TUSM Office of Educational Affairs Educational Resources Writing Learning Objectives Handout
|
|
|
- Britton Nelson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TUSM Office of Educational Affairs Educational Resources Writing Learning Objectives Handout Why are learning objectives so important? Setting observable and measurable learning objectives: Provides a structure for the learning and teaching process (i.e. teachers and students know what they are striving for) Guides teachers in planning the teaching (i.e. content and teaching strategies) Provides a basis for assessment (i.e. assessment strategies should be aligned with learning objectives in order to measure whether or not the objectives are achieved) Definition of Goals and Objectives GOALS: Very general and global statements used as an overall frame of reference. EXAMPLE: The goal of the course in General Pathology is to acquaint the student with general principles of various diseases processes with particular emphasis on etiology and pathogenesis and the resultant metabolic, functional and structural abnormalities. This course is intended to provide not only the appropriate basic science background essential to the understanding and interpretation of disease patterns in a clinical setting, but also a working knowledge of the terminology used to describe diseases. (General Pathology Syllabus, First Year, Spring Semester 2008, Academic Year ). OBJECTIVES: Precise statements that begin with an action verb. They characterize observable and measurable behaviors that you want learners to accomplish by the end of the course/rotation/lecture/small group session. Learning objectives guide and must be aligned with assessment strategies. EXAMPLES: By the end of the course students will be able to recognize the basic mechanism of inflammation. By the end of this lecture students will be able to describe the therapeutic window and the overlap between efficacy and toxicity. Tips for Writing Objectives Know the learners to align the course objectives with their developmental stage, abilities, experiences and educational needs. Precede your list of objectives with the following statement: By the end of the course/rotation/lecture/small group session students will be able to: Include two basic elements in the statement: -A verb that describes an observable action, e.g. identify (see key words mentioned below). -The acceptable performance level, e.g. identify the four main causes of 1
2 Use clear and concise words to describe student behavior (avoid the use of verbs open to many interpretations). Words Open to Many Interpretations To know To understand To appreciate To learn To enjoy To believe Words Open to Fewer Interpretations To write To compare To identify To sort To solve To build EXAMPLE: By the end of the lecture students will be able to understand the biosynthesis and function of leukotrienes. EXPLANATION: The act of understanding is not an observable and measurable behavior per se. There are different levels of measurable cognitive abilities that promote the achievement of understanding. (See chart below). Learners can manifest their development towards understanding of a core concept by (1) identifying/recalling it; (2) applying it into daily practice; (3) analyzing its components; (4) integrating it into a new idea/plan. Therefore, the objective mentioned above could be rephrased as follows: By the end of the lecture students will be able to distill the biosynthesis and function of leukotrienes. Each level of cognitive ability will in turn be aligned with a specific assessment strategy. For example, closed questions could be used to recall concepts, and case vignettes can be used to assess learners application of concepts. Identify whether you are writing cognitive, attitudinal and/or skills objectives. Chart for Writing Cognitive, Attitudinal and Skills Objectives Cognitive Objectives Cognitive Level (from less to more complex) Knowledge: Recall or recognize information, ideas, and principles in the approximate form in which they were learned. Comprehension: Understands the meaning, translation, interpolation, and Key Words defines, describes, identifies, labels, lists, matches, names, outlines, recalls, recognizes, reproduces, selects, states. converts, defends, distinguishes, estimates, explains, extends, generalizes, Example Identify the various segments of the nephron and their relationships to the structure of the kidney. Describe the histological organization of the lymphoid and organs. Explain the relationship between glomerular filtration rate, absorption rate, secretion 2
3 interpretation of instructions and problems. States a problem in one's own words. Application: Uses a concept in a new situation or unprompted use of an abstraction. Applies what was learned in the classroom into novel situations in the clinical workplace. Analysis: Separates material or concepts into component parts so that its organizational structure may be understood. Distinguishes between facts and inferences. Synthesis: Originates, integrates, and combines ideas into a product, plan or proposal that is new to him or her. Evaluation: Assesses, appraises, or critiques on a basis of specific standards and criteria. gives examples, illustrates, infers, interprets, paraphrases, predicts, rewrites, summarizes, translates. applies, changes, computes, constructs, demonstrates, discovers, manipulates, modifies, operates, predicts, prepares, produces, relates, shows, solves, uses. breaks down, categorizes, compares, contrasts, diagrams, deconstructs, differentiates, discriminates, distinguishes, illustrates, infers, outlines, relates, selects, separates. categorizes, combines, compiles, composes, creates, devises, designs, explains, generates, invents, develops, hypothesizes, modifies, organizes, plans, rearranges, reconstructs, relates, reorganizes, revises, rewrites, summarizes, tells, writes. appraises, compares, concludes, contrasts, criticizes, critiques, defends, describes, discriminates, evaluates, explains, interprets, justifies, relates, recommends, summarizes, supports. rate and the rate of excretion of a compound in the urine. Distinguish ethologic factors of cardiovascular diseases. Apply anatomical knowledge to clinical diagnostic problemsolving. Calculate how acidic and basic drugs dissociate and distribute themselves at different ph values. Diagram the short loop and long loop negative feedback secretory control of the anterior pituitary hormones. Break down the biosynthesis and function of lipoxins. Compare and contrast the surface membrane procoagulant reactions of the platelet and endothelial cell. Develop mathematical predictions of drug behavior in a variety of clinical circumstances. Predict the functional loss and cutaneous areas affected by a given nerve injury to the hip and posterior thigh region. Assess the clinical significance of different stages of atherosclerosis. Interprets major consequences and complications of myocardial infarcts. Attitudinal Objectives Attitudes Key Words Example Shows awareness, willingness Listen, follows, replies, uses. Listen to others with respect to hear, and selected attention Participates actively by attending, reacting and answers, assists, aids, complies, conforms, discusses, Participate in discussions. Give a presentation. 3
