How To Treat A Heart Attack With Depression
|
|
|
- Erik Henderson
- 3 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 W. Grady Carter M.D. Community Associate Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Science Mercer University School of Medicine
2 Depressed Patients in Primary Care?
3 What percentage of antidepressant prescriptions are written by primary care providers? A.25% B. 50% C. 70% D. 90% Correct answer C
4 Depression in Primary Care 20% of patients presenting in primary care 2/3 of depressed patients present with somatic symptoms The number of patients receiving care for psychiatric illness in primary care settings is increasing. Primary care doctors write 62-70% of all prescriptions for anti-depressants.
5 Depression Facts The first episode usually occurs in the late teens or twenties but can occur at any time of life. The first episode is often precipitated by a stress or a loss. The degree of stress needed to precipitate an episode may go down over time. MDD is remitting and relapsing which means it will usually go away on its own (after 8-16 months) but often recurs. Each episode increases the risk of a subsequent episode. Non-recurrent late life depression may be different, more closely associated with dementia
6 - Medical Consequences of Depression Depression is a risk factor for heart disease (OR 4.5 for MI) and stroke. People who are depressed after a heart attack are 4 times more likely to die in the next year. Recurrent depression probably increases the risk for Alzheimer s. Depression worsens the course of diabetes. Depression is a systemic illness increases platelet aggregation, decreases beat to beat heart rate variability, causes increased immune system activation. Depression is associated with poorer self care.
7 Diabetes and Depression 4623 Primary care patients with type II diabetes followed for 5 years MDD associated with 1.36 greater risk for advanced microvascular complications (blindness, ESRD, amputation) and 1.24 for macrovascular complications (MI, stroke) Depression is associated with greater incidence, symptom severity, complications, disability, cost and mortality. The relationship between depression and diabetes is bidirectional. Depression activates the HPA axis, stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, increases inflammatory responses, and increases platelet aggregation. Depression impairs glycemic control through negative effects on adherence to diet, glucose monitoring, medication adherence, diet, and exercise. Lin et al 2010
8 Differential Diagnosis of Depression Worried well Major depressive disorder Dysthymia (chronic mild depression) Bipolar depression Adjustment disorder Secondary depression (medical illness, substances or medications) Complicated grief
9
10 Major Depressive Episode Two weeks of depressed mood and/or loss of interest as well as 3-4 (total of 5): --change in weight --insomnia or hypersomnia --Psychomotor agitation or retardation --fatigue or loss of energy --feelings of worthlessness or guilt --decreased concentration or indecisiveness --recurrent thoughts of death The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment
11 Bipolar Depression Episodes of depression which may be identical to MDD plus episodes of mania or hypomania Sometimes hard to diagnose Bipolarity may emerge with antidepressant treatment Requires mood stabilizing medications
12
13 Bipolar Depression--clues BPI eat and sleep more, slow down BPII are more agitated Abrupt on set or termination of episodes Wired or agitated or anxious on ADs Improve on ADs but relapse Seasonal Family history of bipolar Post partum depressions
14 Secondary Depression The medical condition is a biological contributor, not just a stressor. Endocrine and brain disorders are most likely to cause depression. 50% of people with Parkinson s disease get depressed. 33% of people with Alzheimer s dementia get depression % of people who have had a stroke suffer from post-stroke depression. Pancreatic cancer can present as depression.
15 Secondary Depression Most drugs of abuse can cause depression. Alcohol dependence often contributes to depression. Often difficult to determine which came first. Even brain stimulants can contribute to depression. B blockers, retinoic acid, interferon, chronic steroid use can all cause depression.
16 Screening Two Question During the past month have you often been bothered by feeling down, depressed, or hopeless? During the past month have you often been bothered by little interest or pleasure in doing things 96% sensitivity and 57% specificity for major depression
17
18 Myths About Depression It represents moral failure I don t have anything to be depressed about. I can just think (or pray) my way out of it. It is a normal response to life s trouble. It is a normal response to illness.
19 Is it Depression? The normal things most like depression are sadness, grief, and existential angst although the distinction is often difficult to make. Clinical depression is often a perversion of normal sadness and grief which can impair true emotional healing. Fallacy of good reasons/human tendency to normalize Physical symptoms, social withdrawal, loss of interest, suicidal thoughts are warning signs
20 Treatment Medications Psychotherapy Support/Encouragement Education Exercise
21 What percentage of patients experience remission with an initial trial of an antidepressant? A. 33% B. 50% C. 66% D. 90% Correct answer is A.
22 What percentage of patients (cumulatively) experience remission after 4 trials of antidepressants? A. 40% B. 60% C. 80% D. 100% Correct answer is C
23 Medications Antidepressants vary more by side effects than by efficacy % respond to a given medication, 33% experience complete remission. Antidepressants and psychotherapy are equally efficacious (with caveats.) Antidepressants plus psychotherapy may be more efficacious. Antidepressants treat more than depression!
24 Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression STAR*D What do you do when patients fail their first anti-depressant trial? 5 year NIMH trial, N=4041 Included patients in a primary care setting (who were no different in terms of symptom severity, illness variables or co morbidity) Real world patients with shared decision making (augmentation vs. switch, medications vs. therapy) Outcome measure was remission (HRS<7)
25 STAR*D Level I All patients take citalopram Level II Non-remitters or those who do not tolerate citalopram switch to bupropion, CBT, venlafaxine,sertraline or augment with bupropion, CBT, or buspirone Level III Switch to mirtazapine or nortriptyline or augment with lithium or T3 Level IV Switch to tranylcypromine or venlafaxine and mirtazapine
26 STAR*D Level I--Citalopram Citalopram for weeks. Remission rate of 28% with a mean dose of 41.8mg A majority responded by six weeks but many required up to 12 weeks. Associated with remission--white, female, employed, better educated, higher income Negatively associated with remission--longer episode, psychiatric or medical co morbidity, lower baseline function
27 STAR*D Level II Switch or Augment Switch to bupropion 21% remission, switch to sertaline 18% remission, switch to venlafaxine 25% remission Augmentation with bupropion 29.7% remission, buspirone 30.1% remission Bupropion was better tolerated Remission rate 25%; 50%-55% after 2 sequential trials CBT was comparable but took longer. It had less adverse events.
