Sound and Music Adams, W.K. & Clark, A.
|
|
|
- Hannah Underwood
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acoustical Society of America Edited by: Kelseigh Schneider Reviewed by: American Association of Physics Teachers Physics Teacher Resource Agents ASA Activity Kit Committee Sound and Music Adams, W.K. & Clark, A. Students explore the physics of sound, how the ear hears and how musical instruments work through interactive demonstrations and student activities. Science Topics Process Skills Subject Integration Sound Vibrations Resonance Frequency Anatomy of the ear Conservation of Energy Observing Predicting Making models Scientific Inquiry Comparing Communicating Physical Science Musical acoustics Speech Psychological & Physiological Acoustics Grade Level 3-12 Time Required Advanced Preparation Set-Up Activity* Clean-Up 10 minutes (with kit) gather materials 5 minutes minutes 5 minutes *If you are using the optional worksheet, then we believe it may add an extra 10 minutes to the activity. Learning Goals Students will be able to describe and identify the source of a sound vibrations. identify the difference between the direction a wave travels and the direction the medium moves. explain that Sound carries energy and identify how sound energy transfers explain resonant or natural frequency. relate the terms pitch, frequency and high/low sounds. demonstrate the path that sound vibrations follow through the ear. Describe how ears can be permanently damaged by loud sounds Materials Kit: (free from ASA to K-12 teachers) 1 cup instrument Tuning forks (10) Ping pong balls with string attached (10) Posters (four) Straws that slide together (30 of each kind = 60) Pipe cleaners (150) Visit our website at for other classroom resources such as career profiles of acousticians, fun educational videos and new lesson plans as we get them developed! Please forward any questions or comments to: Wendy Adams Education Coordinator Acoustical Society of America Wendy.Adams@colorado.edu
2 Materials not in kit: Scissors (1 per group) Pasta Noodles 3 long and dry 3 Raisins or small marshmallows Optional Materials (not in kit): Rubber mallets (other objects such as text books, rubber soles on shoes or a knee work just as well) Instructor Computer* o (10 sec wave) o o Assistant** Student worksheet to fill out during the lesson (page 13-15)*** *If no computers are available, then skip the sections requiring computers **With more than 15 students it s helpful to have an assistant to distribute and collect materials ***The worksheet is an option if a written log of the activity is desired. All of our testing has been successful without it so far. Advanced Preparations Watch pasta demonstration and practice o Kit demo or original source Acquire materials o Many materials can be obtained through the kit and the rest can be easily found. Set Up Gather supplies (see materials list) Set up materials so they can be easily passed out to students during the lesson o Tuning forks o Ping Pong Balls w/ string attached o Fuzzy sticks o Straws Introducing the Activity Students will assemble into groups of two or three. Students will sit quietly and listen to the sounds around them, then share one or two of the sounds they heard with their groups.
3 Tell the class that even though all these sounds seem very different, all sounds are caused by the same thing. Explain that they will be sound detectives for the day to try to find out what causes sound. Doing the Activity All of this information can be found in the accompanying power point file. The power point can be used for the teacher s view only or can be shown to the class. It is animated so that the answers do not appear on the screen until the teacher presses the arrow, or return keys. What is Sound? Tell the students they will make a sound using the tuning fork and that the tuning forks always make the same clear sound. Show students that you are holding the rounded handle and that the two tines make a narrow U. Show them how to strike the fork properly. If struck on a hard surface the fork could be damaged changing the frequency. Note: Tuning forks should NOT be struck against hard surfaces like desks. A mallet is ideal but the heal of your tennis shoe, your kneecaps, your palm, or a textbook are good substitutes. Have the students strike the tuning fork and: Listen to the fork Look very closely at the fork while it s making a sound. Ask the class what they observed. Have the students touch the fork when it is making a sound. Note: Don t touch tuning forks to your glasses or teeth- they can chip. Try eyelashes, lips (not teeth), bridge of your nose, tip of your nose, ear lobes, fingers, etc instead. Ask the class: What do you feel when it s making a sound? What do you feel if it s silent? When the fork is making a sound, how can you make the sound stop? Students guess what is vibrating. To check their hunches they try to stop the sound by stopping the vibration.
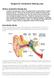
4 Sympathetic Vibration Set the handle end of your tuning fork (not the tines!) on the tabletop and ask the class: What happens? Why? Tell the class that this is called sympathetic vibration, and explain what is happening. Note: this is different than resonance. Ping Pong Balls see video Each group should take their tuning fork and ping-pong balls. One student will hang a ball from the string, and another will gently touch the quiet (not vibrating) tuning fork to the pingpong ball. What did you observe? Now touch a vibrating tuning fork to the ping-pong ball. What happens? Why is this? Your Ear Show the large anatomy of the ear poster. Ask students if any of them have learned anything about the ear before. Let students offer ideas for a minute or so the get them thinking about the ear. How We Hear see video Ask the class what the outside of the ear is called. (The pinna or auricle.) Explain how sound vibrations are funneled into the ear by the pinna and then travel along the ear canal into the ear. Point to the eardrum and ask what the pink part at the end of the ear canal is called. Repeat again that vibrations are funneled into the ear canal by the pinna, travel along the cannal to the ear drum and make the ear drum vibrate. Ask the class what the three tiny bones are called. (The ossicles: the malleus, the incus, and the stapes). Repeat the route through the ear again, explaining now how the ear drum vibrations then make the ossicles each vibrate one at a time. The eardrum vibrations make the malleus vibrate because it s attached to the eardrum. The malleus is attached to the incus so it makes it vibrate and then the incus is attached to the stapes. Finally the stapes sends the vibrations into this snail shaped thing (point to the cochlea).
5 Ask the class what the snail shaped thing is called. The vibrations continue through the tree tiny bones in your middle ear (the ossicles) to the cochlea. The cochlea is filled with thousands of tiny sensors like this: Hold up the hair cell picture next to the ear anatomy poster. Ask the class what it looks like to them. (It s fun the ask students to tell you what they think the hair cell looks like. You might get a candle or other choices, but our favorite is a flaming pickle!) Ask if anyone knows what it is called. Tell the class it is a tiny sensor called a hair cell and that the cochlea is filled with them. The green part is the cell body and the yellow part is the hair bundle. Explain that the hair cells are what turn those vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain so your brain can interpret what the sound is, whether it s a piano playing, someone playing a guitar, or the teacher talking. Maybe even a fire alarm. Hold up the healthy hair bundle poster. Tell them this is what a healthy hair bundle looks like (the yellow part of the pickle). See how the hairs are standing straight up? But when you listen to loud sounds you can actually damage them. It s the hair bundle at the top that can be damaged when you listen to your music too loud or you are around some loud sounds for too long. Show the unhealthy hair bundle poster and explain that they are damaged hair cells. See how some of them are laying down and others are broken off? What could have caused this? The loud sounds have bent and broken them. Build a Model see video Ask the class if anyone has ever built a model before. You should get all sorts of offers, model car, model of the solar system etc.. Tell them good, you know what a model is. Explain that the class is going to make a model. Pass out pipe cleaners to each student, and instruct them not to bend or mess with them yet! Students will make a fist and hold it out. The fist is the green (pickle) part- the body of the hair cell. Students will place their pipe cleaners in their fist. The pipe cleaners are the hair bundle. Any ideas what your arm will be? It s the nerve taking the signal from the hair cells to the brain.
