PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT: I
|
|
|
- Matthew Mosley
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT: I 2 MARKS 1. Define Management. According to KOONTZ & WEIHRICH, Management is the process of designing and maintaining of an environment in which individuals working together in groups efficiently accomplish selected aims. Management is the art of getting things through and with people in formally organized groups. Ex: Human Resource Management, Financial Management. 2. Is Management - an art or science? Managing as practice is an art; the organized knowledge underlying the practice is a science. Managing has the following features that make it an art. 1. Creative 2. Individual approach 3. Application and dedication 4. Initiative and 5. Intelligence. The following features make it a science. 5. Systematic decision making 6. Universal management process 7. Situational output and 8. Universally accepted management. Thus management can be called both as an art and science. 3. What are the essential skills of Managers? The major skills required or expected out of managers are:- Technical skills Pertaining to knowledge and proficiency in activities involving methods and procedures; Human skills Ability to work effectively with other persons and to build up cooperative group relations to accomplish organizational objectives; Conceptual skills Ability to recognize significant elements in a situation; and to understand the relationship among those elements; and Design skills Ability to solve problems in ways that will benefit the enterprise. 4.Define Scientific Management. Scientific management involves specific method of determination of facts through observation. The concept of scientific management was introduced by Frederick Winslow Taylor in the USA in the beginning of 20th century. It was further carried on by Frank and Lillian Gilbreth, Henry Gantt, etc. It was concerned essentially with improving the operational efficiency at the shop floor level. Scientific Management is concerned with knowing exactly what you want men to do and then see in that they do it best and cheapest way.
2 5. List the principles of Scientific Management. Scientific management was introduced by F.W Taylor who is known as the Father of Scientific Management. He adopted scientific methods to increase the productivity and greater efficiency in production. The principles of Scientific Management are:- Separation of planning and working Functional foremanship Job analyzers 6.List the contributions of Fayol towards Management. Henry Fayol is a French industrialist whose contributions are termed as operational management or administrative management. He followed The Classical Approach to the evolution of management thought. His contributions are given as follows:- Grouping of activities of an industrial organization into six groups, namely- Technical, commercial, financial, security, accounting and managerial; Identified six types of qualities of a manager are- Physical, mental, moral, educational, technical and experience; Fourteen principles of Management namely- Division of Work, Authority and responsibility and so on; and Five elements/functions of management- Planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating and controlling. 7. List out the Functions of management Planning Organizing Staffing Leading or Direction or Coordination Controlling 8. List out the Management level and functions. Top-level management Middle level management Lower level management Top level management functions 1. To formulate goals and policies 2. To formulate budgets 3. To appoint top executives Middle level management functions. 1. To train motives &develop supervisory level 2. To monitor and control the operations performance Low level management To train &develop workers To assign job To give orders and instructions To report the information about the workers
3 9. What are the roles played by a Manager? Interpersonal roles 1. Figurehead role 2. The leader role 3. The liaison role Informational roles 4. The recipient role 5. The disseminator role 6. The spokesperson role Decision roles 7. The entrepreneurial role 8. The disturbance-handler role 9. The resource allocator role 10. Define Sole proprietorship. A Business unit that is owned and controlled by a single individual is known as sole trading or sole proprietorship concern. He uses his own savings for running the business. The sole trader makes all purchases and sells on his own and maintains all the accounts. He alone enjoys all the profits and bears all the losses. Ex: A Fancy store. 11. What do you mean by a Partnership firm? A partnership is an association of two or more persons to carry on business and to share its profit and losses. The relation of a partnership arises from contract. The maximum number of partners is limited to 10 in the case of banking business and 20 in the case of other business. Ex: Chand & Co. 12. What do you understand by the term Joint Stock Company? By a Company we mean an association of many persons who contribute money or money s worth to a common stock and employs it in some trade or business and also shares the profit and loss as the case may be arising there from. There are two types of Joint stock companies:- * Private Limited company Ex: M/s Key Media Pvt. Ltd. * Public Limited company Ex: M/s Pearl credits Ltd. 13. Who is (i) an active partner (ii) a sleeping partner? Active partner: Any partner who is authorized by others to manage the business is known as active partner. Sleeping partner: Any partner who does not express his intention to participate in the business can be called as a sleeping partner. He will be just an investor who has a right to share profits. 14. What is a Co-operative Enterprise? A Co-operative enterprise is a voluntary association of persons for mutual benefit and its aims are accomplished through self-help and collective effort. It may be described as a protective device used by the relatively less strong sections of society to safeguard their economic interests in the face of exploitation by producers and sellers working solely for maximizing profits. Ex: AAVIN Milk
4 Federation Cooperative Society. 15. What is a Private limited company? A Private limited company is a company which has a minimum paid up capital as may be prescribed. It can be incorporated with just two persons. It can have a maximum of 50 members. It cannot go in for a public issue. It restricts the transfer of its shares. It is particularly suitable for industrial ventures which can get many concessions in respect of income tax. Ex: M/s Key Media Pvt. Ltd. 16. What is a Public limited company? A Public limited company should have a minimum of 7 members and the maximum limit is unlimited. It can issue shares to the Public. The financial statement should be sent to all the members and to the Registrar of Companies. The shares of a public limited company can be transferred by the members to the others without any restriction by the company. Such transfers are made through organized markets called stock markets or stock exchanges. Ex: M/s Pearl credits Ltd. 17. What is a Public sector Enterprise? Public enterprise or State enterprise is an undertaking owned and controlled by the local or state or central government. They are financed and managed by the government. They are started with a service motive. Ex: NLC Ltd. 18. What is a Public Corporation? A Public corporation is an autonomous body corporate created by a special statute of a state or central government. A public corporation is a separate legal entity created for a specific purpose. Ex: LIC. 16 Marks 1. Trace the evolution of management with reference to the contributions made by management thinkers. Management is defined for conceptual, theoretical and analytical purposes as that process by which managers direct, maintain and operate purposive organizations through systematic, coordinated, cooperative human efforts. Management is a process involving planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling human efforts to achieve stated objective in an organization. Contributions of: Peter Drucker F.W. Taylor Elton Mayo Henri Fayol Max Weber Henry Gantt Frank & Lillian Gilbreth. These contributions came bit by bit and in haphazard manner and have failed to stimulate to study management as a distinct discipline. However their ideas created awareness about managerial problems. 2. What is the role of scientific management in the modern era? Scientific management involves specific method of determination of facts through observation. The concept of scientific management was introduced by Frederick Winslow Taylor in the USA in the
5 beginning of 20th century. It was further carried on by Frank and Lillian Gilbreth, Henry Gantt, etc. It was concerned essentially with improving the operational efficiency at the shop floor level. Scientific Management is concerned with knowing exactly what you want men to do and then see in that they do it best and cheapest way. Scientific management was introduced by F.W Taylor who is known as the Father of Scientific Management. He adopted scientific methods to increase the productivity and greater efficiency in production. The Features of Scientific Management are:- Separation of planning and working Functional foremanship Job analyzers Time study or Work measurement Method study Motion study Role of scientific management in the modern era Paved way for progress in productivity Employee-Employer relationship to be harmonious Training & Development is the necessity of the hour Elimination of wastes through quality management is a control measure Optimal utilization of resources made possible. 3. Explain the contributions of F.W.Taylor to Management. Scientific Management is concerned with knowing exactly what you want men to do and then see in that they do it best and cheapest way. Scientific management was introduced by F.W Taylor who is known as the Father of Scientific Management. He adopted scientific methods to increase the productivity and greater efficiency in production. Principles of Scientific Management: Replacing Rule of thumb with science Harmony in group action Cooperation Maximum output and Development of workers. The Features of Scientific Management are:- Separation of planning and working Functional foremanship Job analyzers Time study or Work measurement Method study Benefits of scientific management: Taylor s scientific management is more relevant to mechanization and automation-technical aspect of efficiency- than the broader aspects of management of an organization. It created awareness about operational efficiency at the shop floor level than at the higher levels.
