Definition of Coaching. Serene Koh and Susan B. Neuman University of Michigan
|
|
|
- Augusta Daniels
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Definition of Coaching Serene Koh and Susan B. Neuman University of Michigan Suggested Citation: Koh, S. & Neuman, S.B. (2006). Exemplary elements of coaching: Ann Arbor MI: University of Michigan Research Program on Ready to Read. As described in Joyce and Showers (1983), Mello (1984), and Smith and Acheson (1991), coaching provides professionals with the following opportunities: - To receive support and encouragement through the opportunity to review experiences, discuss feelings, describe frustrations, and check perceptions with a partner - To fine-tune skills or strategies through technical feedback and technical assistance from a coaching partner - To analyze practices and decision making at a conscious level - To adapt or generalize skills or strategies by considering what is needed to facilitate particular outcomes, how to modify the skill or practice to better fit interactions with specific families or practitioners, or what results may occur from using the skill or practice in different ways - To reflect on what they perceive or how they make decisions, which helps improve their knowledge and understanding of professional practices and activities Exemplary Elements of Coaching 1) On-site Coaching - There is some literature to suggest that coaching which takes place in the teachers own classroom is more effective because it allows the teacher to see elements of coaching put into practice in the here and now. It is also less disruptive of the teacher s schedule. On-site coaching also allows teachers to more specifically identify issues or areas of need within their classroom which can be improved by coaching. (Black et al, 2003) - Teachers are more likely to "buy in" and change their own instructional practices when coaches come into their classrooms and model instructional techniques. Of all the techniques coaches employ, modeling instruction in individual classrooms is most likely to result in modifications in instructional practices and adherence to the instructional delivery formats. (Poglinco & Bach, 2004) - Feger et al call this demonstration and co-teaching which can also allow teachers to experience a paradigm outside of their own (2004). - Teachers often ask for a demonstration lesson because that's what they see as coaching or they want to assess a coach's credibility. Demonstrating a lesson can let a coach communicate to a teacher that she is willing to collaborate and take on the challenges the teacher tackles every day. - Teachers reported that guidance from coaches in classrooms themselves were most valuable as these forms of coaching dealt with instruction specifically and enabled coaches to best identify areas where teachers knowledge and capacity needed assistance. (Herll and O Drobinak, 2004). 1
2 2) Coaching Should Be Balanced and Sustained - The 9-month school calendar is indicted for not only limiting student learning but also teacher learning. - Teachers generally have very sporadic summer learning for themselves unless they initiate it individually; basically, these are separate, discrete activities based on the individual teacher's motivation. - When school ends in late May or early June teachers might have a short in-service day after which they are then are left alone for the long summer. Just before school starts in late August, teachers are generally infused with a rapid fire string of professional development activities completed in 1 or 2 days. This is done in preparation for the start of the new school year. - However, research tells us that this type of temporary infusion of learning for teacher development does not work (Darling-Hammond, 1997). - Research and proven practice provides several models for reallocating time within the year for learning and quality professional development. Some possible options are: balanced calendar and year-round education, expanded professional development hours and days, accumulated or banked time, alternative grouping, alternative scheduling, expanded staffing, and school-university partnerships. (Speck, 2002) 3) Good Coaches Don t Dictate - They don t just dictate the right answer, they facilitate other people s reflection. Good coaches are often the best teachers: Who listens to students? Who seeks to engender understanding in students, instead of looking for them to recite the right answers? The same behaviors make people good coaches. (Harwell-Kee, 1999) - Good coaches must have the ability to know when to push and when to stand back and regroup in the long-term process of adopting new approaches to galvanize a school to function differently. To succeed, a coach must be a leader who is willing not to be recognized as such and, at the same time, who is able to foster leadership among teachers who rarely regard themselves as leaders. (Guiney, 2001) 4) Student Outcome Benefits from Strong Interaction with Coaches - A study in Ontario investigated the conditions within which coaching was most effective in engendering positive student outcomes (Ross, 1992). - The main findings are: o Student achievement is higher in the classrooms of teachers who interacted more extensively with their coaches; o Student achievement is higher in the classrooms of teachers with higher teacher efficacy beliefs; o All teachers, regardless of their level of efficacy, were more effective with increased contact with their coaches. - One important aspect of this strong interaction is a high level of trust. More so than student learners, Adult learning is enhanced by behaviors that demonstrate respect, trust, and concern for the learner, and adults want to be the originators of their own learning - that is, involved in selecting objectives, content, activities, and assessment. (Herll and O Drobinak, 2004) 2
3 5) Provide Descriptive Feedback - Specifically, teachers find that immediacy of feedback to be very valuable in terms of interaction. (Ai and Rivera, 2003). Tips for giving descriptive feedback have been outlined by Gallacher (1995), Hutto et al. (1991), Schreiber (1990), and Wolfe (1994). - The general guidelines for feedback include the following: a. be descriptive, not evaluative or judgmental; b. be specific rather than general; c. describe observable events or behaviors rather than give opinions; d. focus on behavior rather than the person; e. share information rather than give advice; f. explore alternatives rather than give the answer or solution (use provisional language); g. begin with positive information; h. describe observed relationships between behaviors or events so the partner can make cause-and-effect inferences; and i. offer the amount of information the receiver can use rather than the amount one would like to give. 6) Match/ Complement Teachers Behavioral Style - This requires the coach to modify the level of support and direction provided depending on the level of assistance teachers requests and on the amount of support the coach perceives is needed to accomplish the coaching process. - The teacher s degree of self-direction often is influenced by several contextual variables, including knowledge and understanding of the topic or content, technical skills regarding a particular topic, sense of personal competence, and the context of the learning event (Gallacher, 1997). - Complementing teachers behavioral style or preferences is another specialized skill that coaches employ in matching the teachers style. Coaches are to consider their partner s style and preference regarding interaction, the process for receiving information, the kind of information that would be most salient, methods for decision making, and ways to structure or organize coaching activities. For example, some teachers may prefer more details initially, while others prefer the big picture at the beginning. (Gallacher, 1995). 7) Promote Professional Reflection - According to Gallacher (1995) and Swarzman (1993), reflection is a powerful impetus for continued personnel development and self-directed learning. The coach prompts and facilitates the teacher s analysis of his or her individual learning objectives, performance, and decision making regarding the use of particular techniques or practices. - Through reflection, the teacher examines the effectiveness of particular methods or practices, interprets situations or events, and considers how values, expectations, and 3
