Skull Osteology & Cranial Cavity. Rebecca S Lufler, PhD Head and Neck Anatomy February 23, 2012
|
|
|
- Emery Wilcox
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Skull Osteology & Cranial Cavity Rebecca S Lufler, PhD Head and Neck Anatomy February 23, 2012
2 Lecture Overview Cranium osteology External features of skull Paranasal Sinuses Cranial fossae Internal features of skull Meninges Dural venous sinuses Intracranial hemorrhage
3 The Cranium Neurocranium Made up of the bones and Ossues (meninges) surrounding the brain Viscerocranium Made up of the facial bones
4 Neurocranium Eight bones Frontal Parietal (2) Occipital Temporal (2) Sphenoid Ethmoid (part) Anterior Frontal Parietal Parietal Occipital Posterior
5 Neurocranium Eight bones Frontal Parietal (2) Occipital Temporal (2) Sphenoid Ethmoid (part) Calvaria roof Parietal Occipital Parietal
6 Neurocranium Eight bones Frontal Parietal (2) Occipital Temporal (2) Sphenoid Ethmoid (part)
7 Neurocranium Eight bones Frontal Parietal (2) Occipital Temporal (2) Sphenoid Ethmoid (part) Basicranium floor
8 Neurocranium Meninges Membranous coverings which serve to: Protect the brain within the cranial cavity Provide support for arteries, veins, and venous sinuses Enclose the subarachnoid space filled with fluid nourishment for the brain
9 15 bones Ethmoid (part) Vomer Mandible Maxilla (2) Inferior nasal concha (2) ZygomaOc (2) Nasal (2) PalaOne (2) Lacrimal (2) Viscerocranium
10 Viscerocranium 15 bones Ethmoid (part) Vomer Mandible Maxilla (2) Inferior nasal concha (2) ZygomaOc (2) Nasal (2) PalaOne (2) Lacrimal (2)
11 Fontanelles Anterior fontanelle Age at closure: ~18-24 months Sphenoid (Anterolateral) fontanelle Age at closure: < 6 months Mastoid (Posterolateral) fontanelle Age at closure: < 24 months
12 Sutures Coronal suture Pterion Lambdoid suture Asterion
13 Fontanelles Anterior fontanelle Age at closure: ~18-24 months Posterior fontanelle Age at closure: < 24 months
14 Sutures Coronal suture Lambdoid suture Sagittal suture Bregma Lambda
15 External Skull Features - Anterior Nasion Glabella Orbit Anterior nasal aperture Angle Body Alveolar process Alveolar process Ramus Mental protuberance
16 Supraorbital foramen Superior orbital fissure Optic canal Posterior ethmoid foramen Inferior orbital fissure Anterior ethmoid foramen Infraorbital foramen
17 Supraorbital n. (CN V 1 ) CN III CN IV CN V 1 CN VI Optic n. (CN II) Posterior ethmoidal n. (CN V 1 ) Anterior ethmoidal n. (CN V 1 ) Zygomatic n. (CN V 2 ) Infraorbital n. (CN V 2 )
18 Mandible Coronoid process Mandibular notch Mandibular foramen Mylohyoid groove Mylohyoid line Ramus Lingula Head Neck Digastric fossa Superior & Inferior genial spines Body Mental foramen Angle
19 External Skull Features - Lateral Lacrimal groove Zygomaticofacial foramen Pterygomaxillary fissure External acoustic meatus Styloid process Mastoid process Zygomatic arch = Zygomatic process of temporal bone + Temporal process of zygomatic bone
20 External Skull Features - Lateral Nasolacrimal duct Zygomaticofacial n. (CN V 2 ) Mental n. (CN V 3 ) Pterygomaxillary fissure = Lateral entrance into the pterygopalatine fossa, housing pterygopalatine ganglion with CN V 2
21 Lecture Overview Cranium osteology External features of skull Paranasal Sinuses Cranial fossae Internal features of skull Meninges Dural venous sinuses Intracranial hemorrhage
22 Paranasal Sinuses Air filled spaces within bone lined with respiratory epithelium. Develop prenatally and cononue to grow throughout life. FuncOon is debated, includes to lighten weight of skull, increasing voice resonance, humidifying inhaled air.
