Guide to machine safety standards and safety terminology
|
|
|
- Constance Thornton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guide to machine safety standards and safety terminology White Paper January, 2013 Objective of safety systems The objective of safety systems is to keep potential hazards for both people and the environment as low as possible by using suitable technical equipment, without restricting more than absolutely necessary, industrial production, the use of machines and thereby increasing productivity. There are different concepts and requirements to guarantee safety in the various regions and countries around the globe. For example, in the EU, there are requirements placed both on the manufacturer of a plant or system as well as the operating company, which are regulated using the appropriate European Directives, Laws and Standards. On the other hand, in the US, requirements differ both at a regional and even at a local level. What is important for machinery manufacturers and plant construction companies is that the legislation and rules of the location where the machine or plant is being operated always apply. For instance, the control system of a machine, which is operated and used in the US, must fulfill US requirements, even if the machine manufacturer (i.e. the OEM) is based in Europe. Although the technical concepts with which safety is to be achieved are subject to clear technical principles, it is still important to observe as to whether legislation or specific restrictions apply. However, throughout the USA there is a basic requirement that an employer must guarantee a safe place of work. In the case of damage, as a result of the product liability laws, a manufacturer can be made liable for damage caused by his product. On the other hand, in other countries and regions, other requirements apply.
2 Safety systems and functional safety From the perspective of the object to be protected, safety cannot be segregated. The causes of danger and also the technical measures to avoid them can vary widely. This is the reason that a differentiation is made between various types of safety, e.g. by specifying the particular cause of a hazard. For instance, the term electrical safety is used if protection has to be provided against electrical hazards and the term functional safety is used if the safety is dependent on the correct function. This differentiation is now reflected in the most recent standards, in so much that there are special standards that are involved with functional safety. In the area of machine safety, EN ISO (derived from EN 954) and IEC specifically address the requirements placed on safety-related control systems and therefore concentrate on functional safety. In the basis safety standard IEC (also EN and DIN EN / VDE 0803) IEC addresses the functional safety of electrical, electronic and programmable electronic systems, independent of any specific application area. In order to achieve the functional safety of a machine or plant, the safety-relevant parts of the protective and control systems must function correctly and must respond in the event of a fault in such a way that the system remains in a safe state or is brought into a safe state. To achieve this, specifically qualified technology is required, which fulfills the requirements described in the relevant standards. The requirements to achieve functional safety are based on the following basic goals: Avoiding systematic faults, controlling systematic faults and controlling random faults or failures. The measure for the level of achieved functional safety is the probability of the occurrence of dangerous failures, the fault tolerance and the quality that should be guaranteed by avoiding systematic faults. Various terminology is used to express this in the standards. In IEC 61508: Safety Integrity Level (SIL) and EN ISO Performance Level (PL) and Categories. Standards ensure safety The demand to make plant, machines and other equipment as safe as possible using state-of-the-art technology comes from the fact that manufacturers and users of equipment and products are responsible for their safety. By maintaining and fulfilling the machine safety standards, it can be ensured that state-of-the-art technology is achieved therefore ensuring that a company, erecting a plant or a manufacturer producing a machine or a device has fulfilled his responsibility for ensuring safety. European standards for safety of machinery European machine safety standards are hierchically structured as follows: Basic safety standards Type A standards Basic definitions for all machinery EN ISO Safety of machinery - Basic terminology, general principles for design - Principles for risk assessment Group safety standards Specialist standards Type B1 standards Higher-level safety aspects Type B2 standards Requirements for safety devices (Reference to special protective device/guards) Type C standards Specialist standards for specific requirements on specific machines Maximum gaps to avoid crushing of parts of the human body Safety-related parts of control systems EN 349 EN EN ISO Two-hand control device Safety distances to prevent danger zones being reached by the upper limbs Emergency stop equipment, functions, aspects - Principles for design Electrical equipment of machines Safety of machinery interlocking devices with and without tumbler EN 294 EB EN 1088 Light barriers, light curtains EN 574 EN ISO EN Lifts Injection molding machinery EN 81-3 EN 201 EN 692 EN 693 Presses & shears Numerically controlled turning machines EN ISO 23125
3 Recommendation Technology is progressing at a tremendous pace, which is also reflected in changes made to machine concepts. For this reason, especially when using type C Standards, they should be checked to ensure that they are up-to-date. It should also be noted that it is not mandatory to apply the standard, but instead, the safety objectives must be achieved. If there are no harmonized European standards, or they cannot be applied for specific reasons, then a manufacturer can apply National Standards. All of the other technical rules fall under this term of the machinery directive, e.g. also the accident prevention regulations and standards, which are not listed in the European Council Journal (also IEC or ISO standards, which were ratified as EN). By applying ratified standards, the manufacturer can prove that recognized state-of-the-art technology was fulfilled. However, when such standards are applied, this does not automatically represent a presumption of conformity as for a harmonized standard. US machine safety standards Understanding machine safety standards and terms remains a challenging first step to spotting and reducing risks and increasing profitability. Sources for help are many. Standards organizations covering machine safety include American National Standards Institute (ANSI), National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), Robotics Industries Association (RIA), and U.S. Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA), among others. Requirements are numerous; some are more obvious than others. Watch for these common safety violations When doing any plant walk-through, open your eyes (behind safety glasses, of course) to the most common safety violations, which may include: E-Stop pushbutton: Must be red palm or mushroom head with yellow background; Non-inspected fire extinguishers: approx. $1,200 fine; Fan guard opening greater than 1/2-in.: approx. $1,500 fine; If a machine is modified, a new risk assessment is required; and Almost all new or revised US machine safety standards require risk assessment to be done. General information The Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) from 1970 regulates the requirements for employers to ensure safe working conditions. The core requirements of the OSH Act are administered through the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (also known as OSHA). OSHA deploys regional inspectors to check whether workplaces comply with the valid rules and regulations. The rules and regulations of OSHA relevant for safety at the workplace are defined in OSHA 29 CFR 1910.xxx ( OSHA Regulations (29 CFR) PART 1910 Occupational Safety and Health ) (CFR: Code of Federal Regulations), Subpart O - Machinery and Machine Guarding. Additional information can be found in the Internet ( Minimum requirements of the OSHA The OSHA Rules under 29 CFR 1910 Subpart O, include general requirements for machines ( ) and a series of specific requirements for certain machine types. OSHA regulations define minimum requirements to guarantee safe places of employment. However, they should not prevent employers from applying innovative methods and techniques, e.g. state-of-the-art protective systems in order to maximize the safety of employees. In conjunction with specific applications, OSHA specifies that all electrical equipment used to protect employees must be certified for the intended application by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) authorized by OSHA. OSHA general duties clause section 5: It s the LAW Each Employer: Shall furnish to each of his employees employment and a place of employment, which are free from recognized hazards that are causing or likely to cause death or serious physical harm to his employees; Shall comply with occupational safety and health standards promulgated under this Act. Each Employee: Shall comply with occupational safety and health standards and all rules, regulations and orders issued pursuant to this Act, which are applicable to his own actions and conduct. Application of other standards In addition to the OSHA regulations, it is important to carefully observe the up-to-date standards of organizations such as ANSI, NFPA and RIA as well as the extensive product liability legislation in the US. As a result of the product liability, it is in the interest of manufacturers and operating companies to carefully observe and maintain the regulations and they are more or less forced to fulfill the state-ofthe-art technology requirement.