28 STAR*D Level III Switch to mirtazapine or nortriptyline or augment with lithium or T3 Mirtazapine 12% Nortriptyline 20% Remission Rates Lithium 16% (more adverse events) T3 25% No significant difference
29 STAR*D Step IV Tranylcypromine 7% remission vs venlafaxine/mirtazapine 14% remission
30 STAR*D Lower remission rates with each successive trial Remission rate of 53% after 2 trials and 81% after 4 trials Higher relapse rates with more refractory patients Remission is more durable than response
31 Basic Algorithm Start with an SSRI or Bupropion, titrate to an appropriate dose and wait 4-8 weeks. For a partial response raise dose or augment or wait For no response switch medications Consider a tricyclic, monamine oxidase inhibitor, ECT, TMS, VNS, DBS SSRI non response is not predictive of failure of another SSRI but can also change to bupropion or an SSNRI Always consider psychotherapy
32 Augmentation SSRI or venlafaxine or duloxetine bupropion and/ or mirtazapine + Any anti-depressant + lithium, T3, buspirone, aripiprazole, quitiapine, lamotrigine Psychotherapy
33 Dosing Strategies Wait and see dose a potentially therapeutic dose Titration how you get there Maximum dose dose after which you augment or change if it is not effective Speed of action vs. dose/side effects Proving the medicine a failure
34 Medication Resistance Consider the adequacy of the medication trial. Reassess the diagnosis. Consider psychiatric and medical co- morbidities. Assess compliance. Consider pharmacokinetics. Is medication contributing to depression?
35 When to Stop Medications? Most people should be treated for 8-12 months after remission. After 8-12 months treatment is to prevent a new episode. Anxiety may re-emerge quickly. Factor in patient preference, number of episodes, severity of episodes, efficacy of medication, side effects.
36 How to Stop Medications Discontinuation Symptoms (DS) vs. Re-emergence of psychiatric symptoms Fluoxetine has minimal DS Venlafaxine, paroxetine, and duloxetine have significant DS Taper as slowly as one increment a month in order to monitor for returning symptoms
37 Psychotherapy Either as primary treatment or with medications Cognitive behavioral therapy and interpersonal therapy are evidence based Other therapies probably work Evidence is good for time-limited, directive psychotherapy that focuses on current problems and changing current behavior. Feeling Good by David Burns
38 Education/Resources Feeling Good by David Burns Darkness Revealed by William Styron Night Falls Fast by Kay Redfield Jamison An Unquiet Mind by Kay Redfield Jamison The Noonday Demon by Andrew Solomon Ordinary People Mr. Jones
39 Supporting People with Depression Encourage proper treatment Decrease stigma Encourage social interaction Watch for signs of danger People with depression should push themselves but not too much
40 How much more do non-generic antidepressants cost compared to generics? A. 10 times more B. 50 times more C. 75 times more D. 100 times more Correct answer is C.
41 High Value Care Consumer Reports Best Buy Antidepressants Citalopram Sertraline Fluoxetine Bupropion Escitalopram
42 SSRIs First choice for patients with anxiety. Good side effect profile. Often inexpensive. Fluoxetine activating, very long half life, CYP2D6 inhibitor, cheap Paroxetine short half life, discontinuation symptoms, sedating, anticholinergic, cheap Sertraline longer titration in some patients, cheap Citalopram tires some, cheap, may cause arrhythmias Escitalopram can start at theraputic dose, may be better tolerated, tires some
43 SSRI Side Effects --GI --Anxiety --Headache --Sexual side effects (delayed orgasm, decreased libido) Bleeding SIADH/hyponatremia Osteoporosis Two fold increased risk of clinical fragility fracture, increased odds of falling, lower mineral density of the hip Monitor for suicidal thoughts
44 Dosing SSRIs Sertraline start at 25-50mg, wait at 100mg or 50mg, max. at 200mg Fluoxetine start at 5mg, 10mg, or 20mg, wait at 20mg or 40mg, max at 60-80mg Paroxetine start at 10mg or 20mg, wait at 20mg or 40mg, max at 60mg Citalopram start at 10-20mg, wait at 40mg or 20mg, max at 40mg* Escitalopram start at 5mg or 10mg, wait at 10mg or 20mg, max at 20mg Fluvoxamine start at 50mg, wait at 200mg, max at 300mg *20 mg for those over 60, hepatic insufficiency, cardiac problems
45 Venlafaxine (Effexor) SNRI (more norepinephrine reuptake inhibition at 225mg and higher) Indications for MDD, GAD, panic disorder and social phobia Dosing--venlafaxine XR start at 37.5mg or 75mg, wait at 75mg, 150mg, or 225mg, max at 225mg but has been used up to 375mg and 450mg Discontinuation syndrome, sweating, GI, HTN
46 Duloxetine (Cymbalta) SSNRI Indications for MDD, GAD, fibromyalgia, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, chronic musculoskeletal pain Dosing--start at 20mg or 30mg, wait at 60mg, max at 90mg or 120mg More expensive generic Discontinuation syndrome, sweating, GI
47 Tricyclic Antidepressants Norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitors (vary in how much) May be better for severe or treatment resistant depression Caution with cardiac patients Treats chronic pain Nortriptyline and desipramine have less side effects than amitriptyline and imipramine Lethal in overdose Metabolized by 2D6
48 Bupropion (Wellbutrin) Norepinephrine, dopamine reuptake inhibitor Activating, with less sedation, weight gain, and sexual side effects Less used for anxiety disorders, may increase anxiety Lowers seizure threshold, dose related use with caution in patients with seizure risk
49 Bupropion--Dosing IR mg in 3 divided doses, maximum 150mg/dose SR 100mg, 150mg or 200mg BID. Second dose at 4pm to avoid insomnia. XL 150mg, 300mg, or 450mg once a day in the morning.
