Two New Coccidia, a Goussia and an Eimeria spp. from the Gut of Kessler s Goby (Gobius kessleri Günther) in the River Danube
|
|
|
- Randolph Alfred Boyd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Protozool. (2000) 39: Two New Coccidia, a Goussia and an Eimeria spp. from the Gut of Kessler s Goby (Gobius kessleri Günther) in the River Danube Kálmán MOLNÁR Veterinary Medical Research Institute, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest, Hungary Summary. Kessler s goby, a recently introduced fish species in the Budapest region of the river Danube, proved to be infected with two previously undescribed coccidian species. The species having a smaller oocyst (7-8.5 µm) proved to be a Goussia and was named G. kessleri sp. n. The species having larger oocysts measuring µm showed characteristics typical of an Eimeria and was designated as E. daviesae sp. n. Oocyst of G. kessleri were spherical, contained four ellipsoidal sporocysts lacking Stieda body. Sporocysts measured 5.8 (5-6) x 3.9 (3.8-4) µm. Oocysts of E. kessleri were spherical, contained four short ellipsoidal sporocysts which tapered at one end and formed at that end a cap-like Stieda body. Sporocysts measured 8 ( ) x 4.9 ( ) µm. Both species formed oocysts in the intestinal epithelium. The oocysts of the Goussia were released sporulated, while those of the Eimeria passed in unsporulated or semisporulated condition. Key words: Coccidia, Eimeria daviesae sp. n., Goussia kessleri sp. n., Pisces, Gobius, new species. INTRODUCTION Relatively little is known about the coccidian parasites of gobiid fishes. Known species include Eimeria gobii from Gobius medius and E. glossogobii from Glossogobius giuris, but the species E. variabilis (Thélohan, 1893) common in cottid fishes has also been recorded in Gobius bicolor and G. paganellus (Dyková and Lom 1983). Recently Abollo et al. (1998) reported the occurrence of the latter species in G. paganellus from the coastal waters of Spain. Coccidian infection of freshwater gobies was reported by Moshu (1992), who described the species Address for correspondence: Kálmán Molnár, Veterinary Medical Research Institute, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, POB 18, H-1581 Budapest, Hungary; Fax: (36-1) ; kalman@novell.vmri.hu E. credintsi from the gut of the tube-nosed goby (Proterorhinus marmoratus) in natural waters of Moldavia. In specimens of the tube-nosed goby occurring in the river Danube, Molnár (1996) found, in addition to E. credintsi, another coccidian species and described it as E. marmorata. The occurrence of coccidia in Kessler s goby, a species common in both brackish waters and freshwaters, has not been known until now. The present paper reports the occurrence of two new coccidia species from Kessler s gobies that have become numerous in the Budapest region of the river Danube. MATERIALS AND METHODS Forty-two Kessler s goby (Gobius kessleri Günther, 1861) specimens measuring 3-10 cm were collected with the help of an electrofishery
2 324 K. Molnár device from reaches of the river Danube north and south of Budapest on several occasions in the period between June and October in 1998 and The fish were kept in aquarium for 1-2 days, killed by decapitation and subjected to parasitological examination. Fresh mucus from the intestinal tract was examined for the presence of oocysts and parts of the foregut were fixed for histological examination in Bouin s solution. Drawings of sporulated oocysts were made, and measurements taken using an Olympus interference contrast microscope immediately after the oocysts had been detected or when sporulation had been completed. Unsporulated oocysts were placed in small Petri dishes with tap water at room temperature and allowed to sporulate. To prevent excess proliferation of bacteria, a few micrograms of penicillin were added. For histological examination, guts showing mixed infection with the two coccidian species were fixed in addition to guts in which the oocysts of only one of the two coccidia species could be detected by the examination of fresh preparations. Fixed material was embedded in paraffin and serially sectioned at 4 µm; sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin. Histological preparations were photographed using a photographic attachment mounted on a Jenaval microscope. Fresh preparations and other histological preparations were photographed with an Olympus Dp 10 digital camera mounted on an Olympus BH-2 microscope. All measurements are in µm. RESULTS Two types of coccidia were found in the gut of the examined gobies. The species with smaller oocysts proved to be a Goussia sp. while that with the larger oocysts was an Eimeria sp. In the majority of cases a mixed infection with the two species was recorded. However, Eimeria-type oocysts were found only in fish collected in June and July, while Goussia oocysts were found from June through October. Mixed infection was characterised by the dominance of one or the other species. The smaller oocysts of the Goussia species occurred mostly in the sporulated stage in the mucus, and unsporulated oocysts were obtained only from the mucosal scrapings. The larger oocysts of the Eimeria species were mostly found in unsporulated stage in the mucus covering the epithelium and in the mucosal scrapings but semisporulated oocysts and less frequently sporulated ones were found as well. By the morphological characteristics of the sporulated oocysts both species proved to be new for science and are described below. Description of the species Goussia kessleri sp. n. (Figs. 1, 3) Type host: Gobius kessleri Günther, 1861, Kessler s goby (Perciformes: Gobiidae). Type locality: River Danube, near Budapest. Site: mucus and epithelium of the foregut. Prevalence of infection: 41/42 infected specimens, 98%. Type material: syntypes in paraffin blocks and video images are in the author s possession. Histological preparations and photosyntypes (Coll. No. HNHM-67394) have been deposited in the parasitological collection of the Natural History Museum, Budapest, Hungary. Etymology: the nomen triviale is derived from the name of the fish host. Oocysts spherical, 8.1 (7-8.5) (n=25). Wall of the oocyst smooth, colourless and thin. Micropyle, polar granule and oocyst residuum absent. Sporocysts ellipsoidal. Stieda-body absent, an indistinct suture along the longitudinal axis present. Size of sporocysts 5.8 (5-6) x 3.9 (3.8-4); sporocyst wall very thin. Sporocysts compact, tightly filling the space of the oocyst. Four sporocysts arranged in oocyst either in pairs or three oocysts in one plane. Sporozoites vermiform, with