Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) in canine liver examination
|
|
|
- Teresa Boyd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Polish Journal of Veterinary Sciences Vol. 3, No. 4 (200), DOI /v Review Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) in canine liver examination M. Wdowiak, A. Rychlik, R. Nieradka, M. Nowicki Department of Clinical Diagnostics, University of Warmia and Mazury M. Oczapowskiego 4, 0-79 Olsztyn, Poland Abstract Ultrasonography is a noninvasive diagnostic tool used to image size, shape, parenchyma and vascularization of various body organs. Unfortunately, the ultrasonographic image is characterized by a low contrast due to similar acoustic properties of the soft tissue. The Doppler mode provides information about blood flow, but is incapable of imaging small vessels and capillaries because of their low blood flow velocity ( mm/s). However, a possibility to increase the effectiveness of ultrasonographic diagnostics exists, thanks to intravenous ultrasound contrast agents (UCAs) consisted of gas microbubbles. The purpose of this review paper is to characterize specific imaging techniques necessary to conduct a contrast-enhanced liver examination and indications for CEUS as an alternative diagnostic method. Key words: ultrasonography, liver, canine, neoplasm, differential diagnostics Specific contrast-enhanced imaging techniques The basic B-mode (Haers and Saunders 2009) is not effective enough for ultrasound contrast agent detection in tissue, so it can not be used in contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS). All Doppler modalities are too sensitive to the microbubbles and this hypersensitivity causes artifacts such as color blooming (color Doppler) and flash (power Doppler), which decreases the usefulness of these modes. Color blooming artifact (Nilsson 200) presents itself as extravascular color induced by reverberation and/or a high gain setting. The flash artifact appears when tissue or transducer movement disturbs the desired flow signal. Specific contrast-enhanced imaging techniques (Haers and Saunders 2009) are deprived of these defects and bring satisfying clinical results and artifact reduction. Many techniques have been created e.g. second harmonic imaging, pulse/phase inversion harmonic imaging, cadence-contrast pulse sequencing and power (amplitude) modulation. These specific imaging techniques take advantage of the nonlinear properties of UCAs which manifests in asymmetrical oscillation of the gas microbubbles under ultrasonic wave influence. The nonlinear properties of UCAs (Quaia 2007) increase contrast detection in tissues, thus increasing the contrast to tissue ratio and decreasing artifacts and noise. The principles of the second harmonic imaging are to create an image based on a frequency twice the value of the wave emitted by the transducer. The fundamental wave is filtered. If the fundamental wave is 2 MHz, then the second harmonic is 4 MHz, third harmonic 6 MHz and so on. Conventional USG sys- Correspondence to: M. Wdowiak, ktmtombstone@interia.pl
2 768 M. Wdowiak et al. Table. Ultrasound contrast agents characteristics. Name Optison Definity Levovist Sonovue Sonazoid Manufacturer GE Healthcare Bristol-Myers Squibb, North Billerica, Mass. Shell Human serum albumin Lipid Microsphere Schering Galactose (999 mg) + palmitic acid ( mg) Bracco Pharmaceutical Geneva Phospholipid Gas Perflutren C3F8 Perflutren C3F8 Air Sulfur hexafluoride SF6 GE Healthcare Phospholipid Perfluorobutane C4F0 tems emit and receive sound waves with identical frequencies. On the contrary to conventional methods (Szatmári et al. 2003), second harmonic imaging receives echoes of twice the frequency than the fundamental pulse. The limitations of this technique are low spatial axial resolution and a possibility of contrast resolution reduction if the transmit pulse bandwidth and the receive bandwidth overlap (harmonic signal contamination). Harmonic imaging (O Brien and Holmes 2007, Quaia 2007) improves the good artifacts (shadow and through transmission diagnosis of mineralization and fluid) and reduces the bad artifacts (ring-down). Pulse (phase) inversion (Szatmári et al. 2003) imaging also is based on harmonic frequencies, but every other emitted pulse is inverted. The two subsequent echoes are added and each scanning line consists of two pulses. The added tissue echoes are nulled, but the echoes from the nonlinear microbubbles are not. This results in a strong harmonic signal. The advantages of this technique (Stewart and Sidhu 2006, Quaia 2007), are good spatial resolution and no transmission spectrum restrictions. The disadvantage is a reduction in frame rate due to the need to interrogate each scan line twice. Cadence-contrast pulse sequencing (CPS) is a technique developed by Siemens, which principles are to emit a sequence of sound waves effects in microbubble oscillation, and the echoes originating from the microbubbles are filtered from tissue echoes by computer software. This technique (Quaia 2007) uses amplitude and phase modulation, and enables the visualization of all nonlinear contrast response, even the strong, nonlinear fundamental frequency. This technique (O Brien and Holmes 2007) allows imaging with higher frequencies resulting in increased spatial resolution with the disadvantage of decreased temporal resolution. CPS, pairing the linear fundamental signal beside the nonlinear fundamental image, also allows anatomical orientation. Power (amplitude) modulation (Quaia 2007) in every scanning line two pulses are emitted, one with half and the other with a full frequency. Then, the received echoes are subtracted in the scanner to separate microbubble and tissue signals. Ultrasound contrast agents (UCAs) The first efforts (Calliada 998) to enhance ultrasonic signals were based on i.v. admission of agitated 0.9% NaCl and receive sound wave reflections from the air microbubbles diluted in the patients blood. Feinstein continued research in this field and discovered that blood albumins improve microbubble stability. His investigations resulted in the development of the first pharmaceutical contrast agent, Albunex TM. The first echo-enhancing substances were applied in cardiology and were incapable of penetrating the pulmonary bed. Ultrasound contrast media (Nyman et al. 2005) are classified into two generations according to the gas present inside the microbubbles: I gen agents (Albumex, Levovist) contain air, while II gen agents contain perfluorocarbon or sulfur hexafluoride (SonoVue, Optison, Definity). New generation UCAs consist of small, gas-filled, mainly by prefluorane derivatives of saturated hydrocarbons (e.g. perfluoropropane, perfluorohexane, octafluoropropane) microbubbles stabilized by an external shell (denaturated human albumin, surfactant or phospholipids). The gas enhances the sound wave reflection and the gas type determines the quality of enhancement and microbubble durability. Gases with high molecular mass are poorly dissolved in serum thus are more durable and extend the enhancement effect. The shell determines elasticity which allows the ability of oscillation in a ultrasonic field and a more effective and longer enhancement effect. The diameter (Szatmári et al. 2003) of the microbubbles (-7 μm) is smaller than the red blood cells diameter; this excludes the possibility of capillary embolization. In comparison to contrast agents used in computer tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, UCAs remain in the intravascular space and do not diffuse outside blood vessels. Not all UCAs (Nyman et al. 2005) allow the imaging of the third, delayed phase (parenchymal, Kuppfer). This probably depends (Stewart and Sidhu 2006, Kanemoto et al. 2008) on UCAs elimination by phagocytes, e.g. Sonazoid (99% is phagocytosed) and Levovist (47% is phagocytosed) image the parenchymal phase, but Sonovue does not.