4 beliefs influenced his or her choices and the situation. The coach promotes reflection by encouraging the teacher to recall a specific event in detail, examine feelings associated with the experience, and contemplate what he or she would do differently to be even more effective. - Related to this is the ability of the coach to be a good listener and to allow time for teachers to reflect. Coaches must maintain a collaborative, trusting relationship with teachers so the teacher sees the coach s questions as prompts for reflection, not critical judgments that put the teacher on the defensive. - For the coach, this means phrasing genuine questions for reflection rather than questions with a single correct answer, and waiting for the teacher to respond. Silence following a question can make a coach feel uncomfortable, but that may be time in which the teacher reflects. (Feger et al, 2004) 8) Coaches Must be Well-trained - Coaches must have a solid repertoire of techniques to call upon. They must also be able to effectively critique and provide useful feedback to teachers. Both prior experience and individual personality factor into how coaches deal with the multiple demands of their role. - Some skills/ knowledge coaches should be armed with: o Interpersonal skills o Content knowledge o Pedagogical knowledge o Knowledge of the curriculum o Awareness of coaching resources o Knowledge of the practice of coaching (Feger et al, 2004) 9) Good Coaching is Collaborative - In a case study in Boston, researchers found that coaches who spent time talking and working with teachers on specific issues of assessment, curriculum and instruction were able to better effect positive results. This was accompanied by common planning sessions every day which coaches attend once a week. (Guiney, 2001). This is related to the notion that coaches cannot direct; teachers gain most from coaching if they are treated as equals even if they may be less experienced or knowledgeable as coaches. - Another successful case study in Texas focused on coaches who regularly conducted debriefing sessions to hear the teacher's perception of their demonstration lessons and to share the coaches' own reflections, including how to use the experience to plan the next lesson. The coaches reflected on why they chose that particular lesson, how they planned its delivery and chose materials appropriate to the children's needs, and what they thought and did as the lesson progressed. Teachers found this kind of collaborative sharing very effective. (Redell, 2004). 10) Prioritize - Research shows that good coaching is about identifying priorities, not just what areas of teacher practice require your help, but also in assisting teachers in identifying their own priority of needs in their training. (Herll and O Drobinak, 2004). 4
5 - Coaches must dialogue with teachers about their perceived strengths and weaknesses not only individually but also in a group. Thereafter, coaches are to prioritize these needs in a way which will best benefit all teachers. References Ai, X. and Rivera, N. (2003). Linking Ideas to Practice: Effectiveness of Coaching upon Teacher Practice. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Chicago, Illinois, April 23, 2003, p Black, R, Molseed, T, and Sayler, B. (2003) Fresh view from the back of the classroom in Clinical supervision: Coaching for higher performance (pp ). Lancaster, PA: Technomic Publishing Co. Darling-Hammond, L. (1997). The right-to learn: blueprint for creating schools that work. Francisco: Jossey-Bass. San Feger, S., Woleck, K., and Hickman, P. (2004). How to develop a coaching eye. in Journal of Staff Development. 25(2), p Gallacher, K. (1995). Coaching partnerships: Refining early intervention practices. Missoula: Montana University Affiliated Rural Institute on Disabilities. Gallacher, K. (1997). Supervision, mentoring and coaching. In P. Winton, J. McCollum, & C. Catlett (Eds), Reforming personnel in early intervention (p ). Baltimore, MD: Brookes. Guiney, E. (2001). Coaching Isn't Just For Athletes: The Role of Teacher Leaders in Phi Delta Kappan. 82 (7), p Harwell-Kee, K. (1999). Coaching in Journal of Staff Development. 20(3), p Herll, S. and O Drobinak, B. (2004). Role of a coach: Dream keeper, supporter, friend. in Journal of Staff Development. 25(2), p Hutto, N., Holden, J., & Haynes, L. (Eds.). (1991). Mentor training manual for Texas teachers. Dallas: Texas Education Agency. Joyce, B., & Showers, B. (1983). Power in staff development through research on training. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Mello, L. (1984). Peer-centered coaching: Teachers helping teachers to improve classroom performance. Idaho Springs, CO: Associates for Human Development. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED ) Poglinco, S. and Bach, S. (2004) The Heart of the Matter: Coaching as a Vehicle for Development in Phi Delta Kappan, 85(5), p ) Professional 5
6 Redell, P. (2004). Coaching can benefit children who have a harder hill to climb. in Journal of Staff Development. 25(2), p Ross, J. A. (1992). Teacher Efficacy and the Effects of Coaching on Student Achievement. in Canadian Journal of Education, 17(1), p Schreiber, B. (1990). Colleague to colleague: Peer coaching for effective in-house training. in Education Libraries, 15(1 2), p Smith, N., & Acheson, K. (1991). Peer consultation: An analysis of several types of programs (Vol.34, 6). Eugene: University of Oregon, Oregon School Study Council. Speck, M. (2002). Balanced and Year-Round Professional Development: Time and Learning. in Catalyst for Change, 32(1), p Swarzman, J.B. (1993). Communication and coaching. In R.H. Anderson & K.J. Snyder (Eds.), 6
As schools and districts explore how coaching fits into their
 th e m e/ SCHOOL-BASED How to develop a coaching eye When coaching first emerged as a term for on-site staff development, the image that came to mind for many was demonstration lessons. I go in and model,
th e m e/ SCHOOL-BASED How to develop a coaching eye When coaching first emerged as a term for on-site staff development, the image that came to mind for many was demonstration lessons. I go in and model,
Section 2b: Observation/Feedback Approach
 Section 2b: Observation/Feedback Approach Observation/Feedback is a collegial, professional development approach that encourages practitioners to analyze, critique, practice, reflect, and revise instructional
Section 2b: Observation/Feedback Approach Observation/Feedback is a collegial, professional development approach that encourages practitioners to analyze, critique, practice, reflect, and revise instructional
Source- Illinois State Board of Education (www.isbe.net)
 Wise Ways / Center on Innovation & Improvement CL17 Indicator: Professional development for teachers is determined by data (including classroom observations and review of lesson plans) that demonstrate
Wise Ways / Center on Innovation & Improvement CL17 Indicator: Professional development for teachers is determined by data (including classroom observations and review of lesson plans) that demonstrate
The information and application for completing the Coaching and Mentoring models application is available to you from several sources:
 Getting Started The information on the following pages is for the Coaching and Mentoring Models of Professional Development Credit The information and application for completing the Coaching and Mentoring
Getting Started The information on the following pages is for the Coaching and Mentoring Models of Professional Development Credit The information and application for completing the Coaching and Mentoring
If I knew then what I know now, I wouldn t have been afraid to ask for help or materials.
