Accounts Receivable (A/R) Management The objective of this chapter is to provide an overview of
|
|
|
- Leona Charles
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 69 Section One: Section Title Chapter 6 Accounts Receivable (A/R) Management The objective of this chapter is to provide an overview of patient account transactions and accounts receivable management. Hospitals provide services to patients for treatment of conditions utilizing highly specialized equipment and personnel. It is critical for hospitals to maintain an efficient cash flow by obtaining timely compensation for resources utilized in order to provide services in the hospital environment. Claim forms and patient statements are prepared to bill for services rendered on an outpatient and inpatient basis. Once the claim is submitted or patient statement is sent, the hospital must monitor outstanding accounts to ensure that payment is received within an appropriate time frame. This function is critical to maintaining a positive cash flow for the hospital. This chapter provides a brief overview of the life cycle of a hospital claim. A discussion of the payer s review of a claim and the remittance advice will provide an understanding of communications from the payer regarding a claim. Payer determinations are reviewed to provide an overview of issues handled by the Patient Financial Services and the Credit and Collection Departments. The chapter will close with a discussion of accounts receivable follow-up and the appeals process to provide a greater understanding of aspects involved in managing accounts receivable. Chapter Objectives Define terms, phrases, abbreviations, and acronyms related to patient account transactions and accounts receivable follow-up. Demonstrate an understanding of the life cycle of a hospital claim. Discuss elements related to patient transactions. Provide an overview of key information found on an explanation of benefits or remittance advice. List common reasons for claim denials and delays. Demonstrate an understanding of A/R management. Provide an overview of the purpose and function of an accounts receivable report. Describe the process of monitoring and follow-up of outstanding accounts. Demonstrate an understanding of the appeals process. Outline Chapter 00: Chapter Title 69 LIFE CYCLE OF A HOSPITAL CLAIM HOSPITAL BILLING PROCESS Insurance Claims and Patient Statements Third-Party Payer (TPP) Claim Processing Remittance Advice (RA) PATIENT TRANSACTIONS Patient Payments Third-Party Payer Payments Adjustments Balance Billing Secondary Billing ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE (A/R) MANAGEMENT Accounts Receivable Reports Accounts Receivable Procedures LOST, REJECTED, DENIED, AND PENDED CLAIMS Lost Claim Rejected Claim Denied Claim Pended Claim COLLECTION ACTIVITIES Prioritizing Collection Activities Patient and Third-Party Follow-up Procedures Uncollectible Patient Accounts Insurance Commissioner Inquiries CREDIT AND COLLECTION LAWS Statute Of Limitations Fair Credit Billing Act Fair Debt Collection Practices Act OUTSTANDING PATIENT ACCOUNTS Patient Statements Patient Phone Contact Collection Letters OUTSTANDING THIRD-PARTY CLAIMS Prompt Pay Statutes Insurance Telephone Claim Inquiry Insurance Computer Claim Inquiry Insurance Claim Tracer THE APPEALS PROCESS Claim Determinations That Can Be Appealed Who Can Request an Appeal Time Requirement for Appeal Submission Levels of Appeals Appeal Submission Procedures 69
2 70 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process Key Terms Accounts receivable (A/R) Accounts receivable (A/R) aging report Accounts receivable ratio (A/R ratio) Adjustment Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN) Aging Appeal Balance billing Clean claim Contractual adjustment CMS-450 (UB-92) CMS-500 Days in accounts receivable (A/R) Denied claim Dun message Electronic remittance advice (ERA) Explanation of benefits (EOB) Fair Credit Billing Act Fair Debt Collection Practices Act Financial class Hospital Issued Notice of Noncoverage (HINN) Insurance claim tracer National Correct Coding Initiatives (CCI) Outstanding accounts Payer data files Pended claim Prompt pay statutes Rejected claim Remittance advice (RA) Statute of Limitations Unbundling Write-off Acronyms and Abbreviations ABN Advance Beneficiary Notice APC Ambulatory payment classifications A/R Accounts receivable CCI National Correct Coding Initiatives CMS Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services COB Coordination of benefits DRG Diagnosis Related Group EOB Explanation of Benefits EOMB Explanation of Medicare Benefits EMC Electronic media claim ERA Electronic remittance advice HIM Health Information Management HINN Hospital Issued Notice of Noncoverage MCE Medicare Code Editor OCE Outpatient Code Editor PFS Patient Financial Services RA Remittance advice TPP Third-party payer LIFE CYCLE OF A HOSPITAL CLAIM The life cycle of a hospital claim begins when the patient arrives at the hospital for diagnosis and treatment of a condition(s) and ends when the claim is paid, as illustrated in Figure 6-. As discussed in previous chapters, the Admissions Department is responsible for obtaining required demographic, financial, and insurnce information from the patient. Another function that is equally important is obtaining appropriate referrals and authorizations. Information obtained by the Admissions Department is entered into the computer on the patient s account. Patient care services are rendered and documented by various departments within the hospital, and charges are generated. Most charges are posted at the department level through the chargemaster during the patient stay (Figure 6-2). Charges posted through the chargemaster are automatically dropped to the claim and submitted after the patient is discharged. Generally the hospital does not submit a claim or send a patient statement for inpatient services until after the patient is discharged. On discharge, the Health Information Management (HIM) Department receives the patient s chart for review and coding. The HIM Department codes services, procedures, and items that were not posted Payer determination (denial or pended) Resubmit/appeal Accounts receivables (A/R) management Figure 6- Payer determination Reimbursement (payment processed) Patient presents for diagnosis and treatment of conditions. (Patient admission) Claim submission (CMS-450/ CMS-500) Life cycle of a hospital claim. Information referral/ authorization obtained at admission HIM chart review/ coding (APC/DRG assignment) Patient services rendered (documentation) Charge capture (chargemaster)
3 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 7 Chargemaster Number/ Department #/ General Ledger # 00/ /64 300/6 300/69 400/37 700/38 700/38 700/39 700/40 700/67 700/69 700/69 Community General Hospital Charge Description Master (CDM) Item/Service Description Room C532 Cefepime inj 2 G Tray hyperal dre ABD/KUB flatplat Oximeter Prothrombin time CBC with diff Blood culture Basic metabolic Dopp-venous lowe X-ray chest X-ray chest fluoroscopy Procedure/ Item Code HCPCS/ NDC and Modifier J0692 A S Revenue Code Quantity/ Dose 2 g Charge Figure 6-2 Charge Description Master (CDM), commonly referred to as the chargemaster. BOX 6- Life Cycle of a Hospital Claim Information obtained at admission Patient care services rendered and documented Charges captured through chargemaster HIM review, coding, and APC or DRG assignment Process and submit insurance claims and patient statements Payer review and determination remittance advice BOX 6-2 Hospital Encoder and GROUPER Programs An encoder program is computer software that allows the HIM professional to enter specified information regarding patient care services and the patient s condition. The program utilizes data entered to identify potential codes. A GROUPER program is software that allows the HIM professional to enter specified information regarding the patient s care including condition(s) and procedure(s). The program utilizes the information to assign an APC or DRG. Admission Registration Admitting department Patient care Order entry Ancillary/clinical departments Charge capture Charge Description Master (CDM) HCPCS Codes Department personnel Reimbursement Post transactions Patient Financial Services (PFS) Charge submission Patient invoice/ statement PFS Chart reviewing/coding Post discharge procedures Health Information Management (HIM) Reimbursement Paid PFS Reimbursement Denied PFS Collections Payer review Payment determination Third-party payers A/R Management Monitor and follow-up on outstanding claims PFS Credit and collections Charge submission Claims process Claim preparation (scrubber) Patient Financial Services (PFS) Claim submission CMS-500 CMS-450 manual/electronic Patient Financial Services (PFS) Figure 6-3 functions. Hospital billing process highlighting charge submission, payer review, A/R management, and reimbursement
4 72 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process through the chargemaster, such as surgeries. The patient s diagnoses are also coded by the HIM Department. Coding is generally performed through an encoder program, which utilizes information entered by the HIM coder to assign procedure and diagnosis codes. The codes and other information entered are also used to assign a Diagnosis Related Group (DRG) or ambulatory payment classification (APC) to the hospital case. HOSPITAL BILLING PROCESS As discussed in previous chapters, the hospital billing process involves a series of functions required to submit charges for services rendered. The process involves collection of all financial, insurance, and medical information during the patient visit. Information obtained during the patient visit is utilized to submit charges to payers and patients. A critical part of the billing process is charge submission, which involves preparation of insurance claims and patient statements (Figure 6-3). BOX 6-3 Hospital Billing Process Patient admission Patient care Charge capture Chart review/coding Charge submission A/R management Payer processing and payment determination Insurance Claims and Patient Statements Patient Financial Services (PFS) may also be referred to as the Business Office or the Patient Accounts Department. PFS is responsible for managing the hospital s patient financial transactions, which include charge submission, patient transactions, and accounts receivable (A/R) management. Charge submission involves preparation of insurance claims and patient statements (Figure 6-4). Board of Directors Administration Finance Operations Clinical Human Resources Accounting Support Services Quality assurance Medical/ attending staff Other clinical services Volunteer Services Marketing Public Relations Purchasing Legal Services Compliance Admitting Patient Financial Services (PFS) Credit and Collections Plant Operations Grounds and maintenance Satellite Development Outpatient clinics Risk Management Utilization Management (Utilization review) Nursing in various areas Medical Surgical Unit, Labor/ Delivery, OR, ER Ancillary Services Pharmacy Surgery Medicine Anesthesia Medical staff Central credentialing supply Pathology/ Pulmonary laboratory Finance Social Departments Responsibilities services Cardiology Record, monitor, and analyze financial transactions Radiology and prepare reports as required. Health Perform tasks to receive Emergency information a patient in the hospital including: obtain and enter information Physical department management in the computer, obtain consents and authorizations, prepare a chart, assign a room and bed, where rehabilitation appropriate. Prepare claim forms and patient statements for charge submission. Record charges, payments, adjustments, and write-offs. Provide assistance to patients in understanding Respiratory their account and therapy resolving billing issues. Monitor and follow-up on accounts receivables. Figure 6-4 Hospital organizational chart illustrating the finance departments and their responsibilities.