3 Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) Table 2. Liver parameters in 3 phases by various researchers. Author Hepatic arterial phase Portal vein phase Hepatic Parenchymal phase (HA) (PV) (HP) Phase start Phase start Phase start (time post Duration (time post Duration (time post Duration injection) injection) injection) 7-0 s 0-5 s s 2 min 4-20 min UCAs s s s Sonovue s s (45-60s early PV phase) s Sonovue 4 0 s 30s (peak) 45 s (peak) 5 min Sonazoid 5 do 20 s 20 s 40 s 8 min 7 min Sonazoid ±.52 s 3.5±3.37 s (peak) 6.03±3.39 s 27.5±4.09 s (peak) Levovist. Haers H., Saunders J.H. (2009) 2. Nyman H.T., Kristensen A.T., Kjelgaard-Hansen M., McEvoy F.J. (2005) 3. Nyman H.T., Kristensen A.T., Flagstad A., McEvoy F.J. (2004) 4. Kanemoto H., Ohno K., Nakashima K., Takahashi M., Fujino Y., Tsujimoto H. (2008) 5. Kanemoto K. Ohno K., Nakashima K., Takahashi M., Fujino Y., Nishimura R., Tsujimoto H. (2009) 6. Kutara K., Asano K., Kiot A., Teshima K., Kato Y., Sasaki Y., Edamura K., Shibuya H., Sato T., Hasegawa A., Tanaka S. (2006) CEUS clinical applications Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (Haers and Saunders 2009) is mainly used to evaluate the liver and spleen. Other organs in case of which CEUS is useful are the kidneys, pancreas, lymph nodes and portal systemic shunts (PSS) diagnostics. CEUS liver evaluation consists of lesion detection (mainly focal, but also diffuse), lesion characteristics and monitoring after tumor resection. Liver examination the examination of focal lesions is the main CEUS indication in the canine and feline patient. The evaluation of focal lesions (Haers and Saunders 2009) by conventional ultrasonography is based on lesion morphology (echogenicity) and blood flow parameters (Doppler mode hyper/hypovascularization). This enables the diagnose of liver cysts (anechogenic) or calcifications (acoustic shadow), but not always liver soft tissue lesions. Hepatic nodules are common in dogs, focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) occurs in 70% of the canine population over the age of six, and in all dogs over 4 years of age. Other causes of hepatic nodules (O Brien et al. 2007, Haers and Saunders 2009) are haematomas, abscesses, focal hepatic necrosis, primary neoplasm (hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocellular carcinoma, sarcoma, carcinoid) and metastases (hemangiosarcoma, pancreatic cancer, neuroendocrine tumors). The assessment of liver lesions in CEUS is based on two necessary elements: lesion detection and lesion characteristics. After a lesion is detected (O Brien et al. 2007, Haers and Saunders 2009) a description (lesion characteristics) is useful in differentiating between neoplasm/non neoplasm lesions, benign/malignant neoplasm, and even between certain types of malignant tumors. The CEUS pattern of healthy dogs has been described. As a result of the double vascularization of the hepatic tissue by the hepatic artery (20% to 30% of blood) and the portal vein (70% to 80% of blood), the following phases have been described (Nyman et al. 2004, Kutara et al. 2006, Kanemoto et al. 2008, Kanemoto et al. 2009, Haers and Saunders 2009):. Hepatic arterial phase (HA) enhancement of the hepatic artery and its tributaries begins at 7 to 0 seconds post UCAs injection and has a duration time of 0 to 5 seconds. 2. Portal vein phase (PV) begins at 30 to 45 seconds post UCAs injection, duration time up to 2 minutes post injection. In cirrhotic patients (Szatmári et al. 2003) a delay is possible. 3. Hepatic parenchymal phase (HP) also known as the Kuppfer or delayed phase enhancement of the hepatic parenchymal sinusoids lasts until the UCAs are eliminated from the parenchyma, about 4 to 20 minutes, depending on contrast agent type. Lesion detection CEUS (Haers and Saunders 2009) is useful in detecting small and unclear malignant or isoechoegenic lesions, which are often invisible on a conventional USG image.
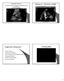
4 770 M. Wdowiak et al. Fig.. A conventional US liver image with 3 hypoechoic lesions. Two small (asterisk) lesions and one large (white arrows) targeted lesion. Fig. 2. Late phase CEUS image. The isoechogenic liver parenchyma indicates the benign nature of the hypoechoic lesions.
