Physio Med Self Help for Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylalgia)
|
|
|
- Madison Lee
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physio Med Self Help for Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylalgia) Lateral epicondylalgia (previously known as epicondylitis) is commonly known as tennis elbow. This does not mean that only tennis players have this condition. But a backhand racket swing is a common cause of lateral epicondylalgia. Many other repetitive activities with an extended wrist can also lead to tennis elbow: painting with brush or roller, using a chain saw, and using many types of hand tools even typing with poor technique (overly extended wrists). Any activities that stress the same forearm muscles can cause symptoms of tennis elbow. Anatomy of the Area Tennis elbow causes pain that starts on the outside bump of the elbow, the lateral epicondyle. Wrist extensors are the muscles of the forearm that pull the hand backward. The wrist extensors are on the side of the forearm lined up with the back of the hand. Most of the wrist extensors attach to one main tendon on the lateral epicondyle. This tendon is called the common extensor tendon. Tendons connect muscle to bone. Tendons are made up of strands of a material called collagen. The collagen strands are lined up in bundles next to each other. Because the collagen strands in tendons are lined up, tendons have high tensile strength. This means they can withstand high forces that pull against both ends of the tendon. When muscles work, they pull on one end of the tendon. The other end of the tendon pulls on the bone, causing the bone to move.
2 The wrist flexor muscles contract when you flex your wrist (bend your wrist in the direction of your palm), twist your forearm down, or grip with your hand. The contracting muscles pull on the flexor tendon. The forces that pull on the tendon can build when you grip and swing a racket with your wrist pulled back into extension or do other similar actions. In some cases, the symptoms of tennis elbow are due to inflammation. In an acute injury, the body undergoes an inflammatory response. Special inflammatory cells make their way to the injured tissues to help them heal. However, tennis elbow often is not caused by inflammation. Rather, it is a problem within the cells of the tendon. Wear and tear is thought to lead to tissue degeneration. Instead of inflammatory cells, the body produces a type of cells called fibroblasts. When this happens, the collagen loses its strength. The affected area becomes fragile and be easily injured. Each time the collagen breaks down, the body responds by forming scar tissue in the tendon. Eventually, the tendon becomes thickened from extra scar tissue. Some doctors think that the forearm tendon develops small tears with too much activity. The tears try to heal, but constant strain and overuse keep re-injuring the tendon. After a while, the tendons stop trying to heal. The scar tissue never has a chance to fully heal, leaving the injured areas weakened and painful. Occasionally the pain may be associated with neck pain and pinched nerves in the neck which may, without you realising, it make the muscles weaker than normal. NERVES OF THE NECK AND ARM The brachial plexus which has 3 major trunks of nerves (the median, radial and ulnar nerves) originates from the neck. Each nerve comes out between a pair of neck vertebrae and they join together to form the trunks. The nerves then travel down the arm. A pinched nerve produces symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling and hot and cold feelings anywhere down the arm and hand depending on which nerve is affected. Common sites for the nerve to be pinched are up in the neck between the vertebra and also around the outside of the elbow.
3 The radial nerve can be particularly affected with tennis Elbow The nerve passes down the back of the upper arm. It then spirals outward and crosses the outside (the lateral part) of the elbow before it winds its way down the back of the forearm and hand. It supplies the extensor muscles of the wrist and fingers and is therefore the most likely nerve root to be involved in tennis elbow. Potential causes of tennis Elbow and Advice to prevent it Overuse of the muscles and tendons of the forearm and elbow are the most common reason people develop tennis elbow. Repeating some types of activities over and over again can put too much strain on the elbow tendons. These activities are not necessarily high-level sports competition. It can be associated with certain types of gripping (or holding an object) with an extended wrist such as painting, using tools and other work related activities such as typing with wrists extended upwards away from a straight line. In both tennis / squash and other activities it may be associated with playing the game after a long break or doing unaccustomed activity such as a lot of DIY and over gripping. It may be due to a racket being too heavy or poor action. ACTIVITY Where possible, try to avoid the repetitive activity If avoidance is not possible, break the repetitive task down into shorter sessions and intersperse them with tasks / activities that rest the forearm muscles (this is called pacing) Reduce the load i.e., use a lighter / shorter paint roller or racket or type with less force Position the task and the arm in the most advantageous position - where less effort is required from the forearm muscles and they are working in their mid-range (not fully bent or extended) Work on technique e.g. tennis stance and swing, when typing use a wrist rest to prevent your wrist resting on the desk while you extend your hand upwards to reach the keyboard Do not undertake multiple activities that load the forearm on the same day e.g. DIY, followed by a game of tennis / squash to relax After a significant break from your usual level of activity, graduate or phase your return over a sensible period of time Graduate or pace an unaccustomed activity OVER GRIPPING Where possible, try to avoid over gripping, ensure that you let go of your mouse / gearstick when not using them Try to ensure that you have the right tools for the job (they are correctly maintained) and they fit you Correct / alter grip during activity Correct grip size on a racket, mouse is not too small for the hand size Grip surface is not slippery No additional friction or stiffness in controls Ensure that you use the right tools for the job Hoists for lifting Trolleys for carrying Spanners / wrenches / electronic screwdrivers for loosening and tightening Loppers instead of secateurs for larger stems Avoid serial multitasking with equipment e.g. use your mouse just to position the curser on the screen and click to change texts or numbers, do not try to use it as a pen to trace around the outside of pictures on the screen (combining clicking, gripping and manipulation of the mouse itself all at the same time!)
