Glossary 2. About this chapter An introduction to strategic business planning 6
|
|
|
- Adam Higgins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents Glossary 2 About this chapter An introduction to strategic business planning What is strategic business planning? Why does the Board need a strategic business plan? Features of a successful strategic business plan Conclusion 9 Chapter The planning process Introduction Preparation Developing the plan Finalising and documenting the plan Implementation Monitoring Evaluation Board responsibilities at different stages of the planning process Conclusion Developing the strategic business plan Introduction Establishing the organisation s vision Analysis of the organisation s current situation Setting strategic directions Resource analysis Risk analysis and contingency planning Conclusion Finalising and documenting the plan Introduction Finalising the plan Documenting the plan Conclusion Monitoring and evaluation Introduction Monitoring by the Board Evaluation Conclusion 24 Resources 25 1
2 Glossary Disclaimer: DADHC does not warrant that these definitions are correct. Directors should seek professional legal advice relevant to their issues. Actions (strategies or tasks) the activities needed to achieve objectives and vision. Action plan the details of the activities (what will be done, the timeframes, resource and staff allocation) to be carried out during the period of the strategic business plan. Board the governing body of a non-government organisation, made up of Directors or members of a management committee. Brainstorming a group discussion to generate ideas. Budget a financial plan, describing estimated future income and expenses, how these costs fall within a given period of time and the implications for the future financial wellbeing of the organisation. Director a person formally elected and/or appointed under law to a Board, in accordance with the organisation s constitution. Note: Associations refer to the members of their governing body as management committee members. The term Director is used in this manual to include management committee members. Contingency an additional or alternative action to manage situations when they do not go according to plan. Core business the main activities of an organisation. Environment analysis an examination of the context in which an organisation works and the identification of the key factors which impact on the organisation. Evaluation the formal process of assessing whether the implementation of a strategic business plan, or an activity, has been successful. Governance the legal authority of a Board to make decisions and establish policies and plans. The Board is accountable for the outcome of such decisions. Implementation putting a plan into action. 2
3 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) the benchmarks or targets that have been chosen to measure how successfully an organisation has achieved its objectives. Mandate the authority of a Board to act on behalf of members of the organisation. Chapter 3 Milestones the measurable stages of progress towards achieving a planned objective, such as the date something is achieved or the quantity of an output. Monitor to check, supervise, observe critically, or record the progress of an activity, action or system on a regular basis to identify change. Objectives what an organisation wants to achieve as a result of its planned activities. Sometimes the term objective is used interchangeably with the terms goals or aims. Outcomes the results of planned actions. Outputs the products or instances of service produced by a set of actions that can be counted. Planning cycle the continual process of preparing to plan, developing a plan, implementing the plan and reviewing the success of the plan. Purpose statement an organisation s written summary of its values and core business. Qualitative a measure of the quality or qualities of an outcome. Quantitative a numeric measure of an outcome. Risk the chance of something happening that will have an adverse impact on an organisation s objectives. Risk is measured in terms of likelihood and consequences. Risk analysis the process of identifying and assessing the likelihood and consequences of potential risks. Risk management the process of identifying strategies to prevent or control the impact of risks. Stakeholders any person or organisation with an interest in the operations of an organisation. 3
4 Strategic business planning a process to map how an organisation can use its resources to successfully achieve its objectives over a period of time (usually three to five years). Strategic directions the parameters for defining what an organisation will do, based on an analysis of its operating environment and its internal capacity. SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis a snapshot assessment of an organisation s environment and capacity. Values the core principles that guide an organisation s service delivery and management. Vision where an organisation wants to be at the end of the planning period. 4
5 About this chapter As a Director you have responsibility for organisational planning and setting and reviewing goals. Taking a strategic approach to business planning enables the Board to carefully consider the financial sustainability of services and activities and how diversification or expansion can be achieved in the future. Chapter 3 The strategic business plan gives an overview of the service, describes the organisation s future directions, identifies key milestones, promotes better governance and helps the Board to do their job well. This chapter has been designed to assist Directors in the strategic business planning process. It describes the importance of having a regular cycle of planning, monitoring and evaluation and of thinking beyond the constraints of your current funding. Policy Checklists are included at the end of this chapter. They can be copied and worked through by your entire Board on an annual basis, or as required. 5
6 3.1 An introduction to strategic business planning What is strategic business planning? Planning is a process of organising resources and applying them to activities to achieve intended results. Strategic business planning maps out how an organisation can successfully achieve its objectives over a period of time (usually three to five years). Strategic business planning involves: Analysing and assessing the current situation, including the external environment Identifying what the organisation wants to achieve Confirming the ongoing work Deciding any changes to ongoing work and any new activities Identifying the resources Documenting agreed actions, timeframes and responsibilities Describing how the organisation will know that the plan is being followed and objectives are being achieved. A strategic business plan is a document that outlines where the organisation is now, its vision for the future and the actions and resources that will move it from where it is now to where it wants to be. The plan is linked to a budget (or financial plan). The strategic business plan specifically identifies what is required to take each step forward, including: Actions Budget Human and other resources Individual and team responsibilities Timelines Milestones Monitoring and evaluation. 6
7 3.1.2 Why does the Board need a strategic business plan? Effective strategic business planning provides a number of benefits for an organisation: Direction and common purpose Chapter 3 Clarity about what is to be done Increased control over future development A basis for monitoring and evaluating performance A clear way of communicating. A strategic business plan enables a Board to provide leadership and maintain an overview of the organisation s priorities and direction. A strategic business plan is a logical, considered plan for the organisation s future, based on an assessment of the present and a best guess about the future. The strategic business planning process requires Directors and senior staff to make a commitment to working towards a shared vision for the future. As part of the strategic business planning process, the Board will agree on a broad vision and set of values, approve the steps needed to achieve objectives and determine how progress and success will be measured. The strategic business planning process helps the Board to: Fulfil its governance responsibility to set direction and monitor performance Understand, communicate and demonstrate the organisation s purpose Identify opportunities Confirm a shared commitment Reach agreement Be confident the organisation will remain financially viable and sustainable Identify clear responsibilities, resource needs and timeframes Guide the organisation s progress and keep on track towards the future vision. The strategic business planning process encourages an organisation to be innovative, creative, open to change and forward looking. 7
8 3.1.3 Features of a successful strategic business plan There are seven key features of a successful strategic business plan 1 regardless of the planning process or the format of the plan. 1. Vision the shared sense of purpose of where the organisation wants to be at the end of the planning period. 2. Commitment commitment from Directors, staff, volunteers and (where relevant) key stakeholders is essential to making sure the vision is realised. 3. Timelines plans with target times for achieving each milestone and reaching goals are more successful than those that leave the timing open. Timelines clarify priorities and the order in which things need to happen for them to work best. 4. Clear objectives and actions objectives and actions should accurately describe what must be done to realise the vision. 5. Regular reporting reporting against a plan enables an organisation to keep an eye on what is being achieved, whether actions are being done within budget and on time and how the organisation is performing. 6. Contingencies considering potential problems and setbacks in advance enables a Board to respond quickly and make changes to get back on track. 7. Responsiveness to change it is important that any major changes affecting the organisation are quickly reflected within the strategic business plan as they can affect the organisation s ability to realise its vision. A well-designed strategic business plan that deals with these seven elements will assist Directors in their role. 1 Adapted from Australian Sports Commission: 8
9 3.1.4 Conclusion Strategic business planning provides structure and rigor to organisational decision making and plays an important role in good governance. Members of the Board have a responsibility to be active participants in strategic business planning. The role of the Board is to: Chapter 3 Develop and set overall directions Monitor progress towards the achievement of goals Evaluate the continued relevance of the plan Agree to changes to the plan. Active participation in the strategic business planning process will inform and equip Board members to undertake their governance role. 9
10 3.2 The planning process Introduction Strategic business planning needs to be thought of as a cycle of thinking, doing and checking. The process for developing and implementing a strategic business plan is often called the planning cycle. The diagram below illustrates the different stages of the planning cycle: Preparation Evaluation Development of the plan: - Vision - Analysis - Strategic direction - Resource and risk analysis Review and change Monitoring Finalisation and documentation Implementation of plan The evaluation at the end of the cycle informs future planning Preparation Before planning starts the Board will need to consider the following: The scope of the exercise How the plan will be developed Who needs to participate, and how Resources 10
11 How the plan will be used The most suitable format of the plan What information will be needed and where this can be gathered Chapter 3 Links with other planning processes Timeframe. Directors may be able to contribute to the gathering of information. Information may be gathered from a range of sources including: Service delivery records Board and staff records Financial performance Trends or direction in social policy Other services or agencies Stakeholders, including service users. All stakeholders can contribute to the planning process where relevant. Views of stakeholders can be canvassed through face to face consultations or workshops, or through surveys or interviews Developing the plan The process of developing the strategic business plan involves the following: Establishing and confirming the organisation s vision Analysis of the organisation s current situation, including services, resources, financial analysis and an analysis of the external environment Setting strategic directions for future business opportunities and actions to achieve planned results Resource and risk analysis. 11
