Timekeeping: From the Sun to the Atomic Second
|
|
|
- Eric McDowell
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Timekeeping: From the Sun to the Atomic Second Dr E Anne Curtis National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, UK Celebration of Science 17 October 2015
2 Our History I believe that in the National Physical Laboratory we have the first instance of the State taking part in scientific research. The object of the scheme is, I understand, to bring scientific knowledge to bear practically on our everyday industrial and commercial life; to break down the barrier between theory and practice; to effect a union between science and commerce. - HRH the Prince of Wales 1902
3 The UK s National Measurement Institute World-leading NMI 700+ staff 500+ scientists BIS s largest science and technology asset (a government laboratory) In partnership with the universities of Strathclyde and Surrey 400 laboratories, state of the art facilities
4 Metrology SI base units: electrical quantity thermodynamic temperature length time luminous intensity mass amount of substance How did we get from the sun to the atomic second? The second is the duration of periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium 133 atom
5 Overview Historical overview of timekeeping what drives our need for clocks the technology of metrology Current state-of-the art how to make an atomic clock what do we need it for today
6 Stability - averaging data can give a more precise result Systematics - understanding the offset Accuracy vs Precision Increasing precision Increasing accuracy Inaccurate Imprecise Inaccurate Precise Accurate Imprecise Accurate Precise For clocks: accuracy getting to work on time stability/precision measuring heart beat reproducibility do you trust your clock? Reproducibility - same results?
7 What is a clock? Oscillator something periodic - repeating (pendulum, electromagnetic radiation) Counter something that can measure the oscillations rf counter Reference for accuracy and reproducibility from place to place (how do you check your clock is still on time?)
8 Two questions: Local solar time Measuring Time Why do people need to know what time it is? How do these needs change over time? based on the motion of the sun across the sky Egyptian obelisks (3500 BC), portable shadow clocks (1500 BC) Systematics: changes throughout the year overcast days ~12 hours a day without a clock! Oscillator Counter Reference
9 Measuring Time Water clocks Among the first timekeepers that didn t depend on the motion of celestial bodies Simple Egyptian clocks (1500 BC), more elaborate Greek & Roman clocks (100 BC to 500 AD) Inflow and outflow types Invented to measure time at night timing of the night watch night time religious ceremonies also used to time debate in court portable version to measure pulse rate Systematics: sloping sides only give near constant drip/flow temperature and humidity affect flow rate evaporation Calibrate with sundial
10 Measuring Time Egyptian Waterclocks Innovations: markers to measure the passing of time gears to enable mechanical readout mechanism Elaborate Su Song Chinese Waterclock (1088 AD)
11 Measuring Time Pendulum Clocks Concept credited to Galileo (1582) First clock constructed by Huygens (1656) Systematics: Period of a pendulum (small oscillation amplitude) l T~2p g l = length of pendulum g = acceleration due to gravity change in temperature/humidity (length of pendulum) change in air pressure (friction on pendulum) To compensate temperature changes: mercury pendulums (1721) maintains centre of mass bimetal construction (1726) compensates length change Error to less than 10 seconds / day
12 What is the longitude problem? Latitude is measured by the sun s angle at noon Easy to measure local time by the sun, but to find your horizontal position (longitude) you need to know the time at a known reference point Measuring Time Navigation in the 17 th century Founding of the Royal Observatory by King Charles II in 1675 Purpose to solve the problem of longitude at sea Earth circumference 360 o 24 hour day 15 o = 1 hour Pendulum clocks were accurate enough on land, but problematic at sea Large variation in humidity and temperature Rocking of the ship (storms) Corrosion from the sea air
13 Longitude Act of 1714 Measuring Time 20,000 prize for measuring longitude to 0.5 (> 2 million) error of 35 miles at equator equivalent to an accuracy of 3 seconds per day But how accurate are your seconds? Prize won by John Harrison Sea-going clock H4 accurate to 0.2 seconds / day ~30 km over the 7-week trip
14 Measuring Time Greenwich Mean Time Noon is not the same as the sun being directly overhead (±15 min over year) Instead use mean annual average of the non-uniform motion of the real sun 1 second = 1 / of the mean solar day Established as the global standard in 1884 Any standard based on the rotation of the earth was going to run into problems, as measurement technology and timing needs became more sophisticated.
15 Milliseconds seconds Variation in the earth s rotation What causes changes in earth s rotation? Conservation of angular momentum weather patterns, tidal patterns changes in mass distribution of the earth (fluid core, earthquakes) moon and earth getting farther apart The difference between Earth rotational time (UT1) and the mean solar day. Variability of Earth s Rotation Length of Day seconds Calendar year Need a better reference than the earth
16 The introduction of atomic time 1955: First caesium atomic clock produced by Essen & Parry at NPL, accurate to 1 part in : International Atomic Time (TAI) began, following the development of further caesium clocks at NBS (USA) and ON (Switzerland) Reproducibility 1967: Caesium clock adopted as the basis for the international definition of time The second is the duration of periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium-133 atom. 1 part in is ~1 second error in 300 years compared to 0.2 s per day, (a few parts in 10 6 ) for the Harrison clock 1972: GMT was replaced as the international time reference by Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) maintained by an ensemble of atomic clocks around the world (40 countries, ~260 clocks) Leap seconds keep UTC and earth rotational time consistent
17 Mircowave atomic standards today Caesium fountain clock Accuracy ~ (with several days averaging time) error of 1s in 3 billion years. How do atoms take us from errors of second/day to second/billion years?