 Coaching Cycle: Stage III R eflection is a key element in stimulating professional growth and improving professional practice. After the classroom observation, it is important that both the mentor or mentor
Coaching Cycle: Stage III R eflection is a key element in stimulating professional growth and improving professional practice. After the classroom observation, it is important that both the mentor or mentor
Section 2: Professional Development Approaches
 Section 2: Professional Development Approaches Overview In this section of the Guide, four approaches to professional development that are especially applicable to adult education are discussed as follows:
Section 2: Professional Development Approaches Overview In this section of the Guide, four approaches to professional development that are especially applicable to adult education are discussed as follows:
Job-Embedded Graduate Education for Teachers: Working Intensively in High Needs Schools
 130 Job-Embedded Graduate Education for Teachers: Working Intensively in High Needs Schools Raquel Munarriz-Diaz, Magdalena Castañeda, and Phillip Poekert University of Florida, USA Abstract: The researchers
130 Job-Embedded Graduate Education for Teachers: Working Intensively in High Needs Schools Raquel Munarriz-Diaz, Magdalena Castañeda, and Phillip Poekert University of Florida, USA Abstract: The researchers
From What to Why Reflective Storytelling as Context for Critical Thinking
 Fornreris and Campbell, Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning in the Health Sciences, Facione and Facione (eds.), California Academic Press. 1 Measuring Thinking Worldwide This document is a best practices
Fornreris and Campbell, Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning in the Health Sciences, Facione and Facione (eds.), California Academic Press. 1 Measuring Thinking Worldwide This document is a best practices
1-to-1 Classroom Routines and Instructional Routines
 1 1-to-1 Classroom Routines and Instructional Routines 1-to-1 classroom routines and instructional routines provide students with the opportunity to be selfdirected and independent learners and to use
1 1-to-1 Classroom Routines and Instructional Routines 1-to-1 classroom routines and instructional routines provide students with the opportunity to be selfdirected and independent learners and to use
Mentoring and Coaching CPD Capacity Building Project National Framework for Mentoring and Coaching
 Mentoring and Coaching CPD Capacity Building Project National Framework for Mentoring and Coaching Contents: Principles of Mentoring and Coaching Mentoring and Coaching: Core Concepts Skills for Mentoring
Mentoring and Coaching CPD Capacity Building Project National Framework for Mentoring and Coaching Contents: Principles of Mentoring and Coaching Mentoring and Coaching: Core Concepts Skills for Mentoring
Teachers as Adult Learners: A New Perspective
 2 As professional developers, it is imperative that we view the teacher of adults as an adult learner and the professional development activity as adult learning. This chapter presents the Adult Learning
2 As professional developers, it is imperative that we view the teacher of adults as an adult learner and the professional development activity as adult learning. This chapter presents the Adult Learning
Taking the Lead Role in Intern Supervision: The Mentor Teacher Intern Project
 Perspectives in Learning: A Journal of the College of Education & Health Professions Volume 11, Number 1, Spring 2010 Columbus State University Taking the Lead Role in Intern Supervision: The Mentor Teacher
Perspectives in Learning: A Journal of the College of Education & Health Professions Volume 11, Number 1, Spring 2010 Columbus State University Taking the Lead Role in Intern Supervision: The Mentor Teacher
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The roles and responsibilities expected of teachers at each classification level are specified in the Victorian Government
 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The roles and responsibilities expected of teachers at each classification level are specified in the Victorian Government Schools Agreement 2004: Leading teacher Leading teachers
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The roles and responsibilities expected of teachers at each classification level are specified in the Victorian Government Schools Agreement 2004: Leading teacher Leading teachers
How To Know If An Instructional Program Works
 What is an Instructional Program? The term, instructional program, refers to a replicable instructional activity that is designed and implemented to achieve an instructional goal, namely, some clearly
What is an Instructional Program? The term, instructional program, refers to a replicable instructional activity that is designed and implemented to achieve an instructional goal, namely, some clearly
Educators Perceptions and Reported Behaviors Associated With the Use of Social Media. for Informal Professional Learning.
 Educators Perceptions and Reported Behaviors Associated With the Use of Social Media for Informal Professional Learning by Debbie Fucoloro Few comprehensive, descriptive studies regarding educator use
Educators Perceptions and Reported Behaviors Associated With the Use of Social Media for Informal Professional Learning by Debbie Fucoloro Few comprehensive, descriptive studies regarding educator use
Teachers as Learners: Elements of Effective Professional Development
 Teachers as Learners: Elements of Effective Professional Development Kathy A. Dunne In this age of standards, a primary focus in education has become establishing benchmarks for knowledge and skills for
Teachers as Learners: Elements of Effective Professional Development Kathy A. Dunne In this age of standards, a primary focus in education has become establishing benchmarks for knowledge and skills for
Self-Assessment Duval County School System. Level 3. Level 3. Level 3. Level 4
 Standard 1: Purpose and Direction 1.1 The system engages in a systematic, inclusive, and comprehensive process to review, revise, and communicate a system-wide propose for the student success. The system
Standard 1: Purpose and Direction 1.1 The system engages in a systematic, inclusive, and comprehensive process to review, revise, and communicate a system-wide propose for the student success. The system
How to Plan and Guide In Class Peer Review Sessions
 How to Plan and Guide In Class Peer Review Sessions Incorporating peer review into your course can help your students become better writers, readers, and collaborators. However, peer review must be planned
How to Plan and Guide In Class Peer Review Sessions Incorporating peer review into your course can help your students become better writers, readers, and collaborators. However, peer review must be planned
Sample Completed Summative Report Form for a Secondary Teacher 1*
 Sample Completed Summative Report Form for a Secondary Teacher 1* This form must be used for each performance appraisal. The duties of the principal may be delegated to a vice-principal in the same school,
Sample Completed Summative Report Form for a Secondary Teacher 1* This form must be used for each performance appraisal. The duties of the principal may be delegated to a vice-principal in the same school,
Coaching. environmental scan. Summary of selected literature, models and current practices. Hay Group - November 2013. Coaching
 Coaching environmental scan Summary of selected literature, models and current practices Hay Group - November 2013 Coaching Contents Executive summary 3 What is coaching? 4 Common themes emerging from
Coaching environmental scan Summary of selected literature, models and current practices Hay Group - November 2013 Coaching Contents Executive summary 3 What is coaching? 4 Common themes emerging from
Revised 2012. Ontario College of Teachers Foundations of Professional Practice INTRODUCTION 2
 Revised 2012 Ontario College of Teachers Foundations of Professional Practice INTRODUCTION 2 Table of Contents 3 Foundations of Professional Practice 4 Introduction 5 Self-Regulation and Standards 7
