IN FLIGHT MANEUVERS AND OPERATING PROCEDURES C-172
|
|
|
- Helen Booth
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Flight Training and Aircraft Rentals SW 129th St. MIAMI, FL IN FLIGHT MANEUVERS AND OPERATING PROCEDURES C-172 Normal Cruise: Straight and level flight should be with the airplane trimmed for level attitude and using RPM. There should be no altitude gain or loss and heading should remain constant. Slow Flight: Select an entry altitude for the maneuver that allows completion no lower than 1500 foot AGL or the recommended altitude whichever is high Dean International altitude: 2000 ft. Start by making two 60 degree clearing turns, maintaining altitude. Upon completion, look and say heading, altitude and horizon. Complete the pre-maneuver checklist: fuel selector: both, flaps up, mixture rich, carburetor heat on; look and say Gradually apply back pressure on the yoke to maintain altitude, slow to 85 knots using coordination (rudder) and maintain heading (looking outside) Lower 10 degrees of flaps, heading, altitude and horizon re-trim, adjust power and stabilize speed around 80 knots Lower 20 degrees of flaps, heading, altitude and horizon re-trim, adjust power and stabilize speed around 70 knots Lower full flaps, heading, altitude and horizon, re-trim, adjust power and stabilize speed at 60 knots (stabilize the airspeed at 1.2 V S1 +10/-5 knots Make necessary corrections for altitude using throttle adjustments and for speed using pitch adjustments (carburetor heat off above 2000 RPM). Recover to straight and level flight by adding full power; retract flaps in 10- increments resume normal cruise without gain or loss of altitude. Go-Around Procedure Add full power Nose to the horizon Turn the carburetor heat off. Retract 10 degrees of flaps Establish positive rate of climb Retract 10 degrees of flaps Establish positive rate of climb Retract 10 degrees of flaps
2 Approach to Landing Stall (Power off Stall) Select an entry altitude for the maneuver that allows completion no lower than 1500 ft. AGL or the recommended altitude whichever is higher Dean International altitude: altitude 2000 ft Make two 90 degree clearing turns, maintaining altitude. Complete the pre-maneuver checklist: fuel selector: both, flaps up, mixture rich, carburetor heat on; look and say heading, altitude and horizon Gradually apply back pressure on the yoke to maintain altitude slow to 85 knots using coordination (rudder) and maintain heading (looking outside). Start lowering the flaps in 10 degree increments as specified in slow flight procedure. With the airplane trimmed to the normal approach speed for the landing configuration, reduce power to idle. Start gradually increasing angle of attack until the stall buffet is detected. Recover by lowering the nose to the horizon, adding full throttle and right rudder and level the wings as necessary, maintaining heading. As flying speed is regained adjust the pitch attitude to stop the descent and initiate a climb. Retract the flaps in 10 degree increments. Recovery should occur with minimum loss altitude. Take-off and Departure Select an entry altitude for the maneuver that allows completion no lower than 1500 ft. AGL or the recommended altitude whichever is higher Dean International altitude: altitude 2000 ft Make two 90 degree clearing turns, maintaining altitude. Complete the pre-maneuver checklist: fuel selector: both, flaps up, mixture full rich, carburetor heat: on, power: 1700 RPM and trim. Reduce speed to 70 knots (simulation take-off speed). Close the carburetor heat, add full throttle and gradually increase the angle of attack maintaining proper coordination of the flight controls (right rudder and heading). When the first stall buffet is detected, recover by smoothly lowering the nose to the horizon and level the wings as necessary (maintain right rudder). Establish V X (best angle of climb speed) until a positive rate of climb is noted. Return to normal cruise S Turns Across a Road Establish normal cruise at 1000 ft, AGL. Establish the airplane on a downwind heading and note the heading. Select a road or prominent straight line that runs crosswind. Enter downwind and perpendicular to the reference line. As the airplane crosses the reference line, enter a steep bank, because the ground speed is fastest at that point. The bank angle is gradually reduced as necessary to describe a ground track, which is a perfect half circle. As the roll out is completed, the airplane should be crossing the road perpendicular to it and headed upwind.
3 Since the airplane is on the upwind side of the maneuver, a shallow bank should be started in the opposite direction to begin the second half of the S. The bank angle should be gradually increased as necessary to describe a headed downwind. Outside references: road altitude outside the traffic. Turns Around a Point Establish a normal cruise at 1000 ft. AGL Establish the airplane on a downwind course and not the heading. Select a prominent reference point on the ground. Enter the maneuver flying downwind past the point at a distance equal to the desired radius of the turn. As you arrive exactly abeam the point, enter a medium banked turn toward track over the ground. Vary the bank from that point as necessary to fly in a perfect circle with constant radius around that point. When any wind exists, it will be necessary to enter the steepest bank immediately since the airplane is headed downwind. Thereafter, that bank should be shallowed gradually until the crosswind segments; crab technique must be utilized to maintain the desired track. Outside references: point altitude outside for traffic. Rectangular Course Establish normal cruise at 1000 ft. AGL Select a reference rectangular course on the ground, big enough to fly outside its boundaries while maintaining the same distance from the sides. Enter the downwind, while making all necessary wind corrections. Turn crosswind by using a moderate to steep bank angle, depending on the wind to keep the airplane from drifting away from the rectangle and to join the crosswind side of the maneuver, maintaining the same distance from the side. Turn upwind by using a moderate to shallow bank angle in such a way that the same distance with the rectangle is maintained when the roll out is complete, and make all necessary wind corrections. Steep Turns Select an altitude that will allow the maneuver to be performed no lower than 1500 ft. AGL Dean International altitude: 2000 ft. Establish normal cruise speed. Make two 90 degree clearing turns. Smoothly roll into a 30 degree bank and apply some back elevator pressure. Upon reaching 45 degrees apply a little more back elevator pressure. Maintain a coordinated steep turn with a constant bank and roll out on the original heading after 360 degree of turn. It is important to maintain a constant altitude as well as constant bank. For commercial practice, the bank should be at 50 degrees.
4 Short Field Take-off Complete the before take-off checklist. Lineup for take-off utilizing all available runway, hold brakes, and smoothly apply full throttle, call out temperature-pressure and RPM; then release the brakes. Rotate at the recommended take-off speed and reach V X (best angle of climb speed) 60 knots as soon as possible, maintain this speed until the obstacle is cleared (normally 50 ft. above the obstacle). Accelerate to V Y (best rate of climb speed) 75 knots until reaching a safe altitude and establish normal climb. Short Field Landing Enter downwind leg at normal cruise and perform pre-landing checklist. Reduce the power to 1700 RPM, trim off as required and start descent. Target speed during this phase should be 85 knots. Lower 10 degrees of flaps; target speed is 75 knots altitude 800 ft. When established on base leg, set the flaps to 20 degrees and the target speed should be 70 knots. Turn to final approach and set full flaps; target speed should be 60 knots. Make wind drift corrections as necessary. Touch down should be made in a full stall attitude with a minimum rate of descent; power is reduced during round out slowly to prevent the airplane from dropping. After the airplane is on the ground, retract the flaps and apply aerodynamic braking with power at idle. Soft Field Take-off Complete the before take-off checklist, flaps 10 degrees Taxi into take-off position while pulling the elevator full up and do not stop the airplane. Apply full power, as nose comes up, release back pressure slightly to maintain an attitude where the nose wheel is clear of the runway, without dragging the tail looking at the far end of the runway. Maintain this attitude and life-off at the slowest possible airspeed. As soon as the airplane is off the ground, slightly lower the nose to remain in until crossing over the obstacle. After crossing the obstacle, lower the nose to obtain V Y and retract the flaps. Resume normal climb at 75 knots. References look at the end of the runway (look for trees, buildings, etc.) Soft Field Landing Enter downwind at normal cruise and complete the pre-landing checklist. Opposite point of touchdown. Reduce the power to 1700 RPM, trim off as required and start descent. Target speed during this phase should be 85 knots. Lower 10 degrees of flaps, trim as required and establish 75 knots.
