THE APPLICATION OF FINITE FOURIER TRANSFORMS TO ANALOG COMPUTER SIMULATIONS. Eric Liban. Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corp. Bethpage, New York
|
|
|
- Aubrie Walters
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 55 THE APPLICATION OF FINITE FOURIER TRANSFORMS TO ANALOG COMPUTER SIMULATIONS Eri Liban Grumman Airraft Engineering Corp. Bethpage, New York SUIIl!Ilary An Analog Computer tehnique for the solution of ertain lasses of boundary value problems of partial differential equation based on Finite Fourier Transforms is presented, whih requires onsiderably less omputer omponents than onventional finite differene methods. The derivation of the Finite Fourier Transform method is briefly stated and then applied to analog omputer simulations of heat transfer equations with linear and nonlinear boundary onditions. Introdution A well known method for the solution of ordinary linear differential equations with onstant oeffiients is the Laplae transform method whih redues the differential equation to an algebrai equation. The solution of the latter is a funtion of a parameter "s" and given initial onditions, and its inverse Laplae transform is the solution of the differential equation. This method is easily extended to partial differential equations in two independent variables. A Laplae transform with respet to one of the independent variables gives an ordinary differential equation, whose solution is the Laplae transform of the funtion satisfying the partial differential equation and its initial and boundary onditions. The inappliability of this method for analog omputations arises from the fat that the inverse Laplae transform, a neessary step to extrat the solution, is an integration over an infinite path in the omplex domain. To solve partial differential equationson an Analog Computer by a transform method the inverse transform must be obtainable by operations in the real domain only. The partiular transform disussed in this paper is the Finite Fourier Transform, whih is appliable to equations in whih only the even order derivatives (of the funtion) with respet to the transformed variable appear. The heat equation, wave equation and bending beam equation are of suh nature. Many other transforms exist whih may be used for other types of equations. (Refs. 1,, and 3). A feature, whih makes the Finite Transform a very eonomial method for analog omputers, is that the inverse transform may be solved only for regions of interest. The trunation error in the analog simulation may be made smaller than the error in the amplifiers themselves, and therefore the solution obtained by the Finite Fourier Transform method is the exat solution within the auray of the Analog Computer; and the bounds on the deviation from the true solution an be stated preisely in terms of the usually small amplifier noise and integrator drifts. Finite Fourier Transforms The transform exists for all bounded, pieewise ontinuous funtions over a finite interval. The extension of a ontinuous funtion F(x) defined for o < x <~, into an odd periodi funtion F(x) ;ith period ~ may be expressed by the Fourier series ""' F(x) o f (n)sin nx. s The oeffiients are given by I ~ f (n) s F(x) sin nx dx, o,,.... (1) () From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
2 56 ANALOG APPLICATIONS AND TECHNIQUES This set of oeffiients, defined by Eq. (), is the Finite Fourier Sine Transform of t{x), and the inverse Sine Transform is F{~) as defined by Eq. (l). Note ~hat F(x) = F(x) for 0 < x <~. But F(O) and F(~) will always equal zero, whatever F{O) and F{~) may be. This follows from the extension of F(x) into an odd funtion and the property of Fourier series to onverge at finite disontinuities to the average value of the limits the funtion approahes from the right and left respetively. The following expression is obtained by two suessive integrations by parts and a substitution using Eq. (): r - n f (n) s o (3) + n[f{o) - (-l)~{~)]. E~panding F{x) tion F{x) of period Fourier series into an even fun- ~ leads to the - n f (n) - F' (0) + (-l) ~' (71") (6) by integrating the left side by parts twie and substituting Eq. (5), F'{O) and F' (71") are the values of the derivative of F(x) at x = 0 and 71", respetively. Two other useful Finite Fourier Transforms are stated below: Finite A-Transform n-l F{x) sin -- x dx,,,.... Inverse A-Transform ()() (7) F(x) 1. f (O) + ~ 71" C 71" f (n)os nx (4) where the set of oeffiients f(n) is the Finite Fourier Cosine Transform (FPC~ given by f (n) 71" J F(x)os nx dx, o n=o, 1,,.... (5) The inverse FFCT is the funtion F(x) as given by Eq. (4). Here F{x) = F{x) fqr the losed interval 0 < x < 71"; while df/dx = df/dx holds generally only fqr o < x < 71", sine the derivative of F may be disontinuous at x = n71". The following relations are obtained for the FFCT: and F{x) S1.n n-l fa (n) sin -- x,~_~ n-l + (n -l)f(0) - (-l)~' (71"). Finite ~-Transform o...,.,_, \ ).LA \11) 71" n-l f (n) F(x)os -- x dx, ~ J,,.... (8) (9) (10) From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