reflexed end in the sporocyst. Size of the sporozoites 7 x 1.5. Sporocyst residuum finely granulated and globular. Oocysts passed the gut sporulated. Goussia kessleri sp. n. resembles G. carpelli (Léger et Stankovitch, 1921) in size and by its compact sporocysts, but differs from that species by the more elongated shape of sporocysts. Goussia kessleri sp. n. somewhat resembles Goussia spp. of the percid fishes Goussia laureleus (Molnár et Fernando, 1973) and G. acerinae (Pellérdy et Molnár, 1971) but the sporocysts of the latter two species have triangular shape in the transversal axis, while G. kessleri has a regular round shape. Eimeria daviesae sp. n. (Figs. 2, 4) Type host: Gobius kessleri Günther, 1861, Kessler s goby (Perciformes: Gobiidae). Type locality: River Danube, near Budapest. Site: mucus and epithelium of the foregut. Prevalence of infection: 17/42 infected specimens, 40%. Type material: video images are in the author s possession. Histological preparations and photosyntypes (Coll. No. HNHM-67395) have been deposited in the parasitological collection of the Natural History Museum, Budapest, Hungary. Etymology: the nomen triviale is given in honour of Dr. Angela J. Davies, the well-known specialist of fish apicomplexans. Oocysts spherical 13.4 (13-14) (n=25). Wall of the oocyst smooth, colourless and thin. Micropyle and oocyst residuum absent, an amorphous small polar granule
3 New coccidia: Goussia and Eimeria spp. 325 Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of the sporulated oocysts of Goussia kessleri. Scale bar - 5 µm Fig. 2. Schematic illustration of the sporulated oocyst of Eimeria daviesae. Scale bar - 5 µm Fig. 3. Sporulated and unsporulated oocysts of Goussia kessleri in a mucosal scraping of the intestine. x 1500 Fig. 4. Sporulated oocysts of Eimeria daviesae after 48 h of sporulation. x 2000 with a diameter of 2 present. Sporocyst short ellipsoidal but tapered at one end and forms at that end a cap-like Stieda-body; no substieda body found. Size of sporocysts 8 ( ) x 4.9 ( ); sporocyst wall very thin. Sporocysts moderately compact with a narrow space separating them from oocyst wall. Four sporocysts arranged randomly in oocyst. Sporozoites vermiform, with reflexed end in the sporocyst. Size of the mechanically excysted sporozoites 9.6 (9.5-10) x 2 ( ). Sporocyst residuum globular, compact in mature oocysts, but composed of some rough granules in more mature oocysts.
4 326 K. Molnár Fig. 5. Unsporulated and semisporulated oocysts of Eimeria daviesae in the intestinal mucus. x 2000 Fig. 6. Histological section of the anterior part of the intestine of a Kessler s goby. A group of sporulated oocysts of Goussia kessleri in the intestinal epithelium. H & E, x 1000 Fig. 7. Histological section of the anterior part of the intestine of a Kessler s goby. Solitary oocysts of Eimeria daviesae in the basal part of the epithelium. H & E, x 1000 Fig. 8. Histological section of the anterior part of the intestine of a Kessler s goby. Unsporulated oocyst (arrow) and a meront with crosssectioned merozoites (arrow head) of Goussia kessleri in the epithelium. H & E, x 800 Fig. 9. Unsporulated oocysts of Goussia kessleri in the basal cytoplasm of epithelial cells. H & E, x 1000 Fig. 10. Goussia kessleri microgamonts (arrow heads) in the apical cytoplasm of epithelial cells. H & E, x 1000
5 New coccidia: Goussia and Eimeria spp. 327 Fig. 11. Eimeria daviesae meront with merozoites (arrowhead) in the epithelial cell. H & E, x 1000 Fig. 12. Unsporulated oocyst of Eimeria daviesae (arrowhead) just leaving the apical part of the epithelial cell. H & E, x 1000 Fig. 13. Young Eimeria daviesae microgamonts (arrowheads) in the epithelium. H & E, x 1000 Fig. 14. Eimeria daviesae microgamont with microgametes (arrowhead) in the apical part of the epithelial cell. H & E, x 1000 Oocysts passed the gut unsporulated or semisporulated, less frequently sporulated (Fig. 5). Unsporulated oocysts proved to be globules with coarse granules. Sporocysts filled by rough granules of the residual body were formed 24 hours after sporulation, fully sporulated oocysts were obtained after 48 hours sporulation in room temperature. Of the coccidia of gobiid fishes E. daviesae resembles E. variabilis (Thélohan, 1893) but differs from it by the more tapered end of the oocyst and by having polar granule in the oocyst. E. daviesae also resembles E. marmorata Molnár, 1996, a parasite of the tubenosed goby, but differs from it by the larger size of the oocysts, by the less compact sporocysts and by having polar granule. Histology The histological picture was dominated by mixed infection in the majority of cases. However, even in these cases the smaller sporulated oocysts of Goussia kessleri, aggregated in the epithelium in larger groups (Fig. 6) were well distinguishable from the larger solitary sporulated oocysts of Eimeria daviesae located in the basal part of the epithelium (Fig. 7). Besides the oocysts, meronts, macrogamonts and microgamonts were also frequently seen. The developmental stages of the two
6 328 K. Molnár species, which were less easily distinguishable by morphological characteristics and size, were studied in preparations in which only one or the other species was found by the examination of fresh preparations. Infection with merogonic, gamogonic and sporogonic stages of G. kessleri was mostly found in the foregut and in the middle portion of the intestine. Ellipsoidal or round meronts x 7-10 in size were located in the apical part of the epithelial cells and contained 16 merozoites (Fig. 8). Macrogamonts and young oocysts measuring µm could not be distinguished with certainty. Those located in the apical cytoplasm were considered macrogamonts, while others lying in the basal region of the epithelial cells were regarded as young oocysts (Fig. 9). Microgamonts (Fig. 10) were located in the apical zone of the epithelial cells; the younger ones had dark colour and were smaller in size (7-8 x 4-5) than the macrogamonts. The larger microgamonts stained less intensively, contained a large number of microgametes, and measured 10 x 7. Sporulated oocysts 8-9 in diameter were in most cases aggregated in small batches (Fig. 6); however, unsporulated solitary oocysts scattered in the epithelial cells were also found in the same preparations (Figs. 8, 10). Local damage of the intestinal epithelium was evident, but a general pathogenic effect of the infection could not be demonstrated. In preparations in which only E. daviesae oocysts had been detected by the examination of fresh preparations, meronts, macrogamonts and microgamonts were found