NewNet. SMserver. Wireless Short Message Service Tutorial
|
|
|
- Daisy Fleming
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SMserver TM Wireless Short Message Service Tutorial
2 DEFINITION Short message service (SMS) is a globally accepted wireless service that enables the transmission of alphanumeric messages between mobile subscribers and external systems such as electronic mail, paging, and voice mail systems. TUTORIAL OVERVIEW This tutorial provides an introduction to basic SMS concepts, specifications, networks, and services. TOPICS 1. Introduction - Short Message Service 2. Benefits of Short Message Service 3. Network Elements and Architecture 4. Signaling Elements 5. Mobile-Terminated Short Message Example 6. Mobile-Originated Short Message Example 7. Acronyms 8. Self-Test 9. Answers to Self-Test Copyright 1999 Page i
3 This Page is Left Blank Intentionally Copyright 1999 Page ii
4 1. Introduction - Short Message Service SMS appeared on the wireless scene in 1991 in Europe, where digital wireless technology first took hold. The European standard for digital wireless, now known as the global standard for mobiles (GSM), included short messaging services from the outset. In North America, SMS was initially made available on digital wireless networks built by early pioneers such as BellSouth Mobility and Nextel. In 1998, as the build out of PCS networks based on GSM, code division multiple access (CDMA), and time division multiple access (TDMA) access methods is completed, SMS is expected to enjoy fullfledged deployment. The point-to-point SMS provides a mechanism for transmitting "short" messages to and from wireless handsets. The service makes use of a short message service center (SMSC) which acts as a store and forward system for short messages. The wireless network provides for the transport of short messages between the SMSCs and wireless handsets. In contrast to existing text message transmission services, such as alphanumeric paging, the service elements are designed to provide guaranteed delivery of text messages to the destination. A distinguishing characteristic of the service is that an active mobile handset is able to receive or submit a short message at any time, independent of whether or not a voice or data call is in progress. SMS also guarantees delivery of the short message by the network. Temporary failures are identified, and the short message is stored in the network until the destination becomes available. SMS is characterized by out-of-band packet delivery and low-bandwidth message transfer. Initial applications of SMS focused on eliminating alphanumeric pagers by permitting twoway general purpose messaging and notification services, primarily for voice mail. As technology and networks matured, a variety of services were introduced, including electronic mail and fax integration, paging integration, interactive banking, and information services such as stock quotes. Wireless data applications include downloading of SIM cards for activation, debit, and profile editing purposes. Copyright 1999 Page 1
5 2. Benefits of Short Message Service In today's competitive world, differentiation is a significant factor in the success of the service provider. Once the basic services, such as voice telephony, are deployed, SMS provides a powerful vehicle for service differentiation. The benefits of SMS to the service provider are as follows: Increased call completion on wireless and wireline networks by leveraging the notification capabilities of SMS An alternative to alphanumeric paging services Enabling wireless data access for corporate users Provision of value-added services such as , voice mail, and fax mail integration, reminder service, stock and currency quotes, and airline schedules Provision of key administrative services such as advice of charge, over-the-air downloading, and service provisioning All of these benefits are attainable quickly with modest incremental cost, and typical investment payback periods are less than six months. The benefits of SMS to subscribers center around convenience, flexibility, and seamless integration of messaging services and data access. From this perspective, the benefit is to be able to use the handset as an extension of the computer. SMS also eliminates the need for separate devices for messaging since services can be integrated into a single wireless device the mobile terminal. Copyright 1999 Page 2
6 3. Network Elements and Architecture The basic network structure of the SMS is depicted in Figure 1. Figure 1: Network Elements and Architecture SMC HLR VLR SMC SMC SMSC SMC G/IWMSC SS7 MSC BSS SMC 3.1 Short Messaging Entities Short messaging entity (SME) is an entity which may receive or send short messages. The SME may be located in the fixed network, a mobile station, or another service center. 3.2 Short Message Service Center Short message service center (SMSC) is responsible for the relaying and store-andforwarding of a short message between an SME and mobile station. SMS-Gateway/Interworking Mobile Switching Center The SMS gateway MSC (SMS-GMSC) is an MSC capable of receiving a short message from an SMSC, interrogating a home location register (HLR) for routing information, and delivering the short message to the "visited" MSC of the recipient mobile station. The SMS interworking MSC (SMS-IWMSC) is an MSC capable of receiving a short message from the mobile network and submitting it to the appropriate SMSC. The SMS- GMSC/SMS-IWMSC are typically integrated with the SMSC. Copyright 1999 Page 3
7 3.3 Home Location Register The home location register (HLR) is a database used for permanent storage and management of subscriptions and service profiles. Upon interrogation by the SMSC, the HLR provides the routing information for the indicated subscriber. The HLR also informs the SMSC, which has previously initiated unsuccessful short message delivery attempts to a specific mobile station, that the mobile station is now recognized by the mobile network to be accessible. 3.4 Mobile Switching Center The mobile switching center (MSC) performs the switching functions of the system and controls calls to and from other telephone and data systems. 3.5 Visitor Location Register The visitor location register (VLR) is a database that contains temporary information about subscribers. This information is needed by the MSC in order to service visiting subscribers. 3.6 The Base Station System All radio-related functions are performed in the base station system (BSS). The BSS consists of base station controllers (BSCs) and the base transceiver stations (BTSs), and its primary responsibility is to transmit voice and data traffic between the mobile stations. 3.7 The Mobile Station The mobile station (MS) is the wireless terminal capable of receiving and originating short messages as well as voice calls. The wireless network signaling infrastructure is based on Signaling System No 7 (SS7). SMS makes use of the mobile application part (MAP) which defines the methods and mechanisms of communication in wireless networks, and uses the services of the SS7 transaction capabilities application part (TCAP). An SMS service layer makes use of the MAP signaling capabilities and enables the transfer of short messages between the peer entities. Copyright 1999 Page 4