4 Third-party insurance contracts generally demand that the parties involved fulfill the applicable standards of the standardization organizations. Companies who are selfinsured initially do not have this requirement. However, in the case of an accident, they must prove that they had applied generally recognized safety principles. NFPA 70 (known as the National Electric Code (NEC)) and NFPA 79 (Electrical Standard for Industrial Machinery) are two especially important standards regarding safety in industry. Both of these describe the basic requirements placed on the features and the implementation of electrical equipment. The National Electric Code (NFPA 70) predominantly applies to buildings, but also to the electrical connections of machines and parts of machines. NFPA 79 applies to machines. The NFPA 79, 2012 is said to be the benchmark for industrial machinery safety and is aligned with the NEC and NFPA 70E. NFPA 79 This standard applies to the electrical equipment of industrial machines with rated voltages of less than 600 V. (A group of machines that operate together in a coordinated fashion is considered to be a machine.) Original NFPA Restricted machine safety t electromechanical devices Where a Category 0 stop is used for the emergency stop function, it shall have only hardwired electromechanical components. In addition, its operation shall not depend on electronic logic (hardware or software). NFPA Allowed the use of safety PLC in safety-related functions Use in Safety-Related Functions. Software and firmware-based controllers to be used in safety-related functions shall be listed for such use. [Annex to NFPA , A IEC 61508] NFPA Allowed drives as a final switching device Drives or solid-state output devices designed for safety-related functions shall be allowed to be the final switching element, when designed according to relevant safety standards. NFPA Allowed the use of cableless control, see below * General. Cableless control (e.g., radio, infrared) techniques for transmitting commands and signals between a machine control system and operator control station(s) shall meet the requirements of through The core requirements placed on programmable electronics and buses include: System requirements (refer to NFPA ). Control systems incorporating software- and firmware based controllers performing safety related functions shall be self-monitoring and conform to all of the following: (1) In the event of any single failure, the failure shall: Not lead to the loss of the safety-related function(s) Lead to the shutdown of the system in a safe state Prevent subsequent operation until the component failure has been corrected Prevent unintended startup of equipment upon correction of the failure (2) Provide protection equivalent to that of control systems incorporating hardwired/hardware components (3) Be designed in conformance with an approved standard that provides requirements for such systems. Requirements placed on programmable equipment (see NFPA ) Software and firmware-based controllers to be used in safety-related functions shall be listed for such use. (OSHA states listed as being certified by an NRTL) UL In order to implement the requirements listed in NFPA 79: 2007, UL has defined a special category Programmable Safety Controllers (code NRGF). This category involves control devices that contain software and are intended to be used for safety-related functions. IEC or EN ISO should also be considered when taking into account functional safety and when using new technologies, e.g. wireless-based suspended operator panels incorporating electronic shutdown devices. A precise description of the categories as well as a list of the devices that fulfill these requirements are provided in the Internet: > certifications directory > UL Category code / Guide information > search for category NRGF In addition to Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (UL), TÜV SÜD Product Services GmbH (TUVPSG) and TUV Rheinland of North America, Inc. (TUV) are also NRTL s for these applications. UL functional safety mark program With the advent and evolution of functional safety standards in North America and Europe, UL is now offering a UL Functional Safety Listing Mark that can be added for those qualifying companies in the process of getting a traditional Listing from UL. For more details visit
5 ANSI B11 The ANSI B11 standards are common standards, which have been developed by associations - e.g. the Association for Manufacturing Technology (AMT), National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and the Robotic Industries Association (RIA). For more details, visit Cooperation between OSHA and ANSI The ANSI and OSHA memorandum of understanding allows ANSI to use its technical resources to assist OSHA in carrying out its responsibilities. Some applicable standards and guidance follow. ANSI B : Performance criteria for safeguarding Standards below are referenced in and are intended to be used with ANSI B : Performance Criteria for Safeguarding. Standards always are subject to revision; investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions of any standard referenced. ANSI / NFPA : Electrical Standard for Industrial Machinery. Some standards below are for informative reference and are included for information only, for full list see pages 9-11 of the ANSI B CFR ISO , IEC , IEC /2/3 ANSI / NFPA , ANSI B11.1/.2/.3/.4/.5/.6/.7/.8/.9/.10/.11/.12/.13/.14/.15/. 16/.17/.18/.19/.20/.21/.22/.23/.24 See the appropriate ANSI B11 machine tool safety standard for safeguarding selection requirements based on a specific application. (See examples below.) Selection of the safeguarding requires task and hazard identification, and the application of risk assessment and risk reduction of the total production system. (See ANSI B11.TR3 on risk assessment and risk reduction). ANSI B (R2007): Power Press Brakes ANSI/RIA 15.06: Safety Requirements for Industrial Robots and Robot Systems ANSI B20.1: Conveyors TR : Risk Analysis TR : Failsafe PLC Application TR : Safety Control Systems for Machine tools ANSI B : The user shall ensure that when any change of the tooling, process or procedure occurs, the safeguarding continues to meet the requirements of the standard and the ANSI B11. base standard (the standard dealing with the specific machine), see ANSI B11-0. Changes in the production system that may affect the safeguarding include, but are not limited to tooling changes, addition or removal of auxiliary equipment, modification to the machine systems, operation method (program) change in operation personnel, adjustment location of safeguarding, and part configuration. Adjustments to the safeguarding or supplemental safeguarding may be necessary. ANSI B : Hazard Control: Hazards associated with the use of the safeguarding shall be identified and controlled as part of the overall risk reduction strategy. The overall hazard identification and risk reduction strategy is identified in each ANSI B11 base standard or in ANSI B11.0 (B11.TR3). These documents are used to select safeguarding appropriate to the foreseeable tasks and identified hazards. Risk assessment standards The risk analysis is used to assess the hazards that a machine presents. Risk analysis is an important requirement according to NFPA , ANSI/RIA , ANSI B and SEMI S10. A suitable safety technology/ system can be selected using the documented results of a risk analysis - based on the specified safety class of the particular application. As a result of their design and functionality, machinery and plants represent potential risks. Therefore, the machinery directive requires a risk assessment for every machine and, if relevant, risk reduction, so that the remaining risk is less than the tolerable risk. The following standards should be applied for the techniques to evaluate and assess these risks: For Europe: EN ISO Safety of machinery basic terminology, general principles for design risk assessment and risk reduction EN ISO mainly describes the risks to be considered and design guidelines to minimize risk and also focuses on the iterative process with risk assessment and risk reduction to achieve safety. For USA: ANSI B , Safety of Machinery; General Requirements and Risk Assessment This standard applies to new, modified or rebuilt power driven machines, not portable by hand, used to shape and/or form metal or other materials by cutting, impact, pressure, electrical or other processing techniques, or a combination of these processes. Incorporates the bulk of ANSI B (R2008) and ANSI B11.TR3
6 Safety standards reduce operating costs By now it is well understood, as shown by numerous safety research studies, customer application case studies and testimonies that not only does safety protect plant personnel but increases productivity and provides a cost saving of at least 30%. Companies that implement safety functions, perform functional safety evaluations, and implement safety in manufacturing processes by following the guidelines mentioned in the machine safety standards and complying with their requirements are finding benefits where few expected to on the bottom line. There are other financial benefits of implementing safety standards. One, is global acceptance which opens up the more global opportunities. Another important one is insurance companies have started to recognize machine safety compliance, its benefits and that can reflect favorably on the insurance premiums. Additional organizations and links: For more information on these topics, reference the following links. Siemens Industry Inc. ANSI (American National Standards Institute) OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) NFPA (Occupational Fire Protection Association) TUV Rheinland of N.A. Inc. UL (Underwriter Laboratories) CSA (Canadian Standards Association) CCOHS (Canadian Center for Occupational Health and Safety) NIOSH (National Institute of Occupational Health and Safety) NSC (National Safety Council) ASSE (American Society of Safety Engineers) RIA (Robotic Industries Association)
7 Machine safety definitions explained Actuating control(s): An operator control(s) used to initiate or maintain machine motion(s) or other machine function(s). Automatic start: A safety function is automatically restored (without an ON button). This for example is only permissible for moving protective guards that cannot be bypassed. However this is not permissible for an Emergency Stop device. This start type is only permissible after the hazard has been assessed. B10: The B10 value for devices subject to wear is expressed in the number of switching cycles. The failure rate of electromechanical components can be calculated using the B10 value and the operating cycle. Blanking: Bypassing a portion of the sensing field of a presence-sensing safeguarding device (light curtain). Cable-operated Switch: This is mainly used in EMERGENCY STOP protective safety devices and is a signal transmitter whose switching state changes if a cable / line - connected to the switch - is pulled or the line / cable breaks. This device is used to monitor long lengths (for example, along conveyor belts). Cascading input Safety Relay: Safety, single-channel input of a safety relay that is internally evaluated just like a sensor signal; logical and operational with the other signal transmitter / sensor inputs. If a voltage is not connected, the safety relay safely disables the enable circuits (outputs). CCF (Common Cause Failure): Failure with a common cause (short-circuit). Contact less electro-sensitive protective device (laser scanners, light grids, and light curtains). Contact less / electro-sensitive protective devices that essentially comprise the sensor function and the associated control monitoring function with output switching element also known as OSSD (output safe switching device). Control reliability: The capability of the machine control system, the safeguarding, other control components and related interfacing to achieve a safe state in the event of a failure within their safety-related functions. Cross-circuit fault: This can occur for multi channel control circuits for equipment/devices and is a short circuit between channels (e.g. in a two-channel sensor circuit) Cross-circuit fault detection: This is the ability of the safety device to detect cross-circuit faults either immediately or as part of a cyclic monitoring routine: The device goes into a safe condition after the fault has been detected. Discrepancy time: The discrepancy time monitoring tolerates, within a defined time window that associated signals not available at the same time. Diversity: The use of different means, such as use of different processors or other hardware such as relays, storage media, programming languages and software to perform the same function. Emergency stop: A manually actuated control device that can be used to initiate an EMERGENCY STOP function (red mushroom button with yellow background). Note: The EMERGENCY STOP function is initiated by a single action of a person and must always be available and capable of functioning irrespective of the operating mode. Enabling switch: An enabling switch is a manually operated signal transmitter which can be actuated to withdraw the protective effect of protection equipment. It is not possible or permissible to initiate hazardous states using the enabling switch alone a second, conscious start command is required for this. Energy source: Any electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, thermal, potential, kinetic or other sources of power / movement. Feedback circuit: This is used to monitor controlled actuators (e.g. relays or load contactors with positively-driven contacts). The evaluation unit can only be activated when the feedback circuit is closed. Note: The NC contacts (these are positively-driven contacts) of the load contactors to be monitored are connected in series and integrated into the feedback circuit of the safety controller/relay. If a contact welds in the enable circuit, then it is no longer possible to re-activate the safety controller/relay because the feedback circuit remains open. The (dynamic) monitoring of the feedback circuit does not have to be safety-related because it is only used for fault detection. The ON button is generally switched using the positively-driven contacts of the actuator in series (fault detection when starting) Hand tool: Any device used for manual feeding or removal or a work piece, freeing of a jammed work piece or removal of scrap. Harmonized standard: Type A (Basic Standards), Type B (Group Standards) and Type C (Products Standards) are listed in the Machinery Directive and therefore allow an assumption to be made that the Machinery Directive is complied with. Hazard: The hazard (as the result of a specific event) represents danger for the user and can result in injury (potential source of damage). Hazard assessment: Evaluation of a danger (resulting from a hazard) for the user. Interlocking equipment and devices: This is a mechanical, electrical or another interlocking device that has the function of preventing the operation of a machine under certain specific conditions (generally as long as a guard is not closed). Life cycle of a machine: The phases of a machine including design and construction, transport and commissioning, re-assembly, installation, initial adjustment, relocation, use (such as setting, teaching / programming or process changeover, operation) and care (cleaning, trouble shooting, maintenance (planned or unplanned) de-commissioning, dismantling and, as far as safety is concerned, disposal.