4 showing awareness. Accepts the importance of the attitude; displays behavior consistent with a belief or attitude Skills Objectives greets, helps, labels, performs, practices, presents, reads, recites, reports, selects, tells, writes. demonstrates, displays, differentiates, relates, selects, explains, justifies, proposes, reports, formulates, follows, forms, initiates, invites, joins, cooperates, shares, works, adheres, alters, accepts, defends Question new concepts, models to fully understand them. Treat cadavers with professionalism and decency. Show sensitiveness to individual and cultural differences. Accept responsibility for his/her behaviors. Accept professional ethical standards. Display a professional commitment to ethical practice on a daily basis. Cooperate in group activities (displays teamwork). Change behavior in light of new evidence. Skills Key Words Example Perception: Uses sensory cues to guide performance Observation: Observes visual information Imitation: Repeats what is done Practice/Manipulation: Exercises skills following chooses, describes detects, distinguishes, identifies, isolates, selects describes, looks, sees, observes, examines, does, imitates, repeats, replicates, recaps practices, exercises, reproduces, rehearses, carries Detect non-verbal communication cues. Observe the superficial arteries and veins. Describe the patient s body language. Distinguish primary, observable, confirmable visual information from secondary, derived inferences. Replicate a procedure as demonstrated by the instructor. Make skin incisions. 4
5 guidelines out, performs, follows, prepares Practice how to perform a physical exanimation. Mastery: Performs skills perfectly in different contexts (e.g. simulation, real patient). Adaptation: Modifies patterns to fit a particular situation or specific problem performs, displays, shows arranges, combines, creates, initiates, makes, develops Show ability to conduct a complete mental examination regardless of patient peculiarities Develop a new dietary routine to meet the patient s specific needs. References Albanese MA, Mejicano G, Mullan P, Kokotailo P & Gruppen L. Defining characteristics of educational competencias. Medical Education 2008; 42: Diamond, R. (1998). Clarifying Instructional Goals and Objectives. In Diamond, R. Designing and Assessing Courses and Curricula. A practical Guide (2 nd. ed., pp ). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass. Huitt, W. (2004). Bloom et al.'s taxonomy of the cognitive domain. Educational Psychology Interactive. Valdosta, GA: Valdosta State University. Retrieved June 2008, from (Contributed by Dr. Ralph Aarons) Thorndike RL, Hagen EP. Measurement and Evaluation in Psychology and Education, 4 th ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1977; 200 in Albanese et al
Cognitive Domain (Bloom)
 Bloom s Taxonomy So what exactly is this thing called Bloom s Taxonomy, and why do education people keep talking about it? Well, Bloom was the head of a group in the 1950 s and 1960 s that created the
Bloom s Taxonomy So what exactly is this thing called Bloom s Taxonomy, and why do education people keep talking about it? Well, Bloom was the head of a group in the 1950 s and 1960 s that created the
TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed)
 TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed) Table 1 Major categories in the cognitive domain of the taxonomy of educational objectives
TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed) Table 1 Major categories in the cognitive domain of the taxonomy of educational objectives
Writing learning objectives
 Writing learning objectives This material was excerpted and adapted from the following web site: http://www.utexas.edu/academic/diia/assessment/iar/students/plan/objectives/ What is a learning objective?
Writing learning objectives This material was excerpted and adapted from the following web site: http://www.utexas.edu/academic/diia/assessment/iar/students/plan/objectives/ What is a learning objective?
Resources for Writing Program Learning Outcomes
 Resources for Writing Program Learning Outcomes Supplementary Materials for Writing and Revising Learning Outcomes Workshop Presented Jointly by TLA and Student Affairs LEVEL OF SPECIFICITY AND REACH Learning
Resources for Writing Program Learning Outcomes Supplementary Materials for Writing and Revising Learning Outcomes Workshop Presented Jointly by TLA and Student Affairs LEVEL OF SPECIFICITY AND REACH Learning
5. Formally register for INS299 for the number of semester hours indicated on your contract.
 HONORS INDEPENDENT STUDY GUIDELINES: According to the Lake Land College catalog course description, independent study is designed to permit the student to pursue a course of study not typically available
HONORS INDEPENDENT STUDY GUIDELINES: According to the Lake Land College catalog course description, independent study is designed to permit the student to pursue a course of study not typically available
Using the PRECEDE- PROCEED Planning Model PRECEDE-PROCEED P R E C E D E. Model for health promotion programming Best known among health scientists
 Using the PRECEDE- PROCEED Planning Model Dr. McKinley Thomas Associate Professor Department of Community Medicine Mercer University PRECEDE-PROCEED Model for health promotion programming Best known among
Using the PRECEDE- PROCEED Planning Model Dr. McKinley Thomas Associate Professor Department of Community Medicine Mercer University PRECEDE-PROCEED Model for health promotion programming Best known among
TIPS FOR WRITING LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 TIPS FOR WRITING LEARNING OBJECTIVES N ational ACEP receives numerous requests from chapters for assistance on how to write good learning objectives. The information presented in this section has been
TIPS FOR WRITING LEARNING OBJECTIVES N ational ACEP receives numerous requests from chapters for assistance on how to write good learning objectives. The information presented in this section has been
Writing Goals and Objectives If you re not sure where you are going, you re liable to end up some place else. ~ Robert Mager, 1997
 Writing Goals and Objectives If you re not sure where you are going, you re liable to end up some place else. ~ Robert Mager, 1997 Instructional goals and objectives are the heart of instruction. When
Writing Goals and Objectives If you re not sure where you are going, you re liable to end up some place else. ~ Robert Mager, 1997 Instructional goals and objectives are the heart of instruction. When
Writing Good Learning Objectives
 I - T E C H T E C H N I C A L I M P L E M E N T A T I O N G U I D E # 4 Writing Good Learning Objectives I-TECH s Technical Implementation Guides are a series of practical and instructional papers designed
I - T E C H T E C H N I C A L I M P L E M E N T A T I O N G U I D E # 4 Writing Good Learning Objectives I-TECH s Technical Implementation Guides are a series of practical and instructional papers designed
Writing Learning Objectives
 Writing Learning Objectives Faculty Development Program Office of Medical Education Boston University School of Medicine All Rights Reserved 2004 No copying or duplication of this presentation without
Writing Learning Objectives Faculty Development Program Office of Medical Education Boston University School of Medicine All Rights Reserved 2004 No copying or duplication of this presentation without