8 4. Signaling Elements The mobile application part (MAP) layer defines the operations necessary to support the short message service. Both American and international standards bodies have defined a MAP layer using the services of the signaling system No. 7 transaction capabilities part. The American standard is published by Telecommunication Industry Association and is referred to as IS-41. The international standard is defined by the European Telecommunication Standards Institute and is referred to as GSM MAP. The following basic MAP operations are necessary to provide the end-to-end short message service: Routing information request: Before attempting short message delivery, the SMSC needs to retrieve routing information in order to determine the serving MSC for the mobile station at the time of the delivery attempt. This is accomplished by way of an interrogation of the HLR which is accomplished via the use of the SMSrequest and sendroutinginfoforshortmsg mechanisms in IS41 and GSM respectively. Point-to-point short message delivery: The mechanism provides a means for the SMSC to transfer a short message to the MSC which is serving the addressed mobile station and attempts to deliver a message to an MS whenever the MS is registered, even when the MS is engaged in a voice or data call. The short message delivery operation provides a confirmed delivery service. The operation works in tandem with the base station subsystem while the message is being forwarded from the MSC to the MS. Therefore, the outcome of the comprises either success (i.e., delivery to the mobile) or failure caused by one of several possible reasons. The point-to-point short message delivery is accomplished via the use of the Short Message Delivery-Point-to- Point (SMD-PP) and forwardshortmessage mechanisms in IS-41 and GSM respectively. Short message waiting indication: The operation is activated when a short message delivery attempt by the SMSC fails due to a temporary failure and provides a means for the SMSC to request the HLR to add an SMSC address to the list of SMSCs to be informed when the indicated mobile station becomes accessible. This short message waiting indication is realized via the use of the SMS notification indicator and set message waiting data mechanisms in IS41 and GSM respectively. Service center alert: The operation provides a means for the HLR to inform the SMSC which has previously initiated unsuccessful short message delivery attempts to a specific mobile station, that the mobile station is now recognized by the mobile network to be accessible. This service center alert is accomplished via the use of the SMS notification and alert service mechanisms in IS41 and GSM respectively. Copyright 1999 Page 5
9 4.1 Service Elements SMS comprises several service elements relevant to the reception and submission of short messages: Validity period: The validity period indicates how long the SMSC shall guarantee the storage of the short message before delivery to the intended recipient. Priority: Priority is the information element provided by an SME to indicate the priority message. In addition, SMS provides a time stamp reporting the time of submission of the message and an indication to the handset of whether or not there are more messages to send (GSM) or the number of additional messages to send (IS-41). 4.2 Subscriber Services SMS comprises two basic point-to-point services: Mobile-originated short message (MO-SM) Mobile-terminated short message (MT-SM) Mobile-originated short messages are transported from the handset to the SMSC and can be destined to other mobile subscribers or for subscribers on fixed networks such as paging networks or electronic mail networks. Mobile-terminated short messages are transported from the SMSC to the handset and can be submitted to the SMSC by other mobile subscribers via MO-SM or by other sources such as voice mail systems, paging networks, or operators. For MT-SM, a report is always returned to the SMSC either confirming the short message delivery to the handset or informing the SMSC of the short message delivery failure and identifying the reason for failure. Similarly, for MO-SM, a report is always returned to the handset either confirming the short message delivery to the SMSC or informing the handset of the encountered failure identifying the reason. Depending on the access method and the encoding of the bearer data, the point-to-point short messaging service conveys up to 190 characters to a short message entity (SME). For messages requiring immediate delivery, only one message delivery attempt is made per service request. For messages not requiring immediate delivery, one or more delivery attempts are made until an acknowledgment is received. Copyright 1999 Page 6
10 In GSM networks, the type of messaging service is identified by the protocol identifier information element which identifies the higher level protocol or interworking being used. Examples are telex, group 3 telefax, X.400 messaging, ERMES, and voice telephone. In IS41 networks, the service type is distinguished by use of the teleservice identifier. Basic teleservices include the following: Cellular messaging teleservice (CMT) Cellular paging teleservice (CPT) Voice mail notification teleservice (VMN) CMT differs from the CPT due to the inclusion of a reply mechanism which enables a user or network acknowledgment to be selected on a per message basis. The user acknowledgment includes a response code which paves the way for powerful interactive services between SMCs. Many service applications can be implemented combining these service elements. Besides the obvious notification services, SMS can be used in one-way or interactive services providing wireless access to any type of information anywhere. Leveraging new emerging technologies combining browsers, servers, and new markup languages designed for mobile terminals, SMS can enable wireless devices to securely access and send information from the Internet or intranets quickly and cost-efficiently. A generic network infrastructure for realizing the innovative SMS services is depicted in Figure 2. Figure 2: Network Infrastructure PC Operator Wireline Network Paging Terminal CCBS Short Message Service Center SS7 Wireless Network Operator Corporate Intranet Public Internet CCBS (Customer Care & Billing System) DBMS ( Data Base Management System) Server Transaction Gateway DBMS Corporate Data Stock Quotes Airline Schedules Banking Services Internetworking Notification Directory Assistance Copyright 1999 Page 7