5 Turn to base leg using the 45 degree reference from the runway and set the flaps to 20 degrees. Trim as necessary. Target speed should be 70 knots. Turn to final approach and set full flaps; speed should be 60 knots. Make wind drift correction as necessary. Keep reducing power during the descent once the runway is made, there should be no power. Just before touchdown, add a little power so the airplane settles down as smooth as possible with nose up attitude (some power may be required during the landing roll to prevent the airplane from digging on the ground). Once the wheels touch the ground, cut the power completely. Full elevator up should be held in order to maintain the nose wheel off the ground as long as possible. Apply brakes only as required. Lazy Eights Establish normal cruise. Make two 90 degree clearing turns. Lower the nose if necessary to accelerate to the maneuvering speed (V A ) of 97 knots. Begin to raise the nose, then immediately begin a turn with the pitch and the bank slowly increasing in a smooth, coordinated manner. The pitch should reach its maximum nose high attitude at the 45 degree point with the bank approximately half of the maximum bank angle used in the maneuver. The maximum bank used should not exceed 30 degrees. As the turn continues to the 90 degree point the nose should descend slowly to the level flight attitude with the bank gradually increasing to the maximum (not more than 30 degrees). Between 90 degrees and 135 degrees of turn the nose should reach its maximum nose down pitch attitude, which should equal the nose up pitch attitude of the first 45 degree turn. The bank should decrease gradually to a 15 degree bank or half the maximum bank used whichever is less. Between 135 and 180 degrees of turn the nose should return to the normal level attitude with the bank slowly shallowing to wings level and the airspeed returning to the maneuvering speed. Without stopping the maneuver the same process is then executed in the opposite direction. Note: The Lazy Eight consists of two 180 degree turns directions with a symmetrical climb and dive performed during each of the turns. The airplane should be constantly rolled from one of climb to dive. The loops should be symmetrical with the segments above and below the horizon equal in size. At no time during the maneuver should the airplane attitude, control positions or control forces be held constant. Airspeed, attitude, altitude and direction should be constantly and very smoothly changing. Chandelle Make two 90 degree clearing turns. Lower the nose slightly if necessary to accelerate to V A.
6 Establish a 30 degree bank and increase the back pressure smoothly, raise the nose to an attitude where the 90 degree point will produce a maximum performance climbing turn. Smoothly advance the power as the nose is raised. Power and pitch should be maximum at the 90 degree point of the turn. Begin a coordinated roll out after 90 degrees of turn while maintaining the pitch attitude. The 180 degree point should be reached as the wings level with the airspeed just above a stall. Hold the pitch attitude momentarily, then lower the nose to the level flight and normal cruise RPM. Note: A chandelle is a maneuver wherein the pilot tires to accomplish a maximum gain of altitude during a 180 degree change of direction. Use of a 30 degree bank is the maximum bank allowable; however, a smaller bank may produce a better climb in lower performance aircraft. Determine what angle of bank gives the most climb for the aircraft and utilize that bank. Eight on Pylons Before starting this maneuver calculate the pivotal altitude applicable for the C- 172 and show how it is accomplished; KTAS squared divided by 11.5 knots or 15 MPH. Perform clearing turns. Complete pre-maneuver checklist: fuel selector: proper tank, mixture: rich, carburetor heat: off seat belts fastened. Determine wind direction and select 2 pylons which are located perpendicular to the wind. Select the appropriate pivotal altitude depending on the aircraft true airspeed. Start the maneuver by flying downwind between the pylons at a 45 degree angle of entry. Reach to the first pylon and roll in to a coordinated medium to steep bank so the airplanes lateral axis pivots on the pylon. Since the airplane is turning around the pylon there will be a point where it going to face the wind (upwind side of the maneuver). At this point, the ground speed is going to decrease which is evident by observing the pylon moving ahead of the reference point on the airplane; this needs to be corrected by lowering the nose and decreasing bank and for instance, building up more speed to catch the pylon. When the airplane is located between the pylons at 45 degree angle, the other pylon should be the target by flying momentarily straight and level until the airplane is exactly abeam. Since the airplane is flying in the downwind side of the maneuver, the ground speed is increasing so the pylon appears to be moving behind the airplane; bank to decrease ground speed, so the pylon catches the airplane.
7 Normal Traffic Patterns Once the clearance is obtained from the control tower, align the airplane to the runway centerline, smoothly add full power, check engine instruments, maintain directional control and rotate at knots. Establish V Y if no obstacles on the climb path. At 500 ft above the ground, turn to crossword leg, maintaining V Y with full power and proper coordination. At 45 degrees from the departure the runway, turn downwind leg, maintaining proper coordination and continue climbing to the pattern altitude (1000 ft AGL). Reaching pattern altitude, level off by lowering the nose to the horizon, let the speed build up to cruise, reduce the power to 2200 RPM, trim as necessary. When established abeam the numbers for the landing runway, begin the prelanding checklist: fuel selector: both, flaps: up, mixture: rich, carburetor heat: on, power 1700 RPM, trim as required and start a shallow descent. Target speed at this moment should be 85 knots. Lower 10 degrees of flaps, trim as necessary and establish 75 knots target altitude 800 ft. At 45 degrees from the landing runway, turn base and set 20 degrees of flaps, trim and obtain 70 knots. Using common sense, turn to final approach, so no overshoot or undershoot results, considering wings. Set flaps and establish a speed, which in any case should NOT be slower than 60 knots and make all necessary wind corrections. Touch down at the slowest possible speed with no drift and the airplane s longitudinal axis is aligned with the runway centerline. N OTE: A LL C OMMERCIAL PILOT MANEUVERS ALONG WITH THE PTS ARE IN THE JEPPESEN INSTRUMENT/C /COMMERCIAL M ANUAL C HAPTER 14. PLEASE FOLLOW THESE GUIDELINES.
Cessna 172SP & NAV III Maneuvers Checklist
 Cessna 172SP & NAV III Maneuvers Checklist Introduction Power Settings This document is intended to introduce to you the standard method of performing maneuvers in Sunair Aviation s Cessna 172SP and NAV
Cessna 172SP & NAV III Maneuvers Checklist Introduction Power Settings This document is intended to introduce to you the standard method of performing maneuvers in Sunair Aviation s Cessna 172SP and NAV
Cessna 172S. Flight Training Standardization Guide REVISION: ORIGINAL
 Cessna 172S Flight Training Standardization Guide REVISION: ORIGINAL Contents Purpose... 4 Normal and Crosswind Takeoff and Climb... 5 Normal and Crosswind Landing... 6 Soft Field Takeoff and Climb...
Cessna 172S Flight Training Standardization Guide REVISION: ORIGINAL Contents Purpose... 4 Normal and Crosswind Takeoff and Climb... 5 Normal and Crosswind Landing... 6 Soft Field Takeoff and Climb...
BE76 Beechcraft Duchess Maneuvers Checklist
 BE76 Beechcraft Duchess Maneuvers Checklist Introduction Power Settings This document is intended to introduce to you the standard method of performing maneuvers in Sunair Aviation s Beechcraft Duchess
BE76 Beechcraft Duchess Maneuvers Checklist Introduction Power Settings This document is intended to introduce to you the standard method of performing maneuvers in Sunair Aviation s Beechcraft Duchess
Light Sport West Standard Flight Training Procedures for N110GX (Remos GX, 100 H.P.)