6 4. Explain the contributions of Henri Fayol. Management is simply the process of decision-making and control over the action of human beings for the expressed purpose of attaining pre-determined goals. Management is the art of getting things through and with people in formally organized groups. Administrative Theory of Management Usage of the term Administration ; the six activities of an industrial organization namely, technical, commercial, financial security, accounting and managerial. Fourteen general Principles of Management Division of work, Espirit de corps. Five Elements of management Planning, Organizing, Commanding, Coordinating, Controlling Six Managerial qualities Physical, Mental, Moral, Educational, Technical and Experience. Fayol made a clear distinction between management principles and management elements. These principles are flexible and capable of being adapting to every need. It is a matter of knowing how to use each of them which is a difficult art requiring intelligence, experience and proportion. 5. Discuss the functions of management with neat diagram. (Study using author book) 6. What are the various environmental factors that a manager should consider in an organization? Environment is a collectivity of all factors within the control of individual business and beyond the control of individual business. Environment includes all the conditions, circumstances, and influences surrounding the total organization or any of its part. The environment may be External and Internal EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT It greatly influences the working of every business. Its major components are: Economic- capital, labor, suppliers, consumers and customers Technological Social Political Ethical INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT It is considered with the day to day work of the various departments of an organization. They may be Financial aspects HR policies and procedures Production activities Marketing and selling activities Information system 7. Outline the various forms of Business organizations. Ownership of business is represented by the right of an individual or a group of individuals to acquire legal title to assets for the purpose of controlling them and to enjoy gains or profits from such possession and use. Definition of Business organization A Business organization comes into existence when there are a number of persons in communication and relationship to each other and are willing to contribute towards a common objective. The classifications of Business Organizations are: * Sole proprietorship concern * Partnership concern
7 * Joint Stock Companies - Private Limited Company - Public Limited Company * Co-operative societies * Non- Profit Organizations. UNIT: 2 2 Marks 1. What is planning? Planning is a process of selecting the objectives & determining the course of action required to achieve these objectives. EG: The goal set for limited period like five year plans 2. Important observations subjected about planning? a) Planning is obtaining a future course of action in order to achieve an objective. b) Planning is looking ahead. c) Planning is getting ready to do something tomorrow. d) Plan is a trap laid down to capture the future. 3. Define mission and vision? Mission may be defines as a statement which defines the role that an organization plays in the society. EG: Canara Bank Good People to Grow With. A vision statement indicates how the organization should be, after a particular time Period. 4. Define policies? Policies are general statement or understanding which provides guidance in decisions making to various managers. 5. Defining planning premises? Planning premises are defined as the anticipated environment in which plans are expected to operate. They include assumptions or forecasts of the future & known conditions that will effects the operation of plans. 6. Explain in brief about the two approaches in which the hierarchy of objectives can be explained? There are two approaches in which the hierarchy can be explained. 1. top-down approach 2. bottom-up approach In the top-down approach, the total organization is directed through corporate objective provided by the top-level management. In the bottom up approach, the top level management needs to have information from lower level in the form of objectives. 7. Definitions of MBO: KOONTZ &WEIHRICH: Management by objectives (MBO) is defined as a comprehensive managerial system that integrates many key managerial activities in a systematic manner and that is
8 consciously directed towards the effective and efficient achievement of organizational and individual objective. 8. Define strategy? A strategy may be defined as special type of plan prepared for meeting the challenges posted by the activities of competitors and other environment forces. 9. Steps involved in strategic planning: 1. Mission and objectives. 2. Environmental analysis 3. Corporate analysis 4. Identification of alternatives. 5. Strategic decision making 6. Implementations review & control. 10. Name the classification of planning premises? 1. Internal and external 2. Tangible and intangible premises. 3. Controllable and uncontrollable premises 11. Define Decision Making Decision Making is defined as selection of a course of action from among alternatives. It is a core of planning. A plan cannot be said to exist unless a decision a commitment of resources, direction or reputation has been made. Until that point, there is only planning studies and analysis. 12. What are the three approaches in selecting an alternative? 1. Experience 2. Experimentation 3. Research and Analysis 13. What is tows metrics? The tows metrics is a conceptual frame work for a systematic analysis, which facilitates matching the external threats and opportunities with the internal weakness & strength of the organization. In the tows metrics T stands for threat s stands for opportunities W for weakness and S for strength. 14. Define forecasting. Forecasting is the process of predicting future conditions that will influence and guide the activities, behavior and performance of the organization. EG: forecasting the output by sales department. 16 Marks 1. Explain the Process of decision making with neat diagram. 2. Define MBO. Explain the process of MBO with the merits and demerits. 3. Explain the various types of planning. 4. Mention and explain the steps in planning with neat diagram.
9 UNIT 3 2 marks 1. Define Organization. An identified group of people contributing their efforts towards the attainment of goals is called an organization. Organization is the process of establishing relationships among the members of the enterprise. 2. What is the purpose of Organization? Facilitates Administration Increases the efficiency management Stimulates creativity and innovation Facilitates growth and diversification and Facilitates co-ordination and communication. 3. What is organizing? Organizing refers to the formal grouping of people and activities facilitate achievement of the firm s objectives. Organizing may be defined as the process of i) Identifying and classifying the required activities i.e. Job Design ii) Grouping the work to be performed i.e., Departmentation iii) Defining and delegating responsibility and authority i.e. Delegation of authority iv) Span of Control 4. What is Job design? Job design is usually broad enough to accommodate people s needs and desires. It may be especially appropriate to design jobs for exceptional persons in order to utilize their potential. People spend a great deal of time on the job and it is therefore important to design jobs so that individuals feel good about their work. Two important goals of job design are:- To meet the organizational requirements such as higher productivity, operational efficiency, quality of products/service etc. To satisfy the needs of the individual employees like interests, challenge, achievement etc. 5. What is Organization Structure? In organization structure simply by means the systematic arrangement of people working for the organization. The organization is concerned with establishment of positions and relationship between positions. The organization structure has two dimensions. 1. Horizontal 2. Vertical 6. What is an Organizational chart? According to George Terry, Organizational chart is a diagrammatical form, which shows the important aspects of an organization including the major functions and their respective relationships, the channels of supervision, and the relative authority of each employee who is in charge of each respective function. It is a representation of the framework or structure of an organization. It may be a vertical or top-down chart, horizontal or left to right chart and circle or concentric chart.
