Preparing Yourself for Pregnancy
|
|
|
- Frederick Robbins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fact Sheet Preparing Yourself for Pregnancy The reproductive system of a woman is internal. The vagina is the passage that leads from the outside of the body to the cervix, which is the opening to the uterus. The uterus is the muscular organ where a fertilized egg attaches and develops. It is about the size and shape of a pear, and is lined with a rich and nourishing mucous membrane called the endometrium. From the top of the uterus extend the fallopian tubes, which lead backward and downward to the ovaries. The ovaries are the two small organs that contain the eggs. A woman is born with about 400,000 eggs and this number declines as she ages. Each month during her reproductive years, a number of eggs (ova) begin to mature inside follicles within an ovary. By midcycle, usually only one egg has completed maturation and this egg is released from its follicle during ovulation. The egg is then picked up by the fimbria or "fingers" of the fallopian tube. Fertilization by the man's sperm then takes place in the outer one third of the tube within about 24 hours of ovulation. The resulting embryo is pushed along the fallopian tube and into the uterus about four days later. Implantation of the developing embryo into the endometrium then begins. This sequence of events is controlled by monthly changes in a woman's hormone levels. To help understand the process a little better, it is important to understand the menstrual cycle and the hormones involved. The Menstrual Cycle The menstrual cycle refers to the maturation and release of an egg, and to the preparation of the uterus to receive and nurture an embryo. The typical cycle, which is central to a woman's fertility, takes approximately 26 to 35 days and occurs in three phases: follicular - the stage of egg maturation; ovulatory - the time of the egg release; and luteal - the time of fertilization and implantation. The cycle is managed by two hormones, Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinising hormone (LH)
2 During the first, or follicular, phase of the cycle, FSH stimulates the development of follicles within both ovaries. Usually only one follicle grows to produce a mature egg (the dominant follicle). The developing follicles secrete oestrogen, which has several effects. One is to produce midcycle changes in the cervical mucus, preparing it to receive and nourish the man's sperm. Another is to thicken and prime the endometrium for implantation of a developing embryo. The ovulatory phase occurs when LH levels dramatically increase or "surge", causing the release of the egg from the dominant follicle. This usually occurs midway through the cycle or about 12 to 16 days after the first day of a woman's period in a typical 28-day cycle. The luteal phase follows ovulation. The ovarian follicle that nurtured the egg before ovulation now becomes known as the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum begins to produce oestrogen and progesterone, the two hormones necessary for developing and maintaining the uterine lining, or endometrium, so a fertilized egg, now an embryo, may implant and develop. If fertilization does not occur during the monthly cycle, hormone production by the corpus luteum declines, causing the uterine lining to break down and shed. This in turn leads to menstruation and so the cycle begins again. The unfertilized egg simply breaks down in the fallopian tube or uterus and is absorbed. The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system is also under the influence of hormones and is responsible for producing sperm. The male reproductive system is both internal and external. The testes are located within the scrotal sac, the pouch of skin located below the man's penis. These are the two organs that produce both sperm and testosterone, the male hormone that helps maintain the male sexual characteristics. As sperm are produced, they pass from the testes through the coiled channels of the epididymis, an organ that stores and nourishes them as they mature. Once sperm are completely mature, they move into the vas deferens. This tubal structure connects the epididymis with the seminal vesicles, the two pouch like glands that provide storage for the mature sperm. When a man ejaculates, sperm from the seminal vesicles combine with a thick fluid from the prostate gland. This seminal fluid (or ejaculate) is deposited into the woman's vagina during intercourse. The Role of Spermatogenesis The development of normal, mature sperm is key in establishing male fertility and involves interplay of several factors: An exchange of hormonal messages between the brain and the testicles The secretion of necessary reproductive hormones and normal sperm development Normal transport of developing sperm from testicles via the epididymis and vas deferens to the seminal vesicles.