 Light Sport West Standard Flight Training Procedures for N110GX (Remos GX, 100 H.P.) Welcome to Light Sport West! Thank you for giving us the opportunity to provide all of your flight training needs. Our
Light Sport West Standard Flight Training Procedures for N110GX (Remos GX, 100 H.P.) Welcome to Light Sport West! Thank you for giving us the opportunity to provide all of your flight training needs. Our
Multi-Engine Training And The PTS
 Multi-Engine Training And The PTS GHAFI John Sollinger/Larry Hendrickson October 28, 2000 Overview FAR differences between original and add-on Multi-Engine PTS Training methods Common training scenarios
Multi-Engine Training And The PTS GHAFI John Sollinger/Larry Hendrickson October 28, 2000 Overview FAR differences between original and add-on Multi-Engine PTS Training methods Common training scenarios
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR FLIGHT STUDENTS
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR FLIGHT STUDENTS This pamphlet provides information to assist flight students in learning standardized procedures at the University of Oklahoma Aviation Department and guidance
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR FLIGHT STUDENTS This pamphlet provides information to assist flight students in learning standardized procedures at the University of Oklahoma Aviation Department and guidance
LAND LIKE A PRO. Jul 10, 2011 19 Comments by John Reid
 LAND LIKE A PRO Jul 10, 2011 19 Comments by John Reid We ve all heard the old adage, Takeoffs are optional; landings are mandatory. Bringing a plane back to the ground safely is a pilot s top goal. Unfortunately,
LAND LIKE A PRO Jul 10, 2011 19 Comments by John Reid We ve all heard the old adage, Takeoffs are optional; landings are mandatory. Bringing a plane back to the ground safely is a pilot s top goal. Unfortunately,
FLIGHT TRAINING (AEROPLANE) BASED ON JAR FCL - PPL(A) FLIGHT INSTRUCTION Syllabus
 FLIGHT TRAINING (AEROPLANE) BASED ON JAR FCL - PPL(A) FLIGHT INSTRUCTION Syllabus for MARSPOLAR, DUBAI UAE Exercise 1 Familiarisation with the aeroplane characteristics of the aeroplane cockpit layout
FLIGHT TRAINING (AEROPLANE) BASED ON JAR FCL - PPL(A) FLIGHT INSTRUCTION Syllabus for MARSPOLAR, DUBAI UAE Exercise 1 Familiarisation with the aeroplane characteristics of the aeroplane cockpit layout
SPORT PILOT TRAINING SYLLABUS
 Checked out from the Members Only Library Page 1 of 13 Society of Aviation and Flight Educators www.safepilots.0rg SPORT PILOT TRAINING SYLLABUS LESSON ONE: INTRODUCTORY FLIGHT TIME: 1 hour Ground Instruction;
Checked out from the Members Only Library Page 1 of 13 Society of Aviation and Flight Educators www.safepilots.0rg SPORT PILOT TRAINING SYLLABUS LESSON ONE: INTRODUCTORY FLIGHT TIME: 1 hour Ground Instruction;
Private Pilot Syllabus
 Private Pilot Syllabus A Roadmap to Change Your Life Forever Featuring King Schools: Private Pilot Knowledge Test Course Private Pilot Practical Test Course Special Subject Takeoff Courses King Schools,
Private Pilot Syllabus A Roadmap to Change Your Life Forever Featuring King Schools: Private Pilot Knowledge Test Course Private Pilot Practical Test Course Special Subject Takeoff Courses King Schools,
ENGINE FIRE / SEVERE DAMAGE / SEPARATION ON TAKEOFF
 ENGINE FIRE / SEVERE DAMAGE / SEPARATION ON TAKEOFF According to RYANAIR Procedures PF PM REMARKS Control the aircraft (FULL T/O thrust can be manually selected) Announce «ENGINE FAILURE» or «ENGINE FIRE»
ENGINE FIRE / SEVERE DAMAGE / SEPARATION ON TAKEOFF According to RYANAIR Procedures PF PM REMARKS Control the aircraft (FULL T/O thrust can be manually selected) Announce «ENGINE FAILURE» or «ENGINE FIRE»
AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE Pressure Altitude And Density Altitude
 Performance- Page 67 AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE Pressure Altitude And Density Altitude Pressure altitude is indicated altitude corrected for nonstandard pressure. It is determined by setting 29.92 in the altimeter
Performance- Page 67 AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE Pressure Altitude And Density Altitude Pressure altitude is indicated altitude corrected for nonstandard pressure. It is determined by setting 29.92 in the altimeter
High Alpha 3D Maneuvers
 High Alpha 3D Maneuvers Harrier Pass Elevator Back Flip Parachute Whip Stalls Rolling Harrier 3D Rolling Turn 3D Knife Edge C-82 Rudder Warmup Note: Every flight mode and maneuver presented in this section
High Alpha 3D Maneuvers Harrier Pass Elevator Back Flip Parachute Whip Stalls Rolling Harrier 3D Rolling Turn 3D Knife Edge C-82 Rudder Warmup Note: Every flight mode and maneuver presented in this section
General Characteristics
 This is the third of a series of Atlantic Sun Airways CAT C pilot procedures and checklists for our fleet. Use them with good judgment. Note, the start procedures may vary from FS9 Panel to Panel. However
This is the third of a series of Atlantic Sun Airways CAT C pilot procedures and checklists for our fleet. Use them with good judgment. Note, the start procedures may vary from FS9 Panel to Panel. However
This is the fourth of a series of Atlantic Sun Airways CAT B pilot procedures and checklists for our fleet. Use them with good judgment.
 This is the fourth of a series of Atlantic Sun Airways CAT B pilot procedures and checklists for our fleet. Use them with good judgment. Dimensions: Wing Span: 112 ft 7 in Length: 129 ft 6 in Height: 41
This is the fourth of a series of Atlantic Sun Airways CAT B pilot procedures and checklists for our fleet. Use them with good judgment. Dimensions: Wing Span: 112 ft 7 in Length: 129 ft 6 in Height: 41
AIRCRAFT GENERAL www.theaviatornetwork.com GTM 1.1 2005 1-30-05 CONTENTS
 www.theaviatornetwork.com GTM 1.1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1.2 GENERAL AIRPLANE... 1.2 Fuselage... 1.2 Wing... 1.2 Tail... 1.2 PROPELLER TIP CLEARANCE... 1.2 LANDING GEAR STRUT EXTENSION (NORMAL)... 1.2
www.theaviatornetwork.com GTM 1.1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1.2 GENERAL AIRPLANE... 1.2 Fuselage... 1.2 Wing... 1.2 Tail... 1.2 PROPELLER TIP CLEARANCE... 1.2 LANDING GEAR STRUT EXTENSION (NORMAL)... 1.2
Compiled by Matt Zagoren
 The information provided in this document is to be used during simulated flight only and is not intended to be used in real life. Attention VA's - you may post this file on your site for download. Please
The information provided in this document is to be used during simulated flight only and is not intended to be used in real life. Attention VA's - you may post this file on your site for download. Please
This section includes performance data on the King Air B200. Information consists of:
 King Air B200 POH Pilot's Operating Handbook: This section includes performance data on the King Air B200. Information consists of: 1. Critical Airspeeds 2. Operating NOTAMS 3. Fuel Loading Formula Checklists:
King Air B200 POH Pilot's Operating Handbook: This section includes performance data on the King Air B200. Information consists of: 1. Critical Airspeeds 2. Operating NOTAMS 3. Fuel Loading Formula Checklists:
APPENDIX 3-B Airplane Upset Recovery Briefing. Briefing. Figure 3-B.1
 APPENDIX 3-B Airplane Upset Recovery Briefing Industry Solutions for Large Swept-Wing Turbofan Airplanes Typically Seating More Than 100 Passengers Briefing Figure 3-B.1 Revision 1_August 2004 Airplane
APPENDIX 3-B Airplane Upset Recovery Briefing Industry Solutions for Large Swept-Wing Turbofan Airplanes Typically Seating More Than 100 Passengers Briefing Figure 3-B.1 Revision 1_August 2004 Airplane
FLYBLOCKTIME PA-28-140/160 Aircraft Type Checkout and Currency Quiz. NOTE: There may be one or more correct answers to each question.
 FLYBLOCKTIME PA-28-140/160 Aircraft Type Checkout and Currency Quiz Pilot s Name Date NOTE: There may be one or more correct answers to each question. 1 ) The engine in a PA-28-140/160 is a A. Continental
FLYBLOCKTIME PA-28-140/160 Aircraft Type Checkout and Currency Quiz Pilot s Name Date NOTE: There may be one or more correct answers to each question. 1 ) The engine in a PA-28-140/160 is a A. Continental
This is the third of a series of Atlantic Sun Airways CAT B pilot procedures and checklists for our fleet. Use them with good judgment.
