EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 16 - Synchronization
|
|
|
- Merilyn Hancock
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 16 - Synchronization March 8, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 1
2 Asynchronous Inputs to Synchronous Systems Many synchronous systems need to interface to asynchronous input signals: Consider a computer system running at some clock frequency, say 1GHz with: Interrupts from I/O devices, keystrokes, etc. Data transfers from devices with their own clocks Ethernet has its own 100MHz clock PCI bus transfers, 66MHz standard clock. These signals could have no known timing relationship with the system clock of the CPU. (On FPGAs we can use FIFOs - separate clocks for input and output - as the interface. In general, this is overkill - and too expensive). Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 2
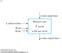
3 Synchronizer Circuit For a single asynchronous input, we use a simple flip-flop to bring the external input signal into the timing domain of the system clock: The D flip-flop samples the asynchronous input at each cycle and produces a synchronous output that meets the setup time of the next stage. Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 3
4 Synchronizer Circuit It is essential for asynchronous inputs to be synchronized at only one place. Two flip-flops may not receive the clock and input signals at precisely the same time (clock and data skew). When the asynchronous changes near the clock edge, one flip-flop may sample input as 1 and the other as 0. Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 4
5 Synchronizer Circuit Single point of synchronization is even more important when input goes to a combinational logic block (ex. FSM) The CL block can accidentally hide the fact that the signal is synchronized at multiple points. The CL magnifies the chance of the multiple points of synchronization seeing different values. Sounds simple, right? Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 5
6 Synchronizer Failure & Metastability We think of flip-flops having only two stable states - but all have a third metastable state halfway between 0 and 1. When the setup and hold times of a flip-flop are not met, the flip-flop could be put into the metastable state. Noise will be amplified and push the flip-flop one way or other. However, in theory, the time to transition to a legal state is unbounded. Does this really happen? The probability is low, but the number of trials is high! Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 6
7 Synchronizer Failure & Metastability If the system uses a synchronizer output while the output is still in the metastable state synchronizer failure. Initial versions of several commercial ICs have suffered from metastability problems - effectively synchronization failure: AMD9513 system timing controller AMD9519 interrupt controller Zilog Z-80 Serial I/O interface Intel 8048 microprocessor AMD microprocessor To avoid synchronizer failure wait long enough before using a synchronizer s output. Long enough, according to Wakerly, is so that the mean time between synchronizer failures is several orders of magnitude longer than the designer s expected length of employment! In practice all we can do is reduce the probability of failure to a vanishing small value. Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 7
8 Reliable Synchronizer Design The probability that a flip-flop stays in the metastable state decreases exponentially with time. Therefore, any scheme that delays using the signal can be used to decrease the probability of failure. In practice, delaying the signal by a cycle is usually sufficient: If the clock period is greater than metastability resolution time plus FF2 setup time, FF2 gets a synchronized version of ASYNCIN. Multi-cycle synchronizers (using counters or more cascaded flipflops) are even better but often overkill. Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 8
9 Purely Asynchronous Circuits Many researchers (and a few industrial designers) have proposed a variety of circuit design methodologies that eliminate the need for a globally distributed clock. They cite a variety of important potential advantages over synchronous systems. To date, these attempts have remained mainly in Universities. A few commercial asynchronous chips/systems have been build. Sometimes, asynchronous blocks sometimes appear inside otherwise synchronous systems. Asynchronous techniques have long been employed in DRAM and other memory chips for generation internal control without external clocks. (Precharge/sense-amplifier timing based on address line changes. Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec16-synch Page 9
To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC.