Writing Instructional Objectives
 Writing Instructional Objectives Babbi J. Winegarden, Ph.D. Assistant Dean for Educational Development and Evaluation UCSD School of Medicine Department of Medical Education Begin with the end in mind
Writing Instructional Objectives Babbi J. Winegarden, Ph.D. Assistant Dean for Educational Development and Evaluation UCSD School of Medicine Department of Medical Education Begin with the end in mind
Writing Student Learning Outcomes for an Academic Program
 Writing Student Learning Outcomes for an Academic Program Student learning outcomes (SLOs) are statements of the knowledge, skills, competencies, or attitudes that students are expected to gain through
Writing Student Learning Outcomes for an Academic Program Student learning outcomes (SLOs) are statements of the knowledge, skills, competencies, or attitudes that students are expected to gain through
Three domains of learning
 Three domains of learning Leslie Owen Wilson all rights reserved Three domains of learning What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? There are three main domains
Three domains of learning Leslie Owen Wilson all rights reserved Three domains of learning What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? There are three main domains
Writing Quality Learning Objectives
 http://captain.park.edu/facultydevelopment/writing_learning_objectives.htm 1 Writing Quality Learning Objectives Learning objectives (often called performance objectives or competencies) are brief, clear,
http://captain.park.edu/facultydevelopment/writing_learning_objectives.htm 1 Writing Quality Learning Objectives Learning objectives (often called performance objectives or competencies) are brief, clear,
HSU Division of Enrollment Management and Student Affairs. Assessment Workbook
 HSU Division of Enrollment Management and Student Affairs Assessment Workbook Contents Introduction..... 3 Mission Statements...... 4 Goals......5 Outcomes.6 Program Outcomes Learning Outcomes Methods
HSU Division of Enrollment Management and Student Affairs Assessment Workbook Contents Introduction..... 3 Mission Statements...... 4 Goals......5 Outcomes.6 Program Outcomes Learning Outcomes Methods
Alignment of Taxonomies
 Alignment of Taxonomies Bloom s Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain Bloom s Taxonomy Cognitive Domain Revised Cognitive Demand Mathematics Cognitive Demand English Language Arts Webb s Depth of Knowledge Knowledge
Alignment of Taxonomies Bloom s Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain Bloom s Taxonomy Cognitive Domain Revised Cognitive Demand Mathematics Cognitive Demand English Language Arts Webb s Depth of Knowledge Knowledge
COURSE COMPETENCY GUIDELINES
 COURSE COMPETENCY GUIDELINES GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPING COMPETENCIES Format: 1. Begin with a present tense action verb. (Example: Convert picas to points and inches.) 2. Each action verb requires an object.
COURSE COMPETENCY GUIDELINES GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPING COMPETENCIES Format: 1. Begin with a present tense action verb. (Example: Convert picas to points and inches.) 2. Each action verb requires an object.
Framework for the Doctoral Transformation: Application of a Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
 Framework for the Doctoral Transformation: Application of a Taxonomy of Educational Objectives The doctoral learning process is life changing. It begins with the decision to seek the doctorate and becomes
Framework for the Doctoral Transformation: Application of a Taxonomy of Educational Objectives The doctoral learning process is life changing. It begins with the decision to seek the doctorate and becomes
Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002. Reading (based on Wixson, 1999)
 Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002 Language Arts Levels of Depth of Knowledge Interpreting and assigning depth-of-knowledge levels to both objectives within
Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002 Language Arts Levels of Depth of Knowledge Interpreting and assigning depth-of-knowledge levels to both objectives within
Mortgage Broker Qualifying Standards (MBQS)
 OBJECTIVES A. Compliance and Consumer Protection A1 Recognize the impact of regulation and legislation on the mortgage industry A1.1 Recognize requirements related to financial reporting and other reporting
OBJECTIVES A. Compliance and Consumer Protection A1 Recognize the impact of regulation and legislation on the mortgage industry A1.1 Recognize requirements related to financial reporting and other reporting
Webb s Depth of Knowledge Guide
 Webb Webb s Depth of Knowledge Guide Career and Technical Education Definitions 2009 1 H T T P : / / WWW. MDE. K 12.MS. US H T T P : / / R E D E S I G N. R C U. M S S T A T E. EDU 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview...
Webb Webb s Depth of Knowledge Guide Career and Technical Education Definitions 2009 1 H T T P : / / WWW. MDE. K 12.MS. US H T T P : / / R E D E S I G N. R C U. M S S T A T E. EDU 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview...
CREATING LEARNING OUTCOMES
 CREATING LEARNING OUTCOMES What Are Student Learning Outcomes? Learning outcomes are statements of the knowledge, skills and abilities individual students should possess and can demonstrate upon completion
CREATING LEARNING OUTCOMES What Are Student Learning Outcomes? Learning outcomes are statements of the knowledge, skills and abilities individual students should possess and can demonstrate upon completion
MOUNTAIN VIEW COLLEGE CORE CURRICULUM EVALUATION COMMITTEE STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES COURSE LEVEL VICTOR J. SOTO INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGNER PREPARED BY
 1 MOUNTAIN VIEW COLLEGE CORE CURRICULUM EVALUATION COMMITTEE WRITING INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES COURSE LEVEL PREPARED BY VICTOR J. SOTO INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGNER 2 WRITING INSTRUCTIONAL
1 MOUNTAIN VIEW COLLEGE CORE CURRICULUM EVALUATION COMMITTEE WRITING INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES COURSE LEVEL PREPARED BY VICTOR J. SOTO INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGNER 2 WRITING INSTRUCTIONAL
AANN CNE CE Applications Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
 1. What documentation is needed to complete a CNE CE Application? a. Application b. Payment page c. Commercial support agreement (if needed) d. Sponsorship agreement (if needed) e. Joint- Provider agreement
1. What documentation is needed to complete a CNE CE Application? a. Application b. Payment page c. Commercial support agreement (if needed) d. Sponsorship agreement (if needed) e. Joint- Provider agreement
Revised Bloom s Taxonomy
 Revised Bloom s Taxonomy Revised Bloom s Taxonomy (RBT) employs the use of 25 verbs that create collegial understanding of student behavior and learning outcome. Bloom s Revised Taxonomy Taxonomy of Cognitive
Revised Bloom s Taxonomy Revised Bloom s Taxonomy (RBT) employs the use of 25 verbs that create collegial understanding of student behavior and learning outcome. Bloom s Revised Taxonomy Taxonomy of Cognitive
Bloom s Taxonomy. List the main characteristics of one of the main characters in a WANTED poster.