 This is the third of a series of Atlantic Sun Airways CAT B pilot procedures and checklists for our fleet. Use them with good judgment. Dimensions: Span 107 ft 10 in Length 147 ft 10 in Height 29ft 7 in
This is the third of a series of Atlantic Sun Airways CAT B pilot procedures and checklists for our fleet. Use them with good judgment. Dimensions: Span 107 ft 10 in Length 147 ft 10 in Height 29ft 7 in
TAXI, TAKEOFF, CLIMB, CRUISE, DESCENT & LANDING
 OPERATIONS MANUAL FLT CREW TRAINING COMMERCIAL LEVEL SIMULATIONS TAXI, TAKEOFF, CLIMB, CRUISE, DESCENT & LANDING Commercial Level Simulations www.commerciallevel.com 1 Disclaimer This manual is not provided
OPERATIONS MANUAL FLT CREW TRAINING COMMERCIAL LEVEL SIMULATIONS TAXI, TAKEOFF, CLIMB, CRUISE, DESCENT & LANDING Commercial Level Simulations www.commerciallevel.com 1 Disclaimer This manual is not provided
Lesson 7: Your First Solo
 Page 1 of 7 Lesson 7: Your First Solo Fly This Lesson Now by Rod Machado One of the greatest pleasures a flight instructor can have is to solo a student. Since you are my student, I have the great pleasure
Page 1 of 7 Lesson 7: Your First Solo Fly This Lesson Now by Rod Machado One of the greatest pleasures a flight instructor can have is to solo a student. Since you are my student, I have the great pleasure
Introduction. The Normal Takeoff. The Critical Engine. Flying Light Twins Safely
 Note: The graphics and some of the material in this document have been modified from the original printed version. Introduction The major difference between flying a light twin and a single-engine airplane
Note: The graphics and some of the material in this document have been modified from the original printed version. Introduction The major difference between flying a light twin and a single-engine airplane
Flightlab Ground School 5. Longitudinal Static Stability
 Flightlab Ground School 5. Longitudinal Static Stability Copyright Flight Emergency & Advanced Maneuvers Training, Inc. dba Flightlab, 2009. All rights reserved. For Training Purposes Only Longitudinal
Flightlab Ground School 5. Longitudinal Static Stability Copyright Flight Emergency & Advanced Maneuvers Training, Inc. dba Flightlab, 2009. All rights reserved. For Training Purposes Only Longitudinal
B777. Automatic Flight DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT
 B777 Automatic Flight DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT 4.10 Automatic Flight-Controls and Indicators Mode Control Panel (MCP) A/T ARM L R IAS MACH HDG TRK V/S FPA ALTITUDE A/P F/D ON OFF CLB CON IAS LNAV VNAV AUTO
B777 Automatic Flight DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT 4.10 Automatic Flight-Controls and Indicators Mode Control Panel (MCP) A/T ARM L R IAS MACH HDG TRK V/S FPA ALTITUDE A/P F/D ON OFF CLB CON IAS LNAV VNAV AUTO
Aerospace Engineering 3521: Flight Dynamics. Prof. Eric Feron Homework 6 due October 20, 2014
 Aerospace Engineering 3521: Flight Dynamics Prof. Eric Feron Homework 6 due October 20, 2014 1 Problem 1: Lateral-directional stability of Navion With the help of Chapter 2 of Nelson s textbook, we established
Aerospace Engineering 3521: Flight Dynamics Prof. Eric Feron Homework 6 due October 20, 2014 1 Problem 1: Lateral-directional stability of Navion With the help of Chapter 2 of Nelson s textbook, we established
CESSNA 172 CHECKLIST TAXI PRE-EXTERNAL CHECKS. 1. Lights - As required 2. Brakes - CHECK 3. Rolling Instruments Check - L/R
 CESSNA 172 CHECKLIST PRE-EXTERNAL CHECKS TAXI 1. Wing & Engine covers - REMOVED 2. Control lock - REMOVED 3. Trim Check - Full Movement 4. Master - BATTERY ONLY - On 5. Flaps - Down to 20 Degrees 6. Lights
CESSNA 172 CHECKLIST PRE-EXTERNAL CHECKS TAXI 1. Wing & Engine covers - REMOVED 2. Control lock - REMOVED 3. Trim Check - Full Movement 4. Master - BATTERY ONLY - On 5. Flaps - Down to 20 Degrees 6. Lights
Aviation Supplies & Academics, Inc. 7005 132nd Place SE Newcastle, Washington 98059-3153 www.asa2fly.com
 The Pilot s Manual 1: Flight School Aviation Supplies & Academics, Inc. 7005 132nd Place SE Newcastle, Washington 98059-3153 www.asa2fly.com Originally published by Aviation Theory Centre 1990 1993. Fourth
The Pilot s Manual 1: Flight School Aviation Supplies & Academics, Inc. 7005 132nd Place SE Newcastle, Washington 98059-3153 www.asa2fly.com Originally published by Aviation Theory Centre 1990 1993. Fourth
Oral Preparation Questions
 Oral Preparation Questions The oral section of the practical test is the time when you need to demonstrate your understanding of the various tasks listed in the practical test standards and the factors
Oral Preparation Questions The oral section of the practical test is the time when you need to demonstrate your understanding of the various tasks listed in the practical test standards and the factors
2014 NIFA CRM Contestant Briefing Guide San Diego, California
 2014 NIFA CRM Contestant Briefing Guide San Diego, California Region 2 SAFECON 2014 November 12 15 This document supports the 2014 NIFA Collegiate Cockpit Resource Management Simulation and is not for
2014 NIFA CRM Contestant Briefing Guide San Diego, California Region 2 SAFECON 2014 November 12 15 This document supports the 2014 NIFA Collegiate Cockpit Resource Management Simulation and is not for
This file contains the full script of the corresponding video, published on YouTube. November 2014: http://youtu.be/wbu6x0hsnby
 This file contains the full script of the corresponding video, published on YouTube. November 2014: http://youtu.be/wbu6x0hsnby Background papers and links to formal FAA and EASA Aviation Regulations and
This file contains the full script of the corresponding video, published on YouTube. November 2014: http://youtu.be/wbu6x0hsnby Background papers and links to formal FAA and EASA Aviation Regulations and
BOMBARDIER CRJ700. Bombardier CRJ700 Aircraft Reference
 Bombardier CRJ700 Aircraft Reference V 1 Takeoff Decision Speed, dry runway 50,000 lbs, (flaps 8) 144 KIAS 50,000 lbs, (flaps 20) 134 KIAS V R Rotation Speed, dry runway 50,000 lbs, (flaps 8) 144 KIAS
Bombardier CRJ700 Aircraft Reference V 1 Takeoff Decision Speed, dry runway 50,000 lbs, (flaps 8) 144 KIAS 50,000 lbs, (flaps 20) 134 KIAS V R Rotation Speed, dry runway 50,000 lbs, (flaps 8) 144 KIAS
Exam questions for obtaining aircraft licenses and ratings
 Exam questions for obtaining aircraft licenses and ratings Subject: PPL (A) Flight performance and planning Revision 1 07.10.2009. Period of validity: 01 January 2010 th - 31 December 2010 th Belgrade
Exam questions for obtaining aircraft licenses and ratings Subject: PPL (A) Flight performance and planning Revision 1 07.10.2009. Period of validity: 01 January 2010 th - 31 December 2010 th Belgrade
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
 Chapter 10 Advanced Flight Maneuvers Introduction The maneuvers presented in this chapter require more skill and understanding of the helicopter and the surrounding environment. When performing these maneuvers,
Chapter 10 Advanced Flight Maneuvers Introduction The maneuvers presented in this chapter require more skill and understanding of the helicopter and the surrounding environment. When performing these maneuvers,
NIFA NATIONAL SAFECON
 NIFA NATIONAL SAFECON 2007 Manual Flight Computer Accuracy Explanations Note to competitor: This will offer some basic help in solving the problems on the test. There is often more than one way to correctly
NIFA NATIONAL SAFECON 2007 Manual Flight Computer Accuracy Explanations Note to competitor: This will offer some basic help in solving the problems on the test. There is often more than one way to correctly
S-Tec System Thirty Autopilot
 Cirrus Design Section 9 Pilot s Operating Handbook and FAA Approved Airplane Flight Manual Supplement for S-Tec System Thirty Autopilot When the S-Tec System Thirty Autopilot is installed in the Cirrus
Cirrus Design Section 9 Pilot s Operating Handbook and FAA Approved Airplane Flight Manual Supplement for S-Tec System Thirty Autopilot When the S-Tec System Thirty Autopilot is installed in the Cirrus
Flight Safety Foundation. Approach-and-landing Accident Reduction. Tool Kit. FSF ALAR Briefing Note 4.2 Energy Management
 Flight Safety Foundation Approach-and-landing Accident Reduction Tool Kit FSF ALAR Briefing Note 4.2 Energy Management The flight crew s inability to assess or to manage the aircraft s energy condition
Flight Safety Foundation Approach-and-landing Accident Reduction Tool Kit FSF ALAR Briefing Note 4.2 Energy Management The flight crew s inability to assess or to manage the aircraft s energy condition
3. FLYING TECHNIQUES. 3.1 Speed Management. 3.2 Attitude Management. 3.3 Height Management. 3.4 Transit Flying
 3. FLYING TECHNIQUES 3.1 Speed Management Maintaining an appropriate airspeed can be very challenging in mountainous terrain. Pilots need to be aware of the speed limitations from the RFM especially in