18 visible/optical Energy Atoms as references for clocks Quantum Mechanics - quantized energy levels excited UV/X-ray frequency (f) Energy (E) The atomic clock counter measures radiation ground oscillator produces radiation radio/ir feedback atomic signal to oscillator precision of the atomic reference atoms are identical reproducibility atomic reference
19 What is driving modern day clock development? Navigation - GPS + satellite control - missile guidance systems - deep space missions Synchronisation - very long base-line interferometry and arrays (radio telescopes) - global economy Standards - economic and public needs
20 Global Navigation Satellite Systems Image courtesy of ESA 1. How does satellite navigation work? 2. What do clocks have to do with any of this? Proposed constellation of Galileo satellites in space
21 Time of Arrival (TOA) Ranging Foghorn example Dx Dx 3 Dx 2 speed of sound v ~ 335 m/s v= Dx Dt (meters) (seconds) Dx = v Dt
22 Time of Arrival (TOA) Ranging timing error Foghorn example e Dx Dx 2 e timing offset = 1 s speed of sound ~ 335 m/s e = v t offset e = 335 m error! Dx 3 e Timing errors reduce the accuracy of the position measurement
23 Satellite Navigation Dx = v Dt Dx Satellite Receiver speed of sound v ~ 335 m/s speed of electromagnetic radiation v ~ m/s for e ~ 0.3 m (1 ft), nanosecond timing is necessary
24 What s next? Clocks keep getting better and better - optical clocks would not lose 1 second in the lifetime of the universe Earth-based clocks start to run into problems - gravitational redshift (frequency of clock changes depending on its distance from the geoid) - atmospheric effects (communicating from satellites to earth) Solution? Put your optical clocks in space!
25 Optical master clock in space Necessary for intercomparison of ground-based optical clocks Fundamental physics Tests of general relativity, e.g. STE-QUEST mission Geoscience Direct measurement of earth s geopotential with high resolution Tracking tectonic plate movement Navigation Upgrade of GPS/Galileo to optical clocks VLBI Very Long Baseline interferometry (LISA gravity wave detection) VLA Very Large (telescope) Arrays (Radio astronomy timing) Deep space missions Communications Space-based optical clocks What has history shown us? The better the clock, the longer the list
26 Title of Presentation Name of Speaker Date The National Measurement System delivers world-class measurement science & technology through these organisations NPL Open House 17 May pm - 8pm The National Measurement System is the UK s national infrastructure of measurement Laboratories, which deliver world-class measurement science and technology through four National Measurement Institutes (NMIs): LGC, NPL the National Physical Laboratory, TUV NEL The former National Engineering Laboratory, and the National Measurement Office (NMO).
27 SI-bot. The Movie. Are you, or do you know a budding young film maker? Or perhaps you're keen to share your science know-how? NPL's SI-bot movie challenge could win you a tour of our facilities and a cash prize of 500.Register now to take part and to receive your free SI-bot! Here at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL), to celebrate what we do, we have created a range of SI-bot figures, each one representing a different unit of measurement. The second SI-bot represents all things related to time. The challenge is to make a film about time, less than one-minute long, using the second SI-bot. To receive your SI-bot, follow the link to register and let us know where you would like it sent. Two lucky winners will receive cash prizes ( 500) to further their film-making experience. In addition, the creator(s) of the best overall film will be given a personal tour of NPL with their friends or family. Details and registration link at
28 1 second 1 1 minute 60 1hour day month year years 3.15E years 3.15E years 3.15E+10 1 million years 3.15E million years 3.15E million years 3.15E+13 1 billion years 3.15E billion years 3.15E+15
Local Sidereal Time is the hour angle of the First Point of Aries, and is equal to the hour angle plus right ascension of any star.
 1 CHAPTER 7 TIME In this chapter we briefly discuss the several time scales that are in use in astronomy, such as Universal Time, Mean Solar Time, Ephemeris Time, Terrestrial Dynamical Time, and the several
1 CHAPTER 7 TIME In this chapter we briefly discuss the several time scales that are in use in astronomy, such as Universal Time, Mean Solar Time, Ephemeris Time, Terrestrial Dynamical Time, and the several
Best Practices for Leap Second Event Occurring on 30 June 2015
 Best Practices for Leap Second Event Occurring on 30 June 2015 26 May 2015 Sponsored by the National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center in coordination with the United States Naval Observatory,
Best Practices for Leap Second Event Occurring on 30 June 2015 26 May 2015 Sponsored by the National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center in coordination with the United States Naval Observatory,
Earth In Space Chapter 3
 Earth In Space Chapter 3 Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Earth casts a circular shadow on the moon during a lunar eclipse Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Ships were observed to disappear below the
Earth In Space Chapter 3 Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Earth casts a circular shadow on the moon during a lunar eclipse Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Ships were observed to disappear below the
Newton s Law of Gravity
 Gravitational Potential Energy On Earth, depends on: object s mass (m) strength of gravity (g) distance object could potentially fall Gravitational Potential Energy In space, an object or gas cloud has
Gravitational Potential Energy On Earth, depends on: object s mass (m) strength of gravity (g) distance object could potentially fall Gravitational Potential Energy In space, an object or gas cloud has
EDMONDS COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASTRONOMY 100 Winter Quarter 2007 Sample Test # 1
 Instructor: L. M. Khandro EDMONDS COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASTRONOMY 100 Winter Quarter 2007 Sample Test # 1 1. An arc second is a measure of a. time interval between oscillations of a standard clock b. time
Instructor: L. M. Khandro EDMONDS COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASTRONOMY 100 Winter Quarter 2007 Sample Test # 1 1. An arc second is a measure of a. time interval between oscillations of a standard clock b. time
An Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology. 1) Astronomy - an Observational Science
 An Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology 1) Astronomy - an Observational Science Why study Astronomy 1 A fascinating subject in its own right. The origin and Evolution of the universe The Big Bang formation
An Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology 1) Astronomy - an Observational Science Why study Astronomy 1 A fascinating subject in its own right. The origin and Evolution of the universe The Big Bang formation
Distributed Systems Theory 6. Clock synchronization - logical vs. physical clocks. November 9, 2009
 Distributed Systems Theory 6. Clock synchronization - logical vs. physical clocks November 9, 2009 1 Synchronization: single CPU sys vs. dist sys. Single CPU: DS: critical regions, mutual exclusion, and
Distributed Systems Theory 6. Clock synchronization - logical vs. physical clocks November 9, 2009 1 Synchronization: single CPU sys vs. dist sys. Single CPU: DS: critical regions, mutual exclusion, and
California Standards Grades 9 12 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping
 California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
The history of time and frequency from antiquity to the present day