Revised 2012 Ontario College of Teachers Foundations of Professional Practice INTRODUCTION 2 Table of Contents 3 Foundations of Professional Practice 4 Introduction 5 Self-Regulation and Standards 7
Developing an In-House Singapore Math "Go-To" Expert
 Developing an In-House Singapore Math "Go-To" Expert Professional training is absolutely critical to the success of your Singapore Math implementation. Here are the tools needed to transform an in-house
Developing an In-House Singapore Math "Go-To" Expert Professional training is absolutely critical to the success of your Singapore Math implementation. Here are the tools needed to transform an in-house
Cooperative Learning for the Middle Level
 Cooperative Learning for the Middle Level Debbie Silver, Ed.D. www.debbiesilver.com debbie@debbiesilver.com What is Cooperative Learning? Cooperative learning is an instructional strategy that uses small
Cooperative Learning for the Middle Level Debbie Silver, Ed.D. www.debbiesilver.com debbie@debbiesilver.com What is Cooperative Learning? Cooperative learning is an instructional strategy that uses small
ACTIVITY 15 Set Goals and Plan for Action
 Title: Focus: Time: Guiding Question: Connections: Rationale/ Background: ACTIVITY 15 Set Goals and Plan for Action Self-assessment: What do I know about myself? 2 lessons @ 50-60 minutes A snapshot view:
Title: Focus: Time: Guiding Question: Connections: Rationale/ Background: ACTIVITY 15 Set Goals and Plan for Action Self-assessment: What do I know about myself? 2 lessons @ 50-60 minutes A snapshot view:
Learning. Framework for Teaching and
 Framework for Teaching and Learning Baltimore County Public Schools 2013 The following document provides an overview of the Framework for Teaching and Learning developed by Baltimore County Public Schools
Framework for Teaching and Learning Baltimore County Public Schools 2013 The following document provides an overview of the Framework for Teaching and Learning developed by Baltimore County Public Schools
SALT LAKE CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT MENTOR SUPPORTED COLLABORATIVE ASSESSMENT/REFLECTION LOG 2 nd and 3 rd Year Provisional Teachers
 SALT LAKE CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT MENTOR SUPPORTED COLLABORATIVE ASSESSMENT/REFLECTION LOG 2 nd and 3 rd Year Provisional Teachers Mentor Signature: Mentee Signatures: MONTH: What s Working: Current Focus
SALT LAKE CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT MENTOR SUPPORTED COLLABORATIVE ASSESSMENT/REFLECTION LOG 2 nd and 3 rd Year Provisional Teachers Mentor Signature: Mentee Signatures: MONTH: What s Working: Current Focus
Wyoming s Instructional Facilitator Program: Teachers Beliefs about the Impact of Coaching on Practice
 Wyoming s Instructional Facilitator Program: Teachers Beliefs about the Impact of Coaching on Practice Leslie S. Rush University of Wyoming Suzanne Young University of Wyoming In 2006, the Wyoming state
Wyoming s Instructional Facilitator Program: Teachers Beliefs about the Impact of Coaching on Practice Leslie S. Rush University of Wyoming Suzanne Young University of Wyoming In 2006, the Wyoming state
THE FRAMEWORK FOR INSTRUCTIONAL COACH ENDORSEMENT GUIDELINES PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION
 THE FRAMEWORK FOR INSTRUCTIONAL COACH ENDORSEMENT GUIDELINES PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Definition of an Endorsement Certificate... 3 Introduction to Instructional Coach Endorsement
THE FRAMEWORK FOR INSTRUCTIONAL COACH ENDORSEMENT GUIDELINES PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Definition of an Endorsement Certificate... 3 Introduction to Instructional Coach Endorsement
How to Support Faculty as They Prepare to Teach Online Susan C. Biro Widener University Abstract: A survey, an in-depth interview, and a review of
 How to Support Faculty as They Prepare to Teach Online Susan C. Biro Widener University Abstract: A survey, an in-depth interview, and a review of the literature were used to explore the changes faculty
How to Support Faculty as They Prepare to Teach Online Susan C. Biro Widener University Abstract: A survey, an in-depth interview, and a review of the literature were used to explore the changes faculty
Recruiting, Selecting and Hiring TAP Leaders
 Recruiting, Selecting and Hiring TAP Leaders Tap Recruitment Process Overview Sample Job Advertisement for Master/Mentor Teachers Sample Recruitment Flier for Master/Mentor Teachers Sample Meeting Agenda
Recruiting, Selecting and Hiring TAP Leaders Tap Recruitment Process Overview Sample Job Advertisement for Master/Mentor Teachers Sample Recruitment Flier for Master/Mentor Teachers Sample Meeting Agenda
Games and Activities that Build Academic Vocabulary
 Games and Activities that Build Academic Vocabulary 21 st CCLC Summer Institute July 10-12, 2006 San Diego, CA Danette Parsley, McREL dparsley@mcrel.org 303.632.5560 Heather Martindill, McREL hmartindill@mcrel.org
Games and Activities that Build Academic Vocabulary 21 st CCLC Summer Institute July 10-12, 2006 San Diego, CA Danette Parsley, McREL dparsley@mcrel.org 303.632.5560 Heather Martindill, McREL hmartindill@mcrel.org
Self Assessment Tool for Principals and Vice-Principals
 The Institute for Education Leadership (IEL) brings together representatives from the principals' associations, the supervisory officers' associations, councils of directors of education and the Ministry
The Institute for Education Leadership (IEL) brings together representatives from the principals' associations, the supervisory officers' associations, councils of directors of education and the Ministry
Cognitive Coaching: A Strategy For Reflective Teaching
 Cognitive Coaching: A Strategy For Reflective Teaching By Arthur Costa and Robert Garmston Cognitive Coaching is a marriage of the professional experiences of Art Costa and Bob Garmston. Art had been working
Cognitive Coaching: A Strategy For Reflective Teaching By Arthur Costa and Robert Garmston Cognitive Coaching is a marriage of the professional experiences of Art Costa and Bob Garmston. Art had been working
Classroom Teacher, Prekindergarten Teacher & Student Support Teacher
 Human Resources 2013-14 Classroom Teacher, Prekindergarten Teacher & Student Support Teacher Professional Growth, Supervision and Evaluation Document Revised June 24, 2014 Table of Contents Page Belief
Human Resources 2013-14 Classroom Teacher, Prekindergarten Teacher & Student Support Teacher Professional Growth, Supervision and Evaluation Document Revised June 24, 2014 Table of Contents Page Belief
Performance Evaluation System Protocol. Licensed Executive Professionals
 Colorado Springs School District 11 Dr. Nicholas Gledich, Superintendent Performance Evaluation System Protocol Licensed Executive Professionals Revised March 2014 235169.6 Department of Human Resources
Colorado Springs School District 11 Dr. Nicholas Gledich, Superintendent Performance Evaluation System Protocol Licensed Executive Professionals Revised March 2014 235169.6 Department of Human Resources
POWAY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT CONTINUUM OF TEACHING STANDARDS
 POWAY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT CONTINUUM OF TEACHING STANDARDS Poway Unified School District Teaching Standards Domain I Domain II Domain III Domain IV Domain V Planning and Designing Instruction Element
POWAY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT CONTINUUM OF TEACHING STANDARDS Poway Unified School District Teaching Standards Domain I Domain II Domain III Domain IV Domain V Planning and Designing Instruction Element
Instructional Coaching Model
 Instructional Coaching Model Spokane Public Schools April, 2010 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION I: INTRODUCTION 3 A. HISTORY AND BACKGROUND AND COMMITTEE MEMBERS B. THE PURPOSE OF INSTRUCTIONAL COACHING C.
Instructional Coaching Model Spokane Public Schools April, 2010 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION I: INTRODUCTION 3 A. HISTORY AND BACKGROUND AND COMMITTEE MEMBERS B. THE PURPOSE OF INSTRUCTIONAL COACHING C.