3. FLYING TECHNIQUES 3.1 Speed Management Maintaining an appropriate airspeed can be very challenging in mountainous terrain. Pilots need to be aware of the speed limitations from the RFM especially in
Flight Operations Briefing Notes
 Flight Operations Briefing Note I Introduction Operations in crosswind conditions require strict adherence to applicable crosswind limitations or maximum recommended crosswind values, operational recommendations
Flight Operations Briefing Note I Introduction Operations in crosswind conditions require strict adherence to applicable crosswind limitations or maximum recommended crosswind values, operational recommendations
VFR Day Emergencies - C172R
 Pilot Level: References: Note: VFR Day Emergencies - C172R Student Pilot. FAA-H-8083-3A, Chapter 16, Federal Aviation Regulations, Cessna 172R PIM, Aeronautical Information Manual, King Schools (DVDs):
Pilot Level: References: Note: VFR Day Emergencies - C172R Student Pilot. FAA-H-8083-3A, Chapter 16, Federal Aviation Regulations, Cessna 172R PIM, Aeronautical Information Manual, King Schools (DVDs):
Mountain Air Country Club Pilot s Manual Version 1.07 Mountain Air Pilots Association
 Mountain Air Country Club Pilot s Manual Version 1.07 Mountain Air Pilots Association John M. Cuckler, Editor Educational Committee: John Ransom, Eddie Franco, Doug Pilkington, Clark Jernigan, Lionel Kuhn
Mountain Air Country Club Pilot s Manual Version 1.07 Mountain Air Pilots Association John M. Cuckler, Editor Educational Committee: John Ransom, Eddie Franco, Doug Pilkington, Clark Jernigan, Lionel Kuhn
FLIGHT CONTROLS 1. GENERAL 2. MAIN COMPONENTS AND SUBSYSTEMS ROLL CONTROL. Smartcockpit.com BOEING 737 SYSTEMS REVIEW Page 1
 Smartcockpit.com BOEING 737 SYSTEMS REVIEW Page 1 FLIGHT CONTROLS 1. GENERAL The primary flight controls, ailerons, elevators and rudders, are hydraulically powered. Hydraulic power is provided from hydraulic
Smartcockpit.com BOEING 737 SYSTEMS REVIEW Page 1 FLIGHT CONTROLS 1. GENERAL The primary flight controls, ailerons, elevators and rudders, are hydraulically powered. Hydraulic power is provided from hydraulic
Turbulence: The Invisible Hazard presented by Scott Miller PIA Symposium 2005 Jacksonville, Florida, USA
 1300 E. International Speedway Blvd DeLand, FL 32724 USA Tel: +1.386.738.2224 Fax: +1.734.8297 www.performancedesigns.com Turbulence: The Invisible Hazard presented by Scott Miller PIA Symposium 2005 Jacksonville,
1300 E. International Speedway Blvd DeLand, FL 32724 USA Tel: +1.386.738.2224 Fax: +1.734.8297 www.performancedesigns.com Turbulence: The Invisible Hazard presented by Scott Miller PIA Symposium 2005 Jacksonville,
Multi Engine Oral Exam Questions
 Multi Engine Oral Exam Questions 1. What are the requirements for a multi-engine rating? 2. What is the max rated horse power at sea level? At 12,000 msl? 3. What is the rated engine speed? 4. What is
Multi Engine Oral Exam Questions 1. What are the requirements for a multi-engine rating? 2. What is the max rated horse power at sea level? At 12,000 msl? 3. What is the rated engine speed? 4. What is
Helicopter Emergencies and Hazards
 Chapter 11 Helicopter Emergencies and Hazards Introduction Today, helicopters are quite reliable. However, emergencies do occur, whether a result of mechanical failure or pilot error, and should be anticipated.
Chapter 11 Helicopter Emergencies and Hazards Introduction Today, helicopters are quite reliable. However, emergencies do occur, whether a result of mechanical failure or pilot error, and should be anticipated.
FLIGHT TEST SCHEDULE. Pagina 1 of 5. Examiner(s): TRAINING/SKILL TEST/PROFICIENCY CHECK. single pilot aeroplanes (except HPA complex aeroplanes)
 A SECTION 1 1 Departure 1.1 Pre-flight including: Documentation ass and Balance Weather briefing NOTA 1.2 Pre-start checks P 1.2.1 External P# P 1.2.2 Internal P 1.3 Engine starting: Normal alfunctions
A SECTION 1 1 Departure 1.1 Pre-flight including: Documentation ass and Balance Weather briefing NOTA 1.2 Pre-start checks P 1.2.1 External P# P 1.2.2 Internal P 1.3 Engine starting: Normal alfunctions
Multi-Engine Class Rating
 TP 219E (04/2010) Flight Test Guide Multi-Engine Class Rating Aeroplane Seventh Edition April 2010 TC-1003710 *TC-1003710* Please direct your comments, orders and inquiries to: The Order Desk MultiMedia
TP 219E (04/2010) Flight Test Guide Multi-Engine Class Rating Aeroplane Seventh Edition April 2010 TC-1003710 *TC-1003710* Please direct your comments, orders and inquiries to: The Order Desk MultiMedia
Commercial Pilot Licence
 TP 13462E (04/2010) Flight Test Guide Commercial Pilot Licence Aeroplane Third Edition April 2010 TC-1003716 *TC-1003716* Please direct your comments, orders and inquiries to: The Order Desk MultiMedia
TP 13462E (04/2010) Flight Test Guide Commercial Pilot Licence Aeroplane Third Edition April 2010 TC-1003716 *TC-1003716* Please direct your comments, orders and inquiries to: The Order Desk MultiMedia
Automation at Odds. A 737 stalled when a radio altimeter malfunction caused the autothrottle and autopilot to diverge during an approach to Schiphol.
 Automation at Odds The pilots of a Boeing 737-800 did not heed indications of a significant decrease in airspeed until the stick shaker activated on final approach to Runway 18R at Amsterdam (Netherlands)
Automation at Odds The pilots of a Boeing 737-800 did not heed indications of a significant decrease in airspeed until the stick shaker activated on final approach to Runway 18R at Amsterdam (Netherlands)
MEMO AIRBUS A319/A320/A321. SOP / Flow Pattern
 MEMO AIRBUS A319/A320/A321 SOP / Flow Pattern F/O side only ( or ) A320 Flow Pattern SOP Visual Pattern Engine Out Memory Items Emergency procedures Laurent ALAPHILIPPE Page 1/18 Année 2011 Summary Memo
MEMO AIRBUS A319/A320/A321 SOP / Flow Pattern F/O side only ( or ) A320 Flow Pattern SOP Visual Pattern Engine Out Memory Items Emergency procedures Laurent ALAPHILIPPE Page 1/18 Année 2011 Summary Memo
The SeaRey - An Introduction
 The SeaRey - An Introduction Welcome to the beautiful Progressive Aerodyne SeaRey. The SeaRey is a very special aircraft. Created by a small team of engineers the SeaRey is perhaps the ultimate kit built
The SeaRey - An Introduction Welcome to the beautiful Progressive Aerodyne SeaRey. The SeaRey is a very special aircraft. Created by a small team of engineers the SeaRey is perhaps the ultimate kit built
NIFA REGIONAL SAFECON 2006 Manual Flight Computer Accuracy Explanations
 NIFA REGIONAL SAFECON 2006 Manual Flight Computer Accuracy Explanations Note to competitor: This will offer some basic help in solving the problems on the test. There is often more than one way to correctly
NIFA REGIONAL SAFECON 2006 Manual Flight Computer Accuracy Explanations Note to competitor: This will offer some basic help in solving the problems on the test. There is often more than one way to correctly
Certification Specifications for Very Light Aeroplanes CS-VLA
 European Aviation Safety Agency Certification Specifications for Very Light Aeroplanes CS-VLA Amendment 1 5 March 2009 1-0-1 CONTENTS (Layout) CS VLA VERY LIGHT AEROPLANES BOOK 1 AIRWORTHINESS CODE SUBPART
European Aviation Safety Agency Certification Specifications for Very Light Aeroplanes CS-VLA Amendment 1 5 March 2009 1-0-1 CONTENTS (Layout) CS VLA VERY LIGHT AEROPLANES BOOK 1 AIRWORTHINESS CODE SUBPART
Aviation Safety Prize ecfi Tasks
 2008 NASA "The PAV Challenge" Aviation Safety Prize ecfi Tasks The Aviation Safety Prize (ASP) will be based upon a set of defined tasks that can be flight demonstrated to the CAFE Test Pilots by each
2008 NASA "The PAV Challenge" Aviation Safety Prize ecfi Tasks The Aviation Safety Prize (ASP) will be based upon a set of defined tasks that can be flight demonstrated to the CAFE Test Pilots by each
Flight Operations Briefing Notes
 Flight Operations Briefing Notes I Introduction Encountering wake turbulence in flight can be a surprising experience, both for crews and passengers. Wake turbulence occurs suddenly, and is usually accompanied
Flight Operations Briefing Notes I Introduction Encountering wake turbulence in flight can be a surprising experience, both for crews and passengers. Wake turbulence occurs suddenly, and is usually accompanied
European Aviation Safety Agency
 European Aviation Safety Agency ED Decision 2003/2/RM Final 17/10/2003 The Executive Director DECISION NO. 2003/2/RM OF THE EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR OF THE AGENCY of 17 October 2003 on certification specifications,
European Aviation Safety Agency ED Decision 2003/2/RM Final 17/10/2003 The Executive Director DECISION NO. 2003/2/RM OF THE EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR OF THE AGENCY of 17 October 2003 on certification specifications,
a. AC 25-7, Flight Test Guide for Certification of Transport Category Airplanes.