 Eur. Phys. J. H DOI: 10.1140/epjh/e2016-70004-3 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL H The history of time and frequency from antiquity to the present day Judah Levine a Time and Frequency Division and JILA,
Eur. Phys. J. H DOI: 10.1140/epjh/e2016-70004-3 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL H The history of time and frequency from antiquity to the present day Judah Levine a Time and Frequency Division and JILA,
PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY THE DYNAMIC UNIVERSE TOWARD A UNIFIED PICTURE OF PHYSICAL REALITY TUOMO SUNTOLA
 PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY THE DYNAMIC UNIVERSE TOWARD A UNIFIED PICTURE OF PHYSICAL REALITY TUOMO SUNTOLA Published by PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY Espoo, Finland www.physicsfoundations.org Printed by
PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY THE DYNAMIC UNIVERSE TOWARD A UNIFIED PICTURE OF PHYSICAL REALITY TUOMO SUNTOLA Published by PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY Espoo, Finland www.physicsfoundations.org Printed by
CHAPTER 18 TIME TIME IN NAVIGATION
 CHAPTER 18 TIME TIME IN NAVIGATION 1800. Solar Time The Earth s rotation on its axis causes the Sun and other celestial bodies to appear to move across the sky from east to west each day. If a person located
CHAPTER 18 TIME TIME IN NAVIGATION 1800. Solar Time The Earth s rotation on its axis causes the Sun and other celestial bodies to appear to move across the sky from east to west each day. If a person located
The Celestial Sphere. Questions for Today. The Celestial Sphere 1/18/10
 Lecture 3: Constellations and the Distances to the Stars Astro 2010 Prof. Tom Megeath Questions for Today How do the stars move in the sky? What causes the phases of the moon? What causes the seasons?
Lecture 3: Constellations and the Distances to the Stars Astro 2010 Prof. Tom Megeath Questions for Today How do the stars move in the sky? What causes the phases of the moon? What causes the seasons?
Solar System. 1. The diagram below represents a simple geocentric model. Which object is represented by the letter X?
 Solar System 1. The diagram below represents a simple geocentric model. Which object is represented by the letter X? A) Earth B) Sun C) Moon D) Polaris 2. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered
Solar System 1. The diagram below represents a simple geocentric model. Which object is represented by the letter X? A) Earth B) Sun C) Moon D) Polaris 2. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered
Night Sky III Planetary Motion Lunar Phases
 Night Sky III Planetary Motion Lunar Phases Astronomy 1 Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 Quotes & Cartoon of the Day Everything has a natural explanation. The moon is not a god, but
Night Sky III Planetary Motion Lunar Phases Astronomy 1 Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 Quotes & Cartoon of the Day Everything has a natural explanation. The moon is not a god, but
A long time ago, people looked
 Supercool Space Tools! By Linda Hermans-Killam A long time ago, people looked into the dark night sky and wondered about the stars, meteors, comets and planets they saw. The only tools they had to study
Supercool Space Tools! By Linda Hermans-Killam A long time ago, people looked into the dark night sky and wondered about the stars, meteors, comets and planets they saw. The only tools they had to study
Exploration of the Solar System
 Exploration of the Solar System I. Phases of the Moon all about perspective. In this section you will use WWT to explore how the moon appears to change phases from our vantage point on Earth over the course
Exploration of the Solar System I. Phases of the Moon all about perspective. In this section you will use WWT to explore how the moon appears to change phases from our vantage point on Earth over the course
CPO Science and the NGSS
 CPO Science and the NGSS It is no coincidence that the performance expectations in the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are all action-based. The NGSS champion the idea that science content cannot
CPO Science and the NGSS It is no coincidence that the performance expectations in the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are all action-based. The NGSS champion the idea that science content cannot
CHAPTER 2 Energy and Earth
 CHAPTER 2 Energy and Earth This chapter is concerned with the nature of energy and how it interacts with Earth. At this stage we are looking at energy in an abstract form though relate it to how it affect
CHAPTER 2 Energy and Earth This chapter is concerned with the nature of energy and how it interacts with Earth. At this stage we are looking at energy in an abstract form though relate it to how it affect
Astronomy 110 Homework #04 Assigned: 02/06/2007 Due: 02/13/2007. Name:
 Astronomy 110 Homework #04 Assigned: 02/06/2007 Due: 02/13/2007 Name: Directions: Listed below are twenty (20) multiple-choice questions based on the material covered by the lectures this past week. Choose
Astronomy 110 Homework #04 Assigned: 02/06/2007 Due: 02/13/2007 Name: Directions: Listed below are twenty (20) multiple-choice questions based on the material covered by the lectures this past week. Choose
The Moon. Nicola Loaring, SAAO
 The Moon Nicola Loaring, SAAO Vital Statistics Mean distance from Earth Orbital Period Rotational Period Diameter 384,400 km 27.322 days 27.322 days 3476 km (0.272 x Earth) Mass 7.3477 10 22 kg (0.0123
The Moon Nicola Loaring, SAAO Vital Statistics Mean distance from Earth Orbital Period Rotational Period Diameter 384,400 km 27.322 days 27.322 days 3476 km (0.272 x Earth) Mass 7.3477 10 22 kg (0.0123
compass Encyclopedic Entry
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations
 Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Our Solar System is a collection of gravitationally interacting bodies that include Earth and the Moon. Universal
Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Our Solar System is a collection of gravitationally interacting bodies that include Earth and the Moon. Universal
CELESTIAL MOTIONS. In Charlottesville we see Polaris 38 0 above the Northern horizon. Earth. Starry Vault
 CELESTIAL MOTIONS Stars appear to move counterclockwise on the surface of a huge sphere the Starry Vault, in their daily motions about Earth Polaris remains stationary. In Charlottesville we see Polaris
CELESTIAL MOTIONS Stars appear to move counterclockwise on the surface of a huge sphere the Starry Vault, in their daily motions about Earth Polaris remains stationary. In Charlottesville we see Polaris
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Science Grade 6. Unit Organizer: UNIVERSE AND SOLAR SYSTEM (Approximate Time 3 Weeks)
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were increased,
1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were increased,
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Correlation to. EarthComm, Second Edition. Project-Based Space and Earth System Science
 The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Achieve, Inc. on behalf of the twenty-six states and partners that collaborated on the NGSS Copyright 2013 Achieve, Inc. All rights reserved. Correlation to,
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Achieve, Inc. on behalf of the twenty-six states and partners that collaborated on the NGSS Copyright 2013 Achieve, Inc. All rights reserved. Correlation to,
Activity 10 - Universal Time
 Activity 10 - Universal Time Teacher s Guide Scientists use the Universal Time reference to talk about data that is taken around the globe. Universal Time is the time kept in the time zone centered on
Activity 10 - Universal Time Teacher s Guide Scientists use the Universal Time reference to talk about data that is taken around the globe. Universal Time is the time kept in the time zone centered on
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery. How does your eye form an image? Refraction. Example: Refraction at Sunset.
 Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors Our goals for learning:! How does your eye form an image?! How do we record images? How does your eye form an image?
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors Our goals for learning:! How does your eye form an image?! How do we record images? How does your eye form an image?
Today. Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses. Ancient Astronomy. Lunar, Solar FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME
 Today Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME The Reason for Seasons Hypothesis check: How would seasons in the northern
Today Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME The Reason for Seasons Hypothesis check: How would seasons in the northern
Examination Space Missions and Applications I (AE2103) Faculty of Aerospace Engineering Delft University of Technology SAMPLE EXAM
 Examination Space Missions and Applications I AE2103 Faculty of Aerospace Engineering Delft University of Technology SAMPLE EXAM Please read these instructions first: This are a series of multiple-choice
Examination Space Missions and Applications I AE2103 Faculty of Aerospace Engineering Delft University of Technology SAMPLE EXAM Please read these instructions first: This are a series of multiple-choice
CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS
 INTRODUCTION CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS This is a scientific presentation to provide you with knowledge you can use to understand the sky above in relation to the earth. Before
INTRODUCTION CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS This is a scientific presentation to provide you with knowledge you can use to understand the sky above in relation to the earth. Before
Smart Science Lessons and Middle School Next Generation Science Standards
 Smart Science Lessons and Middle School Next Generation Science Standards You have chosen the right place to find great science learning and, beyond learning, how to think. The NGSS emphasize thinking
Smart Science Lessons and Middle School Next Generation Science Standards You have chosen the right place to find great science learning and, beyond learning, how to think. The NGSS emphasize thinking
Oscillations: Mass on a Spring and Pendulums
 Chapter 3 Oscillations: Mass on a Spring and Pendulums 3.1 Purpose 3.2 Introduction Galileo is said to have been sitting in church watching the large chandelier swinging to and fro when he decided that
Chapter 3 Oscillations: Mass on a Spring and Pendulums 3.1 Purpose 3.2 Introduction Galileo is said to have been sitting in church watching the large chandelier swinging to and fro when he decided that
Celestial Sphere. Celestial Coordinates. Lecture 3: Motions of the Sun and Moon. ecliptic (path of Sun) ecliptic (path of Sun)
 Lecture 3: Motions of the and Moon ecliptic (path of ) ecliptic (path of ) The 23.5 degree tilt of Earth s spin axis relative to its orbital axis around the causes the seasons Celestial Sphere Celestial
Lecture 3: Motions of the and Moon ecliptic (path of ) ecliptic (path of ) The 23.5 degree tilt of Earth s spin axis relative to its orbital axis around the causes the seasons Celestial Sphere Celestial
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due in class Tuesday, Jan. 20, 2015
 Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due in class Tuesday, Jan. 20, 2015 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due in class Tuesday, Jan. 20, 2015 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around
What causes Tides? If tidal forces were based only on mass, the Sun should have a tidegenerating
 What are Tides? Tides are very long-period waves that move through the oceans as a result of the gravitational attraction of the Moon and the Sun for the water in the oceans of the Earth. Tides start in
What are Tides? Tides are very long-period waves that move through the oceans as a result of the gravitational attraction of the Moon and the Sun for the water in the oceans of the Earth. Tides start in
Thursday 23 May 2013 Morning
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Thursday 23 May 2013 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE PHYSICS A A181/02 Modules P1 P2 P3 (Higher Tier) *A137270613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A calculator
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Thursday 23 May 2013 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE PHYSICS A A181/02 Modules P1 P2 P3 (Higher Tier) *A137270613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A calculator
TI GPS PPS Timing Application Note
 Application Note Version 0.6 January 2012 1 Contents Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 2 1PPS CHARACTERISTICS... 3 3 TEST SETUP... 4 4 PPS TEST RESULTS... 6 Figures Figure 1 - Simplified GPS Receiver
Application Note Version 0.6 January 2012 1 Contents Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 2 1PPS CHARACTERISTICS... 3 3 TEST SETUP... 4 4 PPS TEST RESULTS... 6 Figures Figure 1 - Simplified GPS Receiver
Essential Question. Enduring Understanding
 Earth In Space Unit Diagnostic Assessment: Students complete a questionnaire answering questions about their ideas concerning a day, year, the seasons and moon phases: My Ideas About A Day, Year, Seasons
Earth In Space Unit Diagnostic Assessment: Students complete a questionnaire answering questions about their ideas concerning a day, year, the seasons and moon phases: My Ideas About A Day, Year, Seasons
Curriculum Map Earth Science - High School
 September Science is a format process to use Use instruments to measure Measurement labs - mass, volume, to observe, classify, and analyze the observable properties. density environment. Use lab equipment
September Science is a format process to use Use instruments to measure Measurement labs - mass, volume, to observe, classify, and analyze the observable properties. density environment. Use lab equipment
Motion & The Global Positioning System (GPS)
 Grade Level: K - 8 Subject: Motion Prep Time: < 10 minutes Duration: 30 minutes Objective: To learn how to analyze GPS data in order to track an object and derive its velocity from positions and times.
