Chapter 1: Introduction to EMS Systems--Quiz. Circle the letter of the best answer to each multiple-choice question.
|
|
|
- Henry Nicholson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Handout 1-1 Student s Name Chapter 1: Introduction to EMS Systems--Quiz Circle the letter of the best answer to each multiple-choice question. 1. As an Emergency Medical Responder, which of the following should you set as your top priority at the scene of an emergency? a. CPR b. Safety c. Patient care d. Traffic control 2. An Emergency Medical Responder possesses all of the following skills EXCEPT: a. defibrillation. b. oxygen administration. c. medication administration. d. bleeding control. 3. Emergency Medical Responder care is usually authorized by: a. the National Registry. b. state laws. c. the patient s physician. d. department bylaws. 4. The is involved in quality improvement and protocol development. a. Medical Director b. chief of the emergency department c. EMT d. agency administrator 5. The highest level of EMS provider is: a. Advanced Emergency Medical Technician. b. Emergency Medical Technician. c. Emergency Transport Technician.
2 d. Paramedic. 6. A 47-year-old patient has been injured in a serious motor vehicle crash. Which is the most appropriate specialty hospital for this patient? a. Pediatric center b. Trauma center c. Cardiovascular care center d. Stroke center 7. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA of the United States Department of Transportation), how many classic components make up an EMS system? a. 5 b. 15 c. 10 d One of the important components of the medical legal standards in patient care is: a. confidentiality. b. community relations. c. communications. d. advocacy. 9. The place where 911 calls are answered is called a: a. dispatch headquarters. b. communication coordination center. c. public safety answering point. d. radio call center. 10. Demeanor is part of professionalism for the Emergency Medical Responder, and it has which of the following as an attribute? a. Advanced education b. A take-charge attitude c. Fearlessness d. Respect
3
4 Handout 1-2 Student s Name The Call: First on Scene Read the scenario. Then, in the space provided, answer the questions that follow. You and your partner are assigned to EMS Unit 5 one morning in September. At 10:35 A.M., the emergency dispatcher directs you to a collision on Pumpkin Hollow Road. Someone called to report that the car ahead of her had swerved to avoid a dog, gone off the road, plunged into a ditch, and hit a tree. Dispatch reports that an ambulance is en route and will arrive on scene in about 15 minutes. Your unit pulls up to the scene six minutes later. After determining that the scene is safe to enter, you approach the crash site. As you don your personal protective equipment, you focus on the young man sitting on the ground beside the crashed car. His shirt and pants are soaked with blood. He is apparently alert and is holding his wrist tightly with his other hand. The patient tells you that after the crash, he had not believed himself injured and so attempted to get out of the car. In doing so, he sliced his wrist on jagged metal. He tells you that he had been wearing a seat belt. Your partner applies direct pressure to the wound. Meanwhile, you introduce yourself to the patient and begin your assessment of his condition. The patient seems anxious and restless. As you continue to assess him, you explain what you are doing and try to calm him. Because of the possible mechanisms of injury involved in the crash, you are especially alert to the possibility of spine and other internal injuries. You administer highflow oxygen to the patient and join your partner in manually stabilizing the patient to avoid any further injury. Seven minutes later, the Paramedics arrive. You provide them with a concise report of the patient s condition and your interventions. The Paramedics assume care of the patient, contact medical direction, and report on their findings and expected time of arrival at the hospital. Just a few minutes after 11:00 A.M., the ambulance reaches the hospital. The Paramedics brief the emergency department staff on the patient s status and the care that he has received. The hospital crew takes over and wheels the young man off to surgery. 1. What EMS resources are involved in this scenario? 2. What roles/responsibilities and examples of professionalism for an Emergency Medical Responder are demonstrated in this scenario?
5
6 Handout 1-3 Student s Name Chapter 1 Review In the space provided, write the word or words that best complete each sentence. 1. In general, the system is a network of resources, from 911 to the emergency department, that provides emergency medical care to victims of sudden illness or injury. 2. A typical example of an emergency call begins with a member of the public calling or another emergency number. 3. An important member of the EMS team, the Emergency Medical, receives the emergency call at a public safety answering point. 4. An emergency communication system that automatically records a caller s phone number and location is known as a(n) 911 system. 5. There are four levels of training. They are,,, and. 6. A(n) is the first person with emergency medical training on the scene. 7. At the next level of EMS training after Emergency Medical Responder, the can also perform complex immobilization procedures, restrain patients, and staff and drive ambulances. 8. is a dynamic system for continually evaluating and improving care. 9. involves a physician Medical Director in quality improvement and developing protocols. 10. The of is a national model that defines the scope of care for all levels of EMS training.
7 Handout 1-4 Student s Name True or False Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false by writing T or F in the space provided. 1. As an Emergency Medical Responder, you provide emergency care that comforts a patient at the height of crisis. 2. Emergency Medical Responders may be called to emergencies in which they are the only trained rescuers on scene. 3. As an Emergency Medical Responder, you must consider your own safety only after you have provided emergency care to your patients. 4. Being well-dressed and groomed is not important to the professional responsibilities of an Emergency Medical Responder. 5. When a patient needs transport to a hospital, you may leave the scene after you verify that an ambulance will arrive within five minutes. 6. Once an Emergency Medical Responder has provided care, he must continue to do so until it is turned over to another qualified provider. 7. Professionalism means, in the most important sense, that the Emergency Medical Responder is perceived as a caring and competent member of the EMS system. 8. One of the factors in professionalism is patient advocacy. 9. A trained Emergency Medical Responder will always perform without making errors. 10. A trauma center is a medical facility specializing in the treatment of pediatric care.