 U.S. Department of Transportation Federal Aviation Administration Advisory Circular Subject: Runway Overrun Prevention Date: 11/06/07 Initiated by: AFS-800 AC No: 91-79 Change: 1. PURPOSE. This advisory
U.S. Department of Transportation Federal Aviation Administration Advisory Circular Subject: Runway Overrun Prevention Date: 11/06/07 Initiated by: AFS-800 AC No: 91-79 Change: 1. PURPOSE. This advisory
CHAPTER 7 CLIMB PERFORMANCE
 CHAPTER 7 CLIMB PERFORMANCE 7 CHAPTER 7 CLIMB PERFORMANCE PAGE 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.1 7.2 PURPOSE OF TEST 7.1 7.3 THEORY 7.2 7.3.1 SAWTOOTH CLIMBS 7.2 7.3.2 STEADY STATE APPROACH TO CLIMB PERFORMANCE 7.4
CHAPTER 7 CLIMB PERFORMANCE 7 CHAPTER 7 CLIMB PERFORMANCE PAGE 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.1 7.2 PURPOSE OF TEST 7.1 7.3 THEORY 7.2 7.3.1 SAWTOOTH CLIMBS 7.2 7.3.2 STEADY STATE APPROACH TO CLIMB PERFORMANCE 7.4
AVIATION OCCURRENCE REPORT A98W0192 ENGINE FAILURE
 Transportation Safety Board of Canada Bureau de la sécurité des transports du Canada AVIATION OCCURRENCE REPORT A98W0192 ENGINE FAILURE MARTINAIR HOLLAND N.V. BOEING 767-300 PH-MCI CALGARY INTERNATIONAL
Transportation Safety Board of Canada Bureau de la sécurité des transports du Canada AVIATION OCCURRENCE REPORT A98W0192 ENGINE FAILURE MARTINAIR HOLLAND N.V. BOEING 767-300 PH-MCI CALGARY INTERNATIONAL
Basic Aviation Training Device
 FLYIT SIMULATORS, Inc. Basic Aviation Training Device Model PHS - 1 FLYIT Simulators Inc. 5931Sea Lion Pl #110 Carlsbad, CA 92010 USA Revised on 10/30/2014 Page 1 of 53 Device Description and Overview
FLYIT SIMULATORS, Inc. Basic Aviation Training Device Model PHS - 1 FLYIT Simulators Inc. 5931Sea Lion Pl #110 Carlsbad, CA 92010 USA Revised on 10/30/2014 Page 1 of 53 Device Description and Overview
Science in. Wind WHAT S GOING ON? In the Terminal or in the Airplane. Try This:
 Science in Your Airplane Seat Why are airplane wings shaped the way they are? What can pretzels tell you about flying? Instead of catching a nap or flipping through the in-flight magazine, do some experiments
Science in Your Airplane Seat Why are airplane wings shaped the way they are? What can pretzels tell you about flying? Instead of catching a nap or flipping through the in-flight magazine, do some experiments
OPERATIONS CIRCULAR. OC NO 2 OF 2014 Date: 1 st May 2014. Continuous Descent Final Approach (CDFA) 1. PURPOSE
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA CIVIL AVIATION DEPARTMENT DIRECTOR GENERAL OF CIVIL AVIATION OC NO 2 OF 2014 Date: 1 st May 2014 OPERATIONS CIRCULAR Subject: Continuous Descent Final Approach (CDFA) 1. PURPOSE This
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA CIVIL AVIATION DEPARTMENT DIRECTOR GENERAL OF CIVIL AVIATION OC NO 2 OF 2014 Date: 1 st May 2014 OPERATIONS CIRCULAR Subject: Continuous Descent Final Approach (CDFA) 1. PURPOSE This
Cessna Skyhawk II / 100. Performance Assessment
 Cessna Skyhawk II / 100 Performance Assessment Prepared by John McIver B.Eng.(Aero) Temporal Images 23rd January 2003 http://www.temporal.com.au Cessna Skyhawk II/100 (172) Performance Assessment 1. Introduction
Cessna Skyhawk II / 100 Performance Assessment Prepared by John McIver B.Eng.(Aero) Temporal Images 23rd January 2003 http://www.temporal.com.au Cessna Skyhawk II/100 (172) Performance Assessment 1. Introduction
CUB CRAFTERS, INC. CC11-160 PILOT S OPERATING HANDBOOK AND FLIGHT TRAINING SUPPLEMENT
 CUB CRAFTERS CUB CRAFTERS, INC. PILOT S OPERATING HANDBOOK AND FLIGHT TRAINING SUPPLEMENT Airplane Serial Number: Airplane Registration Number: This airplane is approved as a special light-sport category
CUB CRAFTERS CUB CRAFTERS, INC. PILOT S OPERATING HANDBOOK AND FLIGHT TRAINING SUPPLEMENT Airplane Serial Number: Airplane Registration Number: This airplane is approved as a special light-sport category
Amendment List Date Amended by Incorporated No Date 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 i
 No Amendment List Date Amended by Date Incorporated 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 i ACP 33 FLIGHT CONTENTS Volume 1... History of Flight Volume 2... Principles of Flight Volume 3... Propulsion
No Amendment List Date Amended by Date Incorporated 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 i ACP 33 FLIGHT CONTENTS Volume 1... History of Flight Volume 2... Principles of Flight Volume 3... Propulsion
Certification Specifications for Large Rotorcraft CS-29
 European Aviation Safety Agency Certification Specifications for Large Rotorcraft CS-29 11 December 2012 CS-29 CONTENTS (general layout) CS 29 LARGE ROTORCRAFT BOOK 1 CERTIFICATION SPECIFICATIONS SUBPART
European Aviation Safety Agency Certification Specifications for Large Rotorcraft CS-29 11 December 2012 CS-29 CONTENTS (general layout) CS 29 LARGE ROTORCRAFT BOOK 1 CERTIFICATION SPECIFICATIONS SUBPART
Winch Launching of Gliders. An Introduction To A Rather Un-American Activity
 Winch Launching of Gliders An Introduction To A Rather Un-American Activity 2 Herbert Kilian, Chicago Glider Club 3 Herbert Kilian, Chicago Glider Club 4 Herbert Kilian, Chicago Glider Club 5 Herbert Kilian,
Winch Launching of Gliders An Introduction To A Rather Un-American Activity 2 Herbert Kilian, Chicago Glider Club 3 Herbert Kilian, Chicago Glider Club 4 Herbert Kilian, Chicago Glider Club 5 Herbert Kilian,
Teacher Edition. Written By Tom Dubick. 2011 by Fly To Learn. All rights reserved.