4 NECK CONDITION If you also have a feeling of pins and needles and your grip / wrist extension is particularly weak this may indicate that there is a nerve root from the neck that is pinched. Please seek advice from a physiotherapist. Symptoms of Tennis Elbow The main symptom of tennis elbow is tenderness and pain that starts at the lateral epicondyle of the elbow. The pain may spread down the forearm. It may go as far as the back of the middle and ring fingers. The forearm muscles may also feel tight and sore. The pain usually gets worse when you bend your wrist backward, turn your palm upward, or hold something with a stiff wrist or straightened elbow. Grasping items also makes the pain worse. Just reaching into the refrigerator to get a carton of milk can cause pain. Sometimes the elbow feels stiff and won t straighten out completely. If you also have a feeling of pins and needles and your grip (stiff wrist / elbow) is particularly weak this may indicate that there is a nerve root from the neck that is pinched. Aiding Recovery with a Home Exercise Programme The healing of tennis elbow is often slow when compared to other injuries. This is mainly due to its poor blood supply. The body s tissues need a good supply of the oxygen and nutrients carried in the blood to repair. Activities such as ice, heat, massage and gentle stretching of the forearm and wrist help to promote blood flow. In order to reverse the degenerative aspect of tennis elbow, rehabilitation needs to include loading and strengthening of the tendon at the appropriate time, alongside stretching. Self Help Treatment Advice Application of ice to the forearm extensors to ease pain and reduce spasm. It is advised to apply ice in the form of crushed ice cubes, frozen peas or an ice pack. DO NOT apply directly to your skin. All of these are to be wrapped in a damp tea towel and applied to the knee for approximately 20 minutes. It is advised that you check the skin every 5-10 minutes to avoid the possibility of an ice burn from the cold temperature. Self-massage of the tendon and the forearm. This may be painful initially but will increase blood flow and help healing of the tendon and should become easier as you go. Remember to give yourself time with the massage as the tissue needs time to relax and let go as you massage the knots away. This could be done while at lunch or sitting during a tea break at work or watching a favourite programme at home. Gentle heat on the forearm (10-20 minutes) will also help to relax it and increase the blood flow. When using heat, this should be a mild heat and never feel hot. Self-massage of the front of the forearm. This area contains the forearm flexors - muscles that oppose the forearm extensors that you have just massaged (above bullet point). If the forearm extensors are tight, they can cause these muscles to tighten too; therefore can affect healing if not kept supple. Use the same guidance as above. Medication can be used to help control pain. The oral forms of these medications are easy to take and manage to control the pain associated with tennis elbow. Please seek advice from your GP or Pharmacist. Maintain elbow range of movement with full bending and straightening of the elbow, especially when getting out of bed in the morning or after sitting with it in one position for long periods. Maintain wrist range of movement with full bending and extending of the wrist, and turning the palm of your hand to face the ceiling and then the floor (supination and pronation) - especially when getting out of bed in the morning or after sitting with it in one position for long periods.
5 Relative rest, especially from gripping or repetitive exercise involving the wrist and forearm (see above prevention section). This may include modifying your work duties for a determined period of time (with the agreement of your manager) to include a reduction of the aggravating activities, pacing, use of correct and properly maintained equipment and workstation and activity assessment by occupational health. Take regular breaks (see above bullet point) and stretch while at work, also avoid heavy or power handshakes! If you also have a feeling of pins and needles and your grip is particularly weak this may indicate that there is a nerve root from the neck that is pinched. Please seek advice from a physiotherapist who will check your posture and mobility of the joints in your neck and upper back, shoulder and arm. If the nerve is being pinched in the neck it would require specific neck treatment to realign the joints and stretches to maintain mobility in both the muscles and the nerves GOOD POSTURE Improving your posture whilst sitting at your desk will optimise the position of your neck joints and also the position of your forearms at the desk. This limits the chance of irritation to the nerves at your neck and also reduces the strain on the muscles in your forearm. The secret of sitting correctly is to encourage the spine to lengthen into its neutral balanced position. The pelvis should tilt forwards (slightly) allowing the spine to hold its natural S shape. This means that weight is evenly distributed across the intervertebral discs and there is better balance in the supporting musculature. Get your lower back into a good position and your neck will automatically follow! GOOD SITTING POSITIONS Sit well back into the chair to maintain support of the spine / pelvis (do not perch on the front of the seat Tilt the seat pan forwards (if possible, or flat with a small wedge to create a slight forward tilt) this rotates the top of the pelvis so the spine is in its natural S shape (as seen from the side this is the postural opposite to the C shape which is to be avoided) Adjust chair height so that hip is slightly higher than the knee Adjust the chair back so that it supports your lumbar curve so that you can relax into it and maintain the S shape You should now be sat in a balanced upright posture with your ear in line with your shoulder and hip (side view) do not slouch into a C shape Move your chair close to the desk to avoid stretching your arms or leaning your upper body forward, you should be able to undertake your task with your elbows resting by your waist, bent to 90 degrees STRETCHES Stretches are important to keep the muscles and tendon mobile and flexible and promotes good blood flow to aid healing WRIST EXTENSOR STRETCH This movement stretches the muscles in the back of the forearm and also helps to maintain the movement in the wrist. Extend one arm out with the elbow straight and use the other hand to grasp the opposing hand at the side of the thumb and then bend the wrist downwards to apply the stretch to the area Hold the stretch for 30 seconds, repeat twice and then do the same on the other arm Please remember to keep the elbow straight during this stretch If you do this exercise just twice per day, you will really assist in reducing the stiffness and tightness in the front of the forearm and reducing your pain