Striving for Success: Teacher Perspectives of a Vertical Team Initiative
 VOLUME 16 NUMBER 3, 2006 Striving for Success: Teacher Perspectives of a Vertical Team Initiative Dr. Lisa Bertrand Educational Administration and Counseling Southeast Missouri State University Dr. Ruth
VOLUME 16 NUMBER 3, 2006 Striving for Success: Teacher Perspectives of a Vertical Team Initiative Dr. Lisa Bertrand Educational Administration and Counseling Southeast Missouri State University Dr. Ruth
Almost everyone recognizes the importance of having an effective early
 National Professional Development Center on Inclusion Helping states achieve an integrated professional development system that supports high quality inclusion What Do We Mean by Professional Development
National Professional Development Center on Inclusion Helping states achieve an integrated professional development system that supports high quality inclusion What Do We Mean by Professional Development
Towards Reflective Teaching
 The Teacher Trainer Back Articles Saved from: http://www.tttjournal.co.uk Towards Reflective Teaching by Jack C. Richards Department of English, City Polytechnic of Hong Kong Most teachers develop their
The Teacher Trainer Back Articles Saved from: http://www.tttjournal.co.uk Towards Reflective Teaching by Jack C. Richards Department of English, City Polytechnic of Hong Kong Most teachers develop their
Integrating Technology into the Classroom: Eight Keys to Success
 Jl. of Technology and Teacher Education (2002) 10(1), 95-100 Integrating Technology into the Classroom: Eight Keys to Success NOEL BITNER AND JOE BITNER Southeastern Louisiana University Hammond, LA 70402
Jl. of Technology and Teacher Education (2002) 10(1), 95-100 Integrating Technology into the Classroom: Eight Keys to Success NOEL BITNER AND JOE BITNER Southeastern Louisiana University Hammond, LA 70402
Section III. An Excellent Christian Teacher. Characteristics and Expectations. GRCS Handbook 1
 Section III An Excellent Christian Teacher Characteristics and Expectations GRCS Handbook 1 Beliefs and Vision Statement In the sphere of home, church, community and school, Grand Rapids Christian schools
Section III An Excellent Christian Teacher Characteristics and Expectations GRCS Handbook 1 Beliefs and Vision Statement In the sphere of home, church, community and school, Grand Rapids Christian schools
EXAMPLE FIELD EXPERIENCE PLANNING TEMPLATE CCSU MAT Program
 EXAMPLE FIELD EXPERIENCE PLANNING TEMPLATE CCSU MAT Program Secondary Education (Math, History/Social Studies, Science, World Languages) and Special Education (K-12) Goal: The MAT program focuses on preparing
EXAMPLE FIELD EXPERIENCE PLANNING TEMPLATE CCSU MAT Program Secondary Education (Math, History/Social Studies, Science, World Languages) and Special Education (K-12) Goal: The MAT program focuses on preparing
Teacher Reaction to On-Demand Professional Development: Motivation to Apply and Share
 Teacher Reaction to On-Demand Professional Development: Motivation to Apply and Share Valerie (Howell) Simmons Sanford Inspire Program Mary Lou Fulton Teachers College Arizona State University Valerie.Simmons@asu.edu
Teacher Reaction to On-Demand Professional Development: Motivation to Apply and Share Valerie (Howell) Simmons Sanford Inspire Program Mary Lou Fulton Teachers College Arizona State University Valerie.Simmons@asu.edu
Ten Tips for Facilitating Classroom Discussions on Sensitive Topics
 Ten Tips for Facilitating Classroom Discussions on Sensitive Topics By Alicia L. Moore and Molly Deshaies All teachers will inevitably teach about sensitive topics. These topics may range from racism,
Ten Tips for Facilitating Classroom Discussions on Sensitive Topics By Alicia L. Moore and Molly Deshaies All teachers will inevitably teach about sensitive topics. These topics may range from racism,
Coaching in Context. A paper written for the Teaching & Learning and Ultranet Coaches Initiative JULIE BOYD
 Coaching in Context A paper written for the Teaching & Learning and Ultranet Coaches Initiative JULIE BOYD PO Box 66 Hastings Point NSW 2489 Email: info@julieboyd.com.au URL: www.julieboyd.com.au Coaching
Coaching in Context A paper written for the Teaching & Learning and Ultranet Coaches Initiative JULIE BOYD PO Box 66 Hastings Point NSW 2489 Email: info@julieboyd.com.au URL: www.julieboyd.com.au Coaching
What Are the Benefits of Analyzing Student Work?
 01-Bella.qxd 11/17/03 3:40 PM Page 1 What Are the Benefits of Analyzing Student Work? 1 W hat s in it for me? That s the question many educators secretly ask themselves when they are presented with a new
01-Bella.qxd 11/17/03 3:40 PM Page 1 What Are the Benefits of Analyzing Student Work? 1 W hat s in it for me? That s the question many educators secretly ask themselves when they are presented with a new
Possible examples of how the Framework For Teaching could apply to Instructional Coaches
 Possible examples of how the Framework For Teaching could apply to 1b. Specific Examples 1b. Demonstrating Knowledge of Students 1a. Specific Examples 1a. Demonstrating knowledge of Content and Pedagogy
Possible examples of how the Framework For Teaching could apply to 1b. Specific Examples 1b. Demonstrating Knowledge of Students 1a. Specific Examples 1a. Demonstrating knowledge of Content and Pedagogy
1 of 5 10/30/2008 7:22 AM
 1 of 5 10/30/2008 7:22 AM September 2007 Volume 65 Number 1 Teachers as Leaders Pages 74-77 Ten Roles for Teacher Leaders Cindy Harrison and Joellen Killion The ways teachers can lead are as varied as
1 of 5 10/30/2008 7:22 AM September 2007 Volume 65 Number 1 Teachers as Leaders Pages 74-77 Ten Roles for Teacher Leaders Cindy Harrison and Joellen Killion The ways teachers can lead are as varied as
Research Brief for Schools
 Research Brief for Schools Social and Emotional Learning The Foundation of Student Success in School, Work, and Life Imagine a school where students Show up eager and ready to learn Feel a sense of connectedness
Research Brief for Schools Social and Emotional Learning The Foundation of Student Success in School, Work, and Life Imagine a school where students Show up eager and ready to learn Feel a sense of connectedness
DEEPER LEARNING COMPETENCIES April 2013
 DEEPER LEARNING COMPETENCIES April 2013 Deeper learning is an umbrella term for the skills and knowledge that students must possess to succeed in 21 st century jobs and civic life. At its heart is a set
DEEPER LEARNING COMPETENCIES April 2013 Deeper learning is an umbrella term for the skills and knowledge that students must possess to succeed in 21 st century jobs and civic life. At its heart is a set
Tips for Designing a High Quality Professional Development Program
 BUILDING A COMMUNITY OF R E A D I N G E X P E RT S Tips for Designing a High Quality Professional Development Program PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT. A critical component of Reading First is a strategic, systematic
BUILDING A COMMUNITY OF R E A D I N G E X P E RT S Tips for Designing a High Quality Professional Development Program PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT. A critical component of Reading First is a strategic, systematic
Instructional Coaching Field Guide
 Poudre School District Instructional Coaching Field Guide Contents Purpose for instructional coaching 2 Rationale 2 Roles of instructional coach, principal, educator & coordinator 3 What the role of instructional