11 Some of the potential applications of SMS technology, utilizing both MT-SM and MO- SM where appropriate, are: Notification services: Notification services are currently the most widely deployed SMS services. Examples of notification services using SMS include the following: voice/fax message notification, which indicates that voice mail messages are present in a voice mailbox; notification, which indicates that messages are present in an mailbox; and reminder/calendar services, which enables reminders for meetings and scheduled appointment. interworking: Existing services (e.g., SMTP, X.400) can be easily integrated with SMS to provide duplex to short messaging. Paging interworking: Paging services (e.g., TAP, TNPP, TDP) integrated with SMS would allow digital wireless subscribers to be accessible via existing paging interfaces. Information services: A wide variety of information services can be provided by the SMS, including weather reports, traffic information, entertainment information (e.g., cinema, theater, concerts), financial information (e.g., stock quotes, exchange rates, banking, brokerage services), and directory assistance. 4.3 Mobile Data Services The SMSC can also be used to provide "short" wireless data. The wireless data may be in interactive services where voice calls are involved. Some examples of services of this nature include fleet dispatch, inventory management, itinerary confirmation, sales order processing, and customer contact management. 4.4 Customer Care and Management The SMSC can also be used to transfer binary data which can be interpreted by the mobile station without presentation to the customer. This capability allows the operators to administer their customers by providing capabilities for programming the mobile station. Examples of such services include mobile station programming, which allows customer profiles and subscription characteristics to be downloaded to the mobile station (customers can be activated/deactivated based on the data downloaded) and advice of charge, which enables the SMS to be used to report charges incurred for the phone call (e.g., taxi pay phone). Copyright 1999 Page 8
12 5. Mobile-Terminated Short Message Example Figure 3 depicts the successful MT-SM scenario. For convenience, the GSM method is illustrated. However, the IS41 method is similar. Figure 3: MT-SM Scenario SMC SMSC HLR MSC VLR MS 1. Submit-SM 2. sendrouting InfoForShortMsg 3. forwardshortmessage 4a. sendinfo ForMT-SMS 4b. sendinfo ForMT-SMS (Ack) Page Authent. 5. Message Transfer 7. Status Report 6. Delivery Report Operation invocation or message transfer Successful operation invocation or message transfer 1. The short message is submitted from the SME to the SMSC. 2. After completing its internal processing, the SMSC interrogates the HLR and receives the routing information for the mobile subscriber. 3. The SMSC sends the short message to the MSC using the forwardshortmessage operation. 4. The MSC retrieves the subscriber information from the VLR. This operation may include an authentication procedure. 5. The MSC transfers the short message to the MS. 6. The MSC returns to the SMSC the outcome of the forwardshortmessage operation. 7. If requested by the SME, the SMSC returns a status report indicating delivery of the short message. Copyright 1999 Page 9
13 6. Mobile-Originated Short Message Example Figure 4 depicts the successful MO-SM scenario. For convenience, the GSM method is shown. However, the IS41 method is similar. Figure 4: MO-SM Scenario SMC SMSC HLR MSC VLR MS Access Request and Authentication 1. Message Transfer 2. sendinfo ForMO-SMS 4. Submit-SM 3. forwardshortmessage 5. Delivery Report 6. Delivery Report Operation invocation or message transfer Successful operation invocation or message transfer 1. The MS transfers the SM to the MSC. 2. The MSC interrogates the VLR to verify that the message transfer does not violate the supplementary services invoked or the restrictions imposed. 3. The MSC sends the short message to the SMSC using the forwardshortmessage operation. 4. The SMSC delivers the short message to the SME. 5. The SMSC acknowledges to the MSC the successful outcome of the forwardshortmessage operation. 6. The MSC returns to the MS the outcome of the MO-SM operation. Copyright 1999 Page 10
14 7. Acronyms AC Authentication Center AIN Advanced Intelligent Networks BSC Base Station Controllers BSS Base Station System BTS Base Transceiver Station CDMA Code Division Multiple Access CMT Cellular Messaging Teleservice CPT Cellular Paging Teleservice GMSC Gateway Mobile Switching Center GSM Global Standard for Mobiles HLR Home Location Register MAP Mobile Application Part MIN Mobile Identification Number MO-SM Mobile-Originated Short Message MS Mobile Station MSC Mobile Switching Center MT-SM Mobile-Terminated Short Message SM Short Message SMD-PP Short Message Delivery Point-to-Point SME Short Message Entity SMS Short Message Service SMSC Short Message Service Center SMS-GMSC Gateway Mobile Switching Center SMS-IWMSC SMS Interworking Mobile Switching Center SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol SS7 Signaling System 7 TAP Telocator Alphanumeric Protocol TCAP Transaction Capabilities Application Part TDMA Time Division Multiple Access TDP Telocator Data Protocol TNPP Telocator Network Paging Protocol VLR Visitor Location Register VMN Voice Mail Notification Copyright 1999 Page 11
15 8. Self-Test 1. Short message service (SMS) enables a user to receive a message at any time, whether or not a voice or data call is in progress. a. True b. False 2. Like alphanumeric paging service, SMS does not guarantee that the message will be delivered. a. True b. False 3. SMS is a delivery-only service and does not provide capabilities for interactive services. a. True b. False 4. The SMSC can also transfer binary data which is never seen by the customer. a. True b. False 5. The SMSC interfaces directly with the BSC to receive the result of the message transmission to the handset. a. True b. False 6. SMS is limited to the transmission of 40 characters. a. True b. False Copyright 1999 Page 12
16 8. Self-Test Continued 7. SMS utilizes existing digital cellular infrastructure. a. True b. False 8. The provides routing information for mobile subscribers. a. SMSC b. HLR 9. Which access method supports CPT? a. GSM b. CDMA c. TDMA d. All of the above 10. In a mobile-terminated short message delivery (MT-SM), the first query is to the. a. VLR b. HLR c. Mobile station d. None of the above Copyright 1999 Page 13
17 9. Answers to Self-Test 1. A - True 2. B - False 3. B - False 4. A - True 5. B - False 6. B - False 7. A - True 8. B - HLR 9. B - CDMA 10. B - HLR ADC NewNet, Inc. Enterprise Drive, Shelton, CT Tel: (203) (toll free newnet) Fax: (203) smsinfo@newnet.com Copyright 1999 Page 14
Wireless Short Message Service (SMS)
 Wireless Short Message Service (SMS) Definition Short message service (SMS) is a globally accepted wireless service that enables the transmission of alphanumeric messages between mobile subscribers and
Wireless Short Message Service (SMS) Definition Short message service (SMS) is a globally accepted wireless service that enables the transmission of alphanumeric messages between mobile subscribers and
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
1. Introduction: The Evolution of Mobile Telephone Systems
 IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
INTELLIGENT NETWORK SERVICES MIGRATION MORE VALUE FOR THE