8 Listed for use: Equipment, materials or services included in a list published by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) and concerned with evaluation of products or services, that maintains periodic inspection of production of listed equipment or materials or periodic evaluation of services, and whose listing states that either the equipment, material or services meets identified standards or has been tested and found suitable for a specified purpose. Manual reset: A function to restore one or several safety functions before the machine restarts. After a stop command has been initiated by a protective device, the stop state must be maintained until a manual reset device is actuated and the safe state has been reached for a restart. Mirror contact: A typical application of mirror contacts is to provide high reliable monitoring of the switching state in the control circuits of machinery. Monitored start: The safety function is restored by monitoring a dynamic signal change, e.g. using an ON pushbutton. This is absolutely mandatory to achieve a higher safety level for an emergency stop protective device since it provides protection against manipulation. This start type is only permissible after a hazard has been assessed. Muting: A type of bypass function: The safety-related function is correctly and deliberately disabled using additional sensors for a limited time. Note: This is used in the field to make a differentiation between persons and objects. Performance level: Capability of safety-relevant parts to execute a safety function under predictable conditions (that should be taken into account) to fulfill the expected risk minimization. From PLa (the highest probability of failure) to PLe (the lowest probability of failure) PES (Programmable Electronic System): A system for control or monitoring using one or more programmable electronic devices, including all elements of the system, such as power supplies, sensors and other input devices, data links and other communication paths, and actuators, and other output devices. Positively-driven contacts: For positively-driven contacts of a relay/contactor, the NC contact and the NO contact may never be simultaneously closed over the complete lifetime of the device. This also applies if the relay/contactor is in an incorrect state (faulted). E.g. If a NO contact is welded, then all of the other NC contacts of the relay/contactor involved remain open no matter whether the relay/contactor is energized or not. Siemens Industry, Inc Old Milton Parkway Alpharetta, GA Positively-opening: For positively-opening contacts, the contacts separate as a direct result of a defined motion of the switch actuator using non-spring mechanical linkage. For the electrical equipment of machinery, the positivelyopening contacts are expressly specified in all safety circuits. Note: Positively-opening contacts are designated according to IEC by the symbol (arrow in a circle) (function to protect persons). Presence-sensing device: A device that creates a sensing field, area or plane to detect the presence of an individual or project. Proof test: Repeated test that is executed to detect faults in a SRECS so that if necessary the system can be brought into an as new state, or as close as is practically possible to an as new state. Protective device: Device (other than a guard), which reduces a risk, either alone or associated with a guard (does not include personal protective equipment). Residual risk: That risk that remains after safeguarding devices have been applied and a risk assessment performed. Risk: A combination of the probability and the degree of the possible injury or damage to health in a hazardous situation in order to select appropriate safeguards. Risk assessment: The process by which the intended use of the machine, the tasks and hazards, and the level of risk are performed. Safeguarding: Guards, safeguarding devices, awareness devices, safeguarding methods and safe work procedures. Safety distance: The calculated distance between a hazard and its associated safeguard. Safety function: Function of a machine, the malfunction of which would increase the risk of harm. SIL: One of three possibilities to define safety integrity specifications of the safety function that can be assigned to an SRECS. Safety integrity level 3 (SIL 3) is the highest possible level and level 1 (SIL1) is the lowest. Tolerable risk: Risk that is accepted for a given task and hazard combination (hazardous situation). Two hand control device: An actuating control that requires the concurrent use of the operators hands to initiate machine motion during the hazardous portion of the machine cycle. Validation: Confirmation by examination and testing that the particular requirements for a specific intended use are met. Verification: The process or act of confirming that a device or function conforms or performs to its design. Order No. SIWP-SSTDS-0113 All rights reserved. All trademarks used are owned by Siemens or their respective owners. Siemens Industry, Inc., October All rights reserved.
Trends in Machinery/ Automation Safety
 Trends in Machinery/ Automation Safety by Roberta Nelson Shea Director, Safety & Compliance Symbotic LLC and C&S Wholesale Grocers 2013 SES - The Society for Standards Professionals Why Machinery Safety
Trends in Machinery/ Automation Safety by Roberta Nelson Shea Director, Safety & Compliance Symbotic LLC and C&S Wholesale Grocers 2013 SES - The Society for Standards Professionals Why Machinery Safety
Risk Assessment in Accordance with EN ISO 14121-1 and EN ISO 12100:2010
 Risk Assessment in Accordance with EN ISO 14121-1 and EN ISO 12100:2010 Introduction Safety Integrated siemens.com/safety-integrated Contents 1 General 3 1.1 Warranty and Liability 3 1.2 Description of
Risk Assessment in Accordance with EN ISO 14121-1 and EN ISO 12100:2010 Introduction Safety Integrated siemens.com/safety-integrated Contents 1 General 3 1.1 Warranty and Liability 3 1.2 Description of
Application Technique. Safety Function: Magnetic Door Switch Monitoring
 Application Technique Safety Function: Magnetic Door Switch Monitoring Products: MC1 Magnetically-coded Door Switch, Guardmaster Dual-input Safety Relay Safety Rating: CAT. 3, PLd to EN ISO 13849-1: 2008
Application Technique Safety Function: Magnetic Door Switch Monitoring Products: MC1 Magnetically-coded Door Switch, Guardmaster Dual-input Safety Relay Safety Rating: CAT. 3, PLd to EN ISO 13849-1: 2008
functional Safety UL Functional Safety Mark
 functional Safety UL Functional Safety Mark Program UL Functional Safety Mark Program With the advent and evolution of functional safety standards in North America and Europe, UL is now offering a UL Functional
functional Safety UL Functional Safety Mark Program UL Functional Safety Mark Program With the advent and evolution of functional safety standards in North America and Europe, UL is now offering a UL Functional
Machinery Safety. Presented by Paul Laidler. TÜV SÜD Product Service
 Machinery Safety Presented by Paul Laidler Machinery Division Safety Solutions Assistance in meeting the requirements of machinery safety legislation Machinery, Low Voltage and Electro Magnetic Compatibility
Machinery Safety Presented by Paul Laidler Machinery Division Safety Solutions Assistance in meeting the requirements of machinery safety legislation Machinery, Low Voltage and Electro Magnetic Compatibility
 Hydraulic/pneumatic drive Cylinder (machine actuator) Optoelectronics Light curtain (sensor) Electronics Control system Danger! Hydraulics/pneumatics Valves (actuators) Safety control SRP/CS subsystem
Hydraulic/pneumatic drive Cylinder (machine actuator) Optoelectronics Light curtain (sensor) Electronics Control system Danger! Hydraulics/pneumatics Valves (actuators) Safety control SRP/CS subsystem
Safety Requirements Specification Guideline
 Safety Requirements Specification Comments on this report are gratefully received by Johan Hedberg at SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute mailto:johan.hedberg@sp.se -1- Summary Safety Requirement