in the same locations as in the case of G. kessleri infection. On morphological basis these stages could not be clearly differentiated from similar stages of the above species. Round or short ellipsoidal meronts contained 16 merozoites and measured x (Fig. 11). Macrogamonts and young oocysts 10 (9-11) in diameter occupied mostly the apical region of the cells, but were found also in the median region (Fig. 12). On the other hand, microgamonts were always found in the apical cytoplasm of the cells. Developing microgametes in young stages of 7-10 were located in the centre of the microgamonts (Fig.13), while in more developed microgamonts in diameter the microgametes were scattered in the cytoplasm (Fig. 14). Young unsporulated oocysts measuring 13 (12-14) were found in both the median and the basal regions, but sporulated oocysts in diameter were always located in basal position, just above the propria layer, without gathering into groups (Fig. 7). In contrast to what was found by the examination of fresh preparations, the majority of E. daviesae oocysts were found in sporulated state. DISCUSSION Either as a result of active, intentional fish introductions (Holcik 1991) or as a passive consequence of human activity (Leach 1995), the appearance of different fish species in new habitats has become increasingly common. In the wake of ill-considered fish translocations, the fish host is accompanied to the new habitat by its pathogens, which sometimes cause major diseases among the introduced, and the indigenous fishes alike (Bauer and Hoffman 1976, Molnár 1984). The passive transfer of fish is facilitated primarily by the movement of ships, which occasionally carry spawn and fish specimens to distant regions. Some parasites of these fish species may also get to the new habitat. Leach (1995) pointed out that the percid ruffe (Gymnocephalus cernuus) and the gobiid round goby (Neogobius melanostomus) and tube-nosed goby (Proterorhinus marmoratus) had probably been carried to the American Great Lakes with the ballast of ships. Supposedly Kessler s goby, first recorded in Hungary by Erös and Guti (1997), had also gotten in a similar manner from its original habitat in the Lower Danube to reaches of the river near Budapest, where its population became very numerous (Molnár and Baska 1998). Studies on the coccidian fauna of Kessler s goby indicate that this fish species, not recorded in the Hungarian reaches of the river Danube until 1997, shows infection of high prevalence and high intensity with the Goussia and Eimeria species found during the survey. Almost 100% of the Kessler s goby specimens examined during the five months of the survey were infected with G. kessleri, and in June and July the oocysts of E. daviesae could also be detected frequently. This species seems to have brought along its coccidian infection from its original habitat, and that infection has become stabilised during the short time spent in the new habitat. Few reliable data exist on the host specificity of coccidian species. Doubts regarding host specificity may arise especially in the case of the morphologically similar Goussia species of small size. The same coccidian species can probably parasitise different closely related fish species. Paterson and Desser (1982) demonstrated that the species G. iroquoina could parasitise both the fathead minnow and the common shiner. At the same time, it is unquestionable that several morphologically distinct Goussia species (G. carpelli, G. sinensis, G. legeri, G. iroquoina) occur also in cyprinids. It is unlikely that Kessler s goby could have obtained its coccidia from these taxonomically distant fish species. Even the parasites of the perch and the ruffe, which are
7 New coccidia: Goussia and Eimeria spp. 329 percid fishes common in the river Danube though taxonomically distant from Kessler s goby, are morphologically well distinguishable from the species E. daviesae and G. kessleri. The tube-nosed goby, which is taxonomically closer to Kessler s goby and lives in the same habitat (Molnár and Baska 1998), is also infected by welldistinguishable Eimeria species. The notion that the described Eimeria is a distinct species could most of all be queried by the example of the species Eimeria variabilis, which is a common parasite of marine cottid fish species (Davies 1978, 1990) but has also been recorded, probably erroneously, from gobiid fishes (see Dyková and Lom 1983, Abollo et al. 1998). On the basis of the morphologically differences found, the occurrence of this, presumably collective, species in Kessler s gobies examined from the Hungarian reaches of the river Danube can also be excluded. It seems to be contradictory that in the case of E. daviesae, a species characterised by oocysts passed unsporulated on the basis of the examination of fresh preparations, masses of sporulated oocysts were detectable in the epithelium histologically. This contradiction is virtual; namely, from the work of Marincek (1973) it is known that in E. subepithelialis infection a certain proportion of the oocysts are passed unsporulated, while other oocysts sink to deep layers of the epithelium, undergo sporulation, and leave the fish gut only later. Probably a similar phenomenon occurs in the case of E. daviesae, and the numerous oocysts found by fresh examination obviously represent oocyst stages passed earlier. Both coccidian species are typical epithelial parasites that complete their entire life cycle in the columnar epithelial cells of the gut. While, however, the merogonic stages and the early gamonts are located in the apical cytoplasm of the epithelial cells, unsporulated and sporulated oocysts are gradually pushed to deep layers of the epithelium. According to Molnár (1995), this is a consequence of epithelial regeneration, since infected cells of impaired function are being gradually replaced by proliferating intact epithelial cells. Oocysts driven to deep layers of the epithelium show a different location in the case of the two species. While the smaller oocysts of the Goussia species are aggregated into smaller or larger groups, the larger E. daviesae oocysts are isolated separately by the host reaction. Acknowledgements. The author is indebted to Dr. Ferenc Baska, Dr. Csaba Székely and Miss Edit Eszterbauer for their help in the collection of host fish and in preparing digital pictures. The histological sections were made by Zsuzsa Kis. This study was rendered possible by grants from the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (project no. T and T ). REFERENCES Abollo E., Gestal C., Pascual S. (1998) Parasites in the rock goby Gobius paganellus L. (Pisces: Gobiidae) and the shanny Lipophrys pholis (L.) (Pisces: Blenniidae) in NW Spain. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 18: Bauer O. N., Hoffman G. L. (1976) Helminth range extension by translocation of fish. In: Wildlife Diseases, (Ed. L. A. Page). Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York, Davies A. J. (1978) Coccidian parasites of interdial fishes from Wales: systematics, development and cytochemistry. J. Protozool. 25: Davies A. J. (1990) Ultrastructural studies on the endogeneous stages of Eimeria variabilis (Thélohan, 1893) Reichenow, 1921, from Cottus (Taurulus) bubalis Euphrasen (Teleostei: Cottidae). J. Fish Dis. 13: Dyková I., Lom J. (1983) Fish coccidia: an annotated list of described species. Folia Parasitol. 30: Erös T., Guti G. (1997) The first record of Neogobius kessleri Günther, 1861 in the Hungarian section of the Danube. Halászat 90: (in Hungarian) Holcik J. (1991) Fish introduction in Europe with particular reference to its central and eastern part. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 48 (Suppl. 1): Leach J. H. (1995) Non-indigenous species in the Great Lakes: were colonisation and damage to ecosystem health predictable? J. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health 4: Marincek M. (1973) Dévelopment d Eimeria subepithelialis (Sporozoa, Coccidia) parasite de la carpe. Acta Protozool. 19: Molnár K. (1984) Parasite range extension by introduction of fish to Hungary. EIFAC Techn. Paper 42 (Suppl. 2): Molnár K. (1995) Phylum Apicomplexa. In: Fish Diseases and Disorders. Protozoan and Metazoan Infections, (Ed. P. T. K. Woo). CAB International, Wallingford, 1: Molnár K. (1996) Eimerian infection in the gut of the tube-nosed goby Proterorhinus marmoratus (Pallas) of the River Danube. Syst. Parasitol. 34: Molnár K., Baska F. (1998) Remarks on the occurrence of some fish species in the Danube in connection with the mass occurrence of Kessler s goby, Neogobius kessleri. Halászat 91: (in Hungarian) Moshu A. B. (1992) New species of coccidia (Protista: Apicomplexa, Eimeriidae) from fishes of the Hidigichki Water Reservoir (Moldova). Bul. Acad. Stiinte Rep. Moldova 4: (in Russian) Paterson W. B., Desser S. S. (1982) The biology of two Eimeria species (Protista: Apicomplexa) in their mutual fish host in Ontario. Can. J. Zool. 60: Received on 11th April, 2000; accepted on 4th July, 2000
Eimeria bahatica sp. n. (Protozoa: Coccidia) from European Hare (Lepus europaeus Pallas) in Hungary
 Paraíit. Hung. 11. 1978 Eimeria bahatica sp. n. (Protozoa: Coccidia) from European Hare (Lepus europaeus Pallas) in Hungary Dr. László SUGÁR University of Agricultural Sciences, Gödöllő, Research Station
Paraíit. Hung. 11. 1978 Eimeria bahatica sp. n. (Protozoa: Coccidia) from European Hare (Lepus europaeus Pallas) in Hungary Dr. László SUGÁR University of Agricultural Sciences, Gödöllő, Research Station
A New Species of Isospora Schneider, 1881 (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the Himalayan Black Bulbul Hypsipetes leucocephalus
 Acta Protozoologica Acta Protozool. (2012) 51: 81 85 http://www.eko.uj.edu.pl/ap doi: 10.4467/16890027AP.12.007.0390 A New Species of Isospora Schneider, 1881 (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the Himalayan
Acta Protozoologica Acta Protozool. (2012) 51: 81 85 http://www.eko.uj.edu.pl/ap doi: 10.4467/16890027AP.12.007.0390 A New Species of Isospora Schneider, 1881 (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the Himalayan
Organisms of Concern. Roundworms (nematodes) Anisakis spp., Pseudoterranova spp., Eustrongylides spp. and Gnathostoma spp.
 Parasites in Fish Parasites are a natural occurrence The parasites do not make the fish sick Thorough cooking of fish will make parasites harmless to humans Organisms of Concern Roundworms (nematodes)
Parasites in Fish Parasites are a natural occurrence The parasites do not make the fish sick Thorough cooking of fish will make parasites harmless to humans Organisms of Concern Roundworms (nematodes)
How To Identify A Gregarine From A Grasshopper
 Acta protozoologica Acta Protozool. (2011) 50: 141 153 http://www.eko.uj.edu.pl/ap Description of Two New Species of Phleobum Haldar and Chakraborty, 1974 along with a Major Taxonomic Revision of the Genus
Acta protozoologica Acta Protozool. (2011) 50: 141 153 http://www.eko.uj.edu.pl/ap Description of Two New Species of Phleobum Haldar and Chakraborty, 1974 along with a Major Taxonomic Revision of the Genus
h. Large intestine 3
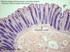 (1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
(1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
Zoo}({))giC/ffl} fl{fjldi(f;
 Zoological Studies 33(2): 160-164 (1994) Zoo}({))giC/ffl} fl{fjldi(f; Descriptions of a New Species in a New Genus, Kiransus, and Five New Species of Hydrochus (Coleoptera, Hydrophilidae) Dewanand Makhan
Zoological Studies 33(2): 160-164 (1994) Zoo}({))giC/ffl} fl{fjldi(f; Descriptions of a New Species in a New Genus, Kiransus, and Five New Species of Hydrochus (Coleoptera, Hydrophilidae) Dewanand Makhan
Histopathology of Kabatana arthuri (Microspora) infection in sutchi catfish, Pangasius sutchi
 FOLIA PARASITOLOGICA 47: 161-166, 2000 Dyková, Lom: Kabatana infection in sutchi catfish Histopathology of Kabatana arthuri (Microspora) infection in sutchi catfish, Pangasius sutchi Iva Dyková and Jiří
FOLIA PARASITOLOGICA 47: 161-166, 2000 Dyková, Lom: Kabatana infection in sutchi catfish Histopathology of Kabatana arthuri (Microspora) infection in sutchi catfish, Pangasius sutchi Iva Dyková and Jiří
Animal & Plant Cell Slides
 Animal & Plant Cell Slides Category: Biology Type: Class Experiment, 60 min class Materials: 2 Glass Slides 2 Cover Slips 1 Bottle of methylene blue (optional) 1 Plastic tray 1 Bottle of iodine 1 Plastic
Animal & Plant Cell Slides Category: Biology Type: Class Experiment, 60 min class Materials: 2 Glass Slides 2 Cover Slips 1 Bottle of methylene blue (optional) 1 Plastic tray 1 Bottle of iodine 1 Plastic
Lesson 3: Fish Life Cycle
 Lesson 3: Fish Life Cycle Activity: Diagram fish life cycle. Grade level: 4-8 Subjects: Science, social studies Setting: Classroom Duration: 50 minutes Key Terms: Fry, life cycle, life history, spawn,
Lesson 3: Fish Life Cycle Activity: Diagram fish life cycle. Grade level: 4-8 Subjects: Science, social studies Setting: Classroom Duration: 50 minutes Key Terms: Fry, life cycle, life history, spawn,
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
Tumor-like Anomalies in Lake Michigan Zooplankton