3 The production of sperm is primarily regulated by three hormones which, unlike in women, are secreted in a fairly constant, rather than cyclic, way: FSH LH Testosterone In the male, FSH and LH from the pituitary are responsible for maintaining the sperm production process. The pituitary gland, which is located at the base of the brain, secretes the same hormones in regulating the female's reproductive functions. FSH is responsible for stimulating sperm production in the testicles. LH stimulates the production of testosterone. Under the influence of Sertoli cells and specific hormones, immature sperm cells develop through several stages and eventually become mature sperm cells, called spermatozoa. These spermatozoa then pass through the epididymis where, after 18 to 24 hours, they gain motility (movement). After acquiring the ability to move, mature sperm are stored in the vas deferens and seminal vesicles until ejaculation. Fertilisation and Pregnancy A woman's "fertile time" is around midcycle, when ovulation occurs. When a couple has intercourse during this time, sperm enter into the cervical mucus. This mucus is normally receptive to sperm around the time of ovulation. Gradually, sperm advance into the uterus and up to the fallopian tube, where the egg is positioned near the ovary. Here, it can be fertilized by the man's sperm. The egg is probably able to be fertilized for about 24 hours following ovulation. Since the sperm have to bio chemically change or "capacitate" prior to fertilization, intercourse before egg release is important. Sperm may live in the cervix and fallopian tube for up to four days. If a woman's menstrual cycle is on average 28 days long, intercourse every other day between days 10 and 17 gives the best chance of success. Intercourse does not have to occur on the actual day of ovulation for conception to occur. Over the next two to three days, a fertilized egg, which is now an embryo, will develop within the tube and move to the uterus where it attaches to the uterine lining. The lining of the uterus (endometrium) has been prepared to receive the embryo by the female hormone progesterone. A pregnancy test may be positive as early as one or two days after an expected period. Home pregnancy tests may be a good first step, but your physician will want to confirm pregnancy with either a urine or blood test. Preparing For Pregnancy Your overall health can have a significant impact on your fertility. This is why it is important to take extra special care of yourself even before you start trying to conceive. Several things can impact the ability to conceive:
4 Behavioral Factors Certain personal habits or lifestyle factors may impact your health and, thus, affect your ability to conceive. Many of these factors can be regulated to increase overall health and improve your chances of conceiving: Diet and Exercise - Proper diet and exercise are important for optimal reproductive function. Women who are significantly overweight or underweight may have difficulty conceiving. Smoking - Cigarette smoking appears to reduce fertility. Women who smoke 20 cigarettes per day may be 20 percent less likely to conceive than non-smokers. Also, the risks of miscarriage, premature birth and low-birth-weight babies are elevated. It is safest to give up and, if both partners smoke, easier to do as a couple. Men who give up will see some improvement in sperm quality. Alcohol - Alcohol intake can also impact sperm counts in men. In women, it may contribute to an increased risk of babies born with birth defects. It is best to avoid alcohol at least for the first three months of pregnancy. Medications - A number of medications, including some of those used to treat depression, ulcers and high blood pressure, can influence a man's sperm count and libido (sex drive). Couples should advise their physician of any medications they are taking prior to undergoing fertility investigation and/or treatment. Recreational Drugs - Drugs, such anabolic steroids, may affect sperm counts in men. Cocaine use in pregnant women may seriously impair a baby's health. Drug addiction is easily passed from the mother to the fetus during pregnancy; controlled and/or addictive substances should not be taken immediately prior to or during pregnancy. Caffeine - Extensive caffeine use (six to eight cups of coffee per day) may increase the risk of miscarriage. However, there is no clear understanding of what amount affects fertility. It is wise to drink no more than two cups of coffee per day and decaffeinated coffee may be preferable. Lubricants - A number of products used for lubrication during intercourse, such as petroleum jelly or vaginal creams, have been shown to affect sperm quality and should be avoided if you are trying to conceive. Products containing spermicide (e.g. nonoxynol-9) should definitely be avoided. Lead - Extensive exposure to lead has been shown to impact fertility in humans. Individuals working with paints/varnishes and auto manufacturing may be at risk. Medical Treatments and Materials - Repeated exposure to sources of radiation, such as x-rays and cancer treatments (e.g. chemotherapy), have been shown to affect sperm production and contribute to ovarian problems. 4 Modern diagnostic x-ray equipment is very safe but whenever possible, it makes sense to shield the testes and ovaries. Ethylene Oxide - Exposure to ethylene oxide, a chemical used in the sterilization of surgical instruments and in the manufacture of certain pesticides, may cause birth defects in early pregnancy. It also has the potential to cause early miscarriage.