Grade Level: K - 8 Subject: Motion Prep Time: < 10 minutes Duration: 30 minutes Objective: To learn how to analyze GPS data in order to track an object and derive its velocity from positions and times.
Günter Seeber. Satellite Geodesy 2nd completely revised and extended edition
 Günter Seeber Satellite Geodesy 2nd completely revised and extended edition Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York 2003 Contents Preface Abbreviations vii xvii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Subject of Satellite Geodesy...
Günter Seeber Satellite Geodesy 2nd completely revised and extended edition Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York 2003 Contents Preface Abbreviations vii xvii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Subject of Satellite Geodesy...
Exam # 1 Thu 10/06/2010 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti
 Exam # 1 Thu 10/06/2010 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
Exam # 1 Thu 10/06/2010 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
2. Orbits. FER-Zagreb, Satellite communication systems 2011/12
 2. Orbits Topics Orbit types Kepler and Newton laws Coverage area Influence of Earth 1 Orbit types According to inclination angle Equatorial Polar Inclinational orbit According to shape Circular orbit
2. Orbits Topics Orbit types Kepler and Newton laws Coverage area Influence of Earth 1 Orbit types According to inclination angle Equatorial Polar Inclinational orbit According to shape Circular orbit
Practice Test SHM with Answers
 Practice Test SHM with Answers MPC 1) If we double the frequency of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion, which of the following statements about that system are true? (There could be more than one
Practice Test SHM with Answers MPC 1) If we double the frequency of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion, which of the following statements about that system are true? (There could be more than one
PHYS 1624 University Physics I. PHYS 2644 University Physics II
 PHYS 1624 Physics I An introduction to mechanics, heat, and wave motion. This is a calculus- based course for Scientists and Engineers. 4 hours (3 lecture/3 lab) Prerequisites: Credit for MATH 2413 (Calculus
PHYS 1624 Physics I An introduction to mechanics, heat, and wave motion. This is a calculus- based course for Scientists and Engineers. 4 hours (3 lecture/3 lab) Prerequisites: Credit for MATH 2413 (Calculus
EXPERIMENT 2 Measurement of g: Use of a simple pendulum
 EXPERIMENT 2 Measurement of g: Use of a simple pendulum OBJECTIVE: To measure the acceleration due to gravity using a simple pendulum. Textbook reference: pp10-15 INTRODUCTION: Many things in nature wiggle
EXPERIMENT 2 Measurement of g: Use of a simple pendulum OBJECTIVE: To measure the acceleration due to gravity using a simple pendulum. Textbook reference: pp10-15 INTRODUCTION: Many things in nature wiggle
Grade Level Expectations for the Sunshine State Standards
 for the Sunshine State Standards FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION http://www.myfloridaeducation.com/ The seventh grade student: The Nature of Matter uses a variety of measurements to describe the physical
for the Sunshine State Standards FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION http://www.myfloridaeducation.com/ The seventh grade student: The Nature of Matter uses a variety of measurements to describe the physical
Douglas Adams The Hitchhikers Guide to the Galaxy
 There is a theory which states that if ever anybody discovers exactly what the Universe is for and why it is here, it will instantly disappear and be replaced by something even more bizarre and inexplicable.
There is a theory which states that if ever anybody discovers exactly what the Universe is for and why it is here, it will instantly disappear and be replaced by something even more bizarre and inexplicable.
Mission To Mars! A dialogue activity for upper KS2
 Mission To Mars! A dialogue activity for upper KS2 Teacher s Sheet Mission to Mars: Dialogue activity for upper KS2 Part One: As a class or in groups. pupils read the Fact or Fiction cards. On each card
Mission To Mars! A dialogue activity for upper KS2 Teacher s Sheet Mission to Mars: Dialogue activity for upper KS2 Part One: As a class or in groups. pupils read the Fact or Fiction cards. On each card
AS COMPETITION PAPER 2008
 AS COMPETITION PAPER 28 Name School Town & County Total Mark/5 Time Allowed: One hour Attempt as many questions as you can. Write your answers on this question paper. Marks allocated for each question
AS COMPETITION PAPER 28 Name School Town & County Total Mark/5 Time Allowed: One hour Attempt as many questions as you can. Write your answers on this question paper. Marks allocated for each question
Physics 9e/Cutnell. correlated to the. College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives
 Physics 9e/Cutnell correlated to the College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring
Physics 9e/Cutnell correlated to the College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring
TIDES. 1. Tides are the regular rise and fall of sea level that occurs either once a day (every 24.8 hours) or twice a day (every 12.4 hours).
 TIDES What causes tides? How are tides predicted? 1. Tides are the regular rise and fall of sea level that occurs either once a day (every 24.8 hours) or twice a day (every 12.4 hours). Tides are waves
TIDES What causes tides? How are tides predicted? 1. Tides are the regular rise and fall of sea level that occurs either once a day (every 24.8 hours) or twice a day (every 12.4 hours). Tides are waves
Computer Time Synchronization
 Michael Lombardi Time and Frequency Division National Institute of Standards and Technology Computer Time Synchronization The personal computer revolution that began in the 1970's created a huge new group
Michael Lombardi Time and Frequency Division National Institute of Standards and Technology Computer Time Synchronization The personal computer revolution that began in the 1970's created a huge new group
Sample Questions for the AP Physics 1 Exam
 Sample Questions for the AP Physics 1 Exam Sample Questions for the AP Physics 1 Exam Multiple-choice Questions Note: To simplify calculations, you may use g 5 10 m/s 2 in all problems. Directions: Each
Sample Questions for the AP Physics 1 Exam Sample Questions for the AP Physics 1 Exam Multiple-choice Questions Note: To simplify calculations, you may use g 5 10 m/s 2 in all problems. Directions: Each
Neutron Stars. How were neutron stars discovered? The first neutron star was discovered by 24-year-old graduate student Jocelyn Bell in 1967.