6 Tell the following story to the class: You re sitting at the table talking to your parents. Demonstrate how to gently brush their hands back and forth over the fuzzy sticks as your dad talks to you in a normal conversational voice. Dad says we re going to the fireworks show today. We get to sit in the (insert your stadium name here) stadium the best seats there are! But if you want to go, you have to mow the lawn first. Do you think a lawn mower is kind of loud? After students guess, tell them a typical push lawn mower is actually a safe sound for up to two hours. Is your yard safe? It depends on how big your yard is! So, we re going to go out to the yard and start the lawn mower. It s going to get a little louder brush the hair cells a little harder (not too hard). Now we get to go to the (insert local name here) stadium. How loud are fireworks if you get really, really close? We re pretty excited and then they start! Boom!, bang, boom. Have students hit their hair bundles hard now as their hands go past. What do your hair bundles look like now? Can you fix them? That s what happens in our ears. These are nerve cells and we can t regrow them (unless you re a bird or a frog.) Your Ear Listen to a range of sounds from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz using the ten second wave from (links also in power point file accompanying this lesson plan) Then play each frequency from the following website: Have students raise their hands when they hear the sound. Students enjoy hearing the high sound and seeing what they are able to hear, and love to see that they can hear high sounds better than their teacher! (or any other adults in the room) Explain that not everyone s ears are the same; some are more sensitive, so if you can t hear the Hz, even when you re young, it doesn t have to be because of damage. Most adults can t hear higher than 12-15,000 Hz.
7 Use the words low pitch and high pitch Your Voices see video Instruct the students to hold their fingers on the front of their throats and say Aaaah. Notice the vibration? Now have the class make a high-pitched Aaaah and a low-pitched Aaaah. Do low and high voices feel different? Straw Instrument see video To build a straw instrument students: Take the smaller straw and the scissors, and cut off the tip of the straw to a point, like so. (Try to get both sides to be the same.) Gently chew on the straw to soften the tip, and to get the edges to be smooshed together. The two tips should be almost touching each other. Blow really hard into the pointy end. If it is done correctly (it might take some practice), a very loud sound will emit from the straw instrument! Some students will nibble with their front teeth and not get the straw very warm. We ve seen a few who do this have trouble making sound. Instruct the students to chew with their side teeth and their lips closed. This helps it soften up and work better. What is vibrating? The tips of the straw are vibrating Have students try gently touching their tongue to the tips of the straw while they make a sound. They will feel it tickling their tongue. It s quite annoying!! Does the person across the room hear your straw instrument? Does the air you blow into the straw go in his/her ear for them to hear?
8 If you have bad breath (eat tuna) can the person across the room smell it when they hear you talk? Why is that? Sound Travels Use (also in powerpoint file accompanying this lesson plan) to illustrate the following ideas. Do the wave! (Students stand up and sit down across the room) Did the wave make it across the room? How did you move? Did the people who started it move across the room? Name a student or two who were at the beginning of the wave. Ask them if they actually went with the wave across the room. Students will describe that they did not. Ask what their arms did? Now show the sound wave sim at the above link. Show how the wave travels through the air but the air molecules just move back and forth and then stop. Straw Instrument trombone see video Put the bigger straw over the end of your straw instrument. This makes a straw trombone! Have the class: Make the lowest pitch (bass notes) that you can. Make the highest pitch (treble notes) that you can. Is the buzzing on your lips different with low and high sounds? High sounds make a high pitch High sounds are caused by higher frequencies more wiggles per second. Tell the students that they get to keep their straw instruments. Instruct them to put their instruments away (not just on a desk- out of sight!) Resonance Explain following two terms: frequency (rate) and resonant or natural frequency Frequency (rate) wiggles per second (moves back and forth) Natural frequency the frequency at which an object likes to vibrate. Resonance When one object is vibrating and it is put in contact with another object, if the frequency of the first object is at the natural frequency for the second object, the second object will start vibrating vigorously at its natural frequency. (see the pasta demo below) Pasta Demo - see video
9 This is a demonstration done by the teacher. Hold three sticks of pasta in one hand, each held at a different length. First shake your hand slowly, and the long pasta will swing vigorously back and forth. Shake at a medium frequency for the middle to swing vigorously. A high frequency will cause the short one to vigorously wave back and forth. Doing any of the three fast enough will cause the past to snap off. Why does the longer pasta shake more when the hand is moved slowly? Straw resonance Straws are similar. Different lengths of straws like different frequencies or pitches. Air moves a lot at the resonant frequency (like the pasta) so the sound is loud. For a low (bass) frequency, was your straw longer or shorter? Cup Instrument see video This is a teacher demonstration. Have one student come up to the front of the room and help you play the cup instrument. Tie the string to a table leg (don t try to just hold it) and pull the cup very tight. Then have a student pluck the string. What happens? Now try plucking the string when it s shorter. Try several lengths (always using the up to amplify) How does the sound change? Try plucking the string without using the cup (hold the string right before the cup so the vibrations cannot travel into the cup). There is an entire activity Musical Instruments Part II that allows students to build and investigate their own cup instrument. Review Review what the class has learned and put ideas together while using the anatomy of the ear poster and hair cell posters. Explanation In-depth background information for teachers and interested students We used Science of Sound, 3 rd Ed. by Rossing, Moore and Wheeler as a reference. Sound is used to describe two different things: 1. An auditory sensation in the ear; 2. The disturbance in a medium that can cause this sensation.