10 7. Uses of Organization Chart 1. The organization chart pinpoints the weakness of an organization. This will helps to overcome the short coming of organization. 2. It tells quickly who is responsible for particular function. 3. It is useful in showing nature of an organization and changes if any in the existing staff and new comers. 8. Distinguish between authority and power Power is the ability of individuals or groups to induce r influence the beliefs or actions of other persons or groups. Authority in organization is the right in a position to exercise discretion in making decisions and affecting others. 9. What are the different bases of power? 1. Legitimate Power 2. Referent Power 3. Reward Power 4. Coercive Power 10. Functional Authority It is the right which is delegated to an individual or a department to control specified processes practices, policies or other matters relating to activities, undertaken by persons in other departments. 11. Formal Organization The structure of jobs and positions with clearly defined functions and relationship as prescribed by the top management and bound by rules, systems and procedures. 12. Informal Organization A network of interpersonal relationships that arise when people associate with each other. 13. Departmentation The organizational process of determining how activities are to be grouped is called departmentation. 14. Empowerment Empowerment means that employees, managers or teams at all levels in the organization are given the power to make decision without asking their superiors for permission. 15. Decentralization The tendency to disperse decision making authority in an organized structure. 16. What do you mean by a strategy? Strategy is defined as the determination of long-term objectives of an organisation. Making the best choices for the future and allocating the resources necessary to accomplish the objectives. 17. What is decision making? Decision making is defined as the selection of a course of action among alternative courses of
11 action. Decision making should be rational. Decision making involves a choice among alternatives. 18. What is the purpose of planning? a. To determine the direction of an organization b. To provide a basis for team work c. To minimize wastages in the future d. To facilitate decision making e. To improve morale of the employees. 19. State the importance of HRM? 1. To achieve competitive advantage over other organization. 2. To improve the efficiency of the organization. 3. For the fuller utilization of available resources. 4. Cost effective administration. 16 Marks 1. Enumerate in detail about the selection process which is widely followed in selecting IT professionals. Also highlight the different techniques used in selection process. (Draw the figure) 2. Bring out the factors affecting centralization / decentralization. Also highlight the merits and demerits of centralization and decentralization with examples. 3. Explain in detail about delegation of authority. 4. What do you mean by departmentation? Discuss in detail about the different strategies adopted in departmentation? 5. Explain detail about performance appraisal with neat diagram. UNIT 4 1. Define Direction. Direction may be defined as the process of instructing, guiding and inspiring human factors in the organization to achieve organization objectives. 2. State two important characteristics of Directing. Any two characteristics of Directing are: Directing is an important managerial function through which the management initiates actions in the organization. It is a continuous process and it continues throughout the life of the Organization. 3. Mention the importance of Leadership 1. Motivating Employees 2. Leader develops team work 3. Better utilization of manpower 4. Creating confidence to followers 5. Directing group activities 6. Building morale 7. Maintaining discipline
12 4. Name the various leadership styles. 1. Autocratic or Dictatorial leadership 2. Participative or Democratic leadership 3. Laissez faire or Free rein leadership 5. What are the advantages of democratic leadership? 1. The subordinates are motivated by participation in decision making process. This will also increase job satisfaction 2. Absence of leader does not affect output 3. Labour absenteeism and turn over will be minimum 4. The quality of decision is improved 5. The leader multiplies his abilities through the contribution of his followers 6. What is Laissez faire? Complete freedom is given to the subordinates so that they plan, motivate, control and otherwise be responsible for their own actions. 7. List out the human factors in managing. The Human factors in managing include: Multiplicity of roles Individuality and Personal dignity. 8. Define creativity. Creativity is defined as the ability to produce new and useful ideas through the combination of known principles and components in novel and non-obvious ways. Creativity exists throughout the population largely independent of age, sex and education. 9. What are the steps involved in creative process? Creativity is defined as the ability to produce new and useful ideas through the combination of known principles and components in novel and non-obvious ways. The steps involved in creative process are: Saturation Preparation Frustration and incubation Inspiration or illumination Verification 10. How are problems solved by creative tool? Creativity tools are designed to help you devise creative and imaginative solutions to problems. Creativity tools are designed to help you devise creative and imaginative solutions to problems. 11. What is a SCAMPER tool? SCAMPER is a checklist that helps us to think of changes where S - Substitute
13 C - Combine A - Adapt M - Modify P - Put to another use E - Eliminate and R - Reverse. 12. What is a meant by reframing matrix? Reframing matrix is a simple technique that helps to look at business problems from a number of different viewpoints. The approach relies on the fact that different people with different experience approach problems in different experience approach in different ways. 13. What are the steps involved in simplex tool? Simplex tool is an industrial-strength creativity tool. The steps involved in simplex tool are:- Problem finding Fact finding Problem definition Idea finding Selection and evaluation Planning Sell data and Action. 14. Differentiate Innovation and Invention. Innovation means the use of creative ideas. It is not only relevant to high-tech enterprises but also crucial for old-line, traditional companies, which may not service without the infusion of innovation. Ex: A new product or a service. Invention means really finding new things that are not already available. It is mostly applicable in the field of science. Ex: Invention of radio. 15. How can be harmonizing objectives achieved? Harmonizing objectives can be achieved through: Mutual trust Cooperation and understanding and Workers participation in management. 16. Define Multiplicity of Roles. Individuals are not only the productive factor in management Plans. They are members of social system of many organizations. 17. Mention the various factors involved in using motivational techniques: 1. Money 2. Reward : intrinsic and extrinsic 3. Participation 4. Quality of working life
14 18. What is job enrichment? Building into jobs a higher sense of challenge and achievement. (or) Job enrichment is therefore based on the assumption that in order to motivate personnel, the job itself must provide opportunities for the achievement, recognition, responsibility, advancement and growth 19. What are the limitations of job enrichment? 1. Job enrichment is based on the assumption that workers want more responsibility. But, in practice, most of the workers may prefer less responsible jobs with good social interaction. Such workers may show feelings of inadequacy and fear of failure to job enrichment. 2. Some jobs cannot be enriched beyond a certain point. 20. Give the required guidelines to make effective job enrichment. 1. Use job enrichment selectively after taking into account situational variables such as job characteristics, personal characteristics of employees, Organizational level etc. 2. Provide a supportive climate for innovation and change. 21. Define Leadership Leadership is the process of influencing the behavior of others towards the accomplishment of goals in a given situation. Leadership is the ability to influence others and enthusiastically making them to achieve the desired results. 22. What is Communication? It is passing of information from one person to another person with understandable Manner. 23. Mention the various elements in the process of communication. 1. Sender 2. Communication Channels 3. Symbols 4. Receiver 5. Noise and feedback in communication 24. List the different types of communication flow 1. Downward Communication 2. Upward communication 3. Horizontal or Lateral Communication 25. Explain the creative process? Creativity: Creativity is the ability to create large number of ideas quickly. Creative process has interacting and over lapping phase. It has four phases: Unconscious Scanning Intuition Insight Logical Formulation
15 Unconscious Scanning: A condition beyond consciousness. Intuition: It connects unconscious with conscious Insight: It is the result of hard work Logical Formulation: referred to as verification Techniques to enhance creativity: The following are the techniques to enhance Creativity: 1. Brainstorming Technique used for problem solving by using new methods 2. Synectics In this technique group members are selected according to problem of organization. Then a group leader chose who plays a vital role in this process. 26. What is brainstorming? This kind of training is given to increase people s creativity and decisional ability. These types of training individual participants are encouraged to give their own ideas to resolve the existing problem. UNIT 5 1. What is Feed Forward Control? Feed Forward Control involves evaluation of input and corrective measures before a particular sequence of operation is completed. It is based on timely and accurate information about changes in the environment. 2. What is Concurrent Control? Concurrent Control is also known as "real-time" or steering" control. It provides for taking corrective actions or making adjustments while the programmers is still in operation and before any major damage occurs. 3. List out the important features of controlling? a) Function of Management. b) Continuous function c) Future -oriented and d) Action-oriented. 4. What is Flexible Budget? Flexible Budget is one which is designed to change in accordance with the level of activity actually attained. It is suitable when the estimation of demand is uncertain and the enterprise works under conditions of lack of material and labor power. 5. What are the benefits of control? 1. Control eliminates actions which deviate or which is not in conformity with the cherished goals of the firm. 2. It offers enough information for future planning and Organizing. 6. List out the characteristics of Control function? 1) Functional Management
16 2) Continuous function 3) Future-oriented 4) Action-oriented 5) Measuring the performance and 6) Planning the control 7. What are the basic steps involved in the process of controlling? 1 establishment of standards 2 measurement of performance 3 comparing performance with the slandered 4 taking corrective action 8. What is performance Appraisal? Performance appraisal is the system of measuring Employee performance and giving feedback to the employee regarding his performance. 9. What are the advantages of performance Appraisal? 1. Getting performance Feedback 2. Identifying training needs 3. Motivating Personnel 4. Promotional consideration 5. Pay fixation. 10. What is Globalization? Doing business without geographical boundaries is known as globalization.