 Bloom s Taxonomy Bloom s Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. By providing a hierarchy of levels, this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing
Bloom s Taxonomy Bloom s Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. By providing a hierarchy of levels, this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing
Articulating Instructional Goals
 Janet Russell CNDLS Workshop Goals: 1) Teaching vs. Learning goals Participants will be able to distinguish between teacher-centered and student-centered learning goals. 2) Articulate a set of learning
Janet Russell CNDLS Workshop Goals: 1) Teaching vs. Learning goals Participants will be able to distinguish between teacher-centered and student-centered learning goals. 2) Articulate a set of learning
National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP)
 Exploring Cognitive Demand in Instruction and Assessment Karin K. Hess Over the past decades, educators and psychologists have attempted to develop models for understanding cognitive complexity as it relates
Exploring Cognitive Demand in Instruction and Assessment Karin K. Hess Over the past decades, educators and psychologists have attempted to develop models for understanding cognitive complexity as it relates
6 Week Strategic Onboarding Program:
 6 Week Strategic Onboarding Program: Creating a Culture of Learning to Increase Success for Financial Services First Timers Matt Ragan- GMAC Mortgage The New Hire Process A successful New Hire On-boarding
6 Week Strategic Onboarding Program: Creating a Culture of Learning to Increase Success for Financial Services First Timers Matt Ragan- GMAC Mortgage The New Hire Process A successful New Hire On-boarding
Exhibit memory of previously-learned materials by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. Key Words
 The Six Levels of Questioning Level 1 Knowledge Exhibit memory of previously-learned materials by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. who what why when where which omit choose find how
The Six Levels of Questioning Level 1 Knowledge Exhibit memory of previously-learned materials by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. who what why when where which omit choose find how
ABET & NCAAA ACCREDITATION Course Design Workshop
 ABET & NCAAA ACCREDITATION Prof. Ali M. Al-Bahi Director of the Academic Accreditation Unit Faculty of Engineering, King Abdulaziz University Modified and Presented by Dr. Faisal Iskanderani UBTVR for
ABET & NCAAA ACCREDITATION Prof. Ali M. Al-Bahi Director of the Academic Accreditation Unit Faculty of Engineering, King Abdulaziz University Modified and Presented by Dr. Faisal Iskanderani UBTVR for
Five High Order Thinking Skills
 Five High Order Introduction The high technology like computers and calculators has profoundly changed the world of mathematics education. It is not only what aspects of mathematics are essential for learning,
Five High Order Introduction The high technology like computers and calculators has profoundly changed the world of mathematics education. It is not only what aspects of mathematics are essential for learning,
Chapter 4: Types of coaching
 Tool 4.1 Relationship between training outcomes and training components Purpose Use this tool to demonstrate the impact of coaching on teachers practices. 4.2 Coaching interactions Gain an understanding
Tool 4.1 Relationship between training outcomes and training components Purpose Use this tool to demonstrate the impact of coaching on teachers practices. 4.2 Coaching interactions Gain an understanding
Curriculum Development. Workbook
 Curriculum Development Workbook PERFORMANCE-BASED LEARNING CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT Schoolcraft College supports a performance-based learning (PBL) model of curriculum development. This model focuses on
Curriculum Development Workbook PERFORMANCE-BASED LEARNING CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT Schoolcraft College supports a performance-based learning (PBL) model of curriculum development. This model focuses on
Writing Educational Goals and Objectives
 Writing Educational Goals and Objectives What are Goals? Goals are broad, generalized statements about what is to be learned. Think of them as a target to be reached, or "hit." What are Instructional Objectives?
Writing Educational Goals and Objectives What are Goals? Goals are broad, generalized statements about what is to be learned. Think of them as a target to be reached, or "hit." What are Instructional Objectives?
ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES IN THE MAJOR A PRIMER FOR DEPARTMENT ASSESSMENT LIAISONS
 ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES IN THE MAJOR A PRIMER FOR DEPARTMENT ASSESSMENT LIAISONS I. WHAT IS ASSESSMENT? Assessment is the systematic collection, review and use of information about educational
ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES IN THE MAJOR A PRIMER FOR DEPARTMENT ASSESSMENT LIAISONS I. WHAT IS ASSESSMENT? Assessment is the systematic collection, review and use of information about educational
CHAPTER 5 : COURSE AND UNIT DESIGN AND QUALITY
 CHAPTER 5 : COURSE AND UNIT DESIGN AND QUALITY All Curtin Courses are designed to ensure graduates are skilled in; leadership, research, Australian Indigenous knowledges and perspectives; and work-integrated
CHAPTER 5 : COURSE AND UNIT DESIGN AND QUALITY All Curtin Courses are designed to ensure graduates are skilled in; leadership, research, Australian Indigenous knowledges and perspectives; and work-integrated
Educational Goals and Objectives A GUIDE TO DEVELOPING LEARNER BASED INSTRUCTION
 Educational Goals and Objectives A GUIDE TO DEVELOPING LEARNER BASED INSTRUCTION Educational Objectives for this Presentation At the end of this presentation you will be able to: Compare and contrast educational
Educational Goals and Objectives A GUIDE TO DEVELOPING LEARNER BASED INSTRUCTION Educational Objectives for this Presentation At the end of this presentation you will be able to: Compare and contrast educational
Communication Process
 Welcome and Introductions Lesson 7 Communication Process Overview: This lesson teaches learners to define the elements of effective communication and its process. It will focus on communication as the
Welcome and Introductions Lesson 7 Communication Process Overview: This lesson teaches learners to define the elements of effective communication and its process. It will focus on communication as the
Performance Development and Review Template Guide
 Performance Development and Review Template Guide 1. OVERVIEW This guide has been developed to assist both staff and supervisor in the use of the Performance Development & Review template (PD&R) for the
Performance Development and Review Template Guide 1. OVERVIEW This guide has been developed to assist both staff and supervisor in the use of the Performance Development & Review template (PD&R) for the
Core Competencies for Public Health Practice Lessons Learned (USA)
 Core Competencies for Public Health Practice Lessons Learned (USA) Joan P. Cioffi, Ph.D. Member, Council on Linkages Between Academia and Public Health Practice Core Competency Workgroups 2001 and 2009
Core Competencies for Public Health Practice Lessons Learned (USA) Joan P. Cioffi, Ph.D. Member, Council on Linkages Between Academia and Public Health Practice Core Competency Workgroups 2001 and 2009
Industrial Engineering Definition of Tuning
 Industrial Engineering Definition of Tuning Tuning is a faculty-led pilot project designed to define what students must know, understand, and be able to demonstrate after completing a degree in a specific
Industrial Engineering Definition of Tuning Tuning is a faculty-led pilot project designed to define what students must know, understand, and be able to demonstrate after completing a degree in a specific
Writing Learning Objectives
 The University of Tennessee, Memphis Writing Learning Objectives A Teaching Resource Document from the Office of the Vice Chancellor for Planning and Prepared by Raoul A. Arreola, Ph.D. Portions of this