10 By making this distinction, the age-old question If a tree falls in a forest and no one is there to hear it, does it make a sound? can be answered. Key Points Sound waves consist of very small but rapid variations in air pressure. (If traveling in air). Here we focus on Vibrations make sound. It is also true that changing airflow (sirens, speech & singing) and changing heat sources (lightning/thunder) make sound and are technically not vibrations. This is a more advanced idea however and might be best to present after a solid more thorough understanding of sound and energy are acquired by students. Presenting it in the beginning could confuse students and these details are not included in most elementary standards. Sound carries energy. It can make things move. Build a Model Loud sounds carry more energy than soft sounds. Listening to loud sounds for too long can damage the hair cells, and these can t be fixed. High pitch is a high sound and low pitches are low (bass) sounds. Pitch is how we hear frequency Sound Travels Sound carries energy- it travels through air. Air is not the sound. Air moves back and forth as sound energy goes past. Straw Instrument When the combination of the two straws is as long as possible, you can get the lowest sounds. Low pitch has a lower rate of vibration lower frequency or less wiggles per second. However frequency and pitch are different things. Pitch is what your ear senses and frequency is the vibrations per second and is something that can be measured with an instrument. Note: A straw instrument is a reed instrument with the ends of the straw forming a double reed. Trombones are brass instruments where sound is created by blowing into a mouthpiece. The slide on the straw instrument adjusts pitch similar to the slide on a trombone by creating a longer cavity for the air to flow. Key Terms: Pinna The visible part of the outer ear also called the auricle- if you can wiggle your ears, the pinna is what you wiggle Ossicles Three bones found in the ears of all mammals. These bones are the smallest bones in a person s body and they act like a system of levers. o Malleus Also called the hammer. The bone of the middle ear that is attached to the eardrum and the incus (anvil). o Incus Also called the anvil. The bone of the middle ear that is attached to the malleus (hammer) and the stapes (stirrup). o Stapes The tiny stirrup-shaped bone of the middle ear that is connected to a window (oval window) in the cochlea. Cochlea The snail-shaped part of the inner ear which contains the organ of Corti also known as the organ of hearing. Hair cell signal the auditory nerve Vibrations a shaking back and forth movement
11 Pitch How low or high a tone sounds to a person it is how a person perceives the frequency of a sound. High frequency sound has a high pitch or tone (treble notes), but low frequency has a low/deep pitch or tone (bass notes). High sounds are usually above 2000 Hertz and low below 200 Hertz. Sympathetic vibration When a vibrating object causes another object to vibrate at the same frequency, which may or may not be a resonance frequency. For example, if you place the handle of a vibrating tuning fork onto a table it becomes a soundboard and will vibrate at the same frequency. The table top moves more air than the tuning fork so the sound is louder. A piano string causes the soundboard of a piano to vibrate at the same frequency as the string. Frequency (rate) wiggles per second (moves back and forth) Natural frequency the frequency at which an object likes to vibrate. Resonance When one object is vibrating and it is put in contact with another object, if the frequency of the first object is at the natural frequency for the second object, the second object will start vibrating vigorously at its natural frequency. (pasta demo is an nice clean example of resonance) Sympathetic Vibration Some of the energy from the tuning fork is transferred to the table and makes the tabletop vibrate. The tabletop moves a lot more air than the tuning fork does. Air moving is sound so this makes a louder sound. Notice that the tabletop vibrates for a shorter time than the fork alone. Energy is conserved: the tuning fork dissipates less energy (quieter sound) for a longer time. The table dissipates more energy (louder sound) for a shorter time. Sound travels in waves that spread onward from the source to our ears. All things are made up of molecules. The molecules in solids like metal or wood are tightly packed together and they can carry sound waves more efficiently than the spread-out molecules in air. Solids are good transmitters of sound. Sound travels through steel 15 times faster than through air. Water s good too, carrying sound four times faster than air. Ping Pong Balls Students should note that nothing happens when a quiet fork is touched to a ball. The ball should bounce vigorously away from the vibrating tuning fork. The ball is very light and the fork is vibrating with a fair amount of energy, so it makes the ball move a lot by transferring some of its vibrational energy to the ball when touched. How We Hear The outside of the ear is called the pinna. It collects the sound and funnels that sound into the ear. Sound waves travel through the air, reach the pinna, and are funneled down to the eardrum.
12 Sound waves hit the eardrum and cause it to vibrate. The three tiny bones are the ossicles: the Malleus, the Incus, and the Stapes (stape-ees). That s Latin for hammer, anvil, and stirrup. The bones are named for their shapes. The vibrations continue through the tree tiny bones in your middle ear (the ossicles) The green part is the cell body. The yellow part is made up of hair bundles. How We Hear Low pitch has a lower rate of vibration- less wiggles per second. Resonance With the Pasta Demo: Longer pasta shakes at lower frequencies o Lower frequencies have longer wavelengths Remember: Low pitch is a low sound and low pitch has less wiggles per second Frequency is wiggles per second that air shakes. Pitch is how we hear frequency. Review Review what the class has learned and put ideas together. Different parts of the cochlea have different resonant frequencies so are sensitive to different pitches. The hairs in the front of the cochlea sense higher sounds and the hairs towards the back are sensitive to lower sounds. This is partly due to the tension of the basilar membrane in different parts of the cochlea. The hair cells in the front typically get damaged first since they are closer to the sound. This means when you have hearing damage the sound is messed up, not just quieter. Sound is caused by vibrations Sound carries energy The vibrations travel through the ear canal, eardrum, ossicles (the three tiny bones) and then into the cochlea. Different parts of the cochlea resonate with certain frequencies o Some like high pitches o Some like low pitches The hair cells sense the sound and send electrical signals to your brain. Optional Extensions /Modifications Modifications: It s important to tell students with modifications what they should be looking for ahead of time so they are more willing to stay engaged with the activity and understand what they re getting out of the experience. Hard of hearing students can feel vibrations through speakers by touching them, or by touching the instrument itself. With the straw instrument, they can feel the vibrations ont their lips and their tongue.
13 Extensions: There is an activity called How musical Instruments Work that helps students sort out the difference between resonance and sympathetic vibration and their respective roles in musical instruments. This activity is recommended as a follow on the Musical Instruments I and II. There is a game on the Dangerous Decibels virtual lab that lets you hear what different sounds will sound like if you have hearing damage. What is Sound Extension: Look at other objects that make sounds with highly visible vibrations. Musical instruments: triangles, tambourine, guitar, drum, cymbal Household items: wind-up clock with an alarm, kitchen timer, hand bell, wind chimes Sympathetic Vibration Extension: Students can place a vibrating fork on other surfaces A chair, the floor, the teacher s desk, a recess ball, a lunch box, etc. Ask if they detected any patterns in what made the fork s sound louder? Softer? If necessary, guide their theorizing by pointing out that some things- like a rubber recess ballhave spaces filled largely with air, while others- the table- are packed quite solid. Can the vibrations move more easily through air or a solid? Sound Travels Extension: If you have a computer in the room, show the PhET Sound simulation. Choose the last tab- Listen with Varying Pressure. What happens to the sound when the air is removed from the box? Cup Instrument Extension: The activity called Musical Instruments Part II is an entire lesson that utilizes the cup instrument and investigates other stringed instruments.
14 Sound and Music Name: 1. After striking the fork, what do you observe? 2. What do you feel when the fork is making a sound? 3. How can you make the sound stop? 4. What is making the sound? 5. What happens when you set the handle on a table top? 6. What happens if you touch a vibrating tuning fork to a ping pong ball? Why? 7. Do you know what the outside of the ear is called? 8. When looking at the diagram of the ear, what is the pink part at the end of the ear canal? 9. What are the three tiny little bones? 10. What is the snail shaped part of the ear called? 11. Look at the picture of the green and yellow object. What does it look like to you? (be creative) What is it really?
15 12. Write down any models you ve made at school or at home. 13. What would your arm represent in our model of the ear? 14. Do you think when you mow the lawn that your lawnmower is loud enough to damage y our ears? Does it matter how long you mow your lawn? 15. How about fireworks when you sit in the best seats are they loud enough to damage your ears? 16. Can you fix your hair bundles after modeling the sound of close fireworks? 17. What is the highest frequency you can hear? 18. When your fingers are on your throat, how do high and low aaaaahs feel different? 19. What is vibrating when you play your straw instrument? 20. How does the sound get from your straw instrument to the person across the room?
