Emergency Care Workbook
|
|
|
- Verity Parks
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Emergency Care Workbook Emergency Medical Responder
2 EMERGENCY CARE WORKBOOK
3 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior written permission from The Canadian Red Cross Society. Permission is granted to current Training Partners, currently certified Canadian Red Cross Instructors, and participants of Canadian Red Cross First Aid Programs to reproduce and transmit this publication for the purposes of instructing and completing the Canadian Red Cross First Aid Programs. This publication is available in English and French. The terms he and she have been used throughout the document to ensure representation of both genders. Composition by JEZ Graphics Illustrations by Scott Mooney Produced in Canada by: The StayWell Health Company Ltd. 2 Quebec Street, Suite 107, Guelph ON N1H 2T3 A part of Krames StayWell Strategic Partnerships Division 780 Township Line Road, Yardley, PA USA
4 ! The Responder... 1 The Emergency Scene... 7 Preventing Disease Transmission Anatomy and Physiology Secondary Survey Choking Respiratory Emergencies Airway and Ventilation Circulatory Emergencies Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Bleeding, Shock, and Soft Tissue Injuries Musculoskeletal Injuries Head and Spine Injuries Chest, Abdominal, and Pelvic Injuries Sudden Illnesses Poisoning Heat- and Cold-Related Emergencies Special Populations and Crisis Intervention Childbirth Reaching and Moving Patients Multiple Casualty Incidents Communications and Transportation... 96
5 The Responder For Your Review Read Chapter 1 of Emergency Care, then complete the following activities. Key Terms Referring to Emergency Care, define the following terms: Abandonment: Confidentiality: Consent: Critical incident stress management: Duty to act: Emergency medical responder (EMR): Emergency medical services (EMS) system: First responder: Good Samaritan laws: Interpersonal communication: Medical control: Medical terminology: Negligence: Refusal of care: Standard of care: Emergency Care Workbook 1
6 Do You Know 1. List six signs and symptoms of critical incident stress: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. What Would You Do? Read the following scenario and answer the questions below. While you are driving to work one morning, you see someone has fallen off his bicycle and seems to be bleeding from his leg quite severely. As you get closer, you notice that the bike is badly damaged and the person has several cuts and scrapes all over him. 1. In this situation, do you have a duty to act? If so, why? If not, why not? 2. If you do decide to act in this situation, your first concern should be to: a. Bandage the wounds b. Determine if there are any other injuries you can t see c. Ensure your safety and the safety of any bystanders d. Call work and tell them you will be late 3. What types of hazards may be present? What can you do to protect yourself from these? Test Your Knowledge Circle the best answer to each of the following questions. 1. Which of these is not a level recognized by the Paramedic Association of Canada? a. Primary care paramedic b. Initial care paramedic c. Critical care paramedic d. Emergency medical responder 2. As a responder, you should have good communication skills. Which of the following people is a responder least likely to need to communicate with? a. The patient and his family b. His partner or co-workers c. Bystanders d. The lawyer of the patient 3. When obtaining consent before caring for someone, which of the following do you NOT have to do? a. Have the person sign the Acceptance of Treatment form b. Identify yourself with your name c. Indicate what you think may be wrong and what you plan to do d. State your level of training 4. All documentation should be: a. Perfectly handwritten, accurate, and without error b. Bulleted, with the diagnosis clearly indicated c. Legible, professional, and complete d. Typed, on time, and signed by the patient 5. Ending care of a patient without his consent, or without ensuring that someone with equal or greater training will continue the care, is called: a. Abandonment b. Refusal of care c. Transfer of function d. Competence Emergency Care Workbook 2
7 6. What are the first two critical actions that someone from the general public should take in an emergency? a. Recognize that an emergency exists and begin prompt care b. Recognize that an emergency exists and obtain more advanced medical care c. Obtain more advanced medical care and move the patient out of any hazardous situations d. Transport the patient to a hospital and wait until the family arrives 7. Critical incident stress management is a process meant solely for emergency responders who have had to deal with a high-stress incident. T or F 8. Which of the following is NOT a common component of a radio system? a. Base station b. Mobile radios c. Global positioning system units d. Repeaters 9. If you are speaking with a physician, it is important that you: a. Write down everything he says b. Repeat any orders back to the physician c. Present all information rapidly d. Verify that everything said by the physician is located within your written protocols 10. Which of the following should you keep in mind when using a radio? a. Speak slowly and clearly b. Begin speaking at the same time you push the push to talk button c. Hold the radio right up to your mouth d. Relay all information you have collected at the scene up to that point Emergency Care Workbook 3