8 Answer Key Handout 1-1: Chapter 1 Quiz 1. b 2. c 3. b 4. a 5. d 6. b 7. d 8. a 9. c 10. d Handout 1-2: The Call: First on Scene 1. a 911 dispatcher, Emergency Medical Responders, Paramedics, a medical director, and a hospital emergency department 2. Possible answers include the following: personal safety, patient assessment and administering of care, maintaining a caring and compassionate attitude, continuity of care, emotional support, and communications. Handout 1-3: Chapter 1 Review 1. emergency medical services dispatcher 4. enhanced 5. Emergency Medical Responder, Emergency Medical Technician, Advanced EMT, Paramedic 6. Emergency Medical Responder 7. Emergency Medical Technician 8. Quality improvement 9. Medical oversight 10. Scope of Practice Model Handout 1-4: True or False 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. F 5. F 6. T 7. T 8. T 9. F 10. F
9
10 Handout 2-1 Student s Name Chapter 2: Legal and Ethical Principles of Emergency Care--Quiz Circle the letter of the best answer to each multiple-choice question. 1. Patients of legal age who are competent and who accept your care are giving consent. a. implied b. expressed c. guardian d. minor s 2. In an emergency in which a patient is so severely injured that a clear decision cannot be made, you have the right to provide care based on consent. a. implied b. expressed c. guardian d. minor s 3. The law that protects the confidentiality of protected health information is commonly called: a. HIPAA. b. SEPA. c. INPRO. d. H-ACT. 4. If a competent adult refuses your care but you then provide it against his will, you could be charged with: a. inadvertence. b. abandonment. c. negligence. d. battery. 5. A(n) is a form, requested by a patient and signed by a physician, refusing CPR if the heart stops.
11 a. health care proxy b. power of attorney c. do not resuscitate order d. ethics statement for the living 6. A(n) is a legal document that outlines instructions regarding a patient s medical decisions. a. breach of duty b. power of attorney c. advance directive d. release of confidence 7. Failure to perform a required assessment or treatment or the incorrect performance of an action is a(n): a. proximate causation. b. breach of duty. c. abandonment. d. disregard of proper action. 8. An Emergency Medical Responder s legal obligation to provide emergency care is referred to as a(n): a. duty to act. b. scope of care. c. implied consent. d. standard of care. 9. A 16-year-old who is financially independent and living away from home as an adult by permission of the courts is called a(n) minor. a. guardian b. released c. emancipated d. jurisdictional 10. Written guidelines or instructions describing assessment and care are known as: a. hospital care directives.
12 b. online medical controls. c. prescription services. d. protocols.
13 Handout 2-2 Student s Name The Call: A Crime Scene Read the scenario. Then, in the space provided, answer the questions that follow. All the ambulances from your station are presently tied up on calls, so you are dispatched to handle a possible shooting. When you arrive at the scene, a police officer assures you that the scene is safe and secured. You take standard precautions, grab your jump kit, and step out of your vehicle. Just then a woman runs from the house, screaming for you to help her husband. When you enter the house, you immediately see a police officer and overturned chairs, broken lamps, and a trail of blood leading into the next room. Following the officer s directions, you find a man, appearing to be in his mid-50 s, lying on the floor and bleeding. His wife is behind you, yelling that someone broke into the house and shot him. 1. What instructions should you give to the rest of your crew before they enter the scene? 2. What are some ways in which you can assist the police, even while performing patient care?
14 Handout 2-3 Student s Name Chapter 2 Review Select the term from the list that best completes each sentence. Then write it in the space provided. Use proper capitalization if necessary. (HINT: Each term on the list is used only once.) [COMP: Set this bulleted list in multiple columns.] abandonment competent consent directive emancipated ethical expressed implied protocols scope 1. The of practice defines the actions that are legally allowed for an Emergency Medical Responder. 2. A(n) adult is one who has the mental capacity to make an informed decision about medical care. 3. By law, a patient must first, or give permission, before an Emergency Medical Responder may provide care. 4. consent may consist of verbal consent, a nod, or an affirming gesture from a competent adult. 5. consent may be applied when an unresponsive patient is at risk of death, disability, or deterioration of condition. 6. are written guidelines or instructions that describe appropriate assessment and care in specific situations. 7. A(n) minor is one who is married, pregnant, a parent, or in the armed forces, or who has the rights of an adult with permission of the courts. 8. An advance, such as a DNR order, is written prior to an emergency and must be signed by both the patient and a physician.
15 9. Honesty, compassion, and advocacy are important approaches to EMS. 10. Leaving a sick or injured patient before equal or more highly trained personnel assume responsibility for patient care is called.