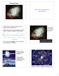 Neutron Stars How were neutron stars discovered? The first neutron star was discovered by 24-year-old graduate student Jocelyn Bell in 1967. Using a radio telescope she noticed regular pulses of radio
Neutron Stars How were neutron stars discovered? The first neutron star was discovered by 24-year-old graduate student Jocelyn Bell in 1967. Using a radio telescope she noticed regular pulses of radio
1. Large ships are often helped into port by using two tug boats one either side of the ship. April 5, 1989 (Anchorage Daily News / Erik Hill)
 1. Velocity and displacement vectors and scalars Vector and scalar quantities: force, speed, velocity, distance, displacement, acceleration, mass, time and energy. Calculation of the resultant of two vector
1. Velocity and displacement vectors and scalars Vector and scalar quantities: force, speed, velocity, distance, displacement, acceleration, mass, time and energy. Calculation of the resultant of two vector
Interaction of Energy and Matter Gravity Measurement: Using Doppler Shifts to Measure Mass Concentration TEACHER GUIDE
 Interaction of Energy and Matter Gravity Measurement: Using Doppler Shifts to Measure Mass Concentration TEACHER GUIDE EMR and the Dawn Mission Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) will play a major role in
Interaction of Energy and Matter Gravity Measurement: Using Doppler Shifts to Measure Mass Concentration TEACHER GUIDE EMR and the Dawn Mission Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) will play a major role in
Scale of the Solar System. Sizes and Distances: How Big is Big? Sizes and Distances: How Big is Big? (Cont.)
 Scale of the Solar System Scale of the Universe How big is Earth compared to our solar system? How far away are the stars? How big is the Milky Way Galaxy? How big is the Universe? How do our lifetimes
Scale of the Solar System Scale of the Universe How big is Earth compared to our solar system? How far away are the stars? How big is the Milky Way Galaxy? How big is the Universe? How do our lifetimes
PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AND UNITS
 1 PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AND UNITS Introduction Physics is the study of matter, its motion and the interaction between matter. Physics involves analysis of physical quantities, the interaction between them
1 PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AND UNITS Introduction Physics is the study of matter, its motion and the interaction between matter. Physics involves analysis of physical quantities, the interaction between them
Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond
 Stellarium 1 Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond Stephen Hughes Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Gardens
Stellarium 1 Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond Stephen Hughes Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Gardens
Grade 6 Standard 3 Unit Test A Astronomy. 1. The four inner planets are rocky and small. Which description best fits the next four outer planets?
 Grade 6 Standard 3 Unit Test A Astronomy Multiple Choice 1. The four inner planets are rocky and small. Which description best fits the next four outer planets? A. They are also rocky and small. B. They
Grade 6 Standard 3 Unit Test A Astronomy Multiple Choice 1. The four inner planets are rocky and small. Which description best fits the next four outer planets? A. They are also rocky and small. B. They
Review 1. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei a. the nuclei die. c. particles collide. b. energy
Review 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei a. the nuclei die. c. particles collide. b. energy
Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies
 Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies Dette er en oversettelse av den fastsatte læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsatt på Bokmål Laid down as a regulation
Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies Dette er en oversettelse av den fastsatte læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsatt på Bokmål Laid down as a regulation
Science Focus 9 Space Exploration Topic Test
 SPACE EXPLORATION UNIT TEST ASSESSMENT Student Name Class 1. The axis for the frame of reference to identify locations on the earth are A. Equinox and Solstice B. Ecuador and Madagascar C. Equator and
SPACE EXPLORATION UNIT TEST ASSESSMENT Student Name Class 1. The axis for the frame of reference to identify locations on the earth are A. Equinox and Solstice B. Ecuador and Madagascar C. Equator and
Beginning of the Universe Classwork 6 th Grade PSI Science
 Beginning of the Universe Classwork Name: 6 th Grade PSI Science 1 4 2 5 6 3 7 Down: 1. Edwin discovered that galaxies are spreading apart. 2. This theory explains how the Universe was flattened. 3. All
Beginning of the Universe Classwork Name: 6 th Grade PSI Science 1 4 2 5 6 3 7 Down: 1. Edwin discovered that galaxies are spreading apart. 2. This theory explains how the Universe was flattened. 3. All
Activity 1 Reading Universal Time Level 2 http://www.uni.edu/storm/activities/level2/index.shtml
 Activity 1 Reading Universal Time Level 2 http://www.uni.edu/storm/activities/level2/index.shtml National Science Education Standards: As a result of activities in grades 5-8, all students should develop
Activity 1 Reading Universal Time Level 2 http://www.uni.edu/storm/activities/level2/index.shtml National Science Education Standards: As a result of activities in grades 5-8, all students should develop
Making A Sundial. Key Words gnomon sundial
 Solar Matters II Teacher Page Making A Sundial Student Objectives: The student will: design, construct and demonstrate the use of a gnomon by constructing a sundial track the movement of a shadow cast
Solar Matters II Teacher Page Making A Sundial Student Objectives: The student will: design, construct and demonstrate the use of a gnomon by constructing a sundial track the movement of a shadow cast
The Solar System. Unit 4 covers the following framework standards: ES 10 and PS 11. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 4 The Solar System Chapter 7 ~ The History of the Solar System o Section 1 ~ The Formation of the Solar System o Section 2 ~ Observing the Solar System Chapter 8 ~ The Parts the Solar System o Section
Unit 4 The Solar System Chapter 7 ~ The History of the Solar System o Section 1 ~ The Formation of the Solar System o Section 2 ~ Observing the Solar System Chapter 8 ~ The Parts the Solar System o Section
1Physical quantities and units