16 21. When the whole class does the wave, how did you move? Did you go with the wave? 22. How does sound travel across the room? 23. How do you make the lowest possible pitch with your straw instrument when you have two straws? 24. Is the vibration of the straw tip different with low and high sounds? If so, how is it different? 25. Why do you think the long pasta wiggled the most when the hand is shaken slowly but the other sticks only wiggled a little bit? 26. What do you think will happen if the string on the cup instrument is shorter? 27. What do you remember about how the ear works from today? Write a description of how sound travels from the Pinna to your brain.
www.ptg.org Visit the Piano Learning Center of the Piano Technicians Guild at www.ptg.org for more fun ways to learn about the piano.
 Piano Science Connect Music and Science Age: Elementary, Middle School The piano is one of the most interesting musical instruments you can learn to play. www.ptg.org It is also one of the most versatile
Piano Science Connect Music and Science Age: Elementary, Middle School The piano is one of the most interesting musical instruments you can learn to play. www.ptg.org It is also one of the most versatile
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
What Is Sound? 20 minutes. Materials For the teacher. 1 pr. *cymbals, large 1 pr. cymbals, small 1 xylophone *Not provided in kit
 Share with Your Students Vocabulary pitch STUDENT RESOURCE 1.1 INFORMATION SHEET how high or low a sound is What Is Sound? 1. Make copies of Student Resource 1.1, Vocabulary, and cut it up to make flashcards.
Share with Your Students Vocabulary pitch STUDENT RESOURCE 1.1 INFORMATION SHEET how high or low a sound is What Is Sound? 1. Make copies of Student Resource 1.1, Vocabulary, and cut it up to make flashcards.
Engineering with Sound Lesson Plan
 Type of lesson: Challenge Teaching Plan: Engineering with Sound Lesson Plan Goal The goal of this lesson is to introduce the students to sound and its properties and have them apply what they learn to
Type of lesson: Challenge Teaching Plan: Engineering with Sound Lesson Plan Goal The goal of this lesson is to introduce the students to sound and its properties and have them apply what they learn to
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED
 Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who has a hearing loss? How does hearing work?
 This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.)
 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.) Sound Waves Test -- each multiple choice question is worth 3 points. 1. Sound waves are
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.) Sound Waves Test -- each multiple choice question is worth 3 points. 1. Sound waves are
Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound
 Science Benchmark: 06:06 Heat, light, and sound are all forms of energy. Heat can be transferred by radiation, conduction and convection. Visible light can be produced, reflected, refracted, and separated
Science Benchmark: 06:06 Heat, light, and sound are all forms of energy. Heat can be transferred by radiation, conduction and convection. Visible light can be produced, reflected, refracted, and separated
Chapter 21 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 21 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a fire engine is traveling toward you, the Doppler
Chapter 21 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a fire engine is traveling toward you, the Doppler
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology
 Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
Presbycusis. What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis?
 Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Noise and Hearing Protection
 Noise and Hearing Protection Noise and Hearing Safety Training This training module is designed to teach you about the purpose and benefits of a hearing conservation program. After completing the training,
Noise and Hearing Protection Noise and Hearing Safety Training This training module is designed to teach you about the purpose and benefits of a hearing conservation program. After completing the training,
family games Taking the kids swimming is a great way of making sure they re moving around and having fun. And to help you get them into
 swim family games Taking the kids swimming is a great way of making sure they re moving around and having fun. And to help you get them into the pool, we ve come up with loads of great swimming games to
swim family games Taking the kids swimming is a great way of making sure they re moving around and having fun. And to help you get them into the pool, we ve come up with loads of great swimming games to
The Physics of Music: Brass Instruments. James Bernhard
 The Physics of Music: Brass Instruments James Bernhard As a first approximation, brass instruments can be modeled as closed cylindrical pipes, where closed means closed at one end, open at the other Here
The Physics of Music: Brass Instruments James Bernhard As a first approximation, brass instruments can be modeled as closed cylindrical pipes, where closed means closed at one end, open at the other Here
v = λ f this is the Golden Rule for waves transverse & longitudinal waves Harmonic waves The golden rule for waves Example: wave on a string Review
 L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3] resonance clocks pendulum springs harmonic motion mechanical waves sound waves golden rule for waves musical instruments The Doppler effect Doppler radar radar guns Review
L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3] resonance clocks pendulum springs harmonic motion mechanical waves sound waves golden rule for waves musical instruments The Doppler effect Doppler radar radar guns Review
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
THE CHOIR: SING WHILE YOU WORK. THE BASICS OF SINGING bbc.co.uk/thechoir
 THE BASICS OF ING THE BASICS OF ING Gareth Malone Welcome to The Choir: Sing While You Work guide to singing. If you re reading this, congratulations, as you have either already taken that first step and
THE BASICS OF ING THE BASICS OF ING Gareth Malone Welcome to The Choir: Sing While You Work guide to singing. If you re reading this, congratulations, as you have either already taken that first step and
Tonal Analysis of Different Materials for Trumpet Mouthpieces
 Greg Formosa PHYS 199 POM Project Write-up Tonal Analysis of Different Materials for Trumpet Mouthpieces INTRODUCTION: Trumpets have been noted as one of the oldest instruments in the world, and ever since
Greg Formosa PHYS 199 POM Project Write-up Tonal Analysis of Different Materials for Trumpet Mouthpieces INTRODUCTION: Trumpets have been noted as one of the oldest instruments in the world, and ever since
Look, listen and note how well children: Preparation. Resources. Plan this into your singing time activities.