PBL: Management Concepts. Competency: Business Environment
 Competency: Business Environment 1. Explain the impact of business on the environment. 2. Explain the nature of managerial ethics and demonstrate ethical behaviors in the work place responsible behavior,
Competency: Business Environment 1. Explain the impact of business on the environment. 2. Explain the nature of managerial ethics and demonstrate ethical behaviors in the work place responsible behavior,
PLAN INTRODUCTION 1. DEFINITION OF MANAGEMENT 2. HISTORY OF MANAGEMENT 3. BASIC FONCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT 4. SKILLS OF THE MANAGER
 PLAN INTRODUCTION 1. DEFINITION OF MANAGEMENT 2. HISTORY OF MANAGEMENT 3. BASIC FONCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT 4. SKILLS OF THE MANAGER 5. JUNIOR MANAGERS AND SENIOR MANAGERS CONCLUSION INTRODUCTION Management
PLAN INTRODUCTION 1. DEFINITION OF MANAGEMENT 2. HISTORY OF MANAGEMENT 3. BASIC FONCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT 4. SKILLS OF THE MANAGER 5. JUNIOR MANAGERS AND SENIOR MANAGERS CONCLUSION INTRODUCTION Management
Principles of Management
 Principles of Management 1 Process of management aims at 1 Cooperating with a number of persons pursuing a goal 2 Coordinating work of number of persons to achieve objectives 3 Supervising a number of
Principles of Management 1 Process of management aims at 1 Cooperating with a number of persons pursuing a goal 2 Coordinating work of number of persons to achieve objectives 3 Supervising a number of
Management: Theory and Practice
 CHAPTER 1 Management: Theory and Practice WHAT IS MANAGEMENT? Management, in simple terms, can be defined as the attainment of organizational goals in an effective and efficient manner through: Planning,
CHAPTER 1 Management: Theory and Practice WHAT IS MANAGEMENT? Management, in simple terms, can be defined as the attainment of organizational goals in an effective and efficient manner through: Planning,
RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT
 RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT COURSE OBJECTIVE The objective of this course is to clarify the principles of Internal Audit along with the Audit process and arm internal auditors with a good knowledge of risk
RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT COURSE OBJECTIVE The objective of this course is to clarify the principles of Internal Audit along with the Audit process and arm internal auditors with a good knowledge of risk
UNIT - 1 MANAGMENT DEVELOPMENT Lesson:-01 Nature of Management
 UNIT - 1 MANAGMENT DEVELOPMENT Lesson:-01 Nature of Management Chapter overview: Nature, scope and process of management, historical evolution of management thought, different approaches and systems of
UNIT - 1 MANAGMENT DEVELOPMENT Lesson:-01 Nature of Management Chapter overview: Nature, scope and process of management, historical evolution of management thought, different approaches and systems of
Objectives. Managing our Team. Why People Work. What is Human Resource Management?
 Objectives HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT What is Human Resource Management? Why do people work? What power does a Project Manager have? How do we motivate people? How do we manage a team? What is Human Resource
Objectives HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT What is Human Resource Management? Why do people work? What power does a Project Manager have? How do we motivate people? How do we manage a team? What is Human Resource
Management Principles CORPORATE LEARNING COURSE TEAM BUILDING BLOCK SEMINAR 3.4
 LESSON PLAN Management Principles CORPORATE LEARNING COURSE TEAM BUILDING BLOCK SEMINAR 3.4 SCOPE This seminar discusses the basic principles of management. This lesson will help you comprehend how to
LESSON PLAN Management Principles CORPORATE LEARNING COURSE TEAM BUILDING BLOCK SEMINAR 3.4 SCOPE This seminar discusses the basic principles of management. This lesson will help you comprehend how to
Leading Self. Leading Others. Leading Performance and Change. Leading the Coast Guard
 Coast Guard Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are the knowledge, skills, and expertise the Coast Guard expects of its leaders. The 28 leadership competencies are keys to career success. Developing
Coast Guard Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are the knowledge, skills, and expertise the Coast Guard expects of its leaders. The 28 leadership competencies are keys to career success. Developing
Developing an Organisational Vision
 Ralph Lewis Associates 1 Developing an Organisational Vision Why do you exist as an organisation? Who do you serve? Where is the passion? What is the dream, Where is the fire, What is the spirit? www.ralphlewis.co.uk
Ralph Lewis Associates 1 Developing an Organisational Vision Why do you exist as an organisation? Who do you serve? Where is the passion? What is the dream, Where is the fire, What is the spirit? www.ralphlewis.co.uk
Leadership and Management Competencies
 Leadership and Management Competencies 0 The Saskatchewan Public Service Vision: The Best Public Service in Canada Our Commitment to Excellence Dedicated to service excellence, we demonstrate innovation,
Leadership and Management Competencies 0 The Saskatchewan Public Service Vision: The Best Public Service in Canada Our Commitment to Excellence Dedicated to service excellence, we demonstrate innovation,
The Different Approaches and Systems of Management
 Lesson:-12 The Different Approaches and Systems of Management Students, you should know that the year 1911, the year Frederick Winslow Taylor s Principles of Scientific Management was published, is generally
Lesson:-12 The Different Approaches and Systems of Management Students, you should know that the year 1911, the year Frederick Winslow Taylor s Principles of Scientific Management was published, is generally
Chapter 8: The Internal Environment
 Chapter 8: The Internal Environment Key Revision Points The Internal Functions of Commercial Organisations In competitive business environments, customers are at the centre of all of an organisation's
Chapter 8: The Internal Environment Key Revision Points The Internal Functions of Commercial Organisations In competitive business environments, customers are at the centre of all of an organisation's
Human Resources Management Philosophy JAGODA MRZYGŁOCKA-CHOJNACKA PHD 1
 Human Resources Management Philosophy JAGODA MRZYGŁOCKA-CHOJNACKA PHD 1 Human Resources Management Philosophy The HR Management Philosophy is not mainly about Human Resources Function. It is more about
Human Resources Management Philosophy JAGODA MRZYGŁOCKA-CHOJNACKA PHD 1 Human Resources Management Philosophy The HR Management Philosophy is not mainly about Human Resources Function. It is more about
Strategic human resource management toolkit
 19 205 Strategic human resource management toolkit The purpose of the toolkit is to provide the basis for conducting a strategic review of human resource management practices in order to develop and implement
19 205 Strategic human resource management toolkit The purpose of the toolkit is to provide the basis for conducting a strategic review of human resource management practices in order to develop and implement
1.0 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT
 1.0 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT 1.1 INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT In most aspect of our lives we are member of one organization or another a college, a sport team, a musical, religions or theatre
1.0 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT 1.1 INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT In most aspect of our lives we are member of one organization or another a college, a sport team, a musical, religions or theatre
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Business Studies Stage 6 Support Document
 Business Studies Stage 6 Support Document Support material for the revised syllabus Contents Introduction Key aspects of the syllabus Programming the courses Samples Preliminary Course Scope and Sequence
Business Studies Stage 6 Support Document Support material for the revised syllabus Contents Introduction Key aspects of the syllabus Programming the courses Samples Preliminary Course Scope and Sequence
MANDARIN ORIENTAL HOTEL GROUP REPORT SUMMARY
 MANDARIN ORIENTAL HOTEL GROUP REPORT SUMMARY THE COMPANY Established in Hong Kong in 1963. Mandarin Oriental Hotel Group is an international hotel investment and management group operating ten hotels in
MANDARIN ORIENTAL HOTEL GROUP REPORT SUMMARY THE COMPANY Established in Hong Kong in 1963. Mandarin Oriental Hotel Group is an international hotel investment and management group operating ten hotels in
HRQM AND COLLIDING GYROSCOPES AN ALTERNATIVE WAY OF LOOKING AT VALUE CREATION IN ORGANIZATIONS
 HRQM AND COLLIDING GYROSCOPES AN ALTERNATIVE WAY OF LOOKING AT VALUE CREATION IN ORGANIZATIONS Study stream Human resource and Quality management JOOP VINKE Arnhem Business School Arnhem, HAN University