50 Mirtazapine (Remeron) Alpha 2 antagonist Dosing--start at 7.5mg or 15mg, wait at 30mg or 45mg, max 45mg May be more sedating at lower doses Causes weight gain and sedation (so used when those are beneficial) Minimal sexual side effects Mixes well with other antidepressants
51 Vilazodone (Viibryd) SSRI plus 5HT1A agonist (like buspirone) Must be taken with food Dosing 10mg for 1 week, 20 mg for 1 week, then 40mg. SSRI side effect profile, may have less sexual side effects Minimal weight gain
52 Selegeline (EMSAM) MOAI (A and B in the brain, B in the gut) Transdermal patch 6mg, 9mg, 12 mg Side effects include site reaction, headache, dry mouth Tyramine free diet at doses over 6 mg Many drug interactions. Must wash out other antidepressants prior to starting
53 Aripiprazole (Abilify) Partial agonist at D-2 plus;alpha1 blockade mg for MDD FDA indication for augmenting an antidepressant in MDD Usually not sedating Less metabolic side effects, some patients will still have weight gain Some patients will have akathisia, restlessness, anxiety Minimal EPS
54 Vortioxetine (Brintellix) SSRI, 5-HT1A agonist, 5-HT 3 and 5-HT7 antagonist Start at 10 mg, can increase to 20 mg Non-generic GI side effects
55 Levomilnacipran (Fetzima) SNRI, enantiomer of milnacipran mg for two days then 40 mg. Maximum dose 120 mg. Side effects include GI, flushing, sexual side effects
56 Morning or Night? Morning Night Doesn t Matter Fluoxetine paroxetine sertraline Venlafaxine duloxetine citalopram escitalopram If it makes you sleepy, move it to night. If it interferes with your sleep, move it to the morning.
57 Complementary and Alternative Treatments St John s Wort SAMe Omega 3 fatty acids Exercise
58 Antidepressants and Suicide
59 Bibliography Nhu N, McIntyre R. What are the Implications of the STSR*D trial for primary care? A review and synthesis. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry : pp0830.pdf Lin EHB, Rutter CM, Katon W, Heckbert SR, Ciechanowski P, Oliver MM, Ludman EJ, Young BA, Williams LH, McCulloch DK, Von Korff M. Depression and advanced complications of diabetes. Diabetes Care Feb. 33(2):
60 Bridge, S. Suicide prevention, targeting the patient at risk. Australian Family Physician.35(5): 2006 Tylees A, Gandhi P. The importance of somatic symptoms of depression in Primary Care. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2005; 7(4): / Kirmayer,et al. Somatisation and the recognition of depression and anxiety in primary care. Am J Psychiatry :
61 McDowell A, Lineberry T, Bostwick J. Practical suicide-risk management for the busy primary care physician. Mayo Clin Proc Aug;86(8): Epub 2011 Jun 27.
Depression Flow Chart
 Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease
 Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
What are the best treatments?
 What are the best treatments? Description of Condition Depression is a common medical condition with a lifetime prevalence in the United States of 15% among adults. Symptoms include feelings of sadness,
What are the best treatments? Description of Condition Depression is a common medical condition with a lifetime prevalence in the United States of 15% among adults. Symptoms include feelings of sadness,
Depre r s e sio i n o i n i a dults Yousuf Al Farsi
 Depression in adults Yousuf Al Farsi Objectives 1. Aetiology 2. Classification 3. Major depression 4. Screening 5. Differential diagnosis 6. Treatment approach 7. When to refer 8. Complication 9. Prognosis
Depression in adults Yousuf Al Farsi Objectives 1. Aetiology 2. Classification 3. Major depression 4. Screening 5. Differential diagnosis 6. Treatment approach 7. When to refer 8. Complication 9. Prognosis
TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY
 University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
Major Depression. What is major depression?
 Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder. Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice
 Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice 2013 update International Task Force of World Federation of Societies of Biological
Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice 2013 update International Task Force of World Federation of Societies of Biological
Depression. Medicines To Help You
 Medicines To Help You Depression Use this guide to help you talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse about your medicines for depression. The guide lists all of the FDA-approved products now available
Medicines To Help You Depression Use this guide to help you talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse about your medicines for depression. The guide lists all of the FDA-approved products now available
Medicines for Treating Depression. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines for Treating Depression A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor or other health care professional has told you that you have depression. Your doctor
Medicines for Treating Depression A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor or other health care professional has told you that you have depression. Your doctor
TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER
 TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2000.
TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2000.
ANTIDEPRESSANT MEDICINES. A GUIDE for ADULTS With DEPRESSION
 ANTIDEPRESSANT MEDICINES A GUIDE for ADULTS With DEPRESSION August 2007 FAST FACTS ON ANTIDEPRESSANTS The antidepressants in this guide work for treating depression. Most people can find one that makes
ANTIDEPRESSANT MEDICINES A GUIDE for ADULTS With DEPRESSION August 2007 FAST FACTS ON ANTIDEPRESSANTS The antidepressants in this guide work for treating depression. Most people can find one that makes
Treatments for Major Depression. Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are:
 Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression
 Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression Questions about Medications 1. How do antidepressants work? Antidepressants help restore the correct balance of certain
Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression Questions about Medications 1. How do antidepressants work? Antidepressants help restore the correct balance of certain
DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource
 E-Resource March, 2015 DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource Depression affects approximately 20% of the general population
E-Resource March, 2015 DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource Depression affects approximately 20% of the general population
Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center
 Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center First Line Medications SSRIs Prozac (Fluoxetine): 5-605 mg Zoloft (Sertraline):
Medication Management of Depressive Disorders in Children and Adolescents Satya Tata, M.D. Kansas University Medical Center First Line Medications SSRIs Prozac (Fluoxetine): 5-605 mg Zoloft (Sertraline):
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over
 Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Depression in Older Persons
 Depression in Older Persons How common is depression in later life? Depression affects more than 6.5 million of the 35 million Americans aged 65 or older. Most people in this stage of life with depression
Depression in Older Persons How common is depression in later life? Depression affects more than 6.5 million of the 35 million Americans aged 65 or older. Most people in this stage of life with depression
Why are antidepressants used to treat IBS? Some medicines can have more than one action (benefit) in treating medical problems.