 8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
EE552. Advanced Logic Design and Switching Theory. Metastability. Ashirwad Bahukhandi. (Ashirwad Bahukhandi) bahukhan@usc.edu
 EE552 Advanced Logic Design and Switching Theory Metastability by Ashirwad Bahukhandi (Ashirwad Bahukhandi) bahukhan@usc.edu This is an overview of what metastability is, ways of interpreting it, the issues
EE552 Advanced Logic Design and Switching Theory Metastability by Ashirwad Bahukhandi (Ashirwad Bahukhandi) bahukhan@usc.edu This is an overview of what metastability is, ways of interpreting it, the issues
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI. Digital Systems Design. Digital Circuits Advanced Topics
 PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit - FSM A Sequential circuit contains: Storage
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit - FSM A Sequential circuit contains: Storage
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Counters and Decoders
 Physics 3330 Experiment #10 Fall 1999 Purpose Counters and Decoders In this experiment, you will design and construct a 4-bit ripple-through decade counter with a decimal read-out display. Such a counter
Physics 3330 Experiment #10 Fall 1999 Purpose Counters and Decoders In this experiment, you will design and construct a 4-bit ripple-through decade counter with a decimal read-out display. Such a counter
Timing Methodologies (cont d) Registers. Typical timing specifications. Synchronous System Model. Short Paths. System Clock Frequency
 Registers Timing Methodologies (cont d) Sample data using clock Hold data between clock cycles Computation (and delay) occurs between registers efinition of terms setup time: minimum time before the clocking
Registers Timing Methodologies (cont d) Sample data using clock Hold data between clock cycles Computation (and delay) occurs between registers efinition of terms setup time: minimum time before the clocking
Lecture-3 MEMORY: Development of Memory:
 Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops
 Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Bistable Elements Latches and Flip-Flops S-R Latch
Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Bistable Elements Latches and Flip-Flops S-R Latch
Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops
 Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops 1. Overview of a Synchronous Sequential Circuit We saw from last lesson that the level sensitive latches could cause instability in a sequential system. This instability
Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops 1. Overview of a Synchronous Sequential Circuit We saw from last lesson that the level sensitive latches could cause instability in a sequential system. This instability
Experiment # 9. Clock generator circuits & Counters. Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa
 Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits
 Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian E-mail: ahmed.madian@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Rania.Swief E-mail: rania.swief@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian Registers An n-bit register
Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian E-mail: ahmed.madian@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Rania.Swief E-mail: rania.swief@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian Registers An n-bit register
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Prof. Randy Katz (Unified
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Prof. Randy Katz (Unified
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices. Chapter 10 Counters. Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies
 ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog
 A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops. Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI. Digital Systems Design. Digital Circuits Advanced Topics
 PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit A Sequential circuit contains: Storage elements:
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit A Sequential circuit contains: Storage elements:
Learning Outcomes. Simple CPU Operation and Buses. Composition of a CPU. A simple CPU design
 Learning Outcomes Simple CPU Operation and Buses Dr Eddie Edwards eddie.edwards@imperial.ac.uk At the end of this lecture you will Understand how a CPU might be put together Be able to name the basic components
Learning Outcomes Simple CPU Operation and Buses Dr Eddie Edwards eddie.edwards@imperial.ac.uk At the end of this lecture you will Understand how a CPU might be put together Be able to name the basic components
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits
 CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits Last revised 8/15/2007 Objectives: 1. To introduce asynchronous and synchronous flip-flops (latches and pulsetriggered, plus asynchronous preset/clear) 2. To introduce
CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits Last revised 8/15/2007 Objectives: 1. To introduce asynchronous and synchronous flip-flops (latches and pulsetriggered, plus asynchronous preset/clear) 2. To introduce
Wiki Lab Book. This week is practice for wiki usage during the project.
