1.1.2 The heart valves and their functions to include: Tricuspid valve Mitral/bicuspid valve Pulmonary valve Aortic valve
|
|
|
- Chrystal Peters
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 413 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Recommended Guided Learning Hours: 43 Credit value 6 QCF Unit number A/600/9051 Learning Outcome 1. Understand the heart and Circulatory System and its relation to exercise and health 1.1 Explain the function of the heart valves The anatomy of the heart to include: Layers Pericardium Myocardium Endocardium Chambers Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Septum muscular wall separating left and right sides Vessels Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Vein Aorta Control of heart beat Sino-Atrial Node Atrio-Ventricular Node Bundle of His The heart valves and their functions to include: Tricuspid valve Mitral/bicuspid valve Pulmonary valve Aortic valve 1.2 Describe the coronary circulation To include: Left and right coronary arteries branch out from aorta forming a network of capillaries within the heart wall (myocardium) delivering oxygenated blood. Coronary veins take deoxygenated blood away Systemic and coronary circulation include: Sequence of events Atrial systole Ventricular systole Ventricular diastole Cardiac output Heart rate Stroke volume (preload, contractility, afterload) 1.3 Explain the effect of disease processes on the structure and function of blood vessels To include the cause and effects of the following: Anaemia Varicose Veins Haemophilia Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis HIV/Aids High Cholesterol Hepatitis A, B and C Coronary Thrombosis Angina Pacemaker fitted Haemorrhoids Phlebitis Thrombus Leukaemia Raynaud s Disease Nosebleeds Stress Palpitations
2 1.4 Explain the short and long term effects of exercise on blood pressure, including the valsalva effect To include: Short term effects heart rate increases, blood pressure increases Long term effects lower resting heart rate, quicker recovery rate Positive/beneficial effects Negative/detrimental effects Valsalva effect to include: Blood pressure can rise drastically when expiratory force has occurred Pressure that builds up can stop the flow of blood to the heart Venous activity is stalled causing sudden release of pressure causing the heart s output rate to increase rapidly Normal cardiac output is restored after about 24 seconds, pressure usually rising before returning to normal 1.5 Explain the cardiovascular benefits and risks of endurance/aerobic training 1.6 Define blood pressure classifications and associated health risks Learning Outcome 2. Understand the Musculoskeletal System and its relation to exercise 2.1 Explain the cellular structure of muscle fibres 2.2 Describe the sliding filament theory 2.3 Explain the effects of different types of exercises on muscle fibre type To include: Increases blood volume Increases stroke volume Decreases resting heart rate Decreases recovery time Increases VO2 Helps control body weight Helps maintain and build healthy bones, joints and muscles Improves mobility Promotes psychological well-being Reduces depression Reduces stress and anxiety Reduces risk of premature death Reduces risk of dying from heart disease Reduces risk of developing diabetes Reduces risk of developing high blood pressure Reduces risk of dying of colon cancer To include: Define blood pressure Factors which produce, maintain and affect blood pressure Causes and effects of hypo and hyper- tension Way in which blood pressure is measured To include: Cardiac muscle Striated Involuntary Smooth muscle Non-striated (smooth) Involuntary Skeletal muscle Striated Voluntary Fascicle Fibre Myofibril Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium To include: Sarcomeres Sarcolemma Myofibrils - Actin and myosin filaments Troponin Cross bridges Muscle fibre types to include: Slow twitch Type I Red Fast twitch Type IIa (Fast Oxidative Glycolytic) Type IIb (Fast Glycolytic) White
3 2.3.2 Muscle physiology changes between sessions to include: Increased mitochondria Oxidative enzymes and capillaries 2.4 Identify and locate the muscle attachment sites for the major muscles of the body 2.5 Name, locate and explain the function of skeletal muscle involved in physical activity How a muscle contracts to include: The motor unit Axon terminals Acetylcholine Sodium ions The action potential The sodium/potassium pump Sliding filament theory including sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium ions, ATP All-or-none law of muscle physiology Muscle fatigue and oxygen debt To include the origin and insertion of the following muscles: Trunk/torso Sternocleido Mastoid Levator Scapulae Splenius Capitis Scalenes Trapezius Rhomboid Major Rhomboid Minor Infraspinatis Supraspinatis Subscapularis Teres Major Teres Minor Serratus Anterior Latissimus Dorsi Erector Spinae Quadratus Lumborum Piriformis Multifidus Gluteus Maximus Gluteus Medius Gluteus Minimus Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Intercostals Diaphragm Abdominus Rectus Abdominus Transversalis Internal Oblique External Oblique Illiopsoas: Iliacus and Psoas Major Arm