractions to mixed numbers 16 report answers as mixed numbers DIVISION OF FRACTIONS Dividing Fractions 1 review cancelling 2 finding GCF and LCM 3 find factors for each number 4 find greatest factor common to both 5 find multiples 6 find the LCM 7 division of numerator and denominator by the same number 8 divide with fractions and whole numbers 9 division rule: cancel; invert 2 nd fraction; multiply 10 divide mixed numbers 11 express remainders as fractions 12 reduce fractions to lowest terms 13 change improper fractions to mixed numbers 14 report answers as mixed numbers WORD PROBLEMS WITH FRACTIONS Problems 1 demonstrate ability to solve word problems with fractions Strategies 2 develop good work habits 3 read all parts of question carefully
6 4 determine what is asked for or required 5 separate information given from question being asked 6 record information given and solution required separately 7 decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem 8 work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible 9 label the answer in terms of values given in question 10 estimate an answer 11 check every step 12 compare estimated answer with answer found 13 use clue words to solve word problems (e.g. total, sum, how much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer, more, difference, left, remains, times, at, divide, and each) UNDERSTANDING AND COMPARING DECIMALS Decimal System 1 demonstrate and understanding of the decimal system 2 explain the decimal system 3 use of decimal point 4 compare: decimals 5 compare: mixed decimals 6 compare: decimals and fractions 7 read decimals from left to right 8 translate decimal as and in English 9 decimal point is expressed as a comma in many countries 10 convert mixed numbers to mixed decimals 11 compare decimal values by adding zeros to right of decimal 12 place value of each digit in a decimal through thousandths 13 convert fractions to decimals 14 convert decimals to fractions (excluding repeating decimals) ADDITION OF DECIMALS Adding Decimals 1 review addition number facts to 18 2 estimate answer before adding 3 add decimals and mixed decimals 4 placement of decimal points under one another 5 use of zero as a place holder 6 carrying numbers 7 round off decimals to the hundredths place SUBTRACTION OF DECIMALS Subtracting Decimals 1 review subtraction number facts to 18 2 estimate answer before subtracting 3 subtract decimals and mixed decimals 4 placement of decimal points under one another
7 MULTIPLICATION OF DECIMALS Multiplying Decimals 5 use of zero as a place holder 6 borrowing numbers 7 round off decimals to the hundredths place 1 review multiplication facts 2 estimate answer before multiplying 3 multiply decimals and mixed decimals 4 placement of decimal point in final answer 5 no need to line up decimal points in question 6 use of zero as a place holder 7 carry numbers 8 round off decimals to the hundredths place 9 multiply decimals by 10, 100, 1,000 (decimal to right) DIVISION OF DECIMALS Dividing Decimals 1 review division number facts 2 estimate answer before dividing 3 divide decimals and mixed decimals 4 use zero as a place holder in dividing 5 place decimal point in answer directly above that in problem 6 zero as a place holder in expressing answer (i.e. 0.98) 7 express remainder as decimals 8 divide whole numbers and decimals by decimals moving the decimal point in divisor and dividend 9 add zeros to divide 10 round off decimals WORD PROBLEMS WITH DECIMALS Problems 1 demonstrate an understanding of problem solving with decimals Strategies 2 develop good work habits 3 read all parts of question carefully 4 determine what is asked for or required 5 separate information given from question being asked 6 record information given and solution required separately 7 decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem 8 work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible 9 label the answer in terms of values given in question 10 estimate an answer 11 check every step 12 compare estimated answer with answer found 13 use clue words to solve word problems (e.g. total, sum, how
8 much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer, more, difference, left, remains, times, at, divide, and each) UNDERSTANDING AND COMPARING PERCENTS Terms 1 explain percent 2 explain use of the % Percents 3 demonstrate an understanding of percent 4 introduce percent through use of grids or pie charts 5 shade in portions of figure to represent percentage of that figure 6 100% of a number = all of that number 7 0% of a number = none of that number 8 convert fractions to percent (multiply by 100) 9 convert decimals to percent (multiply by 100 or move decimals 2 places to right) 10 convert percent to fractions (divide percent over 100 and reduce fraction) 11 convert percent to decimals (divide percent by 100 or move decimal 2 places to left) USING PERCENTS Using Percents 1 use r/100 = P/W to find percent of a number, what percent one number is of another, and a number when a percent is given SIMPLE INTEREST Terms 1 explain simple interest 2 explain the interest formula I = Prt (where P = principal, r = rate, t = time) Simple Interest 3 demonstrate an understanding of simple interest 4 discuss when simple interest is charged 5 relationship between percentage and interest 6 gather information needed to use I = Prt (implied multiplication between P and r and t) 7 calculate simple interest WORD PROBLEMS WITH PERCENT Problems 1 demonstrate an understanding of problem solving with percent Strategies 2 develop good work habits 3 read all parts of question carefully 4 determine what is asked for or required 5 separate information given from question being asked 6 record information given and solution required separately
9 7 decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem 8 work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible 9 label the answer in terms of values given in question 10 estimate an answer 11 check every step 12 compare estimated answer with answer found 13 use clue words to solve word problems (e.g. total, sum, how much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer, more, difference, left, remains, times, at, divide, and each) TIME Using Time Divisions 1 60 seconds in a minute 2 60 minutes in an hour 3 24 hours in a day 4 7 days in a week 5 approximately four weeks in a month 6 name the days of the week 7 name months of the year 8 correctly use a.m. and p.m. 9 calculate the number of seconds in a given number of minutes 10 calculate the number of minutes in a given number of hours 11 calculate the number of hours in a given number of days 12 state the number of days in a given month 13 explain the term leap year 14 calculate the leap years between two given dates 15 express time in words 16 use timetables (e.g. bus, train, school) Clocks 17 tell time with an analog clock to the nearest minute 18 recognize times (e.g. quarter past four, ten to six) 19 tell time with a digital clock (e.g. 1:50 is ten to one) 20 briefly describe the twenty-four hour clock 21 discuss where the twenty-four hour clock might be found 22 recognize written time (e.g. half hour, quarter hour) 23 use of the colon in writing time (e.g. 2:53) Calendars 24 numeric dating: various styles (d/m/y; y/m/d; m/d/y) Calculating with 25 add time Time 26 subtract time MONEY Coin Values 1 identify value of coins: penny (cent), nickel, dime, quarter, loonie, and toonie 2 use of the $ and signs 3 use of decimal point to write dollar/cent amounts 4 convert cents to dollars and dollars to cents Calculating with 5 use knowledge of decimals to add and subtract money
10 Money 6 use knowledge of decimals to multiply and divide money 7 practice counting money and making change 8 find cost of several items, given the unit cost 9 find unit cost, given number of items and total cost 10 calculate tax payable (HST) 11 calculate discount, given regular price and % discount 12 buying on credit 13 round off to the nearest cent 14 procedure for developing a budget CHARTS AND GRAPHS Chart 1 explain chart/table 2 interpret information in distance tables (map) 3 interpret information in weight/height charts 4 interpret information in nutritive value charts Graphs 5 explain graph 6 interpret information in circle graphs 7 interpret information in bar graphs 8 interpret information in pictographs 9 interpret information in line graphs METRIC MEASUREMENT Terms 1 linear, volume, mass measurement 2 gram (mass), litre (volume), metre (linear) 3 prefixes: milli, centi, deci, (metre, gram, litre), deka, hecto, kilo 4 abbreviations linear measure: mm, dm, m, dam, km, cm, hm 5 abbreviations volume measure: ml, dl, L, dal, hl, kl, cl 6 abbreviations mass measure: mg, cg, g, dag, hg, kg,dg 7 faces, edges, vertex, vertices 8 square, rectangle, triangle 9 perimeter Using Metric Measurement 10 area 11 estimate and measure accurately: linear measurement 12 estimate and measure accurately: volume measurement 13 estimate and measure accurately: mass measurement 14 identify geometric figures by counting faces, edges, and vertices 15 formula: calculate perimeter of rectangle (2l + 2w) and use the correct units: (mm, cm, dm, m, km) 16 formula: calculate area of rectangle (l x w) 17 use correct area units: (e.g. square centimetres, square kilometres, etc.)
