Sonographic Evaluation of Lisfranc Ligament Injuries
|
|
|
- Neal Stewart
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Series Sonographic Evaluation of Lisfranc Ligament Injuries Suzanne Woodward, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Yoav Morag, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, Qian Dong, MD Objective. This study characterized the sonographic appearances of Lisfranc injuries. Methods. Sonography reports ( ) were searched for Lisfranc, resulting in 10 patients. Sonographic images of affected and asymptomatic contralateral feet were reviewed, recording the thickness of the dorsal ligament between the first (medial) cuneiform (C1) and second metatarsal (M2) ligaments, distance between C1 and M2, and change in this distance with weight bearing, hyperemia, and fractures. Correlations were made to clinical, surgical, and other imaging findings. Results. In 5 asymptomatic feet, the dorsal C1-M2 ligament was 0.9 to 1.2 mm thick, and the C1-M2 distance was 0.5 to 1 mm. Of the symptomatic feet, 1 group (n = 3) had normal sonographic findings (thickness, mm; distance, mm; all had normal radiographic findings and follow-up, and 1 had normal magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] findings). Another group (n = 3) had abnormal hypoechogenicity and thickening of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament ( mm), a normal C1-M2 distance ( mm), and no widening with weight bearing (1 of 1), consistent with a ligament sprain (1 had normal computed tomographic [CT] findings, and all had uneventful follow-up). The third group (n = 4) had nonvisualization of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament, an increased C1-M2 distance of 2.5 to 3.1 mm, and further widening with weight bearing (3 of 4) from Lisfranc ligament disruption (shown at surgery in 2, MRI in 1, and CT in 1). Conclusions. Nonvisualization of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament and a C1-M2 distance of 2.5 mm or greater were indirect signs of a Lisfranc ligament tear. Dynamic evaluation with weight bearing showed widening of the space between C1 and M2. Key words: foot; ligament; sonography; trauma. Abbreviations C1, first cuneiform; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; M2, second metatarsal Received October 6, 2008, from the Department of Radiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan USA (S.W., J.A.J., Y.M., D.P.F., Q.D.); and Department of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa USA (J.E.F.). Revision requested October 17, Revised manuscript accepted for publication October 21, Address correspondence to Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Department of Radiology, University of Michigan, 1500 E Medical Center Dr, Ann Arbor, MI USA. jjacobsn@umich.edu Fracture dislocations of the tarsometatarsal joints are often referred to as Lisfranc injuries. Named after the French surgeon who performed amputations through these joints, Lisfranc injuries have been associated with many different injuries to the tarsometatarsal joint complex. The Lisfranc ligament, which extends obliquely between the lateral aspect of the first (medial) cuneiform (C1) ligament to the medial aspect of the second metatarsal (M2) ligament base, is of paramount importance to the stabilization of the tarsometatarsal joints. 1 Complications of Lisfranc ligament injuries can be devastating and may include malreduction resulting in posttraumatic osteoarthrosis and chronic foot pain. 2,3 Accurate diagnosis of Lisfranc injuries may be difficult, and a delayed diagnosis or misdiagnosis occurs in up to 20% of cases. 4 Evaluation typically begins with conventional radiographs of the foot. However, because of overlapping osseous structures on routine radiographic views, 2009 by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28: /09/$3.50
2 Sonographic Evaluation of Lisfranc Ligament Injuries fractures can easily be missed. 5 Furthermore, in cases in which no malalignment is visible on conventional radiographs, ligamentous injuries will be overlooked. Stress radiographs may be helpful but may still be erroneously reported as normal. 6 Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is often performed in inconclusive cases. 3,5,6 Sonography of the foot, including dynamic assessment, is one imaging method that can be performed for unexplained foot pain. At our institution, we have identified Lisfranc joint injuries on sonography, although there is no report of such an evaluation in the literature to our knowledge. The purpose of this study was to retrospectively characterize the sonographic appearances of Lisfranc injuries of the foot. Figure 1. Normal C1-M2 articulation in a 42-year-old man. A, The sonographic evaluation begins in the coronal plane transverse to the first metatarsal (M1) ligament and M2. B, The ultrasound transducer is moved posteriorly across the first tarsometatarsal joint and is positioned in the coronal plane transverse to C1 and M2. Note the normal dorsal C1-M2 ligament (arrows) and characteristic bone contour or plateau of C1 at the ligament attachment (arrowhead). C, A skeletal model shows the two transducer positions (white lines) as described in A and B; yellow indicates the location of the Lisfranc and dorsal C1-M2 ligaments. A Materials and Methods Institutional Review Board approval was obtained, and informed consent was waived. Sonography reports in the radiology