 Tumor-like Anomalies in Lake Michigan Zooplankton Primary Investigator: Henry Vanderploeg - NOAA GLERL Co-Investigators: Maria Manca - CNR - Istituto per lo Studio degli Ecosistemi Background Tumor-like
Tumor-like Anomalies in Lake Michigan Zooplankton Primary Investigator: Henry Vanderploeg - NOAA GLERL Co-Investigators: Maria Manca - CNR - Istituto per lo Studio degli Ecosistemi Background Tumor-like
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Department of Invertebrate Zoology, Faculty of Biology and Soil Science, St. Petersburg State University, Russia
 Protistology 1 (2), 66-71 (1999) July, 1999 Protistology Description of Cochliopodium larifeili n. sp. (Lobosea, Himatismenida), an amoeba with peculiar scale structure, and notes on the diagnosis of the
Protistology 1 (2), 66-71 (1999) July, 1999 Protistology Description of Cochliopodium larifeili n. sp. (Lobosea, Himatismenida), an amoeba with peculiar scale structure, and notes on the diagnosis of the
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF SECRETORY GRANULES FROM RAT ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. II. Ultrastructure of the Beta Granule
 ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF SECRETORY GRANULES FROM RAT ISLETS OF LANGERHANS II Ultrastructure of the Beta Granule MARIE H GREIDER, S L HOWELL, and P E LACY From the Department of Pathology, Washington
ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF SECRETORY GRANULES FROM RAT ISLETS OF LANGERHANS II Ultrastructure of the Beta Granule MARIE H GREIDER, S L HOWELL, and P E LACY From the Department of Pathology, Washington
MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES
 EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
(From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston)
 THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE ELECTRIC ORGAN OF THE ELECTRIC EEL AND TORPEDO RAY* PRELIMINARY COMMUNICATION BY JOHN H. LUFT, M.D. (From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston) PLATE 76 Electric
THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE ELECTRIC ORGAN OF THE ELECTRIC EEL AND TORPEDO RAY* PRELIMINARY COMMUNICATION BY JOHN H. LUFT, M.D. (From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston) PLATE 76 Electric
Review of the Late Pleistocene Soricidae (Mammalia) fauna of the Vaskapu Cave (North Hungary)
 Hantkeniana 8, 163 169, Budapest, 2013 Review of the Late Pleistocene Soricidae (Mammalia) fauna of the Vaskapu Cave (North Hungary) Lukács MÉSZÁROS 1 (with 2 figures, 2 tables and 1 plate) The summary
Hantkeniana 8, 163 169, Budapest, 2013 Review of the Late Pleistocene Soricidae (Mammalia) fauna of the Vaskapu Cave (North Hungary) Lukács MÉSZÁROS 1 (with 2 figures, 2 tables and 1 plate) The summary
Monitoring of sea trout post-smolts, 2013
 Monitoring of sea trout post-smolts, 213 A report to the West Sutherland Fisheries Trust, Report No. WSFT2/14 January 214 Shona Marshall Fisheries Biologist West Sutherland Fisheries Trust Gardeners Cottage
Monitoring of sea trout post-smolts, 213 A report to the West Sutherland Fisheries Trust, Report No. WSFT2/14 January 214 Shona Marshall Fisheries Biologist West Sutherland Fisheries Trust Gardeners Cottage
Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes
 Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains)
 LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
OBJECTIVES PROCEDURE. Lab 2- Bio 160. Name:
 Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
INDEX WORDS: Ruffe, egg predation, Lake Superior, fishery.
 J. Great Lakes Res. 24(2):304-308 Internat. Assoc. Great Lakes Res., 1998 Predation by Ruffe (Gymnocephalus cernuus) on Fish Eggs in Lake Superior James Selgeby U.S. Geological Survey, Biological Resources
J. Great Lakes Res. 24(2):304-308 Internat. Assoc. Great Lakes Res., 1998 Predation by Ruffe (Gymnocephalus cernuus) on Fish Eggs in Lake Superior James Selgeby U.S. Geological Survey, Biological Resources
Algological Investigations of Hungarian Forest Soils III. Soil Algal Surface Communities in Mts. Mátra
 ANNALES HISTORICO-NATURALES MUSEI NATIONALIS HUNGARICI Tomus 67. Budapest 1975. Algological Investigations of Hungarian Forest Soils III. Soil Algal Surface Communities in Mts. Mátra by Zs. P.-KOMÁROMY,
ANNALES HISTORICO-NATURALES MUSEI NATIONALIS HUNGARICI Tomus 67. Budapest 1975. Algological Investigations of Hungarian Forest Soils III. Soil Algal Surface Communities in Mts. Mátra by Zs. P.-KOMÁROMY,
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction
 Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
AQUATIC INVASIVE SPECIES POSSESSION RULES
 AQUATIC INVASIVE SPECIES POSSESSION RULES 312 IAC 9-6-7 Exotic fish Authority: IC 14-22-2-6 Affected: IC 14-22-2-3 Sec. 7. (a) Except as otherwise provided under this section, a person must not import,
AQUATIC INVASIVE SPECIES POSSESSION RULES 312 IAC 9-6-7 Exotic fish Authority: IC 14-22-2-6 Affected: IC 14-22-2-3 Sec. 7. (a) Except as otherwise provided under this section, a person must not import,
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology
 Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist
 Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100
 Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
9.3.7 Advice December 2014
 9.3.7 Advice December 2014 ECOREGION STOCK Widely distributed and migratory stocks European eel Advice for 2015 The status of eel remains critical and ICES advises that all anthropogenic mortality (e.g.
9.3.7 Advice December 2014 ECOREGION STOCK Widely distributed and migratory stocks European eel Advice for 2015 The status of eel remains critical and ICES advises that all anthropogenic mortality (e.g.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB)
 Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
A Fishy Tale. Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope
 A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
Introduction to Medical Microbiology
 Introduction to Medical Microbiology Course Medical Microbiology Unit I Introduction to Microbiology Essential Question What is Medical Microbiology? TEKS 130.207(c) 2A, 3D Prior Student Learning n/a Estimated
Introduction to Medical Microbiology Course Medical Microbiology Unit I Introduction to Microbiology Essential Question What is Medical Microbiology? TEKS 130.207(c) 2A, 3D Prior Student Learning n/a Estimated
Students will identify these animal cell structures: Students should properly answer the pre-activity cell membrane, nucleus. questions.
 WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST. Which graph best shows the relative stream velocities across the stream from A to B?