Deltoid Coracobrachialis Biceps Triceps Brachialis Brachioradialis Pronator Teres Supinator Radii Brevis Extensor Carpi Radialis Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Extensor Carpi Digitorum Flexor Carpi Radialis Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Flexor Carpi Digitorum Leg/Thigh Quadriceps: Rectus Femoris, Vastus Lateralis, Vastus Medialis, Vastus Intermedius Hamstrings: Biceps Femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus Tensa Fascia Lata Ilio-Tibial band Pectinius Adductor Longus Adductor Magnus Adductor Brevis Gracilis Sartorius Lower Leg Gastrocnemius Soleus Tibialis Anterior Peroneus Longus Flexor Digitorum Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Extensor Hallucis Longus To include the position and action of the following muscles: Trunk/torso Sternocleido Mastoid Levator Scapulae Splenius Capitis Scalenes Trapezius Rhomboid Major Rhomboid Minor Infraspinatis Supraspinatis Subscapularis Teres Major Teres Minor Serratus Anterior Latissimus Dorsi Erector Spinae Quadratus Lumborum Piriformis Multifidus Gluteus Maximus Gluteus Medius Gluteus Minimus Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Intercostals Abdominus Rectus Abdominus Transversalis Diaphragm Internal Oblique External Oblique Illiopsoas: Iliacus and Psoas Major Arm Deltoid Coracobrachialis Biceps Triceps Brachialis Brachioradialis Pronator Teres Supinator Radii Brevis Extensor Carpi Radialis Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Extensor Carpi Digitorum Flexor Carpi Radialis Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Flexor Carpi Digitorum
4 Leg/Thigh Quadriceps: Rectus Femoris Vastus Lateralis Vastus Medialis Vastus Intermedius Hamstrings: Biceps Femori Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Tensa Fascia Lata Ilio-Tibial band Pectinius Adductor Longus Adductor Magnus Adductor Brevis Gracilis Sartorius Lower Leg Gastrocnemius Soleus Tibialis Anterior Peroneus Longus Flexor Digitorum Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Extensor Hallucis Longus Understanding the uses of muscles in functional and sporting activities: Muscles acting over the following areas: Trunk Shoulder and upper arm Forearm, wrist and hand Hip and upper leg Lower leg, ankle and foot In terms of improving strength and functioning, understand the need for: Strengthening of specific muscles/muscle groups Achieving balance for optimal results 2.6 Identify the anatomical axis and planes with regard to joint actions and different exercises To include: Sagittal Median Frontal Transverse Joint actions to include: Flexion Extension Hyper-extension Abduction Adduction Internal rotation External rotation Circumduction Elevation Depression Lateral flexion Horizontal flexion and extension Supination Pronation Dorsiflexion Plantarflexion Inversion Eversion 2.7 Explain the joint actions brought about by specific muscle group contractions 2.8 Describe joints/joint structure with regard to range of motion/movement and injury risk 2.9 Describe joint movement potential and joint actions To include: Fibrous Joints Fixed Cartilaginous Joints Slightly moveable Synovial Joints Freely moveable Ball and Socket Hinge Pivot Gliding Saddle Condyloid Give examples of where in the body they would be found Role in producing movement Agonist/Prime mover Antagonist Synergist Fixators/ Stabilisers Types of contraction Isotonic concentric and eccentric Isometric (static) Isokinetic To include: Spine Structure Actions and range of movement Flexion, Extension, Rotation, Side Flexion Postural deformities Kyphosis, Lordosis, Scoliosis Major Synovial Joints Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist, Hip, Knee, Ankle Actions and range of movement To include: Horizontal adduction Horizontal abduction Internal and external rotation Eversion Inversion Elevation Depression Retraction Protraction
5 2.10 Describe the structure of the pelvic girdle and associated muscles and ligaments Learning Outcome 3. Understand postural and core stability 3.1 Describe the structure and function of the stabilising ligaments and muscles of the spine 3.2 Describe local muscle changes that can take place due to insufficient stabilisation To include: Sacrum and Coccyx and caudal part of the axial skeleton in the posterior dorsal Posterior pair of hip bones consisting of - Ischium, Ilium, Pubis Muscles and ligaments of the pelvic girdle To include: Erector spinae Iliocostalis, Longissimus, Spinalis Lumbar Multifidus Quadratus Lumborum Illiopsoas Gluteus Maximus Gluteus Medius Gluteus Minimus Rectus Abdominus Internal and External Obliques Abdominus Tranversalis Tensor Fascia Lata Pelvic floor To include the fundamental principles of core stabilisation: Rationale for stabilisation to exist because of excessive forces on the spine Neutral zone control from the muscular system Intra-abdominal pressure and its role in stabilisation Thoracolumbar fascia and its role in stabilisation Abdominal bracing and its role in stabilisation The gluteal complex and its role in stabilisation of the spine reducing the risk of low back pain To include: Stabilising deep muscles, shorter than mobilizing muscles, working for long