The Appendix. Dr. Naser El-Hammuri
|
|
|
- Marion Hopkins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Appendix Dr. Naser El-Hammuri
2 Anatomy and Function The relationship of the base of the appendix to cecum remains constant, whereas the tip can be found in a retro-cecal, pelvic, sub-cecal, pre-ileal, or right peri-colic position. The three taenia coli converge at the junction of the cecum with the appendix (useful landmark to identify appendix) Appendix length vary from 1cm 30cm (most appendices are 6cm 9cm) Appendix is a immunologic organ that actively participate in secretion of immunoglobulins, particularly (IgA)
3 Anatomy and Function Appendix is an integral component of gut associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) system, however, its function is not essential and appendectomy is not associated with any predisposition to sepsis or any manifestation of immune compromise.
4 Incidence Life time rate of appendectomy is 12% for men and 25% for women, with approximately 7% of all people undergoing appendectomy for appendicitis Rate of appendectomy for appendicitis is 10 per 10,000 patients per year Appendicitis is most frequently seen in patients in their second through fourth decades of life with mean age of 31.3 years Slight male to female predominance (M:F 1.3:1) The rate of misdiagnosis of is significantly higher among women than men (22.2 vs 9.3%)
5 Etiology and Pathogenesis Obstruction of the lumen is the dominant causal factor in acute appendicitis Fecaliths are the usual cause of appendiceal obstruction Less common causes: - Hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue - Inspissated barium from previous x-ray study - Tumors - Vegetable and fruits seeds - Intestinal parasites
6 Etiology and Pathogenesis The predictable sequence of events leading eventually to appendiceal rupture: Proximal obstruction of appendiceal lumen Closed loop obstruction Continuing normal secretion by appendiceal mucosa rapidly produce distension, (lumen capacity of normal appendix is only 0.1 ml, secretion as little as 0.5 ml raises the lntra-luminal pressure to 60 cm H2O) Distension of the appendix stimulates nerve endings of afferent stretch fibers producing vague, dull, diffuse in the mid-abdomen or lower epigastrium
7 Etiology and Pathogenesis Sudden distension stimulates peristalsis resulting in abdominal cramps that may superimpose on the visceral pain early in the course of acute appendicitis As distention continues from continued mucosal secretion and from rapid multiplication of resident bacteria of appendix Distension of this magnitude causes reflex nausea and vomiting and diffuse visceral pain become more severe As pressure on organ increases, venous pressure is exceeded
8 Etiology and Pathogenesis Capillaries and venules get occluded while arteriolar inflow continues resulting in engorgement and vascular congestion Inflammatory process involves the serosa of appendix and in turn the parietal peritoneum in the region, producing the characteristic shift in pain to right lower quadrant Impairment of arterial supply result in mucosal integrity compromise allowing bacterial invasion Infarct develop in areas with poorest blood supply
9 Etiology and Pathogenesis As distension, bacterial invasion, compromise of arterial supply and infarction progress, perforation occurs, usually through one of the infarcted areas on the antimesenteric border Perforation generally occur just beyond the point of obstruction Some episodes of acute appendicitis may subside spontaneously
10 Bacteriology The principal organisms seen in normal appendix, in acute appendicitis and in perforated appendicitis are Escherichia Coli and Bacteroides Fragilis Appendicitis is polymicrobial infection
11 Clinical Manifestations Symptoms Pain is the prime symptom of acute appendicitis, initially diffusely centered in lower epigastrium or umbilical area, moderately severe with intermittent cramping superimposed After a period varying from 1 12 hours (usually 4 6 hours) the pain localizes to right lower quadrant This classic pain sequence is usual but not invariable Variation in the anatomic location of the appendix responsible for many of the variations in the principal locus of the somatic phase of the pain
12 Clinical Manifestations E.g. long appendix with inflamed tip in left lower quadrant causes pain in this area - Retro-cecal appendix cause flank or back pain - Pelvic appendix causes supra pubic pain - Malrotation somatic component of pain is felt at site where the cecum has been arrested in rotation Anorexia nearly always accompanies appendicitis Vomiting 75% of appendicitis, once or twice and caused secondary to neural stimulation and ileus