5 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 73 BOX 6-4 BOX 6-5 Patient Financial Services (PFS) Responsibilities Charge Submission Insurance claim forms Patient statements Patient Transactions Payments, adjustments, and write-offs Accounts Receivable (A/R) Management Monitoring of and follow-up on outstanding accounts Insurance Claim Forms A claim form is prepared for submission of charges to a third-party payer. The goal is to submit a clean claim the first time. A clean claim is defined as one that does not need to be investigated by the payer. The claim passes all internal billing edits and payer-specific edits and is paid without need for additional intervention. Claims that do not meet clean claim status may be denied, rejected, or pended. Preparation of insurance claim forms involves the following steps: A detailed itemized statement that outlines each item and service charged is prepared (Figure 6-5). The appropriate claim form is prepared. As discussed previously, claim form requirements vary by payer. Community General Hospital TAX ID # South Street Mars, Florida (747) Clean Claim A claim that does not require further investigation by the payer. The claim passes all of the edits and is processed accordingly without any additional intervention. BOX 6-6 Clean Claim Status Examples of claims that do not meet clean claim status. Claims that require additional information Claims that require Medicare secondary payer (MSP) screening information Claims that require information to determine coverage Claims that do not pass payer edits BOX 6-7 Universally Accepted Claim Forms and Means of Submission Claim Form CMS-500 is the form utilized to submit physician and outpatient services CMS-450 (UB-92) is the form utilized to submit facility charges for hospitals and other institutions Methods for Submission Manual submission involves printing a paper claim that is sent by mail Electronic claims are submitted utilizing electronic data interchange (EDI) Detailed Itemized Statement Patient no: Med rec no: Patient: Smith, John Bill to: Smith, John th Street Date of Service /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /28/2006 /28/2006 /28/2006 /28/2006 /28/2006 /28/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 Chargemaster # Bill date 2//06 Page Admit date /27/06 Discharged /28/06 Bill type: Admit through discharge Insurance: BC/BS P.O. Box 7272, Tampa, FL Dept Revenue Qty/ Total # Code HCPCS Description Dose Charges Vistaril mg inj Docusate sodium J3590 J0 J275 J2250 Q079 J Cepacol loz Diphenhydramine HCL Demerol Versed mg/ml Zofran vial (inj) 2 mg Percocet Mini synder hemovac (JP) PA surgical profile PA liver profile P-gross & micro, diag sm XR fluro C-arm initial OR time group VI Anesthesia R-time recovery rm Figure 6-5 Detailed itemized statement. The universally accepted claim form for submission of charges for physician and outpatient services is the CMS-500 (Figure 6-6).The CMS-450 (UB-92) is the universally accepted claim used to submit facility charges for hospital outpatient and inpatient services (Figure 6-7). The claim forms are submitted to respective payers electronically or manually. Claim forms submitted electronically are referred to as electronic media claims (EMCs). Manual claims are printed on paper and mailed. A detailed itemized statement is generally included with paper claims. Payers receiving electronic claims may request a detailed itemized statement after initial review of the claim. Copies of insurance claims are filed for follow-up. Patient Statements Patient statements are generated and sent to the patient. The hospital generally has a schedule for batch
6 74 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process PLEASE DO NOT STAPLE IN THIS AREA CITY PICA. MEDICARE MEDICAID CHAMPUS CHAMPVA GROUP FECA OTHER HEALTH PLAN BLK LUNG (Medicare #) (Medicaid #) (Sponsor s SSN) (VA File #) (SSN or ID) (SSN) (ID) 2. PATIENT S NAME (Last Name, First Name, Middle Initial) 3. PATIENT S BIRTH DATE SEX MM DD YY M F 5. PATIENT S ADDRESS (No., Street) 6. PATIENT RELATIONSHIP TO INSURED Self Spouse Child Other ZIP CODE TELEPHONE (Include Area Code) 9. OTHER INSURED S NAME (Last Name, First Name, Middle Initial) a. OTHER INSURED S POLICY OR GROUP NUMBER b. OTHER INSURED S DATE OF BIRTH MM DD YY c. EMPLOYER S NAME OR SCHOOL NAME d. INSURANCE PLAN NAME OR PROGRAM NAME F READ BACK OF FORM BEFORE COMPLETING & SIGNING THIS FORM. 2. PATIENT S OR AUTHORIZED PERSON S SIGNATURE I authorize the release of any medical or other information necessary to process this claim. I also request payment of government benefits either to myself or to the party who accepts assignment below. SIGNED DATE 4. DATE OF CURRENT: MM DD YY ILLNESS (First symptom) OR INJURY (Accident) OR PREGNANCY(LMP) 7. NAME OF REFERRING PHYSICIAN OR OTHER SOURCE 9. RESERVED FOR LOCAL USE ( ) M SEX STATE 5. IF PATIENT HAS HAD SAME OR SIMILAR ILLNESS. GIVE FIRST DATE MM DD YY 7a. I.D. NUMBER OF REFERRING PHYSICIAN 2. DIAGNOSIS OR NATURE OF ILLNESS OR INJURY. (RELATE ITEMS,2,3 OR 4 TO ITEM 24E BY LINE) 8. PATIENT STATUS HEALTH INSURANCE CLAIM FORM Student Student Single Married Other Employed Full-Time Part-Time 0. IS PATIENT S CONDITION RELATED TO: a. EMPLOYMENT? (CURRENT OR PREVIOUS) b. AUTO ACCIDENT? c. OTHER ACCIDENT? YES NO YES NO YES NO 0d. RESERVED FOR LOCAL USE PLACE (State) EXAMPLE ONLY a. INSURED S I.D. NUMBER (FOR PROGRAM IN ITEM ) 4. INSURED S NAME (Last Name, First Name, Middle Initial) 7. INSURED S ADDRESS (No., Street) CITY STATE ZIP CODE TELEPHONE (INCLUDE AREA CODE). INSURED S POLICY GROUP OR FECA NUMBER a. INSURED S DATE OF BIRTH MM DD YY b. EMPLOYER S NAME OR SCHOOL NAME c. INSURANCE PLAN NAME OR PROGRAM NAME d. IS THERE ANOTHER HEALTH BENEFIT PLAN? SEX 3. INSURED S OR AUTHORIZED PERSON S SIGNATURE I authorize payment of medical benefits to the undersigned physician or supplier for services described below. SIGNED 6. DATES PATIENT UNABLE TO WORK IN CURRENT OCCUPATION MM DD YY MM DD YY FROM TO 8. HOSPITALIZATION DATES RELATED TO CURRENT SERVICES MM DD YY MM DD YY FROM TO 22. MEDICAID RESUBMISSION CODE ORIGINAL REF. NO. PICA If yes, return to and complete item 9 a-d. 20. OUTSIDE LAB? $ CHARGES YES YES NO NO ( ) M F CARRIER PATIENT AND INSURED INFORMATION PRIOR AUTHORIZATION NUMBER A B C D E DATE(S) OF SERVICE Place Type PROCEDURES, SERVICES, OR SUPPLIES From To DIAGNOSIS of of (Explain Unusual Circumstances) CODE MM DD YY MM DD YY Service Service CPT/HCPCS MODIFIER 25. FEDERAL TAX I.D. NUMBER SSN EIN 26. PATIENT S ACCOUNT NO. 27. ACCEPT ASSIGNMENT? (For govt. claims, see back) 3. SIGNATURE OF PHYSICIAN OR SUPPLIER INCLUDING DEGREES OR CREDENTIALS (I certify that the statements on the reverse apply to this bill and are made a part thereof.) SIGNED DATE (APPROVED BY AMA COUNCIL ON MEDICAL SERVICE 8/88) YES 32. NAME AND ADDRESS OF FACILITY WHERE SERVICES WERE RENDERED (If other than home or office) PLEASE PRINT OR TYPE NO F G H I J K DAYS EPSDT OR Family RESERVED FOR $ CHARGES EMG COB LOCAL USE UNITS Plan 28. TOTAL CHARGE 29. AMOUNT PAID 30. BALANCE DUE $ $ $ 33. PHYSICIAN S, SUPPLIER S BILLING NAME, ADDRESS, ZIP CODE & PHONE # PIN# GRP# APPROVED OMB FORM CMS-500 (2-90), FORM RRB-500, APPROVED OMB FORM OWCP-500, APPROVED OMB (CHAMPUS) PHYSICIAN OR SUPPLIER INFORMATION Figure 6-6 CMS-500 claim form utilized to submit charges for physician and outpatient services. mailings of patient statements. For example, the hospital s batch schedule may indicate that statements for patient accounts A to M should be mailed on Mondays and Wednesdays and N to Z on Tuesdays and Thursdays. Patient statements include the following information, as illustrated in Figure 6-8. Patient name, address, account number, and medical record number Admission and discharge date Description of services, including a procedure code and charge for each Payments and adjustments made on the account, listed along with the balance owed Message regarding outstanding balance or claim submission Third-Party Payer (TPP) Claim Processing Third-party payer claim processing involves entering claim data into the payer s system, review of the payer s data file, performance of payer edits, and payment determination (Figure 6-9). Insurance claims can be transmitted electronically or sent by mail. Electronic claims are transmitted directly to the payer s computer system. Paper claims are scanned or entered manually into the payer s computer system. The payer s computer system performs a detailed review and electronic edits on each claim. The computerized review and edits are preformed to check information on the claim for the purpose of identifying potential problems with the claim. First, the computer checks information on the claim
7 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 75 ST843PLYUB-92 2 PATIENT NAME 2 3 PATIENT ADDRESS 3 PATIENT CONTROL NO. 5 FED. TAX NO. 6 STATEMENT COVERS PERIOD FROM THROUGH 7 COV D. 8 N-O D. 9 C-I D. 0L-R.D. APPROVED OMB NO TYPE OF BILL 4 BIRTHDATE 5 SEX 6 MS ADMISSION 8 HR 2 D HR 22 STAT 23 MEDICAL RECORD NO. CONDITION CODES DATE 9 TYPE 20 SRC OCCURRENCE 33 OCCURRENCE 34 OCCURRENCE 35 OCCURRENCE 36 OCCURRENCE SPAN 37 CODE DATE CODE DATE CODE DATE CODE DATE CODE FROM THROUGH A a B b C VALUE CODES 40 VALUE CODES 4 VALUE CODES CODE AMOUNT CODE AMOUNT CODE AMOUNT a b c d 42 REV. CD. 43 DESCRIPTION 44 HCPCS/RATES 45 SERV. DATE 46 SERV. UNITS 47 TOTAL CHARGES 48 NON-COVERED CHARGES REL 53 ASG 50 PAYER 5 PROVIDER NO. INFO BEN 54 PRIOR PAYMENTS 55 EST. AMOUNT DUE 56 A B C 57 DUE FROM PATIENT 58 INSURED S NAME 59 P.REL 60 CERT. SSN HIC. ID NO. 6 GROUP NAME 62 INSURANCE GROUP NO. A B C 63 TREATMENT AUTHORIZATION CODES 64 ESC 65 EMPLOYER NAME 66 EMPLOYER LOCATION A B C 67 PRIN. DIAG. CD. 79 P.C ATTENDING PHYS. ID PRINCIPAL PROCEDURE OTHER PROCEDURE OTHER PROCEDURE CODE CODE DATE CODE DATE DATE a 84 REMARKS b c d C 68 CODE OTHER PROCEDURE CODE DATE 69 CODE 70 CODE 7 CODE 72 CODE 73 CODE 74 CODE 75 CODE A D OTHER PROCEDURE CODE DATE B E OTHER PROCEDURE CODE DATE 83 OTHER PHYS. ID 85 PROVIDER REPRESENTATIVE UB-92 HCFA-450 OCR/ORIGINAL I CERTIFY THE CERTIFICATIONS ON THE REVERSE APPLY TO THIS BILL AND ARE MADE A PART HEREOF. X OTHER PHYS. ID 76 ADM. DIAG. CD. 77 E-CODE 78 A B 86 DATE A B C a b c d A B C A B C a b a b Figure 6-7 CMS-450 (UB-92) claim form utilized to submit facility charges for hospital services. BOX 6-8 Third-Party Payer Claim Processing Claim data entered into payer system Review of claim information Payer edits Payment determination against the payer s data files to verify patient coverage and eligibility. Payer s Data File The computerized payer data files contain information regarding covered individuals, including a history of past claims submitted for the patient. Information submitted on the claim regarding the patient, the insurance, and the services billed is compared with information in the payer s data files to verify that the patient is covered under the plan, is eligible to receive benefits, and that all plan requirements are met. The following data are checked against the payer s data file: Patient name and identification number are checked to confirm that the patient is covered under the policy The date of service is checked to ensure that the services were provided within the benefit period and that the patient is eligible to receive benefits Preauthorization information is reviewed to ensure that plan requirements are met Dates of admission and discharge are checked against the plan coverage details to ensure that length of stay is appropriate
8 76 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process Patient no: Med rec no: Patient: Smith, John Bill to: Smith, John th Street Community General Hospital TAX ID # South Street Mars, Florida (747) Patient Statement Bill date 2//06 Page Admit date /27/06 Discharged /27/06 BOX 6-9 Payer Data Files Patient coverage is active. Services were provided within coverage period and the patient is eligible to receive benefits. Preauthorization requirements are met. Length of stay is within plan criteria. Services provided are covered and not duplicated. Date of Service Description Total /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 /27/2006 Laboratory Chemistry Immunology Hematology Bacteriology & microbiology Urinalysis/stool/body fluid TOTAL CHARGES BALANCE DUE $ $ Figure 6-8 Sample patient statement. Claim Data Entered into the payer s system Electronic claims transmitted directly into the payer s system Manual claims scanned or manually keyed into the payer s system Review Claim Information against the Payer s Data File to ensure Patient coverage is active Services were provided within coverage period patient eligible to receive benefits Preauthorization requirements are met Length of stay is within plan criteria Services provided are covered and not duplicate Payer Computerized Edits are performed to identify problems related to services billed including coding errors Procedures that are inappropriate based on gender Procedures that are inappropriate based on age Procedures that are not medically necessary Packaged services that are unbundled Payment Determination Determination of allowed charges APC or DRG rate Determination of deductible co-insurance or co-payment Remittance advice is prepared and forwarded to the hospital Figure 6-9 Phases of the third-party payer claims process. Procedure code data are reviewed to identify covered and noncovered items Services on the claim are also checked against the common data file to identify duplicate services Computer Edits The payer s system performs computerized edits on the claim for the purpose of identifying problems relating to services billed such as coding errors or issues involving medical necessity. Payer computer edits vary according to the payer s criteria and system setup. For example, Medicare s system contains an Outpatient Code Editor (OCE) and a Medicare Code Editor (MCE). The OCE Medicare Outpatient Code Editor (OCE) Coding Edits Inpatient only procedure Invalid diagnosis or procedure code Age conflict Sex conflict Correct coding initiative edits Coverage Edits Non-covered procedures Questionable covered procedure Clinical Edits Invalid age Invalid sex Claim Edits Invalid date Date out of range Units of service edits Observation edits Medicare Code Editor (MCE) Inpatient Coding Edits Invalid diagnosis or procedure code Invalid fourth or fifth digit for diagnosis codes E code used as a principal diagnosis Duplicate of the principal diagnosis Age conflict Sex conflict Manifestation code as principal diagnosis Nonspecific principal diagnosis Questionable admission Unacceptable principal diagnosis Coverage Edits Non-covered procedures Limited coverage Open biopsy Medicare secondary payer (MSP) alert Inpatient Clinical Edits Bilateral procedure Invalid age Invalid sex Invalid discharge status Figure 6-0 Medicare Outpatient Code Editor (OCE) and Medicare Code Editor (MCE) computer edits are incorporated into Medicare s system. OCE is for outpatient claims, and MCE is for inpatient claims.