Poudre School District Instructional Coaching Field Guide Contents Purpose for instructional coaching 2 Rationale 2 Roles of instructional coach, principal, educator & coordinator 3 What the role of instructional
Student Achievement through Staff Development
 ` Student Achievement through Staff Development Bruce Joyce and Beverley Showers In: Bruce Joyce and Beverley Showers, 2002, Designing Training and Peer Coaching: Our needs for learning, VA, USA, ASCD
` Student Achievement through Staff Development Bruce Joyce and Beverley Showers In: Bruce Joyce and Beverley Showers, 2002, Designing Training and Peer Coaching: Our needs for learning, VA, USA, ASCD
On-Site Supervisor Handbook
 On-Site Supervisor Handbook Student Affairs Services Internship Radford University Department of Counselor Education Revised Fall 2010 Radford University Department of Counselor Education PO Box 6994,
On-Site Supervisor Handbook Student Affairs Services Internship Radford University Department of Counselor Education Revised Fall 2010 Radford University Department of Counselor Education PO Box 6994,
Literature Review on Professional Development for Teachers
 Literature Review on Professional Development for Teachers Christie Blazer, Senior Research Analyst Research Services Office of Accountability and Systemwide Performance Miami-Dade County Public Schools
Literature Review on Professional Development for Teachers Christie Blazer, Senior Research Analyst Research Services Office of Accountability and Systemwide Performance Miami-Dade County Public Schools
Conley, D. T. (2005). College Knowledge: What it Really Takes for Students to Succeed and What We Can Do to Get Them Ready
 1 Conley, D. T. (2005). College Knowledge: What it Really Takes for Students to Succeed and What We Can Do to Get Them Ready. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. College Knowledge is based on research conducted
1 Conley, D. T. (2005). College Knowledge: What it Really Takes for Students to Succeed and What We Can Do to Get Them Ready. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. College Knowledge is based on research conducted
Silicon Valley Mathematics Initiative Student Focused Math Content Coaching
 Teacher Learning Content Student Math Assessment Collaborative Silicon Valley Mathematics Initiative Student Focused Math Content Coaching Teacher Learning Content Student Math Assessment Collaborative
Teacher Learning Content Student Math Assessment Collaborative Silicon Valley Mathematics Initiative Student Focused Math Content Coaching Teacher Learning Content Student Math Assessment Collaborative
Learning and Teaching
 B E S T PRACTICES NEA RESEARCH BRIEF Learning and Teaching July 2006 This brief outlines nine leading research-based concepts that have served as a foundation for education reform. It compares existing
B E S T PRACTICES NEA RESEARCH BRIEF Learning and Teaching July 2006 This brief outlines nine leading research-based concepts that have served as a foundation for education reform. It compares existing
Running head: LESSONS LEARNED FROM A BEGINNING MATH COACH 1. Lessons Learned from a Beginning Math Coach. Susan Muir.
 Running head: LESSONS LEARNED FROM A BEGINNING MATH COACH 1 Lessons Learned from a Beginning Math Coach Susan Muir K-4 Math Coach Good Spirit School Division LESSONS LEARNED FROM A BEGINNING MATH COACH
Running head: LESSONS LEARNED FROM A BEGINNING MATH COACH 1 Lessons Learned from a Beginning Math Coach Susan Muir K-4 Math Coach Good Spirit School Division LESSONS LEARNED FROM A BEGINNING MATH COACH
Writing and Presenting a Persuasive Paper Grade Nine
 Ohio Standards Connection Writing Applications Benchmark E Write a persuasive piece that states a clear position, includes relevant information and offers compelling in the form of facts and details. Indicator
Ohio Standards Connection Writing Applications Benchmark E Write a persuasive piece that states a clear position, includes relevant information and offers compelling in the form of facts and details. Indicator
SPEECH LANGUAGE PATHOLOGIST PERFORMANCE AND EVALUATION SYSTEM
 SPEECH LANGUAGE PATHOLOGIST PERFORMANCE AND EVALUATION SYSTEM (Revised 11/2014) 1 Fern Ridge Schools Speech Language Pathologist Performance Review and Evaluation System TABLE OF CONTENTS Timeline of Teacher
SPEECH LANGUAGE PATHOLOGIST PERFORMANCE AND EVALUATION SYSTEM (Revised 11/2014) 1 Fern Ridge Schools Speech Language Pathologist Performance Review and Evaluation System TABLE OF CONTENTS Timeline of Teacher
College of Education and Health Professions School of Nursing
 Annual Performance Evaluations will be considered in promotion and tenure reviews. Criteria for tenure and promotion include (a) superior teaching, (b) scholarship and professional development, and (c)
Annual Performance Evaluations will be considered in promotion and tenure reviews. Criteria for tenure and promotion include (a) superior teaching, (b) scholarship and professional development, and (c)
MODULE 6: INTEGRATING THEORY AND PRACTICE: OUTLINE
 University of Washington School of Social Work Field Instructor Training Program: From Practitioner to Educator MODULE 6: INTEGRATING THEORY AND PRACTICE: OUTLINE Competency Objectives: 1) Describe the
University of Washington School of Social Work Field Instructor Training Program: From Practitioner to Educator MODULE 6: INTEGRATING THEORY AND PRACTICE: OUTLINE Competency Objectives: 1) Describe the
Tools to Use in Assessment
 Tools to Use in Assessment II. Observations and Checklists Teachers have always watched and observed students in the classroom and they have made instructional decisions based on these observations. Too
Tools to Use in Assessment II. Observations and Checklists Teachers have always watched and observed students in the classroom and they have made instructional decisions based on these observations. Too
What is the PYP Perspective on Assessment?
 What is the PYP Perspective on Assessment? Assessment is the gathering and analysis of information about student performance. It identifies what students know, understand, can do and feel at different
What is the PYP Perspective on Assessment? Assessment is the gathering and analysis of information about student performance. It identifies what students know, understand, can do and feel at different
Your Career At CREC. Imagining Your Professional Future
 Your Career At CREC Imagining Your Professional Future Welcome to CREC Welcome to the CREC family! CREC is made up of dreamers, builders, protectors, and doers. As a CREC employee, your work will be filled
Your Career At CREC Imagining Your Professional Future Welcome to CREC Welcome to the CREC family! CREC is made up of dreamers, builders, protectors, and doers. As a CREC employee, your work will be filled
MCH LEADERSHIP SKILLS SELF-ASSESSMENT
 MCH LEADERSHIP SKILLS SELF-ASSESSMENT This self-assessment corresponds to the Maternal and Child Health Leadership Competencies Version 3.0, by the MCH Leadership Competencies Workgroup (Eds), June 2009.
MCH LEADERSHIP SKILLS SELF-ASSESSMENT This self-assessment corresponds to the Maternal and Child Health Leadership Competencies Version 3.0, by the MCH Leadership Competencies Workgroup (Eds), June 2009.