12 3.2.4 Finalising and documenting the plan After the planning process has taken place a draft document is written (by a member of staff or a consultant). The draft should include: Actions and activities Performance measures for evaluating the outcomes Detailed resource analysis Budget details. Following discussion the final plan will be presented to the Board for approval Implementation Responsibility for the implementation of the organisation s strategic business plan generally rests with the senior staff. The plan will inform individual and team work plans and progress will be reported to the Board Monitoring The Board is responsible for undertaking regular (monthly, bi-monthly or quarterly) monitoring of the organisation s performance against the strategic business plan. The Board monitors: The achievement of milestones and objectives in relation to the budget and timeframes General achievements reflected in KPIs Staff may present written reports addressing actions and milestones for the Board to compare against the budget to monitor how well the plan is progressing Evaluation The formal evaluation of the impact of the plan is generally conducted at the end of the planning period and feeds information into the preparation stage of the next planning cycle. 12
13 The evaluation may involve internal and external stakeholders and should be carried out with enough time to develop and agree the new plan before the previous plan ends. Chapter Board responsibilities at different stages of the planning process The Board can delegate responsibility for most aspects of the strategic business planning and implementation process to members of staff. The Board is primarily responsible for establishing the broad strategic directions, for approving the finalised plan and for regular review. To summarise the responsibilities of Directors in relation to strategic business planning, the Board should: Provide leadership in determining the organisation s vision and values Set strategic directions Ensure effective risk analysis is undertaken Be committed to the implementation of the plan Ensure staff accountability for delegated responsibilities Undertake regular and effective performance monitoring Agree and monitor changes Ensure compliance with any external reporting requirements Drive, and participate in, the evaluation of the plan Make sure the next planning cycle starts in good time Conclusion Strategic business planning is a cyclical process that includes planning, developing, implementing and reviewing. The Board should maintain an overview of the entire planning process but need not have a detailed role to play at every stage. 13
14 3.3 Developing the strategic business plan Introduction There are many ways to develop a strategic business plan. The Board will need to make decisions about who is to be involved at particular stages. It is most common for Boards to set aside dedicated time and hold one or two planning sessions (with or without staff). The planning process should be participatory and consultative. External facilitators are commonly used to provide structure to the discussion, ensure that it stays on track and then analyse and document the outcomes Establishing the organisation s vision An organisation s vision should be written as a clear statement that defines and communicates its purpose. A purpose statement is usually accompanied by a statement of core values the beliefs and principles that guide the manner in which an organisation operates. Most organisations will already have a purpose statement. It is important to check that it remains relevant on a regular basis. Having a clear purpose is important for developing a vision of where the organisation hopes to be in three or five years time Analysis of the organisation s current situation Analysis of the current situation is an important part of the planning process. The Board should consider: The market for the organisation s services or activities and how this may be changing. This involves reviewing current services provided, their effectiveness and efficiency, changes in client needs, client responses to current services and trends in funding or policy. The organisation s environment. This involves identifying current trends and likely changes, such as social or population group changes, government changes or policy developments, new requirements or standards, local community developments or activities of other agencies. Internal issues that need to be addressed. Aspects of the organisation s operation may already have been identified as requiring attention, perhaps as a result of an evaluation or review process. These issues may include 14
15 limitations or problems in staffing, systems and processes, administration, management, communication and other operational aspects. The way that external relationships with other agencies and networks (including funding bodies) may impact on the organisation s plans. This should include how the organisation is seen by others and describe any actions needed to build a positive reputation and productive relationships with other agencies. Chapter 3 The financial position of the organisation. The financial analysis informs the business planning in terms of the financial feasibility of existing and new initiatives. Using SWOT A SWOT analysis is a useful process for the Board and the staff to take part in as it combines an assessment of the organisation s internal environment (strengths and weaknesses) and its external environment (opportunities and threats). It is usually conducted as a group discussion. Strengths Strengths focus on the internal abilities in the organisation and its capacity to achieve its objectives. Strengths include: A strong financial base An established and experienced team of capable staff and volunteers A committed and highly skilled Board. Strengths need to be protected and used to reduce the impact of weaknesses and threats. 15
16 Weaknesses Weaknesses often appear as the direct opposite of the strengths. They include: Demoralised and fragmented staff team Inefficient systems. It is essential that the plan addresses issues like these directly with specific action as they will otherwise undermine the achievement of objectives. Opportunities Opportunities are the possibilities for growth, diversification and consolidation because of new or previously untapped sources of support or changes in the external environment. Opportunities include: New sources of grant money or sponsorship Growing public awareness Increasing interest in corporate responsibility programs. The Board needs to ensure that the organisation is able to take advantage of such opportunities when they arise. Threats Threats are the factors that may limit or prevent the growth or further development of the service. Threats include: A core funding program ending A potential partner organisation choosing to work exclusively with another agency Potential increases in expenses such as office rent. Threats can be managed by seeking alternative opportunities or by taking positive action to turn them around. 16
17 Carrying out a SWOT analysis will enable the Board to identify: The positive internal and external influences Potential difficulties Chapter 3 Necessary changes to protect itself from negative influences Opportunities to be explored Setting strategic directions The conclusions of the analysis of the organisation s current situation, the statement of purpose and the values and the vision statement will form the basis for the development of the strategic directions and objectives in the plan. The Board can assist in setting strategic directions by: 1. Identifying results that: Improve the effectiveness of services in terms of the outcomes for clients Develop a more diverse funding base Change the focus of services to align with new policy directions Increase the involvement of organisation members Develop a series of collaborative partnerships with key agencies Improve the productivity and morale of staff. 2. Thinking strategically about how to achieve them, i.e. identifying the actions required to achieve the objectives. Reviewing the results of the SWOT analysis will enable the Board to: Review and discuss the information gathered that will affect the plan (such as a review and evaluation, existing contracts and obligations, existing resources, external requirements, and client feedback) Analyse the impact Identify what the Board wants the organisation to achieve Decide the priorities for activities and initiatives. 17
18 3.3.5 Resource analysis Strategic directions need to be assessed against the resources required. This involves estimating the resources that may be needed, including: Direct costs Impact on staffing Changes or developments Equipment requirements Office space. Some of these items can be estimated in terms of actual financial costs and others will need to be assessed in terms of the impact on overall productivity. It is critical that the Board ensures that appropriate levels of resources are available for all proposed actions Risk analysis and contingency planning The Board has a responsibility to take all reasonable steps to avoid foreseeable harm or loss to the organisation, therefore a risk assessment of the strategic business plan should be carried out Conclusion The organisation s vision statement and an analysis of the operating environment will form the basis for the development of the detailed objectives and strategies in the strategic business plan. The Board s vision and commitment are critical to a strategic business plan. Active participation from the Board will ensure a solid foundation exists to develop the plan. 18
19 3.4 Finalising and documenting the plan Introduction Once the Board has determined the strategic directions and the broad content of the strategic business plan, the plan needs to be finalised and documented. The guiding principle for writing or critically assessing the plan should be to keep it clear, short and simple. Chapter Finalising the plan The finalisation of the strategic business plan involves: Completion of plan details Development of budgets and any associated plans Review and approval by the Board Documenting the plan The plan needs to be documented so that it can be used to: Guide the work of staff Monitor progress and achievements Make adjustments as a result of monitoring and review Provide information to key stakeholders or the community in general (although it is not usually necessary to provide detailed implementation plans to the public). A strategic business plan need not be long or complicated, but should include the following: A description of the purpose and an overview of the organisation The analysis of the environment and identification of key opportunities and challenges Key strategic directions Broad timeframes Key performance indicators Overview of proposed activities and services Analysis of the resource implications 19
20 Risk analysis and contingency plans Plan for the review and update of the plan Conclusion The Board has a critical role to play in overseeing the final content and shape of the strategic business plan. Once the required detail has been added, the Board needs to review the plan to ensure that it accurately reflects the decisions about strategic directions and is achievable. 20