information system were searched from January 1999 through September 2007 for the key word Lisfranc. Cases were excluded if imaging was not available. The search yielded 10 patients. Sonography of the foot in each patient was ordered as part of the clinical care of the patient. The sonographic examinations were completed by 1 of 5 musculoskeletal radiologists (2 13 years of experience) using 7- to 14-MHz linear transducers (iu22 and HDI 5000; Philips Healthcare, Bothell, WA; and LOGIQ 9; GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI). Images were acquired and saved in either digital or hard copy format. With regard to the ultrasound scanning technique, the tarsometatarsal joints were imaged in the coronal and sagittal planes. The C1-M2 interval is located with coronal scanning initially over the first and second metatarsals (Figure 1). As the transducer is moved posteriorly, the first tarsometatarsal joint is visualized. Continuing to scan in a posterior direction will then bring the dorsal surface of C1 into view with the adjacent M2 base. In contrast to the rounded shape of the M2 dorsal surface, the C1 dorsal surface is more angulated. The dorsal C1-M2 ligament will appear hyperechoic and fibrillar, with a characteristic notch in C1 at its attachment (Figure 1). B C 352 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
3 Woodward et al Measurements are taken at this site. Depending on the amount of adjacent hyperechoic fat, the gain setting of the ultrasound machine and the angle between the ligament and ultrasound beam, the normal ligament may appear mildly hypoechoic, although the superficial border will not be convex, and a normal fibrillar echo texture will be seen. Sonographic images and the original sonographic reports were retrospectively reviewed by a radiology resident (third year of training) and fellowship-trained musculoskeletal radiologist (13 years of experience) by consensus. Recorded data included the thickness of the dorsal ligament between C1 and M2, the space (millimeters) between C1 and M2, any change in this distance with weight bearing when applicable, the presence of hyperemia on color or power Doppler imaging, and the presence of a fracture (cortical step-off deformity). Data were recorded from the symptomatic extremity as well as the contralateral asymptomatic extremity when obtained. The medical records were subsequently reviewed to correlate sonographic findings with surgical reports, clinical notes, radiography, CT, and MRI, where available. Results The 10 patients were on average 36 years of age (range, years) and included 5 women and 5 men. Of the symptomatic feet, the right side was affected in 4 and the left in 6. In 5 of the patients, the asymptomatic foot was scanned and used for comparison. Of the 10 patients, all had routine foot radiographs (9 were weight bearing); 3 had CT examinations; 3 had MRI examinations; and 2 had surgery. In the 5 asymptomatic feet, the dorsal C1-M2 ligament was hyperechoic with a thickness of 0.9 to 1.2 mm, and the C1-M2 distance was 0.5 to 1 mm (Figure 2). Given these findings, the symptomatic feet could be divided into 3 groups. One group (n = 3) had similar findings (hyperechoic ligament, thickness of mm, and C1-M2 distance of mm); all had normal clinical follow-up and radiographic findings, and 1 had normal MRI findings. Another group (n = 3) had hypoechogenicity and thickening of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament ( mm) with a convex Figure 2. Normal C1-M2 articulation (asymptomatic foot) in a 40-year-old woman. Sonography in the coronal plane transverse to the metatarsal shafts shows a normal dorsal C1-M2 ligament (arrows; thickness measured as 1 mm). Note the characteristic bone contour of C1 at the ligament attachment (arrowhead). The C1-M2 space measured 0.7 mm. superficial border (Figure 3), a C1-M2 distance of 0.6 to 0.7 mm, and no widening with weight bearing (1 of 1); 1 had negative CT findings; and all 3 had no malalignment on radiography and uneventful clinical follow-up. The third group (n = 4) had findings consisting of hypoechogenicity and nonvisualization of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament, a C1-M2 distance of 2.5 to 3.1 mm, and further widening with weight bearing (3 of 4; Figures 4 and 5); Lisfranc ligament disruption was confirmed at surgery in 2, MRI in 1, and CT in 1. Figure 3. Dorsal C1-M2 ligament sprain in a 41-year-old man. Sonography in the coronal plane transverse to the metatarsal shafts shows a hypoechoic and swollen dorsal C1-M2 ligament (arrows; thickness measured as 2.3 mm). Note the normal C1- M2 space measuring 0.6 mm (arrowhead). J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