HRQM AND COLLIDING GYROSCOPES AN ALTERNATIVE WAY OF LOOKING AT VALUE CREATION IN ORGANIZATIONS Study stream Human resource and Quality management JOOP VINKE Arnhem Business School Arnhem, HAN University
Overview of Leadership Theories By Sue Panighetti
 This is a discussion on various different leadership theories and how they apply to leading others. Use the Leadership Points for Dialogue to help explore each of these theories and how they may or may
This is a discussion on various different leadership theories and how they apply to leading others. Use the Leadership Points for Dialogue to help explore each of these theories and how they may or may
QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY
 QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY ACADEMIC DEVELOPMENT & QUALITY ASSURANCE OFFICE ALPHA UNIVERSITY COLLEGE 1. BACKGROUND The Strategic Plan of 2003-2005 E.C of Alpha University s defines the direction Alpha University
QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY ACADEMIC DEVELOPMENT & QUALITY ASSURANCE OFFICE ALPHA UNIVERSITY COLLEGE 1. BACKGROUND The Strategic Plan of 2003-2005 E.C of Alpha University s defines the direction Alpha University
Guide on Developing a HRM Plan
 Guide on Developing a HRM Plan Civil Service Branch June 1996 Table of Contents Introduction What is a HRM Plan? Critical Success Factors for Developing the HRM Plan A Shift in Mindset The HRM Plan in
Guide on Developing a HRM Plan Civil Service Branch June 1996 Table of Contents Introduction What is a HRM Plan? Critical Success Factors for Developing the HRM Plan A Shift in Mindset The HRM Plan in
MANAGEMENT COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1
 MANAGEMENT COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1 MGT 202: Business Professions 1. Describe and use the elements of effective decision making research, assessment and consequence. 2. Apply elements of effective
MANAGEMENT COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1 MGT 202: Business Professions 1. Describe and use the elements of effective decision making research, assessment and consequence. 2. Apply elements of effective
SOLUTION: BUSINESS MANAGEMENT, MAY 2014. (b) Factors to consider when deciding on the appropriate structure for an organization include the following:
 SOLUTION 1 (a) The structure of an organization defines the patterns of communication, the system of control and the command structure. (b) Factors to consider when deciding on the appropriate structure
SOLUTION 1 (a) The structure of an organization defines the patterns of communication, the system of control and the command structure. (b) Factors to consider when deciding on the appropriate structure
MASTER OF HOSPITAL & HEALTH CARE ADMINISTRATION (M.H.A) SEMESTER - I
 MASTER OF HOSPITAL & HEALTH CARE ADMINISTRATION (M.H.A) PAPER I : MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS SEMESTER - I A. Concept of Management B. Theories of Management C. Function of Management D. Principles of Management
MASTER OF HOSPITAL & HEALTH CARE ADMINISTRATION (M.H.A) PAPER I : MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS SEMESTER - I A. Concept of Management B. Theories of Management C. Function of Management D. Principles of Management
How To Write The Extract Mba
 The Extracted MBA extractedmba.com The Extracted MBA The extracted mba A topical reference for the contemporary MBA Kelly Vinal FIRST EDITION Universal Publishers Parkland, Florida Upublish.com Kelly
The Extracted MBA extractedmba.com The Extracted MBA The extracted mba A topical reference for the contemporary MBA Kelly Vinal FIRST EDITION Universal Publishers Parkland, Florida Upublish.com Kelly
Level 1 Articulated Plan: The plan has established the mission, vision, goals, actions, and key
 S e s s i o n 2 S t r a t e g i c M a n a g e m e n t 1 Session 2 1.4 Levels of Strategic Planning After you ve decided that strategic management is the right tool for your organization, clarifying what
S e s s i o n 2 S t r a t e g i c M a n a g e m e n t 1 Session 2 1.4 Levels of Strategic Planning After you ve decided that strategic management is the right tool for your organization, clarifying what
Frank P.Saladis PMP, PMI Fellow
 Frank P.Saladis PMP, PMI Fellow Success factors for Project Portfolio Management The Purpose of Portfolio Management Organizational Assessment Planning a Portfolio Management Strategy The Portfolio Management
Frank P.Saladis PMP, PMI Fellow Success factors for Project Portfolio Management The Purpose of Portfolio Management Organizational Assessment Planning a Portfolio Management Strategy The Portfolio Management
LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK
 LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK February 13, 2008 LEADERSHJP PERSPECTIVE I consider succession planning to be the most important duty I have as the Director of the NOAA Corps. As I look toward the future,
LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK February 13, 2008 LEADERSHJP PERSPECTIVE I consider succession planning to be the most important duty I have as the Director of the NOAA Corps. As I look toward the future,
EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT
 EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT Empowerment Defined Webster dictionary defines empowerment as : giving the means, ability or authority To empower someone is to give the individual authority To make decisions To contribute
EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT Empowerment Defined Webster dictionary defines empowerment as : giving the means, ability or authority To empower someone is to give the individual authority To make decisions To contribute
HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL
 HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL Creating Values For You and For Organisations Setting Standards Recognising s ABOUT HKIHRM The Hong Kong Institute of Human Resource Management (HKIHRM) is the leading
HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL Creating Values For You and For Organisations Setting Standards Recognising s ABOUT HKIHRM The Hong Kong Institute of Human Resource Management (HKIHRM) is the leading
GLOBAL FINANCIAL PRIVATE CAPITAL Job Description. JOB TITLE: Client Relationship Manager
 GLOBAL FINANCIAL PRIVATE CAPITAL Job Description JOB TITLE: Client Relationship Manager Reports To: Financial Advisor Exempt Prepared by: ADP Resource June 10, 2014 SUMMARY This position is primarily responsible
GLOBAL FINANCIAL PRIVATE CAPITAL Job Description JOB TITLE: Client Relationship Manager Reports To: Financial Advisor Exempt Prepared by: ADP Resource June 10, 2014 SUMMARY This position is primarily responsible
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT Employee Input
 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT Employee Input Employee Name: Social Security Number (or EI No.): School: Degree/Major: Expected Graduation Company/Division: Department: Location: A. What are your career objectives
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT Employee Input Employee Name: Social Security Number (or EI No.): School: Degree/Major: Expected Graduation Company/Division: Department: Location: A. What are your career objectives
An Overview of Organizational Behavior
 CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Organizational Behavior MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Ans: D Page: 3 Group Ans: A Page: 3 Group Page: 4 AACSB: Communication Analytic skills Group Page: 4-5 Group 1. No matter how
CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Organizational Behavior MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Ans: D Page: 3 Group Ans: A Page: 3 Group Page: 4 AACSB: Communication Analytic skills Group Page: 4-5 Group 1. No matter how
1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION
 1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION (i) CHIEF MANAGER - COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS, AND HR ADMINISTRATION (Grade KRA 7 ) JOB DESCRIPTION FORM Date: Kenya Revenue Authority
1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION (i) CHIEF MANAGER - COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS, AND HR ADMINISTRATION (Grade KRA 7 ) JOB DESCRIPTION FORM Date: Kenya Revenue Authority
Managing for Results. Purpose. Managing for Results Practitioner-level Standards
 Managing for Results Practitioner-level Standards Managing for Results Purpose In all sectors and at all levels managers must have the knowledge, understanding and skills to enable them to grasp the right
Managing for Results Practitioner-level Standards Managing for Results Purpose In all sectors and at all levels managers must have the knowledge, understanding and skills to enable them to grasp the right
Page 1. Worldwide. Case problem: Learning objectives:
 Student Self-administered case study Introducing HRM Case duration (Min): 45-60 Human Resource Management (HRM) Introducing HRM Worldwide Case summary: This case introduces some of the essential elements
Student Self-administered case study Introducing HRM Case duration (Min): 45-60 Human Resource Management (HRM) Introducing HRM Worldwide Case summary: This case introduces some of the essential elements