 NAME DATE WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST 1. The diagram below shows a meandering stream. Measurements of stream velocity were taken along straight line AB. Which graph best shows the
NAME DATE WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST 1. The diagram below shows a meandering stream. Measurements of stream velocity were taken along straight line AB. Which graph best shows the
Investigating Husbandry Techniques for the Culture of the White Clawed Crayfish, Austropotamobius pallipes
 Investigating Husbandry Techniques for the Culture of the White Clawed Crayfish, Austropotamobius pallipes Oliver Brown Fish Culture Officer October 2013 Status The population of white-clawed crayfish
Investigating Husbandry Techniques for the Culture of the White Clawed Crayfish, Austropotamobius pallipes Oliver Brown Fish Culture Officer October 2013 Status The population of white-clawed crayfish
CHEM 107. Hair handout. Basic Structure of Hair. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05
 CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
Cherokee County School District Student Performance Standards Unit Guides - Science: Fifth Grade
 Characteristics of Science 1 Cherokee County School District Habits of Mind S5CS1. Students will be aware of the importance of curiosity, honesty, openness, and skepticism in science and will exhibit these
Characteristics of Science 1 Cherokee County School District Habits of Mind S5CS1. Students will be aware of the importance of curiosity, honesty, openness, and skepticism in science and will exhibit these
Chatham Rock Phosphate Marine Consent Application. P Kennedy - Environmental Impact Assessment Evidence Summary
 Chatham Rock Phosphate Marine Consent Application P Kennedy - Environmental Impact Assessment Evidence Summary My evidence and this summary cover the following matters: Seabed and sediment Discharge and
Chatham Rock Phosphate Marine Consent Application P Kennedy - Environmental Impact Assessment Evidence Summary My evidence and this summary cover the following matters: Seabed and sediment Discharge and
The illustrations below reflect other scientists results in identifying and counting the stages of the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula.
 Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Host specificity and the probability of discovering species of helminth parasites
 Host specificity and the probability of discovering species of helminth parasites 79 R. POULIN * and D. MOUILLOT Department of Zoology, University of Otago, P.O. Box 6, Dunedin, New Zealand UMR CNRS-UMII
Host specificity and the probability of discovering species of helminth parasites 79 R. POULIN * and D. MOUILLOT Department of Zoology, University of Otago, P.O. Box 6, Dunedin, New Zealand UMR CNRS-UMII
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Ecology - (BIO.B.4.1.1 ) Ecological Organization, (BIO.B.4.1.2 ) Ecosystem Characteristics, (BIO.B.4.2.
 Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Ecology - (BIO.B.4.1.1 ) Ecological Organization, (BIO.B.4.1.2 ) Ecosystem Characteristics, (BIO.B.4.2.1 ) Energy Flow 1) Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George Date:
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Ecology - (BIO.B.4.1.1 ) Ecological Organization, (BIO.B.4.1.2 ) Ecosystem Characteristics, (BIO.B.4.2.1 ) Energy Flow 1) Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George Date:
Physical & Chemical Properties. Properties
 Physical & Chemical Properties Properties Carbon black can be broadly defined as very fine particulate aggregates of carbon possessing an amorphous quasi-graphitic molecular structure. The most significant
Physical & Chemical Properties Properties Carbon black can be broadly defined as very fine particulate aggregates of carbon possessing an amorphous quasi-graphitic molecular structure. The most significant
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Hair & Fiber. (Unit 5)
 37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES
 PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES Compiled by HOLLY BROWN and MARTIN WILKINSON, School of Life Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland Although
PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES Compiled by HOLLY BROWN and MARTIN WILKINSON, School of Life Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland Although
ATLAS OF HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY THYROID PAPILLARY CARCINOMA
 Papillary carcinoma is the most common of thyroid malignancies and occurs in all age groups but particularly in women under 45 years of age. There is a high rate of cervical metastatic disease and yet
Papillary carcinoma is the most common of thyroid malignancies and occurs in all age groups but particularly in women under 45 years of age. There is a high rate of cervical metastatic disease and yet
Eimeria media Kessel 1929: comparative study of endogenous development between precocious and parental strains
 Eimeria media Kessel 1929: comparative study of endogenous development between precocious and parental strains M Pakandl, K Gaca, D Licois, P Coudert To cite this version: M Pakandl, K Gaca, D Licois,
Eimeria media Kessel 1929: comparative study of endogenous development between precocious and parental strains M Pakandl, K Gaca, D Licois, P Coudert To cite this version: M Pakandl, K Gaca, D Licois,
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display
 The Living World Chapter 1: The Science of Biology Specific Learning Outcomes: 1.1 List the major properties of life. 1.2 Explain how science is distinguished from other ways of seeking understanding of
The Living World Chapter 1: The Science of Biology Specific Learning Outcomes: 1.1 List the major properties of life. 1.2 Explain how science is distinguished from other ways of seeking understanding of
The Effect of Selected Dietary Supplements on the Occurrence of Coccidia in the Alimentary Tract of Chicken
 The Effect of Selected Dietary Supplements on the Occurrence of Coccidia in the Alimentary Tract of Chicken Luboš Zábranský 1, Miloslav Šoch 1, Lenka Pazderková 1, Anna Šimková 1, Kateřina Švejdová 1,
The Effect of Selected Dietary Supplements on the Occurrence of Coccidia in the Alimentary Tract of Chicken Luboš Zábranský 1, Miloslav Šoch 1, Lenka Pazderková 1, Anna Šimková 1, Kateřina Švejdová 1,
Small & Large Intestines
 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Protozoal Diseases. External Protozoal Diseases. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis ("Ich" or White Spot Disease)
 Protozoal Diseases External Protozoal Diseases Internal Protozoal Diseases Ichthyophthirius multifiliis ("Ich") Cryptocaryon irritans Ichthyobodo necatrix (Costiasis) Trichodina species (Trichodiniasis)
Protozoal Diseases External Protozoal Diseases Internal Protozoal Diseases Ichthyophthirius multifiliis ("Ich") Cryptocaryon irritans Ichthyobodo necatrix (Costiasis) Trichodina species (Trichodiniasis)
Development of Teeth
 Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY
 9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
MEPC 56/23 ANNEX 2 Page 1 ANNEX 2 RESOLUTION MEPC.162(56) Adopted on 13 July 2007
 Page 1 RESOLUTION MEPC.162(56) Adopted on 13 July 2007 GUIDELINES FOR RISK ASSESSMENT UNDER REGULATION A-4 OF THE BWM CONVENTION (G7) THE MARINE ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION COMMITTEE, RECALLING Article 38(a)
Page 1 RESOLUTION MEPC.162(56) Adopted on 13 July 2007 GUIDELINES FOR RISK ASSESSMENT UNDER REGULATION A-4 OF THE BWM CONVENTION (G7) THE MARINE ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION COMMITTEE, RECALLING Article 38(a)
IDENTIFICATION OF ADULT CORIXIDS 25
 IDENTIFICATION OF ADULT CORIXIDS 25 THE IDENTIFICATION OF BRITISH ADULT SPECIMENS OF SIGARA LATERALIS (LEACH), SIGARA CONCINNA (FIEBER), CALLICORIXA PRAEUSTA (FIEBER) AND CALLICORIXA WOLLASTONI (DOUGLAS
IDENTIFICATION OF ADULT CORIXIDS 25 THE IDENTIFICATION OF BRITISH ADULT SPECIMENS OF SIGARA LATERALIS (LEACH), SIGARA CONCINNA (FIEBER), CALLICORIXA PRAEUSTA (FIEBER) AND CALLICORIXA WOLLASTONI (DOUGLAS
THE ECOSYSTEM - Biomes
 Biomes The Ecosystem - Biomes Side 2 THE ECOSYSTEM - Biomes By the end of this topic you should be able to:- SYLLABUS STATEMENT ASSESSMENT STATEMENT CHECK NOTES 2.4 BIOMES 2.4.1 Define the term biome.