The University of Tennessee, Memphis Writing Learning Objectives A Teaching Resource Document from the Office of the Vice Chancellor for Planning and Prepared by Raoul A. Arreola, Ph.D. Portions of this
Facilitator: Dr. Mervin E. Chisholm h Manager/Coordinator, IDU
 Developing Your Course Outline Facilitator: Dr. Mervin E. Chisholm h Manager/Coordinator, IDU What Will We Be Doing Today? Use instructional design models and to decide on appropriate it approaches to:
Developing Your Course Outline Facilitator: Dr. Mervin E. Chisholm h Manager/Coordinator, IDU What Will We Be Doing Today? Use instructional design models and to decide on appropriate it approaches to:
Developing Data Workshops
 Developing Data Workshops BDK 31-01 Best practices for engaging audiences and using the BDK resources Jackie Wirz, PhD Oregon Health & Science University BD2K Open Educational Resources Oregon Health &
Developing Data Workshops BDK 31-01 Best practices for engaging audiences and using the BDK resources Jackie Wirz, PhD Oregon Health & Science University BD2K Open Educational Resources Oregon Health &
Bloom s Taxonomy Levels for Three Software Engineer Profiles
 Bloom s Taxonomy Levels for Three Software Engineer Profiles P. Bourque L. Buglione A. Abran A. April pbourque@ele.etsmtl.ca luigi.buglione@computer.org aabran@ele.etsmtl.ca aapril@ele.etsmtl.ca Abstract
Bloom s Taxonomy Levels for Three Software Engineer Profiles P. Bourque L. Buglione A. Abran A. April pbourque@ele.etsmtl.ca luigi.buglione@computer.org aabran@ele.etsmtl.ca aapril@ele.etsmtl.ca Abstract
ENHANCING your PROGRAMS and COURSES through ALIGNED LEARNING OUTCOMES
 ENHANCING your PROGRAMS and COURSES through ALIGNED LEARNING OUTCOMES Page 1 of 12 Liesel Knaack Feb 25, 2015 Centre for Innovation and Excellence in Learning Vancouver Island University AGENDA Defining
ENHANCING your PROGRAMS and COURSES through ALIGNED LEARNING OUTCOMES Page 1 of 12 Liesel Knaack Feb 25, 2015 Centre for Innovation and Excellence in Learning Vancouver Island University AGENDA Defining
Instructional Design What Is It and Why Should I Care?
 Instructional Design What Is It and Why Should I Care? A CEIT Workshop Domenic Screnci, Ed.D. Executive Director Educational Technology, Training and Outreach Information Services and Technology Boston
Instructional Design What Is It and Why Should I Care? A CEIT Workshop Domenic Screnci, Ed.D. Executive Director Educational Technology, Training and Outreach Information Services and Technology Boston
Teaching and Educational Development Institute. Bloom s taxonomy of educational objectives
 Bloom s taxonomy of educational objectives Bloom s taxonomy of educational objectives This material is largely drawn from a handout from Dr Robert Kleinsasser (School of Languages and Comparative Cultural
Bloom s taxonomy of educational objectives Bloom s taxonomy of educational objectives This material is largely drawn from a handout from Dr Robert Kleinsasser (School of Languages and Comparative Cultural
Developing a Course Syllabus: Steps for Syllabus Design
 Developing a Course Syllabus: Steps for Syllabus Design This list of steps breaks down the process of drafting a syllabus. Following these steps in this order will foster an instructor s own critical thinking
Developing a Course Syllabus: Steps for Syllabus Design This list of steps breaks down the process of drafting a syllabus. Following these steps in this order will foster an instructor s own critical thinking
Developing Higher Level Thinking
 Abstract Limbach, Barbara Chadron State College Waugh, Wendy Chadron State College This paper identifies an interdisciplinary, five-step process, built upon existing theory and best practices in cognitive
Abstract Limbach, Barbara Chadron State College Waugh, Wendy Chadron State College This paper identifies an interdisciplinary, five-step process, built upon existing theory and best practices in cognitive
A New Lens for Examining Cognitive Rigor in Standards, Curriculum, & Assessments. for the transition to Common Core State Standards?
 A New Lens for Examining Cognitive Rigor in Standards, Curriculum, & Assessments What are some implications for the transition to Common Core State Standards? Karin K. Hess, Ed.D., Senior Associate National
A New Lens for Examining Cognitive Rigor in Standards, Curriculum, & Assessments What are some implications for the transition to Common Core State Standards? Karin K. Hess, Ed.D., Senior Associate National
Writing Measurable Learning Outcomes
 Writing Measurable Learning Outcomes Sandi Osters, Director of Student Life Studies F. Simone Tiu, Assistant Director for Institutional Effectiveness 3 rd Annual Texas A&M Assessment Conference You got
Writing Measurable Learning Outcomes Sandi Osters, Director of Student Life Studies F. Simone Tiu, Assistant Director for Institutional Effectiveness 3 rd Annual Texas A&M Assessment Conference You got
Some Thoughts on Selecting IDEA Objectives
 ( Handout 1 Some Thoughts on Selecting IDEA Objectives A u g u s t 2 0 0 2 How do we know that teaching is effective or ineffective? The typical student rating system judges effectiveness by the degree
( Handout 1 Some Thoughts on Selecting IDEA Objectives A u g u s t 2 0 0 2 How do we know that teaching is effective or ineffective? The typical student rating system judges effectiveness by the degree
Requirements & Guidelines for the Preparation of the New Mexico Online Portfolio for Alternative Licensure
 Requirements & Guidelines for the Preparation of the New Mexico Online Portfolio for Alternative Licensure Prepared for the New Mexico Public Education Department Educator Quality Division http://www.ped.state.nm.us/
Requirements & Guidelines for the Preparation of the New Mexico Online Portfolio for Alternative Licensure Prepared for the New Mexico Public Education Department Educator Quality Division http://www.ped.state.nm.us/
Instructional Design Basics. Instructor Guide
 Instructor Guide Table of Contents...1 Instructional Design "The Basics"...1 Introduction...2 Objectives...3 What is Instructional Design?...4 History of Instructional Design...5 Instructional Design
Instructor Guide Table of Contents...1 Instructional Design "The Basics"...1 Introduction...2 Objectives...3 What is Instructional Design?...4 History of Instructional Design...5 Instructional Design
Aligning Test Items with Course Learning Objectives
 Aligning Test Items with Course Learning Objectives Dr. Jennifer E. Roberts Director of Academic Assessment Office of Institutional Research, Planning, and Assessment Northern Virginia Community College
Aligning Test Items with Course Learning Objectives Dr. Jennifer E. Roberts Director of Academic Assessment Office of Institutional Research, Planning, and Assessment Northern Virginia Community College
AMERICAN SOCIETY OF CIVIL ENGINEERS COMMENTARY. For Architectural Engineering Programs Draft of September 2010
 COMMENTARY For Architectural Engineering Programs Draft of September 2010 Purpose This document has been prepared by the ASCE Committee on Curriculum and Accreditation (CC&A). The purpose of this document
COMMENTARY For Architectural Engineering Programs Draft of September 2010 Purpose This document has been prepared by the ASCE Committee on Curriculum and Accreditation (CC&A). The purpose of this document
white paper The Dokeos e-learning
 white paper The Dokeos project management guide Dokeos, 2007. All rights reserved. 10/05/2007 1 I. Introduction This guide is the result of a series of meetings with companies HR management teams and training
white paper The Dokeos project management guide Dokeos, 2007. All rights reserved. 10/05/2007 1 I. Introduction This guide is the result of a series of meetings with companies HR management teams and training
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, FRESNO DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, FRESNO DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM GOALS AND OBJECTIVES FOR UNDERGRADUATE PSYCHOLOGY MAJORS Goals -- Knowledge, skills and values unique to psychology 1.