 Teacher Edition Written By Tom Dubick TABLE OF CONTENTS First Flight... 3 May The Force(s) Be With You... 9 Lift A Real Pick Me Up... 17 What a Drag, Man... 23 Thrust It s All About Altitude... 29 Flight
Teacher Edition Written By Tom Dubick TABLE OF CONTENTS First Flight... 3 May The Force(s) Be With You... 9 Lift A Real Pick Me Up... 17 What a Drag, Man... 23 Thrust It s All About Altitude... 29 Flight
Microlight Accident and Incident Summary 01/2010
 Microlight and Incident Summary 01/2010 This accident report summary is collated by the BMAA from information gathered. The information sources used are the Air Investigation Branch of the Department for
Microlight and Incident Summary 01/2010 This accident report summary is collated by the BMAA from information gathered. The information sources used are the Air Investigation Branch of the Department for
B777. Landing Gear DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT
 B777 Landing Gear DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT Introduction The airplane has two main landing gear and a single nose gear. The nose gear is a conventional steerable two wheel unit. Each main gear has six wheels
B777 Landing Gear DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT Introduction The airplane has two main landing gear and a single nose gear. The nose gear is a conventional steerable two wheel unit. Each main gear has six wheels
Cherokee Archer II Pilot s Operating Handbook
 Cherokee Archer II Pilot s Operating Handbook Cherokee Archer II PA-28-181 Handbook Part No. 761 624 New Piper Aircraft And The Notre Dame Pilot Initiative Partners in Aviation Education Not to be used
Cherokee Archer II Pilot s Operating Handbook Cherokee Archer II PA-28-181 Handbook Part No. 761 624 New Piper Aircraft And The Notre Dame Pilot Initiative Partners in Aviation Education Not to be used
SLEIGH I & II L I S T OF CONTENTS
 SLEIGH I & II L I S T OF CONTENTS P A RT I DESCRIPTIVE I NTRODUCTION 5 F UEL SYSTEMS 5 AIRCRAFT CONTROLS 5 E N GINE CONTROLS 6 P A RT II HANDLING P r e - f l i g h t checklist 7 S t a r t i n g t h e engines
SLEIGH I & II L I S T OF CONTENTS P A RT I DESCRIPTIVE I NTRODUCTION 5 F UEL SYSTEMS 5 AIRCRAFT CONTROLS 5 E N GINE CONTROLS 6 P A RT II HANDLING P r e - f l i g h t checklist 7 S t a r t i n g t h e engines
King Air C90A. Speeds (KIAS)
 King Air C90A Speeds (KIAS) V MCA 90 V SSE 97 V X 101 V Y 111 V XSE 100 V YSE 107 V A 169 V REF 100 V MO 208 V FE 178 35% 137 100% V LE 156 129 Retraction only Other 95 Balked landing climb 125 Glide 161
King Air C90A Speeds (KIAS) V MCA 90 V SSE 97 V X 101 V Y 111 V XSE 100 V YSE 107 V A 169 V REF 100 V MO 208 V FE 178 35% 137 100% V LE 156 129 Retraction only Other 95 Balked landing climb 125 Glide 161
VARIABLE STABILITY FLIGHT OPERATIONS MANUAL
 SPACE INSTITUTE VARIABLE STABILITY FLIGHT OPERATIONS MANUAL Prepared by the Aviation Systems and Flight Research Department September 2004 Index 1.1 General Description...1 1.2 Variable Stability System...5
SPACE INSTITUTE VARIABLE STABILITY FLIGHT OPERATIONS MANUAL Prepared by the Aviation Systems and Flight Research Department September 2004 Index 1.1 General Description...1 1.2 Variable Stability System...5
For Flight Simulation purposes only on the VATSIM Network.
 Compiled by Daniel A. Hawton, ZDC Training Administrator For Flight Simulation purposes only on the VATSIM Network. Introduction The goal of the document is to introduce you, the controller, to the appropriate
Compiled by Daniel A. Hawton, ZDC Training Administrator For Flight Simulation purposes only on the VATSIM Network. Introduction The goal of the document is to introduce you, the controller, to the appropriate
Mathematically Modeling Aircraft Fuel Consumption
 Mathematically Modeling Aircraft Fuel Consumption by Kevin Pyatt, Department of Education Jacqueline Coomes, Department of Mathematics Eastern Washington University, Cheney, WA CoCal Airlines April 9,
Mathematically Modeling Aircraft Fuel Consumption by Kevin Pyatt, Department of Education Jacqueline Coomes, Department of Mathematics Eastern Washington University, Cheney, WA CoCal Airlines April 9,
AVIATION OCCURRENCE REPORT
 AVIATION OCCURRENCE REPORT REJECTED LANDING/LOSS OF CONTROL FIRST AIR DHC-6 SERIES 300 C-GNDN IQALUIT, NORTHWEST TERRITORIES 85 NM NW 12 AUGUST 1996 REPORT NUMBER A96Q0126 The Transportation Safety Board
AVIATION OCCURRENCE REPORT REJECTED LANDING/LOSS OF CONTROL FIRST AIR DHC-6 SERIES 300 C-GNDN IQALUIT, NORTHWEST TERRITORIES 85 NM NW 12 AUGUST 1996 REPORT NUMBER A96Q0126 The Transportation Safety Board
Avro RJ100, HB-IYU. 47 years
 ACCIDENT Aircraft Type and Registration: No & Type of Engines: Avro RJ100, HB-IYU 4 Honeywell ALF507-1F turbofan engines Year of Manufacture: 2000 Date & Time (UTC): Location: Type of Flight: 18 August
ACCIDENT Aircraft Type and Registration: No & Type of Engines: Avro RJ100, HB-IYU 4 Honeywell ALF507-1F turbofan engines Year of Manufacture: 2000 Date & Time (UTC): Location: Type of Flight: 18 August
Municipal Airport 1410 Arizona Place S.W. Orange City, IA 51041-7453. www.angelaircraft.com aac@angelaircraft.com 712.737.3344
 Municipal Airport 1410 Arizona Place S.W. Orange City, IA 51041-7453 www.angelaircraft.com aac@angelaircraft.com 712.737.3344 PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATIONS POWERPLANT PROPELLER Lycoming IO-540 300 HP @2700
Municipal Airport 1410 Arizona Place S.W. Orange City, IA 51041-7453 www.angelaircraft.com aac@angelaircraft.com 712.737.3344 PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATIONS POWERPLANT PROPELLER Lycoming IO-540 300 HP @2700
Lab 8 Notes Basic Aircraft Design Rules 6 Apr 06
 Lab 8 Notes Basic Aircraft Design Rules 6 Apr 06 Nomenclature x, y longitudinal, spanwise positions S reference area (wing area) b wing span c average wing chord ( = S/b ) AR wing aspect ratio C L lift
Lab 8 Notes Basic Aircraft Design Rules 6 Apr 06 Nomenclature x, y longitudinal, spanwise positions S reference area (wing area) b wing span c average wing chord ( = S/b ) AR wing aspect ratio C L lift
The Case for Mode 4 Transmitters, or, "How North America Got It Wrong", or, "How Most of the Planet Got It Wrong"
 The Case for Mode 4 Transmitters, or, "How North America Got It Wrong", or, "How Most of the Planet Got It Wrong" Martin Newell October 2009 Updated October 2010 The great majority of RC pilots in North
The Case for Mode 4 Transmitters, or, "How North America Got It Wrong", or, "How Most of the Planet Got It Wrong" Martin Newell October 2009 Updated October 2010 The great majority of RC pilots in North
FLIGHT SIMULATOR QUICK START GUIDE
 FLIGHT SIMULATOR QUICK START GUIDE XPlane 10 Developed by: Laminar Research Copyright: 2012/ Aerosoft GmbH Airport Paderborn/Lippstadt D33142 Bueren, Germany Tel: +49 (0) 29 55 / 76 0310 Fax: +49 (0) 29
FLIGHT SIMULATOR QUICK START GUIDE XPlane 10 Developed by: Laminar Research Copyright: 2012/ Aerosoft GmbH Airport Paderborn/Lippstadt D33142 Bueren, Germany Tel: +49 (0) 29 55 / 76 0310 Fax: +49 (0) 29
CENTURY III AUTOPILOT FLIGHT SYSTEM
 CENTURY III AUTOPILOT FLIGHT SYSTEM PILOT S OPERATING HANDBOOK NOVEMBER 1998 68S25 NOTICE 68S25 This manual contains General Information on operation of Century III Autopilot. specific FAA approved information
CENTURY III AUTOPILOT FLIGHT SYSTEM PILOT S OPERATING HANDBOOK NOVEMBER 1998 68S25 NOTICE 68S25 This manual contains General Information on operation of Century III Autopilot. specific FAA approved information
CAAP 89W-1(0) Guidelines on provision of obstacle information for take-off flight planning purposes
 Civil Aviation Advisory Publication This publication is only advisory. It gives the preferred method for complying with the Civil Aviation Regulations (CAR 1988). It is not the only method, but experience