9 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 77 BOX 6-0 BOX 6- Unbundling The process of coding multiple codes to describe services that are described with one code. For example, reporting the following laboratory codes for three tests that were performed on one specimen at the same time , Cholesterol 8378, Lipoprotein 84478, Triglycerides These tests should be reported as a Lipid Panel using CPT code National Correct Coding Initiatives (CCI) Developed by CMS for the purpose of promoting national coding guidelines and preventing improper coding. CCI outlines code combinations that are inappropriate, including services that are: Integral to a more comprehensive procedure Mutually exclusive Included in the surgical procedure Sequential procedures Bundled and MCE are used to identify data inconsistencies on hospital outpatient and inpatient claims. The OCE contains edits for hospital outpatient claims. The MCE contains edits for hospital inpatient claims (Figure 6-0). The following are examples of computer edits: Procedure conflicts with patient s sex. The procedure code is checked against the patient s sex to determine whether the procedure is appropriate. For example, a hysterectomy would not be performed on a male. Procedure conflict with patient s age. The procedure code is checked against the patient s age to verify that the procedure is age appropriate. For example, Symbol Symbol Symbol Symbol Symbol Symbol Symbol Comprehensive versus component code Misuse of column 2 with column Column Column J200 Most extensive procedure Mutually exclusive procedures CPT/HCPCS coding manual guideline CPT separate procedure definition CPT/HCPCS procedure code definitions Standards of medical/surgical practice G Figure 6- Examples of edits from the National Correct Coding Initiatives (CCI). a hysterectomy would not normally be performed on a 0-year-old. Medical necessity. All services and items provided must be considered medically necessary to obtain third-party reimbursement. Diagnosis codes are checked against procedure codes to identify problems involving medical necessity. Bundled (packaged) services. Services and items billed are reviewed to identify cases of unbundling. Unbundling is the process of coding multiple codes to describe services that should be described with one code. Many payers incorporate the National Correct Coding Initiatives edits into their system. The National Correct Coding Initiatives (CCI) was developed by CMS for the purpose of promoting national coding guidelines and preventing improper coding. CCI outlines code combinations that are inappropriate (Figure 6-). Payment Determination Determination of payment is conducted after the computer edits are performed. It includes the following steps: Determination of allowed charges, APC, or DRG rate Determination of deductible, co-insurance, or co-payment Preparation of a remittance advice or explanation of benefits, which is forwarded to the hospital Payment determination may result in one of the following actions: The claim is paid The claim is placed in a pending status (pending requested information) The claim is denied or rejected Remittance Advice (RA) A remittance advice (RA) is a document prepared by the payer to provide an explanation of payment
10 78 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process MEDICARE PART A P.O. BOX TEMPE AR TEL# VER# 400 A PROV #69542A PROVIDER NAME: Dr Martin Samerston PART A PAID DATE: 06/26/2006 REMIT#: 7654 PAGE: PATIENT NAME PATIENT CNTRL NUMBER ICN HIC NUMBER NUMBERNACHG HICHG TOB FROM DT THRU DT COST COVDY NCOVDY CLMSTATUS RC REM DRG# DRG OUT AMT COINSURANCE PAT REFUND CONTRACT ADJ RC REM OUTCD CAPCD NEW TECH COVDCHGS ESRD NET ADJ PER DIEM RTE Smith John A RC REM PROF COMP MSP PAYMT NCOVD CHGS INTEREST PROC CD AMT 00 RC REM DRG AMT DEDUCTIBLES DENIED CHGS PRE PAY ADJ NET REIMB 49 6,895.72, /0/ /05/ SUBTOTAL FISCAL YEAR-$000 SUBTOTAL PART A TOTAL PART A M M , , , FIgure 6-2 Sample Medicare RA illustrating data elements (page ). BOX 6-2 Payer Payment Determination Payment determination is conducted by the payer after the claim passes all computer edits and can result in one of the following actions. The claim payment is processed The claim is put in a pending status until requested information is received The claim is denied or rejected determination for a claim. The RA is also known by other payers as an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) or Explanation of Medicare Benefits (EOMB). The RA includes detailed information about the charges submitted and an explanation of how the claim was processed. An RA can include information regarding several claims. It can be forwarded to the hospital electronically or it can be printed and sent to the hospital by mail. An electronic remittance advice (ERA) is a document that is electronically transmitted to the hospital to provide an explanation of payment determination for a claim. Remittance Advice Data Elements The design and content of an RA will vary by payer. Most include basic data regarding the patient, service provided, charges submitted, and explanation of the payment determination. Figure 6-2 illustrates the following data elements listed on a sample Medicare remittance advice: Date of the remittance advice and check number Patient s name and identification number Name of provider performing services, if not the same as the hospital Claim control number a number given to the payer as a reference to the claim when the hospital inquires about a claim ICD-9-CM procedure or HCPCS codes and modifiers describing the billed services or items Explanation code or reason code that explains the claim processing, such as whether the claim is denied or reduced The amount of deductible the patient is responsible to meet The co-insurance amount the patient is responsible to pay The payment amount, which is the total amount paid for all claims outlined on the remittance advice MEDICARE PART A P.O. BOX TEMPE AR TEL# VER# 400 A PROV #69542A PROVIDER NAME: Dr Martin Samerston PART A PAID DATE: 06/26/2006 REMIT#: 7654 PAGE: PATIENT NAME PATIENT CNTRL NUMBER ICN HIC NUMBER NUMBERNACHG HICHG TOB FROM DT THRU DT COST COVDY NCOVDY CLMSTATUS RC REM DRG# DRG OUT AMT COINSURANCE PAT REFUND CONTRACT ADJ RC REM OUTCD CAPCD NEW TECH COVDCHGS ESRD NET ADJ PER DIEM RTE Smith John A RC REM PROF COMP MSP PAYMT NCOVD CHGS INTEREST PROC CD AMT 00 RC REM DRG AMT DEDUCTIBLES DENIED CHGS PRE PAY ADJ NET REIMB ,895.72, /0/ /05/ M M SUBTOTAL FISCAL YEAR-$ , , SUBTOTAL PART A , TOTAL PART A 7 FIgure 6-3 Sample Medicare RA (page ) illustrating the steps ( through 8) in analyzing a remittance advice.
11 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 79 BOX 6- LIFE CYCLE OF A HOSPITAL CLAIM: THIRD-PARTY PAYER CLAIM PROCESSING. Explain when the life cycle of a hospital claim begins. 2. Discuss the relationship between information obtained by the Admissions Department and the preparation of a claim form. 3. List the steps involved in processing a hospital claim form. 4. State what claim form(s) is used to submit facility charges for hospital outpatient and inpatient services. 5. Provide a brief overview of data found on a patient statement. 6. Discuss the purpose of checking claim information against the payer s common data file. 7. Explain the two types of review performed on a claim by the payer s computer system. 8. Explain the difference among the Medicare Code Editor (MCE), the Outpatient Code Editor (OCE), and the National Correct Coding Initiatives (CCI). 9. State what items on the claim are checked to determine medical necessity. 0. List and discuss three steps in payment determination. BOX 6-3 Electronic Remittance Advice (ERA) A document prepared by the payer to provide an explanation of payment determination for a claim. Also referred to as the following. Explanation of Benefits (EOB) Explanation of Medicare Benefits (EOMB) Analyzing a Remittance Advice It is important for hospital billing professionals to understand the elements of an RA. Information on the RA is carefully analyzed to ensure that the claim was processed appropriately. This task is complicated by the fact that each payer may adopt a different type of form. Information on the RA is used to post payments to the patient s account. An RA may be several pages long, and it may contain information regarding several patients and several claims (Figures 6-3 and 6-4). Following is an overview of how to analyze the RA.. Identify the patient s name and number for the purpose of opening the correct patient account on the computer system. 2. Match the date of service on the RA to the date of service on the patient s account. 3. Compare the procedure code indicated on the RA with that listed on the patient s account to ensure that the claim was paid based on the correct service.
12 80 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process MEDICARE PART A PROV #69542A PROVIDER NAME: Dr. Martin Samerston SUMMARY CLAIM DATA: DAYS COST 0 COVDY 3 NCOVDY 0 CHARGES COVD.00 NCOVD, DENIED.00 PROF COMP.00 MSP PAYMT.00 DEDUCTIBLES COINSURANCE.00 PAT REFUND.00 INTEREST.00 CONTRACT ADJ, PROC CD , NET REIMB 4, M45 M38 PASS THRU AMOUNTS: CAPITAL.00 RETURN ON EQUITY DIRECT.00 MEDICAL EDUCATION KIDNEY.00 ACQUISITION BAD DEBT.00 NON PHYSICIAN ANESTHETISTS.00 TOTAL PASS THRU PIP PAYMENT SETTLEMENT PAYMENTS.00 ACCELERATED.00 PAYMENTS REFUNDS.00 PENALTY RELEASE.00 TRANS OUTP PYMT.00 HEMOPHILIA ADD-ON.00 NEW TECH ADD-ON WITHHOLD FROM PAYMENTS CLAIMS ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE ACCELERATED PAYMENTS.00 PENALTY.00 SETTLEMENT.00 TOTAL WITHHOLD Missing/incomplete/invalid occurrence code(s) Patient identified as a demonstration participant, coverage limited. PROVIDER PAYMENT RECAP PAYMENTS DRG OUT AMT 6, INTEREST.00 PROC CD AMT 6, NET REIMB.00 TOTAL PASS THRU.00 PIP PAYMENTS.00 SETTLEMENT PYMTS.00 ACCELERATED.00 PAYMENTS.00 REFUNDS.00 PENALTY RELEASE.00 TRANS OUTP PYMT.00 HEMOPHILIA ADD-ON.00 NEW TECH ADD-ON.00 BALANCE FORWARD.00 NET PROVIDER PAYMENT (PAYMENTS 4, MINUS NONCOV/DED) CHECK/EFT NUMBER : WITHHOLD ADJUSTMENT TO BALANCE Figure 6-4 Sample Medicare RA (page 2) illustrating claim data related to payment. 4. Review the charge billed on the RA against the charge listed on the patient s account. 5. Analyze the approved amount and noncovered charges. These amounts indicate what the payer is approving for the service. The payment is determined based on the approved amount. 6. An explanation of the approved amount is indicated using some type of coding system commonly referred to as explanation or reason codes. Definitions of the reason codes are listed on the bottom or the back of the RA, as illustrated in Figure 6-5. The reason X2 on the ABC Insurance RA tells the hospital that the allowed amount was determined based on the contract. BOX 6-4 Patient Transactions The Patient Financial Services (PFS) Department is responsible for posting transactions to the patient s account. Patient transactions include the following. Patient payments Third-party payer payments The account balance will be billed to the patient (balance billing) when appropriate or to a secondary or tertiary insurance (secondary billing). 7. Information on the RA regarding the deductible and co-insurance explains amounts that are billable to the patient. Claim # Patient Name (ID Number) Service Date Procedure ABC Insurance Amount Billed Amount Approved Reason Deductible Coinsurance Payment Amount S. DAVIS A XX 020 $6.00 $43.30 X2 $8.66 $ X. PALATE X A XX $28.00 $25.00 A $ K. TELLAR A 9 20XX $ $52.00 Z90 $30.40 $ F. SIMPSON A XX 9923 $25.00 Z $, $, X2 $ $ H. DEAN A XX $ $56.00 $75.00 $75.00 X2 X0 X0 $35.00 $ $40.00 Reason Codes A - amount applied to deductible X2 - allowed amount determined based on contact X0 - payment reduced-test considered part of panel Z8 - service bundled Z90 - reduced payment-level of service not medically necessary Figure 6-5 ABC Insurance RA illustrating reason codes and their explanations.
13 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 8 BOX 6-5 Patient Transaction Process Payment is posted to the patient s account A contractual adjustment is applied where applicable The balance is billed to the patient or sent to a secondary or tertiary payer where applicable Denials and information requests are researched and processed as appropriate If the claim is denied appropriately, it may be necessary for the claim to be submitted to a secondary insurance 8. The payment amount on the bottom of the page is the total payment for all claims listed on the RA. PATIENT TRANSACTIONS The PFS Department is responsible for processing transactions including payments, adjustments, and other transactions to the patient s account. Patient payments and third-party payments are posted to the patient s account by PFS. The process followed is outlined below: Payment is posted to the patient s account A contractual adjustment is applied where applicable The balance is billed to the patient or sent to a secondary or tertiary payer when applicable Denials and information requests are researched and processed as appropriate If the claim is denied appropriately, the claim may need to be submitted to a secondary insurance Patient Payments Patient payments are posted to the patient s account when payment is received. The patient may pay the entire amount or part of the balance owed. When the entire amount is not paid, a statement reflecting the balance will be sent to the patient in the next billing period. Adjustments may be posted to the patient s account to reflect discounts or amounts that are uncollectible, as discussed later in this section. Third-Party Payer Payments Payments from third-party payers are posted to the patient s account when an RA and check are received from the payer. Payment on a claim is processed in accordance with the payer s determination. The payer may process payment for the claim as appropriate or the payment amount may be lower than expected by the hospital. This may occur when services are billed separately that are bundled or when medical necessity criteria are not met for a higher level of service. If the correct amount is not paid by the payer, a hospital representative will pursue correction of the claim. Incorrect Payment Level When the payer processes a claim at a reduced level or payment is not made for a service reported on the Claim # Patient Name (ID Number) Service Date Procedure ABC Insurance Amount Billed Amount Approved Note Deductible Coinsurance Payment Amount S. DAVIS A XX 020 $6.00 $43.30 X2 $8.66 $ X. PALATE X A XX $28.00 $25.00 A $ K. TELLAR A 9 20XX $ $52.00 Z90 $30.40 $2.60 Service bundled F. SIMPSON A XX 9923 $25.00 Z $, $, X2 $ $ $ H. DEAN A XX $ $56.00 $75.00 $75.00 X2 X0 X0 $35.00 Reason Codes A - amount applied to deductible X2 - allowed amount determined based on contact X0 - payment reduced-test considered part of panel $40.00 Z8 - service bundled Z90 - reduced payment-level of service not medically necessary Figure 6-6 ABC Insurance RA # highlighting a service the payer bundled into another service. The hospital cannot balance bill the patient for this amount.