 The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD What are functional GI disorders? There are more
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD What are functional GI disorders? There are more
NICE Clinical guideline 23
 NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression
 Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression Refer for psychotherapy if patient preference or add cognitive behavioural office skills to antidepressant medication Moderate to Severe depression
Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression Refer for psychotherapy if patient preference or add cognitive behavioural office skills to antidepressant medication Moderate to Severe depression
DEPRESSION IN PRIMARY CARE: An Overview. Jorge R. Petit, MD Quality Health Solutions
 DEPRESSION IN PRIMARY CARE: An Overview Jorge R. Petit, MD Quality Health Solutions Topics In this Session Overview Clinical Importance of Depression Types of Depression Phases of Depression Care Collaborative
DEPRESSION IN PRIMARY CARE: An Overview Jorge R. Petit, MD Quality Health Solutions Topics In this Session Overview Clinical Importance of Depression Types of Depression Phases of Depression Care Collaborative
Elizabeth A. Crocco, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Chief, Division of Geriatric Psychiatry Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Miller
 Elizabeth A. Crocco, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Chief, Division of Geriatric Psychiatry Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Miller School of Medicine/University of Miami Question 1 You
Elizabeth A. Crocco, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Chief, Division of Geriatric Psychiatry Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Miller School of Medicine/University of Miami Question 1 You
Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in Primary Care, Adult 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com 40 05 17 035 3/03 Once a primary care patient presents with depressive symptoms, the primary care physician makes
Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com 40 05 17 035 3/03 Once a primary care patient presents with depressive symptoms, the primary care physician makes
POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS
 Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant
Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs POPULAR DEPRESSION MEDICATIONS A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant Drugs Popular Depression Medications A Helpful Guide to Antidepressant
1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the
 1 Chapter 38. Major Depressive Disorders, Self-Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the long half-life of its potent active metabolite?
1 Chapter 38. Major Depressive Disorders, Self-Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the long half-life of its potent active metabolite?
Remeron (mirtazapine)
 Remeron (mirtazapine) FDA ALERT [07/2005] Suicidal Thoughts or Actions in Children and Adults Patients with depression or other mental illnesses often think about or attempt suicide. Closely watch anyone
Remeron (mirtazapine) FDA ALERT [07/2005] Suicidal Thoughts or Actions in Children and Adults Patients with depression or other mental illnesses often think about or attempt suicide. Closely watch anyone
The Antidepressants: Treating Depression. Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price
 The Antidepressants: Treating Depression Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Antidepressants can improve the symptoms of depression, but they can also have serious side effects.
The Antidepressants: Treating Depression Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Antidepressants can improve the symptoms of depression, but they can also have serious side effects.
Depression. Depress EPRESSION. Depression
 Depress EPRESSION Depression Depression DEPRESSION Most people feel depressed at times. Losing a loved one, getting fired from a job, going through a divorce, and other difficult situations can lead a
Depress EPRESSION Depression Depression DEPRESSION Most people feel depressed at times. Losing a loved one, getting fired from a job, going through a divorce, and other difficult situations can lead a
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION
 MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
A Depression Education Toolkit
 A Depression Education Toolkit Facts about Depression in Older Adults What is Depression? Depression is a medical illness. When sadness persists or interferes with everyday life, it may be depression.
A Depression Education Toolkit Facts about Depression in Older Adults What is Depression? Depression is a medical illness. When sadness persists or interferes with everyday life, it may be depression.
Bipolar Disorder. Mania is the word that describes the activated phase of bipolar disorder. The symptoms of mania may include:
 Bipolar Disorder What is bipolar disorder? Bipolar disorder, or manic depression, is a medical illness that causes extreme shifts in mood, energy, and functioning. These changes may be subtle or dramatic
Bipolar Disorder What is bipolar disorder? Bipolar disorder, or manic depression, is a medical illness that causes extreme shifts in mood, energy, and functioning. These changes may be subtle or dramatic
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS. Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health
 PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health Learning Objectives Learn basics about the various types of medications that
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND WORKING WITH PSYCHIATRY PROVIDERS Juanaelena Garcia, MD Psychiatry Director Institute for Family Health Learning Objectives Learn basics about the various types of medications that
Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents.
 Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents. KAREN KANDO, MD Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Center for Neuroscience and Behavioral Medicine Phoenix Children s Hospital
Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents. KAREN KANDO, MD Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Center for Neuroscience and Behavioral Medicine Phoenix Children s Hospital
New Patient Information. Address: City: State: Zip: Ph#: Cell#:
 Patient Information: Last Name: New Patient Information First Name: Address: City: State: Zip: Ph#: Cell#: S.S.N: Email: May we contact you by email? Yes No Date of Birth: May we send you information about
Patient Information: Last Name: New Patient Information First Name: Address: City: State: Zip: Ph#: Cell#: S.S.N: Email: May we contact you by email? Yes No Date of Birth: May we send you information about
`çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå. aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí=
 `çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí= Overview: Common Mental What are they? Disorders Why are they important? How do they affect
`çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí= Overview: Common Mental What are they? Disorders Why are they important? How do they affect
DEPRESSION DURING THE TRANSITION TO MENOPAUSE: A Guide for Patients and Families
 DEPRESSION DURING THE TRANSITION TO MENOPAUSE: A Guide for Patients and Families David A. Kahn, MD, Margaret L. Moline, PhD, Ruth W. Ross, MA, Lori L. Altshuler, MD, and Lee S. Cohen, MD www.womensmentalhealth.org
DEPRESSION DURING THE TRANSITION TO MENOPAUSE: A Guide for Patients and Families David A. Kahn, MD, Margaret L. Moline, PhD, Ruth W. Ross, MA, Lori L. Altshuler, MD, and Lee S. Cohen, MD www.womensmentalhealth.org
Depression in Long-Term Care
 Depression in Long-Term Care Annette Carron, DO, CMD, FACOI, FAAHPM Director Geriatrics and Palliative Care Botsford Hospital Slide 1 OBJECTIVES Know and understand: Incidence and morbidity of depressive
Depression in Long-Term Care Annette Carron, DO, CMD, FACOI, FAAHPM Director Geriatrics and Palliative Care Botsford Hospital Slide 1 OBJECTIVES Know and understand: Incidence and morbidity of depressive
Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services
 Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services DEPRESSION Pharmacological Treatment of Depression NICE guidelines suggest the following stepped care model also
Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services DEPRESSION Pharmacological Treatment of Depression NICE guidelines suggest the following stepped care model also
Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression
 Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression Special Report on New Depression Treatment Technology Based on 2010 APA Practice Guidelines Best Practices Guideline for the Treatment of Patients
Best Practices Treatment Guideline for Major Depression Special Report on New Depression Treatment Technology Based on 2010 APA Practice Guidelines Best Practices Guideline for the Treatment of Patients
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine
 Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Depression Overview. Symptoms
 1 of 6 6/3/2014 10:15 AM Return to Web version Depression Overview What is depression? When doctors talk about depression, they mean the medical illness called major depression. Someone who has major depression
1 of 6 6/3/2014 10:15 AM Return to Web version Depression Overview What is depression? When doctors talk about depression, they mean the medical illness called major depression. Someone who has major depression
Depression in Older Adults A Guide for Patients and Families
 The Expert Consensus Guideline Series Depression in Older Adults A Guide for Patients and Families Reprinted from: Alexopoulos GS, Katz IR, Reynolds CF III, Carpenter D, and Docherty JP. The Expert Consensus
The Expert Consensus Guideline Series Depression in Older Adults A Guide for Patients and Families Reprinted from: Alexopoulos GS, Katz IR, Reynolds CF III, Carpenter D, and Docherty JP. The Expert Consensus
depression easy to read
 depression easy to read National Institute of Mental Health Contents Depression: When the blues don t go away 2 What are the symptoms of depression? 3 Can a person have depression and another illness
depression easy to read National Institute of Mental Health Contents Depression: When the blues don t go away 2 What are the symptoms of depression? 3 Can a person have depression and another illness
DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 1 DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for depression and any history of depression? 2. Did staff
1 DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for depression and any history of depression? 2. Did staff
BENZODIAZEPINE CONSIDERATIONS IN WORKERS COMPENSATION: IMPLICATIONS FOR WORK DISABILITY AND CLAIM COSTS By: Michael Erdil MD, FACOEM
 3 rd Quarter 2015 BENZODIAZEPINE CONSIDERATIONS IN WORKERS COMPENSATION: IMPLICATIONS FOR WORK DISABILITY AND CLAIM COSTS By: Michael Erdil MD, FACOEM Introduction Benzodiazepines, sometimes called "benzos",
3 rd Quarter 2015 BENZODIAZEPINE CONSIDERATIONS IN WORKERS COMPENSATION: IMPLICATIONS FOR WORK DISABILITY AND CLAIM COSTS By: Michael Erdil MD, FACOEM Introduction Benzodiazepines, sometimes called "benzos",
Mood Disorders. What Are Mood Disorders? Unipolar vs. Bipolar
 Mood Disorders What Are Mood Disorders? In mood disorders, disturbances of mood are intense and persistent enough to be clearly maladaptive Key moods involved are mania and depression Encompasses both
Mood Disorders What Are Mood Disorders? In mood disorders, disturbances of mood are intense and persistent enough to be clearly maladaptive Key moods involved are mania and depression Encompasses both
Depression Assessment & Treatment
 Depressive Symptoms? Administer depression screening tool: PSC Depression Assessment & Treatment Yes Positive screen Safety Screen (see Appendix): Administer every visit Neglect/Abuse? Thoughts of hurting
Depressive Symptoms? Administer depression screening tool: PSC Depression Assessment & Treatment Yes Positive screen Safety Screen (see Appendix): Administer every visit Neglect/Abuse? Thoughts of hurting
Psychopharmacology. Psychopharmacology. Hamish McAllister-Williams Reader in Clinical. Department of Psychiatry, RVI
 Regional Affective Disorders Service Psychopharmacology Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Trust Hamish McAllister-Williams Reader in Clinical Psychopharmacology Department of Psychiatry, RVI Intro NOT
Regional Affective Disorders Service Psychopharmacology Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Trust Hamish McAllister-Williams Reader in Clinical Psychopharmacology Department of Psychiatry, RVI Intro NOT
Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour. Pharmacovigilance Working Party. January 2008
 Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour Pharmacovigilance Working Party January 2008 PhVWP PAR January 2008 Page 1/15 1. Introduction The Pharmacovigilance Working Party has on a number of
Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour Pharmacovigilance Working Party January 2008 PhVWP PAR January 2008 Page 1/15 1. Introduction The Pharmacovigilance Working Party has on a number of
MAJOR DEPRESSION DURING CONCEPTION AND PREGNANCY: A Guide for Patients and Families
 MAJOR DEPRESSION DURING CONCEPTION AND PREGNANCY: A Guide for Patients and Families David A. Kahn, MD, Margaret L. Moline, PhD, Ruth W. Ross, MA, Lee S. Cohen, MD, and Lori L. Altshuler, MD www.womensmentalhealth.org