5 Biological Factors Most couples who do not conceive easily will have one or more identifiable causes. In approximately 40% of cases, the problem is attributable to the male; another 40% is traced to the female. In about 10% of cases, fertility problems are linked to both partners. The remaining 10% of infertility is unexplained, even after exhaustive testing. It is important and helpful for both partners to try to understand the problem(s) and the available treatments. Options should be discussed as a couple with a healthcare provider. Some of the more common conditions which can contribute to fertility problems include: Abnormal Ovulation - Abnormal ovulation is indicated by irregular or absent menstrual periods which can be the result of a hormonal imbalance. In many cases, this can be successfully treated. Problems with ovulation may also be associated with extremely low body weight or with being overweight, as well as any significant change in weight (loss or gain). If you are not having regular monthly periods (every 26 to 35 days), you may wish to consult your physician before trying to conceive. Blocked Fallopian Tubes - Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes may impair fertility by interfering with the egg and sperm transport. Tubal damage is often caused by pelvic infection, most commonly by chlamydia, or gonorrhea. Often, there are no symptoms of tubal or pelvic infection, and damage may only be discovered during an infertility evaluation. Treatment of tubal problems or pelvic scarring may require specialized surgery or in vitro fertilization. Endometriosis - For reasons that are poorly understood, tissue from the uterine lining implants on the ovaries and other pelvic organs, and may contribute to, or cause, infertility. A positive diagnosis of endometriosis can only be made by surgical procedures such as diagnostic laparoscopy that allows the physician to directly view the uterus, fallopian tubes and pelvic cavity (described in the next section). The symptoms of endometriosis may include heavy, painful and long menstrual periods. However, there is often little correlation between the severity of the symptoms and the extent of the disease. Sometimes there are no symptoms at all. Several forms of treatment are available, involving both medications and surgery. Cervical Problems - Cervical problems may be related to the consistency of the cervical mucus or cervical anatomy, which make it a poor environment for sperm transport and survival. Previous cervical surgery such as cone biopsy may impair mucus production. Male Factor - Male infertility may be related to inadequate sperm count or abnormalities relating to shape and movement of sperm. While varicocele, or varicose veins within the scrotum are common, it is unclear how important they are in the process of male infertility. Testicular injury that results in damage to sperm-producing structures or undescended testicles are important causes of infertility. Hormonal imbalances, the presence of other diseases such as diabetes mellitus, and pituitary tumors are uncommon problems affecting fertility. Age - Age is a very important factor in the fertility of a couple. Fertility levels decrease with female age, while male age has little impact. Maximum fertility for women occurs between the ages of 15 and 24. Since many women delay starting a family until they are in their 30s or 40s, infertility has become relatively more common: about one-third of women who defer pregnancy until their mid-30s will have a problem becoming pregnant. Most women over age 40 will have problems conceiving. It may therefore be wise for women over age 35 to seek help after six months of unprotected intercourse rather than waiting a full year.
6 Make An Active Preconception Plan Many women think that in order to conceive they need only stop using their contraceptive method. But some forms of contraception reduce the chances of healthy conception, and some couples are for no obvious reason still waiting long after they expected to conceive. Every couple will benefit from being more active and making positive preparations. The most important aspects of conception is done weeks before the next menses. The egg was created before the mother was born and ripens for about three months before ovulation, two weeks before the next period. The sperm that will fertilize the egg grown about two months beforehand. The fist step to successful pregnancy is to prepare a healthy egg and a healthy sperm. Inadequate food, smoking, alcohol, infection or irradiation at about the time the egg and sperm are being made can have disastrous effects, in fact most eggs that ripen against this background are probably not even viable. Taking active measures means both partners need to take a number of positive and straightforward precautions to improve their general health and create the best possible circumstances for conception. This needs to take place several months before conception is planned. List if actions you should take to ensure best chances of successful conception. Start your planning by setting a pre-conception window 18 months if you re using depo provera or have a hormonal implant, 12 months if you are on the pill, 6 months if you re fitted with an IUD. Extra Zinc (15mg daily), Vitamin C (250mg daily) and Vitamin B6 (100mg daily) will replace deficiencies the pill, depo or implants commonly cause. Have your IUD or implant removed as soon as possible at the beginning of your preconception window Arrange to be fitted with a cap or diaphragm or use condoms instead for the duration of the pre-conception window Keep a calendar with details of your cycle, chat BBT temperatures if possible Your diet should include cauliflower, seeds and nuts, roe, eggs - since these are richer in the nutrients you need Schedule a rubella immunity screen Schedule a pap smear, if not current Schedule an STD screen Start taking 400 mg folic acid daily If you smoke stop Limit alcohol intake to 2 units per day Limit caffeine intake to 3 cups per day Ask your partner to have a sperm level test Stop your barrier contraceptive precautions at the end of your pre-conception window but keep everything else going. Let yourselves relax and leisure in life. Sometimes a holiday sets the right tone. Make sure you re having regular penetrative unprotected sex Achieving orgasm does increase the possibility of conception, orgasm anytime up to 40 minutes after his ejaculation gives the best chance of conceiving