Safety Requirements Specification Comments on this report are gratefully received by Johan Hedberg at SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute mailto:johan.hedberg@sp.se -1- Summary Safety Requirement
Overview of Standards for CO Detection Products
 Overview of Standards for CO Detection Products Rev 1.1 INTEC Controls 12700 Stowe Dr., Suite 100 Poway, CA 92064 The Right Choice info@inteccontrols.com www.inteccontrols.com Phone: (858) 578-7887 Fax:
Overview of Standards for CO Detection Products Rev 1.1 INTEC Controls 12700 Stowe Dr., Suite 100 Poway, CA 92064 The Right Choice info@inteccontrols.com www.inteccontrols.com Phone: (858) 578-7887 Fax:
Machine Guarding and Operator Safety. Leader Guide and Quiz
 4646 Machine Guarding and Operator Safety Leader Guide and Quiz Leader s Guide MACHINE GUARDING & OPERATOR SAFETY INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program and the subject that it addresses. This
4646 Machine Guarding and Operator Safety Leader Guide and Quiz Leader s Guide MACHINE GUARDING & OPERATOR SAFETY INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program and the subject that it addresses. This
Demystifying the European Machinery Directive and SEMI Requirements for the Industrial Automation and Semiconductor Markets
 Demystifying the European Machinery Directive and SEMI Requirements for the Industrial Automation and Semiconductor Markets An Overview of Current Changes and Directions By Andras Szende Senior Engineer
Demystifying the European Machinery Directive and SEMI Requirements for the Industrial Automation and Semiconductor Markets An Overview of Current Changes and Directions By Andras Szende Senior Engineer
Emergency Stop Push Buttons
 Emergency Stop Push Buttons Many users of emergency stop devices are familiar with their use, but are not familiar with many of the global governing standards. The purpose of this white paper is to familiarize
Emergency Stop Push Buttons Many users of emergency stop devices are familiar with their use, but are not familiar with many of the global governing standards. The purpose of this white paper is to familiarize
Safety along the complete line: SIRIUS 3SE7 cable-operated switches. sirius COMMANDING & SIGNALING
 Safety along the complete line: 3SE7 cable-operated switches sirius COMMANDING & SIGNALING Everything well under control. 3SE7 cable-operated switches With cable-operated switches from our 3SE7 product
Safety along the complete line: 3SE7 cable-operated switches sirius COMMANDING & SIGNALING Everything well under control. 3SE7 cable-operated switches With cable-operated switches from our 3SE7 product
KELLER S 5-MINUTE WORKPLACE SAFETY TALKS
 KELLER S 5-MINUTE WORKPLACE SAFETY TALKS Machine Guarding An Overview Overview Of Topic Machine operators who understand a machine s hazards and how to control them will have a reduced risk of injury.
KELLER S 5-MINUTE WORKPLACE SAFETY TALKS Machine Guarding An Overview Overview Of Topic Machine operators who understand a machine s hazards and how to control them will have a reduced risk of injury.
A holistic approach to Automation Safety
 A holistic approach to Automation Safety Mark Eitzman - Manager, Safety Business Development How technology, global standards and open systems help increase productivity and overall equipment effectiveness.
A holistic approach to Automation Safety Mark Eitzman - Manager, Safety Business Development How technology, global standards and open systems help increase productivity and overall equipment effectiveness.
Functional safety. Essential to overall safety
 Functional safety Essential to overall safety What is Functional safety? In public spaces, factories, offi ces or homes; we are surrounded by an increasing number of electric and electronic devices and
Functional safety Essential to overall safety What is Functional safety? In public spaces, factories, offi ces or homes; we are surrounded by an increasing number of electric and electronic devices and
Safety Function: Door Monitoring
 Application Technique Safety Function: Door Monitoring Products: Trojan 5 Switch, GuardLogix Controller Safety Rating: CAT. 3, PLd to ISO 13849-1: 2008 Topic Page Important User Information 2 General Safety
Application Technique Safety Function: Door Monitoring Products: Trojan 5 Switch, GuardLogix Controller Safety Rating: CAT. 3, PLd to ISO 13849-1: 2008 Topic Page Important User Information 2 General Safety
www.ab.com/safety MACHINE SAFETY GUIDE A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO MACHINE SAFETY APPLICATION, LEGISLATION AND STANDARDS
 www.ab.com/safety MACHINE SAFETY GUIDE A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO MACHINE SAFETY APPLICATION, LEGISLATION AND STANDARDS Table of Contents Safety Principles Regulations EU Directive and Legislation..............................
www.ab.com/safety MACHINE SAFETY GUIDE A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO MACHINE SAFETY APPLICATION, LEGISLATION AND STANDARDS Table of Contents Safety Principles Regulations EU Directive and Legislation..............................
You Must Know About the New RIA Automation Standard
 You Must Know About the New RIA Automation Standard AMT Decoding the essentials of RIA R15.06:2012 The new Robotics Industry Association (RIA) standard for robots and robot systems (RIA R15.06:2012) will
You Must Know About the New RIA Automation Standard AMT Decoding the essentials of RIA R15.06:2012 The new Robotics Industry Association (RIA) standard for robots and robot systems (RIA R15.06:2012) will
PABIAC Safety-related Control Systems Workshop
 Health and and Safety Executive PABIAC Safety-related Control Systems Workshop KEY STANDARDS FOR ELECTRICAL & FUNCTIONAL SAFETY OF PAPERMAKING MACHINES: APPLICATION & USE Steve Frost HM Principal Electrical
Health and and Safety Executive PABIAC Safety-related Control Systems Workshop KEY STANDARDS FOR ELECTRICAL & FUNCTIONAL SAFETY OF PAPERMAKING MACHINES: APPLICATION & USE Steve Frost HM Principal Electrical
Machine Safety Switches
 Machine Switches SI-LS31H Series 31 mm Limit-Switch-Style with Hinged Lever Actuators Features Limit switch design (EN 50047) For use on doors or flaps Positive opening safety contacts (IEC 60947-5-1)
Machine Switches SI-LS31H Series 31 mm Limit-Switch-Style with Hinged Lever Actuators Features Limit switch design (EN 50047) For use on doors or flaps Positive opening safety contacts (IEC 60947-5-1)
CONFIGURABLE SAFETY RELAYS
 MSI-s/R, MSI-sx/Rx Configurable MSI provide important functions for the efficient flow of automated production processes Special features Combined guarding types by connecting up to 4 AOPDs Additional
MSI-s/R, MSI-sx/Rx Configurable MSI provide important functions for the efficient flow of automated production processes Special features Combined guarding types by connecting up to 4 AOPDs Additional
ELECTROTECHNIQUE IEC INTERNATIONALE 61508-3 INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL
 61508-3 ª IEC: 1997 1 Version 12.0 05/12/97 COMMISSION CEI ELECTROTECHNIQUE IEC INTERNATIONALE 61508-3 INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION Functional safety of electrical/electronic/ programmable
61508-3 ª IEC: 1997 1 Version 12.0 05/12/97 COMMISSION CEI ELECTROTECHNIQUE IEC INTERNATIONALE 61508-3 INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION Functional safety of electrical/electronic/ programmable
Page85. Lock-out Tag-out Plan
 Page85 Lock-out Tag-out Plan Page86 Lock-out / Tag-Out Plan Table of Contents 1. Policy 2. Purpose 3. Scope 4. General Procedures 5. Application of Control Procedure 6. Release from Control Procedure 7.
Page85 Lock-out Tag-out Plan Page86 Lock-out / Tag-Out Plan Table of Contents 1. Policy 2. Purpose 3. Scope 4. General Procedures 5. Application of Control Procedure 6. Release from Control Procedure 7.
WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING All Euramax Subsidiaries LOCKOUT / TAGOUT. Safety Meeting Contents. Meeting Notice. Leaders Guide.