 Wiki Lab Book Use a wiki as a lab book. Wikis are excellent tools for collaborative work (i.e. where you need to efficiently share lots of information and files with multiple people). This week is practice
Wiki Lab Book Use a wiki as a lab book. Wikis are excellent tools for collaborative work (i.e. where you need to efficiently share lots of information and files with multiple people). This week is practice
WEEK 8.1 Registers and Counters. ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1
 WEEK 8.1 egisters and Counters ECE124 igital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Additional schematic FF symbols Active low set and reset signals. S Active high set and reset signals. S ECE124 igital Circuits
WEEK 8.1 egisters and Counters ECE124 igital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Additional schematic FF symbols Active low set and reset signals. S Active high set and reset signals. S ECE124 igital Circuits
Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin
 BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
DIGITAL TECHNICS II. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute. 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013
 DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 1. Counters,
DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 1. Counters,
Master/Slave Flip Flops
 Master/Slave Flip Flops Page 1 A Master/Slave Flip Flop ( Type) Gated latch(master) Gated latch (slave) 1 Gate Gate GATE Either: The master is loading (the master in on) or The slave is loading (the slave
Master/Slave Flip Flops Page 1 A Master/Slave Flip Flop ( Type) Gated latch(master) Gated latch (slave) 1 Gate Gate GATE Either: The master is loading (the master in on) or The slave is loading (the slave
Chapter 02: Computer Organization. Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures
 Chapter 02: Computer Organization Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures Objective: Understand the IO Subsystem and Understand Bus Structures Understand
Chapter 02: Computer Organization Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures Objective: Understand the IO Subsystem and Understand Bus Structures Understand
Low latency synchronization through speculation
 Low latency synchronization through speculation D.J.Kinniment, and A.V.Yakovlev School of Electrical and Electronic and Computer Engineering, University of Newcastle, NE1 7RU, UK {David.Kinniment,Alex.Yakovlev}@ncl.ac.uk
Low latency synchronization through speculation D.J.Kinniment, and A.V.Yakovlev School of Electrical and Electronic and Computer Engineering, University of Newcastle, NE1 7RU, UK {David.Kinniment,Alex.Yakovlev}@ncl.ac.uk
Memory unit. 2 k words. n bits per word
 9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
White Paper Understanding Metastability in FPGAs
 White Paper Understanding Metastability in FPGAs This white paper describes metastability in FPGAs, why it happens, and how it can cause design failures. It explains how metastability MTBF is calculated,
White Paper Understanding Metastability in FPGAs This white paper describes metastability in FPGAs, why it happens, and how it can cause design failures. It explains how metastability MTBF is calculated,
ASYNCHRONOUS COUNTERS
 LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design
 Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
NOTE: The Flatpak version has the same pinouts (Connection Diagram) as the Dual In-Line Package.
 PRESETTABLE BCD/DECADE UP/DOWN COUNTERS PRESETTABLE 4-BIT BINARY UP/DOWN COUNTERS The SN54/74LS90 is a synchronous UP/DOWN BCD Decade (842) Counter and the SN54/74LS9 is a synchronous UP/DOWN Modulo-6
PRESETTABLE BCD/DECADE UP/DOWN COUNTERS PRESETTABLE 4-BIT BINARY UP/DOWN COUNTERS The SN54/74LS90 is a synchronous UP/DOWN BCD Decade (842) Counter and the SN54/74LS9 is a synchronous UP/DOWN Modulo-6
Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers
 ETEC 23 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 27 by Janna B. Gallaher Latches A temporary
ETEC 23 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 27 by Janna B. Gallaher Latches A temporary
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems
 Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems The distinguishing feature of a synchronous digital system is that the circuit only changes in response to a system clock. For example, consider the edge triggered
Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems The distinguishing feature of a synchronous digital system is that the circuit only changes in response to a system clock. For example, consider the edge triggered
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill
 Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE
 in the name of God the compassionate, the merciful notes on MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE compiled by Jumong Chap. 9 Microprocessor Fundamentals A system designer should consider a microprocessor-based
in the name of God the compassionate, the merciful notes on MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE compiled by Jumong Chap. 9 Microprocessor Fundamentals A system designer should consider a microprocessor-based
BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D.
 BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D. ANOTHER METHOD TO REPRESENT DECIMAL NUMBERS USEFUL BECAUSE MANY DIGITAL DEVICES PROCESS + DISPLAY NUMBERS IN TENS IN BCD EACH NUMBER IS DEFINED BY A BINARY CODE OF 4 BITS.
BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D. ANOTHER METHOD TO REPRESENT DECIMAL NUMBERS USEFUL BECAUSE MANY DIGITAL DEVICES PROCESS + DISPLAY NUMBERS IN TENS IN BCD EACH NUMBER IS DEFINED BY A BINARY CODE OF 4 BITS.
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS. Counters. By: Electrical Engineering Department
 Counters By: Electrical Engineering Department 1 Counters Upon completion of the chapter, students should be able to:.1 Understand the basic concepts of asynchronous counter and synchronous counters, and
Counters By: Electrical Engineering Department 1 Counters Upon completion of the chapter, students should be able to:.1 Understand the basic concepts of asynchronous counter and synchronous counters, and
Decimal Number (base 10) Binary Number (base 2)
 LECTURE 5. BINARY COUNTER Before starting with counters there is some vital information that needs to be understood. The most important is the fact that since the outputs of a digital chip can only be
LECTURE 5. BINARY COUNTER Before starting with counters there is some vital information that needs to be understood. The most important is the fact that since the outputs of a digital chip can only be
Sequential Logic. (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements )
 Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Sequential Logic: Clocks, Registers, etc.