16 Handout 2-4 Student s Name True or False Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false by writing T or F in the space provided. 1. Scope of practice is a set of regulations and laws that designate how an Emergency Medical Responder legally functions. 2. Protocols are verbal instructions given over the radio that are universal to all emergency medical situations. 3. A 10-year-old who has been hit on his bicycle can be treated by Emergency Medical Responders if he is alert enough to give expressed consent. 4. Patients with an altered mental status should not be allowed to refuse care. 5. The Health Information Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) identifies protected health information that cannot be disclosed to others except in certain situations. 6. An advanced directive is a legal document that can appoint a person to make medical decisions for a patient who is unable to do so. 7. Abandonment allows an Emergency Medical Responder to leave a patient before an ambulance arrives for transport as long as the patient is not seriously sick or injured. 8. Breach of duty is a failure to perform a required assessment or treatment or the incorrect performance of an action. 9. When you enter a crime scene to provide patient care, you do not need to be concerned about destroying evidence because patient care is all that matters. 10. If an Emergency Medical Responder is a mandatory reporter for a suspected crime, he/she still can t disclose patient information unless he/she is ordered to do so by a judge s order.
17
18 Answer Key Handout 2-1: Chapter 2 Quiz 1. b 2. a 3. a 4. d 5. c 6. c 7. b 8. a 9. c 10. d Handout 2-2: The Call: A Crime Scene 1. Quickly remind your crew members to touch only those things that must be touched in order to properly care for the patient. Nothing else should be moved or touched if at all possible, and the things that are touched or moved should be reported to the responding police officers. 2. Types of assistance may include the following: Observe and document anything unusual at the scene. Touch only what you need to touch. Move only to provide Emergency Medical Responder care and only what you need to move to protect yourself, other rescuers, and the patient. Do not use the telephone until the police give you permission to do so. Move the patient only if he is in danger or must be moved for you to provide care. If possible, do not cut through holes in the patient s clothing. Communicate your actions and observations of the scene to law enforcement. Handout 2-3: Chapter 2 Review 1. scope 2. competent 3. consent 4. Expressed 5. Implied 6. Protocols 7. emancipated 8. directive 9. ethical 10. abandonment Handout 2-4: True or False 1. T 2. F 3. F 4. T
19 5. T 6. T 7. F 8. T 9. F 10. F
20 Handout 3-1 Student s Name Chapter 3: Wellness and Safety of the EMR --Quiz Circle the letter of the best answer to each multiple-choice question. 1. Appropriate lifestyle changes to aid in dealing with stress would include all of the following EXCEPT: a. cutting down on sugar, fat, and caffeine. b. avoiding exercise in your daily routine. c. avoiding cigarettes and alcohol. d. avoiding the use of relaxation techniques. 2. An Emergency Medical Responder who flees a scene because of potential violence and positions himself behind a brick retaining wall is using which technique? a. Cover b. Concealment c. Distraction d. Misdirection 3. A patient with a terminal illness has an outburst where she yells, "Why is this happening to me?" This patient is exhibiting what stage of the grieving process? a. Bargaining b. Depression c. Denial d. Anger 4. Disease-causing agents are called: a. venoms. b. toxemias. c. pathogens. d. amoebas. 5. Practice to prevent exposure to disease during patient contact is called:
21 a. infection precautions. b. universal isolations. c. disease control methods. d. standard precautions. 6. An Emergency Medical Responder should be screened yearly for: a. tuberculosis. b. tetanus. c. hepatitis. d. HIV. 7. It is critical that all Emergency Medical Responders wear whenever a patient is suspected of having TB. a. eye shields or goggles b. a HEPA respirator or N-95 mask c. a disposable gown and mask d. impervious boots and a helmet 8. If hand washing is indicated but you are in the field without soap and water available, what should you do? a. Wear gloves until soap and water are available b. Do nothing now, but make sure that gloves are used on the next call c. Take yourself out of service until soap and water can be found d. Use an alcohol-based hand cleaner 9. For which type of call would you be most likely to use a gown? a. A child with a fever b. An elderly gentleman complaining of abdominal pain c. A woman giving birth d. An assault victim with no active bleeding 10. If an Emergency Medical Responder has an exposure and the contamination involves the eyes, it is recommended that irrigation be done for a minimum of: a. 10 minutes. b. 20 minutes. c. 30 minutes.
22 d. 45 minutes. 11. Which of the following is most likely to be considered a significant stressor for the Emergency Medical Responder? a. Working a single-vehicle crash b. An uncomplicated childbirth c. A pediatric patient with serious trauma d. An emergency worker with an ankle injury 12. When you are lifting, how should you place your feet? a. One in front of the other b. Shoulder-width apart c. Close together d. As far apart as possible 13. A patient who is breathing adequately but is unresponsive should be placed in a position. a. supine b. prone c. head-down d. recovery 14. A patient who has been restrained should be placed in a(n) position. a. face-up b. facedown c. arm-leg straddle d. fetal 15. What is body mechanics? a. The positioning of a patient for transport b. The way in which a patient responds to commands c. The initial findings of a patient at the scene d. The proper use of the body to lift a patient
23
24 Handout 3-2 Student s Name The Call: An Unknown Condition Read the scenario. Then, in the space provided, answer the questions that follow. A call comes into the station at 0400 hours. The dispatcher sends your engine crew to a shelter for homeless people for an ill person. When you enter the shelter, an attendant says, Hank just came in last night. He lost his job and then his room. He tells us that he can t shake this cough, that it s been troubling him for some time. He s awfully thin, which is to be expected from living on the streets. I found him in the bathroom, on the floor, coughing up blood. I got him back to bed, but I m worried about him. He s only 21. Could you take a look at him? 1. What steps should you take before examining this patient? Why? 2. You believe that you were exposed to this patient s body fluids during the physical exam. After you transfer care of the patient to the EMS ambulance crew, what steps should you take?