5 Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) The liver is frequently the first organ in which neoplasm s metastasize from primary tumors in the abdominal cavity by blood vessels (Nyman et al. 2005). The presence of a metastatic tumor with a diameter of.5 cm results in portal hypertension (blood vessel compression theory). To maintain a constant blood flow (Nyman et al. 2005) (energy) the metastasis supplements its shortage from the hepatic artery or by arteiovenous shunts. The CEUS image (Nyman et al. 2005) of metastatic tumors is various and is characterized by: a vascular ring, growing peripheral, necrotic center and various degree of calcification and density. The effectiveness of ultrasonic imaging of hepatic lesions (Nyman et al. 2005) with a diameter smaller than 2 cm (depending on the information source) is 53% to 84%. The sensitivity for nodular lesions below cm in diameter is 20%. The presumed threshold for detection is 0.5 cm. Lesion characteristics the change in enhancement throughout the phases gives a basis to focal hepatic lesion diagnosis. The arterial phase (Haers and Saunders 2009) provides information about the degree and pattern of vascularization, while the portal vein and parenchymal phases inform about UCAs elimination. Most benign lesions are characterized by a constant enhancement. This determines that the focal lesion is enhanced in a degree equal or higher than the hepatic parenchyma during the portal vein phase. Thus, benign lesions can be differentiated from most malignant lesions which are strongly enhanced in the early, hepatic artery phase, and poorly enhanced and hypoechogenic to the hepatic parenchyma in the portal vein and parenchymal phase (early washout phenomenon). This is due to the malignant tumors blood supply, the hepatic artery. Focal hepatic lesion characteristics in dogs have been described in three phases (Kanemoto et al. 2009):. Hepatic arterial phase degree of vascularization in comparison to the hepatic parenchyma (hyper-/iso-/hypovascular). 2. Portal vein phase lesion perfusion (hyper-/iso-/hypoperfusion). 3. Hepatic parenchymal phase echogenicity enhancement was classified as no lesion presence, unclear lesion or clear lesion visualization in the hepatic parenchyma. The study was conducted on 25 dogs, 6 had malignant lesions and 9 benign lesions; 6 dogs with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), 3 with cholangiocellular carcinoma (CCC), with leiomyosarcoma, with liposarcoma, with sarcoma of unknown origin, with lymphoma, with histiocytosis, with mast cell tumor, 6 with nodular hyperplasia HN and 3 with cirrhotic nodules. The lesion characteristics in each phase are: 5/6 dogs with HCC were hypervascular in the arterial phase, 4/6 hyperperfusion was observered in the portal vein phase and 4/6 had a dysmorphic image in the parenchymal phase. In the parenchymal phase, an uncomplete, irregular or partially enhanced lesion was detected which is a HCC mark. Dogs with CCC: the lesion was hipoechogenic during the artery and portal vein phase in comparison to the hepatic parenchyma. The vascular pattern in the arterial phase was peripheral, rim-like. A clear lesion was apparent in the parenchymal phase. The hemopoietic tumors (lymphoma, malignant histiocytosis and mast cell tumor) were almost identical. Hypovascularity and early washout was observed in the arterial and venous phase. A stippled vascular pattern was observed in the dog with lymphoma, and a peripheral (rim pattern) vascular pattern characterized the malignant histiocytosis and the mast cell tumor. Clear parenchymal lesion was observed. Dogs with leiomyosarcoma and sarcoma of unknown origin: hypovascularity in the artery phase, early washout in the portal vein phase and a clear lesion in the parenchymal phase. Liposarcoma is hypoechogenic to the hepatic parenchyma and has an unclear lesion image in the parenchymal phase. Dogs with benign lesions (6 nodular hyperplasia HN and 3 cirrhotic nodules): 8/9 no lesions visible in the parenchymal phase. Five out of six dogs with HN had a diffused and homogenic pattern, which was isoechogenic or hypoechogenic in the arterial phase. One dog had a decrease in vascularization and was aechogenic in the vessel phases and a clear lesion was imaged in the parenchymal phase. Three dogs with cirrhotic nodules had identical changes in all three enhancement phases with minimally hypoechogenic characteristics. O Brien (2007) on the basis of his studies stated that UCAs decrease the visibility of benign focal lesions, causing isoechogenicity in the ultrasonographic image during the enhancements peak. Also the enhancement patterns of malignant lesions were totally different from benign lesions patterns. Namely, during the peak of parenchymal enhancement all malignant focal lesions were hypoechogenic. This occurrence (O Brien et al. 2004) correlates with the malignancy with a very high sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive and accuracy (00%, 94.%, 93.8%, 00% and 96.9%, respectively).
6 772 M. Wdowiak et al. Table 3. Ultrasound appearance of liver lesions by O Brien et al. *(2004). Histological type Hypoechoic Hyperechoic Target** Mixed Complex Isoechoic Regenerative hyperplasia (n=3) Hepatoma (n=4) Metastatic neuroendocrine tumor (n=5) Hemangiosarcoma (n=3) Hepatocellular carcinoma Histiocytic sarcoma Lymphoma Metastatic spindle cell carcinoma Metastatic carcinoma Sclerosing adenocarcinoma Fibrosarcoma BENIGN 6 3 MALIGNANT TOTAL (n=32) * The sum of dogs in all categories may exceed the total number of dogs if nodules had more than one appearance in a dog. ** Target lesions hyperechoic center and hypoechoic outer rim (O Brien et al. 2004, Nyman et al. 2005). Quantitative CEUS examination via time-intensity curves Quantification of UCAs (Nyman et al. 2005) is necessary for mathematical evaluation of the degree of tissue perfusion and the detection of diffused lesions in tissue. UCAs are used as markers for the dynamic evaluation of organs such as the liver, brain and kidneys. The results presented as time-intensity curves for a ROI (region of interest) are calculated by built-in software installed in ultrasound systems. The following parameters (Ziegler et al. 2003, Nyman et al. 2005) are computed: upslope, downslope, baseline, peak, change and time to peak and additionally: area under curve (AUC), intensity peak (IP), and mean Transit Time (mtt). Arteriovenous UCAs transit times are digitally imaged as time-intensitycurveswhichallowucasuptakeandclearance measurement in a ROI. The shape of the time-intensity curve (Haers and Saunders 2009) is dependent upon the method of UCAs administration. A bolus injection causes a dual phase response, and a constant infusion is characterized by a progressive enhancement with a subsequent plateau that persists until the end of the infusion. Changes in vascuarization and blood flow secondary to pathological processes (Nyman et al. 2005, Haers and Saunders 2009) alternate the curves shape. Comparison of CEUS with other Diagnostic Techniques CEUS, compared to contrast-enhanced CT or MRI (Stewart and Sidhu 2006, Haers and Saunders 2009), allows the analysis of tumor perfusion in real-time without anesthesia. Additionally CEUS is more cost-effective, faster and does not involve ionizing radiation. Compared with cytological examinations (Haers and Saunders 2009), CEUS is noninvasive and relatively easy to perform with the capability of differentiating benign and malignant lesions. In conclusion, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography is an alternative and competitive method to other imaging and cytological techniques.