23 Paranasal Sinuses Frontal Ethmoid Maxillary
24 Paranasal Sinuses Frontal Ethmoid Maxillary Sphenoid Mastoid air cells (NOT paranasal sinus)
25
26 SinusiOs
27 SinusiOs
28 Lecture Overview Cranium osteology External features of skull Paranasal Sinuses Cranial fossae Internal features of skull Meninges Dural venous sinuses Intracranial hemorrhage
29 Cranial Fossae Steps down from anterior posterior Anterior cranial fossa Middle cranial fossa Posterior cranial fossa
30 Anterior Cranial Fossa Frontal crest Crista galli Orbital part of frontal bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Anterior clinoid processes Middle Cranial Fossa Greater wing of sphenoid Sella turcica = Tuberculum sellae Hypophysial fossa Posterior Cranial Fossa Clivus Internal occipital crest Internal occipital protuberance Posterior clinoid processes Dorsum sellae Petrous part of temporal bone
31 Anterior Cranial Fossa Foramen cecum Cribriform plate
32 Anterior Cranial Fossa Emissary vein CN I
33 Groove for lesser petrosal nerve Optic canal Carotid notch Foramen ovale Middle Cranial Fossa Foramen spinosum Groove for middle meningeal artery Groove for greater petrosal nerve Foramen lacerum Foramen rotundum Superior orbital fissure
34 Lesser petrosal n. CN II Internal carotid a. V 3, lesser petrosal n. Middle meningeal a. and recurrent meningeal n. Middle meningeal artery Greater petrosal nerve Nothing Middle Cranial Fossa
35 Optic canal Superior orbital fissure Lesser wing Foramen rotundum Greater wing Pterygoid canal Sphenoid bone, posterior view
36 Posterior Cranial Fossa Internal acoustic meatus Jugular foramen Hypoglossal (anterior condylar) canal Foramen magnum
37 Posterior Cranial Fossa CN VII and VIII CN IX, X, XI, Internal jugular v. CN XII CN XI (spinal root), Spinal cord, vertebral aa.
38 Anterior Cranial Fossa Foramen cecum Cribriform plate Groove for lesser petrosal nerve Posterior Cranial Fossa Internal acoustic meatus Jugular foramen Hypoglossal (anterior condylar) canal Foramen magnum Middle Cranial Optic canal Fossa Carotid notch Foramen ovale Foramen spinosum Groove for middle meningeal artery Groove for greater petrosal nerve Foramen lacerum Foramen rotundum Superior orbital fissure
39 Anterior Cranial Fossa Emissary vein CN I Lesser petrosal n. Posterior Cranial Fossa CN VII and VIII CN IX, X, XI, Internal jugular v. CN XII CN XI (spinal root), Spinal cord, vertebral aa. Middle Cranial Fossa CN II Internal carotid a. V3, lesser petrosal n. Middle meningeal a. and recurrent meningeal n. Middle meningeal artery Greater petrosal nerve Nothing
40 Hamulus Medial pterygoid plate Scaphoid fossa Lateral pterygoid plate Spine of sphenoid Occipital condyle Zygomatic arch Mandibular (glenoid) fossa Styloid process Pharyngeal tubercle Mastoid process Inferior nuchal line Superior nuchal line External occipital protuberance
41 Incisive foramen Inferior orbital fissure Foramen ovale Foramen spinosum Stylomastoid foramen Foramen magnum Hypoglossal (anterior condylar) canal Greater palatine foramen Lesser palatine foramen Pterygoid canal Foramen lacerum Carotid canal Jugular Foramen
42 Nasopalatine n. (CN V 2 ) Infraorbital and zygomatic nn. (CN V 2 ) CN V 3 Middle meningeal a. and recurrent meningeal n. CN VII Spinal cord/brainstem CN XI (spinal component) Vertebral aa. CN XII Greater palatine n. (CN V 2 ) Lesser palatine n. (CN V 2 ) Nerve of the pterygoid canal (CN V 2 ) Internal carotid a. CN IX, X, XI, Internal jugular v.