3 THE APPLICATION OF FINITE FOURIER TRANSFORMS TO ANALOG COMPUTER SIMULATIONS 57 and Inverse I-L-Transform L '=I n-1 F(x) 7T" fl-l (n) os -- x (11} r7t"..lm 1'\ 1 dx (n-1) fl-l(n) dx os -- x J o U l' Ln-.l - F' (0) + (-1)~(7T") (1) Only the relations expressing the transforms of the seond derivative of a funtion, in terms of the transform of the funtion and its boundary values, were shown. However, relations may be obtained for all even order derivatives. For an elementary disussion of the Finite Fourier Transform see Churhill, Modern Operational Mathematis in Engineering.~ For a more advaned treatise on the Finite Fourier Transform and other Integral Transforms see bibliography. Analog Simulations of the Heat Equation The Re-entry Problem The Finite Fourier Transform method is applied first to the one-dimensional heat equation with boundary onditions enountered in the "re-entry problem". Let ~ be the spae oordinate of a onedimensional slab of length L, whih is the idealization of a longitudinal setion of the nose one of a missile, T the time and T(T,~) the temperature. At ~ = 0 a heat input or heat flux is given, while at ~ = L the slab is assumed to be insulated, that is, the temperature gradient is zero at ~ = L. In this problem the main interest is in the temperature of the fae ~ = 0, to determine whether it rises above or remains below the melting point. Also of onern is the temperature at ~ = L, whih must remain below the melting temperature of the bak-up struture. The mathematial statement of this problem for homogeneous slabs with temperature independent thermal onstants and uniform initial temperature TO dt d T is given by dt = a d~ ' o ~ ~ ~L T > 0 (13) Initial Condition: Boundary Conditions: T(O, ~) TO (14) dt k d~ = - q(t) at ~ 0 dt d~ = 0 at L. The symbols used in the above equations are defined in the following table: T _ temperature - or T == time - se ~ _ spae oordinate - in a == k == thermal diffusivity - in/se (15) thermal ondutivity - BTU/se-in-oR q == heat input rate per unit area - BTU/se-in The linear heat equation may be solved for the temperature deviation from the initial temperature, expressed by U(T, ~) = T(T, ~) - T 0 (16) Equation (16) and the substitutions x = E ~ t 7T" L, = a T, L transform Eqs. (13), (14), and (15) to the equation du d U (17) dt = ' o < x < 7T", t > 0 (18) dx From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
4 58 ANALOG APPLICATIONS AND TECHNIQUES Initial Condition: Boundary Conditions: u(o, x) o. (19) eu L ex = - 11"k q(t) - - Q(t) at x = 0 o at x = 11" (0) Equation (18) and boundary onditions as shown in Eq. (0) indiate the use of the Finite Fourier Cosine Transform with respet to x. The FFCT of u(t, x) is given by f (t, n) I~ u(t, x) os nx dx, o (1) n=o, 1, under disussion, equals zero. If the problem were solved for the temperature T with initial onditions T(O, x) = TO, then the initial onditions for Eqs. (3) would still all be zero with the exeption of f(t, 0), sine the integral of a onstant times os nx between 0 and 11" always vanishes when n j O. When the initial temperature distribution is a funtion of x, then the initial onditions for f(t, n) may be either readily omputable by hand or, easily evaluated on the analog omputer. The set of solutions f(t, n) of Eqs. (3) form the FFCT of u(t, x); i.e., they are the Fourier oeffiients as a funtion of time t of the temperature u(t, x). The inverse FFCT, as given by Eq. (4), for x = 0 and x = 11" respetively, beomes: u (t, 0) 1 f (t, 0) + 1 \ f (t, n) (5) 11" 11" ~ C 00 It is easily seen that eu et os nx dx n=o, 1,.... f (t, n), () u(t, 11") 1 f (t 11" C ' +1 0) 00 (_l)n f (t, n) L 11" (6) By multiplying both sides of Eq. (18) with os nx dx and integrating from 0 to 11" using the notation defined hy Eqs. (1) and (), the differential equations for the terms of the FFCT are formed. Equation (6) with the given Boundary Conditions as shown in Eq. (0) gives: f (t, n) n f (t, n) + Q(t) n=o, 1,, with initial onditions: f (0, n) = 0, (3) n=o, 1,,... (4) The initial ondition of f(t, n) equals the FFCT of the initial ondition of u(t, x), whih for the ase Clearly, it is not possible to solve Eqs. (3) for all n from 0 to 00. However, the inverse Ftnite Fouri.er Cosine Transform is a fairly rapidly onvergent series, beause it is a ontinuous funtion for all x. The oeffiients behave like 1/n for inreasing n. When Q(t) > 0 for all t, it an easily be seen from Eqs. (3) that f(t, n) ~ 0 for all nand t. Hene,there exists an N for any E, no matter how small, suh that maxiu(t, 0) - 1 f 11" (t, 0) (7) N _ 1 f (t, n) 1 < E 11" C L From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