11 18 formula: calculate volume of rectangular prism (l x w x h) 19 use correct volume units: (e.g. cubic centimetres, cubic metres, etc.) WORD PROBLEMS WITH MEASUREMENT Problems 1 demonstrate ability to solve word problems with addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of whole numbers, fractions, decimals, percentages, time, money, temperature, and metric measurement Strategies 2 develop good work habits 3 read all parts of question carefully 4 determine what is asked for or required 5 separate information given from question being asked 6 record information given and solution required separately 7 decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem 8 work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible 9 label the answer in terms of values given in question 10 estimate an answer 11 check every step 12 compare estimated answer with answer found 13 use clue words to solve word problems (e.g. total, sum, how much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer, more, difference, left, remains, times, at)
Scope and Sequence KA KB 1A 1B 2A 2B 3A 3B 4A 4B 5A 5B 6A 6B
 Scope and Sequence Earlybird Kindergarten, Standards Edition Primary Mathematics, Standards Edition Copyright 2008 [SingaporeMath.com Inc.] The check mark indicates where the topic is first introduced
Scope and Sequence Earlybird Kindergarten, Standards Edition Primary Mathematics, Standards Edition Copyright 2008 [SingaporeMath.com Inc.] The check mark indicates where the topic is first introduced
Everyday Mathematics CCSS EDITION CCSS EDITION. Content Strand: Number and Numeration
 CCSS EDITION Overview of -6 Grade-Level Goals CCSS EDITION Content Strand: Number and Numeration Program Goal: Understand the Meanings, Uses, and Representations of Numbers Content Thread: Rote Counting
CCSS EDITION Overview of -6 Grade-Level Goals CCSS EDITION Content Strand: Number and Numeration Program Goal: Understand the Meanings, Uses, and Representations of Numbers Content Thread: Rote Counting
Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets
 Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets Year One Maths Target Sheet Key Statement KS1 Maths Targets (Expected) These skills must be secure to move beyond expected. I can compare, describe and solve
Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets Year One Maths Target Sheet Key Statement KS1 Maths Targets (Expected) These skills must be secure to move beyond expected. I can compare, describe and solve
Primary Curriculum 2014
 Primary Curriculum 2014 Suggested Key Objectives for Mathematics at Key Stages 1 and 2 Year 1 Maths Key Objectives Taken from the National Curriculum 1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards,
Primary Curriculum 2014 Suggested Key Objectives for Mathematics at Key Stages 1 and 2 Year 1 Maths Key Objectives Taken from the National Curriculum 1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards,
Everyday Mathematics GOALS
 Copyright Wright Group/McGraw-Hill GOALS The following tables list the Grade-Level Goals organized by Content Strand and Program Goal. Content Strand: NUMBER AND NUMERATION Program Goal: Understand the
Copyright Wright Group/McGraw-Hill GOALS The following tables list the Grade-Level Goals organized by Content Strand and Program Goal. Content Strand: NUMBER AND NUMERATION Program Goal: Understand the
Possible Stage Two Mathematics Test Topics
 Possible Stage Two Mathematics Test Topics The Stage Two Mathematics Test questions are designed to be answerable by a good problem-solver with a strong mathematics background. It is based mainly on material
Possible Stage Two Mathematics Test Topics The Stage Two Mathematics Test questions are designed to be answerable by a good problem-solver with a strong mathematics background. It is based mainly on material
Numeracy Targets. I can count at least 20 objects
 Targets 1c I can read numbers up to 10 I can count up to 10 objects I can say the number names in order up to 20 I can write at least 4 numbers up to 10. When someone gives me a small number of objects
Targets 1c I can read numbers up to 10 I can count up to 10 objects I can say the number names in order up to 20 I can write at least 4 numbers up to 10. When someone gives me a small number of objects
Mathematics K 6 continuum of key ideas
 Mathematics K 6 continuum of key ideas Number and Algebra Count forwards to 30 from a given number Count backwards from a given number in the range 0 to 20 Compare, order, read and represent to at least
Mathematics K 6 continuum of key ideas Number and Algebra Count forwards to 30 from a given number Count backwards from a given number in the range 0 to 20 Compare, order, read and represent to at least
Illinois State Standards Alignments Grades Three through Eleven
 Illinois State Standards Alignments Grades Three through Eleven Trademark of Renaissance Learning, Inc., and its subsidiaries, registered, common law, or pending registration in the United States and other
Illinois State Standards Alignments Grades Three through Eleven Trademark of Renaissance Learning, Inc., and its subsidiaries, registered, common law, or pending registration in the United States and other
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, SPORT AND CULTURE PRIMARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS GRADES 4 5 FIRST EXAMINATION 2008
 MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, SPORT AND CULTURE PRIMARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS GRADES 4 5 FIRST EXAMINATION 2008 Curriculum Development Unit P. O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant HARARE All Rights Reserved 2006
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, SPORT AND CULTURE PRIMARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS GRADES 4 5 FIRST EXAMINATION 2008 Curriculum Development Unit P. O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant HARARE All Rights Reserved 2006
HFCC Math Lab General Math Topics -1. Metric System: Shortcut Conversions of Units within the Metric System
 HFCC Math Lab General Math Topics - Metric System: Shortcut Conversions of Units within the Metric System In this handout, we will work with three basic units of measure in the metric system: meter: gram:
HFCC Math Lab General Math Topics - Metric System: Shortcut Conversions of Units within the Metric System In this handout, we will work with three basic units of measure in the metric system: meter: gram:
Mathematics. Steps to Success. and. Top Tips. Year 5
 Pownall Green Primary School Mathematics and Year 5 1 Contents Page 1. Multiplication and Division 3 2. Positive and Negative Numbers 4 3. Decimal Notation 4. Reading Decimals 5 5. Fractions Linked to
Pownall Green Primary School Mathematics and Year 5 1 Contents Page 1. Multiplication and Division 3 2. Positive and Negative Numbers 4 3. Decimal Notation 4. Reading Decimals 5 5. Fractions Linked to
Florida Math 0018. Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0018 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Lower
 Florida Math 0018 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0018 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Lower Whole Numbers MDECL1: Perform operations on whole numbers (with applications, including
Florida Math 0018 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0018 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Lower Whole Numbers MDECL1: Perform operations on whole numbers (with applications, including
How do you compare numbers? On a number line, larger numbers are to the right and smaller numbers are to the left.