21 3.5 Monitoring and evaluation Introduction It is the role of staff to carry out the implementation of the strategic business plan. The senior manager should ensure the plan is implemented and monitored appropriately. Chapter 3 Effective implementation of the strategic business plan requires the senior manager to: Effectively communicate Document processes Ensure the development of individual and team staff work plans Develop contingency plans Align actions with funding and financial cycles Monitor the budget Regularly report to the Board Monitoring by the Board The Board is responsible for regularly monitoring the successful implementation of the plan. The Board should review: Progress of the plan Performance against the budget Achievements. The Board will also need to be made aware of any new information that may impact on the organisation. Monitoring may indicate that planned work is happening on or ahead of time, or within budget, or meeting or even exceeding objectives. Positive feedback is encouraging and helpful for promoting the reputation and worth of the organisation. Monitoring may show that intended objectives have not been achieved. In these cases the Board will need to respond and may need to make adjustments to the plan to make sure that the objectives and actions are realistic and fit with changed circumstances or new information. 21
22 The following diagram illustrates the relationship between the plan, staff reporting and monitoring by the Board. STRATEGIC BUSINESS PLAN Renew and adjustment of plan REPORT TO BOARD AGAINST PLAN Senior staff review environmental changes and prepare report to Board STAFF WORK PLANS Summary results of staff work plans Organisational performance data related to performance measures Performance measures The Board need not be involved in the actual development of performance measures but they are responsible for approving them for the strategic business plan. The quality of the performance measures is very important for effective monitoring. The Board should consider whether the performance measures are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Timely). Performance measures should not: Be too broad or unachievable Be difficult to collect data on. Performance measures should accurately reflect the activities of the organisation. All performance measures can fit into one of four categories, derived from the intersection of quantity and quality versus effort and effect. This is used by Mark Friedman in his Results Based Accountability Framework 2 : 2 Mark Friedman, Results Accountability: 22
23 EFFORT QUANTITY How much did we do? How much service did we deliver? QUALITY How well did we do it? How well did we deliver our service? Chapter 3 EFFECT Is anyone better off? (number) How much change for the better did we produce Is anyone better off? (percentage) What quality of change for the better did we produce? The two groups of performance measures that are most important for the Board to consider are: Quality and effort these tell whether the service and its related functions are done well. They include business administration issues such as timeliness of service, accessibility, cultural competence, staff turnover and morale. Quality and effect these tell whether clients are better off as a consequence of receiving a service. Performance measures should also: Be directly relevant to the Board s role as decision makers Enable reporting to key stakeholders Be realistic Provide a balance between short and longer term objectives, qualitative and quantitative data and economy, efficiency and effectiveness Be relevant Be unbiased and supported by data that is reliable and easy to collect Evaluation The strategic business planning process is ongoing and should be updated on a yearly basis to reflect any major changes affecting the organisation. This would generally be internal to the organisation, and at the end of the plan a more thorough evaluation, perhaps using an external consultant and seeking input from external stakeholders, should be undertaken. 23
24 The evaluation will help the Board to prepare for the next strategic business planning process. The purpose of evaluation is the same as the plan itself to keep the organisation heading in the right direction, towards the vision it has for the future and consistent with its purpose and values Conclusion The implementation and management of the strategic business plan is primarily the responsibility of staff, whereas monitoring the plan is primarily the responsibility of the Board. The purpose of the Board monitoring the implementation of the strategic business plan is to: Ensure that progress is made Recognise successes and achievements To take action to correct problems Adjust the plan to take advantage of, or address changes in, the organisation s environment. Staff have an advisory role and there should ideally be a collaborative relationship between staff and the Board in the implementation and monitoring of the plan. The timing of the planning process is important. That is, it is important to identify the linkages between the planning cycle and current and / or future accounting period reporting requirements (e.g. annual reports, financial statements). 24
25 Chapter 3 25
26 Resources SWOT Analysis Template INTERNAL FACTORS List items that are strengths within the organisation For each strength, indicate how this strength can be supported and used to support the plan List items that are weaknesses or vulnerable points within the organisation For each weakness, indicate how this area could be strengthened or improved 26
27 Chapter 3 EXTERNAL FACTORS List items that present opportunities for the organisation For each opportunity, indicate how this could be pursued List items that present threats or challenges for the organisation For each threat, indicate how this could be prevented from impacting on the organisation, or even turned into an opportunity 27
28 Working Through the Planning Process The following can be used to guide the involvement of your Board in the strategic business planning process. Tick the boxes as you achieve each step. Stages 10 and 11 will be repeated throughout the period of the plan. 1. Preparation Achieved Ensure the Board is committed to the planning process Start the planning cycle in good time to prepare a new plan before the current one has ended Decide the scope and the period of the plan (e.g. 1, 3 or 5 years) Consider recommendations from senior staff about how to carry out the proposed planning process Decide who is to be involved and the broad process that will be followed Allocate necessary resources Set up planning / coordination team Allocate tasks Set dates for planning sessions that will involve the Board 2. Carry out background research and consultation Identify key stakeholders to be involved Identify the range of information required Approve stakeholder input being gathered (consultations, surveys, interviews) Receive summary reports of research (service data, financial data, relevant population or client data, review of organisational performance, external issues and factors) 3. Establish the organisation s vision Confirm the continued relevance of purpose statement and values (and make agreed changes) Provide leadership in determining the organisation s vision Sign off on the vision and purpose statements 4. Analysis of organisation s current situation Play an active role in analysing the organisation s operating environment Receive reports from staff with delegated responsibilities for other agreed analysis 5. Set strategic directions Achieved 28
29 Chapter 3 Participate in planning sessions involving stakeholders Identify key objectives Identify key actions or strategies Decide on priorities 6. Resource and risk analysis Review resource implications of draft plan Ensure effective risk analysis is undertaken on the draft plan Approve contingency plan 7. Documenting the plan Provide input to drafts of the plan Participate in the development of appropriate performance measures for key objectives 8. Budget setting Provide input to the draft budget Approve the final budget 9. Finalise and approve Approve the final version of the strategic business plan Confirm your commitment to the implementation of the plan 10. Implementation and monitoring Undertake regular and effective performance monitoring Monitor the budget against the financial reports Agree and monitor changes to the plan or to work practices, policies, systems or resource allocation, arising from the monitoring process Ensure compliance with any external reporting requirements in relation to the strategic business plan 11. Evaluation Drive and participate in the evaluation of the plan annually Drive and participate in the evaluation of the plan at the end of the planning period 29
30 Checking Your Plan Does your strategic business plan have these seven features? What can you do to enhance the effectiveness of each feature? Yes/No Actions needed 1. Vision Members of the Board and staff team have participated in a process to agree our organisation s vision for the future. We have a written statement that accurately states our vision. 2. Commitment All members of our Board support the plan. We have a sign off process for confirming the commitment of Directors and key staff to implementing and reviewing the plan. All members of our Board recognise that the plan is a living document that must be used, and adjusted as required. 3. Timelines Our plan covers a set period. Our plan includes clear timeframes for undertaking each action. 4. Objectives All actions in our plan relate to a stated objective. All objectives in our plan relate directly to achieving our vision. Stages in progress towards meeting our objectives (milestones) are identified in our plan. We have developed KPIs that will show we have reached our milestones and our objectives. 30
31 Chapter 3 5. Reporting Our plan clearly states who is responsible for implementing each action in the plan. We have a standard format for staff to report against the plan in relation to their particular areas of responsibility. Our Board regularly discusses progress towards meeting our objectives. When this monitoring process shows that what we have achieved is different to what we planned (in terms of cost, timing, outcome), we carefully analyse the reasons for this. We take decisive action to adjust either our plan, or our policies/practices/ systems, as necessary and appropriate. 6. Contingencies Our organisation undertook a risk analysis of our plan before sign off. Our plan identifies potential risks to achieving our objectives and vision. Our plan includes contingencies (agreed changes to our actions in the event of certain risks occurring). 7. Change Our organisation monitors our environment to identify changes that may impact on the success of our plan, as part of our regular reporting/ monitoring process. We make changes to our plan to respond to significant change in our environment. Yes/No Actions needed 31
32 Checklists Checklist: This checklist contains issues your Board should consider in developing and implementing successful strategic business planning for the organisation. Tick Yes or No to indicate your organisation s status for each item. DIRECTOR S NOTE This checklist might be used by the Board prior to undertaking strategic business planning, and during the planning year. Questions Yes No Comments/Actions Understanding of strategic business planning Our Board Has an existing strategic business plan that has met our needs and/or understands what a strategic business plan is. Has engaged in a strategic business planning process that met our needs and/or has a good understanding of the features of successful strategic business planning. Understands the benefits for our organisation of having a strategic business plan and going through a planning process. 32
33 Chapter 3 Questions Yes No Comments/Actions The planning cycle Do we understand the components of the planning cycle? Do we have a broad understanding of each of the steps in the strategic business planning process? Design the planning process Carry out background research and consultation Develop the broad plan: - Establish the vision - Analyse the organisation s current situation - Identify key objectives and actions - Undertake financial and risk analysis Finalise and document plan Approve and implement plan Monitor and review Evaluate Do we understand the role of the Board at each step in the planning cycle? Do we understand the role of staff at each step of the planning cycle? 33