25 Handout 3-3 Student s Name Chapter 3 Review Select the term from the list that best completes each sentence. Then write it in the space or spaces provided. Use proper capitalization if necessary. (HINT: Each term on the list is used only once.) [COMP: Set this bulleted list in multiple columns.] altered mental status body mechanics concealment exposure hypothermia long axis burnout shock standard precautions supine 1. is the proper use of the body to lift. 2. means moving a patient while keeping the spine in a straight line. 3. Inadequate perfusion of the body is called. 4. occurs when there is contact with a substance. 5. In a(n) position, a patient is flat on his back. 6. A reaction to cumulative stress or to multiple critical incidents that some EMS providers experience is called. 7. A patient who has disorientation of the senses is said to have a(n). 8. are used to prevent the spread of disease. 9. An Emergency Medical Responder who is hiding from danger in a place that offers no protection is using a technique known as. 10. Decreased body temperature is called.
26
27 Handout 3-4 Student s Name Listing Complete each listing activity on the lines provided. 1. List six signs of stress. 2. List the five stages of grieving. 3. List five examples of personal protective equipment. 4. List six vaccinations recommended for active duty Emergency Medical Responders.
28
29 Answer Key Handout 3-1: Chapter 3 Quiz 1. b 2. a 3. d 4. c 5. d 6. a 7. b 8. d 9. c 10. b 11. c 12. b 13. d 14. a 15. d Handout 3-2: The Call: An Unknown Condition 1. This patient has a severe cough. The cause is unknown, but the cough could carry pathogens. Put on a HEPA or N-95 respirator and use standard precautions. You also might consider placing a surgical-style mask on the patient; but if you do, continue to monitor the patient s airway and breathing carefully. 2. Immediately report any suspected exposure to blood or body fluids to your agency according to protocol. Include in your report the date and time of exposure, the type of body fluid involved, the amount, and details of the incident. Laws vary, so be sure to follow all local protocols. Handout 3-3: Chapter 3 Review 1. Body mechanics 2. Long axis 3. shock 4. Exposure 5. supine 6. burnout 7. altered mental status 8. standard precautions 9. concealment 10. hypothermia Handout 3-4: Listing Well-Being Basics 1. any six: irritability; inability to concentrate; difficulty sleeping and/or nightmares; guilt; loss of appetite; isolation; loss of interest in work; hopelessness; misuse of alcohol/drugs; loss of interest in sexual activity; indecisiveness; irritability; sadness; guilt
30 2. denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance 3. eye protection; gloves; gowns; face protection; respiratory protection 4. tetanus, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella), chickenpox, influenza
31 Handout 4-1 Student s Name Chapter 4: Introduction to Medical Terminology, Human Anatomy, and Lifespan Development--Quiz Circle the letter of the best answer to each multiple-choice question. 1. A person who is standing erect, with arms at sides and palms forward, is in a(n) position. a. prone b. supine c. anatomical d. lateral recumbent 2. A person who is lying face up on his back is in a(n) position. a. prone b. supine c. anatomical d. lateral recumbent 3. A person who is lying down on her left side is in a(n) position. a. prone b. supine c. anatomical d. lateral recumbent 4. The opposite of anterior, which refers to the front, is, which refers to the back. a. posterior b. inferior c. lateral d. distal 5. Proximal means close, or near the point of reference, and means distant, or far away from the point of reference.
32 a. posterior b. inferior c. lateral d. distal 6. The opposite of superior, or toward the head, is, or toward the feet. a. lateral b. ventral c. inferior d. ventral 7. A scrape to the elbow is considered to be that is, toward the body surface. a. superficial b. inferior c. dorsal d. medial 8. The internal female reproductive organs are found in the cavity. a. thoracic b. abdominal c. cranial d. pelvic 9. The abdominal cavity is divided into: a. quadrants. b. tridivisions. c. bisectional areas. d. anatomic planes. 10. The prefix that means below normal or slow is: a. hyper-. b. hypo-. c. tachy-. d. brady-.
33 11. The body s state of balance between all the body processes is called: a. homeostasis. b. equealostasis. c. physiostasis. d. anatomical equilibrium. 12. The spinal column is divided into how many sections? a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d How many pairs of ribs are attached anteriorly to the sternum? a. 9 b. 10 c. 11 d The is the longest and strongest bone in the body. a. femur b. humerus c. tibia d. ulna 15. The shoulder girdle consists of: a. the clavicle and the humerus. b. the scapula and the humerus. c. the humerus and the ischium. d. the clavicle and the scapula. 16. An example of a slightly moveable joint is the: a. hip. b. bones of the cranium. c. individual vertebra. d. wrist.