6 WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH This movement stretches the muscles in the front of the forearm and also helps to maintain the movement in the wrist. Extend one arm out with the elbow straight and use the other hand to grasp the opposing hand at the side of the thumb and then bend the wrist backwards to apply the stretch to the area Hold the stretch for 30 seconds and repeat twice and then do the same on the other arm Please remember to keep the elbow straight during this stretch If you do this exercise just twice per day, you will really assist in reducing the stiffness and tightness in the front of the forearm and reducing your pain WRIST EXTENSORS AND FINGER STRETCHES This stretch incorporates the soft tissues of the hand and fingers which can also get tight as they are so closely linked to the wrist flexors. Hold your hands in a reverse prayer position (backs of the hands together rather than palms) Keep your hands and fingers tightly together throughout the whole stretch as you push your wrists downwards in the direction of the floor Hold for 30 seconds and then relax TURNING THE PALM OF THE HAND TOWARDS THE CEILING PRONATOR STRETCH Although this seems like just a wrist exercise, part of the twisting movement comes from the elbow and the forearm muscles are involved. Sit comfortably in a chair with your elbow tucked in by your side and your forearm at 90 degrees to your upper arm Turn your palm up towards the ceiling until you feel a stretch in the wrist or forearm and then hold the end of the movement for 15 seconds Perform this twice and then repeat on the other wrist or stretch both wrists at the same time TURNING THE PALM OF THE HAND TOWARDS THE FLOOR SUPINATOR STRETCH Like the stretch above, part of the twisting movement comes from the elbow and the forearm muscles are involved. Sit comfortably in a chair with your elbow tucked in by your side and your forearm at 90 degrees to your upper arm Turn your palm down towards the floor until you feel a stretch in the wrist or forearm and then hold the end of the movement for 15 seconds Perform this twice and then repeat on the other wrist or exercise both wrists at the same time MOBILISING EXERCISES NECK SIDE BENDS As mentioned previously, the nerves in your neck and arm may become tight, contributing to your elbow pain. Therefore keeping your neck mobile will help to address this. Stand or sit tall with a good concave curve in your lower back and feel that the back of your neck is long Keep your shoulders level throughout this flexibility exercise Tilt your right ear down to your right shoulder, just to the edge of a pulling sensation and return
7 to neutral Repeat on the other side, tilting your left ear down to your left shoulder as far as you can before you feel pulling. The movement may feel stiff at first and you should work through the stiffness without causing pain Repeat this gentle loosening movement 10 times Do this exercise every hour if your neck is stiff and 3 times a day otherwise RADIAL NERVE MOBILISATION It is important to keep the nerves around your elbow mobile to prevent any pinching and compression that may occur with the injury. The Radial nerve supplies the wrist extensors. Stand with your arm by your side Move your thumb across into the palm of your hand and grip it against your palm as you make a fist using your fingers Rotate your arm so that your palm is facing away from you and bend your fist upwards away from you Keeping your arm and fist in the same position and your head facing forwards, raise your arm diagonally away from your body (backwards and sideways) until you feel a pulling sensation / tightness in your forearm Tilt your head from the left to the right Keep the arms stretched all the time but tilt your head from left to right about two seconds on each side and repeat 10 times Any stretch pain that you feel going down the forearm should get better the more you repeat the stretch. If it does not get better or aggravates, stop and seek advice from your physiotherapist STRENGTHENING EXERCISES FOREARM MUSCLE STRETCH AND STRENGTHENING While standing, place the back of your hands on a table shoulder width apart with your elbows straight and your fingers pointing forward Keep your fingers stretched out and fingers and back of hand flat on the table Keeping your elbows straight, slowly lean forwards to take your body over your hands You should feel the outer forearm (extensor) muscles stretch You will also feel that the shoulder and elbow muscles are working harder as you take greater weight from your body through your arms Hold this position for 10 seconds and repeat 5 times. Do these 3 times a day If your hands feel uncomfortable on the table you can use a folded up towel or pillow to cushion the surface ECCENTRIC STRENGTHENING Extending a muscle into a stretched or lengthened position against a force (paying out against a load) rather than contracting it into a shortened position against a weight is called an eccentric mode of contraction. This method of strengthening a muscle has been proved to be helpful with a tendinopathy. For the following exercise the affected hand should be positioned passively by the other hand to start the movement and then the unaffected hand pushes the affected hand down with equal smooth resistance from the affected hand. This action may cause a little discomfort in the tendon at the elbow but it is
8 advisable to work through a moderate amount of discomfort in order to strengthen the muscles. The example below is for a right tennis elbow. Reverse with opposite hands for a left tennis elbow. ECCENTRIC WRIST EXTENSOR STRENGTHENING Turn your right palm down to face the floor. Bend at your right wrist and hand down to a fully flexed position with you left hand. Keep your right hand shoulder totally relaxed. Smoothly push up with your right hand and resist your left hand pushing your right hand down Resist the left hand all the way up to a fully extended wrist position Push with as much pressure as you can manage causing only moderate discomfort at the elbow Do 10 repetitions for 3 sets, 3 times a day. This should be undertaken until the pain in the elbow has gone, which may take several weeks Please remember to use this advice under the guidance of your Physiotherapist. To find out even more about elbow problems, visit the Know Your Body section of our site.