5 THE APPLICATION OF FINITE FOURIER TRANSFORMS TO ANALOG COMPUTER SIMULATIONS 59 That is, there exists an N the trunation error 00 EO max L 'IT n=n+l suh that f (t, n) (8) will be smaller than the auray of the omputer or some other desired auray ompatible with analog omputer harateristis. The maximum absolute errors in the omputer solutions of u(t, x) 1 f (t, 0) 'IT L N + 'IT C f (t, n)os nx (9) for x ~ 0, will all be smaller than EO' sine for positive f(t, n) max 'IT 00 n=n+l < max l. 'IT f (t, n) os nx 00 n=n+l f (t, n). (30) The number of Fourier oeffiients to be generated on the analog omputer may therefore be obtained by an a priori estimate or by inreasing N until f(t, N) ~ 0 for all t. Figure 1 shows the analog omputer setup for the Finite Fourier method solution of Eqs. (18), (19), and (0) with N = 7. For test purposes the heat input Q(t) was a steep saw tooth and it was found that the temperature at x = 0 for all time t differed always by less than 1% from the analytially obtained exat solution. The slab assumes a uniform steady state temperature when the heat input is of finite duration. The Fourier Transform method of simulation will always give the orret steady state temperature regardless of the number of Fourier oeffiients used. This an easily be seen from the fat that the output voltages of all the integrators will eventually be zero, when Q(t) = 0, exept the output of the integrator generating f(t, 0). When the slab is at uniform onstant temperature, then the Fourier series of the temperature distribution is simply the onstant (l/'it)f(t, 0). Convetive Boundary Condition The boundary with onvetive heat transfer may be either ~ = 0 or ~ = L, or both. In addition a heat input q(t) may be given. In this setion the analog simulation of the heat equation is shown for the following boundary onditions: k dt d~ - q(t) at ~ 0 (31) k dt h(t(t, L) - T.) at ~ L, (3) d~ 1 where h - onvetive heat transfer oeffiient - BTU/inse of. The boundary onditions, stated in words, mean that the bar is heated at the rate q(t) at the fae ~ = 0 while the fae ~ = L is in ontat with a substane at temperature Ti' whih may be a funtion of time, and heat is transferred from the bar to this substane aording to Eq. (3). Let the bar be initially at a uniform onstant temperature T(O, ~) = TO. With the substitutions Eqs. (16) and (17), ui = Ti - TO, and (L/'lTk)q(t) = Q(t) the problem is stated: Initial Condition: Boundary Conditions: t > 0. (33) u(o, x) o. (34) - Q(t) at x = 0 (35) From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
6 60 ANALOG APPLICATIONS AND TECHNIQUES du L [ ] -- = - h u(t ~) - u. dx ~, 1 at x = ~. (36) Sine the boundary onditions presribe the derivatives at x ~ 0 and x ~ ~, the use of the Finite Fourier Cosine Transform is indiated; and from Eq. (6) and the above boundary onditions is obtained the set of differential equations f (t, n) = - n f (t, n) + Q(t) The Flat Plate Radiating into Vauum The term IIf1at p1ate" is taken here to mean a solid slab bounded by a pair of parallel planes ; = - Land ; = L. The initial temperature TO is uniform and Stefan-Boltzmann radiation into vauum takes plae at the two faes ~ = ± L. Clearly, the temperature distribution will be symmetrial about ~ = 0 and therefore it is more onvenient to state the problem as follows: + (-1) n b h f u (t. ~) - u. 1 ~ L' 1J (37) dt d T h = a d~ 0 < ~ L T ~ > 0 (39) n=o, 1,,.... The essential differene between Eqs. (37) and the equations for the Fourier Transform of the heat equation with insulated boundary Eqs. (3) is that now the boundary ondition is a funtion of the temperature at x =~. But u(t,~) is given by Eq. (6), as in the previous example and may be generated ontinuously. Hene the last term of Eq. (37) is easily formed and fed bak to the appropriate integrators in the simulation. The analog iruit for the heat equation with a heat input on one fae and a onvetive heat transfer at the other fae is shown in Fig.. The FFCT was solved for n = 0 to n = 7. Radiation Heat Transfer 5 Examples hosen for this type of boundary onditions are a flat plate and a sphere radiating in a vauum. The boundary ondition for radiation heat transfer at the fae ~ = L is given by T_.!.....: _1 Condition:.1.U.1.L..1.Cl.1. Boundary Conditions: T(O, ~) TO (40) dt d~ 0 at ~ 0 (41) - oe[t(t, L)]4 at ~ L (4) Equation (41) follows from the symmetry ondition, and Eq. (4) is obtained from Eq. (38) by letting Ta = 0 for radiation into vauum. Sine Eq. (4) is nonlinear it an no longer be solved for the temperature deviation from the initial temperature TO' It is probably just as simple to simulate the original equations, and ertainly the results would be more easily interpreted; however, for simpliity of presentation let where o _ Stefan-Bo1tzmann's onstant - BTU/se in R4 E _ emissivity - dimensionless (38) and set x = 1L ~ and t = a L T L L g 3 b EO U o 'Tf 1< (43) (44) Ta - temperature to whih surfae radiates - or. and u (45) From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