34 17. Muscles are attached to bones by: a. tendons. b. ligaments. c. joints. d. cartilage. 18. Which type of muscle is found in blood vessels? a. Voluntary b. Cardiac c. Striated d. Involuntary 19. The is the major muscle of the respiratory system. a. diaphragm b. bronchi c. alveoli d. intercostal muscle 20. The inferior chamber of the heart that pumps blood to the body is the: a. right atrium. b. left atrium. c. left ventricle. d. right ventricle. 21. The brain and the spinal cord are referred to together as the: a. peripheral nervous system. b. central nervous system. c. somatic nervous system. d. automatic nervous system. 22. The integumentary system consists of the: a. processes involved in the digestion and elimination of waste. b. skin, hair, and nails.
35 c. testes and ovaries. d. lymphatic and immunity tissues. 23. Which of the following is NOT considered part of the endocrine system? a. Gallbladder b. Pancreas c. Adrenal gland d. Pituitary gland 24. What is the approximate percentage of oxygen found in atmospheric air? a. 19 percent b. 20 percent c. 21 percent d. 22 percent 25. Which component of blood helps it to clot? a. Red blood cells b. Plasma c. White blood cells d. Platelets
36 Handout 4-2a Student s Name The Call: Terminology Applied Read the scenario. Then, in the space provided, answer the questions that follow. You and your crew are dispatched to a fall at a home. As you pull up to the onefamily house, you size up the scene. The truck for a chimney cleaning service is parked in the driveway. There is scaffolding around a chimney at the east end of the house; at its base, two men are kneeling over a third man, who is lying supine on the ground. The scene appears to be safe, so you grab your jump kit and approach. As you do, one of the men runs over to you and tells you that they had been repointing the chimney when Luis lost his footing and fell about 18 feet to the hard ground. Your patient is not conscious when you begin your initial assessment. After determining that he is breathing adequately, you note a large laceration on the left side of his jaw. You observe that an area on the outside of the patient s left arm, just above the elbow, is swollen and deformed. There is also a large laceration on the front side of the patient s upper left thigh just above the kneecap, and it is bleeding profusely. 1. Which of the body s major systems do you suspect have been injured as a result of the fall? 2. Where is the injury to the patient s arm? Use the correct medical terms for body locations. 3. Where is the injury to the patient s lower extremity? Use the correct medical terms for anatomy and location.
37 Handout 4-2b Student s Name The Call: Plate Glass Window vs. Partying Person Read the scenario. Then complete the chart according to the directions that follow. Late on a hot summer Friday night, you are backing your emergency response vehicle into the station when the dispatcher tells you to respond to the report of a 27-yearold who has gone through a plate glass window at a residence at 529 Miracle Way. You notify dispatch that you are responding and that you have a fiveminute ETA. You arrive at the scene and find a party with a group of people tending to the injured person, who has been moved away from the window and who is sitting up. You survey the scene and find it safe. When you make contact with the patient, you observe that he is conscious but that he has numerous cuts over his arms and face. The patient is breathing quickly, but he is talking in full sentences mostly stating that he is in pain. As you start to provide emergency care, you hear the ambulance radio to dispatch that Paramedics are now on the scene. In the second column of this chart, place a check mark next to any body system that was affected in this scenario. In the third column, explain the effect for each system that you checked. Body System Respiratory Circulatory Nervous Digestive Urinary Reproductive Integumentary Endocrine Was the system affected? If so, how?
38 Handout 4-3 Student s Name Chapter 4 Review In the space provided, write the word or words that best complete each sentence. 1. When describing injuries to a patient, remember that the words right and left always refer to the right and left. 2. To describe the anatomical position of the head in relation to the chest, you would say, The head is to the chest. 3. A patient who is lying down on his abdomen is said to be in the position. 4. The elbow is to the shoulder, or farther away from the torso than the shoulder is. 5. A driver is experiencing neck pain, or pain to the back of her neck, because her neck has forcefully impacted the headrest. 6. A left position means that the patient is lying on his left side. It is also is called the recovery position. 7. The term means inside the body. 8. The term is used to describe being closer to the point of attachment, such as the elbow s anatomical relation to the wrist. 9. The prefix is used to describe something as below normal or low. 10. The root refers to the heart. 11. What bodily structures look like to the naked eye is called anatomy. 12. The is the moveable part of the lower jaw. 13. The cervical spine has vertebrae supporting the head and neck. 14. The anatomical name for the collarbone is the. 15. The two bones of the lower leg are the and the.
39 16. The muscle type that is found in the heart is called muscle. 17. Another name for the voice box is the. 18. The are the superior chambers of the heart. 19. The blood cells are the ones that fight infection. 20. arteries supply the heart muscle with blood. 21. The outermost layer of the skin is called the. 22. The voluntary nervous system is also called the nervous system. 23. are the blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart. 24. Chemicals that help to regulate various body systems are called. 25. The fetus develops in the.