13 Clinical Manifestations History of obstipation beginning prior to onset of abdominal pain Diarrhea in some patients (children) Sequence of symptoms - Anorexia is the first symptom (95% of cases) - Followed by abdominal pain - Then vomiting (if vomiting precedes onset of pain, the diagnosis of appendicitis should be questioned)
14 Clinical Manifestations Signs Physical signs are determined principally by the anatomic position of the inflamed appendix, as well as if the organ has already ruptured when the patient is first examined Vital signs minimally changed by uncomplicated appendicitis Patient with appendicitis prefer to lie supine, with thighs, particularly the right thigh, drawn up, as motion cause pain
15 Clinical Manifestations Signs Right lower quadrant signs Tenderness maximal at or near McBurney s point Referred or indirect rebound tenderness indicating localized peritoneal irritation Rovsing s sign Cutaneous hyperasthesia in the area supplied by spinal nerves on the right at T10, T11, and T12 (elicited by needle prick or by gently picking up the skin between forefinger and thumb
16 Clinical Manifestations Signs Muscular resistance to palpation to abdominal wall roughly parallels the severity of inflammatory process, early in disease guarding, if present, consists mainly of voluntary guarding. As peritoneal irritation progresses, muscle spasm increases and becomes largely involuntary, i.e. reflex rigidity due to contraction of muscles directly beneath the inflamed parietal peritoneum
17 Clinical Manifestations Signs Physical signs also depends on the anatomical site of the appendix Retro-cecal appendicitis, the anterior abdominal findings are less striking, with tenderness mainly in the flank Pelvic appendicitis, abdominal findings may be entirely absent, and signs may be missed if rectal examination is not done Psoas sign Obturator sign
18 Laboratory Findings Mild leukocytosis (10,000 18,000), in uncomplicated appendicitis, with polymorphonuclear predominance Higher level of leukocytosis in patients with perforated appendicitis Urine analysis (WBC or RBC may be seen in case of ureteral or bladder irritation) Beta HCG
19 Imaging Studies Plain Films Done to R/O other pathology Abnormal gas pattern (none specific) Fecalith CXR basal pneumonia Barium enema
20 Imaging Studies / Ultrasonography Blind-ending, none-peristaltic, bowel loop originating from cecum None compressible, with anteroposterior diameter of 6mm or greater Presence of appendicolith Thickening of appendiceal wall and peri-appendiceal fluid (demonstration of easily compressible blind ending tubular structure measuring 5 mm or less in diameter excludes the diagnosis of appendicitis)
21 Imaging Studies / Ultrasonography If appendix not visualized and there is no peri-cecal fluid or mass, study is considered inconclusive U/S is also used to evaluate remainder of abdominal cavity to establish alternative diagnosis Sonographic diagnosis of acute appendicitis - Sensitivity 55 96% - Specificity 85 98%
22 Imaging Studies / CT scan High resolution helical tomography Appendix appears dilated with thickened wall Evidence of inflammation with, dirty fat, thickened mesoappendix Phlegmon Fecalith Sensitivity 92 97% Specificity 85 94%
23 Imaging Studies / CT scan Some studies demonstrated that computed tomography resulted in drop in the rate of negative appendectomies from 19 to 12% Other study demonstrated drop in negative appendectomies in women from 24 to 5% The rational approach is the selective use of CT scan (CT scan and Alvarado score)
24 Alvarado Scale Manifestations Value Symptoms Signs Migration of pain Anorexia Nausea/Vomiting RLQ tenderness Rebound Elevated temperature Laboratory Values Leukocytosis Left shift 2 1
25 Alvarado Scale for diagnosis of Appendicitis Score of 9 10 almost certain to have appendicitis, no further work up needed Score of 7 8 high likelihood of appendicitis Score 5 6 compatible but not diagnostic of appendicitis, CT scan is appropriate for this group Score 0 4 extremely unlikely (but not impossible), It is difficult to justify CT scan expenses and radiation in this group
26 Differential Diagnosis Acute Mesenteric Adenitis Upper respiratory tract infection is present or has recently subsided Pain usually diffuse, and tenderness not sharply localized Rigidity is rare Generalized lymphadenopathy may be noted Relative lymphocytosis If still in doubt, exploration
27 Differential Diagnosis Acute Gastroenteritis Nausea, vomiting with perfuse diarrhea Hyper-peristaltic abdominal cramps precede the watery stool Abdomen is relaxed between cramps, and there are no localizing signs Salmonella gastroenteritis can cause more intense localized pain, associated with rebound tenderness Chills and fever are common Leukocyte count is normal