Biomes The Ecosystem - Biomes Side 2 THE ECOSYSTEM - Biomes By the end of this topic you should be able to:- SYLLABUS STATEMENT ASSESSMENT STATEMENT CHECK NOTES 2.4 BIOMES 2.4.1 Define the term biome.
Symptomspesifikke probiotikum. Linda Mulder, MSc. Vårseminaret 2014
 Linda Mulder, MSc. Vårseminaret 2014 Content Background on probiotics Intestinal microbiota & health on 3 levels Indication-specific probiotics Strain-specific characteristics Monostrain vs. multispecies
Linda Mulder, MSc. Vårseminaret 2014 Content Background on probiotics Intestinal microbiota & health on 3 levels Indication-specific probiotics Strain-specific characteristics Monostrain vs. multispecies
THESES OF DOCTORAL (Ph.D.) DISSERTATION
 THESES OF DOCTORAL (Ph.D.) DISSERTATION UNIVERSITY OF KAPOSVÁR FACULTY OF ANIMAL SCIENCE Department of Animal Physiology and Animal Hygiene Director of the Doctoral School: DR. PÉTER HORN Ordinary Member
THESES OF DOCTORAL (Ph.D.) DISSERTATION UNIVERSITY OF KAPOSVÁR FACULTY OF ANIMAL SCIENCE Department of Animal Physiology and Animal Hygiene Director of the Doctoral School: DR. PÉTER HORN Ordinary Member
PROCEDURE MANUAL. This Procedure Replaces None
 4 7 12.06 1 of 6 This Procedure Replaces None Staff, Organizations Directly Affected: General Public Director Permit & Authorization Service Bureau Conservation Officer Service Policy Cross-Reference:
4 7 12.06 1 of 6 This Procedure Replaces None Staff, Organizations Directly Affected: General Public Director Permit & Authorization Service Bureau Conservation Officer Service Policy Cross-Reference:
Dose/Response Experiments on Lettuce Seeds
 Dose/Response Experiments on Lettuce Seeds Name: Date: Lab# Bioassays: Background Information on Dose/Response Experiments A bioassay involves use of a biological organism to test for chemical toxicity.
Dose/Response Experiments on Lettuce Seeds Name: Date: Lab# Bioassays: Background Information on Dose/Response Experiments A bioassay involves use of a biological organism to test for chemical toxicity.
Guidelines for caring for injured turtles
 Guidelines for caring for injured turtles Background The NT is home to six of the world s seven different marine turtles, five of which are listed internationally as endangered. Along with the sea turtles,
Guidelines for caring for injured turtles Background The NT is home to six of the world s seven different marine turtles, five of which are listed internationally as endangered. Along with the sea turtles,
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF STRUCTURAL ZONE MODEL FOR COMPOSITE THIN FILMS IN MAGNETIC RECORDING MEDIA APPLICATION
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF STRUCTURAL ZONE MODEL FOR COMPOSITE THIN FILMS IN MAGNETIC RECORDING MEDIA APPLICATION Hua Yuan and David E. Laughlin Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Carnegie Mellon
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF STRUCTURAL ZONE MODEL FOR COMPOSITE THIN FILMS IN MAGNETIC RECORDING MEDIA APPLICATION Hua Yuan and David E. Laughlin Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Carnegie Mellon
Aspects of Reproduction and the Condition of Gravid Mud Crab (Crustacea: Brachyura: Potamon) in Ebonyi State, Nigeria
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2015, PP 104-109 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Aspects of Reproduction
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2015, PP 104-109 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Aspects of Reproduction
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Biology Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Biology for Achievement Standard 9115 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Biology for Achievement Standard 9115 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Cells. Introduction WSBCTC 1
 Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY RED BLOOD CELLS AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS IN URINALYSIS
 URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY. Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab
 HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
How To Identify Myxobolus Species From Cyprinids
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 58: 35 40, 2004 Published January 28 Dis Aquat Org Genetic relationship among gill-infecting Myxobolus species (Myxosporea) of cyprinids: molecular evidence of importance
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 58: 35 40, 2004 Published January 28 Dis Aquat Org Genetic relationship among gill-infecting Myxobolus species (Myxosporea) of cyprinids: molecular evidence of importance
Ecosystems and Food Webs
 Ecosystems and Food Webs How do AIS affect our lakes? Background Information All things on the planet both living and nonliving interact. An Ecosystem is defined as the set of elements, living and nonliving,
Ecosystems and Food Webs How do AIS affect our lakes? Background Information All things on the planet both living and nonliving interact. An Ecosystem is defined as the set of elements, living and nonliving,
Operating Maintenance Model for Modern Printing Machines
 Operating Maintenance Model for Modern Printing Machines Csaba Horváth Institute of Mediatechnology, Budapest Tech Doberdó út 6, H-1034 Budapest, Hungary E-mail: horvath.csaba@nyt.hu, horvath.csaba@rkk.bmf.hu
Operating Maintenance Model for Modern Printing Machines Csaba Horváth Institute of Mediatechnology, Budapest Tech Doberdó út 6, H-1034 Budapest, Hungary E-mail: horvath.csaba@nyt.hu, horvath.csaba@rkk.bmf.hu
Sedimentary Rocks Practice Questions and Answers Revised September 2007
 Sedimentary Rocks Practice Questions and Answers Revised September 2007 1. Clastic sedimentary rocks are composed of and derived from pre-existing material. 2. What is physical weathering? 3. What is chemical
Sedimentary Rocks Practice Questions and Answers Revised September 2007 1. Clastic sedimentary rocks are composed of and derived from pre-existing material. 2. What is physical weathering? 3. What is chemical
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human
GLOSSARY OF TERMS CHAPTER 11 WORD DEFINITION SOURCE. Leopold
 CHAPTER 11 GLOSSARY OF TERMS Active Channel The channel that contains the discharge Leopold where channel maintenance is most effective, sediment are actively transported and deposited, and that are capable
CHAPTER 11 GLOSSARY OF TERMS Active Channel The channel that contains the discharge Leopold where channel maintenance is most effective, sediment are actively transported and deposited, and that are capable
STOP BALLAST WATER INVASIONS
 STOP BALLAST WATER INVASIONS SOUTHERN LAKE MICHIGAN BALLAST WATER OUTREACH Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant College Program Illinois International Port District Water bodies worldwide are being invaded by non-native