 Safety Meeting Contents Meeting Notice Leaders Guide Employee Handout Employee Quiz Meeting Sign-In Sheet Employee Puzzle PRIOR TO THE WEEKLY MEETING: - Post the meeting notice by the timeclock - Read
Safety Meeting Contents Meeting Notice Leaders Guide Employee Handout Employee Quiz Meeting Sign-In Sheet Employee Puzzle PRIOR TO THE WEEKLY MEETING: - Post the meeting notice by the timeclock - Read
MACHINERY GUARDING. Your Practical Guide
 MACHINERY GUARDING Your Practical Guide WELCOME TO AXA Introducing AXA One of the world s largest insurers With more than 50 million customers across the globe, AXA is one of the world s largest financial
MACHINERY GUARDING Your Practical Guide WELCOME TO AXA Introducing AXA One of the world s largest insurers With more than 50 million customers across the globe, AXA is one of the world s largest financial
section 5 machine guarding and lockout
 section machine guarding and lockout This section covers ways to physically protect people working in and around machinery. It includes information on: machinery guards lockout systems emergency stop confined
section machine guarding and lockout This section covers ways to physically protect people working in and around machinery. It includes information on: machinery guards lockout systems emergency stop confined
Contactor Monitoring Relay CMD Cost-Effective Solution for Safe Machines
 www.eaton.com/moellerproducts Contactor Monitoring Relay CMD Cost-Effective Solution for Safe Machines Technical Paper Dipl.-Ing. Wolfgang Nitschky The way to safe machines During the engineering design
www.eaton.com/moellerproducts Contactor Monitoring Relay CMD Cost-Effective Solution for Safe Machines Technical Paper Dipl.-Ing. Wolfgang Nitschky The way to safe machines During the engineering design
BLR s Safety Training Presentations
 BLR s Safety Training Presentations Machine Guarding 29 CFR 1910.211 to 1910.219 Machine guarding is an integral part of any safety and health program. As statistics can demonstrate, it is also one aspect
BLR s Safety Training Presentations Machine Guarding 29 CFR 1910.211 to 1910.219 Machine guarding is an integral part of any safety and health program. As statistics can demonstrate, it is also one aspect
Machineontwerp volgens IEC 62061
 Machineontwerp volgens IEC 62061 Insert Photo Here Safety solution Architect Safety Local Business Leader Benelux. Stephen Podevyn Safety Solution Seminar Agenda deel 1 1. Richtlijnen en normen 2. Safety
Machineontwerp volgens IEC 62061 Insert Photo Here Safety solution Architect Safety Local Business Leader Benelux. Stephen Podevyn Safety Solution Seminar Agenda deel 1 1. Richtlijnen en normen 2. Safety
MSI-s/R. Modular Safety Interface. CONNECTING AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Original Instructions. without prior notice 603101-2011/05.
 MSI-s/R Modular Safety Interface CONNECTING AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Original Instructions 603101-2011/05 Subject to change without prior notice Notes on connection and operating instructions DEUTSCH
MSI-s/R Modular Safety Interface CONNECTING AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Original Instructions 603101-2011/05 Subject to change without prior notice Notes on connection and operating instructions DEUTSCH
Version: 1.0 Latest Edition: 2006-08-24. Guideline
 Management of Comments on this report are gratefully received by Johan Hedberg at SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute mailto:johan.hedberg@sp.se Quoting of this report is allowed but please
Management of Comments on this report are gratefully received by Johan Hedberg at SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute mailto:johan.hedberg@sp.se Quoting of this report is allowed but please
Safeguarding Applications and Wiring Diagrams
 Table of Contents Safeguarding and Wiring Diagrams General Application Selection Table 0- Notes for Use with Application Circuit Examples 0- Safeguarding and Wiring Diagrams 0- Light Curtain Point of Operation
Table of Contents Safeguarding and Wiring Diagrams General Application Selection Table 0- Notes for Use with Application Circuit Examples 0- Safeguarding and Wiring Diagrams 0- Light Curtain Point of Operation
Overview of IEC 61508 - Design of electrical / electronic / programmable electronic safety-related systems
 Overview of IEC 61508 - Design of electrical / electronic / programmable electronic safety-related systems Simon Brown The author is with the Health & Safety Executive, Magdalen House, Bootle, Merseyside,
Overview of IEC 61508 - Design of electrical / electronic / programmable electronic safety-related systems Simon Brown The author is with the Health & Safety Executive, Magdalen House, Bootle, Merseyside,
CONFIGURABLE SAFETY RELAYS
 MSI-m/R, MSI-mx/Rx Configurable MSI Safety Relay with function for efficient material flow in a packaging application Special features Sequential or Parallel with automatic mode detection MSI-mx for separate
MSI-m/R, MSI-mx/Rx Configurable MSI Safety Relay with function for efficient material flow in a packaging application Special features Sequential or Parallel with automatic mode detection MSI-mx for separate
Safety automation solutions
 Operating principle, characteristics Preventa safety s types XPS AV,, For and switch monitoring Operating principle Safety s XPS AV, and are used for monitoring circuits conforming to standards EN/ISO
Operating principle, characteristics Preventa safety s types XPS AV,, For and switch monitoring Operating principle Safety s XPS AV, and are used for monitoring circuits conforming to standards EN/ISO
Application Technique. Safety Function: Door Monitoring
 Application Technique Safety Function: Door Monitoring Products: Trojan 5 Interlock Switch, GuardLogix Controller, PowerFlex 525 Drive with Safe Torque-off Safety Rating: CAT. 3, PLd to EN ISO 13849-1:
Application Technique Safety Function: Door Monitoring Products: Trojan 5 Interlock Switch, GuardLogix Controller, PowerFlex 525 Drive with Safe Torque-off Safety Rating: CAT. 3, PLd to EN ISO 13849-1:
Safety Relays ESM/ESM-F
 Safety Relays ESM/ESM-F More than safety. Safety More than safety. Emil Euchner, the company s founder and inventor of the multiple limit switch, circa 1928. Around the world the Swabian specialists in
Safety Relays ESM/ESM-F More than safety. Safety More than safety. Emil Euchner, the company s founder and inventor of the multiple limit switch, circa 1928. Around the world the Swabian specialists in
Control of Hazardous Energy LOCKOUT/TAGOUT 29 CFR 1910.147
 Control of Hazardous Energy LOCKOUT/TAGOUT 29 CFR 1910.147 Contents I. Introduction II. Scope and Application III. Definitions IV. Lockout/Tagout Manual V. Energy Control Procedures 1. Applying Energy
Control of Hazardous Energy LOCKOUT/TAGOUT 29 CFR 1910.147 Contents I. Introduction II. Scope and Application III. Definitions IV. Lockout/Tagout Manual V. Energy Control Procedures 1. Applying Energy
Dielectric Withstand Testing in a Production Environment
 Dielectric Withstand Testing in a Production Environment Performing a routine product safety test should not in itself represent a shock hazard to the operator who is conducting the test, yet anytime you
Dielectric Withstand Testing in a Production Environment Performing a routine product safety test should not in itself represent a shock hazard to the operator who is conducting the test, yet anytime you
Understanding Safety Integrity Levels (SIL) and its Effects for Field Instruments
 Understanding Safety Integrity Levels (SIL) and its Effects for Field Instruments Introduction The Industrial process industry is experiencing a dynamic growth in Functional Process Safety applications.
Understanding Safety Integrity Levels (SIL) and its Effects for Field Instruments Introduction The Industrial process industry is experiencing a dynamic growth in Functional Process Safety applications.
Safe and Efficient Hydraulic Systems Review of ISO 4413 Hydraulic Fluid Power General Rules and Safety Requirements for Systems and Their Components
 Safe and Efficient Hydraulic Systems Review of ISO 4413 Hydraulic Fluid Power General Rules and Safety Requirements for Systems and Their Components Jerry Carlin Eaton Hydraulics November 20, 2013 Evolution
Safe and Efficient Hydraulic Systems Review of ISO 4413 Hydraulic Fluid Power General Rules and Safety Requirements for Systems and Their Components Jerry Carlin Eaton Hydraulics November 20, 2013 Evolution
Machine Safety Switch: SI-LM40 Series Limit Switch Style
 Machine Switch: SI-LM40 Series Limit Switch Style SI-LM40 Series Limit Switch Style with Flexible In-Line Actuator Positive-opening safety contacts (IEC 60947-5-1) (not dependent upon springs) Standard
Machine Switch: SI-LM40 Series Limit Switch Style SI-LM40 Series Limit Switch Style with Flexible In-Line Actuator Positive-opening safety contacts (IEC 60947-5-1) (not dependent upon springs) Standard
mecotron Safety relay ESTOP-2 For emergency stop monitoring
 E0006 000824 Safety relay E-2 For emergency stop monitoring Description The safety module E-2 for emergency stop monitoring is used for safety breaking one or more circuits and is designed to be incorporated
E0006 000824 Safety relay E-2 For emergency stop monitoring Description The safety module E-2 for emergency stop monitoring is used for safety breaking one or more circuits and is designed to be incorporated
LOCKOUT/TAGOUT (LOTO) SAFETY PROGRAM
 1 UNIVERSITY OF WEST FLORIDA LOCKOUT/TAGOUT (LOTO) SAFETY PROGRAM (EQUIPMENT HAZARD DE-ENERGIZING AND ISOLATION) DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY 11000University Parkway Pensacola, FL 32514
1 UNIVERSITY OF WEST FLORIDA LOCKOUT/TAGOUT (LOTO) SAFETY PROGRAM (EQUIPMENT HAZARD DE-ENERGIZING AND ISOLATION) DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY 11000University Parkway Pensacola, FL 32514
Safety Integrated. SIMATIC Safety Matrix. The Management Tool for all Phases of the Safety Lifecycle. Brochure September 2010. Answers for industry.