 Tuning into Sounds Plan this into your singing time activities. Music tape / DVD with a clear beat to respond to Articulate their tongues and mouths Activity 1: Mouth movements Explore different mouth
Tuning into Sounds Plan this into your singing time activities. Music tape / DVD with a clear beat to respond to Articulate their tongues and mouths Activity 1: Mouth movements Explore different mouth
Fry Phrases Set 1. TeacherHelpForParents.com help for all areas of your child s education
 Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
Intonation Tendencies of Band Instruments. Whitney Brainard MUS 461 Winter 2011
 + Intonation Tendencies of Band Instruments Whitney Brainard MUS 461 Winter 2011 + Daily tuning In band, make sure you warm up BEFORE tuning. If you are waiting to perform (ex. Festival), have students
+ Intonation Tendencies of Band Instruments Whitney Brainard MUS 461 Winter 2011 + Daily tuning In band, make sure you warm up BEFORE tuning. If you are waiting to perform (ex. Festival), have students
The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software
 Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Grade 2 Lesson 3: Refusing Bullying. Getting Started
 Getting Started Lesson Concepts You can refuse to let bullying happen to you or to others. Being assertive is one way to refuse bullying. Key Words Refuse, assertive Objectives Students will be able to:
Getting Started Lesson Concepts You can refuse to let bullying happen to you or to others. Being assertive is one way to refuse bullying. Key Words Refuse, assertive Objectives Students will be able to:
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking
 The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
Recover. Be Disaster Safe K-2. Disaster Cycle LESSON PLAN 4. Key Terms and Concepts. Purpose. Objectives. Activities
 Be Disaster K-2 Disaster Cycle The concept of recovery shows children that there is hope and a future after a disaster, even though it might require hard work and time. Key Terms and Concepts cleanup debris
Be Disaster K-2 Disaster Cycle The concept of recovery shows children that there is hope and a future after a disaster, even though it might require hard work and time. Key Terms and Concepts cleanup debris
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
Do you have a. of what you want to be when you grow up? Do you look at your teacher and think you might want to have that job
 DREAM BIG Do you look at your teacher and think you might want to have that job when you are bigger, or have you passed the fire station and thought about helping others as a firefighter? What about a
DREAM BIG Do you look at your teacher and think you might want to have that job when you are bigger, or have you passed the fire station and thought about helping others as a firefighter? What about a
Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control
 EVERYONE'S RESPONSIBILITY Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control February 2007 Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Workplace Safety & Health Division 200 401 York Avenue
EVERYONE'S RESPONSIBILITY Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control February 2007 Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Workplace Safety & Health Division 200 401 York Avenue
SOUND IDEAS. Peggy Downs, Peak to Peak Charter School, Lafayette, CO
 SOUND IDEAS Grade Level: Written by: Length of Unit: Third Grade Peggy Downs, Peak to Peak Charter School, Lafayette, CO Seven lessons (50 minutes each) I. ABSTRACT This science unit will give students
SOUND IDEAS Grade Level: Written by: Length of Unit: Third Grade Peggy Downs, Peak to Peak Charter School, Lafayette, CO Seven lessons (50 minutes each) I. ABSTRACT This science unit will give students
PUSD High Frequency Word List
 PUSD High Frequency Word List For Reading and Spelling Grades K-5 High Frequency or instant words are important because: 1. You can t read a sentence or a paragraph without knowing at least the most common.
PUSD High Frequency Word List For Reading and Spelling Grades K-5 High Frequency or instant words are important because: 1. You can t read a sentence or a paragraph without knowing at least the most common.
Plant In a Cup. When considering what to do for our curriculum project, our main goal was
 Sammi Meril and Grace Slone Final Paper Kindergarten Education 200 May/6/2013 Plant In a Cup When considering what to do for our curriculum project, our main goal was to create stimulating lesson that
Sammi Meril and Grace Slone Final Paper Kindergarten Education 200 May/6/2013 Plant In a Cup When considering what to do for our curriculum project, our main goal was to create stimulating lesson that
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
God Sends the Holy Spirit (Pentecost)
 God Sends the Holy Spirit (Pentecost) Teacher Pep Talk: It had been 10 days since Jesus ascended into Heaven. He had promised to send the Holy Spirit to be with His disciples forever. On Pentecost, when
God Sends the Holy Spirit (Pentecost) Teacher Pep Talk: It had been 10 days since Jesus ascended into Heaven. He had promised to send the Holy Spirit to be with His disciples forever. On Pentecost, when
Sound and stringed instruments
 Sound and stringed instruments Lecture 14: Sound and strings Reminders/Updates: HW 6 due Monday, 10pm. Exam 2, a week today! 1 Sound so far: Sound is a pressure or density fluctuation carried (usually)
Sound and stringed instruments Lecture 14: Sound and strings Reminders/Updates: HW 6 due Monday, 10pm. Exam 2, a week today! 1 Sound so far: Sound is a pressure or density fluctuation carried (usually)
Project Teamwork. Theme: Cooperative games encourage students to work together as a team while having fun in a positive environment.
 Project Teamwork August 2007 Theme: Cooperative games encourage students to work together as a team while having fun in a positive environment. Concepts: 1. Any collection of people has the potential to
Project Teamwork August 2007 Theme: Cooperative games encourage students to work together as a team while having fun in a positive environment. Concepts: 1. Any collection of people has the potential to
The Physics of Music - Physics 15 University of California, Irvine. Instructor: David Kirkby dkirkby@uci.edu. Lecture 14.
 Miscellaneous Office hours this week are Wed 9-10am, 3-4pm. Lecture 14 Percussion Instruments Keyboard Instruments Office hours next week are Wed 2-4pm. There is a typo in 2(b) of Problem Set #6. The length
Miscellaneous Office hours this week are Wed 9-10am, 3-4pm. Lecture 14 Percussion Instruments Keyboard Instruments Office hours next week are Wed 2-4pm. There is a typo in 2(b) of Problem Set #6. The length
Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
 Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Sound Perception. Sensitivity to Sound. Sensitivity to Sound 1/9/11. Not physically sensitive to all possible sound frequencies Range
 Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
Setting Up Synthetic Drone Reeds The Kinnaird Way By Rob Kinnaird
 www.kinnairdbagpipes.com 923 Emmeline Terrace Saskatoon, SK. Canada S7J 5G7 Phone: 306-249-2939 Fax: 306-249-2933 sales@kinnairdbagpipes.com Setting Up Synthetic Drone Reeds The Kinnaird Way By Rob Kinnaird
www.kinnairdbagpipes.com 923 Emmeline Terrace Saskatoon, SK. Canada S7J 5G7 Phone: 306-249-2939 Fax: 306-249-2933 sales@kinnairdbagpipes.com Setting Up Synthetic Drone Reeds The Kinnaird Way By Rob Kinnaird
Subject: Math Grade Level: 5 Topic: The Metric System Time Allotment: 45 minutes Teaching Date: Day 1
 Subject: Math Grade Level: 5 Topic: The Metric System Time Allotment: 45 minutes Teaching Date: Day 1 I. (A) Goal(s): For student to gain conceptual understanding of the metric system and how to convert
Subject: Math Grade Level: 5 Topic: The Metric System Time Allotment: 45 minutes Teaching Date: Day 1 I. (A) Goal(s): For student to gain conceptual understanding of the metric system and how to convert
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video. IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
 Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Physics 1230: Light and Color
 Physics 1230: Light and Color Instructor: Joseph Maclennan TOPIC 3 - Resonance and the Generation of Light http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phys1230 How do we generate light? How do we detect light? Concept
Physics 1230: Light and Color Instructor: Joseph Maclennan TOPIC 3 - Resonance and the Generation of Light http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phys1230 How do we generate light? How do we detect light? Concept
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
Pushes and Pulls. TCAPS Created June 2010 by J. McCain
 Pushes and Pulls K i n d e r g a r t e n S c i e n c e TCAPS Created June 2010 by J. McCain Table of Contents Science GLCEs incorporated in this Unit............... 2-3 Materials List.......................................
Pushes and Pulls K i n d e r g a r t e n S c i e n c e TCAPS Created June 2010 by J. McCain Table of Contents Science GLCEs incorporated in this Unit............... 2-3 Materials List.......................................