34 Questions Yes No Comments/Actions Developing the broad plan Do we have a current purpose statement that accurately reflects our organisation s services, capacity, environment and relationships? Does our purpose statement accurately summarise our core business and our values? Do we have an agreed procedure to conduct a strategic analysis of our organisation and its operating environment? Are we able to answer each of these questions: Who are our clients? How do we know that what we do is effective and results in our clients being better off? How do we know if we are delivering our services efficiently? How well are we doing at the moment? Who are the people and organisations, that have a key role to play in working with us to improve what we do? What works and what could work better in our organisation? Where do we want to be? 34
35 Chapter 3 Questions Yes No Comments/Actions Developing the broad plan Do we have a good understanding of key factors affecting our organisation: Legal regulations and requirements? Sources of funds and the requirements of funding bodies? Our operating costs? Our access to financial and human resources? Our profile and reputation? Government policy affecting our sector and area of work? Our relationships with other agencies? Have we undertaken an analysis of our organisation s internal strengths and weaknesses, and the external opportunities and threats? Have we developed a vision for our future based on an understanding of our external operating environment and internal capacity? 35
36 Questions Yes No Comments/Actions Documenting the plan Does our planning process ensure that we develop a strategic business plan with these key features: Vision? Commitment? Timelines and milestones? Clear objectives and actions? Regular reporting? Contingency plans? Responsive to change? Does our plan include: Purpose statement and overview of the organisation? Strategic analysis of the organisation, its environment and key challenges? Key directions vision and objectives? Overview of activities/services? Resource analysis, including human resources and financial resources (budget)? Risk analysis and contingency plan? Plan and performance measures for monitoring? Detailed implementation plan and action plans, with timeframes, responsibilities and resource needs? 36
37 Chapter 3 Questions Yes No Comments/Actions Documenting the plan Do we have a clear understanding of why we need performance measures? Do we have a process to design performance measures that will: Tell us that we have achieved what we set out to do? Be easy to collect information for? Be the best way to know that we have achieved our results? 37
38 Questions Yes No Comments/Actions Implementation and monitoring Do we have a good understanding of the factors that are important to effective implementation of our plan? Do we have a good understanding of the factors that are important to effective performance monitoring? Do we have a process in place that will enable the Board to monitor performance in relation to: Progress of the plan? Quantity of effort? Quality of activities? Impact and outcomes? Efficiency of activities? Performance against the budget? Do staff reports to the Board provide useful information to assist us monitor our performance effectively? Do we use our strategic business plan as a reporting and monitoring tool? Does the Board use the information gained from motoring performance to: Recognise successes? Take action to correct problems? 38
39 Chapter 3 Questions Yes No Comments/Actions Evaluation Do we have a process in place to evaluate the results of our plan every year? Do we fully evaluate the outcomes of our strategic business plan in its final year? Do we have a process in place to feed what we have learned from our current plan into the development of our next plan? Policies, procedures and systems Do we have policies, procedures and systems to: Develop a strategic business plan? Implement a strategic business plan? Monitor performance against our plan? Evaluate our plan? Are Board and staff responsibilities for strategic business planning clearly stated in our schedule of delegations? 39
40 Director: strategic business planning Points to remember Use this checklist to review the information within the decision making section of this resource. Tick to indicate understanding Yes No Limited An introduction to strategic business planning Do you understand what strategic business planning is? Do you understand what a strategic business plan is? Do you know the features of effective planning? Do you understand why the Board needs a strategic business plan? The planning cycle Do you know the components of the planning cycle? Do you know the steps in the planning process and what each entails: Designing the planning process? Carrying out background research and consultation? Developing the broad plan? Establishing the vision? Analysing the organisation s current situation? Identifying key objectives and actions? Undertaking financial and risk analysis? Finalising and documenting the plan? Approving and implementing the plan? Monitoring and reviewing progress and achievements? Evaluating the outcomes of the plan? Do you know your responsibilities as a Director at each step of the planning cycle? Do you know the responsibilities of your staff at each step of the planning cycle? Vision, purpose and values: developing strategic directions Do you understand why your organisation has a purpose statement? Do you understand what a purpose statement should contain and reflect? Do you understand your role as a Director in setting strategic directions for your organisation? 40
41 Do you understand how your purpose statement and a strategic analysis of your organisation and its operating environment form the basis for setting strategic directions? Vision, purpose and values: developing strategic directions Do you understand what a vision or vision statement is? Do you understand the ways your organisation might develop strategic directions? Do you understand what is involved in conducting a SWOT analysis? Chapter 3 Documenting the plan Do you understand the key features of a good strategic business plan? Do you understand what should be documented in a strategic business plan? Do you know what a performance measure is? Do you know what makes a performance measure effective? Do you understand how to identify performance measures for your organisation? Implementation and monitoring Do you know what is required of your staff to undertake effective implementation of the plan? Do you know what is required of the Board to undertake effective performance monitoring? Do you know the different aspects of your organisation and its performance that you can monitor? Do you understand the relationship between reports to the Board and the monitoring undertaken by the Board? Do you know how to analyse and act on the results of monitoring? Evaluation Do you understand the different aspects of your organisation and performance that can be evaluated? Do you have a broad understanding of when and how the Board will evaluate the strategic business plan? If you have ticked the No box please review that section again. 41
Sector Development Ageing, Disability and Home Care Department of Family and Community Services (02) 8270 2218
 Copyright in the material is owned by the State of New South Wales. Apart from any use as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968 and/or as explicitly permitted below, all other rights are reserved. You
Copyright in the material is owned by the State of New South Wales. Apart from any use as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968 and/or as explicitly permitted below, all other rights are reserved. You
THE SOUTH AFRICAN HERITAGE RESOURCES AGENCY MANAGEMENT OF PERFORMANCE INFORMATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES DOCUMENT
 THE SOUTH AFRICAN HERITAGE RESOURCES AGENCY MANAGEMENT OF PERFORMANCE INFORMATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES DOCUMENT ACCOUNTABLE SIGNATURE AUTHORISED for implementation SIGNATURE On behalf of Chief Executive
THE SOUTH AFRICAN HERITAGE RESOURCES AGENCY MANAGEMENT OF PERFORMANCE INFORMATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES DOCUMENT ACCOUNTABLE SIGNATURE AUTHORISED for implementation SIGNATURE On behalf of Chief Executive
Procurement Performance Measurement System
 Public Procurement and Disposal of Public Assets Authority Procurement Performance Measurement System User's Guide August 2008 Public Procurement and Disposal of Public Assets Authority Procurement Performance
Public Procurement and Disposal of Public Assets Authority Procurement Performance Measurement System User's Guide August 2008 Public Procurement and Disposal of Public Assets Authority Procurement Performance
Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements
 National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Handbook for Quality Assurance and Accreditation in Saudi Arabia PART 2 Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements Version 2.0 Internal Quality
National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Handbook for Quality Assurance and Accreditation in Saudi Arabia PART 2 Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements Version 2.0 Internal Quality
Project Management Fact Sheet:
 Project Management Fact Sheet: Project Documentation Version: 2.2, November 2008 DISCLAIMER This material has been prepared for use by Tasmanian Government agencies and Instrumentalities. It follows that
Project Management Fact Sheet: Project Documentation Version: 2.2, November 2008 DISCLAIMER This material has been prepared for use by Tasmanian Government agencies and Instrumentalities. It follows that
4.1 Identify what is working well and what needs adjustment. 4.1.1 Outline broad strategies that will help to effect these adjustments.
 (Overview) Step 1 Prepare 1.1 Identify specific issues or choices that the planning process should address. 1.2 Develop an organizational profile. 1.3 Identify any information that must be collected to
(Overview) Step 1 Prepare 1.1 Identify specific issues or choices that the planning process should address. 1.2 Develop an organizational profile. 1.3 Identify any information that must be collected to
Glossary 2. About this chapter 6. 6.1 About risk management 7
 Contents Glossary 2 Chapter 6 Risk Management About this chapter 6 6.1 About risk management 7 6.1.1 What is risk? 7 6.1.2 What is risk management? 7 6.1.3 The Australian Standard AS/NZS 4360:2004 7 6.1.4
Contents Glossary 2 Chapter 6 Risk Management About this chapter 6 6.1 About risk management 7 6.1.1 What is risk? 7 6.1.2 What is risk management? 7 6.1.3 The Australian Standard AS/NZS 4360:2004 7 6.1.4
Logan City Council. Strategic Planning and Performance Management Framework
 Logan City Council Strategic Planning and Performance Management Framework 1 Table of contents 1. Overview 3 a) Purpose 3 b) Key Features 3 2. Context 4 a) National Framework for Sustainability 4 b) Elements
Logan City Council Strategic Planning and Performance Management Framework 1 Table of contents 1. Overview 3 a) Purpose 3 b) Key Features 3 2. Context 4 a) National Framework for Sustainability 4 b) Elements
STRATEGIC PLANNING TEN-STEP GUIDE. Planning is a critical component of good business and good management of business.
 STRATEGIC PLANNING TEN-STEP GUIDE THE IMPORTANCE OF PLANNING Planning is a critical component of good business and good management of business. Planning helps assure that a business remains relevant and
STRATEGIC PLANNING TEN-STEP GUIDE THE IMPORTANCE OF PLANNING Planning is a critical component of good business and good management of business. Planning helps assure that a business remains relevant and
TOOL D14 Monitoring and evaluation: a framework
 TOOL D14 Monitoring and evaluation: a framework 159 TOOL D14 Monitoring and evaluation: a framework TOOL D14 For: About: Purpose: Use: Resource: Commissioners in primary care trusts (PCTs) and local authorities
TOOL D14 Monitoring and evaluation: a framework 159 TOOL D14 Monitoring and evaluation: a framework TOOL D14 For: About: Purpose: Use: Resource: Commissioners in primary care trusts (PCTs) and local authorities
Hertsmere Borough Council. Data Quality Strategy. December 2009 1
 Hertsmere Borough Council Data Quality Strategy December 2009 1 INTRODUCTION Public services need reliable, accurate and timely information with which to manage services, inform users and account for performance.
Hertsmere Borough Council Data Quality Strategy December 2009 1 INTRODUCTION Public services need reliable, accurate and timely information with which to manage services, inform users and account for performance.