8 The Emergency Scene For Your Review Read Chapter 2 of Emergency Care, then complete the following activities. Key Terms Referring to Emergency Care, define the following terms: Emergency move: Hazardous materials: Do You Know 1. What hazards do you see at this scene? 3. At the site of a collision, list the three situations in which you might park in a roadway to block traffic. i. ii. iii. 4. List the five key elements a responder should pay attention to when approaching an emergency scene. i. ii. iii. iv. v. 2. What would you do to control this scene? Emergency Care Workbook 7
9 Fill in the Blanks 1. Complete the Table Fill in the situations that correspond to each appropriate set of precautions to take. Situation Precautions a. Check doors before opening them, stay close to the floor, avoid using elevators b. Ensure the scene is safe, avoid touching anything unless it hinders care, document everything c. Put up reflectors, flares, or lights well back from the scene, for visibility d. Look for placards on transportation vehicles, clues such as spilled substances, leaking containers, or unusual odours e. Get directions from the incident commander; triage appropriately What Would You Do? Read the following scenario and answer the questions below. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision. One car is perched on its side, and on the other side of the road, a truck has hit a large tree, snapping the trunk and causing the top of the tree to be angled over the truck. 1. Ideally, what personal protective equipment should you wear to ensure your safety at the scene? i. ii. iii. iv. v. 2. As you approach the scene, you see a placard indicating a flammable substance is on board. Which of the following would be an appropriate action to take? a. Open the truck doors and investigate what the substance is b. Ensure that the appropriate services to deal with hazardous materials have been notified c. Have bystanders gather buckets of water in case of fire d. Check to see if any houses nearby have a chainsaw so you can cut down the tree 3. Appropriate resources are on the scene, dealing with the truck and directing traffic. You are clear to begin necessary treatment. The truck driver appears uninjured, and he exits the truck on his own power, where another responder tends to him. You now make your way to the car and its passengers. What should be your first step? a. Climb into the car to assess the people b. Ask the people in the car to climb out c. Ensure the car has been stabilized d. Gather people to help you roll the car upright Test Your Knowledge Circle the best answer to each of the following questions. 1. Which of the following is NOT a primary responsibility of the responder at an emergency scene? a. Ensure safety for yourself and any bystanders b. Gain access to the patient(s) c. Contact the friends and/or family of the patient d. Determine any threats to the patient s life 2. If there is a downed electrical wire at an emergency scene, how far away should the bystanders be moved? a. Twice the length of the span of the wire b. There is no specific place to which they should be moved c. Half the distance between the two poles from which the broken wire has been strung d. The distance from the break in the wire to the closest power pole Emergency Care Workbook 8
10 3. If you are in a burning building, which is the best way to get out safely? a. Cover your mouth and nose with a moist cloth and walk to the nearest exit b. Jump out the nearest window c. Cover your mouth and nose with a moist cloth and stay close to the floor d. None of the above 4. Which of the following are clues that a hazardous material may be present at an emergency? a. Chemical transport tanks and/or placards b. Clouds of vapour or spilled solids or liquids c. Unusual odours d. All of the above 5. An emergency that may overwhelm the capabilities of an EMS system is called: a. Simple Triage And Rapid Treatment (START) b. Triage c. A multiple casualty incident d. Critical incident stress 6. The system used to control and direct the resources at an emergency scene is referred to as the: a. Incident command system b. Simple Triage And Rapid Treatment system c. Emergency medical services system d. Dispatch system 7. To have an effective plan of action, which of the following are crucial? a. Advanced care training and a large human resource base b. Advance preparation and periodic rehearsal c. A complex medical communication network d. Specialized equipment and vehicles 8. When pulling someone out of deep water, it is important to: a. Enter the water and hold onto the patient securely b. Yell for help as you wade in to get the patient c. Keep as low as possible and use something to reach the patient from a stable point d. Both a and b Emergency Care Workbook 9
11 Preventing Disease Transmission For Your Review Read Chapter 3 of Emergency Care, then complete the following activities. Key Terms Referring to Emergency Care, define the following terms: Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS): Airborne transmission: Bacteria: Blood-borne pathogens: Community-associated MRSA: Direct contact transmission: Hepatitis: Herpes: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): Immune system: Immunization: Indirect contact transmission: Infection: Infectious disease: Influenza: Meningitis: Pathogen: Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): Tuberculosis: Vector-borne transmission: Virus: Emergency Care Workbook 13