How This CD Was Produced
 How This CD Was Produced This CD was recorded using simple instrumentation and easy to follow music. Each tune has a short introduction followed by the verses and choruses. Some songs have a voice count
How This CD Was Produced This CD was recorded using simple instrumentation and easy to follow music. Each tune has a short introduction followed by the verses and choruses. Some songs have a voice count
STRING TELEPHONES. Education Development Center, Inc. DESIGN IT! ENGINEERING IN AFTER SCHOOL PROGRAMS. KELVIN Stock #651817
 STRING TELEPHONES KELVIN Stock #6587 DESIGN IT! ENGINEERING IN AFTER SCHOOL PROGRAMS Education Development Center, Inc. DESIGN IT! Engineering in After School Programs Table of Contents Overview...3...
STRING TELEPHONES KELVIN Stock #6587 DESIGN IT! ENGINEERING IN AFTER SCHOOL PROGRAMS Education Development Center, Inc. DESIGN IT! Engineering in After School Programs Table of Contents Overview...3...
Advanced Techniques for the Walkingbass
 Advanced Techniques for the Walkingbass I have seen guys with 5 string basses who can t get half the sounds that you are getting out of just three. -Buddy Fo of the Invitations If you have read the Beginners
Advanced Techniques for the Walkingbass I have seen guys with 5 string basses who can t get half the sounds that you are getting out of just three. -Buddy Fo of the Invitations If you have read the Beginners
Check Your Hearing - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mmu6npeidoy
 The Science of Hearing The human hearing range is between 20 to 20,000 Hz. There is considerable variation in the hearing range between individuals. Most young people can hear up to 18,000 Hz. Our ability
The Science of Hearing The human hearing range is between 20 to 20,000 Hz. There is considerable variation in the hearing range between individuals. Most young people can hear up to 18,000 Hz. Our ability
All Saints (or All Hallows) Celebration
 All Saints (or All Hallows) Celebration Bible base: Mark 10:46 52 Aim: To present an alternative focus to the Hallowe en events that dominate this time of year. Note to leaders Our focus this week will
All Saints (or All Hallows) Celebration Bible base: Mark 10:46 52 Aim: To present an alternative focus to the Hallowe en events that dominate this time of year. Note to leaders Our focus this week will
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) Grade Level Sound and Music EE Outreach @ Berkeley K 5 with CA standards connection at 2 nd and NGSS 1 st and 4 th Standards Connection(s):
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) Grade Level Sound and Music EE Outreach @ Berkeley K 5 with CA standards connection at 2 nd and NGSS 1 st and 4 th Standards Connection(s):
California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3
 California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3 Words were selected using the following established frequency lists: (1) Dolch 220 (2) Fry 100 (3) American Heritage Top 150 Words in English
California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3 Words were selected using the following established frequency lists: (1) Dolch 220 (2) Fry 100 (3) American Heritage Top 150 Words in English
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Lesson 5: School Bus Safety
 Time: approximately 40 minutes Lesson 5: School Bus Safety LESSON PLAN: Lesson 5 This curriculum does not cover every possible scenario that a child may encounter as a pedestrian, but instead addresses
Time: approximately 40 minutes Lesson 5: School Bus Safety LESSON PLAN: Lesson 5 This curriculum does not cover every possible scenario that a child may encounter as a pedestrian, but instead addresses
AUDITION WEEK. Domain and goal. Activities. Shows awareness of sound when directed by parent Environmental sounds Voice
 AUDITION WEEK 1 Shows awareness of sound when directed by parent Environmental sounds Voice The first step in bringing your child to spoken language through audition is to teach him that there is sound.
AUDITION WEEK 1 Shows awareness of sound when directed by parent Environmental sounds Voice The first step in bringing your child to spoken language through audition is to teach him that there is sound.
Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology
 Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology Sophisticated modern hearing aids use a number of complicated technologies and techniques to ensure great improvements in hearing. Not only are the terms used
Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology Sophisticated modern hearing aids use a number of complicated technologies and techniques to ensure great improvements in hearing. Not only are the terms used
Step 1: Come Together
 THE STORY FOR LITTLE ONES: Preschool LESSON GUIDE: Lesson 2 5 ABRAHAM FOLLOWS GOD Bible Basis: Genesis 12:1 9, 17; 21:1 7 Bible Verse: Abram believed the Lord. The Lord accepted Abram because he believed.
THE STORY FOR LITTLE ONES: Preschool LESSON GUIDE: Lesson 2 5 ABRAHAM FOLLOWS GOD Bible Basis: Genesis 12:1 9, 17; 21:1 7 Bible Verse: Abram believed the Lord. The Lord accepted Abram because he believed.
A Note to Parents. 1. As you study the list, vary the order of the words.
 A Note to Parents This Wordbook contains all the sight words we will be studying throughout the year plus some additional enrichment words. Your child should spend some time each week studying this Wordbook
A Note to Parents This Wordbook contains all the sight words we will be studying throughout the year plus some additional enrichment words. Your child should spend some time each week studying this Wordbook
Henry the Hand School Skit
 Henry the Hand School Skit (We encourage the Facilitator to use an assembly program, preferably with multiple grade levels present. Kindergarten through 3 rd grades are most receptive and also very effective
Henry the Hand School Skit (We encourage the Facilitator to use an assembly program, preferably with multiple grade levels present. Kindergarten through 3 rd grades are most receptive and also very effective
2016 Fall Product Program Rally Overview
 2016 Fall Product Program Rally Overview Once again, Ashdon Farms and QSP are excited to offer Councils, service units and troops the opportunity to host Fall Product Program (FPP) Rallies. As with other
2016 Fall Product Program Rally Overview Once again, Ashdon Farms and QSP are excited to offer Councils, service units and troops the opportunity to host Fall Product Program (FPP) Rallies. As with other
Science through LEGO Engineering Design a Musical Instrument: The Science of Sound. Curriculum Resources 2008-2009 Edition
 Science through LEGO Engineering Design a Musical Instrument: The Science of Sound Curriculum Resources 2008-2009 Edition Contributors: G. Michael Barnett, Ph. D., Boston College Kathleen Connolly, Tufts
Science through LEGO Engineering Design a Musical Instrument: The Science of Sound Curriculum Resources 2008-2009 Edition Contributors: G. Michael Barnett, Ph. D., Boston College Kathleen Connolly, Tufts
YEAR 1: The Human Body and Senses
 YEAR 1: The Human Body and Senses Contents Include: What our bodies can do Eyes and Sight Ears and Hearing Touch, Taste and Smell Understanding Sensory Impairment Please Note: The activities included in
YEAR 1: The Human Body and Senses Contents Include: What our bodies can do Eyes and Sight Ears and Hearing Touch, Taste and Smell Understanding Sensory Impairment Please Note: The activities included in
Lesson Plans: Stage 3 - Module One
 Lesson Plans: Stage 3 - Module One TM Music Completes the Child 1 Stage Three Module One Contents Week One Music Time Song 2 Concept Development Focus: Tempo 4 Song Clap Your Hands 5 George the Giant Pitch
Lesson Plans: Stage 3 - Module One TM Music Completes the Child 1 Stage Three Module One Contents Week One Music Time Song 2 Concept Development Focus: Tempo 4 Song Clap Your Hands 5 George the Giant Pitch
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06)
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
STEADYfast Stabilizer Installation Notes Fifth Wheel and Travel Trailers 11/23/13
 STEADYfast Stabilizer Installation Notes Fifth Wheel and Travel Trailers 11/23/13 (See Supplemental Instructions for trailers with heavy duty round footplates and/or Power Leveling Systems) PHONE SUPPORT
STEADYfast Stabilizer Installation Notes Fifth Wheel and Travel Trailers 11/23/13 (See Supplemental Instructions for trailers with heavy duty round footplates and/or Power Leveling Systems) PHONE SUPPORT
Yerkes Summer Institute 2002
 Before we begin our investigations into radio waves you should review the following material on your trip up to Yerkes. For some of you this will be a refresher, but others may want to spend more time
Before we begin our investigations into radio waves you should review the following material on your trip up to Yerkes. For some of you this will be a refresher, but others may want to spend more time
Junior Soldiers. Unit 4 : Lesson 8
 Junior Soldiers Unit 4 : Lesson 8 One body: many parts! PURPOSE : For children to explore and understand that even though those who follow Jesus are all different in some way, God loves each of us and
Junior Soldiers Unit 4 : Lesson 8 One body: many parts! PURPOSE : For children to explore and understand that even though those who follow Jesus are all different in some way, God loves each of us and
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Heat Energy FORMS OF ENERGY LESSON PLAN 2.7. Public School System Teaching Standards Covered
 FORMS OF ENERGY LESSON PLAN 2.7 Heat Energy This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools) in the seven states served
FORMS OF ENERGY LESSON PLAN 2.7 Heat Energy This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools) in the seven states served
Summary Our science project is an investigation into the varying levels of damage that different types of earphones and mp3 players cause to hearing.