 The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of pre-algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in algebra 1. Number Basics
The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of pre-algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in algebra 1. Number Basics
Mathematics Scope and Sequence, K-8
 Standard 1: Number and Operation Goal 1.1: Understands and uses numbers (number sense) Mathematics Scope and Sequence, K-8 Grade Counting Read, Write, Order, Compare Place Value Money Number Theory K Count
Standard 1: Number and Operation Goal 1.1: Understands and uses numbers (number sense) Mathematics Scope and Sequence, K-8 Grade Counting Read, Write, Order, Compare Place Value Money Number Theory K Count
Unit 1 Number Sense. In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions.
 Unit 1 Number Sense In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions. BLM Three Types of Percent Problems (p L-34) is a summary BLM for the material
Unit 1 Number Sense In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions. BLM Three Types of Percent Problems (p L-34) is a summary BLM for the material
Quarter One: August-October
 Quarter One: August-October (Chapters 1 3, 5-6, 10) August - December Quarterly Addition facts with sums through 20 General Math Content 1. Write sums through 20. 1. Choose and enter the appropriate answer.
Quarter One: August-October (Chapters 1 3, 5-6, 10) August - December Quarterly Addition facts with sums through 20 General Math Content 1. Write sums through 20. 1. Choose and enter the appropriate answer.
My Year 1 Maths Targets
 My Year 1 Maths Targets Number number and place value I can count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number. I can count in multiples of twos, fives and
My Year 1 Maths Targets Number number and place value I can count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number. I can count in multiples of twos, fives and
Quick Reference ebook
 This file is distributed FREE OF CHARGE by the publisher Quick Reference Handbooks and the author. Quick Reference ebook Click on Contents or Index in the left panel to locate a topic. The math facts listed
This file is distributed FREE OF CHARGE by the publisher Quick Reference Handbooks and the author. Quick Reference ebook Click on Contents or Index in the left panel to locate a topic. The math facts listed
Math 0306 Final Exam Review
 Math 006 Final Exam Review Problem Section Answers Whole Numbers 1. According to the 1990 census, the population of Nebraska is 1,8,8, the population of Nevada is 1,01,8, the population of New Hampshire
Math 006 Final Exam Review Problem Section Answers Whole Numbers 1. According to the 1990 census, the population of Nebraska is 1,8,8, the population of Nevada is 1,01,8, the population of New Hampshire
EVERY DAY COUNTS CALENDAR MATH 2005 correlated to
 EVERY DAY COUNTS CALENDAR MATH 2005 correlated to Illinois Mathematics Assessment Framework Grades 3-5 E D U C A T I O N G R O U P A Houghton Mifflin Company YOUR ILLINOIS GREAT SOURCE REPRESENTATIVES:
EVERY DAY COUNTS CALENDAR MATH 2005 correlated to Illinois Mathematics Assessment Framework Grades 3-5 E D U C A T I O N G R O U P A Houghton Mifflin Company YOUR ILLINOIS GREAT SOURCE REPRESENTATIVES:
of surface, 569-571, 576-577, 578-581 of triangle, 548 Associative Property of addition, 12, 331 of multiplication, 18, 433
 Absolute Value and arithmetic, 730-733 defined, 730 Acute angle, 477 Acute triangle, 497 Addend, 12 Addition associative property of, (see Commutative Property) carrying in, 11, 92 commutative property
Absolute Value and arithmetic, 730-733 defined, 730 Acute angle, 477 Acute triangle, 497 Addend, 12 Addition associative property of, (see Commutative Property) carrying in, 11, 92 commutative property
MATHS LEVEL DESCRIPTORS
 MATHS LEVEL DESCRIPTORS Number Level 3 Understand the place value of numbers up to thousands. Order numbers up to 9999. Round numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. Understand the number line below zero, and
MATHS LEVEL DESCRIPTORS Number Level 3 Understand the place value of numbers up to thousands. Order numbers up to 9999. Round numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. Understand the number line below zero, and
Unit 6 Number and Operations in Base Ten: Decimals
 Unit 6 Number and Operations in Base Ten: Decimals Introduction Students will extend the place value system to decimals. They will apply their understanding of models for decimals and decimal notation,
Unit 6 Number and Operations in Base Ten: Decimals Introduction Students will extend the place value system to decimals. They will apply their understanding of models for decimals and decimal notation,
PAYCHEX, INC. BASIC BUSINESS MATH TRAINING MODULE
 PAYCHEX, INC. BASIC BUSINESS MATH TRAINING MODULE 1 Property of Paychex, Inc. Basic Business Math Table of Contents Overview...3 Objectives...3 Calculator...4 Basic Calculations...6 Order of Operation...9
PAYCHEX, INC. BASIC BUSINESS MATH TRAINING MODULE 1 Property of Paychex, Inc. Basic Business Math Table of Contents Overview...3 Objectives...3 Calculator...4 Basic Calculations...6 Order of Operation...9
Paramedic Program Pre-Admission Mathematics Test Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Pre-Admission Mathematics Test Study Guide 05/13 1 Table of Contents Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page
Paramedic Program Pre-Admission Mathematics Test Study Guide 05/13 1 Table of Contents Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page
MEASUREMENTS. U.S. CUSTOMARY SYSTEM OF MEASUREMENT LENGTH The standard U.S. Customary System units of length are inch, foot, yard, and mile.