43 Chorda tympani (CN VII) and anterior tympanic a. Nerve of the pterygoid canal (V 2 ) Tympanic n. (CN IX)
44 The Squirrely Internal CaroOd
45 Lecture Overview Cranium osteology External features of skull Paranasal Sinuses Cranial fossae Internal features of skull Meninges Dural venous sinuses Intracranial hemorrhage
46 Meninges First Layer Dura mater Tough, fibrous outer covering, with an external periosteal layer and internal meningeal layer. - These two layers are fused except where there are dural venous sinuses and dural infoldings. Dura mater External periosteal layer Internal meningeal layer
47 Dural Infoldings Meningeal layer reflects away from the periosteal layer and divides the cranial cavity into compartments Falx cerebri separates cerebral hemispheres A[aches to the crista galli and internal occipital protuberance Falx cerebelli lies between the cerebellar hemispheres A[aches to internal occipital crest Tentorium cerebelli separates the occipital lobes of the cerebrum from the cerebellum ( tent ) A[aches to posterior clinoid processes, petrous temporal bone, and internal occipital bone Diaphragma sellae lies over the pituitary gland A[aches to all four clinoid processes
48
49 Dural Venous Sinuses Superior sagi[al sinus Endothelium lined spaces draining blood away from the brain to the internal jugular vein Superior sagi[al sinus Inferior sagi[al sinus Straight sinus Confluence of sinuses Occipital sinus Inferior sagi[al sinus Straight sinus Occipital sinus Confluence of sinuses
50 Straight sinus Transverse sinus Sigmoid sinus Cavernous sinus Inferior petrosal sinus Superior petrosal sinus Cavernous sinus Superior petrosal sinus Straight sinus Inferior petrosal sinus Sigmoid sinus Transverse sinus Confluence of sinuses
51 Dural Venous Sinus Drainage
52 Cavernous sinus Internal carotid a. Occulomotor n. (CN III) Trochlear n. (CN IV) Ophthalmic Division V 1 Maxillary Division V 2 Abducent n. (CN VI)
53 Dural Venous Sinus Drainage Superior sagittal sinus Inferior sagittal sinus Cavernous sinus Occipital sinus Confluence of sinuses Straight sinus Superior petrosal sinus Inferior petrosal sinus Transverse sinus *Note: Emissary veins pass through small holes (foramina) in the skull to the dural sinuses. Provides a channel for transmission of infection from the scalp to the brain/meninges. Sigmoid sinus Internal jugular vein
54 Dural InnervaOon Anterior cranial fossa CN V 1, V 2, and V 3 Middle cranial fossa CN V 2 and V 3 Posterior cranial fossa Floor C2 and C3 Roof (tentorium) CN V 1 Falx cerebri Anterior Anterior meningeal n., V 1 Posterior Tentorial n., V 1 V 3 V 3 V 2 V 2 V 1 V 1
55 Meninges Second layer Arachnoid mater Thin, web- like middle layer. - Covers a space, subarachnoid space, containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), arteries and veins. Arachnoid granulations Dura mater Arachnoid mater
56 Meninges Third layer Pia mater Thinner, shiny inner layer. - Adheres directly to the surface of the brain and follows every curve of the cortex*. *In lab, the dura will adhere to the inside the calvarium at the sutures, the arachnoid will cover the sulci of the brain, and the pia will follow the sulci. Dura mater Pia mater Arachnoid mater
57 Circle of Willis! Anterior cerebral a. Anterior communicating a. Middle cerebral a. Internal carotid a. Posterior communicating a. Posterior cerebral a. Basilar a. Vertebral a.
58 Lecture Overview Cranium osteology External features of skull Paranasal Sinuses Cranial fossae Internal features of skull Meninges Dural venous sinuses Intracranial hemorrhage
59 Intracranial Hemorrhage Epidural hematoma Severe head trauma, ie: automobile accident, skull fracture Arterial bleeding, between skull and dura mater Rapidly worsens and contained by sutures Causes brain shib and compression
60 Biconvex lens shaped
61 Intracranial Hemorrhage Subdural hematoma Rapid acceleraoon or deceleraoon, shearing forces Venous bleeding, between dura mater and arachnoid mater Brain compression
62 Crescent/concave shaped
63 Intracranial Hemorrhage Subarachnoid hematoma Ruptured cerebral aneurysm Oben associated with a severe headache Brain compression, ischemia Lumbar puncture
64 Follows contours of the brain and spaces normally occupied by CSF
65 Reference pages Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6 th Ed., by Moore, Dalley, and Agur pp pp pp pp Bonus!