4 Sonographic Evaluation of Lisfranc Ligament Injuries Four of the 10 subjects had color or power Doppler imaging. Of these, 2 showed increased flow dorsally between C1 and M2 (Figure 4C; both had Lisfranc ligament tears), and 2 did not show any flow (1 had a Lisfranc ligament tear, and the other had a sprain). With regard to fractures, 1 of 10 patients showed a fracture on sonography, confirmed on radiography and MRI. Discussion Prompt diagnosis of a Lisfranc joint injury is important to allow appropriate treatment and avoid long-term disability. This study shows that there are characteristic sonographic findings that indicate a Lisfranc ligament tear. Although visualization of the Lisfranc ligament proper is not possible with sonography because of the narrow space between C1 and M2, assessment of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament and forefoot alignment can indicate a Lisfranc ligament injury. Dynamic imaging in the evaluation of alignment offers additional information. The tarsometatarsal joint complex (Lisfranc joint) articulates the distal tarsal bones with the metatarsal bases. The stabilization of the joint is complex and consists of a dorsal ligament system, plantar ligaments, and interosseous liga- Figure 4. Lisfranc ligament tear (diagnosed at CT) in a 25-year-old man. A, Sonography in the coronal plane transverse to the metatarsal shafts shows abnormal hypoechogenicity, absence of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament (arrow), and widening between C1 and M2 (brace) measuring 3.1 mm. B, Sonography in the coronal plane transverse to the metatarsal shafts with patient weight bearing shows findings similar to those in A (arrow) but with increased widening between C1 and M2 (brace). C, Color Doppler imaging shows increased blood flow dorsally between C1 and M2. D, Non contrast-enhanced axial CT (0.5-mm slice thickness) shows malalignment between the second cuneiform (C2) ligament and M2 (arrow) and widening between C1 and M2. A B C D 354 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
5 Woodward et al Figure 5. Lisfranc ligament tear (diagnosed at surgery) in a 50- year-old man. A, Sonography in the coronal plane transverse to the metatarsal shafts shows abnormal hypoechogenicity, absence of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament (arrow), and widening between C1 and M2 (bracket) measuring 2.5 mm. B, Sonography in the coronal plane transverse to the metatarsal shafts with patient weight bearing shows findings similar to those in A (arrow) but with increased widening between C1 and M2 (brace). C, Non contrast-enhanced axial CT (0.5-mm slice thickness) shows equivocal malalignment between C2 and M2 (arrow) and equivocal widening between C1 and M2. A B C ments. 7,8 The dorsal ligament system represents thin, flat transverse, oblique, and longitudinal bands that connect tarsal bones to tarsal bones, tarsal bones to metatarsals, and metatarsals to metatarsals, including C1 to M2. 7 The plantar ligaments similarly consist of transverse and longitudinal ligaments that interconnect the osseous structures, including C1 to M2. 7 Among the interosseous ligaments is the Lisfranc ligament proper, the largest ligament of the tarsometatarsal joints, arising from the lateral aspect of C1 extending distal, lateral, and plantar to attach to the medial aspect of M2. 7 Of note, there is no mechanically significant ligamentous connection between the first and second metatarsal bases, but instead, the Lisfranc ligament provides stability at this articulation. 7 The Lisfranc joint may be injured with plantar flexion and forced pronation or supination. 5 This can result in ligament disruption, a fracture, and possible malalignment. When a patient has midfoot pain and swelling after trauma, it is important to exclude a fracture and consider a ligamentous injury. When the Lisfranc ligament is disrupted, dislocation most often occurs dorsally, laterally, or dorsolaterally because the M2 base is wider dorsally than ventrally. 9 The evaluation for a Lisfranc joint injury typically begins with conventional radiography. However, radiographs may show false-negative findings, and multiple studies have shown conventional radiographs to be unreliable for detection of Lisfranc dislocation, particularly for detection of subtle injuries or ligamentous injuries without associated fractures. 5 Although a distance of 2 mm or greater between C1 and M2 has been shown to correlate with a complete tear of the Lisfranc ligament, a Lisfranc ligament injury may be associated with distances of less than this. 10 In addition, it has been shown that malalignment of 1 or 2 mm is not reliably identified on radiography. 9 Weight-bearing radiographs may be helpful to show malalignment but are often limited by patient pain and remain unreliable. 5 In a cadaveric model, manual stress radiographs of the foot have been shown to depict more displacement than weight-bearing radiography alone. 11 Several studies have also emphasized the importance of CT in the evaluation for fractures and bony alignment when con- J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
6 Sonographic Evaluation of Lisfranc Ligament Injuries ventional radiographs are unrevealing and clinical suspicion remains high. 5,6,9 Magnetic resonance imaging has been used to show fractures, bony alignment, and the integrity of the Lisfranc ligament. 