7 Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) Equipment CEUS requires (Haers and Saunders 2009) a sophisticated ultrasound system, equipped with Doppler modalities, low frequency transducers of to 3 MHz (such low frequencies are untypical for most US systems used in veterinary medicine), software capable of specific contrast-enhanced imaging and eventually software for quantitative evaluation. Ultrasound contrast agents necessary for the examination need to be reconstituted before usage. Route of administration is intravenous. The half-time of stability after reconstitution depends on the UCAs used (e.g. Definity 5 min, SonoVue h to 2h,Sonazoid2h).Toreducecosts,patientsshould be scheduled within the same period. Conclusion Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography increases the intensity of echo signals in the canine patient. The main indication for CEUS is focal liver lesion evaluation, especially differentiating between benign and malignant lesions, and malignant lesion diagnosis. Noninvasiveness, no anesthesia and the ability to evaluate in real-time are the main advantages of CEUS. The disadvantages are equipment requirements and cost of UCAs. Also the elimination of contrast agents via lungs may limit the use of CEUS in patients with pulmonary diseases. Adverse effects were observed in human medicine after UCAs administration (headaches, diarrhea, neutropenia, nausea, skin reactions, dyspnoe, rhinorrhagia). No adverse effects were observerd in animals. References Calliada F, Campani R, Bottinelli O, Bozzini A, Sommaruga MG (998) Ultrasound contrast agents: basic principles. Eur J Radiol 27: S57-S60. Haers H, Saunders JH (2009) Reviewofclinicalcharacteristics and applications of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 234: Kanemoto H, Ohno K, Nakashima K, Takahashi M, Fujino Y, Nishimura R, Tsujimoto H (2009) Characterization of canine focal liver lesions with contrast-enhanced ultrasound using a novel contrast agent sonazoid. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 50: Kanemoto K, Ohno K, Nakashima K, Takahashi M, Fujino Y, Tsujimoto H (2008) VascularandKupfferimagingof canine liver and spleen using the new contrast agent sonazoid. J Vet Med Sci 70: Kutara K, Asano K, Kiot A, Teshima K, Kato Y, Sasaki Y, Edamura K, Shibuya H, Sato T, Hasegawa A, Tanaka S(2006) Contrastharmonicimagingofcanine hepatic tumors. J Vet Med Sci 68: Nilsson A (200) Artifacts in sonography and Doppler. Eur Radiol : Nyman HT, Kristensen AT, Flagstad A, McEvoy FJ (2004) A review of the sonographic assessment of tumor metastases in liver and superficial lymph nodes. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 45: Nyman HT, Kristensen AT, Kjelgaard-Hansen M, McEvoy FJ (2005) Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in normal canine liver. Evaluation of imaging and safety parameters. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 46: O Brien RT (2007) Improved detection of metastatic hepatic hemangiosarcoma nodules with contrast ultrasound in three dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 48: O Brien RT, Holmes SP (2007) Recent advances in ultrasound technology. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract 22: O Brien RT, Iani M, Matheson J, Delaney F, Young K(2004) Contrast harmonic ultrasound of spontaneous liver nodules in 32 dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 45: Quaia E (2007) Contrast-specific ultrasound techniques. Radiol Med 2: Stewart VR, Sidhu PS (2006) New directions in ultrasound: microbubble contrast. Br J Radiol 79: SzatmáriV,HarkhnyiZ,Vörös K(2003) A review of nonconventional ultrasound techniques and contrast enhanced ultrasonography of noncardiac canine disorders. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 44: Ziegler LE, O Brien RT, Waller KR, Zagrzebski JA (2003) Quantitative contrast harmonic ultrasound imaging of normal canine liver. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 44:
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS)
 Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) Odd Helge Gilja, MD, PhD Professor Department of Medicine Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway The Micro-Bubble Contrast Agents - World View IEEE Transactions
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) Odd Helge Gilja, MD, PhD Professor Department of Medicine Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway The Micro-Bubble Contrast Agents - World View IEEE Transactions
The most relevant new technlogies ULTRASOUND
 The most relevant new technlogies ULTRASOUND 1. Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound Basics Clinical Applications 2. Elastography Mechanical Elastography Transient Dynamic E. 3. Ultrasound Simulation Teaching
The most relevant new technlogies ULTRASOUND 1. Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound Basics Clinical Applications 2. Elastography Mechanical Elastography Transient Dynamic E. 3. Ultrasound Simulation Teaching
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging
 M edical R eview Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging M edical R eview Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging Dr.
M edical R eview Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging M edical R eview Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging Dr.
Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology
 1: US of adrenal glands, KLA Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology Ultrasound has quickly become an important
1: US of adrenal glands, KLA Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology Ultrasound has quickly become an important
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
High-quality/High-resolution Digital Ultrasound Diagnostic Scanner
 Hitachi Review Vol. 52 (2003), No. 4 207 High-quality/High-resolution Digital Ultrasound Diagnostic Scanner Tsuyoshi Otake Toshihiko Kawano Takashi Sugiyama Tsuyoshi Mitake Shinichiro Umemura, Ph. D. OVERVIEW:
Hitachi Review Vol. 52 (2003), No. 4 207 High-quality/High-resolution Digital Ultrasound Diagnostic Scanner Tsuyoshi Otake Toshihiko Kawano Takashi Sugiyama Tsuyoshi Mitake Shinichiro Umemura, Ph. D. OVERVIEW:
Doppler. Doppler. Doppler shift. Doppler Frequency. Doppler shift. Doppler shift. Chapter 19
 Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF ULTRASOUND ECHO FOR SKIN LESIONS CLASSIFICATION HANNA PIOTRZKOWSKA, JERZY LITNIEWSKI, ELŻBIETA SZYMAŃSKA *, ANDRZEJ NOWICKI
 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF ULTRASOUND ECHO FOR SKIN LESIONS CLASSIFICATION HANNA PIOTRZKOWSKA, JERZY LITNIEWSKI, ELŻBIETA SZYMAŃSKA *, ANDRZEJ NOWICKI Institute of Fundamental Technological Research, Department
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF ULTRASOUND ECHO FOR SKIN LESIONS CLASSIFICATION HANNA PIOTRZKOWSKA, JERZY LITNIEWSKI, ELŻBIETA SZYMAŃSKA *, ANDRZEJ NOWICKI Institute of Fundamental Technological Research, Department
Treatment of Hepatic Neoplasm
 I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for treatment of hepatic neoplasm outside of systemic chemotherapy alone when determined to be medically necessary and within the medical criteria
I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for treatment of hepatic neoplasm outside of systemic chemotherapy alone when determined to be medically necessary and within the medical criteria
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Breast Ultrasound: Benign vs. Malignant Lesions
 October 25-November 19, 2004 Breast Ultrasound: Benign vs. Malignant Lesions Jill Steinkeler,, Tufts University School of Medicine IV Breast Anatomy Case Presentation-Patient 1 62 year old woman with a
October 25-November 19, 2004 Breast Ultrasound: Benign vs. Malignant Lesions Jill Steinkeler,, Tufts University School of Medicine IV Breast Anatomy Case Presentation-Patient 1 62 year old woman with a
TISSUE MIMICKING GEL QUALITY LE PHANTOM SERIES DESIGN. performance the ultrasound labs ofand. icking material has the same attenuation mim-
 QUALITY Tissue Benefits Mimicking of s RMI recognized RMI as the ultrasound standard phantoms for quality are performance the ultrasound labs ofand hospitals, manufacturers. clinics Sophisticated and ultrasound
QUALITY Tissue Benefits Mimicking of s RMI recognized RMI as the ultrasound standard phantoms for quality are performance the ultrasound labs ofand hospitals, manufacturers. clinics Sophisticated and ultrasound
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis
 February 2012 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis Reid Merryman, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) introduction Index patient: clinical presentation
February 2012 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis Reid Merryman, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) introduction Index patient: clinical presentation
BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND
 BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND Goals: To become familiar with: Ultrasound wave Wave propagation and Scattering Mechanisms of Tissue Damage Biomedical Ultrasound Transducers Biomedical Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasonic
BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND Goals: To become familiar with: Ultrasound wave Wave propagation and Scattering Mechanisms of Tissue Damage Biomedical Ultrasound Transducers Biomedical Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasonic
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015
 Benign liver diseases Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015 1 Agenda Benign focal liver lesions Fatty liver disease
Benign liver diseases Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015 1 Agenda Benign focal liver lesions Fatty liver disease
Ny teknologi: Fagdagene ved St. Olavs Hospital Lasse Løvstakken Dept. Circulation and Medical Imaging 11.06.2010
 1 Ny teknologi: Ultralyd måler m blodstrøm Fagdagene ved St. Olavs Hospital Lasse Løvstakken Dept. Circulation and Medical Imaging 11.06.2010 2 Conventional imaging methods of blood flow using ultrasound
1 Ny teknologi: Ultralyd måler m blodstrøm Fagdagene ved St. Olavs Hospital Lasse Løvstakken Dept. Circulation and Medical Imaging 11.06.2010 2 Conventional imaging methods of blood flow using ultrasound
Spleen. Anatomy. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Normal. Related Anatomy Anterior to spleen. Medial border. Posteriorly
 Spleen (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy Normal Intraperitoneal, except hilum Left hypochondrium Left hemidiaphragm superior generally considered to be ovoid, with a convex superior and a concave
Spleen (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy Normal Intraperitoneal, except hilum Left hypochondrium Left hemidiaphragm superior generally considered to be ovoid, with a convex superior and a concave
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Sonographic Findings in Skeletal Muscle Metastasis From Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Case Report Sonographic Findings in Skeletal Muscle Metastasis From Renal Cell Carcinoma Chun-Ku Chen, MD, Hong-Jen Chiou, MD, Yi-Hong Chou, MD, Chui-Mei Tiu, MD, Hung-Ta Hondar Wu, MD, Shiuh Ma, MD, Winby
Case Report Sonographic Findings in Skeletal Muscle Metastasis From Renal Cell Carcinoma Chun-Ku Chen, MD, Hong-Jen Chiou, MD, Yi-Hong Chou, MD, Chui-Mei Tiu, MD, Hung-Ta Hondar Wu, MD, Shiuh Ma, MD, Winby
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
Principles of Medical Ultrasound. Pai-Chi Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University
 Principles of Medical Ultrasound Pai-Chi Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University What is Medical Ultrasound? Prevention: actions taken to avoid diseases. Diagnosis: the process
Principles of Medical Ultrasound Pai-Chi Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University What is Medical Ultrasound? Prevention: actions taken to avoid diseases. Diagnosis: the process
Liver tumors: diagnosis and treatment
 Liver tumors: diagnosis and treatment Introduction Primary liver neoplasms are infrequent in the dog and cat, with an estimated prevalence in necropsy studies of 0.6-2.6% in canines and 1.5-2.3% in felines.