 MEASUREMENTS A measurement includes a number and a unit. 3 feet 7 minutes 12 gallons Standard units of measurement have been established to simplify trade and commerce. TIME Equivalences between units
MEASUREMENTS A measurement includes a number and a unit. 3 feet 7 minutes 12 gallons Standard units of measurement have been established to simplify trade and commerce. TIME Equivalences between units
Math Questions & Answers
 What five coins add up to a nickel? five pennies (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 5) Which is longest: a foot, a yard or an inch? a yard (3 feet = 1 yard; 12 inches = 1 foot) What do you call the answer to a multiplication
What five coins add up to a nickel? five pennies (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 5) Which is longest: a foot, a yard or an inch? a yard (3 feet = 1 yard; 12 inches = 1 foot) What do you call the answer to a multiplication
Voyager Sopris Learning Vmath, Levels C-I, correlated to the South Carolina College- and Career-Ready Standards for Mathematics, Grades 2-8
 Page 1 of 35 VMath, Level C Grade 2 Mathematical Process Standards 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Module 3: Lesson 4: 156-159 Module 4: Lesson 7: 220-223 2. Reason both contextually
Page 1 of 35 VMath, Level C Grade 2 Mathematical Process Standards 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Module 3: Lesson 4: 156-159 Module 4: Lesson 7: 220-223 2. Reason both contextually
numerical place value additional topics rounding off numbers power of numbers negative numbers addition with materials fundamentals
 Math Scope & Sequence fundamentals number sense and numeration of the decimal system Count to 10 by units Associate number to numeral (1-10) KN 1 KN 1 KN 2 KN 2 Identify odd and even numbers/numerals and
Math Scope & Sequence fundamentals number sense and numeration of the decimal system Count to 10 by units Associate number to numeral (1-10) KN 1 KN 1 KN 2 KN 2 Identify odd and even numbers/numerals and
4.5.1 The Metric System
 4.5.1 The Metric System Learning Objective(s) 1 Describe the general relationship between the U.S. customary units and metric units of length, weight/mass, and volume. 2 Define the metric prefixes and
4.5.1 The Metric System Learning Objective(s) 1 Describe the general relationship between the U.S. customary units and metric units of length, weight/mass, and volume. 2 Define the metric prefixes and
ISAT Mathematics Performance Definitions Grade 4
 ISAT Mathematics Performance Definitions Grade 4 EXCEEDS STANDARDS Fourth-grade students whose measured performance exceeds standards are able to identify, read, write, represent, and model whole numbers
ISAT Mathematics Performance Definitions Grade 4 EXCEEDS STANDARDS Fourth-grade students whose measured performance exceeds standards are able to identify, read, write, represent, and model whole numbers
1. Metric system- developed in Europe (France) in 1700's, offered as an alternative to the British or English system of measurement.
 GS104 Basics Review of Math I. MATHEMATICS REVIEW A. Decimal Fractions, basics and definitions 1. Decimal Fractions - a fraction whose deonominator is 10 or some multiple of 10 such as 100, 1000, 10000,
GS104 Basics Review of Math I. MATHEMATICS REVIEW A. Decimal Fractions, basics and definitions 1. Decimal Fractions - a fraction whose deonominator is 10 or some multiple of 10 such as 100, 1000, 10000,
Mathematics Navigator. Misconceptions and Errors
 Mathematics Navigator Misconceptions and Errors Introduction In this Guide Misconceptions and errors are addressed as follows: Place Value... 1 Addition and Subtraction... 4 Multiplication and Division...
Mathematics Navigator Misconceptions and Errors Introduction In this Guide Misconceptions and errors are addressed as follows: Place Value... 1 Addition and Subtraction... 4 Multiplication and Division...
LESSON 4 Missing Numbers in Multiplication Missing Numbers in Division LESSON 5 Order of Operations, Part 1 LESSON 6 Fractional Parts LESSON 7 Lines,
 Saxon Math 7/6 Class Description: Saxon mathematics is based on the principle of developing math skills incrementally and reviewing past skills daily. It also incorporates regular and cumulative assessments.
Saxon Math 7/6 Class Description: Saxon mathematics is based on the principle of developing math skills incrementally and reviewing past skills daily. It also incorporates regular and cumulative assessments.
Medium term Plans for Spring Year 5
 Medium term Plans for Spring Year 5 Help these children be in a better position to achieve good results in the Y6 Sats in 2015. Although these tests will officially be based on the old curriculum, it is
Medium term Plans for Spring Year 5 Help these children be in a better position to achieve good results in the Y6 Sats in 2015. Although these tests will officially be based on the old curriculum, it is
Minnesota Academic Standards
 A Correlation of to the Minnesota Academic Standards Grades K-6 G/M-204 Introduction This document demonstrates the high degree of success students will achieve when using Scott Foresman Addison Wesley
A Correlation of to the Minnesota Academic Standards Grades K-6 G/M-204 Introduction This document demonstrates the high degree of success students will achieve when using Scott Foresman Addison Wesley
Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key
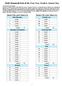 Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key Instructions to the teacher: In order to continue with the Math Mammoth Grade 7 Complete Worktext, I recommend that the student score a minimum of
Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key Instructions to the teacher: In order to continue with the Math Mammoth Grade 7 Complete Worktext, I recommend that the student score a minimum of
DATE PERIOD. Estimate the product of a decimal and a whole number by rounding the Estimation
 A Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (pages 135 138) When you multiply a decimal by a whole number, you can estimate to find where to put the decimal point in the product. You can also place the decimal
A Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (pages 135 138) When you multiply a decimal by a whole number, you can estimate to find where to put the decimal point in the product. You can also place the decimal
Math - 5th Grade. two digit by one digit multiplication fact families subtraction with regrouping
 Number and Operations Understand division of whole numbers N.MR.05.01 N.MR.05.02 N.MR.05.03 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with and without remainders; relate division to and to repeated
Number and Operations Understand division of whole numbers N.MR.05.01 N.MR.05.02 N.MR.05.03 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with and without remainders; relate division to and to repeated
ModuMath Basic Math Basic Math 1.1 - Naming Whole Numbers Basic Math 1.2 - The Number Line Basic Math 1.3 - Addition of Whole Numbers, Part I
 ModuMath Basic Math Basic Math 1.1 - Naming Whole Numbers 1) Read whole numbers. 2) Write whole numbers in words. 3) Change whole numbers stated in words into decimal numeral form. 4) Write numerals in
ModuMath Basic Math Basic Math 1.1 - Naming Whole Numbers 1) Read whole numbers. 2) Write whole numbers in words. 3) Change whole numbers stated in words into decimal numeral form. 4) Write numerals in
FOREWORD. Executive Secretary
 FOREWORD The Botswana Examinations Council is pleased to authorise the publication of the revised assessment procedures for the Junior Certificate Examination programme. According to the Revised National
FOREWORD The Botswana Examinations Council is pleased to authorise the publication of the revised assessment procedures for the Junior Certificate Examination programme. According to the Revised National
Indicator 2: Use a variety of algebraic concepts and methods to solve equations and inequalities.