40 Handout 4-4 Student s Name True or False Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false by writing T or F in the space provided. 1. The left lateral recumbent position is also known as the recovery position. 2. The directions left and right always refer to the Emergency Medical Responder s left and right. 3. The term lateral refers to a position farther away from the midline of the body. 4. The term superior means front and inferior means back. 5. Anatomically speaking, the elbow is distal to the wrist. 6. Internal refers to outside the body, and external refers to inside the body. 7. A wound to the forearm is distal to the wrist. 8. Superficial means toward the surface. 9. The terms anterior and ventral both mean toward the front. 10. The cranial cavity contains the great vessels. 11. The bladder and rectum are in the abdominal cavity. 12. The prefix that is used to describe something as being below normal or slow is tachy-.
404 Section 5 Shock and Resuscitation. Scene Size-up. Primary Assessment. History Taking
 404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
Emergency Medical Responder Safety and Wellness
 Chapter 2 Emergency Medical Responder Safety and Wellness OBJECTIVES DIRECTORY 1. Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 55-56 2. List indications of the potential for danger to yourself or others
Chapter 2 Emergency Medical Responder Safety and Wellness OBJECTIVES DIRECTORY 1. Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 55-56 2. List indications of the potential for danger to yourself or others
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Technician Psychomotor Examination BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT
 BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
CHAPTER 32 QUIZ. Handout 32-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE
 American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPORT State Form 54407 (R / 5-13)
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer
 Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
Lifting, Moving and Positioning Patients From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 44 Questions
 Lifting, Moving and Positioning Patients From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 44 Questions 1. Approximately how much of the log roll will be complete before the rescuer at the patient's head will
Lifting, Moving and Positioning Patients From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 44 Questions 1. Approximately how much of the log roll will be complete before the rescuer at the patient's head will
National Registry Skill Sheets
 Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
TN Emergency Medical Services
 TN Emergency edical ODULES AND UNITS ES System ES Providers: ER and ET Safety and Wellness Body echanics System Communication Documentation Therapeutic Communication Legal and Ethical Issues Intro to Respiratory
TN Emergency edical ODULES AND UNITS ES System ES Providers: ER and ET Safety and Wellness Body echanics System Communication Documentation Therapeutic Communication Legal and Ethical Issues Intro to Respiratory
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT
 BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA
 PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK
 CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough?
 IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Patient Assessment/Management Trauma
 Patient Assessment/Management Trauma Date: / / Test Site Location: Station #: Takes or verbalizes standard precautions (BSI) if appropriate based on patient scenario SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the scene
Patient Assessment/Management Trauma Date: / / Test Site Location: Station #: Takes or verbalizes standard precautions (BSI) if appropriate based on patient scenario SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the scene
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
81 First Responder Respiratory
 81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
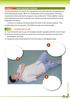 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course
 Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Lifting & Moving Patients. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Lifting & Moving Patients Lesson Goal Learn the correct techniques, equipment, & positioning for moving patients safely and effectively in a variety of situations &locations Lesson Objectives Define body
Lifting & Moving Patients Lesson Goal Learn the correct techniques, equipment, & positioning for moving patients safely and effectively in a variety of situations &locations Lesson Objectives Define body
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 4.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 14, 16 22, 24, 26 32, 34 35, 39 4.2 Describe your scope of practice as an EMT. Slides
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 4.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 14, 16 22, 24, 26 32, 34 35, 39 4.2 Describe your scope of practice as an EMT. Slides
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE
 UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
CFR Exam Study Guide NYS DOH EMR Compliant 2014 0
 October 2014 v.1 CFR Exam Study Guide NYS DOH EMR Compliant 2014 0 Table of Contents Introduction to EMS Pg. 2 Well Being of the First Responder Pg. 7 Medical Legal Pg. 13 Documentation and Communication
October 2014 v.1 CFR Exam Study Guide NYS DOH EMR Compliant 2014 0 Table of Contents Introduction to EMS Pg. 2 Well Being of the First Responder Pg. 7 Medical Legal Pg. 13 Documentation and Communication
Alcohol and drug abuse
 Alcohol and drug abuse This chapter explores how alcohol abuse affects our families, relationships, and communities, as well as the health risks associated with drug and alcohol abuse. 1. Alcohol abuse
Alcohol and drug abuse This chapter explores how alcohol abuse affects our families, relationships, and communities, as well as the health risks associated with drug and alcohol abuse. 1. Alcohol abuse
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Oxygenation. Chapter 21. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing*
 Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
12/5/2012. Introduction. Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries. Recognizing and Caring for Serious Head, Neck and Back Injuries
 Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known
 Page 1 of 26 Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known Page 2 of 26 What s Inside Why Health Care Planning Is Important... 2 What You Can Do... 4 Work through the advance health care planning
Page 1 of 26 Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known Page 2 of 26 What s Inside Why Health Care Planning Is Important... 2 What You Can Do... 4 Work through the advance health care planning
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING
 TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY: With Portable Suction Machine DATE: March 14, 1994 POLICY DEFINITION:
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY: With Portable Suction Machine DATE: March 14, 1994 POLICY DEFINITION:
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector
 OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd. Ready Reference
 Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service. LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide
 Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES
 RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Ambulance Service. Patient Care. and. Transportation Standards
 Ambulance Service Patient Care and Transportation Standards Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Emergency Health Services Branch Patient Care A. General Each operator and each emergency medical attendant
Ambulance Service Patient Care and Transportation Standards Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Emergency Health Services Branch Patient Care A. General Each operator and each emergency medical attendant
38 Assisting with a General Physical Examination
 Learning Outcomes 38-2 38.1 Identify the purpose of a general physical. CHAPTER 38 Assisting with a General Physical Examination 38.2 Describe the role of the medical assistant in a general physical. 38.3
Learning Outcomes 38-2 38.1 Identify the purpose of a general physical. CHAPTER 38 Assisting with a General Physical Examination 38.2 Describe the role of the medical assistant in a general physical. 38.3
Emergency Room (ER) Visits: A Family Caregiver s Guide
 Family Caregiver Guide Emergency Room (ER) Visits: A Family Caregiver s Guide Your family member may someday have a medical emergency and need to go to a hospital Emergency Room (ER), which is also called
Family Caregiver Guide Emergency Room (ER) Visits: A Family Caregiver s Guide Your family member may someday have a medical emergency and need to go to a hospital Emergency Room (ER), which is also called
MEDICAL MALPRACTICE CASE RESULTS
 CASE RESULTS INFORMATION Please note that every case is different and these verdicts and settlements, while accurate, do not represent what we may obtain for you in your case. Nor does it mean that we
CASE RESULTS INFORMATION Please note that every case is different and these verdicts and settlements, while accurate, do not represent what we may obtain for you in your case. Nor does it mean that we
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
Ancillary Staff Training
 Ancillary Staff Training Goals of Infection Prevention Protect the patients Protect the staff Prevent spread of diseases How Does The Virus Spread Between People? Direct contact through broken skin, mouth,
Ancillary Staff Training Goals of Infection Prevention Protect the patients Protect the staff Prevent spread of diseases How Does The Virus Spread Between People? Direct contact through broken skin, mouth,
Emergency Medical Technician Basic. Practical Skills Examination Sheets
 New York State Department of Health Basic Practical Skills Examination Sheets Rev 07/12 Basic Practical Skills Examination Sheets Updates Included on this page are the changes or updates that have been
New York State Department of Health Basic Practical Skills Examination Sheets Rev 07/12 Basic Practical Skills Examination Sheets Updates Included on this page are the changes or updates that have been
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Application for a Medical Impairment Rating (MIR)
 STATE OF TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF LABOR AND WORKFORCE DEVELOPMENT Workers Compensation Division Medical Impairment Rating Program 220 French Landing Drive Nashville, TN 37243-1002 Phone (615) 253-1613 Fax
STATE OF TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF LABOR AND WORKFORCE DEVELOPMENT Workers Compensation Division Medical Impairment Rating Program 220 French Landing Drive Nashville, TN 37243-1002 Phone (615) 253-1613 Fax
Adult Choking and CPR Manual
 Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
PATIENT INFORMATION INSURANCE INFORMATION
 (mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
(mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Heart information. CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation
 Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
STATE OF CONNECTICUT
 STATE OF CONNECTICUT DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH June 7, 2010 The Following Will Be Policy For Emergency Medical Service Care Providers: GUIDELINES FOR EMR, EMT, AEMT, and Paramedic DETERMINATION OF DEATH/DISCONTINUATION
STATE OF CONNECTICUT DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH June 7, 2010 The Following Will Be Policy For Emergency Medical Service Care Providers: GUIDELINES FOR EMR, EMT, AEMT, and Paramedic DETERMINATION OF DEATH/DISCONTINUATION
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
How To Fill Out A Health Declaration
 The English translation has no legal force and is provided to the customer for convenience only. The Dutch health declaration should be filled in. Health declaration for occupational disability insurance
The English translation has no legal force and is provided to the customer for convenience only. The Dutch health declaration should be filled in. Health declaration for occupational disability insurance
DOCUMENTATION TEMPLATES. All patient care reports should include the following information in the narrative:
 DOCUMENTATION TEMPLATES All patient care reports should include the following information in the narrative: Patient Data: -Chief Complaint -Mechanism of injury/nature of illness -Associated signs and symptoms/pertinent
DOCUMENTATION TEMPLATES All patient care reports should include the following information in the narrative: Patient Data: -Chief Complaint -Mechanism of injury/nature of illness -Associated signs and symptoms/pertinent
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation
 Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation Please do not write on this sheet. Indicate your answers on the answer sheet provided. 1. Medical control is the process by which a physician
Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation Please do not write on this sheet. Indicate your answers on the answer sheet provided. 1. Medical control is the process by which a physician
Pediatric Airway Management
 Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Whooping Cough. The Lungs Whooping cough is an infection of the lungs and breathing tubes, both of which are parts of the respiratory system.
 Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center
 Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPORT
 Reset Form EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street, Room E239 Indianapolis,
Reset Form EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street, Room E239 Indianapolis,
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
TEPP Planning Products Model Procedure
 TEPP Planning Products e for Properly Handling and Packaging Potentially Radiologically 02B00215-13.p65 Prepared for the Department of Energy Office of Transportation and Emergency Management table of
TEPP Planning Products e for Properly Handling and Packaging Potentially Radiologically 02B00215-13.p65 Prepared for the Department of Energy Office of Transportation and Emergency Management table of
Motor Vehicle Accident - New Patient
 Motor Vehicle Accident - New Patient Today's Date: Patient Name: Auto Insurance Company of Car You Were In: Phone: Insurance Agent: Phone Was A Police Report Made? Have You Informed Your Agent of Your
Motor Vehicle Accident - New Patient Today's Date: Patient Name: Auto Insurance Company of Car You Were In: Phone: Insurance Agent: Phone Was A Police Report Made? Have You Informed Your Agent of Your
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Throughout this reference summary, you will find out what massage therapy is, its benefits, risks, and what to expect during and after a massage.