QTC Training & Education. Certificate IV of Project Management BSB41507 Study by Correspondence
 Certificate IV of Project Management BSB41507 Study by Correspondence Career-relevant, Accredited and Industry Endorsed Because QTC vocational courses are developed in consultation with relevant industry
Certificate IV of Project Management BSB41507 Study by Correspondence Career-relevant, Accredited and Industry Endorsed Because QTC vocational courses are developed in consultation with relevant industry
TGA key performance indicators and reporting measures
 TGA key indicators and reporting measures Regulator Performance Framework Version 1.0, May 2015 About the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is part of the
TGA key indicators and reporting measures Regulator Performance Framework Version 1.0, May 2015 About the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is part of the
UNIVERSITY OF LONDON GUIDE TO RISK MANAGEMENT. Purpose of the guide... 2
 UNIVERSITY OF LONDON GUIDE TO RISK MANAGEMENT Purpose of the guide... 2 Risk Management The Basics... 2 What is Risk Management?... 2 Applying Risk Management... 2 The Use of Risk Registers in Risk Management...
UNIVERSITY OF LONDON GUIDE TO RISK MANAGEMENT Purpose of the guide... 2 Risk Management The Basics... 2 What is Risk Management?... 2 Applying Risk Management... 2 The Use of Risk Registers in Risk Management...
Benchmarking for Best Practice in School Fundraising
 Benchmarking for Best Practice in School Fundraising Introduction The Association of Development and Alumni Professional in Education (ADAPE) members may find this Benchmarking Checklist useful for the
Benchmarking for Best Practice in School Fundraising Introduction The Association of Development and Alumni Professional in Education (ADAPE) members may find this Benchmarking Checklist useful for the
Wiltshire Council s Behaviours framework
 Wiltshire Council s Behaviours framework It s about how we work Trust and respect Simplicity Responsibility Leadership Working together Excellence Why do we need a behaviours framework? Wiltshire Council
Wiltshire Council s Behaviours framework It s about how we work Trust and respect Simplicity Responsibility Leadership Working together Excellence Why do we need a behaviours framework? Wiltshire Council
Future Council Programme Evaluation Framework
 Future Council Programme Evaluation Framework Overview of the Evaluation Framework for the Future Council Programme DRAFT v0.7 August 2015 Contents 1. Evaluation Framework Overview 2. Evaluation Framework
Future Council Programme Evaluation Framework Overview of the Evaluation Framework for the Future Council Programme DRAFT v0.7 August 2015 Contents 1. Evaluation Framework Overview 2. Evaluation Framework
Specific Measurable Achievable. Relevant Timely. PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT CREATING SMART OBJECTIVES: Participant Guide PROGRAM OVERVIEW
 Specific Measurable Achievable PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT CREATING SMART OBJECTIVES: Participant Guide Relevant Timely PROGRAM OVERVIEW About the Training Program This session is designed to enable participants
Specific Measurable Achievable PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT CREATING SMART OBJECTIVES: Participant Guide Relevant Timely PROGRAM OVERVIEW About the Training Program This session is designed to enable participants
TECHNICALS LEVEL 2016 3 BUSINESS
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 BUSINESS Unit 16 Principles of project management M/507/8163 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016 ocr.org.uk/business LEVEL 3 UNIT
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 BUSINESS Unit 16 Principles of project management M/507/8163 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016 ocr.org.uk/business LEVEL 3 UNIT
THE NATIONAL STANDARDS FOR VOLUNTEER INVOLVEMENT
 THE NATIONAL STANDARDS FOR VOLUNTEER INVOLVEMENT Contents Introduction...3 The National Standards Aims and Principles...4 Using the National Standards...5 Standards Overview...6 STANDARD 1: LEADERSHIP
THE NATIONAL STANDARDS FOR VOLUNTEER INVOLVEMENT Contents Introduction...3 The National Standards Aims and Principles...4 Using the National Standards...5 Standards Overview...6 STANDARD 1: LEADERSHIP
THE NATIONAL STANDARDS FOR VOLUNTEER INVOLVEMENT
 THE NATIONAL STANDARDS FOR VOLUNTEER INVOLVEMENT Volunteering Australia, 2015 April 2015 VOLUNTEERING AUSTRALIA Level 2, 202 City Walk Canberra ACT 2601 T: 02 6251 4060 E: marketing@volunteeringaustralia.org
THE NATIONAL STANDARDS FOR VOLUNTEER INVOLVEMENT Volunteering Australia, 2015 April 2015 VOLUNTEERING AUSTRALIA Level 2, 202 City Walk Canberra ACT 2601 T: 02 6251 4060 E: marketing@volunteeringaustralia.org
<Business Case Name> <Responsible Entity> <Date>
 (The entity Chief Information Officer, Chief Financial Officer and Business Area programme Lead must sign-off the completed business case) Signed: Date:
(The entity Chief Information Officer, Chief Financial Officer and Business Area programme Lead must sign-off the completed business case) Signed: Date:
Corporate Governance Service Business Plan 2011-2016. Modernising Services
 Corporate Governance Service Business Plan 2011-2016 Modernising Services Index 1. Executive Summary 3 2. Vision and Strategy 4 3. Service Overview 3.1 What Services do we and Will we Deliver? 5 3.2 How
Corporate Governance Service Business Plan 2011-2016 Modernising Services Index 1. Executive Summary 3 2. Vision and Strategy 4 3. Service Overview 3.1 What Services do we and Will we Deliver? 5 3.2 How
Reporting Service Performance Information
 AASB Exposure Draft ED 270 August 2015 Reporting Service Performance Information Comments to the AASB by 12 February 2016 PLEASE NOTE THIS DATE HAS BEEN EXTENDED TO 29 APRIL 2016 How to comment on this
AASB Exposure Draft ED 270 August 2015 Reporting Service Performance Information Comments to the AASB by 12 February 2016 PLEASE NOTE THIS DATE HAS BEEN EXTENDED TO 29 APRIL 2016 How to comment on this
Achieve. Performance objectives
 Achieve Performance objectives Performance objectives are benchmarks of effective performance that describe the types of work activities students and affiliates will be involved in as trainee accountants.
Achieve Performance objectives Performance objectives are benchmarks of effective performance that describe the types of work activities students and affiliates will be involved in as trainee accountants.
Strategic Plan 2011 2012 to 2014 2015. Working Together for Australian Sport
 Strategic Plan 2011 2012 to 2014 2015 Working Together for Australian Sport Strategic Plan 2011 2012 to 2014 2015 Working Together for Australian Sport Australian Sports Commission 2011 Ownership of intellectual
Strategic Plan 2011 2012 to 2014 2015 Working Together for Australian Sport Strategic Plan 2011 2012 to 2014 2015 Working Together for Australian Sport Australian Sports Commission 2011 Ownership of intellectual
Supporting effective teamwork
 Supporting effective teamwork A checklist for evaluating team performance CHAPTER 26 : HATCHED Margaret Kilvington and Will Allen Summary Teams can be instruments for achieving changes in culture and practice
Supporting effective teamwork A checklist for evaluating team performance CHAPTER 26 : HATCHED Margaret Kilvington and Will Allen Summary Teams can be instruments for achieving changes in culture and practice
Evaluability Assessment Template
 Evaluability Assessment Template Evaluability Assessment Template An Evaluability Assessment examines the extent to which a project or a programme can be evaluated in a reliable and credible fashion. An
Evaluability Assessment Template Evaluability Assessment Template An Evaluability Assessment examines the extent to which a project or a programme can be evaluated in a reliable and credible fashion. An
Environment Sustainability and Highways
 Job Title: Marketing Intelligence Officer Job Grade: Band 4 Directorate: Environment Sustainability and Highways Job Reference Number: P01851 The Role The Marketing Intelligence Officer will: Devise intelligence
Job Title: Marketing Intelligence Officer Job Grade: Band 4 Directorate: Environment Sustainability and Highways Job Reference Number: P01851 The Role The Marketing Intelligence Officer will: Devise intelligence
Commissioning Strategy
 Commissioning Strategy This Commissioning Strategy sets out the mechanics of how Orkney Alcohol and Drugs Partnership (ADP) will implement its strategic aims as outlined in the ADP Strategy. Ensuring that
Commissioning Strategy This Commissioning Strategy sets out the mechanics of how Orkney Alcohol and Drugs Partnership (ADP) will implement its strategic aims as outlined in the ADP Strategy. Ensuring that
STRATEGIC PLANNING Guide for Managers
 STRATEGIC PLANNING Guide for Managers 1 Strategic Planning Basics for Managers In all UN offices, departments and missions, it is critical that managers utilize the most effective approach toward developing
STRATEGIC PLANNING Guide for Managers 1 Strategic Planning Basics for Managers In all UN offices, departments and missions, it is critical that managers utilize the most effective approach toward developing
RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY (Revised October 2015)
 UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY (Revised October 2015) 1. This risk management policy ( the policy ) forms part of the University s internal control and corporate governance arrangements.
UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY (Revised October 2015) 1. This risk management policy ( the policy ) forms part of the University s internal control and corporate governance arrangements.