periods of time, holding tone, needing endurance, 20-30% of Maximum Voluntary Contraction (MVC) Mobilising big movements, working in phases, lie closer to the surface than stabilising muscles, usually long, fatigue quickly, work at between % of Maximum Voluntary Contraction (MVC) 3.3 Explain the potential effects of abdominal adiposity and poor posture on movement efficiency To include: Medical conditions associated with dysfunctional stabilisation e.g., common spinal disorders The impact of core stabilisation exercise and the potential for injury/aggravation of problems To include the different factors that may influence posture: Hereditary Injury Illness mental and physical Work related factors type of job Hobby/sport related influences Environmental Emotional Sustained positions Repetitive movements Fashion The relationship between centre of gravity excursions and adiposity deviation Posture positioning for everyday situations include: Sitting at a desk/computer/watching TV Standing incorrectly Lying in bed Driving correct mirror positioning/wheel grip Functional professional posture
6 3.4 Explain the potential problems that can occur as a result of postural deviations 3.5 Explain the impact of core stabilisation exercise and the potential for injury/aggravation of problems 3.6 Explain the benefits, risks and applications of the following types of stretching: Static (passive and active) Dynamic Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation Learning Outcome 4. Understand the Nervous System and its relation to exercise 4.1 Describe the specific roles of: the Central Nervous System (CNS) the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) including Somatic and Autonomic Systems Recognise and assess the different postural conditions to include: Dowager s hump Round shoulders Winged scapulae Midriff bulge Protruding abdomen Knock knees Bow legged Flat back Sway back Kyphosis Lordosis Scoliosis Stress related weight changes and postural defect If in doubt refer to the appropriate professional To include the exercises associated with core stabilisation: Methods of contraction of abdominus transversalis Methods of abdominal bracing The use of stabilisation equipment Stability equipment exercises Floor based exercises Reasons for participant exclusion Imbalances associated with incorrect stabilisation To include benefits, risks and applications of: Static (passive and active) Ballistic Dynamic Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) To include the functions of: Central Nervous System Brain: Cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrum Cerebellum Pons varolii Medulla Oblongata Hypothalamus Brain stem Spinal cord: Cerebrospinal fluid Peripheral Nervous System 31 pairs of spinal nerves Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Parasympathetic To include: Understand how regular activity can enhance neurological functioning The effects of stress on the Nervous System Describe the way in which stress affects the fear, fight and flight syndrome Describe the way in which various parts of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems can be affected by stress and its effect on exercise 4.2 Describe nervous control and transmission of a nervous impulse To include: Changes in temperature, pressure and chemicals Neurotransmitters Potassium and sodium ions
7 4.3 Describe the structure and function of a neuron 4.4 Explain the role of a motor unit 4.5 Explain the process of motor unit recruitment and the significance of a motor unit s size and number of muscle fibres 4.6 Explain the function of muscle proprioceptors and the stretch reflex 4.7 Explain reciprocal inhibition and its relevance to exercise 4.8 Explain the neuromuscular adaptations associated with exercise/training 4.9 Explain the benefits of improved neuromuscular coordination/efficiency to exercise performance Structure and function to include: Cell body Dendrites Axon Myelin sheath Neurilemma Nodes of Ranvier End feet/axon terminals Synapse To include: Formed by motor end-plates and each nerve and muscle fibres they supply Serves a functional role in the control of movement To include: All or nothing principle To include: Detecting subtle changes in movement, position, tension and force within the body Golgi tendons The stretch reflex to include: Neural receptors/sense organs Golgi tendon organs Muscle spindle cells Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) To include: An impulse sent from the spinal cord to the antagonistic of the contracting muscle causing the antagonistic to relax To include: Fast twitch motor units Recruitment, order and different metabolic characteristics Hypertrophia and hyperplasia Neural adaptations and atrophy To include: Improved mitotic proprioceptive facilities Improved cardiovascular endurance Improved neuromuscular efficiency (including endurance, strength, etc.) Increased metabolic activity Increased capillarisation Increased number and size of mitochondria Hypertrophy