Management Principles and the RIM Program
 Management Principles and the Records and Information Management (RIM) Program Management Principles and the RIM Program Principles of Management Human Resources/Staffing Methodologies Financial Considerations
Management Principles and the Records and Information Management (RIM) Program Management Principles and the RIM Program Principles of Management Human Resources/Staffing Methodologies Financial Considerations
MBAProgramme. The College of The Bahamas
 c o u r s e o u t l i n e MBAProgramme The College of The Bahamas Year 1 Fall Financial/Managerial Accounting (3 credits) Introduces students to the financial and managerial accounting disciplines; develops
c o u r s e o u t l i n e MBAProgramme The College of The Bahamas Year 1 Fall Financial/Managerial Accounting (3 credits) Introduces students to the financial and managerial accounting disciplines; develops
Supervision. Samuel C. Certo. Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College. I McGraw-Hill I Irwin
 Supervision Concepts and Skill-Building Seventh Edition Samuel C. Certo Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College I McGraw-Hill I Irwin Contents Preface iv About
Supervision Concepts and Skill-Building Seventh Edition Samuel C. Certo Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College I McGraw-Hill I Irwin Contents Preface iv About
Organizational Design Toolkit
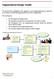 Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Creating the climate to get the most from your team
 Creating the climate to get the most from your team Helping leaders to create high-performing organisations NOVEMBER 2011 SHARON CRABTREE MICHAEL DODDS About Hay Group Our objectives today Look at what
Creating the climate to get the most from your team Helping leaders to create high-performing organisations NOVEMBER 2011 SHARON CRABTREE MICHAEL DODDS About Hay Group Our objectives today Look at what
Agribusiness Management, its meaning, nature and scope, types Of management tasks and responsibilities
 Agribusiness Management, its meaning, nature and scope, types Of management tasks and responsibilities Dr. B. K. Baruah Professor Department of Agril. Economics Farm Management Assam Agricultural University
Agribusiness Management, its meaning, nature and scope, types Of management tasks and responsibilities Dr. B. K. Baruah Professor Department of Agril. Economics Farm Management Assam Agricultural University
The Evolution of Leadership Theory
 1 The Evolution of Leadership Theory Although the practice of leadership has changed considerably over time, the need for leaders and leadership has not (Bass, 1990a; Kouzes & Posner, 1995). Already in
1 The Evolution of Leadership Theory Although the practice of leadership has changed considerably over time, the need for leaders and leadership has not (Bass, 1990a; Kouzes & Posner, 1995). Already in
1.2 ORGNISATION BEHAVIOUR - CONCEPTS. 1.2.1 Organization. 1.2.2 Management. 1.3 Key Elements of Organisational Behavior
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR LESSON 1 IMPORTANCE OF ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR Contents 1.0 Aims and Objectives 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Organization behaviour concepts 1.2.1 Organisation
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR LESSON 1 IMPORTANCE OF ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR Contents 1.0 Aims and Objectives 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Organization behaviour concepts 1.2.1 Organisation
BRICE ROBERTS BUSINESS CONSULTING SERVICES
 BRICE ROBERTS BUSINESS CONSULTING SERVICES BROCHURE: TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMES RE-AWAKENING SPIRIT - TRANSFORMING RESULTS For Further Information: Contact: Brice Roberts Business Consulting Services
BRICE ROBERTS BUSINESS CONSULTING SERVICES BROCHURE: TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMES RE-AWAKENING SPIRIT - TRANSFORMING RESULTS For Further Information: Contact: Brice Roberts Business Consulting Services
the Defence Leadership framework
 the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
Investors in People First Assessment Report
 Investors in People First Assessment Report K.H.Construction Cambridge Assessor: Lesley E Ling On-site Date/s: 3 rd September 2008. Recognition Date: Contents 1. Introduction Page 2 2. Assessment and Client
Investors in People First Assessment Report K.H.Construction Cambridge Assessor: Lesley E Ling On-site Date/s: 3 rd September 2008. Recognition Date: Contents 1. Introduction Page 2 2. Assessment and Client
PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL NON-ACADEMIC ADMINISTRATIVE - SUPERVISORY
 PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL NON-ACADEMIC ADMINISTRATIVE - SUPERVISORY Name: Job Title: Date of Evaluation: Department/School: AAMU Hire Date: Time in Current Position (years/months): Unit: Supervisor: Type of
PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL NON-ACADEMIC ADMINISTRATIVE - SUPERVISORY Name: Job Title: Date of Evaluation: Department/School: AAMU Hire Date: Time in Current Position (years/months): Unit: Supervisor: Type of
ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888)
 GROUP MEMBERS ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888) P W 1 THE HRM BUSINESS MODEL OF ENTERPRISE LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY GHANA (ELAC) CONTENT ENTERPRISE LIFE
GROUP MEMBERS ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888) P W 1 THE HRM BUSINESS MODEL OF ENTERPRISE LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY GHANA (ELAC) CONTENT ENTERPRISE LIFE
Chapter 11: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES: CONCEPTS AND F0RMATS
 Montana, P. and Charnov, B. Management: A Streamlined Course for Students and Business People. (Hauppauge, New York: Barron s Business Review Series, 1993), pp. 155-169. Chapter 11: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES:
Montana, P. and Charnov, B. Management: A Streamlined Course for Students and Business People. (Hauppauge, New York: Barron s Business Review Series, 1993), pp. 155-169. Chapter 11: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES:
Management of Change and Organizational Development. Batch: FO_J11_01 Subject: Management CS Foundation Programme The ICSI Ahmedabad Chapter
 Management of Change and Organizational Development Batch: FO_J11_01 Subject: Management CS Foundation Programme The ICSI Ahmedabad Chapter Meaning of Change Change may be defined as a variation in the
Management of Change and Organizational Development Batch: FO_J11_01 Subject: Management CS Foundation Programme The ICSI Ahmedabad Chapter Meaning of Change Change may be defined as a variation in the
Financial Management
 Different forms business organization Financial Management Sole proprietorship Partnership Cooperative society Company Private limited Vs Public limited company Private co min- two and max fifty, Pub Ltd
Different forms business organization Financial Management Sole proprietorship Partnership Cooperative society Company Private limited Vs Public limited company Private co min- two and max fifty, Pub Ltd
Management and Marketing Course Descriptions
 Management and Marketing Course Descriptions Management Course Descriptions HRM 301 Human Resources Management (3-0-3) Covers all activities and processes of the human resources function that include recruitment,
Management and Marketing Course Descriptions Management Course Descriptions HRM 301 Human Resources Management (3-0-3) Covers all activities and processes of the human resources function that include recruitment,
Quality Manual ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System
 Quality management input comprises the standard requirements from ISO 9001:2015 which are deployed by our organization to achieve customer satisfaction through process control. Quality Manual ISO 9001:2015
Quality management input comprises the standard requirements from ISO 9001:2015 which are deployed by our organization to achieve customer satisfaction through process control. Quality Manual ISO 9001:2015
UNIT I OVERVIEW OF MANAGEMENT
 UNIT I OVERVIEW OF MANAGEMENT DEFINITION According to Harold Koontz, Management is an art of getting things done through and with the people in formally organized groups. It is an art of creating an environment
UNIT I OVERVIEW OF MANAGEMENT DEFINITION According to Harold Koontz, Management is an art of getting things done through and with the people in formally organized groups. It is an art of creating an environment
VPQ Level 6 Business, Management and Enterprise
 VPQ Level 6 Business, Management and Enterprise VPQ Level 6 Certificate in Business, Management and Enterprise The VPQ Level 6 Certificate in Business, Management and Enterprise is a 30 credit qualification.
VPQ Level 6 Business, Management and Enterprise VPQ Level 6 Certificate in Business, Management and Enterprise The VPQ Level 6 Certificate in Business, Management and Enterprise is a 30 credit qualification.