 SIMATIC Safety Matrix The Management Tool for all Phases of the Safety Lifecycle Brochure September 2010 Safety Integrated Answers for industry. Functional safety and Safety Lifecycle Management Hazard
SIMATIC Safety Matrix The Management Tool for all Phases of the Safety Lifecycle Brochure September 2010 Safety Integrated Answers for industry. Functional safety and Safety Lifecycle Management Hazard
Safety at injection moulding machines
 Safety at injection moulding machines HSE information sheet Plastics Processing Sheet No 4 (Revision 1) Introduction This information sheet is one of a series produced by HSE s manufacturing sector and
Safety at injection moulding machines HSE information sheet Plastics Processing Sheet No 4 (Revision 1) Introduction This information sheet is one of a series produced by HSE s manufacturing sector and
ERC-to-MRC JOB TRANSLATOR MANUAL
 Yasnac MRC Controller ERC-to-MRC JOB TRANSLATOR MANUAL Part Number 133110-1 Yasnac MRC Controller ERC-to-MRC Job Translator Manual Part Number 133110-1 June 13, 1995 MOTOMAN 805 Liberty Lane West Carrollton,
Yasnac MRC Controller ERC-to-MRC JOB TRANSLATOR MANUAL Part Number 133110-1 Yasnac MRC Controller ERC-to-MRC Job Translator Manual Part Number 133110-1 June 13, 1995 MOTOMAN 805 Liberty Lane West Carrollton,
CONTROL OF HAZARDOUS ENERGY (Lockout Tagout)
 CONTROL OF HAZARDOUS ENERGY (Lockout Tagout) Many workplace accidents are caused by machinery that accidentally becomes activated while being serviced or maintained. This accidental activation is called
CONTROL OF HAZARDOUS ENERGY (Lockout Tagout) Many workplace accidents are caused by machinery that accidentally becomes activated while being serviced or maintained. This accidental activation is called
Multizone Application 1 2-3 >3. MSR300 System. No Software configurable? GuardPLC. Enet RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS. Time Delay MSR138
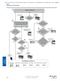 AUDIN - 8, avenue de la malle - 51370 Saint Brice Courcelles - Tel : 03.26.04.20.21 - Fax : 03.26.04.28.20 - Web : http: www.audin.fr - Email : info@audin.fr Selection Flowchart Multizone Application General
AUDIN - 8, avenue de la malle - 51370 Saint Brice Courcelles - Tel : 03.26.04.20.21 - Fax : 03.26.04.28.20 - Web : http: www.audin.fr - Email : info@audin.fr Selection Flowchart Multizone Application General
Funktionale Sicherheit IEC 61508 & IEC 62443
 Funktionale Sicherheit IEC 61508 & IEC 62443 Seite 1 PROFIsafe trifft New York PROFIsafe Senior Safety Expert Siemens AG, DF FA AS E&C-PRM3 bernard.mysliwiec@siemens.com Seite 2 Roosevelt Island Picture
Funktionale Sicherheit IEC 61508 & IEC 62443 Seite 1 PROFIsafe trifft New York PROFIsafe Senior Safety Expert Siemens AG, DF FA AS E&C-PRM3 bernard.mysliwiec@siemens.com Seite 2 Roosevelt Island Picture
Selecting Sensors for Safety Instrumented Systems per IEC 61511 (ISA 84.00.01 2004)
 Selecting Sensors for Safety Instrumented Systems per IEC 61511 (ISA 84.00.01 2004) Dale Perry Worldwide Pressure Marketing Manager Emerson Process Management Rosemount Division Chanhassen, MN 55317 USA
Selecting Sensors for Safety Instrumented Systems per IEC 61511 (ISA 84.00.01 2004) Dale Perry Worldwide Pressure Marketing Manager Emerson Process Management Rosemount Division Chanhassen, MN 55317 USA
Safety Integrated. Introduction and Terminology for Functional Safety of Machines and Systems. Reference Manual November 2012. Answers for industry.
 Siemens AG 2012 Introduction and Terminology for Functional Safety of Machines and Systems Reference Manual November 2012 Safety Integrated Answers for industry. Introduction and Terminology for Functional
Siemens AG 2012 Introduction and Terminology for Functional Safety of Machines and Systems Reference Manual November 2012 Safety Integrated Answers for industry. Introduction and Terminology for Functional
SAFETY LIGHT CURTAINS
 SAFETY LIGHT CURTAINS Overview Safety Light Curtains with resolutions that can be reduced guarantee protection and tolerate work equipment in the protective field The Safety Light Curtains comply with
SAFETY LIGHT CURTAINS Overview Safety Light Curtains with resolutions that can be reduced guarantee protection and tolerate work equipment in the protective field The Safety Light Curtains comply with
BWC Division of Safety and Hygiene
 BWC Division of Safety and Hygiene A SAMPLE LOCKOUT/TAGOUT PROCEDURE A good Lockout/Tagout Procedure, at a minimum, should contain the following elements: 1. All maintenance personnel shall be provided
BWC Division of Safety and Hygiene A SAMPLE LOCKOUT/TAGOUT PROCEDURE A good Lockout/Tagout Procedure, at a minimum, should contain the following elements: 1. All maintenance personnel shall be provided
Risk Assessment as the principal element of the CE Conformity Assessment of Wind Turbines
 Product liability claims caused by an incomplete risk assessment can be avoided! Risk Assessment as the principal element of the CE Conformity Assessment of Wind Turbines Holger Berndt, Germanischer Lloyd
Product liability claims caused by an incomplete risk assessment can be avoided! Risk Assessment as the principal element of the CE Conformity Assessment of Wind Turbines Holger Berndt, Germanischer Lloyd
Lockout Tagout Program. Table of Contents
 Environmental Health and Safety Name: Lockout Tagout Program Date Created: 2/1/2014 Date Revised: 11/17/2014 Created By: Jill Jones Table of Contents Purpose and Regulatory Standards... 1 Scope... 1 Employer
Environmental Health and Safety Name: Lockout Tagout Program Date Created: 2/1/2014 Date Revised: 11/17/2014 Created By: Jill Jones Table of Contents Purpose and Regulatory Standards... 1 Scope... 1 Employer
Understanding Emergency Power Off (EPO)
 Understanding Emergency Power Off (EPO) White Paper #22 Executive Summary Emergency Power Off (EPO) is the capability to power down a piece of electronic equipment or an entire installation from a single
Understanding Emergency Power Off (EPO) White Paper #22 Executive Summary Emergency Power Off (EPO) is the capability to power down a piece of electronic equipment or an entire installation from a single
Lockout / Tagout Program
 Lockout / Tagout Program Table of Contents Page Scope... 2 Definitions... 2 Authorization... 3 Responsibilities... 4 Compliance and Enforcement... 4 When to Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)... 5 Lockout Procedure...
Lockout / Tagout Program Table of Contents Page Scope... 2 Definitions... 2 Authorization... 3 Responsibilities... 4 Compliance and Enforcement... 4 When to Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)... 5 Lockout Procedure...