Civil Aviation Advisory Publication This publication is only advisory. It gives the preferred method for complying with the Civil Aviation Regulations (CAR 1988). It is not the only method, but experience
BRAKE SYSTEM DESIGN AND THEORY
 RAKE SYSTEM DESIGN AND THEORY Aircraft brake systems perform multiple functions. They must be able to hold the aircraft back at full static engine run-up, provide adequate control during ground taxi operations,
RAKE SYSTEM DESIGN AND THEORY Aircraft brake systems perform multiple functions. They must be able to hold the aircraft back at full static engine run-up, provide adequate control during ground taxi operations,
Flight Operations Manual
 451 Airport Road Novato, CA 94945 415-717-1189 Flight Operations Manual Procedures in this publication are derived from procedures in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Approved Airplane Flight
451 Airport Road Novato, CA 94945 415-717-1189 Flight Operations Manual Procedures in this publication are derived from procedures in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Approved Airplane Flight
parts of an airplane Getting on an Airplane BOX Museum Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate in a Series
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration GRADES K-2 Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate Museum in a BOX Series www.nasa.gov parts of an airplane Getting on an Airplane MUSEUM IN A BOX Getting
National Aeronautics and Space Administration GRADES K-2 Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate Museum in a BOX Series www.nasa.gov parts of an airplane Getting on an Airplane MUSEUM IN A BOX Getting
Development of a Flight Test Program for a Homebuilt Zenith STOL CH 701
 Development of a Flight Test Program for a Homebuilt Zenith STOL CH 701 A Senior Project presented to the Faculty of the Aerospace Engineering Department California Polytechnic State University, San Luis
Development of a Flight Test Program for a Homebuilt Zenith STOL CH 701 A Senior Project presented to the Faculty of the Aerospace Engineering Department California Polytechnic State University, San Luis
FOREWORD. Copyright 2010, AOPA Air Safety Foundation
 FOREWORD This booklet is designed to provide pilots and flight instructors with a compact reference guide to frequently used practical test standards and logbook endorsements. Although we ve done our best
FOREWORD This booklet is designed to provide pilots and flight instructors with a compact reference guide to frequently used practical test standards and logbook endorsements. Although we ve done our best
This report is based on research using the AOPA Air Safety Foundation Safety Database, the largest non-governmental
 Flight Instruction Safety: An In-depth Look at Instructional Accidents This report is based on research using the AOPA Air Safety Foundation Safety Database, the largest non-governmental compilation of
Flight Instruction Safety: An In-depth Look at Instructional Accidents This report is based on research using the AOPA Air Safety Foundation Safety Database, the largest non-governmental compilation of
Report. Incident on 2 May 2009 on approach to Antalya (Turkey) to the Boeing 737-300 registered F-GFUF operated by Europe Airpost
 Report Incident on 2 May 2009 on approach to Antalya (Turkey) to the Boeing 737-300 registered F-GFUF operated by Europe Airpost Bureau d Enquêtes et d Analyses pour la sécurité de l aviation civile Ministère
Report Incident on 2 May 2009 on approach to Antalya (Turkey) to the Boeing 737-300 registered F-GFUF operated by Europe Airpost Bureau d Enquêtes et d Analyses pour la sécurité de l aviation civile Ministère
Katana Flight Characteristics and Frequently Asked Questions
 Katana Flight Characteristics and Frequently Asked Questions Introduction Performance Designs Katana is a high-performance canopy designed for experienced canopy pilots. The Katana has been described as
Katana Flight Characteristics and Frequently Asked Questions Introduction Performance Designs Katana is a high-performance canopy designed for experienced canopy pilots. The Katana has been described as
Accident Analysis: Single-pilot versus Two-pilot - Is There a Safety Advantage?
 Accident Analysis: Single-pilot versus Two-pilot - Is There a Safety Advantage? AIN analysis comparing accidents involving one-pilot versus two-pilot business jet operations from 1977 through 2014 reveals,
Accident Analysis: Single-pilot versus Two-pilot - Is There a Safety Advantage? AIN analysis comparing accidents involving one-pilot versus two-pilot business jet operations from 1977 through 2014 reveals,
harbor cub Electric Remote Control Airplane Model 92906 assembly & Operating Instructions
 harbor cub Electric Remote Control Airplane Model 92906 assembly & Operating Instructions IMPORTANT: If damage is caused due to a crash, your warranty is void. Visit our website at: http://www.harborfreight.com
harbor cub Electric Remote Control Airplane Model 92906 assembly & Operating Instructions IMPORTANT: If damage is caused due to a crash, your warranty is void. Visit our website at: http://www.harborfreight.com
File Number MDRA C20 MANUAL of PROCEDURES for INSPECTION of COMPOSITE AMATEUR-BUILT AIRCRAFT, INSPECTION AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION RECORD
 File Number MDRA C20 MANUAL of PROCEDURES for INSPECTION of COMPOSITE AMATEUR-BUILT AIRCRAFT, INSPECTION AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION RECORD GENERAL Section 1.4 FINAL INSPECTION 1. Have all re-inspection
File Number MDRA C20 MANUAL of PROCEDURES for INSPECTION of COMPOSITE AMATEUR-BUILT AIRCRAFT, INSPECTION AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION RECORD GENERAL Section 1.4 FINAL INSPECTION 1. Have all re-inspection
Data Review and Analysis Program (DRAP) Flight Data Visualization Program for Enhancement of FOQA
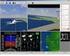 86 Data Review and Analysis Program (DRAP) Flight Data Visualization Program for Enhancement of FOQA Koji MURAOKA and Noriaki OKADA, Flight Systems Research Center, E-mail: muraoka@nal.go.jp Keywords:
86 Data Review and Analysis Program (DRAP) Flight Data Visualization Program for Enhancement of FOQA Koji MURAOKA and Noriaki OKADA, Flight Systems Research Center, E-mail: muraoka@nal.go.jp Keywords:
Understanding Drag, Thrust, and Airspeed relationships
 Understanding Drag, Thrust, and Airspeed relationships Wayne Pratt May 30, 2010 CFII 1473091 The classic curve of drag verses airspeed can be found in any aviation textbook. However, there is little discussion
Understanding Drag, Thrust, and Airspeed relationships Wayne Pratt May 30, 2010 CFII 1473091 The classic curve of drag verses airspeed can be found in any aviation textbook. However, there is little discussion
Survival Skills for Canopy Control A Seminar by Performance Designs, Inc.
 Survival Skills for Canopy Control A Seminar by Performance Designs, Inc. I. Avoid landing accidents by doing all you can to eliminate landing off the DZ. As soon as you're open, evaluate the spot. When
Survival Skills for Canopy Control A Seminar by Performance Designs, Inc. I. Avoid landing accidents by doing all you can to eliminate landing off the DZ. As soon as you're open, evaluate the spot. When
Flight Manual. FM 250 Vampire. Flight Manual
 Flight Manual FM 250 Vampire Flight Manual CONTENT SECTION PAGE 1. General 2. Limitations 3. Normal Procedures 4. Emergency Procedures 5. Performance 6. Airplane Handling, Service & Maintenance Information
Flight Manual FM 250 Vampire Flight Manual CONTENT SECTION PAGE 1. General 2. Limitations 3. Normal Procedures 4. Emergency Procedures 5. Performance 6. Airplane Handling, Service & Maintenance Information