66 Baker et al: Head & Neck Anatomy for Dental Medicine Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions
 The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
6 Diagnosing Injuries of the Skull Base
 Flowchart Injuries of the Skull Base, Chapter 3, p. 17. Treatment of Injuries of the Skull Base, Chapter 17, p. 140. Surgical Anatomy n The bony architecture of the skull base can be divided into three
Flowchart Injuries of the Skull Base, Chapter 3, p. 17. Treatment of Injuries of the Skull Base, Chapter 17, p. 140. Surgical Anatomy n The bony architecture of the skull base can be divided into three
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
The Axial Skeleton. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Skeletal System The skeleton forms the framework for the body Provides support: Attachment
7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Skeletal System The skeleton forms the framework for the body Provides support: Attachment
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
The Skeleton. The word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up THE AXIAL SKELETON THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 PART 1 THE AXIAL SKELETON The Skull (pp. 200 216) The Skeleton The Vertebral Column (pp. 216 223) The Thoracic Cage (pp. 223 225) PART 2 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle (pp. 225
PART 1 THE AXIAL SKELETON The Skull (pp. 200 216) The Skeleton The Vertebral Column (pp. 216 223) The Thoracic Cage (pp. 223 225) PART 2 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle (pp. 225
Anatomy of Bones and Joints
 C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
24, 2006 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN:
 TITLE: Regional Anesthesia in Head and Neck Surgery SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: May 24, 2006 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Jacques Peltier, MD FACULTY ADVISOR: Francis
TITLE: Regional Anesthesia in Head and Neck Surgery SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: May 24, 2006 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Jacques Peltier, MD FACULTY ADVISOR: Francis
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face
 Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face Resident Physician: Leon Martinez, MD Faculty Mentor: Paul Brindley, MD, FACS The University of Texas Medical Branch UTMB Health Department of Otolaryngology
Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face Resident Physician: Leon Martinez, MD Faculty Mentor: Paul Brindley, MD, FACS The University of Texas Medical Branch UTMB Health Department of Otolaryngology
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Human, Male, White. Bone Clones Osteological Evaluation Report. Product Number: 1 intact mandible. General observations:
 Human, Male, White Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-107 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: In general, the molding process has preserved
Human, Male, White Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-107 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: In general, the molding process has preserved
Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
 Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sean M. Healy, D.D.S. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Francis B. Quinn, M.D., FACS Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery The University of Texas
Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sean M. Healy, D.D.S. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Francis B. Quinn, M.D., FACS Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery The University of Texas
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
Vidian Neurectomy. Dr T Balasubramanian. http://www.drtbalu.co.in
 Vidian Neurectomy Dr T Balasubramanian Introduction: Vidius in 1509 identified the vidian nerve in the floor of the sphenoid sinus while performing dissection in that area. This nerve is thought to play
Vidian Neurectomy Dr T Balasubramanian Introduction: Vidius in 1509 identified the vidian nerve in the floor of the sphenoid sinus while performing dissection in that area. This nerve is thought to play
DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE
 2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
The Human Skeleton. Bone and Bone Growth
 The Human Skeleton Bone and Bone Growth Bone is living tissue, and, as such, can grow and remodel during a person s lifetime. The three types of bone cells are the osteoblasts, which are responsible for
The Human Skeleton Bone and Bone Growth Bone is living tissue, and, as such, can grow and remodel during a person s lifetime. The three types of bone cells are the osteoblasts, which are responsible for
PE finding: Left side extremities mild weakness No traumatic wound No bloody otorrhea, nor rhinorrhea
 Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
LECTURE 16 NEUROPATHOPHYSIOLOGY (HEAD INJURY)
 LECTURE 16 Copyright 2000 by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. The approach and organization of this material was developed by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. for specific use in online instruction. All rights reserved. No part