28 Differential Diagnosis Disease of Male Urogenital System Torsion of the testis and epididymitis, and Seminal vesiculitis Meckel s Diverticulitis Located within the distal two feet of ileum Cause clinical picture similar to appendicitis and need requires same treatment
29 Differential Diagnosis Intussusception Important to differentiate intussusception from acute appendicitis as treatment is different Appendicitis is rare under age of 2 years, while nearly all cases of idiopathic intussusception occur in children younger than 2 years Sudden colicky abdominal pain, infant is well between attacks Bloody mucoid stool Sausage shape mass may be palpable in RLQ As intussusception progresses distally, the RLQ feels abnormally empty Treatment, if no peritonitis, is by barium reduction
30 Differential Diagnosis Crohn s Disease Manifestation of acute regional enteritis Fever, RLQ pain and tenderness Diarrhea, and infrequency of anorexia, nausea and vomiting favor a diagnosis of enteritis but not sufficient to exclude appendicitis Perforated Peptic Ulcer Simulate appendicitis if the spilled gastroduodenal contents gravitate down the right gutter To the cecal area and if perforation spontaneously seals, minimizing upper abdominal findings
31 Differential Diagnosis Colonic Lesion Diverticulitis or perforated cecal tumor, or that portion of sigmoid that lies on the right side May be impossible to distinguish from acute appendicitis This entities should be considered in older patients CT scanning is often helpful in making the diagnosis
32 Differential Diagnosis Epiploic Appendigitis Results from infarction of cecal appendages secondary to torsion Symptoms may be minimal, or there may be continuous pain in the area corresponding to the contour of the colon Pain shift is unusual No diagnostic sequence of symptoms, patient doesn t look ill, nausea and vomiting are unusual Localized tenderness with marked rebound
33 Differential Diagnosis Urinary tract infection Acute pyelonephritis on the right side Chills, right costovertebral angle tenderness, pyuria, and bacteriuria are usually sufficient to make diagnosis Uretral Stone May simulate retro-cecal appendicitis Pain referred to labia, scrotum, or penis Hematuria and / or absence of leukocytosis Pyelography and CT scan without contrast confirm diagnosis
34 Differential Diagnosis Primary Peritonitis In patients with nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis, and endogenous or exogenous immunosuppression Mimic diffuse peritonitis secondary to ruptured appendicitis Diagnosed by peritoneal aspiration, if only gram positive cocci are seen on the gram smear, peritonitis is primary and treated with antibiotics, if flora are mixed or gram negative, secondary peritonitis should be suspected
35 Differential Diagnosis Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Syndrome usually occurs 2 3 weeks after streptococcal infection Abdominal pain Joint pains Purpura Nephritis
36 Differential Diagnosis Yerisinosis Human infection with Yersinia enterocolitica or Y. pseudotubercolosis is transmitted through food contaminated by feces or urine Yersinia infection cause variety of clinical syndromes including: - Mesenteric adenitis - Ileitis - Colitis - Acute appendicitis Many of the infections are mild and self-limited, but some lead to systemic septic course Organism sensitive to tetracyclines, streptomycin, ampicillin, and kanamycin
37 Differential Diagnosis Yerisinosis A preoperative suspicion of the diagnosis should not delay the operative intervention because appendicitis caused by yerisenia can t be distinguished from appendicitis from other causes Copylobacter jejuni (stool culture) Salmonella Typhimurium infection (serology)
38 Differential Diagnosis Gynecologic disorders Pelvic Inflammatory disease Usually bilateral, if confined to right side can mimic appendicitis Nausea and vomiting 50% of cases Pain and tenderness are lower Motion of the cervix is exquisitely painful Intracellular diplococci may be demonstrable of smear of the purulent vaginal discharge
39 Differential Diagnosis Gynecologic disorders Rupture Graafian Follicle / mittelschmerz Mid point of menstrual cycle (mittelschmerz) Brief mild lower abdominal pain Pain and tenderness are rather diffuse Leukocytosis and fever are minimal or absent