2,5,8,10 The results of this study suggest a potential role for sonography as well. When performing sonography of the midfoot, evaluation of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament is important because it can be an indirect sign of a Lisfranc ligament tear. The normal dorsal C1-M2 ligament, which appears hyperechoic with a thickness of 0.9 to 1.2 mm, is easily identified given its superficial location and adjacent distinctive osseous landmarks (Figure 1). Of note, a normal dorsal C1-M2 ligament may appear mildly hypoechoic depending on the amount of adjacent hyperechoic fat, the gain setting of the ultrasound machine, and whether the ultrasound beam is perpendicular to the ligament (Figure 1); regardless, a fibrillar echo texture without a convex superficial margin should be seen with a normal dorsal C1-M2 ligament. In this study, the 4 cases of Lisfranc ligament disruption had associated disruption of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament (Figures 4 and 5). In addition, a Lisfranc ligament tear was excluded in every case in which the dorsal C1-M2 ligament was normal on sonography. This may be explained by the relatively small size of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament compared with the Lisfranc ligament. Evaluation of a larger population with midfoot injuries would determine whether these associations are consistent. In 3 cases, the dorsal C1-M2 ligament was intact but hypoechoic and swollen (1.4- to 2.3-mm thickness; Figure 3); imaging and follow-up did not show malalignment, and this was interpreted as a dorsal C1-M2 ligament sprain. In addition to disruption of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament, widening of the space between C1 and M2 is another important and probably more specific indirect sign of a Lisfranc ligament tear. Normally this space between cortical surfaces of C1 and M2 measures 0.5 to 1.0 mm in the coronal plane on sonography. With a Lisfranc ligament tear, this space measured 2.5 mm or greater (Figures 4 and 5). Although a widened C1-M2 space in the setting of a Lisfranc ligament tear was evident on sonography with the patients supine, this space further increased with weight bearing (Figures 4 and 5). The dynamic imaging of sonography is a potential benefit because imaging during weight bearing may increase sensitivity in the diagnosis of a Lisfranc ligament tear. Other sonographic findings associated with Lisfranc ligament tears were more variable. Increased blood flow dorsally between C1 and M2 was shown in 2 of the 3 cases of Lisfranc ligament tears in which color or power Doppler imaging was performed (Figure 4C). A cortical step-off representing a fracture was seen in 1 of 4 cases with Lisfranc ligament tears. Fracture assessment in the midfoot region with sonography is limited because of the complex anatomy. It is also important not to misinterpret an os intermetatarsus as a fracture fragment. The limitations of our study included its retrospective nature and resulting small number of patients included. A larger prospective study would be needed to further validate these results. In addition, not all patients had imaging or surgical proof, although a correlation was made to the clinical outcome in such cases. In conclusion, absence of the dorsal C1-M2 ligament, a C1-M2 interval of 2.5 mm or more, and progressive widening on a dynamic sonographic evaluation are indirect signs of Lisfranc ligament tears. Sonography can play a role in the assessment of forefoot and midfoot pain, and familiarity with these findings is important when performing sonography of the foot. References 1. Sarrafian SK. Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle: Descriptive, Topographic, Functional. Philadelphia, PA: JB Lippincott Co; Preidler KW, Brossmann J, Daenen B, Goodwin D, Schweitzer M, Resnick D. MR imaging of the tarsometatarsal joint: analysis of injuries in 11 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996; 167: Talarico RH, Hamilton GA, Ford LA, Rush SM. Fracture dislocations of the tarsometatarsal joints: analysis of interrater reliability in using the modified Hardcastle classification system. J Foot Ankle Surg 2006; 45: Hardcastle PH, Reschauer R, Kutscha-Lissberg E, Schoffmann W. Injuries to the tarsometatarsal joint: incidence, classification and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1982; 64: Preidler KW, Peicha G, Lajtai G, et al. Conventional radiography, CT, and MR imaging in patients with hyperflexion injuries of the foot: diagnostic accuracy in the detection of bony and ligamentous changes. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999; 173: J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
7 Woodward et al 6. Goiney RC, Connell DG, Nichols DM. CT evaluation of tarsometatarsal fracture-dislocation injuries. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1985; 144: de Palma L, Santucci A, Sabetta SP, Rapali S. Anatomy of the Lisfranc joint complex. Foot Ankle Int 1997; 18: Preidler KW, Wang YC, Brossmann J, Trudell D, Daenen B, Resnick D. Tarsometatarsal joint: anatomic details on MR images. Radiology 1996; 199: Lu J, Ebraheim NA, Skie M, Porshinsky B, Yeasting RA. Radiographic and computed tomographic evaluation of Lisfranc dislocation: a cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int 1997; 18: Potter HG, Deland JT, Gusmer PB, Carson E, Warren RF. Magnetic resonance imaging of the Lisfranc ligament of the foot. Foot Ankle Int 1998; 19: Kaar S, Femino J, Morag Y. Lisfranc joint displacement following sequential ligament sectioning. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007; 89: J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation
 Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury and Midfoot Sprain
 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury and Midfoot Sprain Stephen F. Hatem, MD KEYWORDS Lisfranc injury Midfoot sprain MRI Lisfranc is one of the best known orthopedic eponyms. Unfortunately, the term is imprecise.
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury and Midfoot Sprain Stephen F. Hatem, MD KEYWORDS Lisfranc injury Midfoot sprain MRI Lisfranc is one of the best known orthopedic eponyms. Unfortunately, the term is imprecise.