 INTELLIGENT NETWORK SERVICES MIGRATION MORE VALUE FOR THE Voice over LTE SUBSCRIBER TECHNOLOGY White Paper Mobile operators have invested a lot of time and money in Intelligent Network (IN) services for
INTELLIGENT NETWORK SERVICES MIGRATION MORE VALUE FOR THE Voice over LTE SUBSCRIBER TECHNOLOGY White Paper Mobile operators have invested a lot of time and money in Intelligent Network (IN) services for
M E M O R A N D U M. Wireless Roaming Services for Emergency Medical Facilities
 M E M O R A N D U M TO: FROM: RE: Mr. Jim Bugel, AT&T David Robinson, Syniverse Technologies Wireless Roaming Services for Emergency Medical Facilities DATE: December 13, 2007 Automatic wireless roaming
M E M O R A N D U M TO: FROM: RE: Mr. Jim Bugel, AT&T David Robinson, Syniverse Technologies Wireless Roaming Services for Emergency Medical Facilities DATE: December 13, 2007 Automatic wireless roaming
Mobile Networking. SS7 Network Architecture. Purpose. Mobile Network Signaling
 Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Short Message Service
 GPP C.S00-0 Short Message Service COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational Partners may copyright and issue documents or standards publications
GPP C.S00-0 Short Message Service COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational Partners may copyright and issue documents or standards publications
ETSI TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06)
 TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
GSM and IN Architecture
 GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP Raimo.Kantola@netlab.hut.fi Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP Raimo.Kantola@netlab.hut.fi Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
SMS History. Introduction to SMS and SMS Messaging Services
 Introduction to SMS and SMS Messaging Services The Short Message Service (SMS), as defined within the GSM digital mobile phone standard that is popular in Europe, the Middle East, Asia, Africa and some
Introduction to SMS and SMS Messaging Services The Short Message Service (SMS), as defined within the GSM digital mobile phone standard that is popular in Europe, the Middle East, Asia, Africa and some
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
1 Introduction. 2 Assumptions. Implementing roaming for OpenBTS
 Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET
 Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
Short Message Service (SMS) for Wideband Spread Spectrum Systems
 November 0 Short Message Service (SMS) for Wideband Spread Spectrum Systems 0 GPP GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational Partners may copyright
November 0 Short Message Service (SMS) for Wideband Spread Spectrum Systems 0 GPP GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational Partners may copyright
3GPP TS 23.011 V5.0.0 (2002-06)
 TS 23.011 V5.0.0 (2002-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical realization of Supplementary Services (Release 5) GLOBAL SYSTEM
TS 23.011 V5.0.0 (2002-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical realization of Supplementary Services (Release 5) GLOBAL SYSTEM
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server
 Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS)
 Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS) N.J Croft and M.S Olivier Information and Computer Security Architectures (ICSA) Research Group Department of Computer Science
Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS) N.J Croft and M.S Olivier Information and Computer Security Architectures (ICSA) Research Group Department of Computer Science
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
 Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) Definition Wireless application protocol (WAP) is an application environment and set of communication protocols for wireless devices designed to enable manufacturer-,
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) Definition Wireless application protocol (WAP) is an application environment and set of communication protocols for wireless devices designed to enable manufacturer-,
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks
 Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Optus EmailSMS for MS Outlook and Lotus Notes
 Optus EmailSMS for MS Outlook and Lotus Notes Service Description, August 2005. OVERVIEW This document provides an overview of the Optus EmailSMS service delivered jointly by Optus and redcoal. It highlights
Optus EmailSMS for MS Outlook and Lotus Notes Service Description, August 2005. OVERVIEW This document provides an overview of the Optus EmailSMS service delivered jointly by Optus and redcoal. It highlights
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration
 Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Definition The convergence of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol (IP) data networks promises exciting opportunities
Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Definition The convergence of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol (IP) data networks promises exciting opportunities
Error and Confirmation Codes
 Error and Confirmation s The following two tables list the error and confirmation codes that can be returned within SMS replies or notifications. Table 14: Error s 8 008 10 00A 21 015 27 01B 28 01C 29
Error and Confirmation s The following two tables list the error and confirmation codes that can be returned within SMS replies or notifications. Table 14: Error s 8 008 10 00A 21 015 27 01B 28 01C 29
International Journal of Computing and Business Research (IJCBR)
 AN INVESTIGATION OF GSM ARCHITECTURE AND OVERLAYING WITH EFFICIENT SECURITY PROTOCOL Karun Madan, Surya World Institute of Engg. & Technology, Rajpura, Punjab ABSTRACT The Global System for Mobile Communications
AN INVESTIGATION OF GSM ARCHITECTURE AND OVERLAYING WITH EFFICIENT SECURITY PROTOCOL Karun Madan, Surya World Institute of Engg. & Technology, Rajpura, Punjab ABSTRACT The Global System for Mobile Communications
Mobile IP Network Layer Lesson 01 OSI (open systems interconnection) Seven Layer Model and Internet Protocol Layers
 Mobile IP Network Layer Lesson 01 OSI (open systems interconnection) Seven Layer Model and Internet Protocol Layers Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 OSI (open systems interconnection)
Mobile IP Network Layer Lesson 01 OSI (open systems interconnection) Seven Layer Model and Internet Protocol Layers Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 OSI (open systems interconnection)
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service
 SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service Takuya Shinozaki, Etsuko Matsubara, Masahiro Kadono and Mayumi Takahashi DoCoMo s SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service have been launched. It
SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service Takuya Shinozaki, Etsuko Matsubara, Masahiro Kadono and Mayumi Takahashi DoCoMo s SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service have been launched. It