14 82 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process claim, a hospital representative must investigate the reason for the reduced payment or nonpayment. Common situations when a claim may be paid at a reduced level are outlined below: The diagnosis code(s) submitted does not meet medical necessity criteria for the service level billed Services are billed with more than one code when they should be described with a single code A service that is considered part of a more comprehensive service is billed separately The ABC Insurance RA # illustrated in Figure 6-6 highlights a reduced payment situation. The RA reason, code Z8, indicates that the payer did not pay on procedure 9923, Evaluation and Management (E/M) service. The reason for nonpayment is that the payer considered the E/M to be part of the surgical package. The surgical package outlines services that are bundled into the surgery code. The hospital cannot balance bill the patient for this amount if it participates with the insurance company. Upon investigation, it may be determined that the service should not have been considered part of the surgical package, and payment should have been made. If the E/M service was not related to the surgery or if the decision for surgery was made during the E/M service, the hospital may request that the claim be reprocessed with a modifier attached to the E/M code, or the hospital may appeal the claim. BOX 6-6 Common Reasons for Reduced Claim Payments Level of service is not supported by the patient s condition Service may be bundled, such as services included in the surgical package Service may be considered an integral part of a larger procedure Adjustments An adjustment is the process of reducing the original amount charged by a specified amount. There are several types of adjustments that may be posted to a patient s account, such as discount, contractual adjustment, or write-off, as outlined below. BOX 6-7 Adjustments The original amount charged is reduced by a specified amount. Types of adjustments are as follows. Discount Contractual adjustment Write-off Difference between amount charged and approved amount Claim # Patient Name (ID Number) Service Date Procedure ABC Insurance Amount Billed Amount Approved Reason Deductible Coinsurance Payment Amount S. DAVIS A XX 020 $6.00 $43.30 X2 $8.66 $ X. PALATE X A XX $28.00 $25.00 A $ K. TELLAR A 9 20XX $ $52.00 Z90 $30.40 $ F. SIMPSON A XX 9923 $25.00 Z $, $, X2 $ $ H. DEAN A XX $ $56.00 $75.00 $75.00 X2 X0 X0 $35.00 Reason Codes A - amount applied to deductible X2 - allowed amount determined based on contact X0 - payment reduced-test considered part of panel $ $40.00 Z8 - service bundled Z90 - reduced payment-level of service not medically necessary Figure 6-7 ABC Insurance RA #2 illustrating a contractual adjustment in the amount of $7.70 (the difference between the amount billed and the amount approved).
15 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 83 Discount The original charge may be discounted by a specific amount as an agreement between the patient and the hospital. For example, a hospital may offer a discount to self-pay patients who are responsible for the entire hospital bill. The hospital may offer a 20% discount to the patient for payment of the entire balance. When the payment is received, the adjustment is made to the patient s account to reduce the original charge by the discounted amount. Contractual Adjustment A contractual adjustment is a reduction made to the original charge in accordance with the hospital s contract with a payer. Payer contracts include provisions regarding the amount the hospital is required to accept as payment in full, commonly referred to as the approved amount. The approved amount may represent a case rate, contract rate, DRG or APC rate, or fee schedule amount. In accordance with the contract, the hospital agrees to follow those provisions and therefore may not bill patients for amounts over the approved amount. The difference between the approved amount and the hospital s original charge must be adjusted off the patient s account. The hospital posts a contractual adjustment to the patient s account to reduce the original charge. Most hospitals program the computer billing system to calculate and deduct the contractual amount as required by agreement with the payer. The ABC Insurance RA #2 illustrated in Figure 6-7 highlights a contractual adjustment situation. The difference between the billed amount of $6.00 and the approved amount of $43.30 on claim number is $7.70. A contractual adjustment in the amount of $7.70 must be posted to the patient account if the hospital is participating with the insurance company. The reduction of the claim by $7.70 is a contractual adjustment that is made in accordance with the hospital s contract with the payer. Write-Off A write-off is the process of reducing a patient s balance to zero. Write-offs are made when the balance is deemed uncollectible. In accordance with most contracts, the hospital is not allowed to forgive or write-off a patient deductible, co-insurance, and co-payment amount. The hospital is required to follow the necessary steps required to make every attempt to collect the amount for which the patient is responsible. When all efforts are exhausted to collect the patient s responsibility, the hospital may then write-off the balance. These writeoffs are considered a bad debt. Hospitals establish policies and procedures regarding write-offs that detail the necessary steps required to collect the patient balance and the criteria for write-offs. Balance Billing Balance billing refers to billing the patient for a balance in excess of the payer s approved amount in accordance with the payer contract. When the hospital is participating with the payer, the contractual agreement prohibits balance billing a patient for the following amounts: The difference between the original charge and the approved amount The amount of hospital charges that are greater than a DRG payment rate The amount of hospital charges that are greater than an APC payment rate The hospital is required to bill a patient for amounts related to co-payments, co-insurance, and deductible amounts. In some cases, charges for services that are not covered may also be billed. Medicare requires that beneficiaries be given an Advance notice of services that Medicare may not cover due to medical necessity. The notice required by Medicare is the Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN) or Hospital Issued Notice of Noncoverage (HINN). Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN) An Advance Beneficiary Notice is a written notice that is presented to a Medicare beneficiary before Medicare Figure 6-8 Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN), required for Medicare Part B services. (From the CMS Web site:
16 84 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process BOX 6-8 Balance Billing Law prohibits balance billing Medicare patients for the following amounts The difference between the original charge and the approved amount The amount of hospital charges that are greater than a DRG payment The amount of hospital charges that are greater than an APC payment Part B services are furnished, to inform the beneficiary that the provider believes Medicare will not pay for some or all of the services to be rendered because they are not reasonable and necessary. Figure 6-8 illustrates Medicare s ABN. Hospitals are required to present this form for signature to the beneficiary before services are rendered. The hospital cannot bill the patient for these services if the ABN is not completed and on file. Hospital Issued Notice of Noncoverage (HINN) The HINN is a written notice that is presented to a Medicare beneficiary before Medicare Part A services are furnished to inform the beneficiary that the provider believes that Medicare will not pay for some or all of the services to be rendered because they are not reasonable and necessary. The HINN is required by Medicare for hospital Part A services that may not be covered due to medical necessity. The HINN is written in letter form, and it must be presented and signed by the beneficiary before services are rendered. The content of an HINN varies based on the type of services that may not be covered; for example, an admission. Figure 6-9 illustrates a sample HINN. COMMUNITY HOSPITAL 892 South Street Mars, Florida (747) HOSPITAL ISSUED NOTICE OF NONCOVERAGE (HINN) December 5, 2005 Patient name: Zalma Jerzon Address: 4949 South Street Philadelphia, PA Admission Date: December 5, 2005 Health Insurance Claim (HIC) Number: Attending Physician: Dr. Jason James YOUR IMMEDIATE ATTENTION IS REQUIRED Dear Ms. Jerson: The purpose of this notice is to inform you that we find that your admission for (a total knee replacement) is not covered under Medicare for the following reason(s) MEDICAL NECESSITY. This determination was based upon our understanding and interpretation of available Medicare coverage policies and guidelines. You should discuss with your attending physician other arrangements for any further health care you may require. If you decide to (be admitted to/remain in) the hospital, you will be financially responsible for all customary charges for services furnished during the stay, except for those services for which you are eligible under Part B. This notice, however, is not an official Medicare determination. The QIO Organization is the quality improvement organization (QIO) authorized by the Medicare program to review inpatient hospital services provided to Medicare patients in the State of (Pennsylvania), and to make that determination. If you disagree with our conclusion: (Select as appropriate) Preadmission: Request immediately, but no later than 3 calendar days after receipt of this notice, or, if admitted, at any point in the stay, an immediate review of the facts in your case. You may make this request through us or directly to the QIO by telephone or in writing to the address listed below. Admission: Request immediately, or at any point during your stay, an immediate review of the facts in your case. You may make this request through us or directly to the QIO by telephone or in writing to the address listed below. If you do not wish an immediate review: You may still request a review within 30 calendar days from the date of receipt of this notice by telephoning or writing to the address specified below. Results of the QIO Review: The QIO will send you a formal determination of the medical necessity and appropriateness of your hospitalization, and will inform you of your reconsideration and appeal rights. IF THE QIO DISAGREES WITH THE HOSPITAL (i.e., the QIO determines that your care is covered), you will be refunded any amount collected except for any applicable amounts for deductible, coinsurance, and convenience services or items normally not covered by Medicare. IF THE QIO AGREES WITH THE HOSPITAL, you are responsible for payment for all services beginning on December 5, ACKNOWLEDGMENT OF RECEIPT OF NOTICE This is to acknowledge that I received this notice of non-coverage of services from the Community Hospital on 2/5/04 at 8:35 a.m. I understand that my signature below does not indicate that I agree with the notice, only that I have received a copy of the notice. (Signature of beneficiary or Representative) Date Time cc: QIO and Attending Physician Figure 6-9 Hospital Issued Notice of Noncoverage (HINN), CMS Hospital Manual required for Medicare Part A services. (Modified from Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services: Hospital-issued notice of noncoverage, new.cms.hhs.gov/bni/ Downloads/HINNsto0.pdf, 2005.) BOX 6-9 Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN) and Hospital Issued Notice of Noncoverage (HINN) ABN A written notice presented to a Medicare beneficiary before Part B services are furnished to inform the beneficiary that Medicare may not pay for some or all of the services to be rendered because they are not reasonable and necessary. HINN A written notice presented to a Medicare beneficiary before Part A services are furnished to inform the beneficiary that Medicare will not pay for some or all of the services to be rendered because they are not reasonable and necessary. BOX 6-20 Coordination of Benefits (COB) A clause written into an insurance policy or government program plan that defines how benefits will be paid when the member or beneficiary is covered under multiple plans. Third-party payers combine efforts to coordinate benefits paid by the plan through the coordination of benefits (COB) provisions. These provisions help to ensure the following conditions. The plans pay as primary and secondary payers appropriately Total payments for the claim do not exceed more than 00% charges There is no duplication of payments for health care services
17 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 85 BOX 6-2 REMITTANCE ADVICE (RA): PATIENT TRANSACTIONS. Define an electronic remittance advice. 2. List various names used to describe the document provided by the payer that explains how a claim was processed. 3. Explain the process of posting patient and third-party payments to the patient s account by the PFS. 4. Explain why it is important to compare the procedures listed in a remittance advice with those listed on the patient s account. 5. Describe the purpose of reason codes. 6. List common reasons why a payer may process payment at an incorrect level. 7. Discuss why it is important for a hospital representative to analyze payment made by an insurance company. 8. Outline the actions required when payment is received at the incorrect level. 9. Provide an explanation of an adjustment. 0. List three types of adjustments a hospital may make to a patient s account.. Describe contractual adjustment and explain when this type of adjustment is made to a patient account. 2. State when a hospital may write off a balance. 3. Provide a brief explanation of balance billing. 4. Explain the purpose of an ABN. 5. Discuss the difference between an ABN and HINN.