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department
 Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts
 CME Article Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Variable and Noncystic Appearances George Wang, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Felix Y. Feng, MD, Gandikota Girish, MBBS, FRCS, FRCR, Elaine M. Caoili, MD, Catherine
CME Article Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Variable and Noncystic Appearances George Wang, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Felix Y. Feng, MD, Gandikota Girish, MBBS, FRCS, FRCR, Elaine M. Caoili, MD, Catherine
REVIEW ARTICLE Current concept review on Lisfranc injuries
 Hong HKJOS Kong Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001;5(1):75-80. Chan SCF, Chow SP REVIEW ARTICLE Current concept review on Lisfranc injuries Chan SCF, Chow SP 1 Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Hong HKJOS Kong Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001;5(1):75-80. Chan SCF, Chow SP REVIEW ARTICLE Current concept review on Lisfranc injuries Chan SCF, Chow SP 1 Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Syndesmosis Injuries
 Syndesmosis Injuries Dr. Alex Rabinovich Outline Anatomy Injury types and classification Treatment options Nonoperative vs. Operative Indications for operative Operative technique Postoperative management
Syndesmosis Injuries Dr. Alex Rabinovich Outline Anatomy Injury types and classification Treatment options Nonoperative vs. Operative Indications for operative Operative technique Postoperative management
Running Head: Salter Harris Fractures 1
 Running Head: Salter Harris Fractures 1 Salter Harris Classification of Growth Plate Fractures November 15 th, 2011 Salter Harris Fractures 2 Abstract Salter-Harris Classifications are a straightforward
Running Head: Salter Harris Fractures 1 Salter Harris Classification of Growth Plate Fractures November 15 th, 2011 Salter Harris Fractures 2 Abstract Salter-Harris Classifications are a straightforward
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the
 Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás
 Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings
 Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
PERILUNATE AND LUNATE DISLOCATIONS
 PERILUNATE AND LUNATE DISLOCATIONS Rebecca Morris Advanced Practitioner Plain Film Reporting March 2011 Perilunate and Lunate dislocations Introduction Definition Anatomy Clinical presentation Mechanism
PERILUNATE AND LUNATE DISLOCATIONS Rebecca Morris Advanced Practitioner Plain Film Reporting March 2011 Perilunate and Lunate dislocations Introduction Definition Anatomy Clinical presentation Mechanism
Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures. Outline. Outline. Holmes Criteria. Disclosure:
 Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures C. Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Department of Radiology Virginia Mason Medical Center Affiliate Professor, University of Washington Disclosure: Book Royalties, Springer-Verlag
Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures C. Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Department of Radiology Virginia Mason Medical Center Affiliate Professor, University of Washington Disclosure: Book Royalties, Springer-Verlag
Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography
 Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
Musculoskeletal Trauma of the Wrist
 September 2000 Musculoskeletal Trauma of the Wrist Murat Akalin, Harvard Medical School, Year- IV Gillian Lieberman, MD The Wrist Most common site of injury in entire skeleton Distal radius and ulna fractures
September 2000 Musculoskeletal Trauma of the Wrist Murat Akalin, Harvard Medical School, Year- IV Gillian Lieberman, MD The Wrist Most common site of injury in entire skeleton Distal radius and ulna fractures
RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION
 Jeff Husband MD Objectives Evaluate, diagnose and manage common wrist injuries due to high energy trauma in athletes Appropriately use radiographs, CT scans and MRI Know when to refer patients for additional
Jeff Husband MD Objectives Evaluate, diagnose and manage common wrist injuries due to high energy trauma in athletes Appropriately use radiographs, CT scans and MRI Know when to refer patients for additional
Ankle Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS. Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Ankle Fractures
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete
 Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete Kevin Latz, MD Children s Mercy Hospital Center for Sports Medicine Foot and Ankle Injuries Very common Influenced by the unique properties of growth plates
Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete Kevin Latz, MD Children s Mercy Hospital Center for Sports Medicine Foot and Ankle Injuries Very common Influenced by the unique properties of growth plates
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
63 Tarsometatarsal arthritis
 63 Tarsometatarsal arthritis Contents Introduction Anatomy Biomechanics Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Physical Examination Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Controversy References
63 Tarsometatarsal arthritis Contents Introduction Anatomy Biomechanics Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Physical Examination Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Controversy References
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Low Back Pain Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Ultrasound Evaluation of Low Back Pain Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Vivian Gonzalez Gillian Lieberman, MD. January 2002. Lumbar Spine Trauma. Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 January 2002 Lumbar Spine Trauma Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Anatomy and Biomechanics of Lumbar Spine Three-Column Concept Classification of Fractures Our Patient Imaging Modalities
January 2002 Lumbar Spine Trauma Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Anatomy and Biomechanics of Lumbar Spine Three-Column Concept Classification of Fractures Our Patient Imaging Modalities
Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains
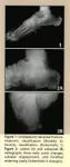 Article Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains Yannick Guillodo, MD, Patrick Riban, MD, Xavier Guennoc, MD, Frédéric Dubrana, MD, PhD, Alain Saraux, MD, PhD Objective.
Article Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains Yannick Guillodo, MD, Patrick Riban, MD, Xavier Guennoc, MD, Frédéric Dubrana, MD, PhD, Alain Saraux, MD, PhD Objective.
Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Drilling
 Technical dvance Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Drilling Juan D. erná-serna, MD, Francisco Martinez, MD, Manuel Reus, MD, Juan D. erná-mestre, MD Objective. The
Technical dvance Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Drilling Juan D. erná-serna, MD, Francisco Martinez, MD, Manuel Reus, MD, Juan D. erná-mestre, MD Objective. The
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
1991 :super specialties perceptions
 Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. II. Elbow
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines II. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines II. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
Distal Radius Fractures. Lee W Hash, MD Affinity Orthopedics and Sports Medicine
 Distal Radius Fractures Lee W Hash, MD Affinity Orthopedics and Sports Medicine The Problem of Distal Radius Fractures Common injury: >450,000/yr. in USA High potential for functional impairment and frequent
Distal Radius Fractures Lee W Hash, MD Affinity Orthopedics and Sports Medicine The Problem of Distal Radius Fractures Common injury: >450,000/yr. in USA High potential for functional impairment and frequent
PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE I. DIGITAL FRACTURES A. Background Digital fractures commonly occur in the workplace and are usually the result of a crush injury from a falling object, or
PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE I. DIGITAL FRACTURES A. Background Digital fractures commonly occur in the workplace and are usually the result of a crush injury from a falling object, or
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem
 Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Scaphoid and Other Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Scaphoid and Other Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department SCOPE (Area): SCOPE (Staff): Emergency Department and Fracture Clinic Medical, Nursing, Patient Service Assistants
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Scaphoid and Other Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department SCOPE (Area): SCOPE (Staff): Emergency Department and Fracture Clinic Medical, Nursing, Patient Service Assistants
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint is viewed using a small camera. This technique allows the surgeon to have a clear view of the
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint is viewed using a small camera. This technique allows the surgeon to have a clear view of the
Case Report Reconstructive Osteotomy for Ankle Malunion Improves Patient Satisfaction and Function
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 549109, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/549109 Case Report Reconstructive Osteotomy for Ankle Malunion Improves Patient Satisfaction and Function
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 549109, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/549109 Case Report Reconstructive Osteotomy for Ankle Malunion Improves Patient Satisfaction and Function
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
SCAPULAR FRACTURES. Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading.
 SCAPULAR FRACTURES Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading. Aims Anatomy Incidence/Importance Mechanism Classification Principles of treatment Specific variations Conclusion Anatomy
SCAPULAR FRACTURES Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading. Aims Anatomy Incidence/Importance Mechanism Classification Principles of treatment Specific variations Conclusion Anatomy
Growth Plate Injuries
 Growth Plate Injuries Richard A. Bernstein, MD The Orthopaedic Group, LLC The Growth Plate Our skeleton is a marvelous thing. It grows as we grow! And it does this without shutting down or closing for
Growth Plate Injuries Richard A. Bernstein, MD The Orthopaedic Group, LLC The Growth Plate Our skeleton is a marvelous thing. It grows as we grow! And it does this without shutting down or closing for
Fractures around wrist
 Fractures around wrist Colles Fracture Smiths fracture Barton s fracture Chauffer s fracture Scaphoid fracture Lunate dislocation Vivek Pandey Colles fracture Definition: Fracture of the distal end radius
Fractures around wrist Colles Fracture Smiths fracture Barton s fracture Chauffer s fracture Scaphoid fracture Lunate dislocation Vivek Pandey Colles fracture Definition: Fracture of the distal end radius
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
Toe fractures are one of the most
 Evaluation and Management of Toe Fractures ROBERT L. HATCH, M.D., M.P.H., and SCOTT HACKING, M.D., University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, Florida Fractures of the toe are one of the most
Evaluation and Management of Toe Fractures ROBERT L. HATCH, M.D., M.P.H., and SCOTT HACKING, M.D., University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, Florida Fractures of the toe are one of the most
Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion
 Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair
 UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair There are two types of cartilage in the knee, articular cartilage and cartilage. Articular cartilage is made up of collagen,
UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair There are two types of cartilage in the knee, articular cartilage and cartilage. Articular cartilage is made up of collagen,
QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY.
 QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY. SOME ARE HINGE BRACED 0-90 DEGREES AND ASKED TO REHAB INCLUDING
QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY. SOME ARE HINGE BRACED 0-90 DEGREES AND ASKED TO REHAB INCLUDING
Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments
 PICTORIL ESSY Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments Dean Smith, MD, FRCPC, Donal Downey, M, Ch, FRCPC, lison Spouge, MD, FRCPC, Sue Soney, RT, RDMS, RCMS The segmental localization of
PICTORIL ESSY Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments Dean Smith, MD, FRCPC, Donal Downey, M, Ch, FRCPC, lison Spouge, MD, FRCPC, Sue Soney, RT, RDMS, RCMS The segmental localization of
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
C H A P T E R 3 5. Thomas J. Merrill, DPM Riquel Gonzalez, DPM INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 C H A P T E R 3 5 CORTICOSTEROID INDUCED AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE RIGHT MEDIAL CUNEIFORM TREATED WITH TRINITY EVOLUTION BONE GRAFT AND ARTHRODESIS: Case Report and Review of the Literature Thomas J. Merrill,
C H A P T E R 3 5 CORTICOSTEROID INDUCED AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE RIGHT MEDIAL CUNEIFORM TREATED WITH TRINITY EVOLUTION BONE GRAFT AND ARTHRODESIS: Case Report and Review of the Literature Thomas J. Merrill,
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013
 Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Evaluation and Treatment of Spine Fractures. Lara C. Portmann, MSN, ACNP-BC
 Evaluation and Treatment of Spine Fractures Lara C. Portmann, MSN, ACNP-BC Nurse Practitioner, Neurosurgery, Trauma Services, Intermountain Medical Center; Salt Lake City, Utah Objectives: Identify the
Evaluation and Treatment of Spine Fractures Lara C. Portmann, MSN, ACNP-BC Nurse Practitioner, Neurosurgery, Trauma Services, Intermountain Medical Center; Salt Lake City, Utah Objectives: Identify the
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
The multitude of symptoms following a whiplash injury has given rise to much discussion because of the lack of objective radiological findings.