8 Learning Outcome 5. Understand the Endocrine System and its relation to exercise 5.1 Describe the functions of the Endocrine System Define the Endocrine System 5.2 Identify the major glands in the Endocrine System 5.3 Explain the function of hormones including: growth hormone thyroid hormones Explain (with the aid of a diagram) the main endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete: Pituitary Posterior Lobe Antidiuretic hormone (ADH or vasopressin) Anterior lobe Prolactin Human Growth Hormone (HGH) Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotrophin Hormone (ACTH) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Thyroid gland Thyroxin Triiodothyronin Calcitonin Parathyroids Parathormone Thymus Secretion of T Lymphocytes Pineal Melatonin Islets of Langerhans Insulin Glucagon Glycogen Adrenal medulla Adrenalin Noradrenalin Adrenal cortex Mineralocorticoids Glucocorticoids Sex hormones Ovaries Oestrogen Progesterone Testes Testosterone Functions to include: Growth hormone: Regulates height and weight Thyroid hormones:
9 corticosteroids catecholamines insulin glucagon Learning Outcome 6. Understand energy systems and their relation to exercise 6.1 Identify the contribution of energy according to: duration of exercise/activity being performed type of exercise/activity being performed intensity of exercise/activity being performed 6.2 Identify the by-products of the three energy systems and their significance in muscle fatigue Stimulate tissue metabolism Maintain basic metabolic rate (BMR) Cortocosteroids: Mineralocorticoids to regulate salts in the body especially sodium chloride and potassium Glucocorticoids to metabolise carbohydrates, fats and proteins Catecholamines: Fight-or-flight hormones released in response to stress Insulin: To regulate blood sugar levels Glucagon: Involved in carbohydrate metabolism To include: Energy systems: Anaerobic System Creatine Phosphate system (ATP-CP) Lactate system Aerobic system By-products include: Blood lactate: Production Clearance Accumulation Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation (OBLA) 6.3 Describe the effect of endurance training/advanced training methods on the use of fuel for exercise To include: Glycolytic system anaerobic glycolysis and aerobic glycolysis Lactic acid Effects of exercise on the cardio-respiratory system including: Short term Increased heart rate Increased breathing rate Build-up of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream Stroke volume Increased blood flow to capillaries Cardiac output Systolic pressure Diastolic pressure Respiratory rate Long term Increase in stroke volume Lower resting heart rate Reduced risk of heart disease Reduction of high blood pressure Improved blood cholesterol Reduced body fat Build-up of carbon dioxide and other metabolic by-products in the blood Increased capillarisation and use of dead space
10 6.3.3 Effects of exercise on muscular strength and muscular endurance including: Muscular strength Use of high resistance and low repetitions so that motor unit recruitment is maximized and contractile limits are reached Muscular endurance Lower resistance loads and high repetitions which may result in build-up of lactic acid and inhibition of further muscle contraction Increased endurance capacity in muscles developed between exercise session by the increased numbers of Mitochondria, Oxidative enzymes and Capillaries Assessment Unit 413 Anatomy and Physiology for Health and Exercise The effects of health related physical activities to include: Resistance training Improved posture Reduced risk of joint and soft tissue injuries Increased bone density Improved neuromuscular efficiency Cardiorespiratory training Reduced risk of coronary heart disease Improved body composition Range of motion training This unit will be assessed by an externally set multiple choice questions paper. This can be completed either on line or in paper format See for test specification
MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise and Health. Unit Accreditation Number A/600/9051
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B.
 Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Practice Chapter 6. Figure 6.3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
The Muscular System General & Anatomy
 The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb
 2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
Anatomy for Sport and Exercise
 Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Figure 6.1. 2) The A band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 188
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8
 Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
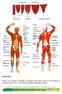 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014
 PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Deltoid Trapezius. Identify the muscle pair(s) that work together to produce the movements listed above.
 Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength
 A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM # 140. Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 2012 by Exercise
A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM # 140. Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 2012 by Exercise
PLEASE COMPLETE THE FOLLOWING BOXES IN BLACK OR BLUE INK. USE BLOCK CAPITALS. DO NOT USE PENCIL.