Liver tumors: diagnosis and treatment Introduction Primary liver neoplasms are infrequent in the dog and cat, with an estimated prevalence in necropsy studies of 0.6-2.6% in canines and 1.5-2.3% in felines.
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Department of Medical Imaging, Toronto General Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
 Local ablation therapy with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for hepatocellular carcinoma: a practical review Tae Kyoung Kim, Korosh Khalili, Hyun-Jung Jang epartment of Medical Imaging, Toronto General
Local ablation therapy with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for hepatocellular carcinoma: a practical review Tae Kyoung Kim, Korosh Khalili, Hyun-Jung Jang epartment of Medical Imaging, Toronto General
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF HYPOECHOIC AND ANECHOIC MASSES WITH GRAY SCALE SONOGRAPHY: NEW OBSERVATIONS
 J Cliri Ultrasound 7:249-254. August 1979 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF HYPOECHOIC AND ANECHOIC MASSES WITH GRAY SCALE SONOGRAPHY: NEW OBSERVATIONS Robert L. Bree, M.D., and Terry M. Silver, M.D. With the
J Cliri Ultrasound 7:249-254. August 1979 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF HYPOECHOIC AND ANECHOIC MASSES WITH GRAY SCALE SONOGRAPHY: NEW OBSERVATIONS Robert L. Bree, M.D., and Terry M. Silver, M.D. With the
Hunting Bats. Diagnostic Ultrasound. Ultrasound Real-time modality
 Diagnostik Ultrasound Basic physics, image reconstruction and signal processing Per Åke Olofsson Dpt of Biomedical Engineering, Malmö University Hospital, Sweden Ultrasound Real-time modality 17-WEEK FETAL
Diagnostik Ultrasound Basic physics, image reconstruction and signal processing Per Åke Olofsson Dpt of Biomedical Engineering, Malmö University Hospital, Sweden Ultrasound Real-time modality 17-WEEK FETAL
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations. Chapter. Grade. CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
CHAPTER 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Preparation iagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview"
 Diagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview The Field - Preparation - Specialty Areas - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Diagnostic imaging
Diagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview The Field - Preparation - Specialty Areas - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Diagnostic imaging
190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein
 Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Benign Liver Tumors. Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013
 Benign Liver Tumors Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013 Outline Benign Liver Tumors are, in general. Asymptomatic Diagnosed: imaging Treatment: Do no harm Unless Malignant potential Causing symptoms Differential
Benign Liver Tumors Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013 Outline Benign Liver Tumors are, in general. Asymptomatic Diagnosed: imaging Treatment: Do no harm Unless Malignant potential Causing symptoms Differential
LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET
 LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET NEOPLASM OF LIVER PRIMARY 1)BENIGN 2)MALIGNANT METASTATIC/SECONDARY LIVER Primary Liver Cancer the Second Killer among tumors high morbidity and mortality(20.40/100,000) etiology
LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET NEOPLASM OF LIVER PRIMARY 1)BENIGN 2)MALIGNANT METASTATIC/SECONDARY LIVER Primary Liver Cancer the Second Killer among tumors high morbidity and mortality(20.40/100,000) etiology
Parametric mapping of contrasted ovarian transvaginal sonography.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Radiology Faculty Papers Department of Radiology 6-6-2015 Parametric mapping of contrasted ovarian transvaginal sonography. Katrina Korhonen
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Radiology Faculty Papers Department of Radiology 6-6-2015 Parametric mapping of contrasted ovarian transvaginal sonography. Katrina Korhonen
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 Abhishek Vadalia Introduction Chemoembolization is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of solid hepatic tumors such as Hepatocellular Carinoma (HCC) & rare Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
Abhishek Vadalia Introduction Chemoembolization is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of solid hepatic tumors such as Hepatocellular Carinoma (HCC) & rare Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
SAMSUNG ULTRASOUND RS80A
 Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
Imaging of Acute Stroke. Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group
 Imaging of Acute Stroke Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group Modalities Non Contrast CT (NCCT) Contrast CT Angiography MRI MR Angiography Perfusion
Imaging of Acute Stroke Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group Modalities Non Contrast CT (NCCT) Contrast CT Angiography MRI MR Angiography Perfusion
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Basics of Ultrasound Imaging
 2 Basics of Ultrasound Imaging Vincent Chan and Anahi Perlas Introduction... Basic Principles of B-Mode US... Generation of Ultrasound Pulses... Ultrasound Wavelength and Frequency... Ultrasound Tissue
2 Basics of Ultrasound Imaging Vincent Chan and Anahi Perlas Introduction... Basic Principles of B-Mode US... Generation of Ultrasound Pulses... Ultrasound Wavelength and Frequency... Ultrasound Tissue
Health Care Careers in the Field of Imaging. Shari Workman, MSM,PHR,CIR MultiCare Health System Senior Recruiter/Employment Specialist
 Health Care Careers in the Field of Imaging Shari Workman, MSM,PHR,CIR MultiCare Health System Senior Recruiter/Employment Specialist What is Health Care Imaging? Technologists working with patients, using
Health Care Careers in the Field of Imaging Shari Workman, MSM,PHR,CIR MultiCare Health System Senior Recruiter/Employment Specialist What is Health Care Imaging? Technologists working with patients, using
LOGIQ E9. Ultrasound agility has arrived.