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, FRESNO DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM GOALS AND OBJECTIVES FOR UNDERGRADUATE PSYCHOLOGY MAJORS Goals -- Knowledge, skills and values unique to psychology 1.
USING THE PRINCIPLES OF ITIL ; SERVICE CATALOGUE
 USING THE PRINCIPLES OF ITIL ; SERVICE CATALOGUE Examination Syllabus V.0 April 01 ITIL is a registered trade mark of the Cabinet Office APMG Service Catalogue 01 Examination Syllabus INTRODUCTION The
USING THE PRINCIPLES OF ITIL ; SERVICE CATALOGUE Examination Syllabus V.0 April 01 ITIL is a registered trade mark of the Cabinet Office APMG Service Catalogue 01 Examination Syllabus INTRODUCTION The
DEFINING, TEACHING AND ASSESSING LIFELONG LEARNING SKILLS
 DEFINING, TEACHING AND ASSESSING LIFELONG LEARNING SKILLS Nikos J. Mourtos Abstract - Lifelong learning skills have always been important in any education and work setting. However, ABET EC recently put
DEFINING, TEACHING AND ASSESSING LIFELONG LEARNING SKILLS Nikos J. Mourtos Abstract - Lifelong learning skills have always been important in any education and work setting. However, ABET EC recently put
2016 Annual Conference & Exhibition Call for Presentations
 485D Route 1 South, Suite 210 Iselin, NJ 08830 Phone (732) 877-1100 Fax (732) 877-1101 2016 Annual Conference & Exhibition Call for Presentations The Home Care & Hospice Association of New Jersey invites
485D Route 1 South, Suite 210 Iselin, NJ 08830 Phone (732) 877-1100 Fax (732) 877-1101 2016 Annual Conference & Exhibition Call for Presentations The Home Care & Hospice Association of New Jersey invites
USING THE PRINCIPLES OF ITIL ; SERVICE CATALOGUE. Examination Syllabus V 1.2. October 2009
 USING THE PRINCIPLES OF ITIL ; SERVICE CATALOGUE Examination Syllabus V 1. October 009 ITIL is a Registered Trade Mark of the Office of Government Commerce in the United Kingdom and other countries APMG
USING THE PRINCIPLES OF ITIL ; SERVICE CATALOGUE Examination Syllabus V 1. October 009 ITIL is a Registered Trade Mark of the Office of Government Commerce in the United Kingdom and other countries APMG
FOUNDATION YEAR Student Evaluation
 FOUNDATION YEAR Student Evaluation I. Cover Sheet Student Name Home Phone Work Phone Cell Phone Email (Please Check) Full-time Part-time Field Instructor Work Phone Email Agency Cell Phone Site Address
FOUNDATION YEAR Student Evaluation I. Cover Sheet Student Name Home Phone Work Phone Cell Phone Email (Please Check) Full-time Part-time Field Instructor Work Phone Email Agency Cell Phone Site Address
Teaching Critical Thinking Skills to English for Academic Purposes Students
 Teaching Critical Thinking Skills to English for Academic Purposes Students Agenda 1. What is critical thinking? 2. Critical thinking and culture 3. Critical thinking tasks, Bloom s Taxonomy 4. Structuring
Teaching Critical Thinking Skills to English for Academic Purposes Students Agenda 1. What is critical thinking? 2. Critical thinking and culture 3. Critical thinking tasks, Bloom s Taxonomy 4. Structuring
PROGRAM CONCENTRATION: Healthcare Science. Services Introduction to Healthcare Science
 PROGRAM CONCENTRATION: Healthcare Science CAREER PATHWAY: Therapeutic Services COURSE TITLE: Applications of Therapeutic Services PRE-REQUISITE: Introduction to Healthcare Science Applications of Therapeutic
PROGRAM CONCENTRATION: Healthcare Science CAREER PATHWAY: Therapeutic Services COURSE TITLE: Applications of Therapeutic Services PRE-REQUISITE: Introduction to Healthcare Science Applications of Therapeutic
Feedback for the 2012-2013 Annual Assessment Report Department of Speech Pathology and Audiology
 Feedback for the 2012-2013 Annual Assessment Report Department of Speech Pathology and Audiology Amy Liu, Ph.D. Director, Office of Academic Program Assessment (OAPA) Professor of Sociology Shannon Datwyler,
Feedback for the 2012-2013 Annual Assessment Report Department of Speech Pathology and Audiology Amy Liu, Ph.D. Director, Office of Academic Program Assessment (OAPA) Professor of Sociology Shannon Datwyler,
TUFTS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Institutional Educational Objectives
 TUFTS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Institutional Educational Objectives The central aim of the School of Medicine is to produce highly competent, intellectually curious and caring physicians. To this
TUFTS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Institutional Educational Objectives The central aim of the School of Medicine is to produce highly competent, intellectually curious and caring physicians. To this
How To Write The English Language Learner Can Do Booklet
 WORLD-CLASS INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN AND ASSESSMENT The English Language Learner CAN DO Booklet Grades 9-12 Includes: Performance Definitions CAN DO Descriptors For use in conjunction with the WIDA English
WORLD-CLASS INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN AND ASSESSMENT The English Language Learner CAN DO Booklet Grades 9-12 Includes: Performance Definitions CAN DO Descriptors For use in conjunction with the WIDA English
ESL I English as a Second Language I Curriculum
 ESL I English as a Second Language I Curriculum ESL Curriculum alignment with NJ English Language Proficiency Standards (Incorporating NJCCCS and WIDA Standards) Revised November, 2011 The ESL program
ESL I English as a Second Language I Curriculum ESL Curriculum alignment with NJ English Language Proficiency Standards (Incorporating NJCCCS and WIDA Standards) Revised November, 2011 The ESL program
Instructional Design Principles in the Development of LearnFlex
 Instructional Design Principles in the Development of LearnFlex A White Paper by Dr. Gary Woodill, Ed.D. Chief Learning Officer, Operitel Corporation gwoodill@operitel.com Dr. Karen Anderson, PhD. Senior
Instructional Design Principles in the Development of LearnFlex A White Paper by Dr. Gary Woodill, Ed.D. Chief Learning Officer, Operitel Corporation gwoodill@operitel.com Dr. Karen Anderson, PhD. Senior
Undergraduate Psychology Major Learning Goals and Outcomes i