 3 rd Grade Math Learning Targets Algebra: Indicator 1: Use procedures to transform algebraic expressions. 3.A.1.1. Students are able to explain the relationship between repeated addition and multiplication.
3 rd Grade Math Learning Targets Algebra: Indicator 1: Use procedures to transform algebraic expressions. 3.A.1.1. Students are able to explain the relationship between repeated addition and multiplication.
Grade 5 Math Content 1
 Grade 5 Math Content 1 Number and Operations: Whole Numbers Multiplication and Division In Grade 5, students consolidate their understanding of the computational strategies they use for multiplication.
Grade 5 Math Content 1 Number and Operations: Whole Numbers Multiplication and Division In Grade 5, students consolidate their understanding of the computational strategies they use for multiplication.
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives. Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers.
 Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Republic of the Philippines Department of Education DepEd Complex, Meralco Avenue Pasig City. K to 12 Curriculum Guide MATHEMATICS
 Republic of the Philippines Department of Education DepEd Complex, Meralco Avenue Pasig City K to 12 Curriculum Guide MATHEMATICS (Grade 1 to Grade 10) January 31, 2012 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK Mathematics
Republic of the Philippines Department of Education DepEd Complex, Meralco Avenue Pasig City K to 12 Curriculum Guide MATHEMATICS (Grade 1 to Grade 10) January 31, 2012 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK Mathematics
Autumn - 12 Weeks. Spring 11 Weeks. Summer 12 Weeks. Not As We Know It Limited 2014
 A Year 5 Mathematician Planning of coverage and resources. Autumn - 12 Weeks Spring 11 Weeks Summer 12 Weeks TARGETS NHM YR 5 Collins 5 Abacus 5 Abacus 6 LA Prior Step NHM 4 CPM 4 Ginn 4 Number, place
A Year 5 Mathematician Planning of coverage and resources. Autumn - 12 Weeks Spring 11 Weeks Summer 12 Weeks TARGETS NHM YR 5 Collins 5 Abacus 5 Abacus 6 LA Prior Step NHM 4 CPM 4 Ginn 4 Number, place
BOSTON REED. Clinical Medical Assistant Program Math Review Handout. Addition... Page 2. Subtraction... Page 3. Multiplication...
 BOSTON REED Clinical Medical Assistant Program Math Review Handout Contents Addition... Page 2 Subtraction... Page 3 Multiplication... Page 4 Decimals... Page 5 Decimal Practice Math... Page 7 Fractions...
BOSTON REED Clinical Medical Assistant Program Math Review Handout Contents Addition... Page 2 Subtraction... Page 3 Multiplication... Page 4 Decimals... Page 5 Decimal Practice Math... Page 7 Fractions...
Sequential Skills. Strands and Major Topics
 Sequential Skills This set of charts lists, by strand, the skills that are assessed, taught, and practiced in the Skills Tutorial program. Each Strand ends with a Mastery Test. You can enter correlating
Sequential Skills This set of charts lists, by strand, the skills that are assessed, taught, and practiced in the Skills Tutorial program. Each Strand ends with a Mastery Test. You can enter correlating
Welcome to Harcourt Mega Math: The Number Games
 Welcome to Harcourt Mega Math: The Number Games Harcourt Mega Math In The Number Games, students take on a math challenge in a lively insect stadium. Introduced by our host Penny and a number of sporting
Welcome to Harcourt Mega Math: The Number Games Harcourt Mega Math In The Number Games, students take on a math challenge in a lively insect stadium. Introduced by our host Penny and a number of sporting
Bridging Documents for Mathematics
 Bridging Documents for Mathematics 5 th /6 th Class, Primary Junior Cycle, Post-Primary Primary Post-Primary Card # Strand(s): Number, Measure Number (Strand 3) 2-5 Strand: Shape and Space Geometry and
Bridging Documents for Mathematics 5 th /6 th Class, Primary Junior Cycle, Post-Primary Primary Post-Primary Card # Strand(s): Number, Measure Number (Strand 3) 2-5 Strand: Shape and Space Geometry and
r the COR Common Core State Standards Learning Pathways
 BUI LT fo COM r the MON COR E 2015 2016 Common Core State Standards Learning Pathways Table of Contents Grade 3...3 Grade 4...8 Grade 5... 13 Grade 6... 18 Grade 7...26 Grade 8...32 Algebra Readiness...36
BUI LT fo COM r the MON COR E 2015 2016 Common Core State Standards Learning Pathways Table of Contents Grade 3...3 Grade 4...8 Grade 5... 13 Grade 6... 18 Grade 7...26 Grade 8...32 Algebra Readiness...36
Wigan LEA Numeracy Centre. Year 3 Time Block 3 Mental Arithmetic Test Questions
 Wigan LEA Numeracy Centre Year 3 Time Block 3 Mental Arithmetic Test Questions Produced by Wigan Numeracy Centre September 2000 Test 3 (end of week 2) Year 3 Block 3 I will read every question twice. In
Wigan LEA Numeracy Centre Year 3 Time Block 3 Mental Arithmetic Test Questions Produced by Wigan Numeracy Centre September 2000 Test 3 (end of week 2) Year 3 Block 3 I will read every question twice. In
Mercer County Schools
 Mercer County Schools PRIORITIZED CURRICULUM Mathematics Content Maps Second Grade Mercer County Schools PRIORITIZED CURRICULUM The Mercer County Schools Prioritized Curriculum is composed of West Virginia
Mercer County Schools PRIORITIZED CURRICULUM Mathematics Content Maps Second Grade Mercer County Schools PRIORITIZED CURRICULUM The Mercer County Schools Prioritized Curriculum is composed of West Virginia
Pocantico Hills School District Grade 1 Math Curriculum Draft
 Pocantico Hills School District Grade 1 Math Curriculum Draft Patterns /Number Sense/Statistics Content Strands: Performance Indicators 1.A.1 Determine and discuss patterns in arithmetic (what comes next
Pocantico Hills School District Grade 1 Math Curriculum Draft Patterns /Number Sense/Statistics Content Strands: Performance Indicators 1.A.1 Determine and discuss patterns in arithmetic (what comes next
UNIT 1 MASS AND LENGTH
 UNIT 1 MASS AND LENGTH Typical Units Typical units for measuring length and mass are listed below. Length Typical units for length in the Imperial system and SI are: Imperial SI inches ( ) centimetres
UNIT 1 MASS AND LENGTH Typical Units Typical units for measuring length and mass are listed below. Length Typical units for length in the Imperial system and SI are: Imperial SI inches ( ) centimetres
Cambridge Primary Mathematics Curriculum Framework (with codes)
 Cambridge Primary Mathematics Curriculum Framework (with codes) Contents Introduction Stage 1...1 Stage 2...5 Stage 3...9 Stage 4...14 Stage 5...18 Stage 6...24 Note on codes Each learning objective has
Cambridge Primary Mathematics Curriculum Framework (with codes) Contents Introduction Stage 1...1 Stage 2...5 Stage 3...9 Stage 4...14 Stage 5...18 Stage 6...24 Note on codes Each learning objective has