 LOGIQ E9 Ultrasound agility has arrived. We started with a blank sheet of paper. Nothing compromised the imaginative thinking that went into designing the new LOGIQ E9 premium ultrasound system. The sheet
LOGIQ E9 Ultrasound agility has arrived. We started with a blank sheet of paper. Nothing compromised the imaginative thinking that went into designing the new LOGIQ E9 premium ultrasound system. The sheet
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
FXA 2008. UNIT G485 Module 4 5.4.3 Ultrasound. Candidates should be able to :
 1 Candidates should be able to : ULTRASOUND Describe the properties of ultrasound. ULTRASOUND is any sound wave having a frequency greater than the upper frequency limit of human hearing (20 khz). Describe
1 Candidates should be able to : ULTRASOUND Describe the properties of ultrasound. ULTRASOUND is any sound wave having a frequency greater than the upper frequency limit of human hearing (20 khz). Describe
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA GI Site Group Hepatocellular Carcinoma Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA GI Site Group Hepatocellular Carcinoma Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION
The Lewin Group undertook the following steps to identify the guidelines relevant to the 11 targeted procedures:
 Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
The Comprehensive Cancer Care Team at Penn Vet s Ryan Hospital CORE TEAM
 The Comprehensive Cancer Care Team at Penn Vet s Ryan Hospital Ryan Hospital s Comprehensive Cancer Care Program is led by a world- class team of board- certified veterinarians who each offer a unique
The Comprehensive Cancer Care Team at Penn Vet s Ryan Hospital Ryan Hospital s Comprehensive Cancer Care Program is led by a world- class team of board- certified veterinarians who each offer a unique
False positive PET in lymphoma
 False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography
 Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microwave_tumor_ablation 12/2011 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Microwave ablation
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microwave_tumor_ablation 12/2011 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Microwave ablation
YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
Diagnostic Sensitivity of Ultrasound-Guided Needle Biopsy in Soft Tissue Masses About Superficial Bone Lesions
 Diagnostic Sensitivity of Ultrasound-Guided Needle Biopsy in Soft Tissue Masses About Superficial Bone Lesions Kee-Min Yeow, MD, Chih-Feng Tan, MD, Jen-Shi Chen, MD, Cheun Hsueh, MD We evaluated the value
Diagnostic Sensitivity of Ultrasound-Guided Needle Biopsy in Soft Tissue Masses About Superficial Bone Lesions Kee-Min Yeow, MD, Chih-Feng Tan, MD, Jen-Shi Chen, MD, Cheun Hsueh, MD We evaluated the value
NEOPLASMS C00 D49. Presented by Jan Halloran CCS
 NEOPLASMS C00 D49 Presented by Jan Halloran CCS 1 INTRODUCTION A neoplasm is a new or abnormal growth. In the ICD-10-CM classification system, neoplastic disease is classified in categories C00 through
NEOPLASMS C00 D49 Presented by Jan Halloran CCS 1 INTRODUCTION A neoplasm is a new or abnormal growth. In the ICD-10-CM classification system, neoplastic disease is classified in categories C00 through
Oncology. Topic-Bile Duct Carcinoma. Topic-Adenocarcinoma, Lung. Topic-Hemangiosarcoma, Spleen and Liver
 Topic-Adenocarcinoma, Lung Figure 1. Pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Figure 2. Pulmonary bronchiolar carcinoma. Figure 3. Pulmonary fibrosarcoma. Topic-Adenocarcinoma, Skin (Sweat Gland, Sebaceous) Figure 1.
Topic-Adenocarcinoma, Lung Figure 1. Pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Figure 2. Pulmonary bronchiolar carcinoma. Figure 3. Pulmonary fibrosarcoma. Topic-Adenocarcinoma, Skin (Sweat Gland, Sebaceous) Figure 1.
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Yttrium-90 Radioembolization
 Yttrium-90 Radioembolization Yttrium-90 radioembolization is generally used as a palliative therapy for selected patients with unresectable tumors of the liver including: Metastatic tumors from colorectal
Yttrium-90 Radioembolization Yttrium-90 radioembolization is generally used as a palliative therapy for selected patients with unresectable tumors of the liver including: Metastatic tumors from colorectal
Soft Tissue Diffuse Neurofibromas
 ase Series Soft Tissue Diffuse Neurofibromas Sonographic Findings Wen hen, MD, Jian-Wen Jia, MD, Jin-Rui Wang, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to describe the sonographic findings of soft tissue
ase Series Soft Tissue Diffuse Neurofibromas Sonographic Findings Wen hen, MD, Jian-Wen Jia, MD, Jin-Rui Wang, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to describe the sonographic findings of soft tissue
MRI of Benign Liver Lesions and Metastatic Disease Characterization with. Gadoxetate Disodium
 MRI of Benign Liver Lesions and Metastatic Disease Characterization with Gadoxetate Disodium Rocky C. Saenz, D.O. Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Botsford Hospital, Farmington Hills, MI Introduction
MRI of Benign Liver Lesions and Metastatic Disease Characterization with Gadoxetate Disodium Rocky C. Saenz, D.O. Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Botsford Hospital, Farmington Hills, MI Introduction
Leading the New Standards
 Samsung Merdison is a global leading medical devices company. Founded in 1985, the company now sells cutting-edge medical devices including diagnostic ultrasound, digital X-ray and blood analyzer, in 110
Samsung Merdison is a global leading medical devices company. Founded in 1985, the company now sells cutting-edge medical devices including diagnostic ultrasound, digital X-ray and blood analyzer, in 110
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery. Torbjørn Dahl
 Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension
 Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
To Whipple or Not to Whipple, that is the Question: Evaluating the Resectability of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
 August 2009 To Whipple or Not to Whipple, that is the Question: Evaluating the Resectability of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Christina Ramirez, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Agenda
August 2009 To Whipple or Not to Whipple, that is the Question: Evaluating the Resectability of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Christina Ramirez, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Agenda
Lecture 14. Point Spread Function (PSF)
 Lecture 14 Point Spread Function (PSF), Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR), Contrast-to-noise Ratio (CNR), and Receiver Operating Curves (ROC) Point Spread Function (PSF) Recollect
Lecture 14 Point Spread Function (PSF), Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR), Contrast-to-noise Ratio (CNR), and Receiver Operating Curves (ROC) Point Spread Function (PSF) Recollect
12th & 13th May 2016 Weston Education Centre, Kings College Hospital London
 EUROSON SCHOOL CEUS Course How to Incorporate CEUS into your Imaging Practice 12th & 13th Weston Education Centre, Kings College Hospital London Course fees: Standard fee - 400 Trainees & Sonographers
EUROSON SCHOOL CEUS Course How to Incorporate CEUS into your Imaging Practice 12th & 13th Weston Education Centre, Kings College Hospital London Course fees: Standard fee - 400 Trainees & Sonographers
Company profile. Quote from the analyst of. Company Milestone. Feel the Difference. Tel: +86-755-26722860 Fax: +86-755-26722850
 Company profile Since the establishment, SonoScape has committed to provide high standard medical equipments for healthcare of human beings. SonoScape specializes in the development and production of diagnostic
Company profile Since the establishment, SonoScape has committed to provide high standard medical equipments for healthcare of human beings. SonoScape specializes in the development and production of diagnostic
VFI Technology to Change the Way You Work
 Technology to Change the Way You Work Vascular Ultrasound Made Easier Vector Flow Imaging VFI VFI is a ground-breaking technology that can revolutionize the workflow for many Doppler ultrasound applications.