 ENEE 245: igital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 2 : Clocks, Registers, etc. ENEE 245: igital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 2 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To design
ENEE 245: igital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 2 : Clocks, Registers, etc. ENEE 245: igital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 2 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To design
Random Access Memory (RAM) Types of RAM. RAM Random Access Memory Jamie Tees SDRAM. Micro-DIMM SO-DIMM
 Random Access Memory (RAM) Sends/Receives data quickly between CPU This is way quicker than using just the HDD RAM holds temporary data used by any open application or active / running process Multiple
Random Access Memory (RAM) Sends/Receives data quickly between CPU This is way quicker than using just the HDD RAM holds temporary data used by any open application or active / running process Multiple
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Lecture 10: Sequential Circuits
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI esign Lecture 10: Sequential Circuits avid Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Outline q Sequencing q Sequencing Element esign q Max and Min-elay q Clock Skew q Time Borrowing
Introduction to CMOS VLSI esign Lecture 10: Sequential Circuits avid Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Outline q Sequencing q Sequencing Element esign q Max and Min-elay q Clock Skew q Time Borrowing
Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit Design
 Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit esign Outline Sequencing Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay Clock Skew Time Borrowing Two-Phase Clocking 2 Sequencing Combinational logic output depends on current
Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit esign Outline Sequencing Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay Clock Skew Time Borrowing Two-Phase Clocking 2 Sequencing Combinational logic output depends on current
Measuring Metastability
 Measuring Metastability Sandeep Mandarapu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, VLSI Design Research Laboratory, Southern Illinois University Edwardsville, Illinois, USA, 62025 ECE595: Masters
Measuring Metastability Sandeep Mandarapu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, VLSI Design Research Laboratory, Southern Illinois University Edwardsville, Illinois, USA, 62025 ECE595: Masters
Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain
 Chapter 3 Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain Counters & Shift Registers Counters, Syllabus Design of Modulo-N ripple counter, Up-Down counter, design of synchronous counters with and without
Chapter 3 Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain Counters & Shift Registers Counters, Syllabus Design of Modulo-N ripple counter, Up-Down counter, design of synchronous counters with and without
Registers & Counters
 Objectives This section deals with some simple and useful sequential circuits. Its objectives are to: Introduce registers as multi-bit storage devices. Introduce counters by adding logic to registers implementing
Objectives This section deals with some simple and useful sequential circuits. Its objectives are to: Introduce registers as multi-bit storage devices. Introduce counters by adding logic to registers implementing
DIGITAL COUNTERS. Q B Q A = 00 initially. Q B Q A = 01 after the first clock pulse.
 DIGITAL COUNTERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/digital_counters.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Counter is a sequential circuit. A digital circuit which is used for a counting
DIGITAL COUNTERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/digital_counters.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Counter is a sequential circuit. A digital circuit which is used for a counting
Quiz for Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 3.10
 Date: 3.10 Not all questions are of equal difficulty. Please review the entire quiz first and then budget your time carefully. Name: Course: Solutions in Red 1. [6 points] Give a concise answer to each
Date: 3.10 Not all questions are of equal difficulty. Please review the entire quiz first and then budget your time carefully. Name: Course: Solutions in Red 1. [6 points] Give a concise answer to each
Lecture 10 Sequential Circuit Design Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 2010
 EE4800 CMOS igital IC esign & Analysis Lecture 10 Sequential Circuit esign Zhuo Feng 10.1 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS igital IC esign & Analysis 2010 Sequencing Outline Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay
EE4800 CMOS igital IC esign & Analysis Lecture 10 Sequential Circuit esign Zhuo Feng 10.1 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS igital IC esign & Analysis 2010 Sequencing Outline Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay
DATA SHEET. HEF40193B MSI 4-bit up/down binary counter. For a complete data sheet, please also download: INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Family Specifications HEF, HEC The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Package Outlines/Information HEF,
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Family Specifications HEF, HEC The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Package Outlines/Information HEF,