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
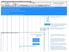 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
GSM GSM 02.67 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.1
 GSM GSM 02.67 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.1 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-010267QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 02.67 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.1 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-010267QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
SMS Access and SMS Bedrift. Whitepaper
 062009 SMS Access and SMS Bedrift Connection to the SMS Centre Whitepaper VERSION 2.3, JUNE 2009 VERSION 2.2 Contents +1 Abbreviations and terms... 4 2 General... 5 3 SMS transmission... 6 3.1 Transmission
062009 SMS Access and SMS Bedrift Connection to the SMS Centre Whitepaper VERSION 2.3, JUNE 2009 VERSION 2.2 Contents +1 Abbreviations and terms... 4 2 General... 5 3 SMS transmission... 6 3.1 Transmission
- SS7 TT & SSN Assignment Repository (as of August 2011)
 - SS7 TT & SSN Assignment Reposiry (as of August 2011) Table 1 - ANSI SS7 Translation Type (TT) code value known assignments: Use of the following TT values are recommended (although the use of other values
- SS7 TT & SSN Assignment Reposiry (as of August 2011) Table 1 - ANSI SS7 Translation Type (TT) code value known assignments: Use of the following TT values are recommended (although the use of other values
Network Support for MDN-Based Message Centers
 GPP N.S00-0 version.0 Version Date: November 00 Network Support for MDN-Based Message Centers COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
GPP N.S00-0 version.0 Version Date: November 00 Network Support for MDN-Based Message Centers COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
Introduction to SS7 Signaling This tutorial provides an overview of Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) network architecture and protocols
 Introduction to SS7 Signaling This tutorial provides an overview of Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) network architecture and protocols SS7 is a set of telephony signaling protocols that are used to set up
Introduction to SS7 Signaling This tutorial provides an overview of Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) network architecture and protocols SS7 is a set of telephony signaling protocols that are used to set up
Unified Messaging. Definition. Overview. Topics
 Unified Messaging Definition Unified messaging is the integration of several different communications media, such that users will be able to retrieve and send voice, fax, and e-mail messages from a single
Unified Messaging Definition Unified messaging is the integration of several different communications media, such that users will be able to retrieve and send voice, fax, and e-mail messages from a single
1. Public Switched Telephone Networks vs. Internet Protocol Networks
 Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Tutorial Definition Internet telephony switches enable voice calls between the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol
Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Tutorial Definition Internet telephony switches enable voice calls between the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol
Bölüm 8. GSM. 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar!
 Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
Enabling Modern Telecommunications Services via Internet Protocol and Satellite Technology Presented to PTC'04, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA
 CASE STUDY Enabling Modern Telecommunications Services via Internet Protocol and Satellite Technology Presented to PTC'04, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA Stephen Yablonski and Steven Spreizer Globecomm Systems,
CASE STUDY Enabling Modern Telecommunications Services via Internet Protocol and Satellite Technology Presented to PTC'04, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA Stephen Yablonski and Steven Spreizer Globecomm Systems,
Mobile SMS and Data Roaming Explained
 Mobile SMS and Data Roaming Explained Mobile SMS and data roaming explained Roaming is the ability of customers to use their mobile phones or other mobile devices outside the geographical coverage area
Mobile SMS and Data Roaming Explained Mobile SMS and data roaming explained Roaming is the ability of customers to use their mobile phones or other mobile devices outside the geographical coverage area
Information Services and Access Mechanism of Mobile Web for the Under-privileged
 Information Services and Access Mechanism of Mobile Web for the Under-privileged Asoke K Talukder International Institute of Information Technology Bangalore Email: asoketalukder @ iiitbacin Abstract To
Information Services and Access Mechanism of Mobile Web for the Under-privileged Asoke K Talukder International Institute of Information Technology Bangalore Email: asoketalukder @ iiitbacin Abstract To
Short Message Service using SMS Gateway
 Short Message Service using SMS Gateway Veena K.Katankar M.E.-4 th Sem (Wireless Communication & Computing) G.H. Raisoni College Of Engg, Nagpur Dr.V.M.Thakare Professor & H.O.D. Dept. Of Computer Science
Short Message Service using SMS Gateway Veena K.Katankar M.E.-4 th Sem (Wireless Communication & Computing) G.H. Raisoni College Of Engg, Nagpur Dr.V.M.Thakare Professor & H.O.D. Dept. Of Computer Science
Analysis of GSM Network for Different Transmission Powers
 Analysis of GSM Network for Different Transmission Powers Mandeep Singh 1, Supreet Kaur 2 1,2 (Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India) Abstract: To
Analysis of GSM Network for Different Transmission Powers Mandeep Singh 1, Supreet Kaur 2 1,2 (Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India) Abstract: To
The Shift to Wireless Data Communication
 The Shift to Wireless Data Communication Choosing a Cellular Solution for Connecting Devices to a WWAN Dana Lee, Senior Product Manager dana.lee@moxa.com Recent developments in the wireless and industrial
The Shift to Wireless Data Communication Choosing a Cellular Solution for Connecting Devices to a WWAN Dana Lee, Senior Product Manager dana.lee@moxa.com Recent developments in the wireless and industrial
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
What is telecommunication? electronic communications. service?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
GSM GSM 02.86 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 02.86 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-010286Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 02.86 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-010286Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems. Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering
 Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP Operations
 Advanced S Series: S and 3GPP Operations, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been chosen by the 3GPP for establishing multimedia sessions in UMTS Release 5 (R5) networks.