 Meet The Team Ella Lyons is our team leader. Whilst we were doing our experiment Ella was the main operator of the data logging device. Ella took charge in any part of our experiment which involved computers
Meet The Team Ella Lyons is our team leader. Whilst we were doing our experiment Ella was the main operator of the data logging device. Ella took charge in any part of our experiment which involved computers
Sound and music. Key concepts of sound and music
 Sound and music Introduction Why do we see lightning before we hear the thunder? How do we amplify sound and how do we reduce it? How is it we can hear at all? Sound is all around us every day and it is
Sound and music Introduction Why do we see lightning before we hear the thunder? How do we amplify sound and how do we reduce it? How is it we can hear at all? Sound is all around us every day and it is
Handale Primary School Music Curriculum Year EYFS ( 4-5 year olds)
 Handale Primary School Music Curriculum Year EYFS ( 4-5 year olds) Music at EYFS stage reflects the different ways in which children learn and engage with other people. Many examples of stories, songs
Handale Primary School Music Curriculum Year EYFS ( 4-5 year olds) Music at EYFS stage reflects the different ways in which children learn and engage with other people. Many examples of stories, songs
Coaching Tips Tee Ball
 Coaching Tips Tee Ball Tee Ball Overview The great thing about tee ball is that there are very few rules to learn and that the game is all about involving lots of kids. It s about making sure all players
Coaching Tips Tee Ball Tee Ball Overview The great thing about tee ball is that there are very few rules to learn and that the game is all about involving lots of kids. It s about making sure all players
YMCA Soccer Warm Up Activities for 6 7 Year Olds
 YMCA Soccer Warm Up Activities for 6 7 Year Olds Warm Up Description Page 1 Begin each practice with 5 to 10 minutes of warm up activities to get players loosened up and ready to go. 1. Players kick or
YMCA Soccer Warm Up Activities for 6 7 Year Olds Warm Up Description Page 1 Begin each practice with 5 to 10 minutes of warm up activities to get players loosened up and ready to go. 1. Players kick or
Classroom Behavior Management Plan
 Haffner 1 Classroom Behavior Management Plan Daniel Haffner November 20, 2009 EDUC 348 Haffner 2 Philosophy of Classroom Management Classroom management is a course taught at every teacher college across
Haffner 1 Classroom Behavior Management Plan Daniel Haffner November 20, 2009 EDUC 348 Haffner 2 Philosophy of Classroom Management Classroom management is a course taught at every teacher college across
Georgia Department of Education Grade 3 Career Development Activity Energy Systems Estimated Time: 45 minutes
 Goal Students will identify Energy as Georgia career cluster Objective define a career cluster as a grouping of occupations with common skills and knowledge identify sample occupations aligned with the
Goal Students will identify Energy as Georgia career cluster Objective define a career cluster as a grouping of occupations with common skills and knowledge identify sample occupations aligned with the
Kino, Juana and Coyotito
 1 Kino, Juana and Coyotito K ino woke up early in the morning. The stars were still shining in the sky. The cockerels were beginning to crow 1 and the pigs were looking for something to eat. Outside the
1 Kino, Juana and Coyotito K ino woke up early in the morning. The stars were still shining in the sky. The cockerels were beginning to crow 1 and the pigs were looking for something to eat. Outside the
Roanoke Pinball Museum Key Concepts
 Roanoke Pinball Museum Key Concepts What are Pinball Machines Made of? SOL 3.3 Many different materials are used to make a pinball machine: 1. Steel: The pinball is made of steel, so it has a lot of mass.
Roanoke Pinball Museum Key Concepts What are Pinball Machines Made of? SOL 3.3 Many different materials are used to make a pinball machine: 1. Steel: The pinball is made of steel, so it has a lot of mass.
Unit Five Organizer: Sound First Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Suitable for: Beginners with absolutely no previous experience. Beginners who appear particularly shy or nervous.
 Lesson plan 1: CHORD STRUMMING FOR THE BEGINNER Suitable for: Beginners with absolutely no previous experience. Beginners who appear particularly shy or nervous. Prerequisites: None General Objective:
Lesson plan 1: CHORD STRUMMING FOR THE BEGINNER Suitable for: Beginners with absolutely no previous experience. Beginners who appear particularly shy or nervous. Prerequisites: None General Objective:
Outline Of Classroom Management Plan (Management plan is designed for an elementary school placement. Refer to classroom map when needed.