Stretching in the Office
 Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation
 Physiotherapy Department Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation Information for patients This information leaflet gives you advice on rehabilitation after your shoulder dislocation. It is not a substitute
Physiotherapy Department Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation Information for patients This information leaflet gives you advice on rehabilitation after your shoulder dislocation. It is not a substitute
Range of Motion. A guide for you after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program
 Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
The Super 7 For Tennis Elbow
 Exercises for Tennis elbow Tennis elbow recovery time varies with each person and may take several weeks. Recovery may be faster and more successful when a combination of local injections (e.g. steroids
Exercises for Tennis elbow Tennis elbow recovery time varies with each person and may take several weeks. Recovery may be faster and more successful when a combination of local injections (e.g. steroids
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
How to treat your injured neck
 How to treat your injured neck Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your neck is made up of a number of bones bound together by strong discs and ligaments. It is also protected by strong muscles.
How to treat your injured neck Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your neck is made up of a number of bones bound together by strong discs and ligaments. It is also protected by strong muscles.
Active Range of Motion: A. Flexion: Gently try to bend your wrist forward. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat for 3 sets of 10.
 Rehabilitation Exercises for Wrist and Hand Injuries If instructed by your medical doctor, you may begin these exercises when the pain has started to decrease. Active Range of Motion: A. Flexion: Gently
Rehabilitation Exercises for Wrist and Hand Injuries If instructed by your medical doctor, you may begin these exercises when the pain has started to decrease. Active Range of Motion: A. Flexion: Gently
Range of Motion Exercises
 Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..?
 Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..? Staying healthy at work is easier than you might think: Try building the following desk based exercises into your
Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..? Staying healthy at work is easier than you might think: Try building the following desk based exercises into your
Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work
 Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work The Optimal Office Work Station Use an adjustable chair with good lumbar support. Keep your feet flat on a supportive surface (floor or foot rest). Your knees should
Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work The Optimal Office Work Station Use an adjustable chair with good lumbar support. Keep your feet flat on a supportive surface (floor or foot rest). Your knees should
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet
 Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES
 CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK
 HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK 1. Standing and Walking For correct posture, balance your head above your shoulders, eyes straight ahead, everything else falls into place. Try to point toes straight ahead
HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK 1. Standing and Walking For correct posture, balance your head above your shoulders, eyes straight ahead, everything else falls into place. Try to point toes straight ahead
Cervical Exercise: How important is it? What can be done? The Backbone of Spine Treatment. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Cervical Exercise: The Backbone of Spine Treatment How important is it? What can be done? North American Spine Society Public Education Series Important: If you have had an accident that started your neck
Cervical Exercise: The Backbone of Spine Treatment How important is it? What can be done? North American Spine Society Public Education Series Important: If you have had an accident that started your neck
Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD)
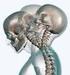 Information for patients Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD) Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 05731-14(RP) Issue 3: December 2014 Review date: November 2017 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust,
Information for patients Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD) Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 05731-14(RP) Issue 3: December 2014 Review date: November 2017 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust,
CONSTRUCTION WORK and CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS
 Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
For Deep Pressure Massage
 T H E R A C A N E O W N E R S M A N U A L For Deep Pressure Massage Thera Cane is a self massager used to apply pressure to sore muscles. The unique design of the Thera Cane lets you apply deep pressure
T H E R A C A N E O W N E R S M A N U A L For Deep Pressure Massage Thera Cane is a self massager used to apply pressure to sore muscles. The unique design of the Thera Cane lets you apply deep pressure
Routine For: OT - General Guidelines/Energy Conservation (Caregiver)
 GENERAL GUIDELINES - 9 Tips for Exercise: Body Mechanics for Helper - To protect back, stay as upright as possible and keep head in line with trunk. - Always position yourself as close as possible to the
GENERAL GUIDELINES - 9 Tips for Exercise: Body Mechanics for Helper - To protect back, stay as upright as possible and keep head in line with trunk. - Always position yourself as close as possible to the
Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation
 Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation Flexibility refers to the amount of movement possible around a joint and is necessary for normal activities of daily living such as stretching,
Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation Flexibility refers to the amount of movement possible around a joint and is necessary for normal activities of daily living such as stretching,
MOON SHOULDER GROUP. Rotator Cuff Home Exercise Program. MOON Shoulder Group
 MOON Shoulder Group For information regarding the MOON Shoulder Group, talk to your doctor or contact: Rosemary Sanders 1215 21 st Avenue South 6100 Medical Center East Vanderbilt University Medical Center
MOON Shoulder Group For information regarding the MOON Shoulder Group, talk to your doctor or contact: Rosemary Sanders 1215 21 st Avenue South 6100 Medical Center East Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Rotator Cuff Home Exercise Program MOON SHOULDER GROUP
 Rotator Cuff Home Exercise Program MOON SHOULDER GROUP Introduction The MOON Shoulder group is a Multi-center Orthopaedic Outcomes Network. In other words, it is a group of doctors from around the country
Rotator Cuff Home Exercise Program MOON SHOULDER GROUP Introduction The MOON Shoulder group is a Multi-center Orthopaedic Outcomes Network. In other words, it is a group of doctors from around the country
General Guidelines. Neck Stretch: Side. Neck Stretch: Forward. Shoulder Rolls. Side Stretch
 Stretching Exercises General Guidelines Perform stretching exercises at least 2 3 days per week and preferably more Hold each stretch for 15 20 seconds Relax and breathe normally Stretching is most effective
Stretching Exercises General Guidelines Perform stretching exercises at least 2 3 days per week and preferably more Hold each stretch for 15 20 seconds Relax and breathe normally Stretching is most effective
Take a few minutes for yourself and incorporate some Office Yoga into your daily routine.