Clocking. Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 Clocks 1
 ing Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 s 1 Why s and Storage Elements? Inputs Combinational Logic Outputs Want to reuse combinational logic from cycle to cycle 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05
ing Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 s 1 Why s and Storage Elements? Inputs Combinational Logic Outputs Want to reuse combinational logic from cycle to cycle 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05
CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS
 CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Set-Reset Latch 11.3 Gated D Latch 11.4 Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop 11.5 S-R Flip-Flop
CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Set-Reset Latch 11.3 Gated D Latch 11.4 Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop 11.5 S-R Flip-Flop
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors
 Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Design Example: Counters. Design Example: Counters. 3-Bit Binary Counter. 3-Bit Binary Counter. Other useful counters:
 Design Eample: ers er: a sequential circuit that repeats a specified sequence of output upon clock pulses. A,B,C,, Z. G, O, T, E, R, P, S,!.,,,,,,,7. 7,,,,,,,.,,,,,,,,,,,. Binary counter: follows the binary
Design Eample: ers er: a sequential circuit that repeats a specified sequence of output upon clock pulses. A,B,C,, Z. G, O, T, E, R, P, S,!.,,,,,,,7. 7,,,,,,,.,,,,,,,,,,,. Binary counter: follows the binary
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield
 DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
Chapter 8. Sequential Circuits for Registers and Counters
 Chapter 8 Sequential Circuits for Registers and Counters Lesson 3 COUNTERS Ch16L3- "Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 Outline Counters T-FF Basic Counting element State
Chapter 8 Sequential Circuits for Registers and Counters Lesson 3 COUNTERS Ch16L3- "Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 Outline Counters T-FF Basic Counting element State
What is a bus? A Bus is: Advantages of Buses. Disadvantage of Buses. Master versus Slave. The General Organization of a Bus
 Datorteknik F1 bild 1 What is a bus? Slow vehicle that many people ride together well, true... A bunch of wires... A is: a shared communication link a single set of wires used to connect multiple subsystems
Datorteknik F1 bild 1 What is a bus? Slow vehicle that many people ride together well, true... A bunch of wires... A is: a shared communication link a single set of wires used to connect multiple subsystems
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter
 NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
Counters. Present State Next State A B A B 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
 ounter ounters ounters are a specific type of sequential circuit. Like registers, the state, or the flip-flop values themselves, serves as the output. The output value increases by one on each clock cycle.
ounter ounters ounters are a specific type of sequential circuit. Like registers, the state, or the flip-flop values themselves, serves as the output. The output value increases by one on each clock cycle.
Memory Elements. Combinational logic cannot remember
 Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
Set-Reset (SR) Latch
 et-eset () Latch Asynchronous Level sensitive cross-coupled Nor gates active high inputs (only one can be active) + + Function 0 0 0 1 0 1 eset 1 0 1 0 et 1 1 0-? 0-? Indeterminate cross-coupled Nand gates
et-eset () Latch Asynchronous Level sensitive cross-coupled Nor gates active high inputs (only one can be active) + + Function 0 0 0 1 0 1 eset 1 0 1 0 et 1 1 0-? 0-? Indeterminate cross-coupled Nand gates
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Finite State Machines. Machine Interpreta4on
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Finite State Machines Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hbp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp15 1 Levels of RepresentaKon/ InterpretaKon High
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Finite State Machines Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hbp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp15 1 Levels of RepresentaKon/ InterpretaKon High
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic. Lecture 16 Timing and Clock Issues
 EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic Lecture 16 Timing and Clock Issues 1 Overview Sequential system timing requirements Impact of clock skew on timing Impact of clock jitter on
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic Lecture 16 Timing and Clock Issues 1 Overview Sequential system timing requirements Impact of clock skew on timing Impact of clock jitter on
So far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs.
 equential Logic o far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs. In sequential logic the output of the
equential Logic o far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs. In sequential logic the output of the
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet
 Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
High Speed, Real-Time Machine Vision. Perry West Automated Vision Systems, Inc.
