Lumbar total disc replacement: A numerical study
|
|
|
- Ernest Boyd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Biomechanics 2010; Vol. 8 no. 2, pp original article Lumbar total disc replacement: A numerical study Valeriano Di Mascio 1,2, Chiara M. Bellini 2, Fabio Galbusera 2, Manuela T. Raimondi 1, Marco Brayda-Bruno 2,3, Roberto Assietti 4 1 LaBS, Department of Structural Engineering, Politecnico di Milano, Milan - Italy 2 IRCCS Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi, Milan - Italy 3 Spine Care Group, Milan - Italy 4 Fatebenefratelli and Oftalmico Hospital, Milan - Italy ABSTRACT Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate the biomechanical effects of the Maverick disc prosthesis at the implanted and adjacent level by the finite element (FE) method. Materials and Methods: A 3D FE model of the L3-L5 segment was built. To simulate the different physiological movements (flexion, extension, lateral bending, axial rotation) pure moments of 10 Nm were applied. To evaluate the effect of the prosthesis, a 3D model of the device was built and inserted in the L3-L5 model. The ROMs obtained with the intact model were imposed as maximal rotations to the instrumented model, therefore implementing the Panjabi hybrid protocol. Results: Increased ROMs at the implanted level and reduced ROMs at the adjacent level were predicted. A similar momentrotation behavior was calculated after simulation of prosthesis insertion. No significant effect was predicted in terms of von Mises stress at the adjacent level after implantation of the prosthesis. Conclusions: Within the limitations of the models, the numerical results of this study predicted a preserved kinematics and stress at the adjacent segment, after insertion of the prosthesis. Key words: Lumbar disc prosthesis, Hybrid protocol, Finite element, Biomechanics Accepted: 09/06/10 INTRODUCTION Spinal fusion has been identified as the gold standard in the treatment of degenerative disc disease (DDD) (1). Literature data indicated a correlation between fusion and the development of radiographic adjacent segment degeneration and symptomatic adjacent segment disease (2). The use of total disc prostheses in the treatment of DDD in the lumbar spine has led to satisfactory clinical outcomes as well as complications, therefore pointing out the need for further investigations (3). The Maverick Total Disc Replacement (Medtronic Sofamor Danek, Inc., Memphis, TN, USA) was developed and first implanted in This is a so called ball-and-socket disc prosthesis made of cobalt-chromium-molybdenum. Tournier et al (4) set up experimental studies to evaluate the effect of this prosthesis for sagittal balance and lumbar spine movement. The motion characteristics of the intact lumbar spine after anterior L4 5 discectomy and after implantation of the Maverick disc prosthesis were investigated in human cadaveric spines under quasistatic loading conditions by Hitchon et al (5). The aim of this study was to evaluate the biomechanical effects of the Maverick disc prosthesis at the implanted and adjacent level by the finite element (FE) method. Motion characteristics, facet forces, von Mises stress of an intact and an instrumented L3-L5 segment were predicted following the hybrid approach. MATERIALS AND METHODS A 3D FE model of the L3-L5 segment was built (Fig. 1a). The geometry was reconstructed from computed tomography scans taken from the Visible Human Dataset. The 3D reconstruction was performed using commercial software (Amira, TGS, San Diego, CA, USA). The geometry was exported to an FE pre-processor software (Gambit, Fluent Inc, Lebanon, NH, USA). The intervertebral discs were represented as continuum structures occupying the intervertebral spaces. Each structure was subdivided in an internal and an external volume representing the nucleus pulposus and the annulus fibrosus, respectively. Each volume was discretized using linear tetrahedral elements. The cortical bone was modeled using triangular shell elements of 0.35 mm thickness at the endplates and 0.5 mm at the lateral side of the vertebral bodies (6). Table I gives the material properties assumed for each structure. In order to include the contribution of the facet joints, a contact condition was defined between the surfaces of the articular facets, with a friction coef- 97
2 Lumbar total disc replacement: a numerical study TABLE I - MATERIAL PROPERTIES ASSUMED FOR THE FE MODELS Material Moduli [MPa] Poisson s ratio References Cortical bone E = ν = 0.3 [13] Posterior bone E = 3500 ν = 0.25 [13] Cancellous bone E xx = 112 ν xy = 0.3 E yy = 112 ν xy = 0.3 [14] E zz = 340 ν zx = 0.1 G xy =52 ν zy = 0.1 G zx = 53 G zy = 53 Annulus ground substance E = 0.7 ν = 0.45 [9] (calibration) Nucleus pulposus E = [9] (calibration) Annulus collagen fibers Force-deflection curves (calibration) [15] Ligaments Force-deflection curves (calibration) [16] Implant Loading beam Fig. 1-3D FE models: (a) intact model, (b) instrumented model. Fig. 2-3D FE model of the Maverick disc prosthesis. ficient of (7). The annulus fibrosus was modeled by three criss-cross layers representing the collagen fibers embedded in a homogeneous volume representing the ground substance (8, 9). The collagen fiber network was modeled by monodimensional, non-linear, tension only spring elements. The same elements were used to model the ligaments. The ligaments included in the model were: anterior longitudinal, posterior longitudinal, flavum, intertransverse, interspinous, supraspinous and capsular. Material properties of the annulus ground substance, the collagen fibers and the ligaments were obtained by a calibration process. For the intact model, the nodes belonging to the inferior endplate of the L5 vertebra were kept fixed. A rigid beam connection was defined between the superior endplate of the L3 vertebra and a node located at the superior space. Pure moments of 10 Nm were applied to this node to simulate the different physiological movements (flexion, extension, lateral bending, axial rotation). To evaluate the effect of the prosthesis, a 3D model of the device was built (Fig. 2) and inserted in the L3-L5 model (Fig. 1b). To simulate the surgical procedure, the nucleus, the anterior longitudinal ligament, the anterior portion of the annulus and part of the posterior portion of the annulus were removed. A contact condition with a friction coefficient equal to 0.04 (10) was assumed between the metal components of the prosthesis, while a fully bonded contact condition was defined between the device and the endplates, therefore, assuming a complete osteointegration. Rotation-controlled simulation was conducted for each loading condition (flexion, extension, lateral ben- 98