Advanced S Series: S and 3GPP Operations, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been chosen by the 3GPP for establishing multimedia sessions in UMTS Release 5 (R5) networks.
SIP Roaming Server Product Overview. Mobile Convergence Technology
 SIP Roaming Server Product Overview Mobile Convergence Technology CONNECTING NETW ORKS Roam, Talk and Text (without a Mobile Network) By interworking with existing communications infrastructures, Session
SIP Roaming Server Product Overview Mobile Convergence Technology CONNECTING NETW ORKS Roam, Talk and Text (without a Mobile Network) By interworking with existing communications infrastructures, Session
What is telecommunication? electronic communications? What is telephony?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu Teletekniikan laboratorio S-38.128 Teletekniikan erikoistyö. General Packet Radio Service
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu Teletekniikan laboratorio S-38.128 Teletekniikan erikoistyö General Packet Radio Service Tekijä: Jani Kokkonen 42916s jkokkone@cc.hut.fi Ohjaaja: Vesa Kosonen Jätetty: 31.1.2000
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu Teletekniikan laboratorio S-38.128 Teletekniikan erikoistyö General Packet Radio Service Tekijä: Jani Kokkonen 42916s jkokkone@cc.hut.fi Ohjaaja: Vesa Kosonen Jätetty: 31.1.2000
Internet, Part 2. 1) Session Initiating Protocol (SIP) 2) Quality of Service (QoS) support. 3) Mobility aspects (terminal vs. personal mobility)
 Internet, Part 2 1) Session Initiating Protocol (SIP) 2) Quality of Service (QoS) support 3) Mobility aspects (terminal vs. personal mobility) 4) Mobile IP Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) SIP is a protocol
Internet, Part 2 1) Session Initiating Protocol (SIP) 2) Quality of Service (QoS) support 3) Mobility aspects (terminal vs. personal mobility) 4) Mobile IP Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) SIP is a protocol
Mobile IP and Wireless Application Protocol
 Mobile IP and Wireless Application Protocol Mobile IP Uses Enable computers to maintain Internet connectivity while moving from one Internet attachment point to another Mobile user's point of attachment
Mobile IP and Wireless Application Protocol Mobile IP Uses Enable computers to maintain Internet connectivity while moving from one Internet attachment point to another Mobile user's point of attachment
SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005
 UN SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005 This is a non-binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (see next page) This is an UN official document Security
UN SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005 This is a non-binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (see next page) This is an UN official document Security
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies
 GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
2G Cellular Data Networks
 1 2 General Mobility Issues 2G Cellular Data Networks Registration and Authentication User Locate local service provider access point Obtain network access Service provider Locate mobile user within network
1 2 General Mobility Issues 2G Cellular Data Networks Registration and Authentication User Locate local service provider access point Obtain network access Service provider Locate mobile user within network
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
DATA SECURITY 1/12. Copyright Nokia Corporation 2002. All rights reserved. Ver. 1.0
 DATA SECURITY 1/12 Copyright Nokia Corporation 2002. All rights reserved. Ver. 1.0 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. REMOTE ACCESS ARCHITECTURES... 3 2.1 DIAL-UP MODEM ACCESS... 3 2.2 SECURE INTERNET ACCESS
DATA SECURITY 1/12 Copyright Nokia Corporation 2002. All rights reserved. Ver. 1.0 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. REMOTE ACCESS ARCHITECTURES... 3 2.1 DIAL-UP MODEM ACCESS... 3 2.2 SECURE INTERNET ACCESS
Mobility and cellular networks
 Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
IMT-2000 Network Architecture
 IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
ARIB STD-T63-22.031 V4.0.0. 3G Security; Fraud Information Gathering System (FIGS); Service description - Stage 1 (Release 4)
 ARIB STD-T63-22.031 V4.0.0 3G Security; Fraud Information Gathering System (FIGS); Service description - Stage 1 (Release 4) Refer to Industrial Property Rights (IPR) in the preface of ARIB STD-T63 for
ARIB STD-T63-22.031 V4.0.0 3G Security; Fraud Information Gathering System (FIGS); Service description - Stage 1 (Release 4) Refer to Industrial Property Rights (IPR) in the preface of ARIB STD-T63 for
Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks
 Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National
Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National
Index. Corporate Profile. Page 2 360Global Company Profile
 Index Corporate Profile. Page 2 360Global Company Profile 1. Introduction Of SMS.. Page 2 1.1. What is SMS? 1.2 Comparison Of SMS Against Other Means Of Advertising 1.3 Where does SMS fit in? 2. Bulk SMS
Index Corporate Profile. Page 2 360Global Company Profile 1. Introduction Of SMS.. Page 2 1.1. What is SMS? 1.2 Comparison Of SMS Against Other Means Of Advertising 1.3 Where does SMS fit in? 2. Bulk SMS
Standardizing Information and Communication Systems
 ECMA Technical Report TR/77 December 1999 Standardizing Information and Communication Systems Telephony System with Integrated Internet Access - Overview Phone: +41 22 849.60.00 - Fax: +41 22 849.60.01
ECMA Technical Report TR/77 December 1999 Standardizing Information and Communication Systems Telephony System with Integrated Internet Access - Overview Phone: +41 22 849.60.00 - Fax: +41 22 849.60.01
A secure, simple, seamless way to communicate quickly with your teams.