7 THE APPLICATION OF FINITE FOURIER TRANSFORMS TO ANALOG COMPUTER SIMULATIONS 61 The problem may now be stated here Radiating Into Vauum Initial Condition: t > 0 (46) The heat equation for a sphere with temperature distribution a funtion of time T and distane p from the enter of the sphere, expressed in polar oordinates is given by Boundary Conditions: u(o, x) 1 (47) au 0 at 0 ax x = (48) au 4 ax - gu (t, 7r) at x = 7r (49) The differential equations for the FFCT are derived in the same way as in the previous examples and are given by The initial the FFCT's u(o, x) = 1 equals zero term in Eq. 1y from u(t, 7r) - n f (t, n) n 4( - (-1) gu t, If) n=o, 1,,.... (50) onditions of f(t, n) are of u(o, x), whih for equals 7r when n = 0, and for all n ~ O. The last (50) is generated ontinuous f (t 7r ' 7r 0) N (-1) n f (t, n) I (51) raised to the 4th power, whih in the simulation indiated in Fig. 3 was performed by two suessive servo-multipliations. The simulation proved to be stable and in agreement with the solution obtained by Abarbane1. 5 If boundary Eq. (4) were replaed by Eq. (38), the simulation would differ only slightly. at a a ( at) JT = 0 op p ap By the hange of variables,- (5) r = 7r 7r R t..i.. p = a T, u = r (53) R TO where R is the radius of the sphere, Eq. (5) beomes for 0 < r < 7r and t > O. Initial Condition from Eq. (53): (54) u(o, r) = r (55) The radiating boundary ondition as given in Eq. (38) beomes au 4 or = u(t, 7r) - gu (t, If) at r = 7r (56) where Boundary Condition: g (57) u(t, 0) = 0 at r = 0 (58) Equation (58) insures that the temperature T(T, 0) remains finite. In this ase the temperature is presribed on the boundary r = 0 while at the boundary r = 7r the temperature gradient au/ar is a given funtion of the temperature. The Finite A-Transform, as given by Eq. (7), is to be used for these boundary From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
8 6 ANALOG APPLICATIONS AND TECHNIQUES onditions. From Eqs. (9), (56), and (58) one obtains the following set of differential equations Sine initially u(t, If) = If from Eq. (53), one an perform a steady state hek on the omputer setup and on the onvergene of the trunated series; namely, from Eqs. (61) and (64) - (-1) n [ u ( t, If) - gu 4 ( t, If)] (59) n 1,,.... N 1 I 1 If (n - ~) ~ Ji (65) From Eq. (8) u(t, r) and ()() ()() f,(t, n)sin(n - ~)r 1\ (60) u(t, If) ~\ "L -( -1) n fa (t, n). (61) Equation (61) is used in the simulation to form the last term in Eq. (59). From Eq. (53) the temperature at p = R is given by T(t, R) TO -:;- u(t, If). (6) The ini.tial onditions f~\(o, n) are obtained from Eqs. (55) and (7) by On the analog omputer (as well as numerially) % auray T~y be ahieved with eight oeffiients. The analog simulation is shown in Fig. 4. Conluding Remarks Problems with onvetive as well as radiating boundary onditions presribed may be solved by this method by the obvious extension of ombining the onvetive term h(u - ui) and the radiation term g (u4 - ua4) in the differential equations generating the Finite Fourier Transforms. The temperature at points other than the boundary, if they should be needed, may be readily obtained by summing the Fourier oeffiients weighted by their proper trigonometri terms. This simply requires a potentiometer for eah term and an inverter when neessary. For onvetion and for radiation the temperature at the boundary should be as aurate as possible, beause the boundary onditions themselves are given by them. The Finite Fourier Transform method whih gives the exat boundary temperature ~AJithin the omputer auray"" an be very suessfully applied. lf f o r sin(n - ~)r dr,,,.., N whih upon integration beomes 1 -( ) (_l)n n - ",,..., N (63) (64) The most widely used methods for the solution of partial differential equations are based on finite differenes. These methods require ertain assumptions about where the finite differene equals the derivative whih by neessity have to be most loosely made on the boundaries; the very points where the greatest auray is required. One must form many grid points, at least, near the boundary in order for the solution of the differene equation to ome lose to the solution of the differential equations. For substanes with low ondutivity, as used for nose ones in missiles, the spaing of the grid points beome even more From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