 Massage Therapy Introduction Massage therapy is the manipulation of the soft tissues of the body, including the skin, tendons, muscles and connective tissue by a professional, for relaxation or to enhance
Massage Therapy Introduction Massage therapy is the manipulation of the soft tissues of the body, including the skin, tendons, muscles and connective tissue by a professional, for relaxation or to enhance
Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin integrity.
 Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
Bloodborne Pathogens. Scott Anderson CCEMTP. Materials used with permission from the Oklahoma State University
 Bloodborne Pathogens Scott Anderson CCEMTP Materials used with permission from the Oklahoma State University What is a Bloodborne Pathogen? Microorganisms that are carried in the blood that can cause disease
Bloodborne Pathogens Scott Anderson CCEMTP Materials used with permission from the Oklahoma State University What is a Bloodborne Pathogen? Microorganisms that are carried in the blood that can cause disease
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
Frontline First Aid EMR Scenario Examples
 Course Type: Start Date: Instructors initial scenarios as they are completed CPR-AED Scenarios CPR with Hypothermia Load and Go CPR with Obstructed Airway Continue CPR after airway clears with NO obvious
Course Type: Start Date: Instructors initial scenarios as they are completed CPR-AED Scenarios CPR with Hypothermia Load and Go CPR with Obstructed Airway Continue CPR after airway clears with NO obvious
EMS Patient Care Report Navigation Logic for Record Creation
 EMS Patient Report Navigation Logic for Record Creation This document serves to provide specifications regarding data entry and data element completion requirements for PreMIS Version 2 web-based application
EMS Patient Report Navigation Logic for Record Creation This document serves to provide specifications regarding data entry and data element completion requirements for PreMIS Version 2 web-based application
Auto Accident Questionnaire
 Auto Accident Questionnaire Patient s Name: Date Of Accident: Date: Social History: (please complete the following, check all boxes that apply) Are you: Married Single Divorced Widowed # of Children: #
Auto Accident Questionnaire Patient s Name: Date Of Accident: Date: Social History: (please complete the following, check all boxes that apply) Are you: Married Single Divorced Widowed # of Children: #
Epinephrine Auto Injector Interim Policy (Amended March 12, 2008)
 Epinephrine Auto Injector Interim Policy (Amended March 12, 2008) Pursuant to the authority conferred by N.J.S.A. 26:2K-47.1, et seq., the Department of Health and Senior Services (the Department) shall
Epinephrine Auto Injector Interim Policy (Amended March 12, 2008) Pursuant to the authority conferred by N.J.S.A. 26:2K-47.1, et seq., the Department of Health and Senior Services (the Department) shall
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace
 A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
REPORT OF EXAMINATION To be on file at the Academy
 SOUTH CAROLINA CRIMINAL JUSTICE ACADEMY 5400 Broad River Road Columbia, South Carolina 29212-3540 (803) 896-7802 * * * * * * MEDICAL HISTORY, EXAMINATION, AND FITNESS FOR TRAINING TO THE EMPLOYER: This
SOUTH CAROLINA CRIMINAL JUSTICE ACADEMY 5400 Broad River Road Columbia, South Carolina 29212-3540 (803) 896-7802 * * * * * * MEDICAL HISTORY, EXAMINATION, AND FITNESS FOR TRAINING TO THE EMPLOYER: This
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
CHAPTER 21 QUIZ. Handout 21-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 21-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. A severe form of allergic reaction is called A. an allergen. C. epinephrine. B. anaphylaxis. D. an immune reaction. 2. Harmless
Handout 21-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. A severe form of allergic reaction is called A. an allergen. C. epinephrine. B. anaphylaxis. D. an immune reaction. 2. Harmless
Overview. Geriatric Overview. Chapter 26. Geriatrics 9/11/2012
 Chapter 26 Geriatrics Slide 1 Overview Trauma Common Medical Emergencies Special Considerations in the Elderly Medication Considerations Abuse and Neglect Expanding the Role of EMS Slide 2 Geriatric Overview
Chapter 26 Geriatrics Slide 1 Overview Trauma Common Medical Emergencies Special Considerations in the Elderly Medication Considerations Abuse and Neglect Expanding the Role of EMS Slide 2 Geriatric Overview
State of Indiana EMR Psychomotor Skills Examination
 SECONDARY ASSESSMENT (Detailed Exam) *Credit should be given to candidates that use a brief exam f life-threatening injuries in the Primary Survey so long as it does not delay appropriate care. Head Neck
SECONDARY ASSESSMENT (Detailed Exam) *Credit should be given to candidates that use a brief exam f life-threatening injuries in the Primary Survey so long as it does not delay appropriate care. Head Neck
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