 VTT - UV30536 natomy and physiology for exercise and health Single unit assessment Multiple choice question paper (Mock paper) Time: Up to: 2 hours PLESE OMPLETE THE FOLLOWING OXES IN LK OR LUE INK. USE
VTT - UV30536 natomy and physiology for exercise and health Single unit assessment Multiple choice question paper (Mock paper) Time: Up to: 2 hours PLESE OMPLETE THE FOLLOWING OXES IN LK OR LUE INK. USE
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
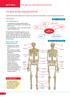 SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) a function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B)
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) a function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B)
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
Muscle Organization and Function. Chapter 10: The Muscular System. Parallel (Fusiform) Muscles. Organization of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
 Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM
 EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9: THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation:
 EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
Chapter 9: Muscular System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 9: Muscular System Chapter 9: Muscular System I. Structure of a Skeletal Muscle A. Introduction 1. A skeletal muscle is
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 9: Muscular System Chapter 9: Muscular System I. Structure of a Skeletal Muscle A. Introduction 1. A skeletal muscle is
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
MUSCULAR SYSTEM. A. K. Sengupta 9/9/2010 1/12
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory
 Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of 4-20 myofibrils Myofibrils are
Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of 4-20 myofibrils Myofibrils are
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Electrode Placement Manual Visit our website: www.veritymedical.co.uk for detailed application protocols
 NeuroTrac Electrode Placement Manual Visit our website: www.veritymedical.co.uk for detailed application protocols 1 Contents Contents Page Introduction 4 Muscle profile 4 Classification of the various
NeuroTrac Electrode Placement Manual Visit our website: www.veritymedical.co.uk for detailed application protocols 1 Contents Contents Page Introduction 4 Muscle profile 4 Classification of the various
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis
 Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Core Training for Improved Performance
 Core Training for Improved Performance Tracy Morgan Handzel, CSCS Core training has penetrated a variety of fitness and performance related fields. Health clubs offer core training group exercise classes.
Core Training for Improved Performance Tracy Morgan Handzel, CSCS Core training has penetrated a variety of fitness and performance related fields. Health clubs offer core training group exercise classes.
Muscle Energy Technique. Applied to the Shoulder
 Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscular System Teacher s lecture notes, curriculum and guides 2012
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
The skeletal and muscular systems
 anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
Muscles of the Spinal Column. Chapter 12
 Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE. Striations Present or Absent?
 BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
Rehabilitation with Pilates
 Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Understanding back pain 1 The anatomy & physiology of back pain
 Understanding back pain 1 The anatomy & physiology of back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, Level 3 Personal Trainer (REP registration no R1045463), Sports Nutritionist
Understanding back pain 1 The anatomy & physiology of back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, Level 3 Personal Trainer (REP registration no R1045463), Sports Nutritionist
Teppe Treppe: A staircase increase in tension production after repeated simulation, even though the muscle is allowed to relax between twitches.
 Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
I have also included the questions from the muscular system quiz 7AB and 8 AB in this practice set.
 1 Practice Questions for Exam 2 As you prepare for the exam you should review all of your lecture notes, study guides, key medical terms, blood test information, and previous quizzes. The following are
1 Practice Questions for Exam 2 As you prepare for the exam you should review all of your lecture notes, study guides, key medical terms, blood test information, and previous quizzes. The following are
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Dr. Enas Elsayed. Brunnstrom Approach
 Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice
 Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Describe the three key functions of muscle. 2. Describe the four special properties of muscle tissue. SKELETAL MUSCLE
Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Describe the three key functions of muscle. 2. Describe the four special properties of muscle tissue. SKELETAL MUSCLE
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Strength Training for the Runner
 Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24
 Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24 Evaluation of breathing function Chart review History Chest X ray Blood test Observation/palpation Chest mobility Shape of chest wall Accessory
Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24 Evaluation of breathing function Chart review History Chest X ray Blood test Observation/palpation Chest mobility Shape of chest wall Accessory
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Hip and Trunk Exercise Program
 Hip and Trunk Exercise Program Hip and Pelvis Exercise Program Gluteus Medius and Minimus (Hip Abductors) Page 2 Lateral Hip Rotators Page 6 Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL) and Illiotibial Band (ITB) Page 7 Lower
Hip and Trunk Exercise Program Hip and Pelvis Exercise Program Gluteus Medius and Minimus (Hip Abductors) Page 2 Lateral Hip Rotators Page 6 Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL) and Illiotibial Band (ITB) Page 7 Lower