3 Di Mascio et al ding, axial rotation) with the instrumented model. The ROMs obtained with the intact model were imposed as maximal rotations to the instrumented model, therefore, implementing the Panjabi hybrid protocol (11). The analyses were conducted using the commercial software Abaqus 6.6 (Simulia, Providence, RI, USA). RESULTS Figure 3 shows the calculated ROMs for the intact model and the instrumented model, in all loading conditions. Insertion of the prosthesis caused an increment in ROM at the implanted level (L4-L5) and a reduction at the adjacent intact level (L3-L4) during flexion, extension and lateral bending, while a significant difference was not detected in axial rotation. Figures 4-6 show the calculated moment as a function of the applied rotation, for the whole segment, in all loading conditions. A similar trend was predicted as comparing the models, but the final moment resulted in a decrease of about 2 Nm in flexion, 4.3 Nm in extension, 2.4 Nm in lateral bending and 1 Nm in axial rotation. Figures 7 and 8 show von Mises stress calculated at the Fig. 3 - Maximal ROM values for the intact model and the instrumented model in flexion, extension, lateral bending and axial rotation. Fig. 4 - Moment-rotation curves for the intact model and the instrumented model during flexion and extension. Fig. 5 - Moment-rotation curves for the intact model and the instrumented model during lateral bending. Fig. 6 - Moment-rotation curves for the intact model and the instrumented model during axial rotation. 99
4 Lumbar total disc replacement: A numerical study Fig. 7 - Von Mises stress at the adjacent intervertebral disc (L3-L4) for the intact model and the instrumented model: (a) flexion; (b) extension. Fig. 9 - Relative facet force (the ratio between the facet force of the instrumented model and the facet force of the intact model) during extension. adjacent intervertebral disc (L3-L4) for both the models. No significant difference was predicted for all loading conditions comparing the intact model to the instrumented model. Figure 9 shows the relative facet force (the ratio between the facet force of the instrumented model and the facet force of the intact model), in extension. A reduction was detected at both the adjacent level (L3-L4) and the implanted level (L4-L5), but the reduction was more significant at the implanted level. DISCUSSION Fig. 8 - Von Mises stress at the adjacent intervertebral disc (L3-L4) for the intact model and the instrumented model: (a) lateral bending; (b) axial rotation. This study was conducted to evaluate the biomechanical effects of the implantation of the Maverick disc prosthesis at the L4-L5 level by an FE model which included the adjacent L3-L4 level. Increased ROMs were predicted at the implanted level, while a reduction was calculated at the adjacent level. At the implanted level, the range of variation was estimated to be between 3.8% and 20% (axial rotation and lateral bending, respectively). The increase in ROM at the implanted level during flexion and extension may be related to the lack of the anterior portion of the annulus and of the ALL, as previously observed (5). In the literature, an increase of flexibility in all directions at the implanted level was predicted after insertion of the Maverick disc prosthesis, compared to the intact condition (5). Different values of variation could be related to the different loading protocol and to the insertion of the prosthesis at a different level. Specifically, to test the prosthesis a load-control protocol was used. This protocol involving the application of pure moments to the intact and instrumented spine is not suitable to evaluate the effects of disc prostheses at the adjacent level (12). This investigation was conducted by using the hybrid protocol which is believed to be more clinically relevant (12) allowing the investigation of the effects of prosthesis implantation at the instrumented and adjacent level. In axial rotation, the non-significant variation in flexibility (3.8%) at the implanted level may be related to the mechanical role of the articular facets, which shift the instantaneous axis of rotation posteriorly, therefore, limiting the movement. A similar load-displacement behavior was predicted as comparing the instrumented model to the intact model (Figs. 4-6). This was particularly accentuated in axial rotation due to the role of the mechanical facet force, as stated above. Generally speaking, under all loading conditions a decrease in moment values after implantation of the prosthesis was predicted, therefore, indicating a reduced resistance to rotation. No significant effect was predicted at the adjacent level after implantation of the prosthesis in terms of von 100