18 86 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process Transaction posting payments, adjustments, rejections/denial/ pended claims A/R management Patient and third-party follow-up Denial management Figure 6-20 BOX 6-2 Secondary Billing Charges billed Patient statements Third-party claims Hospital revenue cycle. Patient received Billing information obtained Patient care rendered Charges generated and posted Accounts Receivable (A/R) Management Functions required to monitor and follow-up on outstanding accounts to ensure that reimbursement is received in a timely manner. BOX 6-22 Accounts Receivable (A/R) Reports Unbilled Accounts Listing of patient accounts that have not been billed Financial Class Outlines claim information such as charges, payments, and outstanding balances, grouped according to type of payer Denials Management Listing of claims that have been denied Accounts Receivable (A/R) Aging Outstanding accounts are categorized based on the number of days the balance is outstanding BOX 6-23 Aging The process of counting the number of days that an account is outstanding from the date billed. Secondary billing may occur when the patient has a supplemental insurance that is designed to cover expenses not covered by the primary insurance. When payment is processed from the primary payer, the hospital representative may initiate billing to a secondary or tertiary payer. Coordination of benefits (COB) provisions for the plan must be followed. Medicare secondary payer guidelines must also be followed. Coordination of benefits and Medicare secondary payer guidelines will be discussed later in this text in the payer chapters. ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE (A/R) MANAGEMENT Accounts receivable is a term used to describe revenue owed to the hospital by patients and third-party payers. Accounts receivable is commonly referred to as A/R. A/R management is a vital function required to monitor and follow-up on outstanding accounts. The financial stability of a hospital is highly dependent on maintaining a positive cash flow. The hospital must maintain a steady flow of revenue (income) to cover expenses required to provide patient care services. To accomplish this, the hospital monitors the revenue cycle. As illustrated in Figure 6-20, the hospital revenue cycle begins when the patient arrives at the hospital for patient care services and ends when payment is received. The primary objective of A/R management is to minimize the amount of time that accounts are outstanding. Outstanding accounts are accounts that have been billed to the patient or thirdparty payer but have not received any payment. A/R management involves tracking accounts that have not been paid, assessing action required to secure payment, and implementing procedures to secure payment. Accounts Receivable (A/R) Reports Hospitals utilize various computerized reports to monitor accounts that have not been paid, such as an unbilled accounts report, financial class report, denials management report, and accounts receivable aging reports. Accounts Receivable (A/R) Aging Report Computer-generated A/R aging reports are utilized to identify and analyze outstanding accounts. The A/R aging report is a listing of outstanding accounts based on the age of the account. The term aging refers to the number of days the account has been outstanding. The computer system counts the number of days the account is outstanding from the date the claim or statement is sent. A/R reports can be run for specified patient accounts or by payer type. The report categorizes accounts based on aging categories in increments of 30 days, as outlined below: 0 to 30 days 3 to 60 days 6 to 90 days 9 to 20 days
19 Chapter 6: Accounts Receivable (AR) Management 87 TABLE 6- Community General Hospital Patient A/R Report, December 30, 2005 Days Outstanding Account Name Phone Current Total Number Balance Applebee, Carla (83) Borden, Andrew (83) Cox, Anthony (83) Freeman, Tina (727) Holtsaver, Marshall (727) James, John (83) Marcus, Xavier (727) Peters, Samantha (43) Snowton, Michael (94) Report Totals % Aged 4.05% 8.07% 26.4% 9.97% 7.34% 0.00% 4.6% TABLE 6-2 Community General Hospital Third-Party Payer A/R Report, December 30, 2005 Days Outstanding Payer Payer Phone Current Total Code Balance Aetna AETNA (800) BlueCross/ BCBS (800) Blue Shield Champus CHMPV (800) Fed Emp FET (800) Trust Medicaid MDCD (800) Medicare MDCR (800) Metropolitan MET (800) Nationwide NAT (800) Workers WCMP (800) Comp Report Totals % Aged 5.88% 6.5% 9.47% 5.39% 9.64% 0.00% 4.6% 2 to 50 days. 5 to 80 days. Table 6- illustrates an A/R aging report based on patient billed date. The report includes the account number, patient name, and phone number. Outstanding amounts owed on the patient account are reported in the column that reflects the aging category of the amount owed. Table 6-2 illustrates an A/R report based on payer type. Payer-based A/R reports include the payer name, payer code, and phone number. Outstanding amounts are reported in the appropriate aging category. A/R reports provide a percentage of aging in each of the aging categories.
20 88 Section Two: Billing and Coding Process A/R Ratio The A/R ratio is a formula that calculates the percentage of accounts receivables in comparison with total charges. Total charges net collections A/R A/R average monthly charges A/R ratio Days in A/R Days in A/R is another formula used to determine the number of days it takes to collect outstanding accounts. Average monthly charges by 30 average daily charges Total A/R by average daily charges days in A/R Figure 6-2 Formula used to assess accounts receivable (A/R ratio) and days in A/R Hospital policies and procedures outline priorities for follow-up on outstanding accounts. Priorities are set based on the age and dollar amount of outstanding accounts. For example, the initial focus is typically directed toward accounts that fall within the 6- to 90-day aging category, then the 9- to 20-day category, and then 20+ days. Accounts with large balances are generally considered a priority. Hospitals utilize the A/R ratio and the days in A/R formula to assess the efficiency of A/R management activity, as illustrated in Figure 6-2. A/R Ratio The A/R ratio is a formula that calculates the percentage of A/R in comparison with total charges. Total charges net collections = A/R [A/R] average monthly charges = A/R ratio Days in A/R Days in A/R is a formula used to determine the number days it takes to collect outstanding accounts. Average monthly charges 30 = average daily charges Total A/R average daily charges = days in A/R. Denials Management Report Denials management reports are utilized to identify claims that have been denied, rejected, or pended. Claims identified with this report are investigated to determine why the claim was denied, rejected, or pended (Table 6-3). Financial Class Reports Hospitals utilize financial class reports to identify outstanding accounts based on the type of payer, or financial class. A financial class is a classification system used to categorize accounts by payer types. A financial TABLE 6-3 Community General Hospital Denial Management Report, 0/0/06 to 06/30/06 Denial Code Patient Name Service Date Total Charges Payment Action Code Status Code 9 WK IN Harold, A 02/02/2006 $, CO INQ PEND 9 WK IN Sanders,P 03/7/2006 $27, CO INQ PEND 9 WK IN Thomas, J 06/22/2006 $42, CO INQ PEND 9 WK IN Peters, X 02/25/2006 $8, CO INQ RESUB 9 WK IN Hanson, T 05/3/2006 $ CO INQ APPEAL 3 PTNCOV Martel, B 06/22/2006 $42, LTR PEND INS 3 PTNCOV Morris, B 03/7/2006 $27, LTR PEND INS 3 PTNCOV Hanna, J 02/25/2006 $8, LTR PEND INS 3 PTNCOV Halbert, A 02/02/2006 $, LTR PEND INS 3 PTNCOV Yandic, M 05/3/2006 $ LTR PEND INS 39 AUTH RQ Steff, H 02/02/2006 $ OB AU REQ AUTH 39 AUTH RQ Albert, A 03/7/2006 $ OB AU REQ AUTH 39 AUTH RQ Baxter, M 06/22/2006 $ OB AU REQ AUTH 39 AUTH RQ Parcon, M 02/25/2006 $72.82 OB AU NO AUTH 39 AUTH RQ Smith, J 05/3/2006 $0, OB AU RESUB WA
The Hospital Billing Process The purpose of this chapter is to provide an overview of the hospital billing process. The
 3 Section One: Section Title Chapter 5 The Hospital Billing Process The purpose of this chapter is to provide an overview of the hospital billing process. The billing process includes submitting charges
3 Section One: Section Title Chapter 5 The Hospital Billing Process The purpose of this chapter is to provide an overview of the hospital billing process. The billing process includes submitting charges
Chapter 8 Billing on the CMS 1500 Claim Form
 8 Billing on the CMS 1500 Claim form INTRODUCTION The CMS 1500 claim form is used to bill for non-facility services, including professional services, freestanding surgery centers, transportation, durable
8 Billing on the CMS 1500 Claim form INTRODUCTION The CMS 1500 claim form is used to bill for non-facility services, including professional services, freestanding surgery centers, transportation, durable
Chapter 5. Billing on the CMS 1500 Claim Form
 Chapter 5 Billing on the CMS 1500 Claim Form This Page Intentionally Left Blank Fee-For-Service Provider Manual April 2012 Billing on the UB-04 Claim Form Chapter: 5 Page: 5-2 INTRODUCTION The CMS 1500
Chapter 5 Billing on the CMS 1500 Claim Form This Page Intentionally Left Blank Fee-For-Service Provider Manual April 2012 Billing on the UB-04 Claim Form Chapter: 5 Page: 5-2 INTRODUCTION The CMS 1500
To submit electronic claims, use the HIPAA 837 Institutional transaction
 3.1 Claim Billing 3.1.1 Which Claim Form to Use Claims that do not require attachments may be billed electronically using Provider Electronic Solutions (PES) software (provided by Electronic Data Systems
3.1 Claim Billing 3.1.1 Which Claim Form to Use Claims that do not require attachments may be billed electronically using Provider Electronic Solutions (PES) software (provided by Electronic Data Systems
CLAIMS AND BILLING INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL
 CLAIMS AND BILLING INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL 2007 TABLE OF ONTENTS Paper Claims and Block Grant Submission Requirements... 3 State Requirements for Claims Turnaround Time... 12 Claims Appeal Process... 13 Third
CLAIMS AND BILLING INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL 2007 TABLE OF ONTENTS Paper Claims and Block Grant Submission Requirements... 3 State Requirements for Claims Turnaround Time... 12 Claims Appeal Process... 13 Third
Domestic Accident & Health Division 80 Pine Street, 13 th Floor New York, NY 10005
 Domestic Accident & Health Division 80 Pine Street, 13 th Floor New York, NY 10005 Welcome to the AIG Companies family of customers. We appreciate that you had a choice when placing your insurance and
Domestic Accident & Health Division 80 Pine Street, 13 th Floor New York, NY 10005 Welcome to the AIG Companies family of customers. We appreciate that you had a choice when placing your insurance and
Revenue Cycle Responsibilities. Revenue Cycle. Objectives 4/9/2013
 Revenue Cycle Kathryn DeVault, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P AHIMA 2013 Objectives Identify responsibilities within the Revenue Cycle Focus on management of the revenue cycle process Discuss the revenue cycle process
Revenue Cycle Kathryn DeVault, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P AHIMA 2013 Objectives Identify responsibilities within the Revenue Cycle Focus on management of the revenue cycle process Discuss the revenue cycle process
Claims Procedures. H.2 At a Glance. H.4 Submission Guidelines. H.9 Claims Documentation. H.17 Codes and Modifiers. H.
 H.2 At a Glance H.4 Submission Guidelines H.9 Claims Documentation H.17 Codes and Modifiers H.22 Reimbursement H.25 Denials and Appeals At a Glance pledges to provide accurate and efficient claims processing.
H.2 At a Glance H.4 Submission Guidelines H.9 Claims Documentation H.17 Codes and Modifiers H.22 Reimbursement H.25 Denials and Appeals At a Glance pledges to provide accurate and efficient claims processing.
SECTION 4. A. Balance Billing Policies. B. Claim Form
 SECTION 4 Participating Physicians, hospitals and ancillary providers shall be entitled to payment for covered services that are provided to a DMC Care member. Payment is made at the established and prevailing
SECTION 4 Participating Physicians, hospitals and ancillary providers shall be entitled to payment for covered services that are provided to a DMC Care member. Payment is made at the established and prevailing
Completing a Paper UB-04 Form
 Completing a Paper UB-04 Information in this policy does not apply to members with the Choice or Choice Plus products offered through Passport Connect S. For UnitedHealthcare s related policies/procedures,
Completing a Paper UB-04 Information in this policy does not apply to members with the Choice or Choice Plus products offered through Passport Connect S. For UnitedHealthcare s related policies/procedures,
Compensation and Claims Processing
 Compensation and Claims Processing Compensation The network rate for eligible outpatient visits is reimbursed to you at the lesser of (1) your customary charge, less any applicable co-payments, coinsurance
Compensation and Claims Processing Compensation The network rate for eligible outpatient visits is reimbursed to you at the lesser of (1) your customary charge, less any applicable co-payments, coinsurance
CMS 1500 Training 101
 CMS 1500 Training 101 HP Enterprise Services Learning Objective Welcome, this training presentation will educate you on how to complete a CMS 1500 claim form; this includes a detailed explanation of all
CMS 1500 Training 101 HP Enterprise Services Learning Objective Welcome, this training presentation will educate you on how to complete a CMS 1500 claim form; this includes a detailed explanation of all
Dental Sleep Medicine
 Dental Sleep Medicine The Patient and Physician Friendly Practice Insurance from A to Pay Dental Sleep Medicine A = Assignment of Benefits A procedure whereby a patient authorizes the administrator of
Dental Sleep Medicine The Patient and Physician Friendly Practice Insurance from A to Pay Dental Sleep Medicine A = Assignment of Benefits A procedure whereby a patient authorizes the administrator of
1500 Claims Processing Manual DHMP Health Insurance Claim Form CMS-1500
 DENVER HEALTH MEDICAL PLAN, INC. 1500 Claims Processing Manual DHMP Health Insurance Claim Form CMS-1500 Box 1 Medicare, Medicaid, Group Health Plan or other insurance Information Show the type of health
DENVER HEALTH MEDICAL PLAN, INC. 1500 Claims Processing Manual DHMP Health Insurance Claim Form CMS-1500 Box 1 Medicare, Medicaid, Group Health Plan or other insurance Information Show the type of health
Patient Resource Guide for Billing and Insurance Information
 Patient Resource Guide for Billing and Insurance Information 17 Patient Account Payment Policies July 2012 Update Lexington Clinic Central Business Office Payment Policies Customer service...2 Check-in...2
Patient Resource Guide for Billing and Insurance Information 17 Patient Account Payment Policies July 2012 Update Lexington Clinic Central Business Office Payment Policies Customer service...2 Check-in...2
Patient Account Services. Patient Reference & Frequently Asked Questions. Admissions
 Patient Account Services Patient Reference & Frequently Asked Questions Admissions Each time you present for a new medical service, a new account number will be assigned. You will be asked to pay any patient
Patient Account Services Patient Reference & Frequently Asked Questions Admissions Each time you present for a new medical service, a new account number will be assigned. You will be asked to pay any patient
INSTITUTIONAL. billing module
 INSTITUTIONAL billing module UB-92 Billing Module Basic Rules... 2 Before You Begin... 2 Reimbursement and Co-payment... 2 How to Complete the UB-92... 5 1 Basic Rules Instructions for completing the UB-92
INSTITUTIONAL billing module UB-92 Billing Module Basic Rules... 2 Before You Begin... 2 Reimbursement and Co-payment... 2 How to Complete the UB-92... 5 1 Basic Rules Instructions for completing the UB-92
STATE OF MARYLAND KIDNEY DISEASE PROGRAM UB-04. Billing Instructions. for. Freestanding Dialysis Facility Services. Revised 9/1/08.