TRAINING AND EDUCATION IN THE SERVICE OF MILITARY TRANSFORMATION
 TRAINING AND EDUCATION IN THE SERVICE OF MILITARY TRANSFORMATION Ecaterina Livia TATAR Lecturer, Regional Department of Defense Resources Management Studies, Brasov, Romania The magnitude and challenges
TRAINING AND EDUCATION IN THE SERVICE OF MILITARY TRANSFORMATION Ecaterina Livia TATAR Lecturer, Regional Department of Defense Resources Management Studies, Brasov, Romania The magnitude and challenges
PERFORMANCE PLANNING WORKSHEET FOR PROFESSIONAL EMPLOYEES (PS-35LC)
 PERFORMANCE PLANNING WORKSHEET FOR PROFESSIONAL EMPLOYEES (PS-35LC) NAME: JOB TITLE: This worksheet should be given to the employee prior to the scheduled performance review. The employee should complete
PERFORMANCE PLANNING WORKSHEET FOR PROFESSIONAL EMPLOYEES (PS-35LC) NAME: JOB TITLE: This worksheet should be given to the employee prior to the scheduled performance review. The employee should complete
Management levels. Middle-level managers
 MANAGEMENT LEVELS 2 Management levels Managers are organizational members who are responsible for the work performance of other organizational members. Managers have formal authority to use organizational
MANAGEMENT LEVELS 2 Management levels Managers are organizational members who are responsible for the work performance of other organizational members. Managers have formal authority to use organizational
Blackblot PMTK Marketing Review. <Comment: Replace the Blackblot logo with your company logo.>
 Company Name: Product Name: Date: Contact: Department: Location: Email: Telephone: Blackblot PMTK Marketing Review Document Revision History:
Company Name: Product Name: Date: Contact: Department: Location: Email: Telephone: Blackblot PMTK Marketing Review Document Revision History:
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement
 Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Total Quality Management
 Total Quality Management 1 Chapter 12: Total Employee involvement 2 Human factor is very important in implementation of any process or principle. It is all the more important in Quality Management. Organization
Total Quality Management 1 Chapter 12: Total Employee involvement 2 Human factor is very important in implementation of any process or principle. It is all the more important in Quality Management. Organization
Transactional Vs Transformational Leadership. Transactional Vs Transformational Leadership
 Transactional Vs Transformational Leadership Transactional Leader: approaches followers with an eye to exchanging one thing for another Burns pursues a cost benefit, economic exchange to met subordinates
Transactional Vs Transformational Leadership Transactional Leader: approaches followers with an eye to exchanging one thing for another Burns pursues a cost benefit, economic exchange to met subordinates
Police Organization and Administration. CJ 3600 Professor James J. Drylie Week 4
 Police Organization and Administration CJ 3600 Professor James J. Drylie Week 4 Organizational Theory To better understand organizations it is important to ask the question cui bono, or who benefits Blatt
Police Organization and Administration CJ 3600 Professor James J. Drylie Week 4 Organizational Theory To better understand organizations it is important to ask the question cui bono, or who benefits Blatt
The Value of Knowledge
 www.pwcacademy.rs The Value of Knowledge PwC Mini MBA Programme Programme Description Content 3 The Value of Knowledge 4 Duration Topics 5 Session 1 - Business Breakdown & Map 6 Session 2 - Corporate &
www.pwcacademy.rs The Value of Knowledge PwC Mini MBA Programme Programme Description Content 3 The Value of Knowledge 4 Duration Topics 5 Session 1 - Business Breakdown & Map 6 Session 2 - Corporate &
Exploring Strategic Change
 Julia Balogun, Veronica Hope Hailey, Gerry Johnson, Kevan Scholes FT Prentice Hall 2003 ISBN: 0273683276, 280 pages Theme of the Book The book links into (and develops further) the ideas on strategic change
Julia Balogun, Veronica Hope Hailey, Gerry Johnson, Kevan Scholes FT Prentice Hall 2003 ISBN: 0273683276, 280 pages Theme of the Book The book links into (and develops further) the ideas on strategic change
Chapter 15 Personnel Management
 Chapter 15 Personnel Management In the corporate sector, it s called human resources. And it makes sense, since your personnel are perhaps your most important resource. You can have the best operating
Chapter 15 Personnel Management In the corporate sector, it s called human resources. And it makes sense, since your personnel are perhaps your most important resource. You can have the best operating
Interviews management and executive level candidates; serves as interviewer for position finalists.
 Plan, direct, and coordinate human resource management activities of the NHBP Tribal government organization to maximize the strategic use of human resources and maintain functions such as employee compensation,
Plan, direct, and coordinate human resource management activities of the NHBP Tribal government organization to maximize the strategic use of human resources and maintain functions such as employee compensation,
Yale University Performance Management Guide
 Yale University Performance Management Guide Table of Contents Section Page Philosophy and Intent 3 FOCUS Annual Performance Management Cycle 4 Expectations 5 Starting With the End in Mind 5 Important
Yale University Performance Management Guide Table of Contents Section Page Philosophy and Intent 3 FOCUS Annual Performance Management Cycle 4 Expectations 5 Starting With the End in Mind 5 Important
ROLE OF HRM & OB IN TODAY S EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION/UNIVERSITY ADMINISTRATION
 ROLE OF HRM & OB IN TODAY S EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION/UNIVERSITY ADMINISTRATION Dr. M.L. Vasitha Associate Professor, Department of Business Administration Jai Narain Vyas University, Jodhpur Mr. B.S. Chauhan
ROLE OF HRM & OB IN TODAY S EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION/UNIVERSITY ADMINISTRATION Dr. M.L. Vasitha Associate Professor, Department of Business Administration Jai Narain Vyas University, Jodhpur Mr. B.S. Chauhan
EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS
 EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS Cezar Vasilescu and Aura Codreanu Abstract: The field of strategic management has offered a variety of frameworks and concepts during
EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS Cezar Vasilescu and Aura Codreanu Abstract: The field of strategic management has offered a variety of frameworks and concepts during
HRM. Human Resource. Health Organizations. A Guide for Strengthening HRM Systems. Management Rapid Assessment Tool for
 HRM Human Resource Management Rapid Assessment Tool for Public- and Private-Sector Health Organizations A Guide for Strengthening HRM Systems All rights reserved. Management Sciences for Health Telephone:
HRM Human Resource Management Rapid Assessment Tool for Public- and Private-Sector Health Organizations A Guide for Strengthening HRM Systems All rights reserved. Management Sciences for Health Telephone:
Job Classification Manual Page 1 of 42 Vol. II
 Job Classification Manual Page 1 of 42 TIER II STANDARD FOR JURISTS INTRODUCTION 1. This grade level standard illustrates the application of the ICSC Master Standard (Tier I) to a specific field of work
Job Classification Manual Page 1 of 42 TIER II STANDARD FOR JURISTS INTRODUCTION 1. This grade level standard illustrates the application of the ICSC Master Standard (Tier I) to a specific field of work
Education Module for Health Record Practice. Module 7 - Administration and Management of the Health Record Department
 Education Module for Health Record Practice Module 7 - Administration and Management of the Health Record Department The health record officer must meet the leadership challenge in his/her quest to develop
Education Module for Health Record Practice Module 7 - Administration and Management of the Health Record Department The health record officer must meet the leadership challenge in his/her quest to develop
FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT STYLES OF LEADERSHIP TYPES OF MANAGER LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT
 FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT STYLES OF LEADERSHIP TYPES OF MANAGER LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT 1. Planning involves selection of goals 1. An Autocratic style means that the 1. Functional Managers is manager 1. Top
FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT STYLES OF LEADERSHIP TYPES OF MANAGER LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT 1. Planning involves selection of goals 1. An Autocratic style means that the 1. Functional Managers is manager 1. Top
Emerson Job Description Matrix
 S2 S3 S4 Job Family Support Support Support Job Level Grade Level Entry Grade 12 Intermediate Grade 13 Senior Grade 14 Aon Hewitt Job Characteristic Definitions and Descriptions Responsible for the delivery
S2 S3 S4 Job Family Support Support Support Job Level Grade Level Entry Grade 12 Intermediate Grade 13 Senior Grade 14 Aon Hewitt Job Characteristic Definitions and Descriptions Responsible for the delivery
ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 114 Management and Economics ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Jaroslav NEKORANEC Jaroslav.Nekoranec@aos.sk Lenka NAGYOVÁ lenka.nagyova@mil.sk
114 Management and Economics ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Jaroslav NEKORANEC Jaroslav.Nekoranec@aos.sk Lenka NAGYOVÁ lenka.nagyova@mil.sk
Accelerated Learning Course Catalogue
 Accelerated Learning Course Catalogue Graduate Program Course Requirements and Descriptions Graduate courses meet one night per week from 6 p.m. to 10 p.m. in six-week terms. The programs are typically