5 Di Mascio et al Mises stress, indicating that the prosthesis does not induce overloading in the adjacent segments. A significant reduction in facet force was calculated at the implanted level during extension. This could be related to posterior location of the center of rotation imposed by the prosthesis, which unloads the facet joints. The numerical results of this study have to be regarded as theoretical predictions of the biomechanical effects of the prosthesis because an FE model represents a simplification of the real structure. Limitations of this study pertain to the physiological model of the biological structures; therefore, neglecting any degenerative condition of the remaining portion of the annulus fibrosus, the adjacent disc and the ligaments. At the implant/bone interface a full osteointegrated condition was assumed by modeling a bonded contact condition, neglecting any possible micromotion and subsidence of the device. Changes in the sagittal balance could be induced by implanting a total disc prosthesis. In this study, due to the lack of muscle tissues these changes could not be evaluated. However, sagittal balance after implantation of the Maverick disc prosthesis was investigated by Tournier et al (4) by in vivo biomechanical studies. They found that after implantation of the prosthesis, patients were able to maintain the preoperative sagittal balance. The current FE model was calibrated to evaluate the intervertebral disc and ligaments mechanical behavior, but no experimental tests on human cadavers were performed. Further developments of the study could concern the evaluation of clinically relevant variables such as prosthesis position, prosthesis size and type of anulotomy. Conflict of interest: There is no conflict of interest with any organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript. Address for correspondence: Fabio Galbusera IRCCS Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi Via R. Galeazzi Milano - Italy fabio.galbusera@polimi.it REFERENCES 1. Nockels RP. Dynamic stabilization in the surgical management of painful lumbar spinal disorders. Spine 2005; 15: S Harrop JS, Youssef JA, Maltenfort M, et al. Lumbar adjacent segment degeneration and disease after arthrodesis and total disc arthroplasty. Spine 2008; 33: Galbusera F, Bellini CM, Zweig T, et al. Design concepts in lumbar total disc arthroplasty. Eur Spine J 2008; 17: Tournier C, Aunoble S, Le Huec JC, et al. Total disc arthroplasty: consequences for sagittal balance and lumbar spine movement. Eur Spine J 2007; 16: Hitchon PW, Eichholz K, Barry C, et al. Biomechanical studies of an artificial disc implant in the human cadaveric spine. J Neurosurg Spine 2005; 2: Silva MJ, Wang C, Keaveny TM, Hayes WC. Direct and computed tomography thickness measurements of the human, lumbar vertebral shell and endplate. Bone 1994; 15: Forster H, Fisher J. The influence of continuous sliding and subsequent surface wear on the friction of articular cartilage. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 1999; 213: Cheung JT, Zhang M, Chow DH. Biomechanical responses of the intervertebral joints to static and vibrational loading: a finite element study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2003; 18: Schmidt H, Heuer F, Simon U, Kettler A, Rohlmann A, Claes L, Wilke HJ. Application of a new calibration method for a threedimensional finite element model of a human lumbar annulus fibrosus. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2006; 21: Unsworth A, Hall RM, Burgess IC, Wroblewski BM, Streicher RM, Semlitsch M. Frictional resistance of new and explanted artificial hip joints. Wear 1995; 190: Panjabi MM. Hybrid multidirectional test method to evaluate spinal adjacent-level effects. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2007; 22: Goel VK, Grauer JN, Patel TCh, et al. Effects of charité artificial disc on the implanted and adjacent spinal segments mechanics using a hybrid testing protocol. Spine 2005; 30: Lee KK, Teo EC, Fuss FK, et al. Finite-element analysis for lumbar interbody fusion under axial loading. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2004; 51: Crawford RP, Cann CE, Keaveny TM. Finite element models predict in vitro vertebral body compressive strength better than quantitative computed tomography. Bone 2003; 33: Shirazi-Adl A, Ahmed AM, Shrivastava SC. Mechanical response of a lumbar motion segment in axial torque alone and combined with compression. Spine 1986; 11: Eberlein R, Holzapfel GA, Frölich M. Multi-segment FEA of the human lumbar spine including the heterogeneity of the annulus fibrosus. Comput Mech 2004; 34:
MATERIALS AND METHODS
 REDISTRIBUTION OF LOAD OF INJURED LOWER CERVICAL SPINE UNDER AXIAL COMPRESSION USING FEM E. C. Teo 1 and H. W. Ng 1 1 School of Mechanical and Production Engineering, Nanyang Technological University,
REDISTRIBUTION OF LOAD OF INJURED LOWER CERVICAL SPINE UNDER AXIAL COMPRESSION USING FEM E. C. Teo 1 and H. W. Ng 1 1 School of Mechanical and Production Engineering, Nanyang Technological University,
This is the author-manuscript version of this work - accessed from http://eprints.qut.edu.au
 This is the author-manuscript version of this work - accessed from http://eprints.qut.edu.au Cunningham, Helen and Little, J.Paige and Pearcy, Mark J. and Adam, Clayton J. (27) The effect of soft tissue
This is the author-manuscript version of this work - accessed from http://eprints.qut.edu.au Cunningham, Helen and Little, J.Paige and Pearcy, Mark J. and Adam, Clayton J. (27) The effect of soft tissue
Biomechanics of the Lumbar Spine
 Biomechanics of the Lumbar Spine Biomechanics of the Spine 6 degrees of freedom Extension & Flexion Translation Rotation Compression & Distraction The disc/annulus/all/pll complex is the major restraint
Biomechanics of the Lumbar Spine Biomechanics of the Spine 6 degrees of freedom Extension & Flexion Translation Rotation Compression & Distraction The disc/annulus/all/pll complex is the major restraint
QUT Digital Repository: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/
 QUT Digital Repository: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/ Little, J. Paige and Pearcy, Mark J. and Adam, Clayton J. (2007) Coupled rotations in the lumbar spine are these a consequence of passive spinal anatomy?.
QUT Digital Repository: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/ Little, J. Paige and Pearcy, Mark J. and Adam, Clayton J. (2007) Coupled rotations in the lumbar spine are these a consequence of passive spinal anatomy?.
THE FUNCTIONS of the spinal facet joints (also called
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 51, NO. 3, MARCH 2004 443 The Biomechanics of Lumbar Graded Facetectomy Under Anterior-Shear Load E. C. Teo*, K. K. Lee, T. X. Qiu, H. W. Ng, and K. Yang
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 51, NO. 3, MARCH 2004 443 The Biomechanics of Lumbar Graded Facetectomy Under Anterior-Shear Load E. C. Teo*, K. K. Lee, T. X. Qiu, H. W. Ng, and K. Yang
Disc Replacement or Fusion: which is best for me?