MAJOR DEPRESSION DURING CONCEPTION AND PREGNANCY: A Guide for Patients and Families David A. Kahn, MD, Margaret L. Moline, PhD, Ruth W. Ross, MA, Lee S. Cohen, MD, and Lori L. Altshuler, MD www.womensmentalhealth.org
Unipolar Depression Management Protocol
 Unipolar Depression Management Protocol All Team Members: Patient Self-Management Education & Support Unipolar depression or Major Depressive Disorder means that the patient feels persistent low mood or
Unipolar Depression Management Protocol All Team Members: Patient Self-Management Education & Support Unipolar depression or Major Depressive Disorder means that the patient feels persistent low mood or
IMR ISSUES, DECISIONS AND RATIONALES The Final Determination was based on decisions for the disputed items/services set forth below:
 Case Number: CM13-0018009 Date Assigned: 10/11/2013 Date of Injury: 06/11/2004 Decision Date: 01/13/2014 UR Denial Date: 08/16/2013 Priority: Standard Application Received: 08/29/2013 HOW THE IMR FINAL
Case Number: CM13-0018009 Date Assigned: 10/11/2013 Date of Injury: 06/11/2004 Decision Date: 01/13/2014 UR Denial Date: 08/16/2013 Priority: Standard Application Received: 08/29/2013 HOW THE IMR FINAL
Depression in the Elderly: Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment
 Depression in the Elderly: Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment LOUIS A. CANCELLARO, PhD, MD, EFAC Psych Professor Emeritus and Interim Chair ETSU Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences Diagnosis
Depression in the Elderly: Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment LOUIS A. CANCELLARO, PhD, MD, EFAC Psych Professor Emeritus and Interim Chair ETSU Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences Diagnosis
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA
 MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA MAJOR DEPRESSION IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE HEALTH CARE GUIDELINE (ICSI) Health Care Guideline Twelfth Edition May 2009. The guideline was reviewed and adopted by the Molina
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA MAJOR DEPRESSION IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE HEALTH CARE GUIDELINE (ICSI) Health Care Guideline Twelfth Edition May 2009. The guideline was reviewed and adopted by the Molina
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Guideline Diagnostic Nomenclature for Clinical Depressive Conditions
 Major Depressive Disorder Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Guideline Diagnostic omenclature for Clinical Depressive Conditions Conditions Diagnostic Criteria Duration Major Depression 5 of the following
Major Depressive Disorder Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Guideline Diagnostic omenclature for Clinical Depressive Conditions Conditions Diagnostic Criteria Duration Major Depression 5 of the following
Depression Treatment Guide
 Depression Treatment Guide DSM V Criteria for Major Depressive Disorders A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous
Depression Treatment Guide DSM V Criteria for Major Depressive Disorders A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous
(4) To characterize the course of illness after adequate response to and continuation on the treatments found effective for individual participants.
 I. Specific Aims/Objectives STAR*D has several main objectives and is powered to assess the effectiveness of a sequence of treatments at various levels of treatment. Most of these objectives entail evaluating
I. Specific Aims/Objectives STAR*D has several main objectives and is powered to assess the effectiveness of a sequence of treatments at various levels of treatment. Most of these objectives entail evaluating
Depression is a medical illness that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. Depression can cause physical symptoms, too.
 The Family Library DEPRESSION What is depression? Depression is a medical illness that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. Depression can cause physical symptoms, too. Also called
The Family Library DEPRESSION What is depression? Depression is a medical illness that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. Depression can cause physical symptoms, too. Also called
Feeling Moody? Major Depressive. Disorder. Is it just a bad mood or is it a disorder? Mood Disorders. www.seclairer.com S Eclairer 724-468-3999
 Feeling Moody? Is it just a bad mood or is it a disorder? Major Depressive Disorder Prevalence: 7%; 18-29 years old; Female>Male DDx: Manic episodes with irritable mood or mixed episodes, mood disorder
Feeling Moody? Is it just a bad mood or is it a disorder? Major Depressive Disorder Prevalence: 7%; 18-29 years old; Female>Male DDx: Manic episodes with irritable mood or mixed episodes, mood disorder
MEDICATION GUIDE WELLBUTRIN (WELL byu-trin) (bupropion hydrochloride) Tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE WELLBUTRIN (WELL byu-trin) (bupropion hydrochloride) Tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start using WELLBUTRIN and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
MEDICATION GUIDE WELLBUTRIN (WELL byu-trin) (bupropion hydrochloride) Tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start using WELLBUTRIN and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents
 TREATMENT GUIDELINES Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Guideline 7 Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Description There are few controlled trials to guide practitioners
TREATMENT GUIDELINES Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Guideline 7 Psychopharmacotherapy for Children and Adolescents Description There are few controlled trials to guide practitioners
Antidepressants. Understanding psychiatric medications. Information for consumers, families and friends. Titles in the.
 Titles in the Understanding psychiatric medications series include: Antidepressants Antipsychotics Benzodiazepines Mood Stabilizers Understanding psychiatric medications Antidepressants For more information
Titles in the Understanding psychiatric medications series include: Antidepressants Antipsychotics Benzodiazepines Mood Stabilizers Understanding psychiatric medications Antidepressants For more information
Table of Contents. Preface...xv. Part I: Introduction to Mental Health Disorders and Depression
 Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 16,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...xv
Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 16,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...xv
Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care
 Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Pharmacotherapy of BPSD. Pharmacological interventions. Anti-dementia drugs. Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence
 Pharmacotherapy of BPSD Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence Pharmacological interventions Reducing medication errors. Reducing potentially inappropriate medication prescription.
Pharmacotherapy of BPSD Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence Pharmacological interventions Reducing medication errors. Reducing potentially inappropriate medication prescription.
Bipolar Disorder. When people with bipolar disorder feel very happy and "up," they are also much more active than usual. This is called mania.
 Bipolar Disorder Introduction Bipolar disorder is a serious mental disorder. People who have bipolar disorder feel very happy and energized some days, and very sad and depressed on other days. Abnormal
Bipolar Disorder Introduction Bipolar disorder is a serious mental disorder. People who have bipolar disorder feel very happy and energized some days, and very sad and depressed on other days. Abnormal
Alzheimer s and Depression: What is the Connection?