7 Preconception Well-being Program Here at the Women s Natural Health Practice we offer a preconception well-being program that consists of four, bi-weekly acupuncture sessions over 2 months, herbal medicine tonics, haematology, blood group, rubella and varicella zoster antibodies screening and any other screening that may be necessary. Our Female Healthcare Philosophy At the Women s Natural Health Practice we specialise in providing comprehensive natural, reproductive, gynaecological, obstetric and general healthcare for females from adolescence to postmenopause. Our approach is to integrate techniques in both oriental and western medical diagnosis in order to formulate a naturally oriented treatment plan combining acupuncture, herbal medicine, nutritional therapy, exercise and lifestyle. Each treatment plan is tailored specifically to each individual woman maximising results. Please us at enquiries@naturalgynae.com with questions, we are more than happy to provide any information via that will assist you in deciding which treatment approach would be best for you For more information, contact details and appointments click here
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Timing is everything. Ovulation Tracking. Patient Information Booklet
 Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO
 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Infertility: An Overview
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Causes for unintentional childlessness
 Causes for unintentional childlessness We can define fertility as the inability to become pregnant after one year of regular sexual intercourse. The causes of infertility are evenly distributed among men
Causes for unintentional childlessness We can define fertility as the inability to become pregnant after one year of regular sexual intercourse. The causes of infertility are evenly distributed among men
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Lesbian Pregnancy: Donor Insemination
 Lesbian Pregnancy: Donor Insemination (Based on an article originally published in the American Fertility Association 2010 National Fertility and Adoption Directory. Much of this information will also
Lesbian Pregnancy: Donor Insemination (Based on an article originally published in the American Fertility Association 2010 National Fertility and Adoption Directory. Much of this information will also
injections injections injections injections injections injection injections injections injections tions njections injections injections injections
 your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
This is Jaydess. Patient Information. What is Jaydess? How does Jaydess work?
 , Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
, Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
How Your Fertility Works
 How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
it right? activity (page 4) to highlight ethical issues associated with IVF
 IN VITRO FERTILIZATION I V F In some cases, a sperm is directly injected into an egg IVF: THE MEETING OF SPERM AND EGG IN GLASS Louise Brown, the first test tube baby was born in 1978. Since then, there
IN VITRO FERTILIZATION I V F In some cases, a sperm is directly injected into an egg IVF: THE MEETING OF SPERM AND EGG IN GLASS Louise Brown, the first test tube baby was born in 1978. Since then, there
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook
 In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Infertility Services Medical Policy For University of Vermont Medical Center and Central Vermont Medical Center employer groups
 Infertility Services Medical Policy For University of Vermont Medical Center and Central Vermont Medical Center employer groups File name: Infertility Services File code: UM.REPRO.01 Last Review: 02/2016
Infertility Services Medical Policy For University of Vermont Medical Center and Central Vermont Medical Center employer groups File name: Infertility Services File code: UM.REPRO.01 Last Review: 02/2016
Baby Steps To A Healthy Pregnancy
 Preconception Middlesex-London Health Unit 50 King Street, London, ON N6A 5L7 519-663-5317 Published 2015. Copyright of the Middlesex London Health Unit. All rights reserved. Baby Steps To A Healthy Pregnancy
Preconception Middlesex-London Health Unit 50 King Street, London, ON N6A 5L7 519-663-5317 Published 2015. Copyright of the Middlesex London Health Unit. All rights reserved. Baby Steps To A Healthy Pregnancy
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Male Health Issues. Survivorship Clinic
 Male Health Issues The effects of cancer therapy on male reproductive function depend on many factors, including the boy s age at the time of cancer therapy, the specific type and location of the cancer,
Male Health Issues The effects of cancer therapy on male reproductive function depend on many factors, including the boy s age at the time of cancer therapy, the specific type and location of the cancer,
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
Clinical Policy Committee
 Northern, Eastern and Western Devon Clinical Commissioning Group South Devon and Torbay Clinical Commissioning Group Clinical Policy Committee Commissioning policy: Assisted Conception Fertility assessment
Northern, Eastern and Western Devon Clinical Commissioning Group South Devon and Torbay Clinical Commissioning Group Clinical Policy Committee Commissioning policy: Assisted Conception Fertility assessment
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD the IUD. the IUD. the the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD.