 STATE OF MARYLAND KIDNEY DISEASE PROGRAM UB-04 Billing Instructions for Freestanding Dialysis Facility Services Revised 9/1/08 Page 1 of 13 UB04 Instructions TABLE of CONTENTS Introduction 4 Sample UB04
STATE OF MARYLAND KIDNEY DISEASE PROGRAM UB-04 Billing Instructions for Freestanding Dialysis Facility Services Revised 9/1/08 Page 1 of 13 UB04 Instructions TABLE of CONTENTS Introduction 4 Sample UB04
CLAIM FORM REQUIREMENTS
 CLAIM FORM REQUIREMENTS When billing for services, please pay attention to the following points: Submit claims on a current CMS 1500 or UB04 form. Please include the following information: 1. Patient s
CLAIM FORM REQUIREMENTS When billing for services, please pay attention to the following points: Submit claims on a current CMS 1500 or UB04 form. Please include the following information: 1. Patient s
Billing Manual for In-State Long Term Care Nursing Facilities
 Billing Manual for In-State Long Term Care Nursing Facilities Medical Services North Dakota Department of Human Services 600 E Boulevard Ave, Dept 325 Bismarck, ND 58505 September 2003 INTRODUCTION The
Billing Manual for In-State Long Term Care Nursing Facilities Medical Services North Dakota Department of Human Services 600 E Boulevard Ave, Dept 325 Bismarck, ND 58505 September 2003 INTRODUCTION The
Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) Billing Instructions
 All related services performed by an ambulatory surgery center must be billed on the UB04 claim form following the instructions listed below. Tips Claim Form Completion Claims for ASC covered services
All related services performed by an ambulatory surgery center must be billed on the UB04 claim form following the instructions listed below. Tips Claim Form Completion Claims for ASC covered services
UB-04 Claim Form Instructions
 UB-04 Claim Form Instructions FORM LOCATOR NAME 1. Billing Provider Name & Address INSTRUCTIONS Enter the name and address of the hospital/facility submitting the claim. 2. Pay to Address Pay to address
UB-04 Claim Form Instructions FORM LOCATOR NAME 1. Billing Provider Name & Address INSTRUCTIONS Enter the name and address of the hospital/facility submitting the claim. 2. Pay to Address Pay to address
Chapter 6. Billing on the UB-04 Claim Form
 Chapter 6 This Page Intentionally Left Blank Chapter: 6 Page: 6-3 INTRODUCTION The UB-04 claim form is used to bill for all hospital inpatient, outpatient, and emergency room services. Dialysis clinic,
Chapter 6 This Page Intentionally Left Blank Chapter: 6 Page: 6-3 INTRODUCTION The UB-04 claim form is used to bill for all hospital inpatient, outpatient, and emergency room services. Dialysis clinic,
Glossary of Insurance and Medical Billing Terms
 A Accept Assignment Provider has agreed to accept the insurance company allowed amount as full payment for the covered services. Adjudication The final determination of the issues involving settlement
A Accept Assignment Provider has agreed to accept the insurance company allowed amount as full payment for the covered services. Adjudication The final determination of the issues involving settlement
You must write REHAB at the top center of the claim form!
 CMS 1500 (02/12 INSTRUCTIONS FOR REHABILITATION CENTER SERVICES You must write REHAB at the top center of the claim form! Locator # Description Instructions Alerts 1 Medicare / Medicaid / Tricare Champus
CMS 1500 (02/12 INSTRUCTIONS FOR REHABILITATION CENTER SERVICES You must write REHAB at the top center of the claim form! Locator # Description Instructions Alerts 1 Medicare / Medicaid / Tricare Champus
SECTION G BILLING AND CLAIMS
 CLAIMS PAYMENT METHODS SECTION G Harbor Advantage (HMO) offers 2 forms of payment for services provided; paper check and electronic funds transfer (direct deposit). Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) Harbor
CLAIMS PAYMENT METHODS SECTION G Harbor Advantage (HMO) offers 2 forms of payment for services provided; paper check and electronic funds transfer (direct deposit). Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) Harbor
Certified Access Manager (CAM) Study Guide
 Certified Access Manager (CAM) Study Guide Revised 08/2015 Table of Contents I. NCAHAM.. II. Registration Basics Forms MPI Co-pay See Glossary Coinsurance See Glossary Deductible See Glossary Out of Pocket
Certified Access Manager (CAM) Study Guide Revised 08/2015 Table of Contents I. NCAHAM.. II. Registration Basics Forms MPI Co-pay See Glossary Coinsurance See Glossary Deductible See Glossary Out of Pocket
CODE DESCRIPTION 011 Claim denial (claim level) due to SF message 012 Line denial (line level) due to SF message 017 Incorrect Alpha Prefix 030
 CODE DESCRIPTION 011 Claim denial (claim level) due to SF message 012 Line denial (line level) due to SF message 017 Incorrect Alpha Prefix 030 Missing service provider zip code (box 32) 031 Missing pickup
CODE DESCRIPTION 011 Claim denial (claim level) due to SF message 012 Line denial (line level) due to SF message 017 Incorrect Alpha Prefix 030 Missing service provider zip code (box 32) 031 Missing pickup
Compensation and Claims Processing
 Compensation and Claims Processing Compensation The network rate for eligible outpatient visits is reimbursed to you at the lesser of (1) your customary charge, less any applicable co-payments, coinsurance
Compensation and Claims Processing Compensation The network rate for eligible outpatient visits is reimbursed to you at the lesser of (1) your customary charge, less any applicable co-payments, coinsurance
CHAPTER 17 CREDIT AND COLLECTION
 CHAPTER 17 CREDIT AND COLLECTION 17101. Credit and Collection Section 17102. Purpose 17103. Policy 17104. Procedures NOTE: Rule making authority cited for the formulation of regulations for the Credit
CHAPTER 17 CREDIT AND COLLECTION 17101. Credit and Collection Section 17102. Purpose 17103. Policy 17104. Procedures NOTE: Rule making authority cited for the formulation of regulations for the Credit
! Claims and Billing Guidelines
 ! Claims and Billing Guidelines Electronic Claims Clearinghouses and Vendors 16.1 Electronic Billing 16.2 Institutional Claims and Billing Guidelines 16.3 Professional Claims and Billing Guidelines 16.4
! Claims and Billing Guidelines Electronic Claims Clearinghouses and Vendors 16.1 Electronic Billing 16.2 Institutional Claims and Billing Guidelines 16.3 Professional Claims and Billing Guidelines 16.4
HCPCS codes should be used to describe outpatient diagnostic laboratory procedures (revenue codes 300 to 319).
 6How Do I Bill Tribal Outpatient Hospital Services? Complete the UB-04 form for outpatient hospital services. Refer to How do I complete the UB-04? in the Billing Guidelines section for specific information
6How Do I Bill Tribal Outpatient Hospital Services? Complete the UB-04 form for outpatient hospital services. Refer to How do I complete the UB-04? in the Billing Guidelines section for specific information
CMS-1500 PART B MEDICARE ADVANTAGE PLAN BILLING INSTRUCTIONS
 Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Office of Systems, Operations & Pharmacy Medical Care Programs CMS-1500 PART B MEDICARE ADVANTAGE PLAN BILLING INSTRUCTIONS Effective September, 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Office of Systems, Operations & Pharmacy Medical Care Programs CMS-1500 PART B MEDICARE ADVANTAGE PLAN BILLING INSTRUCTIONS Effective September, 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Inpatient Hospital Prospective Payment Billing Manual
 Inpatient Hospital Prospective Payment Billing Manual July 2006 INPATIENT HOSPITAL SERVICES Under West Virginia Public Payers prospective payment system (PPS), payments are made prospectively on a per-drg
Inpatient Hospital Prospective Payment Billing Manual July 2006 INPATIENT HOSPITAL SERVICES Under West Virginia Public Payers prospective payment system (PPS), payments are made prospectively on a per-drg
Molina Healthcare of Ohio, Inc. PO Box 22712 Long Beach, CA 90801
 Section 9. Claims As a contracted provider, it is important to understand how the claims process works to avoid delays in processing your claims. The following items are covered in this section for your
Section 9. Claims As a contracted provider, it is important to understand how the claims process works to avoid delays in processing your claims. The following items are covered in this section for your
Surgical/ASC Claims Revenue Cycle Management: An Introduction to Our Processes and Protocols
 Surgical/ASC Claims Revenue Cycle Management: An Introduction to Our Processes and Protocols 200 Old Country Road, Suite 470 Mineola, NY 11501 Phone: 516-294-4118 Fax: 516-294-9268 www.businessdynamicslimited.com
Surgical/ASC Claims Revenue Cycle Management: An Introduction to Our Processes and Protocols 200 Old Country Road, Suite 470 Mineola, NY 11501 Phone: 516-294-4118 Fax: 516-294-9268 www.businessdynamicslimited.com
NC WORKERS COMPENSATION: BASIC INFORMATION FOR MEDICAL PROVIDERS
 NC WORKERS COMPENSATION: BASIC INFORMATION FOR MEDICAL PROVIDERS CURRENT AS OF APRIL 1, 2010 I. INFORMATION SOURCES Where is information available for medical providers treating patients with injuries/conditions
NC WORKERS COMPENSATION: BASIC INFORMATION FOR MEDICAL PROVIDERS CURRENT AS OF APRIL 1, 2010 I. INFORMATION SOURCES Where is information available for medical providers treating patients with injuries/conditions
Patient Billing. Questions/ Answers. Assistance Programs
 Patient Billing Questions/ Answers Assistance Programs Table of Contents Patient billing: an introduction... 1 Patient financial responsibilities... 2 Our promise to you... 3 Frequently asked questions...
Patient Billing Questions/ Answers Assistance Programs Table of Contents Patient billing: an introduction... 1 Patient financial responsibilities... 2 Our promise to you... 3 Frequently asked questions...
You must write AMB at the top center of the claim form!
 CMS 1500 (08/05) INSTRUCTIONS FOR AMBULANCE AND AIR AMBULANCE SERVICES You must write AMB at the top center of the claim form! Locator # Description Instructions Alerts 1 Medicare / Medicaid / Tricare
CMS 1500 (08/05) INSTRUCTIONS FOR AMBULANCE AND AIR AMBULANCE SERVICES You must write AMB at the top center of the claim form! Locator # Description Instructions Alerts 1 Medicare / Medicaid / Tricare
Regulatory Compliance Policy No. COMP-RCC 4.25 Title:
 I. SCOPE: Regulatory Compliance Policy No. COMP-RCC 4.25 Title: HOSPITAL COVERAGE NOTICES FOR MEDICARE INPATIENTS (INCLUDING IMPORTANT MESSAGE FROM MEDICARE) Page: 1 of 16 Effective Date: 03-19-15 Retires
I. SCOPE: Regulatory Compliance Policy No. COMP-RCC 4.25 Title: HOSPITAL COVERAGE NOTICES FOR MEDICARE INPATIENTS (INCLUDING IMPORTANT MESSAGE FROM MEDICARE) Page: 1 of 16 Effective Date: 03-19-15 Retires
HOSPITAL OUTPATIENT BILLING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE
 MOUNTAIN STATE BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD HOSPITAL OUTPATIENT BILLING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE OUTPATIENT PROSPECTIVE PAYMENT SYSTEM (OPPS) TRADITIONAL/PPO/POS/FEP/STEEL Table of Contents Section I. Overview
MOUNTAIN STATE BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD HOSPITAL OUTPATIENT BILLING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE OUTPATIENT PROSPECTIVE PAYMENT SYSTEM (OPPS) TRADITIONAL/PPO/POS/FEP/STEEL Table of Contents Section I. Overview
Please follow these suggestions in order to facilitate timely reimbursement of claims and to avoid timely filing issues:
 Claims/Payment Section K-1 New Claims Submissions All claims must be submitted and received by Molina Healthcare of New Mexico, Inc. (Molina Healthcare) within ninety (90) days from the date of service
Claims/Payment Section K-1 New Claims Submissions All claims must be submitted and received by Molina Healthcare of New Mexico, Inc. (Molina Healthcare) within ninety (90) days from the date of service
University of Mississippi Medical Center. Access Management. Patient Access Specialists II
 Financial Terminology in Access Management University of Mississippi Medical Center Access Management Patient Access Specialists II As a Patient Access Specialist You are the FIRST STAGE in the Revenue
Financial Terminology in Access Management University of Mississippi Medical Center Access Management Patient Access Specialists II As a Patient Access Specialist You are the FIRST STAGE in the Revenue
THE CITY OF VIRGINIA BEACH AND THE SCHOOL BOARD OF THE CITY OF VIRGINIA BEACH
 THE CITY OF VIRGINIA BEACH AND THE SCHOOL BOARD OF THE CITY OF VIRGINIA BEACH OPTIMA November 7, 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary... 1 Process Overview... 4 Areas of Testing... 5 Site Visit Selection...
THE CITY OF VIRGINIA BEACH AND THE SCHOOL BOARD OF THE CITY OF VIRGINIA BEACH OPTIMA November 7, 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary... 1 Process Overview... 4 Areas of Testing... 5 Site Visit Selection...