 Alzheimer s and Depression: What is the Connection? Ladson Hinton MD Professor and Director of Geriatric Psychiatry Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Director, Education Core, Alzheimer
Alzheimer s and Depression: What is the Connection? Ladson Hinton MD Professor and Director of Geriatric Psychiatry Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Director, Education Core, Alzheimer
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES. Depression
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Depression MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 6/2011 3 1 Published by Ministry of Health, Singapore 16 College Road, College of Medicine Building Singapore 169854 Printed by
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Depression MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 6/2011 3 1 Published by Ministry of Health, Singapore 16 College Road, College of Medicine Building Singapore 169854 Printed by
Mental health issues in the elderly. January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca
 Mental health issues in the elderly January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca Cognitive Disorders Outline Dementia (294.xx) Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (early and late
Mental health issues in the elderly January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca Cognitive Disorders Outline Dementia (294.xx) Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (early and late
remeron user reviews remeron medicine remeron suicide
 Overdose symptoms may occur using therapeutic dosages, antidepressants remeron the risk of side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. The most common lorazepam side effects. This material is provided for educational
Overdose symptoms may occur using therapeutic dosages, antidepressants remeron the risk of side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. The most common lorazepam side effects. This material is provided for educational
Coping with depression. Australian treatment guide for consumers and carers
 August 2009 Coping with depression Australian treatment guide for consumers and carers Contents The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, 2009 Compiled by The Royal Australian and
August 2009 Coping with depression Australian treatment guide for consumers and carers Contents The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, 2009 Compiled by The Royal Australian and
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
FACT SHEET 4. Bipolar Disorder. What Is Bipolar Disorder?
 FACT SHEET 4 What Is? Bipolar disorder, also known as manic depression, affects about 1 percent of the general population. Bipolar disorder is a psychiatric disorder that causes extreme mood swings that
FACT SHEET 4 What Is? Bipolar disorder, also known as manic depression, affects about 1 percent of the general population. Bipolar disorder is a psychiatric disorder that causes extreme mood swings that
Paxil/Paxil-CR (paroxetine)
 Generic name: Paroxetine Available strengths: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg tablets; 10 mg/5 ml oral suspension; 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg controlled-release tablets (Paxil-CR) Available in generic: Yes, except
Generic name: Paroxetine Available strengths: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg tablets; 10 mg/5 ml oral suspension; 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg controlled-release tablets (Paxil-CR) Available in generic: Yes, except
WHAT IT MEANS TO BE A TEAM LEADER. Presented by: Arthur Berger, Ed.D Director of Behavioral Health
 WHAT IT MEANS TO BE A TEAM LEADER Presented by: Arthur Berger, Ed.D Director of Behavioral Health Overview of Urban Health Plan (UHP) Federally Qualified Community Health Center JCAHO accredited Located
WHAT IT MEANS TO BE A TEAM LEADER Presented by: Arthur Berger, Ed.D Director of Behavioral Health Overview of Urban Health Plan (UHP) Federally Qualified Community Health Center JCAHO accredited Located
Presently, there are no means of preventing bipolar disorder. However, there are ways of preventing future episodes: 1
 What is bipolar disorder? There are two main types of bipolar illness: bipolar I and bipolar II. In bipolar I, the symptoms include at least one lifetime episode of mania a period of unusually elevated
What is bipolar disorder? There are two main types of bipolar illness: bipolar I and bipolar II. In bipolar I, the symptoms include at least one lifetime episode of mania a period of unusually elevated
Revised 7/05. Copyright 2005 St. Jude Children's Research Hospital www.stjude.org Page 1 of 6
 Antidepressants are drugs used, most often, to treat depression. Depression is a complex illness that involves sad and hopeless feelings that do not go away. Doctors sometimes order these drugs for other
Antidepressants are drugs used, most often, to treat depression. Depression is a complex illness that involves sad and hopeless feelings that do not go away. Doctors sometimes order these drugs for other
Managing Patients with Pain, Psychiatric Co-Morbidity & Addiction
 Managing Patients with Pain, Psychiatric Co-Morbidity & Addiction John A. Renner Jr., MD, CAS Division of Psychiatry Boston University School of Medicine Prescribers Clinical Support System for Opioid
Managing Patients with Pain, Psychiatric Co-Morbidity & Addiction John A. Renner Jr., MD, CAS Division of Psychiatry Boston University School of Medicine Prescribers Clinical Support System for Opioid
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis
 Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing specific issues Aaron, diagnosed in 1995. The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky.
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing specific issues Aaron, diagnosed in 1995. The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky.