Accelerated Learning Course Catalogue Graduate Program Course Requirements and Descriptions Graduate courses meet one night per week from 6 p.m. to 10 p.m. in six-week terms. The programs are typically
Detailed Syllabus \\Iconsserver\projects\MaxValue-Phase2\Purchased_images PGPX IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 Detailed Syllabus \\Iconsserver\projects\MaxValue-Phase2\Purchased_images PGPX IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Smart, Fun & Easy Way to Become A Complete Professional! Index Click on the subject for detailed
Detailed Syllabus \\Iconsserver\projects\MaxValue-Phase2\Purchased_images PGPX IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Smart, Fun & Easy Way to Become A Complete Professional! Index Click on the subject for detailed
Detailed Knowledge, Skills and Abilities Tested on the Computerbased Examination for Accreditation in Public Relations (effective January 2016)
 Detailed Knowledge, Skills and Abilities Tested on the Computerbased Examination for Accreditation in Public Relations (effective January 2016) Objective 1 Researching, Planning, Implementing and Evaluating
Detailed Knowledge, Skills and Abilities Tested on the Computerbased Examination for Accreditation in Public Relations (effective January 2016) Objective 1 Researching, Planning, Implementing and Evaluating
INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZTIONAL PSYCHOLOGY
 SUBJECT INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZTIONAL PSYCHOLOGY SESSION 1 INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY Subject: Introduction Industrial Organizational Psychology Session 1 What Is Industrial
SUBJECT INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZTIONAL PSYCHOLOGY SESSION 1 INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY Subject: Introduction Industrial Organizational Psychology Session 1 What Is Industrial
CHAPTER 12.1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 12 Management Accounting Introduction Divisions of Accounting Financial Accounting Concept of Management Accounting Management Accounting-Definition Importance and Need of Management Accounting
CHAPTER 12 Management Accounting Introduction Divisions of Accounting Financial Accounting Concept of Management Accounting Management Accounting-Definition Importance and Need of Management Accounting
Performance Evaluation Senior Leadership
 Performance Evaluation Senior Leadership Employee Name: Position: Program/Dept.: Supervisor Name: Review Date: For each of the valuation standards, bullet points have been provided to assist you with the
Performance Evaluation Senior Leadership Employee Name: Position: Program/Dept.: Supervisor Name: Review Date: For each of the valuation standards, bullet points have been provided to assist you with the
INTERNATIONAL MARKETING MANAGEMENT
 INTERNATIONAL MARKETING MANAGEMENT Equivalent QCF level: Level 4 Credit Value: 30 Learning time (hours): 300 UNIT PURPOSE This unit provides the learner with an understanding of marketing on a worldwide
INTERNATIONAL MARKETING MANAGEMENT Equivalent QCF level: Level 4 Credit Value: 30 Learning time (hours): 300 UNIT PURPOSE This unit provides the learner with an understanding of marketing on a worldwide
Business Analyst Position Description
 Analyst Position Description September 4, 2015 Analysis Position Description September 4, 2015 Page i Table of Contents General Characteristics... 1 Career Path... 2 Explanation of Proficiency Level Definitions...
Analyst Position Description September 4, 2015 Analysis Position Description September 4, 2015 Page i Table of Contents General Characteristics... 1 Career Path... 2 Explanation of Proficiency Level Definitions...
The New West Point Leader Development System (WPLDS) Outcomes Approved by the Academic Board and Superintendent on 16 January 2014
 Upon commissioning, West Point graduates are leaders of character committed to the ideals of duty, honor, country and prepared to accomplish the mission. They will: 1. Live honorably and build trust. Graduates
Upon commissioning, West Point graduates are leaders of character committed to the ideals of duty, honor, country and prepared to accomplish the mission. They will: 1. Live honorably and build trust. Graduates
Designing Productive and Satisfying Work. Lesson 4
 Designing Productive and Satisfying Work Lesson 4 Learning objectives After this lecture you should be able to: Describe how the design of work tasks and roles can align with overall HR strategy. Explain
Designing Productive and Satisfying Work Lesson 4 Learning objectives After this lecture you should be able to: Describe how the design of work tasks and roles can align with overall HR strategy. Explain
Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements
 National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Handbook for Quality Assurance and Accreditation in Saudi Arabia PART 2 Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements Version 2.0 Internal Quality
National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Handbook for Quality Assurance and Accreditation in Saudi Arabia PART 2 Internal Quality Assurance Arrangements Version 2.0 Internal Quality
IBA. Offers a Two-Day Course on Leadership and Change Management. Institute of Business Administration (IBA) University of Dhaka COURSE ADMINISTRATOR
 COURSE ADMINISTRATOR Ms. Sutapa Bhattacharjee, GPHR MBA (Willamette, USA), MBA in HRM (DU) Assistant Professor CONTACT DETAILS For more details, please contact: Management Development Program (MDP) Room#
COURSE ADMINISTRATOR Ms. Sutapa Bhattacharjee, GPHR MBA (Willamette, USA), MBA in HRM (DU) Assistant Professor CONTACT DETAILS For more details, please contact: Management Development Program (MDP) Room#
Management Update: The Eight Building Blocks of CRM
 IGG-06252003-01 S. Nelson Article 25 June 2003 Management Update: The Eight Building Blocks of CRM Customer relationship management (CRM) represents the key business strategy that will determine successful
IGG-06252003-01 S. Nelson Article 25 June 2003 Management Update: The Eight Building Blocks of CRM Customer relationship management (CRM) represents the key business strategy that will determine successful
Business Administration - Course SLOs
 Business Administration - Course SLOs BA CSLO Cerritos College Date: 11/13/2014 BA110 - Advertising Students prepare a consumer research questionnaire given a specified product. Students describe how to
Business Administration - Course SLOs BA CSLO Cerritos College Date: 11/13/2014 BA110 - Advertising Students prepare a consumer research questionnaire given a specified product. Students describe how to
Business Architecture: a Key to Leading the Development of Business Capabilities
 Business Architecture: a Key to Leading the Development of Business Capabilities Brent Sabean Abstract: Relatively few enterprises consider themselves to be agile, i.e., able to adapt what they do and
Business Architecture: a Key to Leading the Development of Business Capabilities Brent Sabean Abstract: Relatively few enterprises consider themselves to be agile, i.e., able to adapt what they do and
PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
 MODULE - 1 Principles of Management 4 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT 4.0 INTRODUCTION In earlier chapters you have studied how the insurance sector is developing in Indian economy and in the present scenario
MODULE - 1 Principles of Management 4 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT 4.0 INTRODUCTION In earlier chapters you have studied how the insurance sector is developing in Indian economy and in the present scenario
Afroza Bulbul, Assistant Professor in Management Department of Business Administration, International Islamic University Chittagong, Dhaka Campus
 Afroza Bulbul, Assistant Professor in Management Department of Business Administration, International Islamic University Chittagong, Dhaka Campus Paper presented at a Follow-up Workshop on Curriculum Reform
Afroza Bulbul, Assistant Professor in Management Department of Business Administration, International Islamic University Chittagong, Dhaka Campus Paper presented at a Follow-up Workshop on Curriculum Reform
All available Global Online MBA routes have a set of core modules required to be completed in order to achieve an MBA.
 All available Global Online MBA routes have a set of core modules required to be completed in order to achieve an MBA. Those modules are: Building High Performance Organisations Management and Organisational
All available Global Online MBA routes have a set of core modules required to be completed in order to achieve an MBA. Those modules are: Building High Performance Organisations Management and Organisational
Cotrugli MBA & Executive MBA outline
 Cotrugli MBA & Executive MBA outline COTRUGLI MBA programs are not only an investment in knowledge, information and networks, nor are they just an investment in career advancement. Our MBA programs inspire
Cotrugli MBA & Executive MBA outline COTRUGLI MBA programs are not only an investment in knowledge, information and networks, nor are they just an investment in career advancement. Our MBA programs inspire
FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT STYLES OF LEADERSHIP TYPES OF MANAGER LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT
 FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT STYLES OF LEADERSHIP TYPES OF MANAGER LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT 1. Planning involves selection of goals 1. An Autocratic style means that the 1. Functional Managers is manager 1. Top
FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT STYLES OF LEADERSHIP TYPES OF MANAGER LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT 1. Planning involves selection of goals 1. An Autocratic style means that the 1. Functional Managers is manager 1. Top