Fractional Part of a Set
 Addition and Subtraction Basic Facts... Subtraction Basic Facts... Order in Addition...7 Adding Three Numbers...8 Inverses: Addition and Subtraction... Problem Solving: Two-Step Problems... 0 Multiplication
Addition and Subtraction Basic Facts... Subtraction Basic Facts... Order in Addition...7 Adding Three Numbers...8 Inverses: Addition and Subtraction... Problem Solving: Two-Step Problems... 0 Multiplication
Manitoba Curriculum. Alignment with Mathletics. Supported by independent evidence-based research and practice. Powerful reporting.
 Supported by independent evidence-based research practice. Follows provincial curricula Powerful reporting Student centred Content Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 02 04 08 Grade 10 Applied & Pre-Calculus
Supported by independent evidence-based research practice. Follows provincial curricula Powerful reporting Student centred Content Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 02 04 08 Grade 10 Applied & Pre-Calculus
Prealgebra Textbook. Chapter 6 Odd Solutions
 Prealgebra Textbook Second Edition Chapter 6 Odd Solutions Department of Mathematics College of the Redwoods 2012-2013 Copyright All parts of this prealgebra textbook are copyrighted c 2009 in the name
Prealgebra Textbook Second Edition Chapter 6 Odd Solutions Department of Mathematics College of the Redwoods 2012-2013 Copyright All parts of this prealgebra textbook are copyrighted c 2009 in the name
Level 1 - Maths Targets TARGETS. With support, I can show my work using objects or pictures 12. I can order numbers to 10 3
 Ma Data Hling: Interpreting Processing representing Ma Shape, space measures: position shape Written Mental method s Operations relationship s between them Fractio ns Number s the Ma1 Using Str Levels
Ma Data Hling: Interpreting Processing representing Ma Shape, space measures: position shape Written Mental method s Operations relationship s between them Fractio ns Number s the Ma1 Using Str Levels
Arithmetic 1 Progress Ladder
 Arithmetic 1 Progress Ladder Maths Makes Sense Foundation End-of-year objectives page 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 2 End-of-block objectives page 3 Maths Makes Sense 3 4 End-of-block objectives page 4 Maths Makes
Arithmetic 1 Progress Ladder Maths Makes Sense Foundation End-of-year objectives page 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 2 End-of-block objectives page 3 Maths Makes Sense 3 4 End-of-block objectives page 4 Maths Makes
1) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-1) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-1)(2) =
 Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
1A: Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems.
 NCTM STANDARD 1: Numbers and Operations Kindergarten Grade 2 1A: Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems. Kindergarten Grade One Grade Two 1. Count
NCTM STANDARD 1: Numbers and Operations Kindergarten Grade 2 1A: Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems. Kindergarten Grade One Grade Two 1. Count
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS
 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS Compiled by Dewey Gottlieb, Hawaii Department of Education June 2010 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS Compiled by Dewey Gottlieb, Hawaii Department of Education June 2010 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving
Metric Conversion: Stair-Step Method
 ntroduction to Conceptual Physics Metric Conversion: Stair-Step Method Kilo- 1000 Hecto- 100 Deka- 10 Base Unit grams liters meters The Metric System of measurement is based on multiples of 10. Prefixes
ntroduction to Conceptual Physics Metric Conversion: Stair-Step Method Kilo- 1000 Hecto- 100 Deka- 10 Base Unit grams liters meters The Metric System of measurement is based on multiples of 10. Prefixes
Year 3 Mental Arithmetic Test Questions
 Year 3 Mental Arithmetic Test Questions Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required
Year 3 Mental Arithmetic Test Questions Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required
DECIMAL COMPETENCY PACKET
 DECIMAL COMPETENCY PACKET Developed by: Nancy Tufo Revised: Sharyn Sweeney 2004 Student Support Center North Shore Community College 2 In this booklet arithmetic operations involving decimal numbers are
DECIMAL COMPETENCY PACKET Developed by: Nancy Tufo Revised: Sharyn Sweeney 2004 Student Support Center North Shore Community College 2 In this booklet arithmetic operations involving decimal numbers are
The Crescent Primary School Calculation Policy
 The Crescent Primary School Calculation Policy Examples of calculation methods for each year group and the progression between each method. January 2015 Our Calculation Policy This calculation policy has
The Crescent Primary School Calculation Policy Examples of calculation methods for each year group and the progression between each method. January 2015 Our Calculation Policy This calculation policy has
SQUARE-SQUARE ROOT AND CUBE-CUBE ROOT
 UNIT 3 SQUAREQUARE AND CUBEUBE (A) Main Concepts and Results A natural number is called a perfect square if it is the square of some natural number. i.e., if m = n 2, then m is a perfect square where m
UNIT 3 SQUAREQUARE AND CUBEUBE (A) Main Concepts and Results A natural number is called a perfect square if it is the square of some natural number. i.e., if m = n 2, then m is a perfect square where m
Prentice Hall Mathematics: Course 1 2008 Correlated to: Arizona Academic Standards for Mathematics (Grades 6)
 PO 1. Express fractions as ratios, comparing two whole numbers (e.g., ¾ is equivalent to 3:4 and 3 to 4). Strand 1: Number Sense and Operations Every student should understand and use all concepts and
PO 1. Express fractions as ratios, comparing two whole numbers (e.g., ¾ is equivalent to 3:4 and 3 to 4). Strand 1: Number Sense and Operations Every student should understand and use all concepts and
Grade 5 Mathematics Curriculum Guideline Scott Foresman - Addison Wesley 2008. Chapter 1: Place, Value, Adding, and Subtracting
 Grade 5 Math Pacing Guide Page 1 of 9 Grade 5 Mathematics Curriculum Guideline Scott Foresman - Addison Wesley 2008 Test Preparation Timeline Recommendation: September - November Chapters 1-5 December
Grade 5 Math Pacing Guide Page 1 of 9 Grade 5 Mathematics Curriculum Guideline Scott Foresman - Addison Wesley 2008 Test Preparation Timeline Recommendation: September - November Chapters 1-5 December
1st Grade Math Standard I Rubric. Number Sense. Score 4 Students show proficiency with numbers beyond 100.