 High Speed, Real-Time Machine Vision Perry West Automated Vision Systems, Inc. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Latency...3 Imaging...5 Triggering The Stimulus...5 External Sensor...5 Part Detection
High Speed, Real-Time Machine Vision Perry West Automated Vision Systems, Inc. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Latency...3 Imaging...5 Triggering The Stimulus...5 External Sensor...5 Part Detection
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops
 CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
Atmel Norway 2005. XMEGA Introduction
 Atmel Norway 005 XMEGA Introduction XMEGA XMEGA targets Leadership on Peripheral Performance Leadership in Low Power Consumption Extending AVR market reach XMEGA AVR family 44-100 pin packages 16K 51K
Atmel Norway 005 XMEGA Introduction XMEGA XMEGA targets Leadership on Peripheral Performance Leadership in Low Power Consumption Extending AVR market reach XMEGA AVR family 44-100 pin packages 16K 51K
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu 2 Storing data Possible
Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu 2 Storing data Possible
White Paper Utilizing Leveling Techniques in DDR3 SDRAM Memory Interfaces
 White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
The components. E3: Digital electronics. Goals:
 E3: Digital electronics Goals: Basic understanding of logic circuits. Become familiar with the most common digital components and their use. Equipment: 1 st. LED bridge 1 st. 7-segment display. 2 st. IC
E3: Digital electronics Goals: Basic understanding of logic circuits. Become familiar with the most common digital components and their use. Equipment: 1 st. LED bridge 1 st. 7-segment display. 2 st. IC
Computer Organization. and Instruction Execution. August 22
 Computer Organization and Instruction Execution August 22 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 The Main Parts of a Computer CSC201 Section Copyright 2000, Douglas Reeves 2 I/O and Storage Devices (lots of devices,
Computer Organization and Instruction Execution August 22 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 The Main Parts of a Computer CSC201 Section Copyright 2000, Douglas Reeves 2 I/O and Storage Devices (lots of devices,
Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design ECE 52A Winter 22 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7. Basic Latch 7.2 Gated SR Latch 7.2. Gated SR
Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design ECE 52A Winter 22 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7. Basic Latch 7.2 Gated SR Latch 7.2. Gated SR
MICROPROCESSOR. Exclusive for IACE Students www.iace.co.in iacehyd.blogspot.in Ph: 9700077455/422 Page 1
 MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
 CE4: Components and esign Techniques for igital ystems Tajana imunic osing ources: Where we are now What we ve covered so far (Chap -5, App. A& B) Number representations Boolean algebra OP and PO Logic
CE4: Components and esign Techniques for igital ystems Tajana imunic osing ources: Where we are now What we ve covered so far (Chap -5, App. A& B) Number representations Boolean algebra OP and PO Logic
State Machines in VHDL
 State Machines in VHDL Implementing state machines in VHDL is fun and easy provided you stick to some fairly well established forms. These styles for state machine coding given here is not intended to
State Machines in VHDL Implementing state machines in VHDL is fun and easy provided you stick to some fairly well established forms. These styles for state machine coding given here is not intended to
7. Latches and Flip-Flops
 Chapter 7 Latches and Flip-Flops Page 1 of 18 7. Latches and Flip-Flops Latches and flip-flops are the basic elements for storing information. One latch or flip-flop can store one bit of information. The
Chapter 7 Latches and Flip-Flops Page 1 of 18 7. Latches and Flip-Flops Latches and flip-flops are the basic elements for storing information. One latch or flip-flop can store one bit of information. The
Asynchronous counters, except for the first block, work independently from a system clock.
 Counters Some digital circuits are designed for the purpose of counting and this is when counters become useful. Counters are made with flip-flops, they can be asynchronous or synchronous and they can
Counters Some digital circuits are designed for the purpose of counting and this is when counters become useful. Counters are made with flip-flops, they can be asynchronous or synchronous and they can
ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1
 ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Chip level timing Have discussed some issues related to timing analysis. Talked briefly about longest combinational path for a combinational circuit. Talked briefly
ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Chip level timing Have discussed some issues related to timing analysis. Talked briefly about longest combinational path for a combinational circuit. Talked briefly
DAC Digital To Analog Converter
 DAC Digital To Analog Converter DAC Digital To Analog Converter Highlights XMC4000 provides two digital to analog converters. Each can output one analog value. Additional multiple analog waves can be generated
DAC Digital To Analog Converter DAC Digital To Analog Converter Highlights XMC4000 provides two digital to analog converters. Each can output one analog value. Additional multiple analog waves can be generated
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Logical Operations. Control Unit. Contents. Arithmetic Operations. Objectives. The Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic / Logic Unit.
 Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. For a complete data sheet, please also download:
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Family Specifications The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Package Information The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Family Specifications The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Package Information The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router
 Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
A Pausible Bisynchronous FIFO for GALS Systems
 2015 Symposium on Asynchronous Circuits and Systems A Pausible Bisynchronous FIFO for GALS Systems Ben Keller*, Ma@hew FojCk*, Brucek Khailany* *NVIDIA CorporaCon University of California, Berkeley May
2015 Symposium on Asynchronous Circuits and Systems A Pausible Bisynchronous FIFO for GALS Systems Ben Keller*, Ma@hew FojCk*, Brucek Khailany* *NVIDIA CorporaCon University of California, Berkeley May
Module 3: Floyd, Digital Fundamental
 Module 3: Lecturer : Yongsheng Gao Room : Tech - 3.25 Email : yongsheng.gao@griffith.edu.au Structure : 6 lectures 1 Tutorial Assessment: 1 Laboratory (5%) 1 Test (20%) Textbook : Floyd, Digital Fundamental
Module 3: Lecturer : Yongsheng Gao Room : Tech - 3.25 Email : yongsheng.gao@griffith.edu.au Structure : 6 lectures 1 Tutorial Assessment: 1 Laboratory (5%) 1 Test (20%) Textbook : Floyd, Digital Fundamental
AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR
 AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR INTRODUCTION This Project "Automatic Night Lamp with Morning Alarm" was developed using Microprocessor. It is the Heart of the system. The sensors
AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR INTRODUCTION This Project "Automatic Night Lamp with Morning Alarm" was developed using Microprocessor. It is the Heart of the system. The sensors
AGIPD Interface Electronic Prototyping
 AGIPD Interface Electronic Prototyping P.Goettlicher I. Sheviakov M. Zimmer - Hardware Setup, Measurements - ADC (AD9252 14bit x 8ch x 50msps ) readout - Custom 10G Ethernet performance - Conclusions Test
AGIPD Interface Electronic Prototyping P.Goettlicher I. Sheviakov M. Zimmer - Hardware Setup, Measurements - ADC (AD9252 14bit x 8ch x 50msps ) readout - Custom 10G Ethernet performance - Conclusions Test
ADVANCED IC REVERSE ENGINEERING TECHNIQUES: IN DEPTH ANALYSIS OF A MODERN SMART CARD. Olivier THOMAS Blackhat USA 2015
 ADVANCED IC REVERSE ENGINEERING TECHNIQUES: IN DEPTH ANALYSIS OF A MODERN SMART CARD Olivier THOMAS Blackhat USA 2015 About Texplained Texplained [Technology Explained] refers
ADVANCED IC REVERSE ENGINEERING TECHNIQUES: IN DEPTH ANALYSIS OF A MODERN SMART CARD Olivier THOMAS Blackhat USA 2015 About Texplained Texplained [Technology Explained] refers
Computer Performance. Topic 3. Contents. Prerequisite knowledge Before studying this topic you should be able to:
 55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
Modeling Latches and Flip-flops
 Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
FPGA Clocking. Clock related issues: distribution generation (frequency synthesis) multiplexing run time programming domain crossing
 FPGA Clocking Clock related issues: distribution generation (frequency synthesis) Deskew multiplexing run time programming domain crossing Clock related constraints 100 Clock Distribution Device split
FPGA Clocking Clock related issues: distribution generation (frequency synthesis) Deskew multiplexing run time programming domain crossing Clock related constraints 100 Clock Distribution Device split
Modeling Registers and Counters
 Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
Agilent Technologies E8047B Analysis Probe System for the Intel Xeon Processor Family
 Agilent Technologies E8047B Analysis Probe System for the Intel Xeon Processor Family Product Overview Requires an Agilent 16700A/B Series or 16900A Series Logic Analysis System The Agilent E8047B analysis
Agilent Technologies E8047B Analysis Probe System for the Intel Xeon Processor Family Product Overview Requires an Agilent 16700A/B Series or 16900A Series Logic Analysis System The Agilent E8047B analysis