 OFFICE YOGA Working in an office or at a computer for prolonged periods of time can put strain on the neck, shoulder and back muscles which in turn can lead to tension and stiffness. This tension can cause
OFFICE YOGA Working in an office or at a computer for prolonged periods of time can put strain on the neck, shoulder and back muscles which in turn can lead to tension and stiffness. This tension can cause
Shoulder Tendonitis. Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696
 Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain
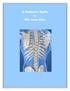 A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain Anatomy Where are the rib joints? Your rib cage is made up of twelve pairs of ribs. The ribs attach to the spine in the back, and to the breastbone in the front. The
A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain Anatomy Where are the rib joints? Your rib cage is made up of twelve pairs of ribs. The ribs attach to the spine in the back, and to the breastbone in the front. The
A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca
 www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear.
 Page 1 Safety Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear. Prepare a space and have your exercise band and a glass of water (for afterwards) ready
Page 1 Safety Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear. Prepare a space and have your exercise band and a glass of water (for afterwards) ready
Computer Workstation Ergonomic Self Evaluation
 Computer Workstation Ergonomic Self Evaluation Use this guidance to perform a preliminary evaluation of your workstation, and make any adjustments that are necessary to achieve a correct neutral posture.
Computer Workstation Ergonomic Self Evaluation Use this guidance to perform a preliminary evaluation of your workstation, and make any adjustments that are necessary to achieve a correct neutral posture.
Back Safety and Lifting
 Back Safety and Lifting Structure of the Back: Spine The spine is the part of the back that supports the trunk and head. It protects the spinal cord as well as giving flexibility to the body. Vertebrae
Back Safety and Lifting Structure of the Back: Spine The spine is the part of the back that supports the trunk and head. It protects the spinal cord as well as giving flexibility to the body. Vertebrae
ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM
 ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information on this and other
ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information on this and other
Psoas Syndrome. The pain is worse from continued standing and from twisting at the waist without moving the feet.
 Psoas Syndrome The iliopsoas muscle is a major body mover but seldom considered as a source of pain. Chronic lower back pain involving the hips, legs, or thoracic regions can often be traced to an iliopsoas
Psoas Syndrome The iliopsoas muscle is a major body mover but seldom considered as a source of pain. Chronic lower back pain involving the hips, legs, or thoracic regions can often be traced to an iliopsoas
stretches and exercises
 stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
ERGONOMICS. Improve your ergonomic intelligence by avoiding these issues: Awkward postures Repetitive tasks Forceful exertions Lifting heavy objects
 ERGONOMICS The goal of ergonomics is to reduce your exposure to work hazards. A hazard is defined as a physical factor within your work environment that can harm your body. Ergonomic hazards include working
ERGONOMICS The goal of ergonomics is to reduce your exposure to work hazards. A hazard is defined as a physical factor within your work environment that can harm your body. Ergonomic hazards include working
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Trochanteric Bursitis Self Management for Patients
 Trochanteric Bursitis Self Management for Patients Updated May 2010 What is the Trochanteric Bursa? The trochanteric bursa is a fluid-filled sac that functions as a gliding surface to reduce friction between
Trochanteric Bursitis Self Management for Patients Updated May 2010 What is the Trochanteric Bursa? The trochanteric bursa is a fluid-filled sac that functions as a gliding surface to reduce friction between
Exercise 1: Knee to Chest. Exercise 2: Pelvic Tilt. Exercise 3: Hip Rolling. Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface.
 Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite leg flat on the surface
Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite leg flat on the surface
Exercises for Low Back Injury Prevention
 DIVISION OF AGRICULTURE RESEARCH & EXTENSION University of Arkansas System Family and Consumer Sciences Increasing Physical Activity as We Age Exercises for Low Back Injury Prevention FSFCS38 Lisa Washburn,
DIVISION OF AGRICULTURE RESEARCH & EXTENSION University of Arkansas System Family and Consumer Sciences Increasing Physical Activity as We Age Exercises for Low Back Injury Prevention FSFCS38 Lisa Washburn,
Getting Your Hand Moving After a Wrist Fracture
 Information for patients Getting Your Hand Moving After a Wrist Fracture Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 703318 DPS ref: 06175-14(RP) Issue 1: April 2015 Review date: March 2018 The Ipswich Hospital
Information for patients Getting Your Hand Moving After a Wrist Fracture Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 703318 DPS ref: 06175-14(RP) Issue 1: April 2015 Review date: March 2018 The Ipswich Hospital
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques
 Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
Mike s Top Ten Tips for Reducing Back Pain
 Mike s Top Ten Tips for Reducing Back Pain The following article explains ways of preventing, reducing or eliminating back pain. I have found them to be very useful to myself, my clients and my patients.
Mike s Top Ten Tips for Reducing Back Pain The following article explains ways of preventing, reducing or eliminating back pain. I have found them to be very useful to myself, my clients and my patients.
Schiffert Health Center www.healthcenter.vt.edu. Neck Pain (Cervical Strain) COMMON CAUSES: QUICK TREATMENT : NECK PAIN TREATING NECK PAIN:
 Schiffert Health Center www.healthcenter.vt.edu Patient Information: Neck Pain (Cervical Strain) COMMON CAUSES: Neck pain may be triggered by a specific event, such a sport injury or motor vehicle accident.
Schiffert Health Center www.healthcenter.vt.edu Patient Information: Neck Pain (Cervical Strain) COMMON CAUSES: Neck pain may be triggered by a specific event, such a sport injury or motor vehicle accident.
Stretch the fingers by either interlocking them or holding your fingers as one unit and pull them downwards gently with the other hand.