 HELPFUL PERSONAL INJURY INFORMATION COURTESY OF RIVERVIEW CHIROPRACTIC FROM ABSTRACT: Dynamic kine magnetic resonance imaging in whiplash patients Pain Research and Management 2009 Nov-Dec 2009;Vol. 14,
HELPFUL PERSONAL INJURY INFORMATION COURTESY OF RIVERVIEW CHIROPRACTIC FROM ABSTRACT: Dynamic kine magnetic resonance imaging in whiplash patients Pain Research and Management 2009 Nov-Dec 2009;Vol. 14,
Cervical Spine Trauma: Pearls and Pitfalls
 Cervical Spine Trauma: Pearls and Pitfalls Mark P. Bernstein 1, Alexander B. Baxter Accurate diagnosis of acute cervical spine injury requires cooperation between clinician and radiologist, a reliable
Cervical Spine Trauma: Pearls and Pitfalls Mark P. Bernstein 1, Alexander B. Baxter Accurate diagnosis of acute cervical spine injury requires cooperation between clinician and radiologist, a reliable
Sports Related Fractures of the Foot and Ankle
 Sports Related Fractures of the Foot and Ankle Patrick Ebeling, MD Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon Twin Cities Orthopedics Burnsville, MN No disclosures Sports Related Fractures of 5 th Metatarsal Fractures
Sports Related Fractures of the Foot and Ankle Patrick Ebeling, MD Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon Twin Cities Orthopedics Burnsville, MN No disclosures Sports Related Fractures of 5 th Metatarsal Fractures
Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique
 *smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique Prepared in Consultation with: C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative
*smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique Prepared in Consultation with: C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
Isolated posterior high ankle sprain: a report of three cases
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2013;21(3):391-5 Isolated posterior high ankle sprain: a report of three cases Rajesh Botchu, 1 Patricia Allen, 2 Winston J Rennie 1 1 Department of Musculoskeletal Radiology,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2013;21(3):391-5 Isolated posterior high ankle sprain: a report of three cases Rajesh Botchu, 1 Patricia Allen, 2 Winston J Rennie 1 1 Department of Musculoskeletal Radiology,
4/13/2016. Injury Rate (%) Common Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Football Player Surgery or Not. Common Injuries. Common Injuries
 Injury Rate (%) Common Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Football Player Surgery or Not Ankle Foot Collegiate 12 3 High School 18 3 Youth 15 4 Daniel Murawski, MD April 22, 2016 1 2 Common Injuries Lateral
Injury Rate (%) Common Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Football Player Surgery or Not Ankle Foot Collegiate 12 3 High School 18 3 Youth 15 4 Daniel Murawski, MD April 22, 2016 1 2 Common Injuries Lateral
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality!
 Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD (C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Diplomate, American Board
Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD (C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Diplomate, American Board
Wrist Fractures: What the Clinician Wants to Know 1
 What the Clinician Wants to Know Charles A. Goldfarb, MD Yuming Yin, MD Louis A. Gilula, MD Andrew J. Fisher, MD Martin I. Boyer, MD Index terms: Bones, CT, 43.1211 Wrist, fractures, 43.41 Wrist, MR, 43.12141,
What the Clinician Wants to Know Charles A. Goldfarb, MD Yuming Yin, MD Louis A. Gilula, MD Andrew J. Fisher, MD Martin I. Boyer, MD Index terms: Bones, CT, 43.1211 Wrist, fractures, 43.41 Wrist, MR, 43.12141,
Color Doppler and Duplex Sonography in 5 Patients With Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
 Case Series Color Doppler and Duplex Sonography in 5 Patients With Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Raju Wadhwani, DMRD, DNB, Nitin Chaubal, MD, Rajan Sukthankar, MD, Manu Shroff, MD, Sanjay Agarwala, MS Purpose.
Case Series Color Doppler and Duplex Sonography in 5 Patients With Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Raju Wadhwani, DMRD, DNB, Nitin Chaubal, MD, Rajan Sukthankar, MD, Manu Shroff, MD, Sanjay Agarwala, MS Purpose.