40 Differential Diagnosis Gynecologic disorders Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy Rupture of right tubal or ovarian pregnancies can mimic appendicitis Recent menstrual changes Pelvic mass with elevated levels of Beta HCG Vaginal examination reveals cervical motion and adnexal tenderness Leukocyte count may be elevated Drop in hematocrit Culdocentesis is diagnostic
41 Differential Diagnosis Gynecologic disorders Twisted Ovarian Cyst Mass on abdominal examination U/S and CT scan can be diagnostic Torsion requires emergent operation, if torsion is complete or long standing, the pedicle undergoes thrombosis and the ovary and tube become gangrenous and require resection Leakage of ovarian cyst resolves the problem
42 Acute Appendicitis in Young Diagnosis more difficult than in adult History Gastrointestinal upset is common in children Rapid progression to rupture and inability of underdeveloped greater omentum to contain a rupture leads to significant morbidity Children younger than 5 years Negative appendectomy rate 25 & compared to 10% in children 5 12 years of age Appendiceal perforation rate of 45% compared to 20%
43 Acute Appendicitis in Elderly Incidence of appendicitis in this elderly is lower Rapid progression to perforation Co-morbid disease
44 Acute Appendicitis During pregnancy Incidence 1 in 2000 pregnancies More frequent during first two trimesters Nausea and vomiting after first trimester or new onset nausea and vomiting Abdominal pain and tenderness will be present, while rebound and guarding are less frequent due to laxity of abdominal muscles WBC count elevation above the normal pregnancy levels, 15,000 20,000 If diagnosis in doubt, do U/S or laparoscopy The performance of operation during pregnancy carries the risk of premature labor of 10 15%. Risk is similar for both negative laparotomy and appendectomy for simple appendicitis Fetal mortality risk increases from 3 5% in early appendicitis to 20% in perforation
45 Treatment Adequate hydration Correct electrolytes abnormalities Antibiotics Appendectomy - Conventional - Laparoscopic
46 Tumors Appendiceal malignancies are extremely rare Primary appendiceal cancer is diagnosed in % of appendectomy specimens Less than 50% of cases are diagnosed at operation Most series report that Carcinoid is most common appendiceal malignancy, however, recent review from the National Cancer institute s Surveillance found that mucinous adenocarcinoma (37% of total cases) to be the most common followed by carcinoid (33%)
47 Tumors Carcinoid Yellow firm bulbar mass in the appendix should raise suspicion of appendiceal carcinoid Appendix is the most common site of Gastrointestinal Carcinoid Carcinoid syndrome rarely associated Tumor can result in obstruction and appendicitis Majority of tumor is located in the tip, malignant potential is related to size Appendectomy is the treatment if smaller than 1cm For tumors 1cm and extending in the mesoappendix or tumors larger than 1.5 cm right hemicolectomy should be performed
48 Tumors Adenocarcinoma Rare neoplasm Three subtypes - Mucinous adenocarcinoma - Colonic adenocarcinoma - Adenocarcinoid Appendicitis is the most common form of presentation, early perforation Mass or ascites (may) Or discovered during operation Treatment is right hemicolectomy
49 Mucocele Progressive enlargement of appendix from intraluminal accumulation of mucoid substance Four histologic subtypes (type dictates course of disease and prognosis) - Retention cyst - Mucosal Hyperplasia - Cyst-adenoma - Cyst-adenocarcinoma Mucocele of benign etiology treated by appendectomy
Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis
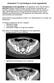 Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis Pathophysiology of acute appendicitis. Acute appendicitis occurs when the lumen is obstructed, leading to fluid accumulation, luminal distention, inflammation
Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis Pathophysiology of acute appendicitis. Acute appendicitis occurs when the lumen is obstructed, leading to fluid accumulation, luminal distention, inflammation
The Acute Abdomen. Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital
 The Acute Abdomen Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital Causes of the Acute Abdomen Hemorrhage in the GI tract Blood vessel GU tract Perforation of the GI tract Ulcer Infection
The Acute Abdomen Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital Causes of the Acute Abdomen Hemorrhage in the GI tract Blood vessel GU tract Perforation of the GI tract Ulcer Infection
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
Diseases of peritoneum Lect. Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32
 Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes
 Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes Vishal Gupta, MCh Associate Professor Deptt Surg. Gastroenterology KGMU Definition Acute abdominal pain: Presentation of previously undiagnosed abdominal pain Lasting
Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes Vishal Gupta, MCh Associate Professor Deptt Surg. Gastroenterology KGMU Definition Acute abdominal pain: Presentation of previously undiagnosed abdominal pain Lasting
Abdominal Pain in a Pregnant Patient
 January 2007 Abdominal Pain in a Pregnant Patient Megan Browning, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 HPI Ms.O is a 21yo pregnant female (23+6 weeks gestation) Woke with 5/10 crampy abdominal pain followed
January 2007 Abdominal Pain in a Pregnant Patient Megan Browning, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 HPI Ms.O is a 21yo pregnant female (23+6 weeks gestation) Woke with 5/10 crampy abdominal pain followed
Simple appendicitis: Complicated appendicitis: Sympathetic nervous system Vague abdominal pain
 Appendicitis: When simple becomes not so simple Appendicitis: When simple becomes not so simple Elizabeth H. Ey, MD Associate Clinical Professor of Pediatrics Department of Medical Imaging Dayton Children
Appendicitis: When simple becomes not so simple Appendicitis: When simple becomes not so simple Elizabeth H. Ey, MD Associate Clinical Professor of Pediatrics Department of Medical Imaging Dayton Children
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient
 Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient Upper GI Series Thought to be malrotation, no evidence of midgut volvulus Needed to repeat UGI Series WHY? Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series No
Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient Upper GI Series Thought to be malrotation, no evidence of midgut volvulus Needed to repeat UGI Series WHY? Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series No
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Introduction. Physiology of the Abdomen. Anatomy & Physiology. Abdominal Pain Introduction (2 of 2) Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies
 Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D.
 Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Surgical Site Infection. Kings County Hospital Center Audrey C. Durrant 6/10/2005
 Surgical Site Infection Kings County Hospital Center Audrey C. Durrant 6/10/2005 Case Presentation HPI patient xx year old presented with approximately xx days periumbillical pain 10/10 on pain scale,
Surgical Site Infection Kings County Hospital Center Audrey C. Durrant 6/10/2005 Case Presentation HPI patient xx year old presented with approximately xx days periumbillical pain 10/10 on pain scale,
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Constipation in Adults. Abdominal Pain, Acute
 1 Constipation in Adults Abdominal Pain, Acute Abdominal pain is common and often inconsequential. Acute and severe abdominal pain, however, is almost always a symptom of intraabdominal disease. It may
1 Constipation in Adults Abdominal Pain, Acute Abdominal pain is common and often inconsequential. Acute and severe abdominal pain, however, is almost always a symptom of intraabdominal disease. It may
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management
 Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Colocutaneous Fistula. Disclosures
 Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries. Simple Cystic Masses
 Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Colic is one of the most dreaded conditions horse owners and trainers encounter with
 Impaction Colic and Hydration Michele Frazer, DVM, DACVIM, DACVECC Impaction Colic Colic is one of the most dreaded conditions horse owners and trainers encounter with their horses. The term colic, however,
Impaction Colic and Hydration Michele Frazer, DVM, DACVIM, DACVECC Impaction Colic Colic is one of the most dreaded conditions horse owners and trainers encounter with their horses. The term colic, however,
K Raja/N Varol FPA 2013. FPA Sydney August 31 2013
 FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Abdominal Pain. Charles Henley, DO, MPH Department of Family Medicine. OSU College of Osteopathic Medicine (Revised 9/2002)
 Abdominal Pain Charles Henley, DO, MPH Department of Family Medicine OSU College of Osteopathic Medicine (Revised 9/2002) Common Causes of Abdominal Pain Infants - colic, gastroenteritis, constipation,
Abdominal Pain Charles Henley, DO, MPH Department of Family Medicine OSU College of Osteopathic Medicine (Revised 9/2002) Common Causes of Abdominal Pain Infants - colic, gastroenteritis, constipation,
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins.
 Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Management of Appendicitis. Anita Chiu, MD Long Island College Hospital June 12, 2009
 Management of Appendicitis Anita Chiu, MD Long Island College Hospital June 12, 2009 Case Presentation ti xx-year-old male presenting with a x-day history of abdominal pain associated with nausea, vomiting,
Management of Appendicitis Anita Chiu, MD Long Island College Hospital June 12, 2009 Case Presentation ti xx-year-old male presenting with a x-day history of abdominal pain associated with nausea, vomiting,
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
United States Department of Transportation National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Paramedic: National Standard Curriculum 1
 UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 4-8 At the completion of this unit, the paramedic student will be able to integrate pathophysiologic principles and the assessment findings to formulate a field impression and implement
UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 4-8 At the completion of this unit, the paramedic student will be able to integrate pathophysiologic principles and the assessment findings to formulate a field impression and implement
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Amylase and Lipase Tests
 Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Differential diagnosis of abdominal pain. Lakatos Péter László
 Differential diagnosis of abdominal pain Lakatos Péter László Precise anamnesis Physical examination are prognosticated to the cause of the pain Anamnesis Sudden pain Perforation Mesenteric infarction
Differential diagnosis of abdominal pain Lakatos Péter László Precise anamnesis Physical examination are prognosticated to the cause of the pain Anamnesis Sudden pain Perforation Mesenteric infarction
3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy
 3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Sisty J. Moshi INTRODUCTION Abdominal pain in pregnancy is very common. Many of the complications of early pregnancy present with some form of
3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Sisty J. Moshi INTRODUCTION Abdominal pain in pregnancy is very common. Many of the complications of early pregnancy present with some form of
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
 Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Advanced Practice Provider Academy
 (+)Dean T. Harrison, MPAS,PA C,DFAAPA Director of Mid Level Practitioners; Assistant Medical Director Clinical Evaluation Unit, Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical
(+)Dean T. Harrison, MPAS,PA C,DFAAPA Director of Mid Level Practitioners; Assistant Medical Director Clinical Evaluation Unit, Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical
ABDOMINAL PAIN. 2. Name the most common abdominal emergencies for each of the major anatomic areas of the abdomen
 ABDOMINAL PAIN Objectives: 1. Distinguish between somatic and referred pain 2. Name the most common abdominal emergencies for each of the major anatomic areas of the abdomen 3. Understand age-related differences
ABDOMINAL PAIN Objectives: 1. Distinguish between somatic and referred pain 2. Name the most common abdominal emergencies for each of the major anatomic areas of the abdomen 3. Understand age-related differences
Billing Guideline. Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16
 Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16 Billing Guideline Background Health First administers benefit packages with full coverage
Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16 Billing Guideline Background Health First administers benefit packages with full coverage
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Abdominal Pain in Adults
 1 Abdominal Pain in Adults Abdominal pain is the most common complaint seen in emergency departments in the United States and one of the 10 most common complaints in family medicine outpatient settings.
1 Abdominal Pain in Adults Abdominal pain is the most common complaint seen in emergency departments in the United States and one of the 10 most common complaints in family medicine outpatient settings.