 1st Grade Math Standard I Rubric Number Sense Students show proficiency with numbers beyond 100. Students will demonstrate an understanding of number sense by: --counting, reading, and writing whole numbers
1st Grade Math Standard I Rubric Number Sense Students show proficiency with numbers beyond 100. Students will demonstrate an understanding of number sense by: --counting, reading, and writing whole numbers
Metric Units of Length
 7.2 Metric Units of Length 7.2 OBJECTIVES. Know the meaning of metric prefixes 2. Estimate metric units of length 3. Convert metric units of length NOTE Even in the United States, the metric system is
7.2 Metric Units of Length 7.2 OBJECTIVES. Know the meaning of metric prefixes 2. Estimate metric units of length 3. Convert metric units of length NOTE Even in the United States, the metric system is
Convert between units of area and determine the scale factor of two similar figures.
 CHAPTER 5 Units of Area c GOAL Convert between units of area and determine the scale factor of two. You will need a ruler centimetre grid paper a protractor a calculator Learn about the Math The area of
CHAPTER 5 Units of Area c GOAL Convert between units of area and determine the scale factor of two. You will need a ruler centimetre grid paper a protractor a calculator Learn about the Math The area of
CAMI Education linked to CAPS: Mathematics
 - 1 - TOPIC 1.1 Whole numbers _CAPS curriculum TERM 1 CONTENT Mental calculations Revise: Multiplication of whole numbers to at least 12 12 Ordering and comparing whole numbers Revise prime numbers to
- 1 - TOPIC 1.1 Whole numbers _CAPS curriculum TERM 1 CONTENT Mental calculations Revise: Multiplication of whole numbers to at least 12 12 Ordering and comparing whole numbers Revise prime numbers to
Decimals and Percentages
 Decimals and Percentages Specimen Worksheets for Selected Aspects Paul Harling b recognise the number relationship between coordinates in the first quadrant of related points Key Stage 2 (AT2) on a line
Decimals and Percentages Specimen Worksheets for Selected Aspects Paul Harling b recognise the number relationship between coordinates in the first quadrant of related points Key Stage 2 (AT2) on a line
CONNECT: Currency, Conversions, Rates
 CONNECT: Currency, Conversions, Rates CHANGING FROM ONE TO THE OTHER Money! Finances! $ We want to be able to calculate how much we are going to get for our Australian dollars (AUD) when we go overseas,
CONNECT: Currency, Conversions, Rates CHANGING FROM ONE TO THE OTHER Money! Finances! $ We want to be able to calculate how much we are going to get for our Australian dollars (AUD) when we go overseas,
Parts and Wholes. In a tangram. 2 small triangles (S) cover a medium triangle (M) 2 small triangles (S) cover a square (SQ)
 Parts and Wholes. L P S SQ M In a tangram small triangles (S) cover a medium triangle (M) small triangles (S) cover a square (SQ) L S small triangles (S) cover a parallelogram (P) small triangles (S) cover
Parts and Wholes. L P S SQ M In a tangram small triangles (S) cover a medium triangle (M) small triangles (S) cover a square (SQ) L S small triangles (S) cover a parallelogram (P) small triangles (S) cover
Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: June 29, 2011
 Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: June 29, 2011 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State Board of Education,
Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: June 29, 2011 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State Board of Education,
MOST COMMON METRIC UNITS USED IN THE MEDICAL FIELD *BASE. deci. King Henry Died (from a) Disease Called Mumps. (k) (h) (da) gram (g) (d) (c) (m)
 MOST COMMON METRIC UNITS USED IN THE MEDICAL FIELD Micro (mc) microgram 0 6 One millionth 0.00000 Milli (m) milligram milliliter* millimeter 0 3 One thousandth 0.00 Centi (c) centimeter 0 2 One hundredth
MOST COMMON METRIC UNITS USED IN THE MEDICAL FIELD Micro (mc) microgram 0 6 One millionth 0.00000 Milli (m) milligram milliliter* millimeter 0 3 One thousandth 0.00 Centi (c) centimeter 0 2 One hundredth
Decimals and other fractions
 Chapter 2 Decimals and other fractions How to deal with the bits and pieces When drugs come from the manufacturer they are in doses to suit most adult patients. However, many of your patients will be very
Chapter 2 Decimals and other fractions How to deal with the bits and pieces When drugs come from the manufacturer they are in doses to suit most adult patients. However, many of your patients will be very
Revision Notes Adult Numeracy Level 2
 Revision Notes Adult Numeracy Level 2 Place Value The use of place value from earlier levels applies but is extended to all sizes of numbers. The values of columns are: Millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands
Revision Notes Adult Numeracy Level 2 Place Value The use of place value from earlier levels applies but is extended to all sizes of numbers. The values of columns are: Millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands
north seattle community college
 INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS If we divide a whole number into equal parts we get a fraction: For example, this circle is divided into quarters. Three quarters, or, of the circle is shaded. DEFINITIONS: The
INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS If we divide a whole number into equal parts we get a fraction: For example, this circle is divided into quarters. Three quarters, or, of the circle is shaded. DEFINITIONS: The
YOU MUST BE ABLE TO DO THE FOLLOWING PROBLEMS WITHOUT A CALCULATOR!
 DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - DECIMALS AND WHOLE NUMBERS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to ingrid.stewart@csn.edu. Thank you! YOU MUST
DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - DECIMALS AND WHOLE NUMBERS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to ingrid.stewart@csn.edu. Thank you! YOU MUST
REVIEW SHEETS BASIC MATHEMATICS MATH 010
 REVIEW SHEETS BASIC MATHEMATICS MATH 010 A Summary of Concepts Needed to be Successful in Mathematics The following sheets list the key concepts that are taught in the specified math course. The sheets
REVIEW SHEETS BASIC MATHEMATICS MATH 010 A Summary of Concepts Needed to be Successful in Mathematics The following sheets list the key concepts that are taught in the specified math course. The sheets
Math 5th grade. Create your own number and explain how to use expanded form to show place value to the ten millions place.
 Number Properties and Operations Whole number sense and addition and subtraction are key concepts and skills developed in early childhood. Students build on their number sense and counting sense to develop
Number Properties and Operations Whole number sense and addition and subtraction are key concepts and skills developed in early childhood. Students build on their number sense and counting sense to develop
The gas can has a capacity of 4.17 gallons and weighs 3.4 pounds.
 hundred million$ ten------ million$ million$ 00,000,000 0,000,000,000,000 00,000 0,000,000 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Session 26 Decimal Fractions Explain the meaning of the values stated in the following sentence.
hundred million$ ten------ million$ million$ 00,000,000 0,000,000,000,000 00,000 0,000,000 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Session 26 Decimal Fractions Explain the meaning of the values stated in the following sentence.
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide Grade 5 2012 2013. First Nine Weeks
 First Nine Weeks s The value of a digit is based on its place value. What changes the value of a digit? 5.NBT.1 RECOGNIZE that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much
First Nine Weeks s The value of a digit is based on its place value. What changes the value of a digit? 5.NBT.1 RECOGNIZE that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much
MEASUREMENT. Historical records indicate that the first units of length were based on people s hands, feet and arms. The measurements were:
 MEASUREMENT Introduction: People created systems of measurement to address practical problems such as finding the distance between two places, finding the length, width or height of a building, finding
MEASUREMENT Introduction: People created systems of measurement to address practical problems such as finding the distance between two places, finding the length, width or height of a building, finding
-- Martensdale-St. Marys Community School Math Curriculum
 -- Martensdale-St. Marys Community School Standard 1: Students can understand and apply a variety of math concepts. Benchmark; The student will: A. Understand and apply number properties and operations.
-- Martensdale-St. Marys Community School Standard 1: Students can understand and apply a variety of math concepts. Benchmark; The student will: A. Understand and apply number properties and operations.
The symbols indicate where the topic is first introduced or specifically addressed.
 ingapore Math Inc. cope and equence U: U.. Edition : ommon ore Edition : tandards Edition : ommon ore tandards 1 2 3 4 5 Reviews in ommon ore Edition cover just the unit whereas those in U.. and tandards
ingapore Math Inc. cope and equence U: U.. Edition : ommon ore Edition : tandards Edition : ommon ore tandards 1 2 3 4 5 Reviews in ommon ore Edition cover just the unit whereas those in U.. and tandards
Questions. Strategies August/September Number Theory. What is meant by a number being evenly divisible by another number?
 Content Skills Essential August/September Number Theory Identify factors List multiples of whole numbers Classify prime and composite numbers Analyze the rules of divisibility What is meant by a number
Content Skills Essential August/September Number Theory Identify factors List multiples of whole numbers Classify prime and composite numbers Analyze the rules of divisibility What is meant by a number
Number Sense and Operations
 Number Sense and Operations representing as they: 6.N.1 6.N.2 6.N.3 6.N.4 6.N.5 6.N.6 6.N.7 6.N.8 6.N.9 6.N.10 6.N.11 6.N.12 6.N.13. 6.N.14 6.N.15 Demonstrate an understanding of positive integer exponents
Number Sense and Operations representing as they: 6.N.1 6.N.2 6.N.3 6.N.4 6.N.5 6.N.6 6.N.7 6.N.8 6.N.9 6.N.10 6.N.11 6.N.12 6.N.13. 6.N.14 6.N.15 Demonstrate an understanding of positive integer exponents
Measurement with Reasoning
 compare, describe and solve practical problems for: * lengths and heights [e.g. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half] * mass/weight [e.g. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than] * capacity
compare, describe and solve practical problems for: * lengths and heights [e.g. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half] * mass/weight [e.g. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than] * capacity
Mathematics standards
 Mathematics standards Grade 6 Summary of students performance by the end of Grade 6 Reasoning and problem solving Students represent and interpret routine and non-routine mathematical problems in a range
Mathematics standards Grade 6 Summary of students performance by the end of Grade 6 Reasoning and problem solving Students represent and interpret routine and non-routine mathematical problems in a range
2nd Grade Math Common Core Curriculum
 Quarter 1 I. Number 2.1.2.B.1 To allow for refinement of curricular content and to guide the creation of quality aligned assessments, the Objectives column is intentionally incomplete. The District s Curriculum
Quarter 1 I. Number 2.1.2.B.1 To allow for refinement of curricular content and to guide the creation of quality aligned assessments, the Objectives column is intentionally incomplete. The District s Curriculum
1 st Grade Math Do-Anytime Activities
 1 st Grade Have your child help create a number line (0-15) outside with sidewalk chalk. Call out a number and have your child jump on that number. Make up directions such as Hop to the number that is
1 st Grade Have your child help create a number line (0-15) outside with sidewalk chalk. Call out a number and have your child jump on that number. Make up directions such as Hop to the number that is
SAMPLE TEST PAPER-1 COMMON APTITUDE TEST (CAT) 2012
 SAMPLE TEST PAPER-1 COMMON APTITUDE TEST (CAT) 2012 CLASS V MATHS Q1. Tick ( ) the correct answer (1.) The sum of place values of 9 and 1 in 479810 is (a.) 9010 (b.) 9001 (c.) 9100 (d.) 1900 (2.) The number
SAMPLE TEST PAPER-1 COMMON APTITUDE TEST (CAT) 2012 CLASS V MATHS Q1. Tick ( ) the correct answer (1.) The sum of place values of 9 and 1 in 479810 is (a.) 9010 (b.) 9001 (c.) 9100 (d.) 1900 (2.) The number
The National Curriculum 2014 Programmes of Study for Mathematics
 The National Curriculum 2014 Programmes of Study for Mathematics Information inserted by the Lancashire Mathematics Team to support schools and teachers in identifying elements of the curriculum that have
The National Curriculum 2014 Programmes of Study for Mathematics Information inserted by the Lancashire Mathematics Team to support schools and teachers in identifying elements of the curriculum that have