MEDICARE CREDIT BALANCE REPORT CERTIFICATION PAGE
 DEPAR ARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Form Approved OMB No. 0938-0600 MEDICARE CREDIT BALANCE REPORT CERTIFICATION PAGE The Credit Balance Report is required under the authority of sections 1815(a),
DEPAR ARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Form Approved OMB No. 0938-0600 MEDICARE CREDIT BALANCE REPORT CERTIFICATION PAGE The Credit Balance Report is required under the authority of sections 1815(a),
University Healthcare Administrative Policy
 Page 1 of 6 APPROVED BY: Signatures on File FINANCIAL POLICY (UH) is a not-for profit teaching hospital committed to providing quality health care services. In order to provide necessary medical services
Page 1 of 6 APPROVED BY: Signatures on File FINANCIAL POLICY (UH) is a not-for profit teaching hospital committed to providing quality health care services. In order to provide necessary medical services
Pre-Employment Test for Business Office Staff Answer Key
 P a g e 1 Pre-Employment Test for Business Office Staff Answer Key 1. Mr. Walker owes $83.25. His health plan requires a 20% coinsurance. How much does he owe? Answer: $16.65 2. Scenario: Your practice
P a g e 1 Pre-Employment Test for Business Office Staff Answer Key 1. Mr. Walker owes $83.25. His health plan requires a 20% coinsurance. How much does he owe? Answer: $16.65 2. Scenario: Your practice
Granville Health System
 Approved by: Granville Health System FINANCIAL POLICY Effective Date: Revised Date(s): FINANCIAL POLICY - DRAFT 09-16-2014 Granville Health System is a not-for profit hospital committed to providing quality
Approved by: Granville Health System FINANCIAL POLICY Effective Date: Revised Date(s): FINANCIAL POLICY - DRAFT 09-16-2014 Granville Health System is a not-for profit hospital committed to providing quality
ebilling Support ebilling Support webinar: ebilling terms Lifecycle of a claim
 ebilling Support ebilling Support webinar: ebilling terms ebilling enrollment Lifecycle of a claim 2 Terms EDI Electronic Data Interchange Flow of electronic information, specifically claims information
ebilling Support ebilling Support webinar: ebilling terms ebilling enrollment Lifecycle of a claim 2 Terms EDI Electronic Data Interchange Flow of electronic information, specifically claims information
Provider Billing Manual. Description
 UB-92 Billing Instructions Revision Table Revision Date Sections Revised 7/1/02 Section 2.3 Form Locator 42 and 46 Description Language is being added to clarify UB-92 billing instructions for form locator
UB-92 Billing Instructions Revision Table Revision Date Sections Revised 7/1/02 Section 2.3 Form Locator 42 and 46 Description Language is being added to clarify UB-92 billing instructions for form locator
professional billing module
 professional billing module Professional CMS-1500 Billing Module Coding Requirements...2 Evaluation and Management Services...2 Diagnosis...2 Procedures...2 Basic Rules...3 Before You Begin...3 Modifiers...3
professional billing module Professional CMS-1500 Billing Module Coding Requirements...2 Evaluation and Management Services...2 Diagnosis...2 Procedures...2 Basic Rules...3 Before You Begin...3 Modifiers...3
Duplicate Claims Verify claims receipt with BCBSNM prior to resubmitting to prevent denials.
 Claims Submission Electronically : Use Payer ID 00790 For information on electronic filing of claims, contact Availity at 1-800-282-4548. Paper claims must be submitted on the Standard CMS-1500 (Physician/Professional
Claims Submission Electronically : Use Payer ID 00790 For information on electronic filing of claims, contact Availity at 1-800-282-4548. Paper claims must be submitted on the Standard CMS-1500 (Physician/Professional
Basics of the Healthcare Professional s Revenue Cycle
 Basics of the Healthcare Professional s Revenue Cycle Payer View of the Claim and Payment Workflow Brenda Fielder, Cigna May 1, 2012 Objective Explain the claim workflow from the initial interaction through
Basics of the Healthcare Professional s Revenue Cycle Payer View of the Claim and Payment Workflow Brenda Fielder, Cigna May 1, 2012 Objective Explain the claim workflow from the initial interaction through
HEALTH INSURANCE CLAIM FORM APPROVED BY THE BERMUDA HEALTH COUNCIL 10/09
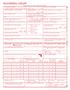 HEALTH INSURANCE CLAIM FORM APPROVED BY THE BERMUDA HEALTH COUNCIL 10/09 1. NAME OF INSURANCE COMPANY PLEASE PRINT OR TYPE IN UPPERCASE LETTERS 1a. INSURED S CERTIFICATE NUMBER ARGUS BF&M COLONIAL FM GEHI
HEALTH INSURANCE CLAIM FORM APPROVED BY THE BERMUDA HEALTH COUNCIL 10/09 1. NAME OF INSURANCE COMPANY PLEASE PRINT OR TYPE IN UPPERCASE LETTERS 1a. INSURED S CERTIFICATE NUMBER ARGUS BF&M COLONIAL FM GEHI
OSCAR Health Insurance Frequently Asked Questions/General Information
 Q: What is the relationship between Oscar and ValueOptions? A. ValueOptions administers the mental health and substance abuse benefits for Oscar Health Insurance. They have contracted with ValueOptions,
Q: What is the relationship between Oscar and ValueOptions? A. ValueOptions administers the mental health and substance abuse benefits for Oscar Health Insurance. They have contracted with ValueOptions,
Provider Manual. Billing and Payment
 Provider Manual Billing and Payment Billing and Payment This section of the Manual was created to help guide you and your staff in working with Kaiser Permanente s billing and payment policies and procedures.
Provider Manual Billing and Payment Billing and Payment This section of the Manual was created to help guide you and your staff in working with Kaiser Permanente s billing and payment policies and procedures.
HOSPITAL-ISSUED NOTICE OF NONCOVERAGE
 HOSPITAL-ISSUED NOTICE OF NONCOVERAGE Citations and Authority for Hospital-Issued Notice of Noncoverage (HINNs) The statutory authorities applicable to your review of a Hospital-Issued Notice of Noncoverage
HOSPITAL-ISSUED NOTICE OF NONCOVERAGE Citations and Authority for Hospital-Issued Notice of Noncoverage (HINNs) The statutory authorities applicable to your review of a Hospital-Issued Notice of Noncoverage
Revenue Cycle Objectives Challenges Management Goals and Expected Benefits Sample Metrics Opportunities Summary Solution Steps
 Common Findings Revealed: Revenue Cycle Review John Bartell, RN, BSN, Partner Tina Nazier, MBA, Director Wipfli LLP Topics for Discussion Revenue Cycle Objectives Challenges Management Goals and Expected
Common Findings Revealed: Revenue Cycle Review John Bartell, RN, BSN, Partner Tina Nazier, MBA, Director Wipfli LLP Topics for Discussion Revenue Cycle Objectives Challenges Management Goals and Expected
Instructions for submitting Claim Reconsideration Requests
 Instructions for submitting Claim Reconsideration Requests A Claim Reconsideration Request is typically the quickest way to address any concern you have with how we processed your claim. With a Claim Reconsideration
Instructions for submitting Claim Reconsideration Requests A Claim Reconsideration Request is typically the quickest way to address any concern you have with how we processed your claim. With a Claim Reconsideration
Top 50 Billing Error Reason Codes With Common Resolutions (09-12)
 Top 50 Billing Error Reason Codes With Common Resolutions (09-12) On the following table you will find the top 50 Error Reason Codes with Common Resolutions for denied claims at Virginia Medicaid. This
Top 50 Billing Error Reason Codes With Common Resolutions (09-12) On the following table you will find the top 50 Error Reason Codes with Common Resolutions for denied claims at Virginia Medicaid. This
COM Compliance Policy No. 3
 COM Compliance Policy No. 3 THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT CHICAGO NO.: 3 UIC College of Medicine DATE: 8/5/10 Chicago, Illinois PAGE: 1of 7 UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS COLLEGE OF MEDICINE CODING AND DOCUMENTATION
COM Compliance Policy No. 3 THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT CHICAGO NO.: 3 UIC College of Medicine DATE: 8/5/10 Chicago, Illinois PAGE: 1of 7 UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS COLLEGE OF MEDICINE CODING AND DOCUMENTATION
INSURANCE BILLING & COLLECTIONS PROCEDURES
 INSURANCE BILLING & COLLECTIONS PROCEDURES I. PURPOSE: To establish logical, consistent methods of billing and collections follow-up for Insurance balances to ensure that all staff members possess a good
INSURANCE BILLING & COLLECTIONS PROCEDURES I. PURPOSE: To establish logical, consistent methods of billing and collections follow-up for Insurance balances to ensure that all staff members possess a good
How to Bill for a School-Based Clinic
 How to Bill for a School-Based Clinic MDwise.org MDwise is a Hoosier Healthwise/HIP Plan A Hoosier Healthwise/HIP Plan Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Importance of School-Based Clinics... 3 Covered
How to Bill for a School-Based Clinic MDwise.org MDwise is a Hoosier Healthwise/HIP Plan A Hoosier Healthwise/HIP Plan Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Importance of School-Based Clinics... 3 Covered
Molina Healthcare of Washington, Inc. CLAIMS
 CLAIMS As a contracted provider, it is important to understand how the claims process works to avoid delays in processing your claims. The following items are covered in this section for your reference:
CLAIMS As a contracted provider, it is important to understand how the claims process works to avoid delays in processing your claims. The following items are covered in this section for your reference:
Publication CM-6 March 2013. Black Lung Medical Benefits: Questions and Answers about the Federal Black Lung Program
 Publication CM-6 March 2013 Black Lung Medical Benefits: Questions and Answers about the Federal Black Lung Program U.S. Department of Labor Office of Workers Compensation Programs Black Lung Medical Benefits:
Publication CM-6 March 2013 Black Lung Medical Benefits: Questions and Answers about the Federal Black Lung Program U.S. Department of Labor Office of Workers Compensation Programs Black Lung Medical Benefits:
Physician, Health Care Professional, Facility and Ancillary Provider Administrative Guide for American Medical Security Life Insurance Company
 Physician, Health Care Professional, Facility and Ancillary Provider Administrative Guide for American Medical Security Life Insurance Company Insureds 2009 Contents How to contact us... 2 Our claims process...
Physician, Health Care Professional, Facility and Ancillary Provider Administrative Guide for American Medical Security Life Insurance Company Insureds 2009 Contents How to contact us... 2 Our claims process...