 1Physical quantities and units By the end of this chapter you should be able to: explain what is meant by a in physics; state the five fundamental quantities recognised and used in physics; explain the
1Physical quantities and units By the end of this chapter you should be able to: explain what is meant by a in physics; state the five fundamental quantities recognised and used in physics; explain the
Robot Perception Continued
 Robot Perception Continued 1 Visual Perception Visual Odometry Reconstruction Recognition CS 685 11 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart
Robot Perception Continued 1 Visual Perception Visual Odometry Reconstruction Recognition CS 685 11 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart
Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System
 Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System Objectives: Compare & Contrast geocentric and heliocentric models of the solar sytem. Describe the orbits of planets explain how gravity and inertia keep the planets
Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System Objectives: Compare & Contrast geocentric and heliocentric models of the solar sytem. Describe the orbits of planets explain how gravity and inertia keep the planets
Math 215 Project (25 pts) : Using Linear Algebra to solve GPS problem
 Due Thursday March 1, 2012 NAME(S): Math 215 Project (25 pts) : Using Linear Algebra to solve GPS problem 0.1 Introduction The age old question, Where in the world am I? can easily be solved nowadays by
Due Thursday March 1, 2012 NAME(S): Math 215 Project (25 pts) : Using Linear Algebra to solve GPS problem 0.1 Introduction The age old question, Where in the world am I? can easily be solved nowadays by
PENDULUM PERIODS. First Last. Partners: student1, student2, and student3
 PENDULUM PERIODS First Last Partners: student1, student2, and student3 Governor s School for Science and Technology 520 Butler Farm Road, Hampton, VA 23666 April 13, 2011 ABSTRACT The effect of amplitude,
PENDULUM PERIODS First Last Partners: student1, student2, and student3 Governor s School for Science and Technology 520 Butler Farm Road, Hampton, VA 23666 April 13, 2011 ABSTRACT The effect of amplitude,
Solar Tracking Application
 Solar Tracking Application A Rockwell Automation White Paper Solar trackers are devices used to orient photovoltaic panels, reflectors, lenses or other optical devices toward the sun. Since the sun s position
Solar Tracking Application A Rockwell Automation White Paper Solar trackers are devices used to orient photovoltaic panels, reflectors, lenses or other optical devices toward the sun. Since the sun s position
barometer 1 of 5 For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit: http://education.nationalgeographic.com/encyclopedia/barometer/
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry For the complete
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry For the complete
Scope and Sequence Interactive Science grades 6-8
 Science and Technology Chapter 1. What Is Science? 1. Science and the Natural World 2.Thinking Like a Scientist 3. Scientific Inquiry Scope and Sequence Interactive Science grades 6-8 Chapter 2. Science,
Science and Technology Chapter 1. What Is Science? 1. Science and the Natural World 2.Thinking Like a Scientist 3. Scientific Inquiry Scope and Sequence Interactive Science grades 6-8 Chapter 2. Science,
Motions of the Earth. Stuff everyone should know
 Motions of the Earth Stuff everyone should know Earth Motions E W N W Noon E Why is there day and night? OR Why do the Sun and stars appear to move through the sky? Because the Earth rotates around its
Motions of the Earth Stuff everyone should know Earth Motions E W N W Noon E Why is there day and night? OR Why do the Sun and stars appear to move through the sky? Because the Earth rotates around its
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 1 Review
 Astronomy 1140 Quiz 1 Review Prof. Pradhan September 15, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. (a) Astrology: nonscience using zodiac sign to predict the future/personality
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 1 Review Prof. Pradhan September 15, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. (a) Astrology: nonscience using zodiac sign to predict the future/personality
Post Processing Service
 Post Processing Service The delay of propagation of the signal due to the ionosphere is the main source of generation of positioning errors. This problem can be bypassed using a dual-frequency receivers
Post Processing Service The delay of propagation of the signal due to the ionosphere is the main source of generation of positioning errors. This problem can be bypassed using a dual-frequency receivers
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision
 The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision Roeland van der Marel (STScI) [based on work with a team of collaborators reported in the Astrophysical Journal July 2012] Hubble Science Briefing
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision Roeland van der Marel (STScI) [based on work with a team of collaborators reported in the Astrophysical Journal July 2012] Hubble Science Briefing
The BIPM, the Time Department and UTC
 The BIPM, the Time Department and UTC Elisa Felicitas Arias Fundamentals for a time and frequency laboratory BIPM, 11 September 2012 BUREAU INTERNATIONAL DES POIDS ET MESURES The BIPM It has headquarters
The BIPM, the Time Department and UTC Elisa Felicitas Arias Fundamentals for a time and frequency laboratory BIPM, 11 September 2012 BUREAU INTERNATIONAL DES POIDS ET MESURES The BIPM It has headquarters
Use the following information to deduce that the gravitational field strength at the surface of the Earth is approximately 10 N kg 1.
 IB PHYSICS: Gravitational Forces Review 1. This question is about gravitation and ocean tides. (b) State Newton s law of universal gravitation. Use the following information to deduce that the gravitational
IB PHYSICS: Gravitational Forces Review 1. This question is about gravitation and ocean tides. (b) State Newton s law of universal gravitation. Use the following information to deduce that the gravitational
Use WITH Investigation 4, Part 2, Step 2
 INVESTIGATION 4 : The Sundial Project Use WITH Investigation 4, Part 2, Step 2 EALR 4: Earth and Space Science Big Idea: Earth in Space (ES1) Projects: Tether Ball Pole Sundial Globe and a Light Indoors
INVESTIGATION 4 : The Sundial Project Use WITH Investigation 4, Part 2, Step 2 EALR 4: Earth and Space Science Big Idea: Earth in Space (ES1) Projects: Tether Ball Pole Sundial Globe and a Light Indoors
Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 13.