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam
 Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Bakman M, Chan K, Bang C, Basu A, Seo G, Monu JUV Department of Imaging Sciences University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY Introduction
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Bakman M, Chan K, Bang C, Basu A, Seo G, Monu JUV Department of Imaging Sciences University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY Introduction
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes
 Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes Kyle Nagle, MD MPH University of Colorado Department of Orthopedics Children s Hospital Colorado Orthopedics Institute June 14, 2014 Disclosures I have
Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes Kyle Nagle, MD MPH University of Colorado Department of Orthopedics Children s Hospital Colorado Orthopedics Institute June 14, 2014 Disclosures I have
Dr Dan Gill Department of Radiology Windsor Regional Hospital Oxford Medical Imaging Erie St Clair Radiology
 Dr Dan Gill Department of Radiology Windsor Regional Hospital Oxford Medical Imaging Erie St Clair Radiology -5000 Olympic athletes and team officials -1350 Paralympic athletes and team officials -82
Dr Dan Gill Department of Radiology Windsor Regional Hospital Oxford Medical Imaging Erie St Clair Radiology -5000 Olympic athletes and team officials -1350 Paralympic athletes and team officials -82
How To Know If You Can Recover From A Knee Injury
 David R. Cooper, M.D. www.thekneecenter.com Wilkes-Barre, Pa. Knee Joint- Anatomy Is not a pure hinge Ligaments are balanced Mechanism of injury determines what structures get damaged Medial meniscus tears
David R. Cooper, M.D. www.thekneecenter.com Wilkes-Barre, Pa. Knee Joint- Anatomy Is not a pure hinge Ligaments are balanced Mechanism of injury determines what structures get damaged Medial meniscus tears
Shoulder Pain and Weakness
 Shoulder Pain and Weakness John D. Kelly IV, MD THE PHYSICIAN AND SPORTSMEDICINE - VOL 32 - NO. 11 - NOVEMBER 2004 For CME accreditation information, instructions and learning objectives, click here. A
Shoulder Pain and Weakness John D. Kelly IV, MD THE PHYSICIAN AND SPORTSMEDICINE - VOL 32 - NO. 11 - NOVEMBER 2004 For CME accreditation information, instructions and learning objectives, click here. A
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. I. Shoulder
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF HIP DYSPLASIA: review. L. Breysem, MD DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY
 ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF HIP DYSPLASIA: review L. Breysem, MD DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY INTRODUCTION Clinical hip examination is part of the first routine examination of every newborn. An abnormal
ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF HIP DYSPLASIA: review L. Breysem, MD DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY INTRODUCTION Clinical hip examination is part of the first routine examination of every newborn. An abnormal
Scaphoid Fractures- Anatomy And Diagnosis: A Systemic Review Of Literature
 Article ID: WMC001268 ISSN 2046-1690 Scaphoid Fractures- Anatomy And Diagnosis: A Systemic Review Of Literature Corresponding Author: Dr. Dharm Meena, junior resident, orthopaedics, PGIMER, E 402, MDH,PGIMER,CHANDIGARH,
Article ID: WMC001268 ISSN 2046-1690 Scaphoid Fractures- Anatomy And Diagnosis: A Systemic Review Of Literature Corresponding Author: Dr. Dharm Meena, junior resident, orthopaedics, PGIMER, E 402, MDH,PGIMER,CHANDIGARH,
Common Pediatric Fractures. Quoc-Phong Tran, MD UNSOM Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellow November 6, 2014
 Common Pediatric Fractures Quoc-Phong Tran, MD UNSOM Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellow November 6, 2014 Pediatric fractures 20% of injured kids found to have fracture on evaluation Between birth and
Common Pediatric Fractures Quoc-Phong Tran, MD UNSOM Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellow November 6, 2014 Pediatric fractures 20% of injured kids found to have fracture on evaluation Between birth and
Ultrasonography in Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
 Article Ultrasonography in Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Masahiro Nagaoka, MD, Hiromi Matsuzaki, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to clarify the diagnostic value of ultrasonography in tarsal tunnel
Article Ultrasonography in Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Masahiro Nagaoka, MD, Hiromi Matsuzaki, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to clarify the diagnostic value of ultrasonography in tarsal tunnel
American Journal of Emergency Medicine
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine 31 (2013) 1551 1555 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect American Journal of Emergency Medicine journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution
American Journal of Emergency Medicine 31 (2013) 1551 1555 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect American Journal of Emergency Medicine journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution
J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC. Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program
 J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program Evidence Category A Recommendation based on consistent and upper quality
J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program Evidence Category A Recommendation based on consistent and upper quality
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs
 Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts
 Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Rotator Cuff Tears in Football
 Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy in the elbow: value of ultrasonography and MRI
 Diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy in the elbow: value of ultrasonography and MRI Poster No.: C-2216 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. L. Pegado, C. A. Santos Ruano, J. Raposo, P. Alves,
Diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy in the elbow: value of ultrasonography and MRI Poster No.: C-2216 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. L. Pegado, C. A. Santos Ruano, J. Raposo, P. Alves,
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY
 George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy
 Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