Depression Pathway. Patient Education Box 4. Guided self help Box 18. pg 11
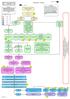 LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
MEDICATION GUIDE. Bupropion Hydrochloride (bue-proe-pee-on HYE-droe-KLOR-ide) Extended-Release Tablets, USP (SR)
 MEDICATION GUIDE Bupropion Hydrochloride (bue-proe-pee-on HYE-droe-KLOR-ide) Extended-Release Tablets, USP (SR) Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking bupropion hydrochloride extendedrelease
MEDICATION GUIDE Bupropion Hydrochloride (bue-proe-pee-on HYE-droe-KLOR-ide) Extended-Release Tablets, USP (SR) Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking bupropion hydrochloride extendedrelease
Major Depressive Disorder
 Treatment Works Major Depressive Disorder A Patient and Family Guide Developed from the American Psychiatric Association Practice Guidelines 1 What Is Depression? Major depressive disorder, also referred
Treatment Works Major Depressive Disorder A Patient and Family Guide Developed from the American Psychiatric Association Practice Guidelines 1 What Is Depression? Major depressive disorder, also referred
Overview of Mental Health Medication Trends
 America s State of Mind Report is a Medco Health Solutions, Inc. analysis examining trends in the utilization of mental health related medications among the insured population. The research reviewed prescription
America s State of Mind Report is a Medco Health Solutions, Inc. analysis examining trends in the utilization of mental health related medications among the insured population. The research reviewed prescription
Pharmacologic Treatment of Acute Major Depression and Dysthymia
 POSITION PAPERS CLINICAL GUIDELINE, PART 1 Pharmacologic Treatment of Acute Major Depression and Dysthymia Vincenza Snow, MD; Steven Lascher, DVM, MPH; and Christel Mottur-Pilson, PhD, for the American
POSITION PAPERS CLINICAL GUIDELINE, PART 1 Pharmacologic Treatment of Acute Major Depression and Dysthymia Vincenza Snow, MD; Steven Lascher, DVM, MPH; and Christel Mottur-Pilson, PhD, for the American
CLINICIAN INTERVIEW COMPLEXITIES OF BIPOLAR DISORDER. Interview with Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD
 COMPLEXITIES OF BIPOLAR DISORDER Interview with Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD Dr Nemeroff is the Reunette W. Harris Professor and Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Emory
COMPLEXITIES OF BIPOLAR DISORDER Interview with Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD Dr Nemeroff is the Reunette W. Harris Professor and Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Emory
Part 1: Depression Screening in Primary Care
 Part 1: Depression Screening in Primary Care Toni Johnson, MD Kristen Palcisco, BA, MSN, APRN MetroHealth System Objectives Part 1: Improve ability to screen and diagnose Depression in Primary Care Increase
Part 1: Depression Screening in Primary Care Toni Johnson, MD Kristen Palcisco, BA, MSN, APRN MetroHealth System Objectives Part 1: Improve ability to screen and diagnose Depression in Primary Care Increase
Understanding Major Depression and Recovery
 Understanding Major Depression and Recovery What you need to know about this medical illness Major depression is a medical illness that affects thoughts, feelings, behavior, mood and physical health. Introduction
Understanding Major Depression and Recovery What you need to know about this medical illness Major depression is a medical illness that affects thoughts, feelings, behavior, mood and physical health. Introduction
Understanding. Depression. The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself. Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members
 TM Understanding Depression The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members Understanding Depression Depression is a biological illness. It affects more than
TM Understanding Depression The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members Understanding Depression Depression is a biological illness. It affects more than
ADOLESCENT DEPRESSION. What we know, what we look for, and what we do.
 ADOLESCENT DEPRESSION What we know, what we look for, and what we do. What we know, what we look for, and what we do. The word depression is used to mean many different things. If asked, most people would
ADOLESCENT DEPRESSION What we know, what we look for, and what we do. What we know, what we look for, and what we do. The word depression is used to mean many different things. If asked, most people would
Sleep Medicine and Psychiatry. Roobal Sekhon, D.O.
 Sleep Medicine and Psychiatry Roobal Sekhon, D.O. Common Diagnoses Mood Disorders: Depression Bipolar Disorder Anxiety Disorders PTSD and other traumatic disorders Schizophrenia Depression and Sleep: Overview
Sleep Medicine and Psychiatry Roobal Sekhon, D.O. Common Diagnoses Mood Disorders: Depression Bipolar Disorder Anxiety Disorders PTSD and other traumatic disorders Schizophrenia Depression and Sleep: Overview
POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm
 E-Resource March, 2014 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
E-Resource March, 2014 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
Antidepressant treatment in adults
 Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
Wellbutrin (bupropion)
 Wellbutrin (bupropion) FDA ALERT [09/2007] - Suicidality and Antidepressant Drugs Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents,
Wellbutrin (bupropion) FDA ALERT [09/2007] - Suicidality and Antidepressant Drugs Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents,
Caring for depression
 Caring for depression Aetna Health Connections SM Disease Management Program Get information. Get help. Get better. 21.05.300.1 B (6/08) Get back to being you How this guide can help you Having an ongoing
Caring for depression Aetna Health Connections SM Disease Management Program Get information. Get help. Get better. 21.05.300.1 B (6/08) Get back to being you How this guide can help you Having an ongoing
Antidepressant Choices in Primary Care: Which to Use First?
 Antidepressant Choices in Primary Care: Which to Use First? Sherri Hansen, MD Doctor Hansen is a clinical assistant professor with the University of Wisconsin Medical School. Please address correspondence
Antidepressant Choices in Primary Care: Which to Use First? Sherri Hansen, MD Doctor Hansen is a clinical assistant professor with the University of Wisconsin Medical School. Please address correspondence
Adolescent Depression. Danielle Bradshaw, DO Diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology Adult and Child/Adolescent Psychiatry
 Adolescent Depression Danielle Bradshaw, DO Diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology Adult and Child/Adolescent Psychiatry Adolescence When does it start? When does it end? Characteristics:
Adolescent Depression Danielle Bradshaw, DO Diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology Adult and Child/Adolescent Psychiatry Adolescence When does it start? When does it end? Characteristics:
Depression, Mental Health and Native American Youth
 Depression, Mental Health and Native American Youth Aisha Mays, MD UCSF Department of Family And Community Medicine Native American Health Center Oakland, CA July 8, 2015 Presenter Disclosures No relationships
Depression, Mental Health and Native American Youth Aisha Mays, MD UCSF Department of Family And Community Medicine Native American Health Center Oakland, CA July 8, 2015 Presenter Disclosures No relationships
Treatment Modalities As in younger patients, the goals of treating depression in elderly patients include alleviating
 Iranian Rehabilitation Journal, Vol. 10, No. 16, Oct. 2012 Reviews/Short communication Treatment of Depression in the Elderly: A systematic review Arash Mirabzadeh, MD. University of Social Welfare and
Iranian Rehabilitation Journal, Vol. 10, No. 16, Oct. 2012 Reviews/Short communication Treatment of Depression in the Elderly: A systematic review Arash Mirabzadeh, MD. University of Social Welfare and
Workshop: Management of Depression in the Primary Care Setting, Kaiser Permanente of Ohio s Multidisciplinary Model
 Workshop: Management of Depression in the Primary Care Setting, Kaiser Permanente of Ohio s Multidisciplinary Model Larissa Elgudin, MD, Chief of Behavioral Health Services Colleen O Malley RN, BSN, Regional
Workshop: Management of Depression in the Primary Care Setting, Kaiser Permanente of Ohio s Multidisciplinary Model Larissa Elgudin, MD, Chief of Behavioral Health Services Colleen O Malley RN, BSN, Regional