LECTURE 16 Copyright 2000 by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. The approach and organization of this material was developed by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. for specific use in online instruction. All rights reserved. No part
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE
 HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE by Greg Doc TrojanIntroduction While motorcycling has been targeted as a public burden and garners most of the public attention concerning head injury, it is actually a minor
HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE by Greg Doc TrojanIntroduction While motorcycling has been targeted as a public burden and garners most of the public attention concerning head injury, it is actually a minor
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs
 6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs As a Maxillofacial SHO you are not required to manage established head injury, however an awareness of the process is essential when dealing with
6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs As a Maxillofacial SHO you are not required to manage established head injury, however an awareness of the process is essential when dealing with
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Normal CT scan of the chest
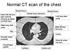 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Coverings of the Brain and Spinal Cord
 Fanny Beerepoot Our brain is a very fragile organ. It is covered by the cranial bones which protect it from external trauma. Covering the brain are also three layers of cranial meninges (membranes). You
Fanny Beerepoot Our brain is a very fragile organ. It is covered by the cranial bones which protect it from external trauma. Covering the brain are also three layers of cranial meninges (membranes). You
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
ACUTE SINUSITIS. Michael E. Prater, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 19, 1997
 ACUTE SINUSITIS Michael E. Prater, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 19, 1997 ANATOMY There are four paired paranasal sinuses, the maxillary, ethmoid,, frontal and sphenoid sinuses Anterior and posterior sinuses
ACUTE SINUSITIS Michael E. Prater, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 19, 1997 ANATOMY There are four paired paranasal sinuses, the maxillary, ethmoid,, frontal and sphenoid sinuses Anterior and posterior sinuses
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
relating to head, neck, and trunk 206 bones organized into structural framework Skeleton relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis
 Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Traumatic Head Injuries
 Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Head Injuries Major contributing cause of trauma deaths Many survivors have permanent disability Commonly occurs in young adults (mostly males) Spokane County EMS
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Head Injuries Major contributing cause of trauma deaths Many survivors have permanent disability Commonly occurs in young adults (mostly males) Spokane County EMS
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
Guidelines for the Triage and Transfer of Patients with Brain Injury to The Queen s Medical Center. April 2007. Revised September 2007
 Guidelines for the Triage and Transfer of Patients with Brain Injury to The Queen s Medical Center April 2007 Revised September 2007 Reviewed March 2012 2 The Queen s Medical Center (QMC) is the only trauma
Guidelines for the Triage and Transfer of Patients with Brain Injury to The Queen s Medical Center April 2007 Revised September 2007 Reviewed March 2012 2 The Queen s Medical Center (QMC) is the only trauma
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Types of Brain Injury
 Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
DRAFT. ICD-10 Clinical Modification Code Sets
 NOTE: The tables provided below are for reference only and should not be programmed or submitted. Table 8.1 Ischemic Stroke ICD-10 Code I6300 I63011 I63012 I63019 I6302 I63031 I63032 I63039 I6309 I6310
NOTE: The tables provided below are for reference only and should not be programmed or submitted. Table 8.1 Ischemic Stroke ICD-10 Code I6300 I63011 I63012 I63019 I6302 I63031 I63032 I63039 I6309 I6310
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
3. Blood vessels of the brain 4. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a watery fluid that is produced by and bathes the brain
 Craniosynostosis (sometimes called craniostenosis) is a disorder in which there is early fusion of the sutures of the skull in childhood. It produces an abnormally shaped head and, at times, appearance
Craniosynostosis (sometimes called craniostenosis) is a disorder in which there is early fusion of the sutures of the skull in childhood. It produces an abnormally shaped head and, at times, appearance