Afterschool Professional Development: Resources, Outcomes, and Considerations
 Afterschool Professional Development: Resources, Outcomes, and Considerations For more information, please contact: New York State Afterschool Network (646) 943-8670 Info@nysan.org Introduction and The
Afterschool Professional Development: Resources, Outcomes, and Considerations For more information, please contact: New York State Afterschool Network (646) 943-8670 Info@nysan.org Introduction and The
EXPLORING LESSON STUDY IN TEACHER PREPARATION
 EXPLORING LESSON STUDY IN TEACHER PREPARATION Maria L. Fernández Florida State University Prospective secondary mathematics teachers continue to lack images of reformed teaching. This investigation studied
EXPLORING LESSON STUDY IN TEACHER PREPARATION Maria L. Fernández Florida State University Prospective secondary mathematics teachers continue to lack images of reformed teaching. This investigation studied
PRINTED NAME WESTERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY - DEPARTMENT OF COUNSELOR EDUCATION - CN 597 INTERNSHIP SCHOOL COUNSELING STUDENTS ONLY TO STUDENTS:
 WESTERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY - DEPARTMENT OF COUNSELOR EDUCATION - CN 597 INTERNSHIP SCHOOL COUNSELING STUDENTS ONLY TO STUDENTS: Students are responsible for the completion of all activities on this form.
WESTERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY - DEPARTMENT OF COUNSELOR EDUCATION - CN 597 INTERNSHIP SCHOOL COUNSELING STUDENTS ONLY TO STUDENTS: Students are responsible for the completion of all activities on this form.
Vista High School. Learn More
 Vista High School - Learn More Lewis Carroll (Alice in Wonderland) Bergman, D. J. (2010). Why do we have to learn this?: Teaching goals beyond content. The Clearing House, 83, 129-132. Dweck, C. S. (2010).
Vista High School - Learn More Lewis Carroll (Alice in Wonderland) Bergman, D. J. (2010). Why do we have to learn this?: Teaching goals beyond content. The Clearing House, 83, 129-132. Dweck, C. S. (2010).
360 Degree Leadership Competencies and Questions
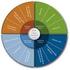 360 Degree Leadership Competencies and Questions Educational Impact 2007 1 360 Degree Leadership Assessment Responses Below is a list of the questions that appear in the Educational Impact 360 Degree School
360 Degree Leadership Competencies and Questions Educational Impact 2007 1 360 Degree Leadership Assessment Responses Below is a list of the questions that appear in the Educational Impact 360 Degree School
North Carolina TEACHER. evaluation process. Public Schools of North Carolina State Board of Education Department of Public Instruction
 North Carolina TEACHER evaluation process Public Schools of North Carolina State Board of Education Department of Public Instruction Rubric for Evaluating North Carolina Teachers ( This form should be
North Carolina TEACHER evaluation process Public Schools of North Carolina State Board of Education Department of Public Instruction Rubric for Evaluating North Carolina Teachers ( This form should be
Developing Life-Long Learners Through Personal Growth Projects
 Developing Life-Long Learners Through Personal Growth Projects Barry Boyd Associate Professor Texas A&M University 2116 TAMU College Station, TX 77843-2116 b-boyd@tamu.edu (979) 862-3693 Jennifer Williams
Developing Life-Long Learners Through Personal Growth Projects Barry Boyd Associate Professor Texas A&M University 2116 TAMU College Station, TX 77843-2116 b-boyd@tamu.edu (979) 862-3693 Jennifer Williams
PREPARING YOUR TEACHING PORTFOLIO
 PREPARING YOUR TEACHING PORTFOLIO WHAT IS A TEACHING PORTFOLIO? A teaching portfolio is a record of your professional development as a teacher. It illustrates your philosophy of teaching and your overall
PREPARING YOUR TEACHING PORTFOLIO WHAT IS A TEACHING PORTFOLIO? A teaching portfolio is a record of your professional development as a teacher. It illustrates your philosophy of teaching and your overall
Coaching for Improved Work Performance. How to get better results from your employees.
 Coaching for Improved Work Performance How to get better results from your employees. Believing the Right Things Purpose: learn how to be more successful as manager of people Specifically: to learn how
Coaching for Improved Work Performance How to get better results from your employees. Believing the Right Things Purpose: learn how to be more successful as manager of people Specifically: to learn how
Mentoring and Coaching Models
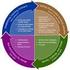 Mentoring and Coaching Models Peer coaching is a of staff development model you can use to help you and your partners develop and try new strategies and determine what does and does not work by critically
Mentoring and Coaching Models Peer coaching is a of staff development model you can use to help you and your partners develop and try new strategies and determine what does and does not work by critically
PART I. The Coach s Work
 PART I The Coach s Work 1 What Is Coaching? Before moving into this opening chapter, consider the following questions for reflection: What is the role of a mathematics coach? How would you define coaching?
PART I The Coach s Work 1 What Is Coaching? Before moving into this opening chapter, consider the following questions for reflection: What is the role of a mathematics coach? How would you define coaching?
The addition in 1994 of professional development of teachers to the original six National Education Goals
 TM 828 Fort Street Mall Suite 500 Honolulu, Hawai i 96813-4321 Tel: (808) 533-6000 FAX: (808) 533-7599 e-mail: askprel@prel.hawaii.edu WEBsite: http://www.prel.hawaii.edu The Role of Teacher Mentoring
TM 828 Fort Street Mall Suite 500 Honolulu, Hawai i 96813-4321 Tel: (808) 533-6000 FAX: (808) 533-7599 e-mail: askprel@prel.hawaii.edu WEBsite: http://www.prel.hawaii.edu The Role of Teacher Mentoring
Castilion Primary School Coaching Handbook: a guide to excellent practice. Growing excellent teachers
 Castilion Primary School Coaching Handbook: a guide to excellent practice Growing excellent teachers Coaching Handbook: a guide to excellent practice Page 1 Contents Section Page Coaching at Castilion
Castilion Primary School Coaching Handbook: a guide to excellent practice Growing excellent teachers Coaching Handbook: a guide to excellent practice Page 1 Contents Section Page Coaching at Castilion
Chapter 3. Methodology
 22 Chapter 3 Methodology The purpose of this study is to examine the perceptions of selected school board members regarding the quality and condition, maintenance, and improvement and renovation of existing
22 Chapter 3 Methodology The purpose of this study is to examine the perceptions of selected school board members regarding the quality and condition, maintenance, and improvement and renovation of existing
Peer Review Self Assessment Exercise
 Peer Review Self Assessment Exercise The following Exercise will ask for your analysis of various peer review experiences and your thoughts following several peer review scenarios. Satisfactory completion
Peer Review Self Assessment Exercise The following Exercise will ask for your analysis of various peer review experiences and your thoughts following several peer review scenarios. Satisfactory completion
Framework for Leadership
 Framework for Leadership Date Leader Self-Assessment Evaluator Assessment Domain 1: Strategic/Cultural Leadership Principals/school leaders systemically and collaboratively develop a positive culture to
Framework for Leadership Date Leader Self-Assessment Evaluator Assessment Domain 1: Strategic/Cultural Leadership Principals/school leaders systemically and collaboratively develop a positive culture to
Key Components of Literacy Instruction
 Key Components of Literacy Instruction The longer I write and read, the more I learn; writing and reading are lifelong apprenticeships --Donald M. Murray W e, in MPS, believe that effort creates ability.
Key Components of Literacy Instruction The longer I write and read, the more I learn; writing and reading are lifelong apprenticeships --Donald M. Murray W e, in MPS, believe that effort creates ability.