 Although often thought of as a technique that requires two people, massage on yourself is also beneficial and can be done at any time during the day. In fact, whenever you rub a tense spot or ease a tight
Although often thought of as a technique that requires two people, massage on yourself is also beneficial and can be done at any time during the day. In fact, whenever you rub a tense spot or ease a tight
Back Injury Prevention. For the Landscaping and Horticultural Services Industry
 Back Injury Prevention For the Landscaping and Horticultural Services Industry Back Injury Prevention Contents Introduction What s Inside?... 3 Lesson 1 Understand Your Back and Back Pain... 4 Lesson 2
Back Injury Prevention For the Landscaping and Horticultural Services Industry Back Injury Prevention Contents Introduction What s Inside?... 3 Lesson 1 Understand Your Back and Back Pain... 4 Lesson 2
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
Exercises for older people
 Exercise for older people Exercises for older people Sitting Getting started If you ve not done much physical activity for a while, you may want to get the all-clear from a GP before starting. For the
Exercise for older people Exercises for older people Sitting Getting started If you ve not done much physical activity for a while, you may want to get the all-clear from a GP before starting. For the
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)
 Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Pendulum Exercise: Wal Walk: Back Scratcher:
 Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Begin these exercises when your pain has decreased about 25% from the time when your injury was most painful. Pendulum Exercise: Lean over with your uninjured
Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Begin these exercises when your pain has decreased about 25% from the time when your injury was most painful. Pendulum Exercise: Lean over with your uninjured
COMMON OVERUSE INJURIES ATTRIBUTED TO CYCLING, AND WAYS TO MINIMIZE THESE INJURIES
 COMMON OVERUSE INJURIES ATTRIBUTED TO CYCLING, AND WAYS TO MINIMIZE THESE INJURIES Listed are a few of the most common overuse injuries associated with cycling long distances. 1. Cervical and upper back
COMMON OVERUSE INJURIES ATTRIBUTED TO CYCLING, AND WAYS TO MINIMIZE THESE INJURIES Listed are a few of the most common overuse injuries associated with cycling long distances. 1. Cervical and upper back
X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary
 X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary Introduction Exercising your neck can make it stronger, more flexible and reduce neck pain that is caused by stress and fatigue. This reference summary describes
X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary Introduction Exercising your neck can make it stronger, more flexible and reduce neck pain that is caused by stress and fatigue. This reference summary describes
How To Stretch Your Body
 Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
A guide for employees
 A guide for employees This booklet has been developed as a guide to assist in the prevention of muscular discomfort and strain that can sometimes be associated with computer use. The information provided
A guide for employees This booklet has been developed as a guide to assist in the prevention of muscular discomfort and strain that can sometimes be associated with computer use. The information provided
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Brachial Plexus Palsy
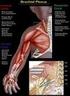 Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
CHAPTER 3: BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES. Standing Quad Stretch Athletic Edge - www.athleticedge.biz - (650) 815-6552
 CHAPTER : BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES Standing Quad Stretch ) Stand and grasp right ankle with same hand, use a wall or chair to Lower maintain Back balance with left hand. Maintain an upright Stretches
CHAPTER : BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES Standing Quad Stretch ) Stand and grasp right ankle with same hand, use a wall or chair to Lower maintain Back balance with left hand. Maintain an upright Stretches
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
ISOMETRIC EXERCISE HELPS REVERSE JOINT STIFFNESS, BUILDS MUSCLE, AND BOOSTS OVERALL FITNESS.
 ISOMETRIC EXERCISE HELPS REVERSE JOINT STIFFNESS, BUILDS MUSCLE, AND BOOSTS OVERALL FITNESS. By Askari A. Kazmi KazmisBioscienceLabs exercise helps reverse joint stiffness, builds muscle, and boosts overall
ISOMETRIC EXERCISE HELPS REVERSE JOINT STIFFNESS, BUILDS MUSCLE, AND BOOSTS OVERALL FITNESS. By Askari A. Kazmi KazmisBioscienceLabs exercise helps reverse joint stiffness, builds muscle, and boosts overall
Throwers Ten Exercise Program
 Throwers Ten Exercise Program The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition,
Throwers Ten Exercise Program The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition,
Westmount UCC 751 Victoria Street South, Kitchener, ON N2M 5N4 519-745-2273 Fairway UCC 385 Fairway Road South, Kitchener, ON N2C 2N9 519-748-2327
 K-W URGENT CARE CLINICS INC. Westmount UCC 751 Victoria Street South, Kitchener, ON N2M 5N4 519-745-2273 Fairway UCC 385 Fairway Road South, Kitchener, ON N2C 2N9 519-748-2327 OPEN Mon-Fri 8am-5pm, Sa
K-W URGENT CARE CLINICS INC. Westmount UCC 751 Victoria Street South, Kitchener, ON N2M 5N4 519-745-2273 Fairway UCC 385 Fairway Road South, Kitchener, ON N2C 2N9 519-748-2327 OPEN Mon-Fri 8am-5pm, Sa
Operating Instructions
 Operating Instructions Table of Contents IMPORTANT INFORMATION 1-2 1 The backrack TM 3-6 Introduction 3 What does it do? 4 How do I use it? 5 How often should I use it? 6 2 Getting On 7-10 3 Basic Exercises
Operating Instructions Table of Contents IMPORTANT INFORMATION 1-2 1 The backrack TM 3-6 Introduction 3 What does it do? 4 How do I use it? 5 How often should I use it? 6 2 Getting On 7-10 3 Basic Exercises
KNEE EXERCISE PROGRAM
 KNEE PROGRAM INTRODUCT ION Welcome to your knee exercise program. The exercises in the program are designed to improve your knee stability and strength of the muscles around your knee and hip. The strength
KNEE PROGRAM INTRODUCT ION Welcome to your knee exercise program. The exercises in the program are designed to improve your knee stability and strength of the muscles around your knee and hip. The strength