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Atypical Skull Base Paragangliomas
 Atypical Skull Base Paragangliomas Edward R. Noble, Wendy R. K. Smoker, and Nitya R. Ghatak Summary: We present two cases of unusually large skull base paragangliomas. The first tumor was accompanied by
Atypical Skull Base Paragangliomas Edward R. Noble, Wendy R. K. Smoker, and Nitya R. Ghatak Summary: We present two cases of unusually large skull base paragangliomas. The first tumor was accompanied by
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Level IA: Submental Group
 IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
Spread of Dental Infection
 Spread of Dental Infection The healthy body usually lives in balance with a number of resident normal flora. However, pathogens can invade and initiate an infectious process. 1 Dental infections involving
Spread of Dental Infection The healthy body usually lives in balance with a number of resident normal flora. However, pathogens can invade and initiate an infectious process. 1 Dental infections involving
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
A Fourth Hominin Skull From Dmanisi, Georgia
 THE ANATOMICAL RECORD PART A 288A:1146 1157 (2006) A Fourth Hominin Skull From Dmanisi, Georgia DAVID LORDKIPANIDZE, 1 * ABESALOM VEKUA, 1,2 REID FERRING, 3 G. PHILIP RIGHTMIRE, 4,5 CHRISTOPH P.E. ZOLLIKOFER,
THE ANATOMICAL RECORD PART A 288A:1146 1157 (2006) A Fourth Hominin Skull From Dmanisi, Georgia DAVID LORDKIPANIDZE, 1 * ABESALOM VEKUA, 1,2 REID FERRING, 3 G. PHILIP RIGHTMIRE, 4,5 CHRISTOPH P.E. ZOLLIKOFER,
Basic brain information
 Basic brain information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic brain information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Developmental Cysts. Non-odontogenic Cysts. Nasopalatine duct cyst. Palatal and gingival cysts of newborns
 Non-odontogenic Cysts Dr. Ioannis G. Koutlas Division of Oral Pathology Developmental Cysts a.k.a. fissural cysts Exact pathogenesis of some of them uncertain Generally, slow increase May be identified
Non-odontogenic Cysts Dr. Ioannis G. Koutlas Division of Oral Pathology Developmental Cysts a.k.a. fissural cysts Exact pathogenesis of some of them uncertain Generally, slow increase May be identified
Lu L m u b m a b r a rta T p a Figure 12.30
 SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Unilateral Nasal Polyps
 Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
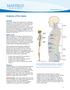 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Chapter 10. All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES
 Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink
 The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink Introduction We commonly perform nerve conduction studies on three cranial nerves. Two of these, the trigeminal nerve (CN V) and the facial nerve (CN
The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink Introduction We commonly perform nerve conduction studies on three cranial nerves. Two of these, the trigeminal nerve (CN V) and the facial nerve (CN
FERNE / EMRA 2009 Mid-Atlantic Emergency Medicine Medical Student Symposium: ABCs of Head CT Interpretation; Heather M. Prendergast MD, MPH.
 ABCs of Head CT Interpretation in the Emergency Department: CT Interpretation Workshop Guide Heather M. Prendergast, MD, MPH, FACEP Associate Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois
ABCs of Head CT Interpretation in the Emergency Department: CT Interpretation Workshop Guide Heather M. Prendergast, MD, MPH, FACEP Associate Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois
Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD
 Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD 12/13/2010 History 16 year old female with four day history of headache and acute change in mental status. History of two days of oral contraceptive use
Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD 12/13/2010 History 16 year old female with four day history of headache and acute change in mental status. History of two days of oral contraceptive use
1 )~ ~V? 1) I, \ Chapter One: Introduction. b. g._----- h. 1. _ )...lii('---:-----':----;-~.k.-- h... I l«=~.. \! a. _. a. _. e. _
 Chapter One: Introduction ANATOMICAL POSITION AND TERMS OF DIRECTION When studying the human body it is important to place the body in anatomical position. Anatomical position is described as the body
Chapter One: Introduction ANATOMICAL POSITION AND TERMS OF DIRECTION When studying the human body it is important to place the body in anatomical position. Anatomical position is described as the body
Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
IOM References. CCI Version 20.0
 Coding and Payment Guide for Anesthesia Services 00100 00100 Anesthesia for procedures on salivary glands, including biopsy The appropriate modifier indicating the type of provider (i.e., physician, CRNA)
Coding and Payment Guide for Anesthesia Services 00100 00100 Anesthesia for procedures on salivary glands, including biopsy The appropriate modifier indicating the type of provider (i.e., physician, CRNA)
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