 Undergraduate Psychology Major Learning Goals and Outcomes i Goal 1: Knowledge Base of Psychology Demonstrate familiarity with the major concepts, theoretical perspectives, empirical findings, and historical
Undergraduate Psychology Major Learning Goals and Outcomes i Goal 1: Knowledge Base of Psychology Demonstrate familiarity with the major concepts, theoretical perspectives, empirical findings, and historical
DRAFT TJ PROGRAM OF STUDIES: AP PSYCHOLOGY
 DRAFT TJ PROGRAM OF STUDIES: AP PSYCHOLOGY COURSE DESCRIPTION AP Psychology engages students in a rigorous appraisal of many facets of our current understanding of psychology. The course is based on the
DRAFT TJ PROGRAM OF STUDIES: AP PSYCHOLOGY COURSE DESCRIPTION AP Psychology engages students in a rigorous appraisal of many facets of our current understanding of psychology. The course is based on the
Implementation Date Fall 2008. Marketing Pathways
 PROGRAM CONCENTRATION: CAREER PATHWAY: COURSE TITLE: Marketing, Sales & Service Optional Course for All Marketing Pathways Marketing Research In this course, high school students will gain an understanding
PROGRAM CONCENTRATION: CAREER PATHWAY: COURSE TITLE: Marketing, Sales & Service Optional Course for All Marketing Pathways Marketing Research In this course, high school students will gain an understanding
Dr. Ryan McLawhon Texas A&M University
 Dr. Ryan McLawhon Texas A&M University Introduction to Assessment Components of an Assessment Plan Mission Outcomes Measures Achievement Targets Question and Answer Session NCAAA Standard 4 (&5, etc.)
Dr. Ryan McLawhon Texas A&M University Introduction to Assessment Components of an Assessment Plan Mission Outcomes Measures Achievement Targets Question and Answer Session NCAAA Standard 4 (&5, etc.)
ACADEMIC DIRECTOR: Carla Marquez-Lewis Email Contact: THE PROGRAM Career and Advanced Study Prospects Program Requirements
 Psychology (BA) ACADEMIC DIRECTOR: Carla Marquez-Lewis CUNY School of Professional Studies 101 West 31 st Street, 7 th Floor New York, NY 10001 Email Contact: Carla Marquez-Lewis, carla.marquez-lewis@cuny.edu
Psychology (BA) ACADEMIC DIRECTOR: Carla Marquez-Lewis CUNY School of Professional Studies 101 West 31 st Street, 7 th Floor New York, NY 10001 Email Contact: Carla Marquez-Lewis, carla.marquez-lewis@cuny.edu
Mentoring and Coaching Models
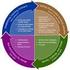 Mentoring and Coaching Models Peer coaching is a of staff development model you can use to help you and your partners develop and try new strategies and determine what does and does not work by critically
Mentoring and Coaching Models Peer coaching is a of staff development model you can use to help you and your partners develop and try new strategies and determine what does and does not work by critically
Competency-based Approach to support Learning Objectives in Learning, Education and Training
 Competency-based Approach to support Learning Objectives in Learning, Education and Training Christian Saul, Peter Hofmann, Martina Lucht, Peter Pharow Data Representation and Interfaces Fraunhofer IDMT
Competency-based Approach to support Learning Objectives in Learning, Education and Training Christian Saul, Peter Hofmann, Martina Lucht, Peter Pharow Data Representation and Interfaces Fraunhofer IDMT
Principles of Data-Driven Instruction
 Education in our times must try to find whatever there is in students that might yearn for completion, and to reconstruct the learning that would enable them autonomously to seek that completion. Allan
Education in our times must try to find whatever there is in students that might yearn for completion, and to reconstruct the learning that would enable them autonomously to seek that completion. Allan
Integrating Field Research, Problem Solving, and Design with Education for Enhanced Realization
 Integrating Field Research, Problem Solving, and Design with Education for Enhanced Realization Mohamed El-Sayed Kettering University Mechanical Engineering Flint, MI, 48504 USA and Jacqueline El-Sayed
Integrating Field Research, Problem Solving, and Design with Education for Enhanced Realization Mohamed El-Sayed Kettering University Mechanical Engineering Flint, MI, 48504 USA and Jacqueline El-Sayed
Autism Spectrum Disorder Performance Standards and Evaluation Criteria Rubric
 Autism Spectrum Disorder Performance Standards and Evaluation Criteria Rubric 1. Professional Knowledge The teacher demonstrates an understanding of curriculum, subject content, and the developmental needs
Autism Spectrum Disorder Performance Standards and Evaluation Criteria Rubric 1. Professional Knowledge The teacher demonstrates an understanding of curriculum, subject content, and the developmental needs
LECTURE AND NOTE TAKING
 LECTURE AND NOTE TAKING Goals of Note Taking Taking notes helps with classroom concentration, test preparation and for clues as to what the instructor feels is most important. Prepare to take effective
LECTURE AND NOTE TAKING Goals of Note Taking Taking notes helps with classroom concentration, test preparation and for clues as to what the instructor feels is most important. Prepare to take effective
Evaluating Students in the Classroom. 2007 Faculty Development Conference February 2007 D. P. Shelton, MSN, RN, CNE, EdD (c)
 Evaluating Students in the Classroom 2007 Faculty Development Conference February 2007 D. P. Shelton, MSN, RN, CNE, EdD (c) Objectives Describe assessment strategies for use in the classroom. Explore the
Evaluating Students in the Classroom 2007 Faculty Development Conference February 2007 D. P. Shelton, MSN, RN, CNE, EdD (c) Objectives Describe assessment strategies for use in the classroom. Explore the
Learning theories Judy McKimm
 Learning theories Judy McKimm There has been a lot of research into the way people learn and certain theories have been influential on developments in all areas of education, but particularly in adult
Learning theories Judy McKimm There has been a lot of research into the way people learn and certain theories have been influential on developments in all areas of education, but particularly in adult
Students are required to undertake placement activities in mixed gender environments which reflect the Australian health care context.