9 THE APPLICATION OF FINITE FOURIER TRANSFORMS TO ANALOG COMPUTER SIMULATIONS 63 ritial. The Finite Fourier Transform method may also be used for equations with more than one spae variable. Stephens and Karplus6 have employed this transform for analog simulations of two-dimensional diffusion equations. Two approahes are given in their paper. In the first only one spae variable is transformed, whih redues the given problem to a partial differential equation with one independent spae variable. This they solve then by a finite differene method. In the seond approah the dependent funtion is transformed with respet to both spae variables, thus produing a system of ordinary differential equations. In priniple, this method may be extended to analog simulations of heat equations in three spae variables. The number of ordinary differential equations, however, beomes quite large when Fourier transformations are performed with respet to three variables. Their analog simulation would be pratial only if the analog omputer is apable of time sharing or repetitive modes of operation, and possesses dynami storage elements. The Finite Fourier Transform method may also be a very effiient tehnique for the solution of multidimensional heat equations on a linked Analog-Digital omputing system Churhill, IlModern Operational Mathematis in Engineering,1I MGraw-Hill, New York, Abarbanel, P.S., "Time Dependent Temperature Distribution in Radiating Solids,1I Journal of Mathematis and Physis, Vol. 30, Stephens, P.A., Jr. and Karplus W.J., IIAppliation of Finite Integral Transforms to Analog Simulations,1I AlEE Transations, Vol. 78, Part I, Burns, A.J. and Kopp, R.E., IICombined Analog-Digital Simulation,1I Proeedings of the Eastern Joint Computer Conferene, Deember The number of amplifiers required for the solution of the heat equation by the Finite Fourier Transform method is about one-half to one-fifth of the number of amplifiers needed for a finite differene simulation of equal auray. The ratio depends on the shape of the heat input urve, the thermal onstants, and the physial dimensions. Referenes Sneddon. I.N. "Fourier Transforms. II MGraw-Hill, New York, ' Tranter, C.J., "Integral Transforms in Mathematial Physis,1I Wiley & Sons, In., New York, Leonard, J.L., flintegral Transforms for Appliation to Partial Differential Equations,1I Grumman Airraft Engineering Corporation, Researh Department Report RE-I03, September From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
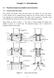
10 64 ANALOG APPLICATIONS AND TECHNIQUES -Q (t) J _ 7 f,. (t,7) ~~ I 'lj I 7r'( I~~I u(t,o) ~ Fig. 1 - Analog Simulation Of The Re-entry Problem Fig. - Heat Equation With Convetive Boundary Conditions From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
11 THE APPLICATION OF FINITE FOURIER TRANSFORMS TO ANALOG COMPUTER SIMULATIONS _gu 4 (t,7t) 65 Fig. 3 - Flat Plate Radiating Into Vauum I.e.: 40.0 Fig. 4 - Sphere Radiating Into Vauum From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
12 From the olletion of the Computer History Museum (
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
cos t sin t sin t cos t
 Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I
 DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
HEAT EXCHANGERS-2. Associate Professor. IIT Delhi E-mail: prabal@mech.iitd.ac.in. P.Talukdar/ Mech-IITD
 HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Isaac Newton. Translated into English by
 THE MATHEMATICAL PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL PHILOSOPHY (BOOK 1, SECTION 1) By Isaa Newton Translated into English by Andrew Motte Edited by David R. Wilkins 2002 NOTE ON THE TEXT Setion I in Book I of Isaa
THE MATHEMATICAL PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL PHILOSOPHY (BOOK 1, SECTION 1) By Isaa Newton Translated into English by Andrew Motte Edited by David R. Wilkins 2002 NOTE ON THE TEXT Setion I in Book I of Isaa
Draft Notes ME 608 Numerical Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer
 Draft Notes ME 608 Numerial Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer Instrutor: Jayathi Y. Murthy Shool of Mehanial Engineering Purdue University Spring 2002 1998 J.Y. Murthy and S.R. Mathur. All Rights
Draft Notes ME 608 Numerial Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer Instrutor: Jayathi Y. Murthy Shool of Mehanial Engineering Purdue University Spring 2002 1998 J.Y. Murthy and S.R. Mathur. All Rights
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
The Reduced van der Waals Equation of State
 The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsica, vol. 21, no. 4, Dezembro, 1999 469. Surface Charges and Electric Field in a Two-Wire
 Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
1.3 Complex Numbers; Quadratic Equations in the Complex Number System*
 04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
5.2 The Master Theorem
 170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
USA Mathematical Talent Search. PROBLEMS / SOLUTIONS / COMMENTS Round 3 - Year 12 - Academic Year 2000-2001
 USA Mathematial Talent Searh PROBLEMS / SOLUTIONS / COMMENTS Round 3 - Year - Aademi Year 000-00 Gene A. Berg, Editor /3/. Find the smallest positive integer with the property that it has divisors ending
USA Mathematial Talent Searh PROBLEMS / SOLUTIONS / COMMENTS Round 3 - Year - Aademi Year 000-00 Gene A. Berg, Editor /3/. Find the smallest positive integer with the property that it has divisors ending
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS
 J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA
 WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
Trade Information, Not Spectrum: A Novel TV White Space Information Market Model
 Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
10 UNSTEADY FLOW IN OPEN CHANNELS
 0 UNTEY FLOW IN OEN CHNNEL 0. Introdution Unsteady flow in open hannels differs from that in losed onduits in that the eistene of a free surfae allows the flow ross-setion to freely hange, a fator whih
0 UNTEY FLOW IN OEN CHNNEL 0. Introdution Unsteady flow in open hannels differs from that in losed onduits in that the eistene of a free surfae allows the flow ross-setion to freely hange, a fator whih
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
Relativity in the Global Positioning System
 Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: ashby@boulder.nist.gov July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: ashby@boulder.nist.gov July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
A Robust Optimization Approach to Dynamic Pricing and Inventory Control with no Backorders
 A Robust Optimization Approah to Dynami Priing and Inventory Control with no Bakorders Elodie Adida and Georgia Perakis July 24 revised July 25 Abstrat In this paper, we present a robust optimization formulation
A Robust Optimization Approah to Dynami Priing and Inventory Control with no Bakorders Elodie Adida and Georgia Perakis July 24 revised July 25 Abstrat In this paper, we present a robust optimization formulation
Intuitive Guide to Principles of Communications By Charan Langton www.complextoreal.com
 Intuitive Guide to Priniples of Communiations By Charan Langton www.omplextoreal.om Understanding Frequeny Modulation (FM), Frequeny Shift Keying (FSK), Sunde s FSK and MSK and some more The proess of
Intuitive Guide to Priniples of Communiations By Charan Langton www.omplextoreal.om Understanding Frequeny Modulation (FM), Frequeny Shift Keying (FSK), Sunde s FSK and MSK and some more The proess of
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
Heat Transfer and Energy
 What is Heat? Heat Transfer and Energy Heat is Energy in Transit. Recall the First law from Thermodynamics. U = Q - W What did we mean by all the terms? What is U? What is Q? What is W? What is Heat Transfer?
What is Heat? Heat Transfer and Energy Heat is Energy in Transit. Recall the First law from Thermodynamics. U = Q - W What did we mean by all the terms? What is U? What is Q? What is W? What is Heat Transfer?
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
The Application of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Zoom Function of a Digital Camera
 (IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
(IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
Dispersion in Optical Fibres
 Introdution Optial Communiations Systems Dispersion in Optial Fibre (I) Dispersion limits available bandwidth As bit rates are inreasing, dispersion is beoming a ritial aspet of most systems Dispersion
Introdution Optial Communiations Systems Dispersion in Optial Fibre (I) Dispersion limits available bandwidth As bit rates are inreasing, dispersion is beoming a ritial aspet of most systems Dispersion
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Procurement auctions are sometimes plagued with a chosen supplier s failing to accomplish a project successfully.
 Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Convergence of c k f(kx) and the Lip α class
 Convergene of and the Lip α lass Christoph Aistleitner Abstrat By Carleson s theorem a trigonometri series k osπkx or k sin πkx is ae onvergent if < (1) Gaposhkin generalized this result to series of the
Convergene of and the Lip α lass Christoph Aistleitner Abstrat By Carleson s theorem a trigonometri series k osπkx or k sin πkx is ae onvergent if < (1) Gaposhkin generalized this result to series of the
Application of Fourier Transform to PDE (I) Fourier Sine Transform (application to PDEs defined on a semi-infinite domain)
 Application of Fourier Transform to PDE (I) Fourier Sine Transform (application to PDEs defined on a semi-infinite domain) The Fourier Sine Transform pair are F. T. : U = 2/ u x sin x dx, denoted as U
Application of Fourier Transform to PDE (I) Fourier Sine Transform (application to PDEs defined on a semi-infinite domain) The Fourier Sine Transform pair are F. T. : U = 2/ u x sin x dx, denoted as U
International Journal of Supply and Operations Management. Mathematical modeling for EOQ inventory system with advance payment and fuzzy Parameters
 nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
Pattern Recognition Techniques in Microarray Data Analysis
 Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA faramarz@sienes.sdsu.edu
Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA faramarz@sienes.sdsu.edu
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
In this chapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use directed graphs.