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
IN VITRO FERTILISATION IVF and ICSI
 IN VITRO FERTILISATION IVF and ICSI Page 1 of 7 WHAT ARE IVF and ICSI? IVF is short for in vitro fertilisation which means fertilisation outside the body. It usually involves stimulation of the ovaries
IN VITRO FERTILISATION IVF and ICSI Page 1 of 7 WHAT ARE IVF and ICSI? IVF is short for in vitro fertilisation which means fertilisation outside the body. It usually involves stimulation of the ovaries
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
Fertility-related choices. A decision aid for younger women with early breast cancer
 Fertility-related choices A decision aid for younger women with early breast cancer Fertility-related choices Section 1 About this booklet 1 Overview 3 Summary of fertility options 4 Section 2 Some background
Fertility-related choices A decision aid for younger women with early breast cancer Fertility-related choices Section 1 About this booklet 1 Overview 3 Summary of fertility options 4 Section 2 Some background
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013
 Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
HEALTH UPDATE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
1. AMOUNT OF FSH PRESENT
 The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
 Centre for Diabetes and Endocrinology - Patient information Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Approximately 1 in 5 women have polycystic ovaries. This describes the appearance of the ovaries when they are
Centre for Diabetes and Endocrinology - Patient information Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Approximately 1 in 5 women have polycystic ovaries. This describes the appearance of the ovaries when they are
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
progestog progestogen stogen-only pill progestogen progestogen-only pill he progestogen-only pill progestogen-onl progestogen-o the progestogenonly
 your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
The causes of infertility include abnormalities of any portion of the male or female reproductive system.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY Defined as 1 year of unprotected intercourse during which
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY Defined as 1 year of unprotected intercourse during which
Ectopic Pregnancy. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Final Version Two (Sept 2014) Eastern Cheshire Clinical Commissioning Group NHS Funded Treatment for Subfertility Policy
 Final Version Two (Sept 2014) Eastern Cheshire Clinical Commissioning Group NHS Funded Treatment for Subfertility Policy NHS FUNDED TREATMENT FOR SUBFERTILITY ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA Table of Contents 1.
Final Version Two (Sept 2014) Eastern Cheshire Clinical Commissioning Group NHS Funded Treatment for Subfertility Policy NHS FUNDED TREATMENT FOR SUBFERTILITY ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA Table of Contents 1.
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court. A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and
 Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Endometriosis, Fertility and Pregnancy
 This leaflet covers endometriosis and fertility. It provides information for women who have been diagnosed with endometriosis who would like to know if and how this can affect their fertility, and for
This leaflet covers endometriosis and fertility. It provides information for women who have been diagnosed with endometriosis who would like to know if and how this can affect their fertility, and for
Alcohol and Reproduction
 The facts about... Alcohol and Reproduction Five key things you need to know Even small amounts of alcohol can interfere with our reproductive systems. The more you drink, the greater the effect it can
The facts about... Alcohol and Reproduction Five key things you need to know Even small amounts of alcohol can interfere with our reproductive systems. The more you drink, the greater the effect it can
Reproductive Technology. Chapter 21
 Reproductive Technology Chapter 21 Assisted Reproduction When a couple is sub-fertile or infertile they may need Assisted Reproduction to become pregnant: Replace source of gametes Sperm, oocyte or zygote
Reproductive Technology Chapter 21 Assisted Reproduction When a couple is sub-fertile or infertile they may need Assisted Reproduction to become pregnant: Replace source of gametes Sperm, oocyte or zygote
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
East and North Hertfordshire CCG Fertility treatment and referral criteria for tertiary level assisted conception. December 2014
 East and North Hertfordshire CCG Fertility treatment and referral criteria for tertiary level assisted conception December 2014 1 1. Introduction This policy sets out the entitlement and service that will
East and North Hertfordshire CCG Fertility treatment and referral criteria for tertiary level assisted conception December 2014 1 1. Introduction This policy sets out the entitlement and service that will
Lakeview Endocrinology and Diabetes Consultants. 2719 N Halsted St C-1. Chicago IL 60614 P: 773 388 5685 F: 773 388 5687. www.lakeviewendocrinolgy.