We Need to Talk. Heidi L. Hollingsworth
 Communicating About Student Learning We Need to Talk Communication Strategies for Effective Collaboration Heidi L. Hollingsworth TEACHING Exceptional Children, Vol. 33, No. 5, pp. 4-8. Copyright 2001 CEC.
Communicating About Student Learning We Need to Talk Communication Strategies for Effective Collaboration Heidi L. Hollingsworth TEACHING Exceptional Children, Vol. 33, No. 5, pp. 4-8. Copyright 2001 CEC.
Greenville City Schools. Teacher Evaluation Tool
 Greenville City Schools Teacher Evaluation Tool Table of Contents Introduction to Teacher Evaluation 2 Glossary 3 Record of Teacher Evaluation Activities 5 Teacher Evaluation Rubric 6 Self-Assessment 11
Greenville City Schools Teacher Evaluation Tool Table of Contents Introduction to Teacher Evaluation 2 Glossary 3 Record of Teacher Evaluation Activities 5 Teacher Evaluation Rubric 6 Self-Assessment 11
Effective intervention practices + Effective implementation practices = Increased likelihood for positive youth outcomes
 Publication #2007-29 information for practitioners seeking to use evidence-based practices to enhance program outcomes. October 2007 IMPLEMENTING EVIDENCE-BASED PRACTICES: SIX DRIVERS OF SUCCESS Part 3
Publication #2007-29 information for practitioners seeking to use evidence-based practices to enhance program outcomes. October 2007 IMPLEMENTING EVIDENCE-BASED PRACTICES: SIX DRIVERS OF SUCCESS Part 3
The Model of Successful School Nursing
 10/13 Ribas Associates and Publications, Inc. 9 Shermans Way Westwood, MA 02090 Phone: 781-551-9120 Fax: 781-349-8160 Email: info@ribasassociates.com Website: www.ribasassociates.com Ribas Associates Framework
10/13 Ribas Associates and Publications, Inc. 9 Shermans Way Westwood, MA 02090 Phone: 781-551-9120 Fax: 781-349-8160 Email: info@ribasassociates.com Website: www.ribasassociates.com Ribas Associates Framework
Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom Classroom Observation Rubric To Guide Leadership for Learning by Instructional Leaders TASK
 1 of 10 Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom Classroom Observation Rubric To Guide Leadership for Learning by Instructional Leaders TASK Task Is Authentic The task requires students to respond
1 of 10 Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom Classroom Observation Rubric To Guide Leadership for Learning by Instructional Leaders TASK Task Is Authentic The task requires students to respond
THE FOUR NON NEGOTIABLES
 THE FOUR NON NEGOTIABLES ACADEMIC EXCELLENCE COLLEGE AND CAREER READINESS SAFE AND SUPPORTIVE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT PURPOSEFUL, TIMELY TWO WAY COMMUNICATION ECISD STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2016 1 Beliefs Definition:
THE FOUR NON NEGOTIABLES ACADEMIC EXCELLENCE COLLEGE AND CAREER READINESS SAFE AND SUPPORTIVE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT PURPOSEFUL, TIMELY TWO WAY COMMUNICATION ECISD STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2016 1 Beliefs Definition:
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS FOR TEACHERS
 INTERVIEW QUESTIONS FOR TEACHERS The following questions are examples of questions frequently asked by school system recruiters. This list is certainly not all inclusive and should be used as a starting
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS FOR TEACHERS The following questions are examples of questions frequently asked by school system recruiters. This list is certainly not all inclusive and should be used as a starting
Arkansas State PIRC/ Center for Effective Parenting
 Increasing Your Child s Motivation to Learn In order to be successful in school and to learn, students must stay involved in the learning process. This requires students to do many different activities
Increasing Your Child s Motivation to Learn In order to be successful in school and to learn, students must stay involved in the learning process. This requires students to do many different activities
PRIMARY TEACHER TRAINEES MATHEMATICAL SUBJECT KNOWLEDGE: THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PEER TUTORING
 PRIMARY TEACHER TRAINEES MATHEMATICAL SUBJECT KNOWLEDGE: THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PEER TUTORING Patti Barber and Caroline Heal University of London, Institute of Education As a matter of course, primary teacher
PRIMARY TEACHER TRAINEES MATHEMATICAL SUBJECT KNOWLEDGE: THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PEER TUTORING Patti Barber and Caroline Heal University of London, Institute of Education As a matter of course, primary teacher
Lessons Learned about Effective School Management Strategies
 Lessons Learned about Effective School Management Strategies N O V E M B E R 1 9 9 7 LESSONS LEARNED ABOUT EFFECTIVE SCHOOL MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES A Best Practices Literature Review Prepared for, A Partnership
Lessons Learned about Effective School Management Strategies N O V E M B E R 1 9 9 7 LESSONS LEARNED ABOUT EFFECTIVE SCHOOL MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES A Best Practices Literature Review Prepared for, A Partnership
Assessment FOR Learning, the Achievement Gap, and Truly Effective Schools* Rick Stiggins ETS Assessment Training Institute Portland, OR
 Assessment FOR Learning, the Achievement Gap, and Truly Effective Schools* Rick Stiggins ETS Assessment Training Institute Portland, OR * A presentation at the Educational Testing Service and College Board
Assessment FOR Learning, the Achievement Gap, and Truly Effective Schools* Rick Stiggins ETS Assessment Training Institute Portland, OR * A presentation at the Educational Testing Service and College Board
Cooperating Teacher s Role
 Student Teaching in Elementary School Education Program Brandeis University Waltham, MA 02454 Brandeis student teachers are given the opportunity to teach classes and groups of students, design curriculum
Student Teaching in Elementary School Education Program Brandeis University Waltham, MA 02454 Brandeis student teachers are given the opportunity to teach classes and groups of students, design curriculum
Graduate Student Perceptions of the Use of Online Course Tools to Support Engagement
 International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning Volume 8 Number 1 Article 5 January 2014 Graduate Student Perceptions of the Use of Online Course Tools to Support Engagement Stephanie
International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning Volume 8 Number 1 Article 5 January 2014 Graduate Student Perceptions of the Use of Online Course Tools to Support Engagement Stephanie
Teacher Evaluation. Missouri s Educator Evaluation System
 Teacher Evaluation Missouri s Educator Evaluation System Teacher Evaluation Protocol Introduction Missouri s Educator Evaluation System was created and refined by hundreds of educators across the state.
Teacher Evaluation Missouri s Educator Evaluation System Teacher Evaluation Protocol Introduction Missouri s Educator Evaluation System was created and refined by hundreds of educators across the state.
CURRICULUM VITAE. Jeffrey L. Davidson. Department of Sociology and Criminal Justice University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 (302) 831-1569
 CURRICULUM VITAE Jeffrey L. Davidson ADDRESSES Department of Sociology and Criminal Justice University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 (302) 831-1569 6 N. Wynwyd Drive Newark, DE 19711 (302) 368-1029 RESEARCH
CURRICULUM VITAE Jeffrey L. Davidson ADDRESSES Department of Sociology and Criminal Justice University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716 (302) 831-1569 6 N. Wynwyd Drive Newark, DE 19711 (302) 368-1029 RESEARCH