 Chapter 19 State Diagrams In this hapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use direted graphs. 19.1 Introdution State diagrams are a type of direted graph, in whih the graph nodes
Chapter 19 State Diagrams In this hapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use direted graphs. 19.1 Introdution State diagrams are a type of direted graph, in whih the graph nodes
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
Nodal domains on graphs - How to count them and why?
 Proeedings of Symposia in Pure Mathematis Nodal domains on graphs - How to ount them and why? Ram Band, Idan Oren and Uzy Smilansky, Abstrat. The purpose of the present manusript is to ollet known results
Proeedings of Symposia in Pure Mathematis Nodal domains on graphs - How to ount them and why? Ram Band, Idan Oren and Uzy Smilansky, Abstrat. The purpose of the present manusript is to ollet known results
INVESTIGATION OF STABILITY ON NONLINEAR OSCILATIONS WITH ONE DEGREE OF FREEDOM
 91 Kragujeva J. Math. 25 (2003) 91 96. INVESTIGATION OF STABILITY ON NONLINEAR OSCILATIONS WITH ONE DEGREE OF FREEDOM Julka Knežević-Miljanović 1 and Ljubia Lalović 2 1 Mathematis faulty of Belgrade, Serbia
91 Kragujeva J. Math. 25 (2003) 91 96. INVESTIGATION OF STABILITY ON NONLINEAR OSCILATIONS WITH ONE DEGREE OF FREEDOM Julka Knežević-Miljanović 1 and Ljubia Lalović 2 1 Mathematis faulty of Belgrade, Serbia
Propagation in Lossy Rectangular Waveguides
 10 Propagation in Lossy Retangular Waveguides Kim Ho Yeap 1, Choy Yoong Tham, Ghassan Yassin 3 and Kee Choon Yeong 1 1 Tunku Abdul Rahman University Wawasan Open University 3 University of Oxford 1, Malaysia
10 Propagation in Lossy Retangular Waveguides Kim Ho Yeap 1, Choy Yoong Tham, Ghassan Yassin 3 and Kee Choon Yeong 1 1 Tunku Abdul Rahman University Wawasan Open University 3 University of Oxford 1, Malaysia
VOLUME 13, ARTICLE 5, PAGES 117-142 PUBLISHED 05 OCTOBER 2005 DOI: 10.4054/DemRes.2005.13.
 Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Conversion of short optical pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
Waveguides. 8.14 Problems. 8.14. Problems 361
 8.4. Problems 36 improving liquid rystal displays, and other produts, suh as various optoeletroni omponents, osmetis, and hot and old mirrors for arhitetural and automotive windows. 8.4 Problems 9 Waveguides
8.4. Problems 36 improving liquid rystal displays, and other produts, suh as various optoeletroni omponents, osmetis, and hot and old mirrors for arhitetural and automotive windows. 8.4 Problems 9 Waveguides
M.7 CONTENTS. Measurement transformers and shunts. Introduction Page 3 TC 5 TC 5,2 TC 6,2 TC 6 TC 8 TC 10 TC 12. Slim line current transformers Page 7
 Current transformers and shunts M7 M.7.01 GB CONTENTS Introdution Page 3 TC TCH T TC 5 TC 5,2 TC 6,2 TC 6 TC 8 TC 10 TC 12 TCH 6,2 TCH 6 TCH 8 TCH 10 TCH 12 T 400 T 0 T 600 Slim line urrent transformers
Current transformers and shunts M7 M.7.01 GB CONTENTS Introdution Page 3 TC TCH T TC 5 TC 5,2 TC 6,2 TC 6 TC 8 TC 10 TC 12 TCH 6,2 TCH 6 TCH 8 TCH 10 TCH 12 T 400 T 0 T 600 Slim line urrent transformers
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
A Context-Aware Preference Database System
 J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, kstef@s.uoi.gr Evaggelia
J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, kstef@s.uoi.gr Evaggelia
An Efficient Network Traffic Classification Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detection Mechanism
 An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers
 Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Decision Tree Induction
 Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Known: long, aluminum cylinder acts as an extended surface.