STOP BALLAST WATER INVASIONS SOUTHERN LAKE MICHIGAN BALLAST WATER OUTREACH Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant College Program Illinois International Port District Water bodies worldwide are being invaded by non-native
Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining. Stem Cells
 Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining Stem Cells He Xi, Masilamani Jeyakumar, Phan Toan Thang Bioengineering, National University of Bioengineering Abstract Cartilage defects, such as
Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining Stem Cells He Xi, Masilamani Jeyakumar, Phan Toan Thang Bioengineering, National University of Bioengineering Abstract Cartilage defects, such as
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Identification of fish-parasitic Myxobolus (Myxosporea) species using a combined PCR-RFLP method
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 44: 35 39, 2001 Published January 26 Dis Aquat Org Identification of fish-parasitic Myxobolus (Myxosporea) species using a combined PCR-RFLP method Edit Eszterbauer 1,
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 44: 35 39, 2001 Published January 26 Dis Aquat Org Identification of fish-parasitic Myxobolus (Myxosporea) species using a combined PCR-RFLP method Edit Eszterbauer 1,
A Practitioner s View. Senior Technical Services Veterinarian
 Coccidiosis Vaccination A Practitioner s View Robert L Owen V M D Ph D Robert L. Owen, V.M.D., Ph.D. Senior Technical Services Veterinarian Acknowledgements Dr. John McCarty Merial Animal Health Hatchpak
Coccidiosis Vaccination A Practitioner s View Robert L Owen V M D Ph D Robert L. Owen, V.M.D., Ph.D. Senior Technical Services Veterinarian Acknowledgements Dr. John McCarty Merial Animal Health Hatchpak
Preparation of Blood Films
 Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts
Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY
 EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY Brightfield Compound Light Microscope The light microscope is an important tool in the study of microorganisms. The compound light microscope uses visible light to directly illuminate
EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY Brightfield Compound Light Microscope The light microscope is an important tool in the study of microorganisms. The compound light microscope uses visible light to directly illuminate
NOTE TO TEACHER: It is appropriate to introduce the mitochondria (where energy is made) as a major structure common to all cells.
 5.2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). Taxonomy level: 1.1 and 1.2-A Remember Factual Knowledge
5.2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). Taxonomy level: 1.1 and 1.2-A Remember Factual Knowledge
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination
 Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Plant and Animal Cells
 Plant and Animal Cells a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow, divide and to make needed materials. S7L2a b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and
Plant and Animal Cells a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow, divide and to make needed materials. S7L2a b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and
hij GCSE Biology 3 Higher Tier Biology 3H SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version 1.0
 hij GCSE Biology 3 Higher Tier Biology 3H SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version.0 Copyright 20 AQA and its licenss. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by
hij GCSE Biology 3 Higher Tier Biology 3H SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version.0 Copyright 20 AQA and its licenss. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
Intraobserver and Interobserver Reproducibility of WHO and Gleason Histologic Grading Systems in Prostatic Adenocarcinomas
 International Urology and Nephrology 28 (1), pp. 73-77 (1996) Intraobserver and Interobserver Reproducibility of WHO and Gleason Histologic Grading Systems in Prostatic Adenocarcinomas $. O. OZDAMAR,*
International Urology and Nephrology 28 (1), pp. 73-77 (1996) Intraobserver and Interobserver Reproducibility of WHO and Gleason Histologic Grading Systems in Prostatic Adenocarcinomas $. O. OZDAMAR,*
Museum Victoria http://museumvictoria.com.au/ CRC National Plant Biosecurity http://www.crcplantbiosecurity.com.au/
 1. PaDIL Species Factsheet Scientific Name: Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense (E.F. Sm.) W.C. Snyder & H.N. Hansen Anamorphic fungi (Ascomycetes) Common Name Panama disease of banana Live link: http://www.padil.gov.au:80/pests-and-diseases/pest/main/136609
1. PaDIL Species Factsheet Scientific Name: Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense (E.F. Sm.) W.C. Snyder & H.N. Hansen Anamorphic fungi (Ascomycetes) Common Name Panama disease of banana Live link: http://www.padil.gov.au:80/pests-and-diseases/pest/main/136609
PACT. PACT Nail Fungus Therapy Treatment Instructions. Photodynamic therapy for nail fungus using light, safely and gently.
 PACT PACT Nail Fungus Therapy Treatment Instructions Photodynamic therapy for nail fungus using light, safely and gently. PACT Nail Fungus Therapy Treatment Instructions Contents 1. Introduction 2. Nail
PACT PACT Nail Fungus Therapy Treatment Instructions Photodynamic therapy for nail fungus using light, safely and gently. PACT Nail Fungus Therapy Treatment Instructions Contents 1. Introduction 2. Nail
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
(Resolutions, recommendations and opinions) RECOMMENDATIONS COUNCIL
 3.7.2009 Official Journal of the European Union C 151/1 I (Resolutions, recommendations and opinions) RECOMMENDATIONS COUNCIL COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION of 9 June 2009 on patient safety, including the prevention
3.7.2009 Official Journal of the European Union C 151/1 I (Resolutions, recommendations and opinions) RECOMMENDATIONS COUNCIL COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION of 9 June 2009 on patient safety, including the prevention
Section 1 The Earth System
 Section 1 The Earth System Key Concept Earth is a complex system made up of many smaller systems through which matter and energy are continuously cycled. What You Will Learn Energy and matter flow through
Section 1 The Earth System Key Concept Earth is a complex system made up of many smaller systems through which matter and energy are continuously cycled. What You Will Learn Energy and matter flow through
3.1 Cells and cell function
 BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