 Outline Of Classroom Management Plan (Management plan is designed for an elementary school placement. Refer to classroom map when needed.) I. Room Preparation A. Bulletin Boards and Walls There will be
Outline Of Classroom Management Plan (Management plan is designed for an elementary school placement. Refer to classroom map when needed.) I. Room Preparation A. Bulletin Boards and Walls There will be
The Fruit of the Spirit is Love
 The Fruit of the Spirit is Love Pre-Session Warm Up (Galatians 5:22-23) Today we are going to learn more about the fruit of the Spirit called, Love. What do you think of when you hear the word love? A
The Fruit of the Spirit is Love Pre-Session Warm Up (Galatians 5:22-23) Today we are going to learn more about the fruit of the Spirit called, Love. What do you think of when you hear the word love? A
DIGITAL MUSIC DAY 1 WHAT IS SOUND? ANALOG AND DIGITAL EARLY RECORDING WAX FOR YOUR EARS ROUND BUT FLAT WIRE AND TAPE PURE SOUND
 DIGITAL MUSIC DAY 1 WHAT IS SOUND? 1. Making a sound playing a musical instrument, moves the surrounding the instrument. 2. Making a sound sends out air which hit your ears. 3. Waves of changing air pressure
DIGITAL MUSIC DAY 1 WHAT IS SOUND? 1. Making a sound playing a musical instrument, moves the surrounding the instrument. 2. Making a sound sends out air which hit your ears. 3. Waves of changing air pressure
Waves: Recording Sound Waves and Sound Wave Interference (Teacher s Guide)
 Waves: Recording Sound Waves and Sound Wave Interference (Teacher s Guide) OVERVIEW Students will measure a sound wave by placing the Ward s DataHub microphone near one tuning fork A440 (f=440hz). Then
Waves: Recording Sound Waves and Sound Wave Interference (Teacher s Guide) OVERVIEW Students will measure a sound wave by placing the Ward s DataHub microphone near one tuning fork A440 (f=440hz). Then
Grade 8 English Language Arts 90 Reading and Responding, Lesson 9
 GRADE 8 English Language Arts Reading and Responding: Lesson 9 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and
GRADE 8 English Language Arts Reading and Responding: Lesson 9 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and
AP1 Waves. (A) frequency (B) wavelength (C) speed (D) intensity. Answer: (A) and (D) frequency and intensity.
 1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
David s Heart: David Praises God
 Teacher s Guide: Ages 4-5 Kings & Kingdoms Part 2: Judges through Esther Unit 8, Lesson 41 David s Heart: David Praises God Lesson Aim: To explore ways to praise the Lord. THE WORSHIP Who God is: The King
Teacher s Guide: Ages 4-5 Kings & Kingdoms Part 2: Judges through Esther Unit 8, Lesson 41 David s Heart: David Praises God Lesson Aim: To explore ways to praise the Lord. THE WORSHIP Who God is: The King
Curriculum links. Learning objective. Introduction
 enses Curriculum links cience c2:1b Life processes, animals (including humans) use their senses to understand the world. nglish 1b peaking, to choose words with precision Learning objective To explore
enses Curriculum links cience c2:1b Life processes, animals (including humans) use their senses to understand the world. nglish 1b peaking, to choose words with precision Learning objective To explore
How to Use a Digital Audio Workstation First course, First grading period, Week 6
 How to Use a Digital Audio Workstation First course, First grading period, Week 6 Students need to learn the basic operation of the digital audio workstation. It is a knowledge and skill they will refine
How to Use a Digital Audio Workstation First course, First grading period, Week 6 Students need to learn the basic operation of the digital audio workstation. It is a knowledge and skill they will refine
Weather Under Pressure
 Primary Subject Integrated Subjects Grade Level Length of Unit Research Sources Science Math 5th 10 days Elementary Science with Vernier Book BrainPop www.areasonfor.com/site/1/docs/science_level_f_swt_lesson_20.pdf
Primary Subject Integrated Subjects Grade Level Length of Unit Research Sources Science Math 5th 10 days Elementary Science with Vernier Book BrainPop www.areasonfor.com/site/1/docs/science_level_f_swt_lesson_20.pdf
Beginner Guitar Level I
 Welcome to Beginner Guitar Level I E A D G B E * Please fill out the student form * Who is this guy? E A D G B E Logistics, etc.. sign in / out everyday start promptly -> don t be late! breaks / bathrooms
Welcome to Beginner Guitar Level I E A D G B E * Please fill out the student form * Who is this guy? E A D G B E Logistics, etc.. sign in / out everyday start promptly -> don t be late! breaks / bathrooms
Days. Day 1. Reflection Teacher Responsibilities. Lesson Plans
 Days Day 1 Lesson Plans Call the students to the carpet by the number of letters in their names. If your name has less than 5 letters, come to the carpet. If your name has more than 5 letters, come to
Days Day 1 Lesson Plans Call the students to the carpet by the number of letters in their names. If your name has less than 5 letters, come to the carpet. If your name has more than 5 letters, come to
Veterans UK Leaflet 10. Notes about War Pension claims for deafness
 Veterans UK Leaflet 10 Notes about War Pension claims for deafness 1 About this leaflet About this leaflet This leaflet tells you how claims for deafness are decided and gives you some information about
Veterans UK Leaflet 10 Notes about War Pension claims for deafness 1 About this leaflet About this leaflet This leaflet tells you how claims for deafness are decided and gives you some information about
Rubber Band Race Car
 Rubber Band Race Car Physical Science Unit Using LEGO Mindstorms NXT Copyright 2009 by Technically Learning 1 of 17 Overview: Through a series of hands-on activities, students will design a rubber band
Rubber Band Race Car Physical Science Unit Using LEGO Mindstorms NXT Copyright 2009 by Technically Learning 1 of 17 Overview: Through a series of hands-on activities, students will design a rubber band
Learn How to Revise 1
 Learn How to Revise 1 SCHOOL EXAM DATES 2016 END OF YEAR EXAMS FOR YEARS 7-9 BEGIN ON MONDAY 6 TH JUNE THEY WILL TAKE PLACE IN LESSONS DURING THIS WEEK AND IF NECESSARY THE WEEK AFTER. Some subjects are
Learn How to Revise 1 SCHOOL EXAM DATES 2016 END OF YEAR EXAMS FOR YEARS 7-9 BEGIN ON MONDAY 6 TH JUNE THEY WILL TAKE PLACE IN LESSONS DURING THIS WEEK AND IF NECESSARY THE WEEK AFTER. Some subjects are
Summary The students will learn how to make a basic musical instrument and how to modify it to get different loudness and pitches.
 Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Sound: 4.D.3B Rubber Band Banjo Grade Level 4 Sessions 50 minutes Seasonality N/A Instructional Mode(s) Whole class Team Size 2 WPS Benchmarks 04.SC.PS.01
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Sound: 4.D.3B Rubber Band Banjo Grade Level 4 Sessions 50 minutes Seasonality N/A Instructional Mode(s) Whole class Team Size 2 WPS Benchmarks 04.SC.PS.01
Short vowel a The Apple huge Short vowel o Cute Baby [Boston accent] standard dialect
![Short vowel a The Apple huge Short vowel o Cute Baby [Boston accent] standard dialect Short vowel a The Apple huge Short vowel o Cute Baby [Boston accent] standard dialect](/thumbs/40/21126341.jpg) Short vowel a The Apple The vowels are Super Stars, because if you didn t have vowels, you couldn t make any words. The vowels know this and make their sounds louder and longer than everyone! This is our
Short vowel a The Apple The vowels are Super Stars, because if you didn t have vowels, you couldn t make any words. The vowels know this and make their sounds louder and longer than everyone! This is our
Lesson Plan for Teaching: Give Respect
 Lesson Plan for Teaching: Give Respect 1. Concept (Expectation) E Give Respect 2. Definition and Critical Attributes To show concern and consideration for others and/or property, behaviors that help people
Lesson Plan for Teaching: Give Respect 1. Concept (Expectation) E Give Respect 2. Definition and Critical Attributes To show concern and consideration for others and/or property, behaviors that help people