 A secure, simple, seamless way to communicate quickly with your teams. Connecting Chances are, you already use text messaging as a business tool While convenient, standard text messages don t always work
A secure, simple, seamless way to communicate quickly with your teams. Connecting Chances are, you already use text messaging as a business tool While convenient, standard text messages don t always work
ENGN4536 Mobile Communications
 ENGN4536 Mobile Communications Dr Thushara Abhayapala Department of Engineering Faculty of Engineering & Information Technology Australian National University thushara@faceng.anu.edu.au http://www.webct.anu.edu.au
ENGN4536 Mobile Communications Dr Thushara Abhayapala Department of Engineering Faculty of Engineering & Information Technology Australian National University thushara@faceng.anu.edu.au http://www.webct.anu.edu.au
Development of Wireless Networks
 Development of Wireless Networks Cellular Revolution In 1990 mobile phone users populate 11 million. By 2004 the figure will become 1 billion Phones are most obvious sign of the success of wireless technology.
Development of Wireless Networks Cellular Revolution In 1990 mobile phone users populate 11 million. By 2004 the figure will become 1 billion Phones are most obvious sign of the success of wireless technology.
How To Understand The Performance Of A Cell Phone Network
 Survivability Analysis for Mobile Cellular Networks David W. Tipper *, Chalermpol Charnsripinyo *, Hyundoo Shin * Teresa A. Dahlberg ** * Department of Information Science and Telecommunications, University
Survivability Analysis for Mobile Cellular Networks David W. Tipper *, Chalermpol Charnsripinyo *, Hyundoo Shin * Teresa A. Dahlberg ** * Department of Information Science and Telecommunications, University
Mobile Application Part (MAP) - Voice Feature Scenarios: Call Forwarding REVISION HISTORY TIA-41.322-E. Revision Date Remarks
 Mobile Application Part (MAP) - Voice Feature Scenarios: Call Forwarding REVISION HISTORY Revision Date Remarks TIA-.-E January 00 Initial publication. Copyright Telecommunications Industry Association
Mobile Application Part (MAP) - Voice Feature Scenarios: Call Forwarding REVISION HISTORY Revision Date Remarks TIA-.-E January 00 Initial publication. Copyright Telecommunications Industry Association
Cellular Technology Sections 6.4 & 6.7
 Overview Cellular Technology Sections 6. & 6.7 CSC 9 December, 0 Cellular architecture evolution Cellular telephony and internet terminology Mobility for cellular mobiles 6- Components of cellular architecture
Overview Cellular Technology Sections 6. & 6.7 CSC 9 December, 0 Cellular architecture evolution Cellular telephony and internet terminology Mobility for cellular mobiles 6- Components of cellular architecture
Chapter 2 PSTN and VoIP Services Context
 Chapter 2 PSTN and VoIP Services Context 2.1 SS7 and PSTN Services Context 2.1.1 PSTN Architecture During the 1990s, the telecommunication industries provided various PSTN services to the subscribers using
Chapter 2 PSTN and VoIP Services Context 2.1 SS7 and PSTN Services Context 2.1.1 PSTN Architecture During the 1990s, the telecommunication industries provided various PSTN services to the subscribers using
ETSI TS 101 107 V7.1.1 (1999-08)
 TS 101 107 V7.1.1 (1999-08) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Fraud Information Gathering System (FIGS); Service description - Stage 1 (GSM 02.31 version 7.1.1
TS 101 107 V7.1.1 (1999-08) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Fraud Information Gathering System (FIGS); Service description - Stage 1 (GSM 02.31 version 7.1.1
ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT
 ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: DTR/SMG-101020Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile communications (GSM)
ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: DTR/SMG-101020Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile communications (GSM)
SERVICE PROVIDER ACCESS IN MOBILE NETWORKS. March 2003
 Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) SERVICE PROVIDER ACCESS IN MOBILE NETWORKS March 2003 Page 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) SERVICE PROVIDER ACCESS IN MOBILE NETWORKS March 2003 Page 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network
 Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin (po@p1sec.com) Alexandre De Oliveira (alex@p1sec.com) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin (po@p1sec.com) Alexandre De Oliveira (alex@p1sec.com) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
redcoal EmailSMS for MS Outlook and Lotus Notes
 redcoal EmailSMS for MS Outlook and Lotus Notes Technical Support: support@redcoal.com Or visit http://www.redcoal.com/ All Documents prepared or furnished by redcoal Pty Ltd remains the property of redcoal
redcoal EmailSMS for MS Outlook and Lotus Notes Technical Support: support@redcoal.com Or visit http://www.redcoal.com/ All Documents prepared or furnished by redcoal Pty Ltd remains the property of redcoal