Technology to Change the Way You Work Vascular Ultrasound Made Easier Vector Flow Imaging VFI VFI is a ground-breaking technology that can revolutionize the workflow for many Doppler ultrasound applications.
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
A pulse is a collection of cycles that travel together. the cycles ( on or transmit time), and. the dead time ( off or receive time)
 chapter 2 Pulsed Ultrasound In diagnostic ultrasound imaging, short bursts, or pulses, of acoustic energy are used to create anatomic images. Continuous wave sound cannot create anatomic images. Analogy
chapter 2 Pulsed Ultrasound In diagnostic ultrasound imaging, short bursts, or pulses, of acoustic energy are used to create anatomic images. Continuous wave sound cannot create anatomic images. Analogy
How To Use An Ultrasound For Medical Research
 Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
2/28/2011. MIPPA overview and CMS requirements. CT accreditation. Today s agenda. About MIPPA. Computed Tomography
 Today s agenda Computed Tomography Presented by: Dina Hernandez, BSRT, RT (R), CT, QM Krista Bush, RT, MBA Leonard Lucey, JD ACR Quality & Safety MIPPA overview and CMS requirements CT accreditation How
Today s agenda Computed Tomography Presented by: Dina Hernandez, BSRT, RT (R), CT, QM Krista Bush, RT, MBA Leonard Lucey, JD ACR Quality & Safety MIPPA overview and CMS requirements CT accreditation How
Update on Mesothelioma
 November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA
 KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Renal Cysts What should I do now?
 Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Moving Beyond RECIST
 Moving Beyond RECIST Ihab R. Kamel, M.D., Ph.D. ikamel@jhmi.edu Associate Professor Clinical Director, MRI Department of Radiology The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Outline Standard measures
Moving Beyond RECIST Ihab R. Kamel, M.D., Ph.D. ikamel@jhmi.edu Associate Professor Clinical Director, MRI Department of Radiology The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Outline Standard measures
Non-coronary Brachytherapy
 Non-coronary Brachytherapy I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for non-coronary brachytherapy when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Non-coronary Brachytherapy I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for non-coronary brachytherapy when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
Common and Uncommon Sonographic Features of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
 Case Series Common and Uncommon Sonographic Features of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Bryan K. Chan, MD, Terry S. Desser, MD, I. Ross McDougall, MD, Ronald J. Weigel, MD, R. Brooke Jeffrey, Jr, MD Objective.
Case Series Common and Uncommon Sonographic Features of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Bryan K. Chan, MD, Terry S. Desser, MD, I. Ross McDougall, MD, Ronald J. Weigel, MD, R. Brooke Jeffrey, Jr, MD Objective.
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer
 Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer Poster No.: C-0201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) Authors: M. A. Portilha, C. Ruivo, I. Santiago, M.
Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer Poster No.: C-0201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) Authors: M. A. Portilha, C. Ruivo, I. Santiago, M.
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Student Investigator: Thomas R. Pace UVM COM Class of 2012 Faculty Mentor: Christopher Filippi Department of Radiology Fletcher
Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Student Investigator: Thomas R. Pace UVM COM Class of 2012 Faculty Mentor: Christopher Filippi Department of Radiology Fletcher
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Ultrasonic Echosignal Applied to Human Skin Lesions Characterization
 ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS Vol.37,No.1, pp.103 108(2012) Copyright c 2012byPAN IPPT DOI: 10.2478/v10168-012-0014-7 Ultrasonic Echosignal Applied to Human Skin Lesions Characterization HannaPIOTRZKOWSKA (1),JerzyLITNIEWSKI
ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS Vol.37,No.1, pp.103 108(2012) Copyright c 2012byPAN IPPT DOI: 10.2478/v10168-012-0014-7 Ultrasonic Echosignal Applied to Human Skin Lesions Characterization HannaPIOTRZKOWSKA (1),JerzyLITNIEWSKI
General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000. Objectives. What is Staging? 5/8/2014
 General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000 Linda Mulvihill Public Health Advisor NCRA Annual Meeting May 2014 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention
General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000 Linda Mulvihill Public Health Advisor NCRA Annual Meeting May 2014 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA
 Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Various Technics of Liquids and Solids Level Measurements. (Part 3)
 (Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
(Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