Care service inspection report
 Care service inspection report Full inspection SSCN Social Care Housing Support Service Suite 3, Floor 2 ELS House 555 Gorgie Road Edinburgh Inspection completed on 03 May 2016 Service provided by: Support
Care service inspection report Full inspection SSCN Social Care Housing Support Service Suite 3, Floor 2 ELS House 555 Gorgie Road Edinburgh Inspection completed on 03 May 2016 Service provided by: Support
FYI HIRING. Recruiting Strategies
 FYI HIRING Recruiting Strategies Revised: March 2011 Summary: This FYI discusses the steps involved establishing or revitalizing an effective recruiting process. It includes considerations for goal setting,
FYI HIRING Recruiting Strategies Revised: March 2011 Summary: This FYI discusses the steps involved establishing or revitalizing an effective recruiting process. It includes considerations for goal setting,
Queensland Government Human Services Quality Framework. Quality Pathway Kit for Service Providers
 Queensland Government Human Services Quality Framework Quality Pathway Kit for Service Providers July 2015 Introduction The Human Services Quality Framework (HSQF) The Human Services Quality Framework
Queensland Government Human Services Quality Framework Quality Pathway Kit for Service Providers July 2015 Introduction The Human Services Quality Framework (HSQF) The Human Services Quality Framework
Strategic Plan: A How-To Guide
 DEVELOPING A TRIBAL HEALTH DEPARTMENT Strategic Plan: A How-To Guide Adapted from Developing a Local Health Department Strategic Plan: A How-To Guide, National Association of County and City Health Officials.
DEVELOPING A TRIBAL HEALTH DEPARTMENT Strategic Plan: A How-To Guide Adapted from Developing a Local Health Department Strategic Plan: A How-To Guide, National Association of County and City Health Officials.
7 Directorate Performance Managers. 7 Performance Reporting and Data Quality Officer. 8 Responsible Officers
 Contents Page 1 Introduction 2 2 Objectives of the Strategy 2 3 Data Quality Standards 3 4 The National Indicator Set 3 5 Structure of this Strategy 3 5.1 Awareness 4 5.2 Definitions 4 5.3 Recording 4
Contents Page 1 Introduction 2 2 Objectives of the Strategy 2 3 Data Quality Standards 3 4 The National Indicator Set 3 5 Structure of this Strategy 3 5.1 Awareness 4 5.2 Definitions 4 5.3 Recording 4
Disability Employment Services Quality Framework Advice V 2.0
 Disability Employment Services Quality Framework Advice V 2.0 Disclaimer This document is not a stand-alone document and does not contain the entirety of Disability Employment Services Providers' obligations.
Disability Employment Services Quality Framework Advice V 2.0 Disclaimer This document is not a stand-alone document and does not contain the entirety of Disability Employment Services Providers' obligations.
Queensland Treasury. Queensland Government. Program Evaluation Guidelines
 Queensland Treasury Queensland Government Program Evaluation Guidelines November 2014 Document details Security Classification Date of Review of Security Classification Authority Author PUBLIC November
Queensland Treasury Queensland Government Program Evaluation Guidelines November 2014 Document details Security Classification Date of Review of Security Classification Authority Author PUBLIC November
Drafting a business plan
 How are you going to do it? Drafting a business plan Background A business plan sets out the business case for a particular project, organisation or venture. It states how you will go about running a specific
How are you going to do it? Drafting a business plan Background A business plan sets out the business case for a particular project, organisation or venture. It states how you will go about running a specific
Guidelines for Corporate Community Engagement
 Guidelines for Corporate Community Engagement February 2012 The Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Western Australia (Inc) Contents 1. Introduction 3 2. Establishing and building community engagement
Guidelines for Corporate Community Engagement February 2012 The Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Western Australia (Inc) Contents 1. Introduction 3 2. Establishing and building community engagement
Key Steps to a Management Skills Audit
 Key Steps to a Management Skills Audit COPYRIGHT NOTICE PPA Consulting Pty Ltd (ACN 079 090 547) 2005-2013 You may only use this document for your own personal use or the internal use of your employer.
Key Steps to a Management Skills Audit COPYRIGHT NOTICE PPA Consulting Pty Ltd (ACN 079 090 547) 2005-2013 You may only use this document for your own personal use or the internal use of your employer.
INTEGRATED PLANNING AND REPORTING
 Government of Western Australia Department of Local Government INTEGRATED PLANNING AND REPORTING Framework and Guidelines Integrated Planning and Reporting Framework and Guidelines p1. Contents Foreword
Government of Western Australia Department of Local Government INTEGRATED PLANNING AND REPORTING Framework and Guidelines Integrated Planning and Reporting Framework and Guidelines p1. Contents Foreword
Risk Management Primer
 Risk Management Primer Purpose: To obtain strong project outcomes by implementing an appropriate risk management process Audience: Project managers, project sponsors, team members and other key stakeholders
Risk Management Primer Purpose: To obtain strong project outcomes by implementing an appropriate risk management process Audience: Project managers, project sponsors, team members and other key stakeholders
Strategic Plan Templates and Funding Agreement Samples
 Strategic Plan Templates and Funding Agreement Samples STRATEGIC PLAN All triennial funding applications must include a three year strategic plan that relates to the proposed funding period. Applications
Strategic Plan Templates and Funding Agreement Samples STRATEGIC PLAN All triennial funding applications must include a three year strategic plan that relates to the proposed funding period. Applications
Process Management: Creating Supply Chain Value
 Process Management: Creating Supply Chain Value Carol L. Marks, C.P.M., Director of Purchasing and Business Management Systems Industrial Distribution Group, Southern Division 704/398-5666; carol.l.marks@idg-corp.com
Process Management: Creating Supply Chain Value Carol L. Marks, C.P.M., Director of Purchasing and Business Management Systems Industrial Distribution Group, Southern Division 704/398-5666; carol.l.marks@idg-corp.com
STRATEGIC REVIEW OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT IN UNICEF. Terms of Reference July 20 2005
 1. Background STRATEGIC REVIEW OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT IN UNICEF Terms of Reference July 20 2005 UNICEF has decided to undertake a Strategic Review of its approach to and performance in Human Resource
1. Background STRATEGIC REVIEW OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT IN UNICEF Terms of Reference July 20 2005 UNICEF has decided to undertake a Strategic Review of its approach to and performance in Human Resource
QUEENSLAND CENTRE FOR PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT (QCPD) TENDERING SERVICE: TENDER BID DECISION, PREPARATION AND SUBMISSION PROCEDURES
 PROCEDURES QUEENSLAND CENTRE FOR PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT (QCPD) TENDERING SERVICE: TENDER BID DECISION, PREPARATION AND SUBMISSION PROCEDURES PURPOSE These procedures provide guidance on the process of
PROCEDURES QUEENSLAND CENTRE FOR PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT (QCPD) TENDERING SERVICE: TENDER BID DECISION, PREPARATION AND SUBMISSION PROCEDURES PURPOSE These procedures provide guidance on the process of
EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS
 EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS Cezar Vasilescu and Aura Codreanu Abstract: The field of strategic management has offered a variety of frameworks and concepts during
EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS Cezar Vasilescu and Aura Codreanu Abstract: The field of strategic management has offered a variety of frameworks and concepts during
QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY
 QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY ACADEMIC DEVELOPMENT & QUALITY ASSURANCE OFFICE ALPHA UNIVERSITY COLLEGE 1. BACKGROUND The Strategic Plan of 2003-2005 E.C of Alpha University s defines the direction Alpha University
QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY ACADEMIC DEVELOPMENT & QUALITY ASSURANCE OFFICE ALPHA UNIVERSITY COLLEGE 1. BACKGROUND The Strategic Plan of 2003-2005 E.C of Alpha University s defines the direction Alpha University
EXERCISE 1: HR System Implementation
 EXERCISE 1: HR System Implementation You have been asked to step in and lead a new HR system implementation project eight months prior to its launch date. The project previously had no Project Manager
EXERCISE 1: HR System Implementation You have been asked to step in and lead a new HR system implementation project eight months prior to its launch date. The project previously had no Project Manager
Funded Peak Activities
 Funded Peak Activities Triennial Service Plan Guidelines Version 2.0 Sector Development Directorate Ageing, Disability and Home Care Department of Family and Community Services NSW July 2012 Final Document
Funded Peak Activities Triennial Service Plan Guidelines Version 2.0 Sector Development Directorate Ageing, Disability and Home Care Department of Family and Community Services NSW July 2012 Final Document
SFJ EFSM14 Manage the performance of teams and individuals to achieve objectives
 Manage the performance of teams and individuals to achieve objectives Overview This standard is about making the best use of your team and its members so that they can achieve your organisation's objectives.
Manage the performance of teams and individuals to achieve objectives Overview This standard is about making the best use of your team and its members so that they can achieve your organisation's objectives.
A C T I V I T Y : U S I N G T H E F I S H B O N E D I A G R A M TO
 C O L L E C T I V E L E A D E R S H I P W O R K S P L A N N I N G F O R AC T I O N 143 A C T I V I T Y : U S I N G T H E F I S H B O N E D I A G R A M TO GENERATE ACTION PL ANS Moving from identifying
C O L L E C T I V E L E A D E R S H I P W O R K S P L A N N I N G F O R AC T I O N 143 A C T I V I T Y : U S I N G T H E F I S H B O N E D I A G R A M TO GENERATE ACTION PL ANS Moving from identifying
Measuring the Impact of Volunteering
 Measuring the Impact of Volunteering Why is measuring the impact of volunteering important? It is increasingly important for organisations or groups to describe the difference that volunteering makes to,
Measuring the Impact of Volunteering Why is measuring the impact of volunteering important? It is increasingly important for organisations or groups to describe the difference that volunteering makes to,
Governance, Risk and Best Value Committee
 Governance, Risk and Best Value Committee 2.00pm, Wednesday 23 September 2015 Internal Audit Report: Integrated Health & Social Care Item number Report number Executive/routine Wards Executive summary
Governance, Risk and Best Value Committee 2.00pm, Wednesday 23 September 2015 Internal Audit Report: Integrated Health & Social Care Item number Report number Executive/routine Wards Executive summary
PRINCIPLES FOR DEVELOPING DESTINATION MANAGEMENT PLANS
 PRINCIPLES FOR DEVELOPING DESTINATION MANAGEMENT PLANS This guide is for organisations and individuals who want to work together with others to gain more benefit for their area from the visitors it receives.