 Prolem : A long, irular aluminium rod attahed at one end to the heated all and transers heat through onvetion to a old luid. (a) I the diameter o the rod is triples, y ho muh ould the rate o heat removal
Prolem : A long, irular aluminium rod attahed at one end to the heated all and transers heat through onvetion to a old luid. (a) I the diameter o the rod is triples, y ho muh ould the rate o heat removal
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
GABOR AND WEBER LOCAL DESCRIPTORS PERFORMANCE IN MULTISPECTRAL EARTH OBSERVATION IMAGE DATA ANALYSIS
 HENRI COANDA AIR FORCE ACADEMY ROMANIA INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE of SCIENTIFIC PAPER AFASES 015 Brasov, 8-30 May 015 GENERAL M.R. STEFANIK ARMED FORCES ACADEMY SLOVAK REPUBLIC GABOR AND WEBER LOCAL DESCRIPTORS
HENRI COANDA AIR FORCE ACADEMY ROMANIA INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE of SCIENTIFIC PAPER AFASES 015 Brasov, 8-30 May 015 GENERAL M.R. STEFANIK ARMED FORCES ACADEMY SLOVAK REPUBLIC GABOR AND WEBER LOCAL DESCRIPTORS
Improved Vehicle Classification in Long Traffic Video by Cooperating Tracker and Classifier Modules
 Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Relativistic Kinematics -a project in Analytical mechanics Karlstad University
 Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
Programming Basics - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physics.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html
 CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE
 UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
3 Game Theory: Basic Concepts
 3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
An Introduction to Partial Differential Equations
 An Introduction to Partial Differential Equations Andrew J. Bernoff LECTURE 2 Cooling of a Hot Bar: The Diffusion Equation 2.1. Outline of Lecture An Introduction to Heat Flow Derivation of the Diffusion
An Introduction to Partial Differential Equations Andrew J. Bernoff LECTURE 2 Cooling of a Hot Bar: The Diffusion Equation 2.1. Outline of Lecture An Introduction to Heat Flow Derivation of the Diffusion
Asimple analytic method for transistor
 A Simple Analyti Method for ransistor Osillator Design his straightforward mathematial tehnique helps optimize osillator designs By Andrei Grennikov Institute of Miroeletronis, Singapore Asimple analyti
A Simple Analyti Method for ransistor Osillator Design his straightforward mathematial tehnique helps optimize osillator designs By Andrei Grennikov Institute of Miroeletronis, Singapore Asimple analyti
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS
 RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Special Relativity Theory
 www.senet.org/apr Applied Physis Researh Vol. 4, No. ; 1 On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Speial Relativity Theory Sergey A. Vasiliev 1 1 Sientifi Researh Institute of Exploration Geophysis
www.senet.org/apr Applied Physis Researh Vol. 4, No. ; 1 On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Speial Relativity Theory Sergey A. Vasiliev 1 1 Sientifi Researh Institute of Exploration Geophysis
Lecture 13 Phonons: thermal properties
 Leture 1 Phonon: thermal propertie Lattie ontribution to the thermal propertie of olid, in -D Aim: Thermal propertie of a rytalline olid: Heat apaity: Debye treatment T law for low temperature heat apaity
Leture 1 Phonon: thermal propertie Lattie ontribution to the thermal propertie of olid, in -D Aim: Thermal propertie of a rytalline olid: Heat apaity: Debye treatment T law for low temperature heat apaity
Second Order Linear Partial Differential Equations. Part I
 Second Order Linear Partial Differential Equations Part I Second linear partial differential equations; Separation of Variables; - point boundary value problems; Eigenvalues and Eigenfunctions Introduction
Second Order Linear Partial Differential Equations Part I Second linear partial differential equations; Separation of Variables; - point boundary value problems; Eigenvalues and Eigenfunctions Introduction
Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objective Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms
 Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism
Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism
Modeling and analyzing interference signal in a complex electromagnetic environment
 Liu et al. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communiations and Networking (016) 016:1 DOI 10.1186/s13638-015-0498-8 RESEARCH Modeling and analyzing interferene signal in a omplex eletromagneti environment Chun-tong
Liu et al. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communiations and Networking (016) 016:1 DOI 10.1186/s13638-015-0498-8 RESEARCH Modeling and analyzing interferene signal in a omplex eletromagneti environment Chun-tong
On Some Mathematics for Visualizing High Dimensional Data
 On Some Mathematis for Visualizing High Dimensional Data Edward J. Wegman Jeffrey L. Solka Center for Computational Statistis George Mason University Fairfax, VA 22030 This paper is dediated to Professor
On Some Mathematis for Visualizing High Dimensional Data Edward J. Wegman Jeffrey L. Solka Center for Computational Statistis George Mason University Fairfax, VA 22030 This paper is dediated to Professor
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
MATE: MPLS Adaptive Traffic Engineering
 MATE: MPLS Adaptive Traffi Engineering Anwar Elwalid Cheng Jin Steven Low Indra Widjaja Bell Labs EECS Dept EE Dept Fujitsu Network Communiations Luent Tehnologies Univ. of Mihigan Calteh Pearl River,
MATE: MPLS Adaptive Traffi Engineering Anwar Elwalid Cheng Jin Steven Low Indra Widjaja Bell Labs EECS Dept EE Dept Fujitsu Network Communiations Luent Tehnologies Univ. of Mihigan Calteh Pearl River,