Sheet 1A. Treating short/tight muscles using MET. Pectorals. Upper trapezius. Levator scapula
 Sheet 1A Treating short/tight muscles using MET Pectorals Once daily lie at edge of bed holding a half-kilo can, arm out sideways. Raise arm and hold for 10 seconds, then allow arm to hang down, stretching
Sheet 1A Treating short/tight muscles using MET Pectorals Once daily lie at edge of bed holding a half-kilo can, arm out sideways. Raise arm and hold for 10 seconds, then allow arm to hang down, stretching
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service. LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide
 Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
LIFTING AND BACK SAFETY TRAINING LESSON PLAN
 LIFTING AND BACK SAFETY TRAINING LESSON PLAN Topic: Back Safety and Proper Lifting Techniques This presentation is designed to assist trainers conducting Lifting and Back Safety training for workers. Back
LIFTING AND BACK SAFETY TRAINING LESSON PLAN Topic: Back Safety and Proper Lifting Techniques This presentation is designed to assist trainers conducting Lifting and Back Safety training for workers. Back
Whole Hand Activities
 Activities Walk & Flip 5 Baton Twirl Rotate the pencil in, around and between all your fingers like it was a baton. 10 Walk your fingers up the pencil (your index will look like an inchworm climbing the
Activities Walk & Flip 5 Baton Twirl Rotate the pencil in, around and between all your fingers like it was a baton. 10 Walk your fingers up the pencil (your index will look like an inchworm climbing the
Coccydynia. (Coccyx Pain) Information for patients. Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312
 Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Self Management Program. Ankle Sprains. Improving Care. Improving Business.
 Ankle Sprains Improving Care. Improving Business. What is an ankle sprain? Ligaments attach to the ankle bones and allow for normal movement and help prevent too much motion within the joint. Ankle sprains
Ankle Sprains Improving Care. Improving Business. What is an ankle sprain? Ligaments attach to the ankle bones and allow for normal movement and help prevent too much motion within the joint. Ankle sprains
Ulnar nerve decompression
 Patient information Ulnar nerve decompression This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your condition and its treatment. It includes the following information:
Patient information Ulnar nerve decompression This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your condition and its treatment. It includes the following information:
Preventing Falls. Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing
 Preventing Falls Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing Exercise should be comfortable and fun. To get the most out of your home exercise book, join a class for older people to check your exercises
Preventing Falls Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing Exercise should be comfortable and fun. To get the most out of your home exercise book, join a class for older people to check your exercises
ADVICE FOR PATIENTS WITH NECK PAIN
 ADVICE FOR PATIENTS WITH NECK PAIN Patient Information Leaflet Physiotherapy Department (Information sheet code SHOT/SHOA) A SMOKING FREE ENVIRONMENT WAHT-TH-007-1 - Version 1.2 Dear Patient This advice
ADVICE FOR PATIENTS WITH NECK PAIN Patient Information Leaflet Physiotherapy Department (Information sheet code SHOT/SHOA) A SMOKING FREE ENVIRONMENT WAHT-TH-007-1 - Version 1.2 Dear Patient This advice
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide
 Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Biceps Tenodesis. An information guide for patients. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Biceps Tenodesis An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Biceps Tenodesis An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Why Back Safety is Important
 Back Safety Why Back Safety is Important Back injuries are considered by OSHA (the Occupational Safety and Health Administration) as the nation's #1 workplace safety problem. Back Injuries are often: Very
Back Safety Why Back Safety is Important Back injuries are considered by OSHA (the Occupational Safety and Health Administration) as the nation's #1 workplace safety problem. Back Injuries are often: Very
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery
 Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
WSN ERGONOMIC SAFETY TALK #3
 What is a safety talk? This safety talk is one of a series of brief meetings held on regular basis with workers and their supervisors to discuss problems and concerns about health and safety. All safety
What is a safety talk? This safety talk is one of a series of brief meetings held on regular basis with workers and their supervisors to discuss problems and concerns about health and safety. All safety
Knee Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Cervicothoracic Mobility Exercises
 Cervicothoracic Mobility Exercises Upper Cervical Mobility Exercises... 2 Lower Cervical Mobility Exercises... 3 Cervicothoracic Junction Mobility Exercises... 4 1 st Rib Mobility Exercises... 5 Cervical
Cervicothoracic Mobility Exercises Upper Cervical Mobility Exercises... 2 Lower Cervical Mobility Exercises... 3 Cervicothoracic Junction Mobility Exercises... 4 1 st Rib Mobility Exercises... 5 Cervical
Physiotherapy Department Acute Neck Pain a guide to help your recovery
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy Department Acute Neck Pain a guide to help your recovery Information for patients Most acute neck injuries are not serious and the pain will improve
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy Department Acute Neck Pain a guide to help your recovery Information for patients Most acute neck injuries are not serious and the pain will improve
Neck Pain HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management
 HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 The neck (cervical spine) anatomy 2 What are the common types of neck pain? 3 What are the common symptoms associated with
HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 The neck (cervical spine) anatomy 2 What are the common types of neck pain? 3 What are the common symptoms associated with
Shoulder Capsular Release
 Shoulder Capsular Release An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Shoulder Capsular Release An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Lateral pterygoid muscle Medial pterygoid muscle