PRINCIPLES FOR DEVELOPING DESTINATION MANAGEMENT PLANS This guide is for organisations and individuals who want to work together with others to gain more benefit for their area from the visitors it receives.
The University of Adelaide Business School
 The University of Adelaide Business School MBA Projects Introduction There are TWO types of project which may be undertaken by an individual student OR a team of up to 5 students. This outline presents
The University of Adelaide Business School MBA Projects Introduction There are TWO types of project which may be undertaken by an individual student OR a team of up to 5 students. This outline presents
Policy Profession. Skills and Knowledge framework. Find out more now by going to www.civilservice.gov.uk/learning
 Policy Profession Skills and Knowledge framework Find out more now by going to www.civilservice.gov.uk/learning Introduction to the Policy Profession Skills and Knowledge framework The policy profession
Policy Profession Skills and Knowledge framework Find out more now by going to www.civilservice.gov.uk/learning Introduction to the Policy Profession Skills and Knowledge framework The policy profession
APPENDIX C. Internal Audit Report South Holland District Council Project Management
 APPENDIX C Internal Audit Report South Holland District Council Project Management Date: 20th December 2012 Contents Introduction and Scope 1 Executive Summary Assurance Opinion Key Messages 2 3 Management
APPENDIX C Internal Audit Report South Holland District Council Project Management Date: 20th December 2012 Contents Introduction and Scope 1 Executive Summary Assurance Opinion Key Messages 2 3 Management
Capacity Assessment Tool
 Capacity Assessment Tool 2013 Government of Yukon all rights reserved All materials, content and forms contained in this document/website are property of Yukon Government and may not be copied, reproduced,
Capacity Assessment Tool 2013 Government of Yukon all rights reserved All materials, content and forms contained in this document/website are property of Yukon Government and may not be copied, reproduced,
Manual Guide of The Induction Program for New Employees in the Federal Government
 United Arab Emirates Federal Authority For Government Human Resources Manual Guide of The Induction Program for New Employees in the Federal Government Building a Productive Institutional Culture @FAHR_UAE
United Arab Emirates Federal Authority For Government Human Resources Manual Guide of The Induction Program for New Employees in the Federal Government Building a Productive Institutional Culture @FAHR_UAE
Section Five Learning Module D:
 Section Five Learning Module D: the Project 5.1 Module D: Objectives At the conclusion of this module you will be able to: implement a project plan; keep control of a project plan; effectively review a
Section Five Learning Module D: the Project 5.1 Module D: Objectives At the conclusion of this module you will be able to: implement a project plan; keep control of a project plan; effectively review a
2016 Charter School Application Evaluation Rubric. For applications submitted to The Louisiana Board of Elementary and Secondary Education
 2016 Charter School Application Evaluation Rubric For applications submitted to The Louisiana Board of Elementary and Secondary Education 2016 Charter School Application Evaluation Rubric The purpose of
2016 Charter School Application Evaluation Rubric For applications submitted to The Louisiana Board of Elementary and Secondary Education 2016 Charter School Application Evaluation Rubric The purpose of
Personal Development Planning and eportfolio. Student Guide
 Personal Development Planning and eportfolio Student Guide 1 Introduction PDP helps you to develop the skills you need to take responsibility for your learning, development and career progression. Engaging
Personal Development Planning and eportfolio Student Guide 1 Introduction PDP helps you to develop the skills you need to take responsibility for your learning, development and career progression. Engaging
100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success. Some Great Tips To Boost Your Sales
 100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success Some Great Tips To Boost Your Sales 100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success By Sean Mcpheat, Managing Director Of The Sales Training Consultancy What makes a successful
100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success Some Great Tips To Boost Your Sales 100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success By Sean Mcpheat, Managing Director Of The Sales Training Consultancy What makes a successful
To be used in conjunction with the Invitation to Tender for Consultancy template.
 GUIDANCE NOTE Tendering for, choosing and managing a consultant Using this guidance This information is not intended to be prescriptive, but for guidance only. Appointing consultants for relatively small
GUIDANCE NOTE Tendering for, choosing and managing a consultant Using this guidance This information is not intended to be prescriptive, but for guidance only. Appointing consultants for relatively small
How to monitor and evaluate your community project
 How to monitor and evaluate your community project So you've set up your project. But how can you tell if it's going well? This guide tells you all you need to know about monitoring and evaluating what
How to monitor and evaluate your community project So you've set up your project. But how can you tell if it's going well? This guide tells you all you need to know about monitoring and evaluating what
PLANNING FOR YOUR PROJECT
 PLANNING FOR YOUR PROJECT This tool kit has been designed to provide an introduction to planning. It will help you to think about the reasons behind why you should plan, what to plan and the variations
PLANNING FOR YOUR PROJECT This tool kit has been designed to provide an introduction to planning. It will help you to think about the reasons behind why you should plan, what to plan and the variations
JOB DESCRIPTION. Leadership: Provide vision, leadership and direction for the college.
 JOB DESCRIPTION Job Title: Reports to: Principal Board of Governors Main Purpose of the Job Leadership: Provide vision, leadership and direction for the college. Learning: Create and maintain a productive
JOB DESCRIPTION Job Title: Reports to: Principal Board of Governors Main Purpose of the Job Leadership: Provide vision, leadership and direction for the college. Learning: Create and maintain a productive
Risk Profiling Toolkit DEVELOPING A CORPORATE RISK PROFILE FOR YOUR ORGANIZATION
 Risk Profiling Toolkit DEVELOPING A CORPORATE RISK PROFILE FOR YOUR ORGANIZATION I Background Under the TBS Risk Management Policy, departments and agencies must identify the potential perils, factors
Risk Profiling Toolkit DEVELOPING A CORPORATE RISK PROFILE FOR YOUR ORGANIZATION I Background Under the TBS Risk Management Policy, departments and agencies must identify the potential perils, factors
1. Trustees annual report
 1. Trustees annual report Accounting and reporting by charities Overview and the purpose of the trustees annual report 1.1. The primary purpose of the trustees annual report (the report) is to ensure that
1. Trustees annual report Accounting and reporting by charities Overview and the purpose of the trustees annual report 1.1. The primary purpose of the trustees annual report (the report) is to ensure that
Planning with purpose: Business planning options for Landcare Networks
 Planning with purpose: Business planning options for Landcare Networks Contents Landcare as a social enterprise... 1 Step 1. Set your goal... 3 Step 2. Identify possible products and services... 3 Step
Planning with purpose: Business planning options for Landcare Networks Contents Landcare as a social enterprise... 1 Step 1. Set your goal... 3 Step 2. Identify possible products and services... 3 Step
U & D COAL LIMITED A.C.N. 165 894 806 BOARD CHARTER
 U & D COAL LIMITED A.C.N. 165 894 806 BOARD CHARTER As at 31 March 2014 BOARD CHARTER Contents 1. Role of the Board... 4 2. Responsibilities of the Board... 4 2.1 Board responsibilities... 4 2.2 Executive
U & D COAL LIMITED A.C.N. 165 894 806 BOARD CHARTER As at 31 March 2014 BOARD CHARTER Contents 1. Role of the Board... 4 2. Responsibilities of the Board... 4 2.1 Board responsibilities... 4 2.2 Executive
The integrated leadership system. ILS support tools. Leadership pathway: Individual profile EL1
 The integrated leadership system ILS support tools Leadership pathway: Individual profile Executive Level 1 profile Shapes strategic thinking Achieves results Cultivates productive working relationships
The integrated leadership system ILS support tools Leadership pathway: Individual profile Executive Level 1 profile Shapes strategic thinking Achieves results Cultivates productive working relationships
Job Grade: Band 5. Job Reference Number:
 Job Title: Business Analyst Job Grade: Band 5 Directorate: Job Reference Number: People and Transformation P01216 The Role: This is a challenging role working with and across all services to support the
Job Title: Business Analyst Job Grade: Band 5 Directorate: Job Reference Number: People and Transformation P01216 The Role: This is a challenging role working with and across all services to support the
Collaborative development of evaluation capacity and tools for natural resource management
 Collaborative development of evaluation capacity and tools for natural resource management Helen Watts (Adaptive Environmental Management, formerly NSW Department of Environment and Climate Change) Sandra
Collaborative development of evaluation capacity and tools for natural resource management Helen Watts (Adaptive Environmental Management, formerly NSW Department of Environment and Climate Change) Sandra
Effective consultation The ACMA s guide to making a submission NOVEMBER 2015