Logic solver application software and operator interface
 Logic solver application software and operator interface By RJ Perry, Control Systems Consultant Correctly implemented and structured functional logic, together with operator interface displays, can improve
Logic solver application software and operator interface By RJ Perry, Control Systems Consultant Correctly implemented and structured functional logic, together with operator interface displays, can improve
OSHA/CalOSHA Overview. Kelly Howard Sr. Safety Engineer Cal/OSHA Consultation Service
 OSHA/CalOSHA Overview Kelly Howard Sr. Safety Engineer Cal/OSHA Consultation Service OSHA Program Created in 1970 Occupational Health and Safety 26 States have their own program At least as stringent as
OSHA/CalOSHA Overview Kelly Howard Sr. Safety Engineer Cal/OSHA Consultation Service OSHA Program Created in 1970 Occupational Health and Safety 26 States have their own program At least as stringent as
ETZGAR CONVEYOR COMPANY Controls Section v12.05
 Section 7 Controls Page Description 7-1 Controls Index 7-2 Motor Data, Enclosure Rating and Abbreviations 7-3 Controls Safety Guidelines 7-4 Fixed Speed Controls Packages 7-5 Three Phase AC Variable Speed
Section 7 Controls Page Description 7-1 Controls Index 7-2 Motor Data, Enclosure Rating and Abbreviations 7-3 Controls Safety Guidelines 7-4 Fixed Speed Controls Packages 7-5 Three Phase AC Variable Speed
LOCK-OUT / TAG-OUT SAFETY TRAINING
 LOCK-OUT / TAG-OUT SAFETY TRAINING Introduction Welcome to Lock-out Tag-out Training "So I m on the job one day, doing some repair on a cutting machine.replacing a guide on the table. Pretty routine everything
LOCK-OUT / TAG-OUT SAFETY TRAINING Introduction Welcome to Lock-out Tag-out Training "So I m on the job one day, doing some repair on a cutting machine.replacing a guide on the table. Pretty routine everything
Automatic Fire Fighting Monitors
 Automatic Fire Fighting Monitors Fire Protection Solutions Automatic Fire Fighting Monitors Foreword Automatic monitors are devices used to deliver large amounts of water or water/foam solution to remote
Automatic Fire Fighting Monitors Fire Protection Solutions Automatic Fire Fighting Monitors Foreword Automatic monitors are devices used to deliver large amounts of water or water/foam solution to remote
Conventional Fire Detection and Extinguishant Control System Specification
 Conventional Fire Detection and Extinguishant Control System Specification Page 1 of 9 Scope Furnish a complete 24VDC Conventional, electrically supervised, combined fire detection and extinguishant release
Conventional Fire Detection and Extinguishant Control System Specification Page 1 of 9 Scope Furnish a complete 24VDC Conventional, electrically supervised, combined fire detection and extinguishant release
www.klmtechgroup.com TABLE OF CONTENT
 Page : 1 of 13 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT SCOPE 2 REFERENCES
Page : 1 of 13 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT SCOPE 2 REFERENCES
Kvaser Mini PCI Express User s Guide
 Kvaser Mini PCI Express User s Guide Copyright 2013-2014 Kvaser AB, Mölndal, Sweden http://www.kvaser.com Printed Sunday 28 th September, 2014 We believe that the information contained herein was accurate
Kvaser Mini PCI Express User s Guide Copyright 2013-2014 Kvaser AB, Mölndal, Sweden http://www.kvaser.com Printed Sunday 28 th September, 2014 We believe that the information contained herein was accurate
Introduction to Safety
 Introduction to Safety 1- Foreword Purpose of this section is to provide the machine manufacturer with a quick introduction on some standards related to machine safety, to clarify some basic principles
Introduction to Safety 1- Foreword Purpose of this section is to provide the machine manufacturer with a quick introduction on some standards related to machine safety, to clarify some basic principles
SAFETY MANUAL SIL SMART Transmitter Power Supply
 PROCESS AUTOMATION SAFETY MANUAL SIL SMART Transmitter Power Supply KFD2-STC4-(Ex)*, KFD2-STV4-(Ex)*, KFD2-CR4-(Ex)* ISO9001 2 3 With regard to the supply of products, the current issue of the following
PROCESS AUTOMATION SAFETY MANUAL SIL SMART Transmitter Power Supply KFD2-STC4-(Ex)*, KFD2-STV4-(Ex)*, KFD2-CR4-(Ex)* ISO9001 2 3 With regard to the supply of products, the current issue of the following
SAFETY MANUAL SIL Switch Amplifier
 PROCESS AUTOMATION SAFETY MANUAL SIL Switch Amplifier KCD2-SR-(Ex)*(.LB)(.SP), HiC282* ISO9001 2 With regard to the supply of products, the current issue of the following document is applicable: The General
PROCESS AUTOMATION SAFETY MANUAL SIL Switch Amplifier KCD2-SR-(Ex)*(.LB)(.SP), HiC282* ISO9001 2 With regard to the supply of products, the current issue of the following document is applicable: The General
Safety and functional safety A general guide
 Safety and functional safety A general guide This document is an informative aid only. The information and examples given are for general use only. They do not describe all the necessary details for implementing
Safety and functional safety A general guide This document is an informative aid only. The information and examples given are for general use only. They do not describe all the necessary details for implementing
Safe Machinery Handbook
 Safe Machinery Handbook 2 Contents Introduction...4 Why safety?...6 Legal framework...10 Risk assessment...16 Safe design and safeguarding...22 Functional Safety...30 Control system standards including
Safe Machinery Handbook 2 Contents Introduction...4 Why safety?...6 Legal framework...10 Risk assessment...16 Safe design and safeguarding...22 Functional Safety...30 Control system standards including
Routers and machining centres
 Routers and machining centres Safe working practices HSE information sheet Introduction This information sheet gives practical guidance on safe working practices when using CNC routers and machining centres,
Routers and machining centres Safe working practices HSE information sheet Introduction This information sheet gives practical guidance on safe working practices when using CNC routers and machining centres,
SOFTWARE-IMPLEMENTED SAFETY LOGIC Angela E. Summers, Ph.D., P.E., President, SIS-TECH Solutions, LP
 SOFTWARE-IMPLEMENTED SAFETY LOGIC Angela E. Summers, Ph.D., P.E., President, SIS-TECH Solutions, LP Software-Implemented Safety Logic, Loss Prevention Symposium, American Institute of Chemical Engineers,
SOFTWARE-IMPLEMENTED SAFETY LOGIC Angela E. Summers, Ph.D., P.E., President, SIS-TECH Solutions, LP Software-Implemented Safety Logic, Loss Prevention Symposium, American Institute of Chemical Engineers,
g9sp Programmable Safety controllers compact Stand-Alone Programmable controller NEW! example of System configuration G9SP
 Programmable Safety controllers g9sp G9SP compact Stand-Alone Programmable controller Stand-alone safety controller for small and mid-sized machinery Easy programming for complex safety control Three types
Programmable Safety controllers g9sp G9SP compact Stand-Alone Programmable controller Stand-alone safety controller for small and mid-sized machinery Easy programming for complex safety control Three types
Lockout/Tagout Training Program
 Lockout/Tagout Training Program (Student Handouts) Name Date This page intentionally left blank. Notes page: 2 Notes page: 3 Sample Written Program for Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout) 4 1910.147
Lockout/Tagout Training Program (Student Handouts) Name Date This page intentionally left blank. Notes page: 2 Notes page: 3 Sample Written Program for Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout) 4 1910.147
How to design safe machine control systems a guideline to EN ISO 13849-1
 How to design safe machine control systems a guideline to EN ISO 13849-1 SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden Johan Hedberg Andreas Söderberg Jan Tegehall SP Electronics SP REPORT 2011:81 How to design
How to design safe machine control systems a guideline to EN ISO 13849-1 SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden Johan Hedberg Andreas Söderberg Jan Tegehall SP Electronics SP REPORT 2011:81 How to design
OSHA Training Guidelines (An Unofficial Summary)
 OSHA Training Guidelines (An Unofficial Summary) Many standards promulgated by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) explicitly require the employer to train employees in the safety
OSHA Training Guidelines (An Unofficial Summary) Many standards promulgated by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) explicitly require the employer to train employees in the safety
SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mat Product information
 SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mat Product information SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mats Safety mats are used for the protection of man on machinery and plants with hazardous movements. Typical fields of application are,
SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mat Product information SMS 4 / SMS 5 safety mats Safety mats are used for the protection of man on machinery and plants with hazardous movements. Typical fields of application are,
Original instructions Tina 3A/Aps Adaptor unit
 Original instructions Tina 3A/Aps Adaptor unit ABB Jokab Safety Varlabergsvägen 11, SE-434 39 Kungsbacka, Sweden www.abb.com/jokabsafety Read and understand this document Please read and understand this
Original instructions Tina 3A/Aps Adaptor unit ABB Jokab Safety Varlabergsvägen 11, SE-434 39 Kungsbacka, Sweden www.abb.com/jokabsafety Read and understand this document Please read and understand this
Reducing Liability through Safety Labeling - Industrial Automation. Todd Fries
 Reducing Liability through Safety Labeling - Industrial Automation Todd Fries Disclaimer HellermannTyton makes no representation or warranty regarding code compliance. The user is solely responsible to
Reducing Liability through Safety Labeling - Industrial Automation Todd Fries Disclaimer HellermannTyton makes no representation or warranty regarding code compliance. The user is solely responsible to
Predictive Maintenance
 PART ONE of a predictive maintenance series Predictive Maintenance Overview Predictive maintenance programs come in all shapes and sizes, depending on a facility s size, equipment, regulations, and productivity
PART ONE of a predictive maintenance series Predictive Maintenance Overview Predictive maintenance programs come in all shapes and sizes, depending on a facility s size, equipment, regulations, and productivity
Basic Fundamentals Of Safety Instrumented Systems
 September 2005 DVC6000 SIS Training Course 1 Basic Fundamentals Of Safety Instrumented Systems Overview Definitions of basic terms Basics of safety and layers of protection Basics of Safety Instrumented
September 2005 DVC6000 SIS Training Course 1 Basic Fundamentals Of Safety Instrumented Systems Overview Definitions of basic terms Basics of safety and layers of protection Basics of Safety Instrumented
Section 1: Safety. General Safety. Recognizing Safety Precautions. Locking Out the Machine. Safety Circuits. Interpreting the Light Column
 Section 1: Safety General Safety Recognizing Safety Precautions Locking Out the Machine Safety Circuits Interpreting the Light Column Energy Isolating Device Location Floor Plan 2007 Douglas Machine Inc.