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
Recent Injuries. www.physiofirst.org.uk
 Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Hip Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Rotator Cuff and Shoulder Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Whiplash Recovery Important Facts 1
 02866328200 Whiplash Recovery Important Facts 1 What is whiplash? You can get whiplash if your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement. The tissues around your neck are overstretched,
02866328200 Whiplash Recovery Important Facts 1 What is whiplash? You can get whiplash if your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement. The tissues around your neck are overstretched,
Physiotherapy Database Exercises for people with Spinal Cord Injury
 Physiotherapy Database Exercises for people with Spinal Cord Injury Compiled by the physiotherapists associated with the following Sydney (Australian) spinal units : Last Generated on Mon Mar 29 16:57:20
Physiotherapy Database Exercises for people with Spinal Cord Injury Compiled by the physiotherapists associated with the following Sydney (Australian) spinal units : Last Generated on Mon Mar 29 16:57:20
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness. and pain
 TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
Injury Prevention for the Back and Neck
 Injury Prevention for the Back and Neck www.csmr.org We have created this brochure to provide you with information regarding: Common Causes of Back and Neck Injuries and Pain Tips for Avoiding Neck and
Injury Prevention for the Back and Neck www.csmr.org We have created this brochure to provide you with information regarding: Common Causes of Back and Neck Injuries and Pain Tips for Avoiding Neck and
SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION
 SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy department to help you understand lumbar
SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy department to help you understand lumbar
[Project name] Standard Operating Procedures. Body Mechanics
![[Project name] Standard Operating Procedures. Body Mechanics [Project name] Standard Operating Procedures. Body Mechanics](/thumbs/27/11986346.jpg) [Project name] Standard Operating Procedures Body Mechanics PURPOSE. The purpose of this SOP is to provide information to minimize staff injuries with the focus on back injuries resulting from improper
[Project name] Standard Operating Procedures Body Mechanics PURPOSE. The purpose of this SOP is to provide information to minimize staff injuries with the focus on back injuries resulting from improper
SHOULDER PULL DOWNS. To learn efficient use of the shoulder blades and arms while maintaining a neutral spine position.
 SHOULDER INTRODUCT ION Welcome to your shoulder exercise program The exercises in the program are designed to improve your shoulder mobility, posture and the control of the muscles in your neck and shoulder
SHOULDER INTRODUCT ION Welcome to your shoulder exercise program The exercises in the program are designed to improve your shoulder mobility, posture and the control of the muscles in your neck and shoulder
FROZEN SHOULDER OXFORD SHOULDER & ELBOW CLINIC INFORMATION FOR YOU. Frozen Shoulder FROZEN SHOULDER
 OXFORD SHOULDER & ELBOW CLINIC INFORMATION FOR YOU Frozen Shoulder The aim of this information sheet is to give you some understanding of the problem you may have with your shoulder. It has been divided
OXFORD SHOULDER & ELBOW CLINIC INFORMATION FOR YOU Frozen Shoulder The aim of this information sheet is to give you some understanding of the problem you may have with your shoulder. It has been divided
Shoulders (free weights)
 Dumbbell Shoulder Raise Dumbbell Shoulder Raise 1) Lie back onto an incline bench (45 or less) with a DB in each hand. (You may rest each DB on the corresponding thigh.) 2) Start position: Bring the DB
Dumbbell Shoulder Raise Dumbbell Shoulder Raise 1) Lie back onto an incline bench (45 or less) with a DB in each hand. (You may rest each DB on the corresponding thigh.) 2) Start position: Bring the DB
Self-mobilization methods
 Self-mobilization methods 5 Muscle energy techniques, as outlined in previous chapters, provide us with an excellent series of methods for relaxation and stretching of specific tight, shortened, contracted
Self-mobilization methods 5 Muscle energy techniques, as outlined in previous chapters, provide us with an excellent series of methods for relaxation and stretching of specific tight, shortened, contracted
SLAP repair. An information guide for patients. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 SLAP repair An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
SLAP repair An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Don t. Hamstrings. Calf Muscles. both legs 2-3 times. stretch is felt in the back of the calf. Repeat with both legs 2-3 times.
 Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching (e.g. stretch after walking). Stretch until you feel mild discomfort, not pain. Never bounce or force a stretch. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds
Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching (e.g. stretch after walking). Stretch until you feel mild discomfort, not pain. Never bounce or force a stretch. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
Keep fit at the workplace! A simple training programme for more exercise at the workplace.
 Keep fit at the workplace! A simple training programme for more exercise at the workplace. INTRODUCTION Dear Readers, Keeping your body in one position, such as sitting or standing for a long time, results
Keep fit at the workplace! A simple training programme for more exercise at the workplace. INTRODUCTION Dear Readers, Keeping your body in one position, such as sitting or standing for a long time, results
HEADACHES, NECK & EYE FATIGUE. Deep tissue massage. Regular upper body stretches. Consult Optometrist/Ophthalmologist
 HEADACHES, NECK & EYE FATIGUE Headaches Vision concerns Itchy and irritated eyes Overall Neck Pain Muscular tension See NECK PAIN and VISION CONCERNS below Need corrective lenses or new prescription Inadequate
HEADACHES, NECK & EYE FATIGUE Headaches Vision concerns Itchy and irritated eyes Overall Neck Pain Muscular tension See NECK PAIN and VISION CONCERNS below Need corrective lenses or new prescription Inadequate