 Disc Replacement or Fusion: which is best for me? After anterior discectomy in either the cervical or lumbar region there is a need to replace the removed disc with something and the choice lies between
Disc Replacement or Fusion: which is best for me? After anterior discectomy in either the cervical or lumbar region there is a need to replace the removed disc with something and the choice lies between
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine on facet joint force and intradiscal pressure -a finite element study
 Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine on facet joint force and intradiscal pressure -a finite element study Ching-Sung Kuo 1,5 *, Hsuan-Teh Hu 1, Ruey-Mo Lin 2, Kuo-Yuan Huang 2,3, Po-Chun Lin 1,
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine on facet joint force and intradiscal pressure -a finite element study Ching-Sung Kuo 1,5 *, Hsuan-Teh Hu 1, Ruey-Mo Lin 2, Kuo-Yuan Huang 2,3, Po-Chun Lin 1,
Introduction to Non-fusion Technologies in the Lumbar and Cervical Spine
 Introduction to Non-fusion Technologies in the Lumbar and Cervical Spine Introduction The term motion-sparing technology has been used to describe newer surgical techniques designed to preserve spinal
Introduction to Non-fusion Technologies in the Lumbar and Cervical Spine Introduction The term motion-sparing technology has been used to describe newer surgical techniques designed to preserve spinal
Experimental determination of cervical spine mechanical properties
 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 10, No. 4, 2008 Experimental determination of cervical spine mechanical properties MAREK GZIK*, WOJCIECH WOLAŃSKI, DAGMARA TEJSZERSKA Division of General Mechanics
Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 10, No. 4, 2008 Experimental determination of cervical spine mechanical properties MAREK GZIK*, WOJCIECH WOLAŃSKI, DAGMARA TEJSZERSKA Division of General Mechanics
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion
 Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f screw Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f intact Primary Stability intact Primary Stability Extension Neutral Position Flexion Coflex
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f screw Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f intact Primary Stability intact Primary Stability Extension Neutral Position Flexion Coflex
Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant
 International Journal Of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline.com) Vol. 3 Issue. 3 Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant 1, M. S. Abo_Elkhair, 2, M. E. Abo-Elnor,
International Journal Of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline.com) Vol. 3 Issue. 3 Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant 1, M. S. Abo_Elkhair, 2, M. E. Abo-Elnor,
Structural behavior of human lumbar spinal motion segments
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of Biomechanics 37 (2004) 205 212 Structural behavior of human lumbar spinal motion segments Mack G. Gardner-Morse*, Ian A.F. Stokes Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation,
ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of Biomechanics 37 (2004) 205 212 Structural behavior of human lumbar spinal motion segments Mack G. Gardner-Morse*, Ian A.F. Stokes Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation,
The biomechanics of the sheep cervical spine: an experimental and finite element analysis
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 2011 The biomechanics of the sheep cervical spine: an experimental and finite element analysis Nicole Ann DeVries University of Iowa Copyright
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 2011 The biomechanics of the sheep cervical spine: an experimental and finite element analysis Nicole Ann DeVries University of Iowa Copyright
Cervical Dynamic Stabilization
 PARADIGM SPINE Dynamic Cervical Implant Cervical Dynamic Stabilization 2 DCI Recurrent Neck Pain due to Adjacent Segment Disease: the Rationale for Motion Preservation The gold standard in stabilizing
PARADIGM SPINE Dynamic Cervical Implant Cervical Dynamic Stabilization 2 DCI Recurrent Neck Pain due to Adjacent Segment Disease: the Rationale for Motion Preservation The gold standard in stabilizing
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DISCECTOMY AND FUSION. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Cervical Spine
 Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash. Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199
 On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash 1 Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199 Nikolai Bogduk, MD, PhD FROM ABSTRACT Objective To summarize the evidence that implicates
On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash 1 Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199 Nikolai Bogduk, MD, PhD FROM ABSTRACT Objective To summarize the evidence that implicates
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF).
 Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Upper Cervical Spine Kinematic Response and Injury Prediction. Duane S. Cronin, Jason B. Fice, Jennifer A. DeWit, Jeff Moulton
 Upper Cervical Spine Kinematic Response and Injury Prediction Duane S. Cronin, Jason B. Fice, Jennifer A. DeWit, Jeff Moulton Abstract The upper cervical spine comprising the base of the skull, first cervical
Upper Cervical Spine Kinematic Response and Injury Prediction Duane S. Cronin, Jason B. Fice, Jennifer A. DeWit, Jeff Moulton Abstract The upper cervical spine comprising the base of the skull, first cervical
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Numerical Modelling of the Human Cervical Spine in Frontal Impact
 Numerical Modelling of the Human Cervical Spine in Frontal Impact by Matthew Brian Panzer A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree of Master
Numerical Modelling of the Human Cervical Spine in Frontal Impact by Matthew Brian Panzer A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree of Master
Cervical Disc Replacement for Treatment of Degenerative Disease: A Prospective Randomized Trial of the Prestige ST Cervical Disc
 Cervical Disc Replacement for Treatment of Degenerative Disease: A Prospective Randomized Trial of the Prestige ST Cervical Disc PERRY ARGIRES, M.D., F.A.C.S. Lancaster Neuroscience & Spine Associates
Cervical Disc Replacement for Treatment of Degenerative Disease: A Prospective Randomized Trial of the Prestige ST Cervical Disc PERRY ARGIRES, M.D., F.A.C.S. Lancaster Neuroscience & Spine Associates
1. Proposal Abstract. Table 1. Degeneration distribution of tested discs Grade I Grade II Grade III Grade IV Grade V # of discs tested 13 9 12 5 1
 1. Proposal Abstract Purpose: Chronic low back pain (LBP) is a common musculoskeletal disorder that significantly impacts public health. However the mechanism of chronic LBP is still not fully understood.
1. Proposal Abstract Purpose: Chronic low back pain (LBP) is a common musculoskeletal disorder that significantly impacts public health. However the mechanism of chronic LBP is still not fully understood.
Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine Robert W. Molinari
 Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine Robert W. Molinari Purpose of review This is a review of the recent literature involving dynamic posterior stabilization in the lumbar spine. Recent findings As
Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine Robert W. Molinari Purpose of review This is a review of the recent literature involving dynamic posterior stabilization in the lumbar spine. Recent findings As
Side Impact Causes Multiplanar Cervical Spine Injuries
 Side Impact Causes Multiplanar Cervical Spine Injuries 1 The Journal of Trauma, Injury, infection and Critical Care Volume 63(6), December 2007, pp 1296-1307 Maak, Travis G. MD; Ivancic, Paul C. PhD; Tominaga,
Side Impact Causes Multiplanar Cervical Spine Injuries 1 The Journal of Trauma, Injury, infection and Critical Care Volume 63(6), December 2007, pp 1296-1307 Maak, Travis G. MD; Ivancic, Paul C. PhD; Tominaga,
visualized. The correct level is then identified again. With the use of a microscope and
 SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
InternatIonal JOURNAL OF ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY and BIOCHEMISTRY
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE http://www.eternalpublication.com InternatIonal JOURNAL OF ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY and BIOCHEMISTRY IJAPB: Volume: 1; Issue: 1; October 2014 ISSN(Online):2394-3440 A Morphometric Study
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE http://www.eternalpublication.com InternatIonal JOURNAL OF ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY and BIOCHEMISTRY IJAPB: Volume: 1; Issue: 1; October 2014 ISSN(Online):2394-3440 A Morphometric Study
Cervical Spine Surgery. Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar. Dr Michelle Atkinson. Friday October 21 st 2011. Cervical Disc Herniation
 Cervical Spine Surgery Dr Michelle Atkinson The Sydney and Dalcross Adventist Hospitals Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar Friday October 21 st 2011 Cervical disc herniation The most frequently treated surgical
Cervical Spine Surgery Dr Michelle Atkinson The Sydney and Dalcross Adventist Hospitals Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar Friday October 21 st 2011 Cervical disc herniation The most frequently treated surgical
Aesculap Spine activ L
 Aesculap Spine activ L Lumbar artificial disc Generation: activ Rotation + translation = mobilization Generation: activ Discover the innovative power of our latest development I N N O V Discover: Rotation
Aesculap Spine activ L Lumbar artificial disc Generation: activ Rotation + translation = mobilization Generation: activ Discover the innovative power of our latest development I N N O V Discover: Rotation
Instability concept. Symposium- Cervical Spine. Barcelona, February 2014
 Instability concept Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd AOSpine Principles Symposium- Cervical Spine Orthopaedic Depatment. Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor UAB Barcelona, February 2014
Instability concept Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd AOSpine Principles Symposium- Cervical Spine Orthopaedic Depatment. Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor UAB Barcelona, February 2014
Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression
 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression 1 Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine November 2009, Volume 11, pp.
Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression 1 Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine November 2009, Volume 11, pp.
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
The patellofemoral joint and the total knee replacement
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) The patellofemoral joint and the total knee replacement J. Pokorný a,, J. Křen a a Faculty of AppliedSciences, UWB inpilsen, Univerzitní 22, 306 14Plzeň, CzechRepublic
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) The patellofemoral joint and the total knee replacement J. Pokorný a,, J. Křen a a Faculty of AppliedSciences, UWB inpilsen, Univerzitní 22, 306 14Plzeň, CzechRepublic
Spinal Anatomy. * MedX research contends that the lumbar region really starts at T-11, based upon the attributes of the vertebra.
 Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C. clinical study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C clinical study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C clinical study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF).
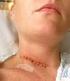 Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra,
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra,
Custom Design of Knee Joint Prosthesis By Using Computerized Tomography (CT) Images and 3D Modelling
 Custom Design of Knee Joint Prosthesis By Using Computerized Tomography (CT) Images and 3D Modelling Qasem Alyazji Near East University, Department of Biomedical Engineering Nicosia, North Cyprus, Turkey
Custom Design of Knee Joint Prosthesis By Using Computerized Tomography (CT) Images and 3D Modelling Qasem Alyazji Near East University, Department of Biomedical Engineering Nicosia, North Cyprus, Turkey
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach.
 Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Study on Structural Behaviour of Human Vertebral Column Using Staad.Pro
 Study on Structural Behaviour of Human Vertebral Column Using Staad.Pro Healtheephan alexis. S Post graduate student, Government College of Technology, Coimbatore 641 013 healtheephan@yahoo.com ABSTRACT
Study on Structural Behaviour of Human Vertebral Column Using Staad.Pro Healtheephan alexis. S Post graduate student, Government College of Technology, Coimbatore 641 013 healtheephan@yahoo.com ABSTRACT
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
Stability of the spine modelled as an arch
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Stability of the spine modelled as an arch This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: XIAO,
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Stability of the spine modelled as an arch This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: XIAO,
Technology Breakthrough in Spinal Implants (Technical Insights)
 Technology Breakthrough in Spinal Implants (Technical Insights) Biomaterial innovations is a growth factor for spinal implant market June 2014 Table of Contents Section Page Number Executive Summary 4
Technology Breakthrough in Spinal Implants (Technical Insights) Biomaterial innovations is a growth factor for spinal implant market June 2014 Table of Contents Section Page Number Executive Summary 4
Biomechanics of Joints, Ligaments and Tendons.