 Introduction to inherent requirements for undergraduate Nursing course These inherent requirements apply to the following course: Bachelor of Nursing The School of Nursing at Avondale College of Higher
Introduction to inherent requirements for undergraduate Nursing course These inherent requirements apply to the following course: Bachelor of Nursing The School of Nursing at Avondale College of Higher
Degree- Level Expectations and Course Learning Outcomes
 Degree- Level Expectations and Course Learning Outcomes Introduction to DLEs Degree-Level Expectations (DLEs) are a threshold framework for the expression of the intellectual and creative development of
Degree- Level Expectations and Course Learning Outcomes Introduction to DLEs Degree-Level Expectations (DLEs) are a threshold framework for the expression of the intellectual and creative development of
Overview & Examples: Program Educational Objectives (PEOs), Program Outcomes (POs), Course Outcomes (COs)
 Overview & Examples: Program Educational Objectives (PEOs), Program Outcomes (POs), Course Outcomes (COs) Program Educational Objectives (Texas Tech University) The mission of Texas Tech University and
Overview & Examples: Program Educational Objectives (PEOs), Program Outcomes (POs), Course Outcomes (COs) Program Educational Objectives (Texas Tech University) The mission of Texas Tech University and
2. SUMMER ADVISEMENT AND ORIENTATION PERIODS FOR NEWLY ADMITTED FRESHMEN AND TRANSFER STUDENTS
 Chemistry Department Policy Assessment: Undergraduate Programs 1. MISSION STATEMENT The Chemistry Department offers academic programs which provide students with a liberal arts background and the theoretical
Chemistry Department Policy Assessment: Undergraduate Programs 1. MISSION STATEMENT The Chemistry Department offers academic programs which provide students with a liberal arts background and the theoretical
Curriculum Development in 6 easy steps for busy Med-Ed types. Curriculum Development in MedEd
 Curriculum Development in 6 easy steps for busy Med-Ed types Joanne Lynn MD Curriculum Development in MedEd Medical educators are often charged to plan educational experiences without specific training
Curriculum Development in 6 easy steps for busy Med-Ed types Joanne Lynn MD Curriculum Development in MedEd Medical educators are often charged to plan educational experiences without specific training
Developing Objectives and Relating them to Assessment
 Developing Objectives and Relating them to Assessment Ms Sue Bannister Assessment Lecturer Education Centre Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry University of Western Australia sbannis@ cyllene.uwa.edu.au May
Developing Objectives and Relating them to Assessment Ms Sue Bannister Assessment Lecturer Education Centre Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry University of Western Australia sbannis@ cyllene.uwa.edu.au May
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 2014-2015
 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 2014-2015 Course Definitions, Designators and Format Courses approved at the time of publication are listed in this bulletin. Not all courses are offered every term. Refer to the online
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 2014-2015 Course Definitions, Designators and Format Courses approved at the time of publication are listed in this bulletin. Not all courses are offered every term. Refer to the online
CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE)
 CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE) The Teaching Performance Expectations describe the set of knowledge, skills, and abilities that California expects of each candidate for a Multiple
CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE) The Teaching Performance Expectations describe the set of knowledge, skills, and abilities that California expects of each candidate for a Multiple
Alignment of the Career and Life Role Common Curriculum Goals with Career-Related Learning Standards Oregon Department of Education October 2002
 Alignment of the Career and Life Role with Oregon Department of Education October 2002 (available on the ODE website at www.ode.state.or.us/cimcam) The Oregon Department of Education hereby gives permission
Alignment of the Career and Life Role with Oregon Department of Education October 2002 (available on the ODE website at www.ode.state.or.us/cimcam) The Oregon Department of Education hereby gives permission
TOOL KIT for RESIDENT EDUCATOR and MENT OR MOVES
 Get to Know My RE Observe Collect Evidence Mentor Moments Reflect Review Respond Tailor Support Provide Provide specific feedback specific Feedback What does my RE need? Practice Habits Of Mind Share Data
Get to Know My RE Observe Collect Evidence Mentor Moments Reflect Review Respond Tailor Support Provide Provide specific feedback specific Feedback What does my RE need? Practice Habits Of Mind Share Data
Updated 2011 CURRICULUM / INSTRUCTION / ASSESSMENT
 Updated 2011 CURRICULUM / INSTRUCTION / ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM / INSTRUCTION / ASSESSMENT C/I/A-1 CURRICULUM / INSTRUCTION / ASSESSMENT Instructional Leadership Development Framework for Data-driven Systems
Updated 2011 CURRICULUM / INSTRUCTION / ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM / INSTRUCTION / ASSESSMENT C/I/A-1 CURRICULUM / INSTRUCTION / ASSESSMENT Instructional Leadership Development Framework for Data-driven Systems
2011-2012 Program Guidebook Industrial and Organizational Psychology, M.A. - Chicago
 2011-2012 Program Guidebook Industrial and Organizational Psychology, M.A. - Chicago Table of Contents Department Educational Model and Goals... 3 TCSPP Individual and Cultural Differences... 3 Program
2011-2012 Program Guidebook Industrial and Organizational Psychology, M.A. - Chicago Table of Contents Department Educational Model and Goals... 3 TCSPP Individual and Cultural Differences... 3 Program
An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment
 An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment Dr. David Seiler, Assistant Professor, Department of Adult and Career Education, Valdosta State University,
An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment Dr. David Seiler, Assistant Professor, Department of Adult and Career Education, Valdosta State University,
Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession
 12 Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession 1 Teachers understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Teachers display knowledge of how
12 Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession 1 Teachers understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Teachers display knowledge of how