Now SMS/MMS Android Modem Quick Start Guide
 Now SMS/MMS Android Modem Quick Start Guide Using a GSM modem, or an Android phone as a modem, is a quick and efficient way to get started with SMS and/or MMS applications. No special service provider
Now SMS/MMS Android Modem Quick Start Guide Using a GSM modem, or an Android phone as a modem, is a quick and efficient way to get started with SMS and/or MMS applications. No special service provider
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
Mobile Access by Axis. Wireless Access Points
 Mobile Access by Axis Wireless Access Points Mobile Internet: Unleashing the Power of Bluetooth Bluetooth Access Point: Going Beyond Cables There s a revolution taking shape today that s fundamentally
Mobile Access by Axis Wireless Access Points Mobile Internet: Unleashing the Power of Bluetooth Bluetooth Access Point: Going Beyond Cables There s a revolution taking shape today that s fundamentally
ETSI TR 101 480 V1.1.2 (1999-12)
 TR 101 480 V1.1.2 (1999-12) Technical Report Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN); Framework for the provision of calling party name information 2 TR 101
TR 101 480 V1.1.2 (1999-12) Technical Report Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN); Framework for the provision of calling party name information 2 TR 101
EXPLOITING SIMILARITIES BETWEEN SIP AND RAS: THE ROLE OF THE RAS PROVIDER IN INTERNET TELEPHONY. Nick Marly, Dominique Chantrain, Jurgen Hofkens
 Nick Marly, Dominique Chantrain, Jurgen Hofkens Alcatel Francis Wellesplein 1 B-2018 Antwerp Belgium Key Theme T3 Tel : (+32) 3 240 7767 Fax : (+32) 3 240 8485 E-mail : Nick.Marly@alcatel.be Tel : (+32)
Nick Marly, Dominique Chantrain, Jurgen Hofkens Alcatel Francis Wellesplein 1 B-2018 Antwerp Belgium Key Theme T3 Tel : (+32) 3 240 7767 Fax : (+32) 3 240 8485 E-mail : Nick.Marly@alcatel.be Tel : (+32)
DraftETSI EN 301 691 V1.1.1 (2000-03)
 Draft EN 301 691 V1.1.1 (2000-03) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Remote Control (RC) service; Service description 2 Draft EN 301 691 V1.1.1 (2000-03)
Draft EN 301 691 V1.1.1 (2000-03) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Remote Control (RC) service; Service description 2 Draft EN 301 691 V1.1.1 (2000-03)
Verizon Wireless White Paper. Verizon Wireless Broadband Network Connectivity and Data Transport Solutions
 Verizon Wireless White Paper Verizon Wireless Broadband Network Connectivity and Data Transport Solutions Verizon Wireless White Paper Verizon Wireless Broadband Network Connectivity and Data Transport
Verizon Wireless White Paper Verizon Wireless Broadband Network Connectivity and Data Transport Solutions Verizon Wireless White Paper Verizon Wireless Broadband Network Connectivity and Data Transport
Private DNS for Mobile Operators
 Private for James Yu Senior Director - Strategic Technical Initiatives NeuStar, Inc. james.yu@neustar.biz +1-571-434-5572 (B) +1-703-622-5187 (M) Richard Xu Chief Architect Aicent, Inc richard.xu@aicent.com
Private for James Yu Senior Director - Strategic Technical Initiatives NeuStar, Inc. james.yu@neustar.biz +1-571-434-5572 (B) +1-703-622-5187 (M) Richard Xu Chief Architect Aicent, Inc richard.xu@aicent.com
Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks. Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802
 Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802 Contents Motivation Solution Overview Methodology Overview 3G Attack Graph
Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802 Contents Motivation Solution Overview Methodology Overview 3G Attack Graph
Designing a Virtual PBX for mobile telephony
 Master Thesis Software Engineering Thesis no: MSE-2003-03 March 2003 Designing a Virtual PBX for mobile telephony - using PARLAY and JAIN technology David Pettersson Department of Software Engineering
Master Thesis Software Engineering Thesis no: MSE-2003-03 March 2003 Designing a Virtual PBX for mobile telephony - using PARLAY and JAIN technology David Pettersson Department of Software Engineering
White Paper. WAP over GPRS. Realizing the potential of mobile services
 WAP over GPRS Realizing the potential of mobile services Contents Introduction 4 WAP and GPRS: key drivers of mobile services 4 Take-off time 4 New operator business models 4 Enabling the breakthrough:
WAP over GPRS Realizing the potential of mobile services Contents Introduction 4 WAP and GPRS: key drivers of mobile services 4 Take-off time 4 New operator business models 4 Enabling the breakthrough:
Emerging Wireless Technologies
 Emerging Wireless Technologies QCHAT The Future of Push-to-Talk Communications Foreword: The Public Safety Wireless Network (PSWN) Program is conducting an ongoing assessment of advancements in the wireless
Emerging Wireless Technologies QCHAT The Future of Push-to-Talk Communications Foreword: The Public Safety Wireless Network (PSWN) Program is conducting an ongoing assessment of advancements in the wireless