 Chapter 5. Gravitation Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 13. 5.1 Newton s Law of Gravitation We have already studied the effects of gravity through the
Chapter 5. Gravitation Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 13. 5.1 Newton s Law of Gravitation We have already studied the effects of gravity through the
Data transport in radio astronomy. Arpad Szomoru, JIVE
 Data transport in radio astronomy Arpad Szomoru, JIVE Some acronyms EVN: European VLBI Network Consortium of radio telescopes Involving 14 different organizations around the world: Europe, China, Puerto
Data transport in radio astronomy Arpad Szomoru, JIVE Some acronyms EVN: European VLBI Network Consortium of radio telescopes Involving 14 different organizations around the world: Europe, China, Puerto
Energy & Conservation of Energy. Energy & Radiation, Part I. Monday AM, Explain: Energy. Thomas Birner, ATS, CSU
 Monday AM, Explain: Energy MONDAY: energy in and energy out on a global scale Energy & Conservation of Energy Energy & Radiation, Part I Energy concepts: What is energy? Conservation of energy: Can energy
Monday AM, Explain: Energy MONDAY: energy in and energy out on a global scale Energy & Conservation of Energy Energy & Radiation, Part I Energy concepts: What is energy? Conservation of energy: Can energy
Space Environment and Satellite Systems: Removing Clutter from Ground-to-Satellite Signals. Sigrid Close
 Space Environment and Satellite Systems: Removing Clutter from Ground-to-Satellite Signals Sigrid Close Background Overview RF propagation through ionosphere can be problematic Goals Traditionally too
Space Environment and Satellite Systems: Removing Clutter from Ground-to-Satellite Signals Sigrid Close Background Overview RF propagation through ionosphere can be problematic Goals Traditionally too
Building a simple seismometer
 Building a simple seismometer Seismometers operate on the principle of inertia, i.e. a body at rest will tend to remain that way unless a force is applied to make it move. An ideal seismometer would be
Building a simple seismometer Seismometers operate on the principle of inertia, i.e. a body at rest will tend to remain that way unless a force is applied to make it move. An ideal seismometer would be
SPEED, VELOCITY, AND ACCELERATION
 reflect Look at the picture of people running across a field. What words come to mind? Maybe you think about the word speed to describe how fast the people are running. You might think of the word acceleration
reflect Look at the picture of people running across a field. What words come to mind? Maybe you think about the word speed to describe how fast the people are running. You might think of the word acceleration
The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems. Long History of Mapping. The Earth is Flat. Long History of Mapping
 The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems Intro to Mapping & GIS The Earth is Flat Day to day, we live life in a flat world sun rises in east, sets in west sky is above, ground is below
The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems Intro to Mapping & GIS The Earth is Flat Day to day, we live life in a flat world sun rises in east, sets in west sky is above, ground is below
SATELLITE TIME-TRANSFER: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS AND PROJECTS
 SATELLITE TIME-TRANSFER: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS AND PROJECTS W. LEWANDOWSKI 1 and J. NAWROCKI 2 1 Bureau International des Poids et Mesures, Sèvres, France e-mail: wlewandowski@bipm.org 2 Astrogeodynamical
SATELLITE TIME-TRANSFER: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS AND PROJECTS W. LEWANDOWSKI 1 and J. NAWROCKI 2 1 Bureau International des Poids et Mesures, Sèvres, France e-mail: wlewandowski@bipm.org 2 Astrogeodynamical
Measuring the Earth Using a GPS M. Scott Wilkerson & M. Beth Wilkerson, DePauw University, May 10, 2007
 Measuring the Earth Using a GPS M. Scott Wilkerson & M. Beth Wilkerson, DePauw University, May 10, 2007 Modified from: Kerski, J.J., 2007, Measuring the Earth s Circumference with GPS, Copyright ESRI,
Measuring the Earth Using a GPS M. Scott Wilkerson & M. Beth Wilkerson, DePauw University, May 10, 2007 Modified from: Kerski, J.J., 2007, Measuring the Earth s Circumference with GPS, Copyright ESRI,
APOPHIS 2029 A UNIQUE MISSION OPPORTUNITY
 APOPHIS 2029 A UNIQUE MISSION OPPORTUNITY Jean-Yves Prado CNES Toulouse - France Presentation Outline APOPHIS reminder The April 2029 flyby Mission objectives Sequence of events Launch Orbit transfer Relative
APOPHIS 2029 A UNIQUE MISSION OPPORTUNITY Jean-Yves Prado CNES Toulouse - France Presentation Outline APOPHIS reminder The April 2029 flyby Mission objectives Sequence of events Launch Orbit transfer Relative
Science Investigations: Investigating Astronomy Teacher s Guide
 Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6 12 Curriculum Focus: Astronomy/Space Duration: 7 segments; 66 minutes Program Description This library of videos contains seven segments on celestial bodies and related science.
Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6 12 Curriculum Focus: Astronomy/Space Duration: 7 segments; 66 minutes Program Description This library of videos contains seven segments on celestial bodies and related science.
Tides and Water Levels
 Tides and Water Levels What are Tides? Tides are one of the most reliable phenomena in the world. As the sun rises in the east and the stars come out at night, we are confident that the ocean waters will
Tides and Water Levels What are Tides? Tides are one of the most reliable phenomena in the world. As the sun rises in the east and the stars come out at night, we are confident that the ocean waters will
PROPOSED SCIENCE OFFERINGS FOR
 PROPOSED SCIENCE OFFERINGS FOR 2014-2015 LEESVILLE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL The following courses are the courses that we are recommending being offered for the following school year. The science teachers recommend
PROPOSED SCIENCE OFFERINGS FOR 2014-2015 LEESVILLE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL The following courses are the courses that we are recommending being offered for the following school year. The science teachers recommend
Plotting a Course Through History A Navigation History Timeline
 Mariners know how to navigate from here to there and back again. But we seldom stop to wonder who figured out how to determine position in the middle of an ocean, who developed the concept of latitude
Mariners know how to navigate from here to there and back again. But we seldom stop to wonder who figured out how to determine position in the middle of an ocean, who developed the concept of latitude
Bangkok Christian College EIP Matayom Course Description Semester One 2011-2012
 Bangkok Christian College EIP Matayom Course Description Semester One 2011-2012 Subject: General Science Grade: Matayom 6 Course Description This semester the General Science course will continue covering
Bangkok Christian College EIP Matayom Course Description Semester One 2011-2012 Subject: General Science Grade: Matayom 6 Course Description This semester the General Science course will continue covering
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