Section 1: Safety General Safety Recognizing Safety Precautions Locking Out the Machine Safety Circuits Interpreting the Light Column Energy Isolating Device Location Floor Plan 2007 Douglas Machine Inc.
Arc Flash Avoidance and its Application to Overhead Traveling Cranes
 Arc Flash Avoidance and its Application to Overhead Traveling Cranes Whitepaper August 2012 Jason Wellnitz, Controls Product Manager Material Handling Numerous technical papers, bulletins, magazine articles
Arc Flash Avoidance and its Application to Overhead Traveling Cranes Whitepaper August 2012 Jason Wellnitz, Controls Product Manager Material Handling Numerous technical papers, bulletins, magazine articles
SAFETY MANUAL SIL RELAY MODULE
 PROCESS AUTOMATION SAFETY MANUAL SIL RELAY MODULE KFD0-RSH-1.4S.PS2 ISO9001 3 With regard to the supply of products, the current issue of the following document is applicable: The General Terms of Delivery
PROCESS AUTOMATION SAFETY MANUAL SIL RELAY MODULE KFD0-RSH-1.4S.PS2 ISO9001 3 With regard to the supply of products, the current issue of the following document is applicable: The General Terms of Delivery
SECTION 13850 DETECTION AND ALARM
 SECTION 13850 DETECTION AND ALARM PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Section Includes 1. Control Panel 2 Associated Equipment B. Products Installed But Not Supplied Under This Section 1. Section 16140 - Wiring
SECTION 13850 DETECTION AND ALARM PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Section Includes 1. Control Panel 2 Associated Equipment B. Products Installed But Not Supplied Under This Section 1. Section 16140 - Wiring
Power presses: A summary of guidance on maintenance and thorough examination
 Power presses: A summary of guidance on maintenance and thorough examination INTRODUCTION Power presses are dangerous machines which have caused many accidents over the years. The causes include poor maintenance
Power presses: A summary of guidance on maintenance and thorough examination INTRODUCTION Power presses are dangerous machines which have caused many accidents over the years. The causes include poor maintenance
Who sets the rules for electrical testing and safety?
 Who sets the rules for electrical testing and safety? Application Note Alphabet soup There s no question that electrical safety is a key concern for electricians and engineers, their employers, unions
Who sets the rules for electrical testing and safety? Application Note Alphabet soup There s no question that electrical safety is a key concern for electricians and engineers, their employers, unions
Achieving Functional Safety with Global Resources and Market Reach
 Achieving Functional Safety with Global Resources and Market Reach 0A 0B Burner management systems Combustion controls Electric vehicle components (on-board, off board) Electrosensitive equipment Elevator
Achieving Functional Safety with Global Resources and Market Reach 0A 0B Burner management systems Combustion controls Electric vehicle components (on-board, off board) Electrosensitive equipment Elevator
Tina 2A/B Adaptor unit
 Original instructions Tina 2A/B Adaptor unit ABB Jokab Safety Varlabergsvägen 11, SE-434 39 Kungsbacka, Sweden www.abb.com/jokabsafety Read and understand this document Please read and understand this
Original instructions Tina 2A/B Adaptor unit ABB Jokab Safety Varlabergsvägen 11, SE-434 39 Kungsbacka, Sweden www.abb.com/jokabsafety Read and understand this document Please read and understand this
Automation and Systems Technology. LABCONTROL TFM/TPM User Manual TroxMConnect Operating Software. 1. Introduction 1. 2. Software Installation 2
 1. Introduction 1 2. Software Installation 2 2.1 System Requirements 2 2.2 TroxMConnect Installation 2 2.3 Connection to the PC 3 3. TroxMConnect Description 4 3.1 Starting the Software 4 3.2 Layout 4
1. Introduction 1 2. Software Installation 2 2.1 System Requirements 2 2.2 TroxMConnect Installation 2 2.3 Connection to the PC 3 3. TroxMConnect Description 4 3.1 Starting the Software 4 3.2 Layout 4
FACILITY SAFETY SIGNAGE GUIDE: 10 SIGNS TO SPOT DURING A PLANT WALKTHROUGH
 FACILITY SAFETY SIGNAGE GUIDE: 10 SIGNS TO SPOT DURING A PLANT WALKTHROUGH Safety signs are the primary way to communicate important warnings and messages to your employees, on-site contractors and other
FACILITY SAFETY SIGNAGE GUIDE: 10 SIGNS TO SPOT DURING A PLANT WALKTHROUGH Safety signs are the primary way to communicate important warnings and messages to your employees, on-site contractors and other
ANSI/RIA R15.06: 2012 - an introduction to Robot and Robot System Safety
 ANSI/RIA R15.06: 2012 - an introduction to Robot and Robot System Safety Roberta Nelson Shea Global Marketing Manager, Safety Components March 2016-5058-CO900H ANSI/RIA R15.06-2012 RIA (print) www.robotics.org
ANSI/RIA R15.06: 2012 - an introduction to Robot and Robot System Safety Roberta Nelson Shea Global Marketing Manager, Safety Components March 2016-5058-CO900H ANSI/RIA R15.06-2012 RIA (print) www.robotics.org
Preventa Machine Safety Products
 Preventa Machine Safety Products Catalog 2009 200 Supplement Safety Relay Modules 2 Contents Preventa safety relay modules Selection guide 2 Electrical Ratings 6 Types XPSAC and XPSAXE For Emergency stop
Preventa Machine Safety Products Catalog 2009 200 Supplement Safety Relay Modules 2 Contents Preventa safety relay modules Selection guide 2 Electrical Ratings 6 Types XPSAC and XPSAXE For Emergency stop
Lockout-Tagout Training for University @ Albany Employees Control of Hazardous Energy OSHA standard 1910.147
 Lockout-Tagout Training for University @ Albany Employees Control of Hazardous Energy OSHA standard 1910.147 University @ Albany SUNY Office of Environmental Health & Safety 518/442-3495 October 2010 Primary
Lockout-Tagout Training for University @ Albany Employees Control of Hazardous Energy OSHA standard 1910.147 University @ Albany SUNY Office of Environmental Health & Safety 518/442-3495 October 2010 Primary
Installation guide H-5500-8554-03-A. HSI hardwired system interface
 Installation guide H-5500-8554-03-A HSI hardwired system interface 2008-2011 Renishaw plc. All rights reserved. This document may not be copied or reproduced in whole or in part, or transferred to any
Installation guide H-5500-8554-03-A HSI hardwired system interface 2008-2011 Renishaw plc. All rights reserved. This document may not be copied or reproduced in whole or in part, or transferred to any
Safe Torque Off Option (Series B) for PowerFlex 40P and PowerFlex 70 Enhanced Control AC Drives
 User Manual Safe Torque Off Option (Series B) for PowerFlex 40P and PowerFlex 70 Enhanced Control AC Drives Catalog Number 20A-DG01 Topic Page General Description 2 What Is the DriveGuard Safe Torque Off
User Manual Safe Torque Off Option (Series B) for PowerFlex 40P and PowerFlex 70 Enhanced Control AC Drives Catalog Number 20A-DG01 Topic Page General Description 2 What Is the DriveGuard Safe Torque Off
Lockout - Tagout Program
 Created by: Nora Velazquez Date: 02/13/03 Approved by: Nora Velazquez Supersedes: New Lockout - Tagout Program 3.1 Purpose 3.1.1 The safe control of hazardous energy is the purpose of the Lockout- Tagout
Created by: Nora Velazquez Date: 02/13/03 Approved by: Nora Velazquez Supersedes: New Lockout - Tagout Program 3.1 Purpose 3.1.1 The safe control of hazardous energy is the purpose of the Lockout- Tagout
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO NC MACHINE TOOLS
 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO NC MACHINE TOOLS Structure 1.1 Introduction Objectives 1.2 NC Machines 1.2.1 Types of NC Machine 1.2.2 Controlled Axes 1.2.3 Basic Components of NC Machines 1.2.4 Problems with Conventional
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO NC MACHINE TOOLS Structure 1.1 Introduction Objectives 1.2 NC Machines 1.2.1 Types of NC Machine 1.2.2 Controlled Axes 1.2.3 Basic Components of NC Machines 1.2.4 Problems with Conventional