 Hippocrates (460-377 B.C.) Biomechanics of Joints, s and Tendons. Course Text: Hamill & Knutzen (some in chapter 2 and 3, but ligament and tendon mechanics is not well covered in the text) Nordin & Frankel
Hippocrates (460-377 B.C.) Biomechanics of Joints, s and Tendons. Course Text: Hamill & Knutzen (some in chapter 2 and 3, but ligament and tendon mechanics is not well covered in the text) Nordin & Frankel
Evaluation and Treatment of Spine Fractures. Lara C. Portmann, MSN, ACNP-BC
 Evaluation and Treatment of Spine Fractures Lara C. Portmann, MSN, ACNP-BC Nurse Practitioner, Neurosurgery, Trauma Services, Intermountain Medical Center; Salt Lake City, Utah Objectives: Identify the
Evaluation and Treatment of Spine Fractures Lara C. Portmann, MSN, ACNP-BC Nurse Practitioner, Neurosurgery, Trauma Services, Intermountain Medical Center; Salt Lake City, Utah Objectives: Identify the
ANTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION (ALIF) Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Lumbar Spine
 (ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
(ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
NEW HORIZONS IN SPINAL SURGERY: SPINE ARTHROPLASTY
 NEW HORIZONS IN SPINAL SURGERY: SPINE ARTHROPLASTY Viral B. Shah*, Appaji Krishnan* and Sajan K. Hegde** From the: Spine Fellows*, Consultant Spinal Surgeon**, Department of Spinal Surgery, Apollo Hospitals,
NEW HORIZONS IN SPINAL SURGERY: SPINE ARTHROPLASTY Viral B. Shah*, Appaji Krishnan* and Sajan K. Hegde** From the: Spine Fellows*, Consultant Spinal Surgeon**, Department of Spinal Surgery, Apollo Hospitals,
Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization
 APPROVED IRN10389-1.1-04 Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization Because it involves accessing the spine through the patient s side, the Direct Lateral approach
APPROVED IRN10389-1.1-04 Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization Because it involves accessing the spine through the patient s side, the Direct Lateral approach
Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques
 Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques By: MS.ME Ahmad A. Abbas Sr. Analysis Engineer Ahmad.Abbas@AdvancedCAE.com www.advancedcae.com Sunday, July 11, 2010 Advanced CAE All contents Copyright
Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques By: MS.ME Ahmad A. Abbas Sr. Analysis Engineer Ahmad.Abbas@AdvancedCAE.com www.advancedcae.com Sunday, July 11, 2010 Advanced CAE All contents Copyright
Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns. Chapter 21
 Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns Chapter 21 Terminology Macrotrauma A specific, sudden episode of overload injury to a given tissue, resulting in disrupted tissue integrity (Acute)
Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns Chapter 21 Terminology Macrotrauma A specific, sudden episode of overload injury to a given tissue, resulting in disrupted tissue integrity (Acute)
Spinal facet joints transmit load, limit motions, and contribute
 SPINE Volume 36, Number 15, pp 1197 1203 2011, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins CERVICAL SPINE Pressure Measurement in the Cervical Spinal Facet Joint Considerations for Maintaining Joint Anatomy and an Intact
SPINE Volume 36, Number 15, pp 1197 1203 2011, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins CERVICAL SPINE Pressure Measurement in the Cervical Spinal Facet Joint Considerations for Maintaining Joint Anatomy and an Intact
A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE SUPPORTED BY CYLINDRICAL AND CONICAL IMPLANTS
 A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE SUPPORTED BY CYLINDRICAL AND CONICAL IMPLANTS Evandro Afonso Sartori, evandroasartori@yahoo.com.br Josué Ricardo Broilo Luiz Oscar
A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE SUPPORTED BY CYLINDRICAL AND CONICAL IMPLANTS Evandro Afonso Sartori, evandroasartori@yahoo.com.br Josué Ricardo Broilo Luiz Oscar
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Compression Fractures
 September 2006 Compression Fractures Eleanor Adams Harvard Medical School Year IV Overview Spine Anatomy Thoracolumbar Fractures Cases Compression Fractures, Ddx Radiologic Tests of Choice Treatment Options
September 2006 Compression Fractures Eleanor Adams Harvard Medical School Year IV Overview Spine Anatomy Thoracolumbar Fractures Cases Compression Fractures, Ddx Radiologic Tests of Choice Treatment Options
Effects of vertebral axial decompression on intradiscal pressure
 This article is reprinted with the permission of the authors from the Journal of Neurosurgery, Volume 81. J Neurosurg 81:350-353, 1994 Effects of vertebral axial decompression on intradiscal pressure GUSTAVO
This article is reprinted with the permission of the authors from the Journal of Neurosurgery, Volume 81. J Neurosurg 81:350-353, 1994 Effects of vertebral axial decompression on intradiscal pressure GUSTAVO
Degenerative Spine Solutions
 Degenerative Spine Solutions The Backbone for Your Surgical Needs Aesculap Spine Backbone for Your Degenerative Spine Needs Comprehensive operative solutions, unique product technology and world-class
Degenerative Spine Solutions The Backbone for Your Surgical Needs Aesculap Spine Backbone for Your Degenerative Spine Needs Comprehensive operative solutions, unique product technology and world-class
Movement in the human body occurs at joint
 Biomechanics of The Spine Richard A. Banton, DPT, OCS, CMPT, ATC Movement in the human body occurs at joint surfaces; movement occurs with bones; movement of muscles moves the bones; coordinated movements
Biomechanics of The Spine Richard A. Banton, DPT, OCS, CMPT, ATC Movement in the human body occurs at joint surfaces; movement occurs with bones; movement of muscles moves the bones; coordinated movements
An Anatomical Comparison of the Human and Bovine Thoracolumbar Spine
 Journal of Orthopaedic Research 4:298-303, Raven Press, New York 0 1986 Orthopaedic Research Society An Anatomical Comparison of the Human and Bovine Thoracolumbar Spine Paul C. Cotterill, J. P. Kostuik,
Journal of Orthopaedic Research 4:298-303, Raven Press, New York 0 1986 Orthopaedic Research Society An Anatomical Comparison of the Human and Bovine Thoracolumbar Spine Paul C. Cotterill, J. P. Kostuik,
A MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE WHOLE HUMAN SPINE FOR WHIPLASH INVESTIGATIONS
 A MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE WHOLE HUMAN SPINE FOR WHIPLASH INVESTIGATIONS Volkan Esat Memis Acar Loughborough University United Kingdom Paper Number 7-437 ABSTRACT This paper presents whiplash simulations
A MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE WHOLE HUMAN SPINE FOR WHIPLASH INVESTIGATIONS Volkan Esat Memis Acar Loughborough University United Kingdom Paper Number 7-437 ABSTRACT This paper presents whiplash simulations
Virtual 3D Model of the Lumbar Spine
 LSNA Virtual 3D Model of the Lumbar Spine Alberto Prats-Galino 1, Miguel Angel Reina 2, Marija Mavar Haramija 1, Anna Puigdellivol-Sánchez 1, Joan San Molina 3 and José Antonio De Andrés 4. 1 Laboratory
LSNA Virtual 3D Model of the Lumbar Spine Alberto Prats-Galino 1, Miguel Angel Reina 2, Marija Mavar Haramija 1, Anna Puigdellivol-Sánchez 1, Joan San Molina 3 and José Antonio De Andrés 4. 1 Laboratory
ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery
 ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery January 2005 Effects of Charite Artificial Disc on the Implanted and Adjacent Spinal Segments Mechanics Using a Hybrid Testing Protocol Spine. 30(24):2755-2764,
ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery January 2005 Effects of Charite Artificial Disc on the Implanted and Adjacent Spinal Segments Mechanics Using a Hybrid Testing Protocol Spine. 30(24):2755-2764,
LUMBAR LAMINECTOMY AND DISCECTOMY. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Posterior View Lumbar Spine
 Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between the ribs and the pelvis. In the spinal column, the last five vertebrae (from superior to inferior, L1-L5) Laminectomy Surgical
Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between the ribs and the pelvis. In the spinal column, the last five vertebrae (from superior to inferior, L1-L5) Laminectomy Surgical
Effects of Vertebral Axial Decompression (VAX-D) On Intradiscal Pressure
 Effects of Vertebral Axial Decompression (VAX-D) On Intradiscal Pressure Gustavo Ramos, M.D., William Marin, M.D. Journal of Neursurgery 81:35-353 1994 Departments of Neurosurgery and Radiology, Rio Grande
Effects of Vertebral Axial Decompression (VAX-D) On Intradiscal Pressure Gustavo Ramos, M.D., William Marin, M.D. Journal of Neursurgery 81:35-353 1994 Departments of Neurosurgery and Radiology, Rio Grande
Institute of Structural Engineering Division of Computer Aided Design Laboratory of Biomechanics
 Institute of Structural Engineering Division of Computer Aided Design Laboratory of Biomechanics About us Division of Computer Aided Design of Institute of Structural Engineering (ISE) is research and
Institute of Structural Engineering Division of Computer Aided Design Laboratory of Biomechanics About us Division of Computer Aided Design of Institute of Structural Engineering (ISE) is research and
Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery
 Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: Thoracolumbar and Cervicothoracic Sigurd Berven, MD Professor in Residence UC San Francisco Disclosures Research/Institutional Support:
Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: Thoracolumbar and Cervicothoracic Sigurd Berven, MD Professor in Residence UC San Francisco Disclosures Research/Institutional Support:
White Paper: Cervical Disc Replacement: When is the Mobi-C Cervical Disc Medically Necessary?
 White Paper: Cervical Disc Replacement: When is the Mobi-C Cervical Disc Medically Necessary? For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Cervical Disc Disease: An Overview The cervical
White Paper: Cervical Disc Replacement: When is the Mobi-C Cervical Disc Medically Necessary? For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Cervical Disc Disease: An Overview The cervical
Spinal Instability as Defined by the Three-column Spine Concept in Acute Spinal Trauma
 Spinal Instability as Defined by the Three-column Spine Concept in Acute Spinal Trauma FRANCIS DENIS, M.D., F.R.C.S.(C.), F.A.C.S.* This article is a presentation of the concept of the three-column spine.
Spinal Instability as Defined by the Three-column Spine Concept in Acute Spinal Trauma FRANCIS DENIS, M.D., F.R.C.S.(C.), F.A.C.S.* This article is a presentation of the concept of the three-column spine.
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope
 Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics
 Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Lateral Translation of the Lumbar Spine: In Vitro Biomechanical Study
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2006; 22:83-92. 2006 Human Kinetics, Inc. Lateral Translation of the Lumbar Spine: In Vitro Biomechanical Study Yuichiro Okushima 1, Nobutoshi Yamazaki
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2006; 22:83-92. 2006 Human Kinetics, Inc. Lateral Translation of the Lumbar Spine: In Vitro Biomechanical Study Yuichiro Okushima 1, Nobutoshi Yamazaki
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
Motion Preservation. Hansen Yuan, MD President, Spine Arthroplasty Society
 Motion Preservation Procedure Codes Hansen Yuan, MD President, Spine Arthroplasty Society Who are we? The Spine Arthroplasty Society (SAS) is a group of medical and associated specialists devoted to the
Motion Preservation Procedure Codes Hansen Yuan, MD President, Spine Arthroplasty Society Who are we? The Spine Arthroplasty Society (SAS) is a group of medical and associated specialists devoted to the
coligne treatment technology
 coligne treatment technology coligne a strategy in spine Leadership begins before the patient enters the surgical theater, among the spine care professionals forming the coalliance. This may be a small
coligne treatment technology coligne a strategy in spine Leadership begins before the patient enters the surgical theater, among the spine care professionals forming the coalliance. This may be a small
The indications for lumbar and cervical disc replacement
 The Spine Journal 4 (2004) 177S 181S The indications for lumbar and cervical disc replacement Paul C. McAfee, MD St. Joseph Hospital, Scoliosis and Spine Center, O Dea Medical Building 104, 7505 Osler
The Spine Journal 4 (2004) 177S 181S The indications for lumbar and cervical disc replacement Paul C. McAfee, MD St. Joseph Hospital, Scoliosis and Spine Center, O Dea Medical Building 104, 7505 Osler
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Postoperative Rehabilitation following Lumbar Disc
 Postoperative Rehabilitation following Lumbar Disc Arthroplasty A Clinical Reasoning & Best Evidence Approach Outline Prevalence Indications for lumbar disc arthroplasty Surgical procedures Post-op rehabilitation
Postoperative Rehabilitation following Lumbar Disc Arthroplasty A Clinical Reasoning & Best Evidence Approach Outline Prevalence Indications for lumbar disc arthroplasty Surgical procedures Post-op rehabilitation
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Artificial Intervertebral Disc: Cervical Spine
 dapplies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
dapplies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Total Hip Joint Replacement. A Patient s Guide
 Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING FOR AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATION USING ABAQUS
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 30 52, Article ID: IJARET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=7&itype=2
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 30 52, Article ID: IJARET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=7&itype=2
CPT Changes in Spine 2012
 CPT Changes in Spine 2012 Are you prepared? Presented by Barbara Cataletto, MBA, CPC Disclaimer The following presentations are not to be considered a replacement for the Current Procedural Terminology
CPT Changes in Spine 2012 Are you prepared? Presented by Barbara Cataletto, MBA, CPC Disclaimer The following presentations are not to be considered a replacement for the Current Procedural Terminology
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances?
 Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 UTILIZING COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY SCANS FOR ANALYSIS OF MOTORCYCLE HELMETS IN REAL-WORLD CRASHES Kathryn L. Loftis 1, Daniel P. Moreno 1, Joshua Tan 2, Hampton C. Gabler 1, Joel D. Stitzel 1 1 Virginia Tech-
UTILIZING COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY SCANS FOR ANALYSIS OF MOTORCYCLE HELMETS IN REAL-WORLD CRASHES Kathryn L. Loftis 1, Daniel P. Moreno 1, Joshua Tan 2, Hampton C. Gabler 1, Joel D. Stitzel 1 1 Virginia Tech-
Loads in the lumbar spine during traction therapy
 Loads in the lumbar spine during traction therapy Raymond YW Lee 1 and John H Evans 2 1 The Hong Kong Polytechnic University 2 Queensland University of Technology The purpose of the present study was to
Loads in the lumbar spine during traction therapy Raymond YW Lee 1 and John H Evans 2 1 The Hong Kong Polytechnic University 2 Queensland University of Technology The purpose of the present study was to
CeSpace Titanium / PEEK
 Aesculap Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion System CeSpace Titanium / PEEK Aesculap Spine CeSpace Content A Foreword 3 B Implant Material 4 C Implant Features 6 D Surgical Technique 8 E Ordering Information
Aesculap Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion System CeSpace Titanium / PEEK Aesculap Spine CeSpace Content A Foreword 3 B Implant Material 4 C Implant Features 6 D Surgical Technique 8 E Ordering Information
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Interspinous Fixation (Fusion) Devices Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See Also: Interspinous Fixation (Fusion) Devices Lumbar Spine
Interspinous Fixation (Fusion) Devices Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See Also: Interspinous Fixation (Fusion) Devices Lumbar Spine
1 REVISOR 5223.0070. (4) Pain associated with rigidity (loss of motion or postural abnormality) or
 1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
SPINAL FUSION. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 SPINAL FUSION North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS SPINAL FUSION? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
SPINAL FUSION North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS SPINAL FUSION? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland
 Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
Cervical Disc Replacement vs ACDF
 Guest Discussants: Michael E. Janssen, DO Spine Education and Research Institute Denver, CO Alan S. Hilibrand, MD Jefferson Medical College/Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA SpineLine Section Editor:
Guest Discussants: Michael E. Janssen, DO Spine Education and Research Institute Denver, CO Alan S. Hilibrand, MD Jefferson Medical College/Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA SpineLine Section Editor:
CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING
 CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Interbody Fusion (ACDF) Anterior interbody fusion, with discectomy and decompression; cervical below C2 22551 first interspace 22552
CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Interbody Fusion (ACDF) Anterior interbody fusion, with discectomy and decompression; cervical below C2 22551 first interspace 22552
Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck
 7th fib International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 2008 September 10-13, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck Noémi Seres
7th fib International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 2008 September 10-13, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck Noémi Seres
Ando A., Nakamura Y., Kanbara R., Kumano H., Miyata T., Masuda T., Ohno Y. and Tanaka Y.
 11. The Effect of Abutment Tooth Connection with Extracoronal Attachment using the Three Dimensional Finite Element Method - Part 2. The Construction of Finite Element Model from CT Data - Ando A., Nakamura
11. The Effect of Abutment Tooth Connection with Extracoronal Attachment using the Three Dimensional Finite Element Method - Part 2. The Construction of Finite Element Model from CT Data - Ando A., Nakamura
Outcome of the L5-S1 Segment after Posterior Instrumented Spinal Surgery in Degenerative Lumbar Diseases
 Original Article 81 Outcome of the L5-S1 Segment after Posterior Instrumented Spinal Surgery in Degenerative Lumbar Diseases Jen-Chung Liao, MD; Wen-Jer Chen, MD; Lih-Huei Chen, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD Results:
Original Article 81 Outcome of the L5-S1 Segment after Posterior Instrumented Spinal Surgery in Degenerative Lumbar Diseases Jen-Chung Liao, MD; Wen-Jer Chen, MD; Lih-Huei Chen, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD Results:
BRYAN. Cervical Disc System. Patient Information
 BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
Spine Surgery Coding
 Spine Surgery Coding Lynn M. Anderanin, CPC,CPC-I,COSC 1 Spine Anatomy 7 cervical (neck) vertebrae, 12 thoracic (chest) vertebrae, 5 lumbar (back) vertebrae, and 5 fused vertebra that make up the sacrum
Spine Surgery Coding Lynn M. Anderanin, CPC,CPC-I,COSC 1 Spine Anatomy 7 cervical (neck) vertebrae, 12 thoracic (chest) vertebrae, 5 lumbar (back) vertebrae, and 5 fused vertebra that make up the sacrum
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
DIAM Spinal Stabilization System Surgical Technique
 DIAM Spinal Stabilization System Surgical Technique The DIAM (Device for Intervertebral Assisted Motion) Spinal Stabilization System provides flexible support of the lumbar spine while treating spinal
DIAM Spinal Stabilization System Surgical Technique The DIAM (Device for Intervertebral Assisted Motion) Spinal Stabilization System provides flexible support of the lumbar spine while treating spinal