 Effective consultation The ACMA s guide to making a submission NOVEMBER 2015 Canberra Red Building Benjamin Offices Chan Street Belconnen ACT PO Box 78 Belconnen ACT 2616 T +61 2 6219 5555 F +61 2 6219
Effective consultation The ACMA s guide to making a submission NOVEMBER 2015 Canberra Red Building Benjamin Offices Chan Street Belconnen ACT PO Box 78 Belconnen ACT 2616 T +61 2 6219 5555 F +61 2 6219
Head of Commercial & Contract Management (BISRID_046)
 Job Description Job Title: Reports to: Team: Location: Head of Commercial & Contract Management (BISRID_046) Head of IS Transition Business Information Services (BIS) Nelson, Treharris As a credible member
Job Description Job Title: Reports to: Team: Location: Head of Commercial & Contract Management (BISRID_046) Head of IS Transition Business Information Services (BIS) Nelson, Treharris As a credible member
How To Manage The Council
 Mole Valley District Council Corporate Communications Strategy 2002-2005 CONTENTS Content Section 1: Introduction Section 2: Stakeholders Section 3: Objectives Section 4: Targets Section 5: Principles
Mole Valley District Council Corporate Communications Strategy 2002-2005 CONTENTS Content Section 1: Introduction Section 2: Stakeholders Section 3: Objectives Section 4: Targets Section 5: Principles
V1.0 - Eurojuris ISO 9001:2008 Certified
 Risk Management Manual V1.0 - Eurojuris ISO 9001:2008 Certified Section Page No 1 An Introduction to Risk Management 1-2 2 The Framework of Risk Management 3-6 3 Identification of Risks 7-8 4 Evaluation
Risk Management Manual V1.0 - Eurojuris ISO 9001:2008 Certified Section Page No 1 An Introduction to Risk Management 1-2 2 The Framework of Risk Management 3-6 3 Identification of Risks 7-8 4 Evaluation
Develop a strategic plan. A tool for NGOs and CBOs M
 Develop a strategic plan A tool for NGOs and CBOs M Developing Strategic Plans: A Tool for Community- and Faith-Based Organizations Developed by the International HIV/AIDS Alliance and Davies & Lee: AIDS
Develop a strategic plan A tool for NGOs and CBOs M Developing Strategic Plans: A Tool for Community- and Faith-Based Organizations Developed by the International HIV/AIDS Alliance and Davies & Lee: AIDS
GUIDELINES FOR PILOT INTERVENTIONS. www.ewaproject.eu ewa@gencat.cat
 GUIDELINES FOR PILOT INTERVENTIONS www.ewaproject.eu ewa@gencat.cat Project Lead: GENCAT CONTENTS A Introduction 2 1 Purpose of the Document 2 2 Background and Context 2 3 Overview of the Pilot Interventions
GUIDELINES FOR PILOT INTERVENTIONS www.ewaproject.eu ewa@gencat.cat Project Lead: GENCAT CONTENTS A Introduction 2 1 Purpose of the Document 2 2 Background and Context 2 3 Overview of the Pilot Interventions
High level principles for risk management
 16 February 2010 High level principles for risk management Background and introduction 1. In their declaration of 15 November 2008, the G-20 leaders stated that regulators should develop enhanced guidance
16 February 2010 High level principles for risk management Background and introduction 1. In their declaration of 15 November 2008, the G-20 leaders stated that regulators should develop enhanced guidance
Monitoring Highways England The monitoring framework
 Monitoring Highways England The monitoring framework October 2015 Contents Executive summary 4 Roads reform 4 ORR s role in monitoring Highways England 5 What we will do next 10 1. Overview of this document
Monitoring Highways England The monitoring framework October 2015 Contents Executive summary 4 Roads reform 4 ORR s role in monitoring Highways England 5 What we will do next 10 1. Overview of this document
Shell Mentoring Toolkit
 Shell Mentoring Toolkit A reference document for mentors and mentees Human Resources LEARNING 25/07/2007 Copyright: Shell International Ltd 2006 CONTENTS What is Mentoring? 4 The Mentor s Role The Role
Shell Mentoring Toolkit A reference document for mentors and mentees Human Resources LEARNING 25/07/2007 Copyright: Shell International Ltd 2006 CONTENTS What is Mentoring? 4 The Mentor s Role The Role
Creating a Customer Advisory Board Overview and Checklist by Clearworks
 Creating a Customer Advisory Board Overview and Checklist by Clearworks Customer insight programs play an important role for both B2B and B2C companies. The programs advise everything from new product
Creating a Customer Advisory Board Overview and Checklist by Clearworks Customer insight programs play an important role for both B2B and B2C companies. The programs advise everything from new product
Communications Strategy
 Communications Strategy 2014-2017 Classification: Internal/Stakeholder 1. Introduction Good communication is central to the perception of City Property (Glasgow) LLP and our credibility. It is at the core
Communications Strategy 2014-2017 Classification: Internal/Stakeholder 1. Introduction Good communication is central to the perception of City Property (Glasgow) LLP and our credibility. It is at the core
Restructure, Redeployment and Redundancy
 Restructure, Redeployment and Redundancy Purpose and Scope From time to time the Lake District National Park Authority will need to reorganise its services and staffing to meet changes that arise in future
Restructure, Redeployment and Redundancy Purpose and Scope From time to time the Lake District National Park Authority will need to reorganise its services and staffing to meet changes that arise in future
the Defence Leadership framework
 the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
Organizational Design Toolkit
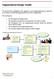 Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Government Communication Professional Competency Framework
 Government Communication Professional Competency Framework April 2013 Introduction Every day, government communicators deliver great work which supports communities and helps citizens understand their
Government Communication Professional Competency Framework April 2013 Introduction Every day, government communicators deliver great work which supports communities and helps citizens understand their
CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
 CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) 3.1 INTRODUCTION The most important purpose of any service orientated organisation is to retain customers. It is critical for any organization to keep
CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) 3.1 INTRODUCTION The most important purpose of any service orientated organisation is to retain customers. It is critical for any organization to keep
ALCOHOL AND OTHER DRUGS (AOD) RESIDENTIAL PROGRAMMES: SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
 ALCOHOL AND OTHER DRUGS (AOD) RESIDENTIAL PROGRAMMES: SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 2015 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 1. About these Service Specifications... 2 Who are these specifications for?...
ALCOHOL AND OTHER DRUGS (AOD) RESIDENTIAL PROGRAMMES: SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 2015 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 1. About these Service Specifications... 2 Who are these specifications for?...
An Approach to Organizational Self Assessment. Developed for the IUCN M&E Team. by Universalia DRAFT. September 2000
 An Approach to Organizational Self Assessment Developed for the IUCN M&E Team by Universalia DRAFT September 2000 5252 de Maisonneuve Ouest #310 Montréal, Québec, Canada H4A 3S5 Tel (514) 485-3565 Fax
An Approach to Organizational Self Assessment Developed for the IUCN M&E Team by Universalia DRAFT September 2000 5252 de Maisonneuve Ouest #310 Montréal, Québec, Canada H4A 3S5 Tel (514) 485-3565 Fax
DCL SECURITY INT LTD. DCL Security Strategic Goals DCL Security Business Plan. www.dclsecurity.co.uk
 DCL SECURITY INT LTD DCL Security Strategic Goals DCL Security Business Plan 2014 2016 2014 2015 2016 Executive Summary This Strategic Goals and Business Plan document 2014 2016, lays out an exciting and
DCL SECURITY INT LTD DCL Security Strategic Goals DCL Security Business Plan 2014 2016 2014 2015 2016 Executive Summary This Strategic Goals and Business Plan document 2014 2016, lays out an exciting and
1 The Role of Accounting
 5 1 The Role of Accounting Accounting Information Accounting provides financial information for a variety of entities to enable them to make informed judgements and decisions. It is important that you
5 1 The Role of Accounting Accounting Information Accounting provides financial information for a variety of entities to enable them to make informed judgements and decisions. It is important that you
Solihull Clinical Commissioning Group
 Solihull Clinical Commissioning Group Business Continuity Policy Version v1 Ratified by SMT Date ratified 24 February 2014 Name of originator / author CSU Corporate Services Review date Annual Target audience
Solihull Clinical Commissioning Group Business Continuity Policy Version v1 Ratified by SMT Date ratified 24 February 2014 Name of originator / author CSU Corporate Services Review date Annual Target audience
Witness information. Investigations
 Witness information Investigations We are the nursing and midwifery regulator for England, Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland and the Islands. We exist to safeguard the health and wellbeing of the public.
Witness information Investigations We are the nursing and midwifery regulator for England, Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland and the Islands. We exist to safeguard the health and wellbeing of the public.
Response from the Department of Treasury, Western Australia, to the Productivity Commission s Draft Report Regulatory Impact Analysis: Benchmarking
 Response from the Department of Treasury, Western Australia, to the Productivity Commission s Draft Report Regulatory Impact Analysis: Benchmarking Context Regulatory Impact Assessment (RIA) began in Western
Response from the Department of Treasury, Western Australia, to the Productivity Commission s Draft Report Regulatory Impact Analysis: Benchmarking Context Regulatory Impact Assessment (RIA) began in Western