New Medicare Policy May Adversely Affect Medi-Cal Dialysis Providers
 Chronic Dialysis Clinics Medi-Cal Bulletin March 2007 New Medicare Policy May Adversely Affect Medi-Cal Dialysis Providers Effective April 1, 2007, Medicare contractors will require End Stage Renal Dialysis
Chronic Dialysis Clinics Medi-Cal Bulletin March 2007 New Medicare Policy May Adversely Affect Medi-Cal Dialysis Providers Effective April 1, 2007, Medicare contractors will require End Stage Renal Dialysis
Provider Adjustment, Time limit & Medicare Override Job Aid
 Provider Adjustment, Time limit & Medicare Override Job Aid Contents Overview... 1 Medicaid Resolution Inquiry Form... 1 Medicare Overrides... 3 Time Limit Overrides... 3 Adjusting a Claim through the
Provider Adjustment, Time limit & Medicare Override Job Aid Contents Overview... 1 Medicaid Resolution Inquiry Form... 1 Medicare Overrides... 3 Time Limit Overrides... 3 Adjusting a Claim through the
UB-04, Inpatient / Outpatient
 UB-04, Inpatient / Outpatient Hospital (Inpatient and Outpatient), Hospice (Nursing Home and Home Services), Home Health, Rural Health linic, Federally Qualified Health enter, IF/MR, Birthing enter, and
UB-04, Inpatient / Outpatient Hospital (Inpatient and Outpatient), Hospice (Nursing Home and Home Services), Home Health, Rural Health linic, Federally Qualified Health enter, IF/MR, Birthing enter, and
Transactions Module. 70 Royal Little Drive. Providence, RI 02904. Copyright 2002-2014 Optum. All rights reserved. Updated: 3/1/14
 70 Royal Little Drive Providence, RI 02904 Copyright 2002-2014 Optum. All rights reserved. Updated: 3/1/14 Table of Contents 1 Transactions Module...1 2 Charge Overview...3 2.1.1 Explosion Codes...3 2.1.2
70 Royal Little Drive Providence, RI 02904 Copyright 2002-2014 Optum. All rights reserved. Updated: 3/1/14 Table of Contents 1 Transactions Module...1 2 Charge Overview...3 2.1.1 Explosion Codes...3 2.1.2
WELLCARE CLAIM PAYMENT POLICIES
 WellCare and Harmony Health Plan s claim payment policies are based on publicly distributed guidelines from established industry sources such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the
WellCare and Harmony Health Plan s claim payment policies are based on publicly distributed guidelines from established industry sources such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the
HCFA-1500 Form Completion. For the RLISYS NSF Electronic Claims Software. 2 Patient Name Patient s name as Last Name, First Name (Example: Doe, John)
 1 HCFA-1500 Form Completion For the RLISYS NSF Electronic Claims Software 2 Patient Name Patient s name as Last Name, First Name (Example: Doe, John) Do not include a prefix, suffix, or middle initial
1 HCFA-1500 Form Completion For the RLISYS NSF Electronic Claims Software 2 Patient Name Patient s name as Last Name, First Name (Example: Doe, John) Do not include a prefix, suffix, or middle initial
CHAPTER 7 (E) DENTAL PROGRAM CLAIMS FILING CHAPTER CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 7 (E) DENTAL PROGRAM CHAPTER CONTENTS 7.0 CLAIMS SUBMISSION AND PROCESSING...1 7.1 ELECTRONIC MEDIA CLAIMS (EMC) FILING...1 7.2 CLAIMS DOCUMENTATION...2 7.3 THIRD PARTY LIABILITY (TPL)...2 7.4
CHAPTER 7 (E) DENTAL PROGRAM CHAPTER CONTENTS 7.0 CLAIMS SUBMISSION AND PROCESSING...1 7.1 ELECTRONIC MEDIA CLAIMS (EMC) FILING...1 7.2 CLAIMS DOCUMENTATION...2 7.3 THIRD PARTY LIABILITY (TPL)...2 7.4
CMS-1500 Billing Guide for PROMISe Audiologists
 CMS-1500 Billing Guide for PROMISe udiologists Purpose of the document Document format The purpose of this document is to provide a block-by-block reference guide to assist the following provider types
CMS-1500 Billing Guide for PROMISe udiologists Purpose of the document Document format The purpose of this document is to provide a block-by-block reference guide to assist the following provider types
How To Pay For A Medical Procedure In The United States
 ANSI REASON CODES Reason codes, and the text messages that define those codes, are used to explain why a claim may not have been paid in full. For instance, there are reason codes to indicate that a particular
ANSI REASON CODES Reason codes, and the text messages that define those codes, are used to explain why a claim may not have been paid in full. For instance, there are reason codes to indicate that a particular
PATIENT FINANCIAL RESPONSIBILITY STATEMENT
 PATIENT FINANCIAL RESPONSIBILITY STATEMENT Thank you for choosing Medical Associates Clinic, P.C., as your healthcare provider. The medical services you seek imply an obligation on your part to ensure
PATIENT FINANCIAL RESPONSIBILITY STATEMENT Thank you for choosing Medical Associates Clinic, P.C., as your healthcare provider. The medical services you seek imply an obligation on your part to ensure
Critical Access Hospital (CAH) and CAH Swingbed Questions and Answers
 Critical Access Hospital (CAH) and CAH Swingbed Questions and Answers The following questions and answers are from the April 2012 CAH and CAH Swingbed web-based trainings: Q1. Is a non-covered/no pay bill
Critical Access Hospital (CAH) and CAH Swingbed Questions and Answers The following questions and answers are from the April 2012 CAH and CAH Swingbed web-based trainings: Q1. Is a non-covered/no pay bill
Molina Healthcare of Puerto Rico (MHPR) Non-Participating Provider Information
 Molina Healthcare of Puerto Rico (MHPR) Non-Participating Provider Information Please refer to Carta Normativa 15-0326 Re Transicion for details regarding the ASES-established Transition of Care and Reimbursement
Molina Healthcare of Puerto Rico (MHPR) Non-Participating Provider Information Please refer to Carta Normativa 15-0326 Re Transicion for details regarding the ASES-established Transition of Care and Reimbursement
IWCC 50 ILLINOIS ADMINISTRATIVE CODE 7110 7110.90. Section 7110.90 Illinois Workers' Compensation Commission Medical Fee Schedule
 Section 7110.90 Illinois Workers' Compensation Commission Medical Fee Schedule a) In accordance with Sections 8(a), 8.2 and 16 of the Workers' Compensation Act [820 ILCS 305/8(a), 8.2 and 16] (the Act),
Section 7110.90 Illinois Workers' Compensation Commission Medical Fee Schedule a) In accordance with Sections 8(a), 8.2 and 16 of the Workers' Compensation Act [820 ILCS 305/8(a), 8.2 and 16] (the Act),
1. All patient services must be billed on a fully completed CMS 1500 or UB04 form, unless otherwise indicated by contract.
 Claims 8.0 As a Participating Provider billing for services with a fee-for-service contract with MAPMG, please follow the procedures listed below. Participating Providers billing for services rendered
Claims 8.0 As a Participating Provider billing for services with a fee-for-service contract with MAPMG, please follow the procedures listed below. Participating Providers billing for services rendered
Zimmer Payer Coverage Approval Process Guide
 Zimmer Payer Coverage Approval Process Guide Market Access You ve Got Questions. We ve Got Answers. INSURANCE VERIFICATION PROCESS ELIGIBILITY AND BENEFITS VERIFICATION Understanding and verifying a patient
Zimmer Payer Coverage Approval Process Guide Market Access You ve Got Questions. We ve Got Answers. INSURANCE VERIFICATION PROCESS ELIGIBILITY AND BENEFITS VERIFICATION Understanding and verifying a patient
Claim Form Billing Instructions CMS 1500 Claim Form
 Claim Form Billing Instructions CMS 1500 Claim Form Item Required Field? Description and Instructions. number 1 Optional Indicate the type of health insurance for which the claim is being submitted. 1a
Claim Form Billing Instructions CMS 1500 Claim Form Item Required Field? Description and Instructions. number 1 Optional Indicate the type of health insurance for which the claim is being submitted. 1a
KPMAS also has the ability to receive your claims electronically through the Emdeon Clearinghouse.
 8.0 Claims As a Participating Provider billing for services with a fee-for-service contract with MAPMG, please follow the procedures listed below. Participating Providers billing for services rendered
8.0 Claims As a Participating Provider billing for services with a fee-for-service contract with MAPMG, please follow the procedures listed below. Participating Providers billing for services rendered
Home Study Course for the Medical Biller
 Chapter 3 M E D I C A L B I L L I N G C O U R S E. C O M, L L C Home Study Course for the Medical Biller Copyright 1999-2014, Medical Billing Course Chapter 3 Internet Resource Downloadable CMS 1500 Form
Chapter 3 M E D I C A L B I L L I N G C O U R S E. C O M, L L C Home Study Course for the Medical Biller Copyright 1999-2014, Medical Billing Course Chapter 3 Internet Resource Downloadable CMS 1500 Form
Hackensack University Medical Center Administrative Policy Manual. Effective Date: January 2016 Page 1 of 11
 Policy #: 1845 Hackensack University Medical Center Administrative Policy Manual Effective Date: January 2016 Page 1 of 11 Purpose: To identify the governing rules for the collection of all fees associated
Policy #: 1845 Hackensack University Medical Center Administrative Policy Manual Effective Date: January 2016 Page 1 of 11 Purpose: To identify the governing rules for the collection of all fees associated
Patient Financial Policy
 Patient Financial Policy We want you to concentrate on feeling better instead of worrying about how you're going to pay your bill. Please review this Patient Financial Policy for answers to commonly asked
Patient Financial Policy We want you to concentrate on feeling better instead of worrying about how you're going to pay your bill. Please review this Patient Financial Policy for answers to commonly asked
Chapter 6 Policies and Procedures Unit 1: Other Party Liability
 Chapter 6 Policies and Procedures Unit 1: Other Party Liability In This Unit Topic See Page Unit 1: Other Party Liability Coordination of Benefits 2 Frequently Asked Questions About COB 5 6.1 Coordination
Chapter 6 Policies and Procedures Unit 1: Other Party Liability In This Unit Topic See Page Unit 1: Other Party Liability Coordination of Benefits 2 Frequently Asked Questions About COB 5 6.1 Coordination
Title 40. Labor and Employment. Part 1. Workers' Compensation Administration
 Title 40 Labor and Employment Part 1. Workers' Compensation Administration Chapter 3. Electronic Billing 301. Purpose The purpose of this Rule is to provide a legal framework for electronic billing, processing,
Title 40 Labor and Employment Part 1. Workers' Compensation Administration Chapter 3. Electronic Billing 301. Purpose The purpose of this Rule is to provide a legal framework for electronic billing, processing,
Medicare Coding and Billing Part 1
 Medicare Coding and Billing Part 1 Medicare Fee ScheduleMedicare has released next year s fee schedule There is a 27% cut in fees. This will be in effect until Congress takes action to delay it again.
Medicare Coding and Billing Part 1 Medicare Fee ScheduleMedicare has released next year s fee schedule There is a 27% cut in fees. This will be in effect until Congress takes action to delay it again.
CLAIMS Section 5. Overview. Clean Claim. Prompt Payment. Timely Claims Submission. Claim Submission Format
 Overview The Claims department partners with the Provider Relations, Health Services and Customer Service departments to assist providers with any claims-related questions. The focus of the Claims department
Overview The Claims department partners with the Provider Relations, Health Services and Customer Service departments to assist providers with any claims-related questions. The focus of the Claims department
Glossary of Terms. Account Number/Client Code. Adjudication ANSI. Assignment of Benefits
 Account Number/Client Code Adjudication ANSI Assignment of Benefits Billing Provider/Pay-to-Provider Billing Service Business Associate Agreement Clean Claim Clearinghouse CLIA Number (Clinical Laboratory
Account Number/Client Code Adjudication ANSI Assignment of Benefits Billing Provider/Pay-to-Provider Billing Service Business Associate Agreement Clean Claim Clearinghouse CLIA Number (Clinical Laboratory
Frequently Asked Questions About Your Hospital Bills
 Frequently Asked Questions About Your Hospital Bills The Registration Process Why do I have to verify my address each time? Though address and telephone numbers remain constant for approximately 70% of
Frequently Asked Questions About Your Hospital Bills The Registration Process Why do I have to verify my address each time? Though address and telephone numbers remain constant for approximately 70% of
Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) Billing No. Yes. Yes. Yes. Yes
 Does an MSP record appear on the beneficiary s ELGA/ELGH file? Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) Billing Do your dates of service fall within the effective and term dates on the MSP record? Is the MSP record
Does an MSP record appear on the beneficiary s ELGA/ELGH file? Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) Billing Do your dates of service fall within the effective and term dates on the MSP record? Is the MSP record
SCAN Member Eligibility & Benefits
 SCAN Member Eligibility & Benefits Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week Toll free number is 877-270-SCAN (7226) Online Eligibility Verification For initial setup, contact
SCAN Member Eligibility & Benefits Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week Toll free number is 877-270-SCAN (7226) Online Eligibility Verification For initial setup, contact
Instructions for Completing the CMS 1500 Claim Form
 Instructions for Completing the CMS 1500 Claim Form The Center of Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) form 1500 must be used to bill SFHP for medical services. The form is used by Physicians and Allied
Instructions for Completing the CMS 1500 Claim Form The Center of Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) form 1500 must be used to bill SFHP for medical services. The form is used by Physicians and Allied
Generali Worldwide Group Health Insurance Health Insurance Claim Form
 Generali Worldwide Group Health Insurance Health Insurance Claim Form Please complete all sections in BLOCK CAPITALS or tick the boxes, where appropriate. Instructions for Submitting a Claim 1. Complete
Generali Worldwide Group Health Insurance Health Insurance Claim Form Please complete all sections in BLOCK CAPITALS or tick the boxes, where appropriate. Instructions for Submitting a Claim 1. Complete
August 2014. SutterSelect Administrative Manual
 August 2014 SutterSelect Administrative Manual Introduction This SutterSelect Administrative Manual has been prepared as a resource for providers who are caring for members of SutterSelect health plans.
August 2014 SutterSelect Administrative Manual Introduction This SutterSelect Administrative Manual has been prepared as a resource for providers who are caring for members of SutterSelect health plans.
Your Revenue Cycle It s not just billing anymore. Presented by: Candy Edie, MBA, CRCE-I
 Your Revenue Cycle It s not just billing anymore Presented by: Candy Edie, MBA, CRCE-I POSITIONS Staff Accountant Chief Financial Officer Financial Systems Analyst Patient Access Director Patient Financial
Your Revenue Cycle It s not just billing anymore Presented by: Candy Edie, MBA, CRCE-I POSITIONS Staff Accountant Chief Financial Officer Financial Systems Analyst Patient Access Director Patient Financial
STATE OF NEVADA DEPARTMENT OF BUSINESS & INDUSTRY DIVISION OF INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS WORKERS COMPENSATION SECTION
 STATE OF NEVADA DEPARTMENT OF BUSINESS & INDUSTRY DIVISION OF INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS WORKERS COMPENSATION SECTION NEVADA MEDICAL FEE SCHEDULE MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE PROVIDER PAYMENT February 1, 2012 through January
STATE OF NEVADA DEPARTMENT OF BUSINESS & INDUSTRY DIVISION OF INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS WORKERS COMPENSATION SECTION NEVADA MEDICAL FEE SCHEDULE MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE PROVIDER PAYMENT February 1, 2012 through January
CODING. Neighborhood Health Plan 1 Provider Payment Guidelines
 CODING Policy The terms of this policy set forth the guidelines for reporting the provision of care rendered by NHP participating providers, including but not limited to use of standard diagnosis and procedure
CODING Policy The terms of this policy set forth the guidelines for reporting the provision of care rendered by NHP participating providers, including but not limited to use of standard diagnosis and procedure