Chapter 2 Lower Abdominal Pain/Suprapubic Pain
 Chapter 2 Lower Abdominal Pain/Suprapubic Pain Paolo Gontero and Bruno Frea Abstract The term lower abdomen refers to the portion of abdomen below the umbilicus in which three topographic regions can be
Chapter 2 Lower Abdominal Pain/Suprapubic Pain Paolo Gontero and Bruno Frea Abstract The term lower abdomen refers to the portion of abdomen below the umbilicus in which three topographic regions can be
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery
 Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery University Colon & Rectal Surgery A Problem with Your Colon Your doctor has told you that you have a colon problem. Now you ve learned that surgery is needed
Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery University Colon & Rectal Surgery A Problem with Your Colon Your doctor has told you that you have a colon problem. Now you ve learned that surgery is needed
THERAPY OF ANAEROBIC INFECTIONS LUNG ABSCESS BRAIN ABSCESS
 THERAPY OF ANAEROBIC INFECTIONS Douglas Black, Pharm.D. Associate Professor School of Pharmacy University of Washington dblack@u.washington.edu LUNG ABSCESS A lung abscess is a localized pus cavity in
THERAPY OF ANAEROBIC INFECTIONS Douglas Black, Pharm.D. Associate Professor School of Pharmacy University of Washington dblack@u.washington.edu LUNG ABSCESS A lung abscess is a localized pus cavity in
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
POSTMENOPAUSAL ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO
 POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
Abdominal Anatomy & Physiology
 CHAPTER 18 Acute Abdominal Emergencies Abdominal Anatomy & Physiology Abdominal A & P 1 Abdominal A & P Most organs contained in the peritoneum Visceral Peritoneum Covers organs Parietal Peritoneum Attached
CHAPTER 18 Acute Abdominal Emergencies Abdominal Anatomy & Physiology Abdominal A & P 1 Abdominal A & P Most organs contained in the peritoneum Visceral Peritoneum Covers organs Parietal Peritoneum Attached
Specimen collection and transport for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae testing
 Specimen collection and transport for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae testing Overview Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) infections are two of the most common sexually
Specimen collection and transport for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae testing Overview Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) infections are two of the most common sexually
The Digestive System
 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING
 COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING By Douglas K. Rex, M.D., FACG & Suthat Liangpunsakul, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis,
COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING By Douglas K. Rex, M.D., FACG & Suthat Liangpunsakul, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis,
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections
 Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Abdominal Complaints in Urgent & Emergency Care
 Abdominal Complaints in Urgent & Emergency Care Mandy Rumley BSc A&E nursing, MA Cert Ed., Nurse Consultant, Urgent & Unscheduled Care, Dorset PCT Mandy.rumley@dorset-pct.nhs.uk Assessment of Abdominal
Abdominal Complaints in Urgent & Emergency Care Mandy Rumley BSc A&E nursing, MA Cert Ed., Nurse Consultant, Urgent & Unscheduled Care, Dorset PCT Mandy.rumley@dorset-pct.nhs.uk Assessment of Abdominal
C. difficile Infections
 C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
טופס הסכמה לטיפולי הפרייה חוץ גופית
 טופס הסכמה לטיפולי הפרייה חוץ גופית CONSENT FORM: IN-VITRO FERTILIZATION (IVF) 1. General In-vitro fertilization is performed in cases of impaired fertility, which may be caused by the following: Obstruction
טופס הסכמה לטיפולי הפרייה חוץ גופית CONSENT FORM: IN-VITRO FERTILIZATION (IVF) 1. General In-vitro fertilization is performed in cases of impaired fertility, which may be caused by the following: Obstruction
ProSono Copyright 2006. Ovarian Pathology
 Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano. Background
 Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano Background Anorectal abscesses are some of the more common anorectal conditions encountered, and they are potentially debilitating conditions. The current theory as
Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano Background Anorectal abscesses are some of the more common anorectal conditions encountered, and they are potentially debilitating conditions. The current theory as
FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS
 FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS Contributed by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) and edited by the Patient Care Committee of the ACG. INTRODUCTION Doctors use the
FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS Contributed by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) and edited by the Patient Care Committee of the ACG. INTRODUCTION Doctors use the
The Large Intestine. General Facts: (everything will be repeated in a more organized matter later on)
 The Large Intestine Let's continue on our wild journey through the GI tract. We have just arrived at the junction between the ileum and cecum, crossing the border between the small and large intestine.
The Large Intestine Let's continue on our wild journey through the GI tract. We have just arrived at the junction between the ileum and cecum, crossing the border between the small and large intestine.
A Left Paraduodenal Hernia Causing Recurrent Small Bowel Obstruction : A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC001308 2046-1690 A Left Paraduodenal Hernia Causing Recurrent Small Bowel Obstruction : A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Prashanth Shetty, Associate Professor, Kasturba Medical College,
Article ID: WMC001308 2046-1690 A Left Paraduodenal Hernia Causing Recurrent Small Bowel Obstruction : A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Prashanth Shetty, Associate Professor, Kasturba Medical College,
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization
 September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias. A simple guide to help answer your questions
 Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma
 Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,

 More details >>> HERE
More details >>> HERE