 Lakeview Endocrinology and Diabetes Consultants 2719 N Halsted St C-1 Chicago IL 60614 P: 773 388 5685 F: 773 388 5687 www.lakeviewendocrinolgy.com Patient information: Early menopause (premature ovarian
Lakeview Endocrinology and Diabetes Consultants 2719 N Halsted St C-1 Chicago IL 60614 P: 773 388 5685 F: 773 388 5687 www.lakeviewendocrinolgy.com Patient information: Early menopause (premature ovarian
MENOPAUSE WOMAN'S TEST (Assessment of hormone balance)
 ATTACHMENT: Useful remarks for patient and doctor, to be associated to the analytical results. Your doctor should interpret this report. Cod. ID: 123456 CCV: 6bf Date: 01/01/2013 Patient: Rossi Mario Rapport
ATTACHMENT: Useful remarks for patient and doctor, to be associated to the analytical results. Your doctor should interpret this report. Cod. ID: 123456 CCV: 6bf Date: 01/01/2013 Patient: Rossi Mario Rapport
Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress
 Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress By Michelle Buchanan, Certified Acupuncturist The History of
Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress By Michelle Buchanan, Certified Acupuncturist The History of
All you need to know about Endometriosis. Nordica Fertility Centre, Lagos, Asaba, Abuja
 All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Signs, symptoms, and treatments What is PCOS? Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects up to 1 in 10 women of reproductive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Signs, symptoms, and treatments What is PCOS? Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects up to 1 in 10 women of reproductive
The IUI procedure Who should consider an IUI IUI success rates IUI cost What to consider if IUI is unsuccessful. The IUI procedure:
 A Complete Guide to understanding IUI (intrauterine insemination) and artificial insemination (Eric Daiter, MD Board Certified in Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility) The IUI procedure Who should
A Complete Guide to understanding IUI (intrauterine insemination) and artificial insemination (Eric Daiter, MD Board Certified in Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility) The IUI procedure Who should
Copper intra-uterine device (IUD)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
Birth Control Methods
 page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
What could endometriosis mean for me?
 Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
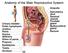 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Gynaecology FAQ s. Correspondence address: 204 Fulham Road London SW10 9PJ Email: enquiries@missayida.com Tel: 02077514489
 Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
THE WELL. Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices WOMAN CENTRE
 THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury
 Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
Patient Information: Endometriosis Disease Process and Treatment
 1 William N. Burns, M. D. Associate Professor Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine Marshall University Huntington, West Virginia, USA Patient Information: Endometriosis
1 William N. Burns, M. D. Associate Professor Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine Marshall University Huntington, West Virginia, USA Patient Information: Endometriosis
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Stay Healthy at Any Age!
 + Stay Healthy at Any Age! February 28, 2013 Kimberly Kelstone A Deaf Health Talk DHCC Partnership with REAP + Overview Introduction Normal healthy processes Diseases specific to women Screening tests
+ Stay Healthy at Any Age! February 28, 2013 Kimberly Kelstone A Deaf Health Talk DHCC Partnership with REAP + Overview Introduction Normal healthy processes Diseases specific to women Screening tests
l family plan natural natural family p natural family planning ily natural family plannin natural fami atural family planning your guide to
 your guide to natural family planning Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you natural family pla al family plannin natural family planning natural family plann atural fam natural
your guide to natural family planning Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you natural family pla al family plannin natural family planning natural family plann atural fam natural
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills
 Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills Abstinence Birth Control Pills Cervical Barriers Condoms
Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills Abstinence Birth Control Pills Cervical Barriers Condoms