12 Do You Know 1. The four conditions that must be present for an infection to be transmitted to someone are: i. ii. iii. iv. 2. List five precautions you can take to prevent disease transmission: i. ii. iii. iv. v. 3. An exposure control plan should include the following elements: i. ii. iii. What Would You Do? Read the following scenario and answer the questions below. You are called to a residence because a 15-year-old teenager is worried about her grandfather, who has fallen and cut his leg. Upon talking to her, you learn that her grandfather has been coughing more than usual, and at times there has been blood on the tissues he uses. She attributed this to his age. As you approach him, he is coughing. 1. What precautions, if any, should you take when caring for the grandfather? 2. Aside from the cut on his leg, what ailment might the grandfather be suffering from? a. Meningitis b. Tuberculosis c. Kidney stones d. Chickenpox/shingles 3. If someone catches an infection from particles expelled during coughing, what method of disease transmission would this be? a. Direct contact b. Indirect contact c. Vector-borne transmission d. Airborne transmission Test Your Knowledge Circle the best answer to each of the following questions. 1. Which of the following can be transmitted by airborne particles? a. HIV/AIDS b. Hepatitis and meningitis c. Meningitis and tuberculosis d. Herpes and tuberculosis Emergency Care Workbook 14
13 2. If you think you have been exposed to an infectious disease at an emergency scene, the first step you should take is: a. Go to a hospital to be tested b. Notify your supervisor and any other responder personnel involved c. Determine what type of disease it is d. Contact the Poison Control Centre 3. In which of the following cases should you wear full protective equipment (gloves, gown, mask, and eyewear)? a. When wiping down a blood pressure cuff after a call b. When caring for bleeding that is spurting c. When caring for someone with signs of an infectious respiratory illness d. Both b and c 4. Which of the following can be transmitted by contaminated food? a. Tuberculosis and rubella b. Typhus and diphtheria c. Meningitis and hepatitis d. Meningitis and herpes 5. Which of the following are basic components of the immune system? a. White blood cells b. Platelets c. Antigens d. Red blood cells 6. Immunizations are available for which of the following diseases? a. Hepatitis A and B, polio, and mumps b. Herpes, meningitis, and hepatitis C c. Influenza, rubella, and tetanus d. Both a and c Emergency Care Workbook 15
14 Anatomy and Physiology For Your Review Read Chapter 4 of Emergency Care, then complete the following activities. Key Terms Referring to Emergency Care, define the following terms: Body system: Cell: Circulatory system: Digestive system: Endocrine system: Genitourinary system: Integumentary system: Musculoskeletal system: Nervous system: Organ: Respiratory system: Tissue: Vital organs: Emergency Care Workbook 16
15 Fill in the Blanks 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct body parts and other terminology below. Respiratory System Directional Terms Circulatory System Body Cavities Emergency Care Workbook 17
16 2. Anatomical position is: 3. Complete the chart below: Body System Nervous Integumentary Endocrine 4. Complete the chart below with the names of each body cavity and the major structures within each cavity. Body Cavity a. b. c. d. e. Major Components Bones, muscles, joints, ligaments, tendons Heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, blood Uterus and genitalia Kidneys and bladder Purpose Supplies the body with oxygen through breathing Breaks down food and eliminates waste Major Structures in the Cavity What Would You Do? Read the following scenarios and answer the questions below. Scenario 1 While at work at a machine shop, a man is turning a piece of steel on a lathe. The chuck is not tight enough, and when the tool makes contact with the steel, the steel projects itself toward the man. He puts his arm up to block his face, and the steel makes a deep laceration in the back of his upper arm. 1. Using correct terminology, describe the location of the injury in relation to these other body structures: a. Elbow: b. Shoulder: 2. Is the injury superior or inferior to the pelvis? 3. Which two body systems will interact to alert the man to his injury? a. Nervous and respiratory b. Endocrine and nervous c. Nervous and integumentary d. Circulatory and digestive Scenario 2 You are called to a school where a teenaged boy is having a severe allergic reaction and has used his prescribed epinephrine auto-injector. He has a MedicAlert medical identification product around his neck that indicates he has a severe allergy to peanuts. The person sitting beside him in the cafeteria was eating a granola bar. 1. Anaphylaxis is a reaction that can affect which of the following body systems? a. Nervous, endocrine, and genitourinary b. Integumentary, endocrine, musculoskeletal, and nervous c. Digestive, respiratory, and genitourinary d. Integumentary, respiratory, cardiovascular, and digestive 2. Hives or redness of the skin may be the visual signs of anaphylaxis on the skin. What signs may be present that indicate an effect on the digestive system? Emergency Care Workbook 18
17 3. Epinephrine opens the airway and stimulates the heart to continue beating. Which two body systems does this indicate that epinephrine affects? Test Your Knowledge Circle the best answer to each of the following questions. 1. The epiglottis prevents liquids and solids from entering what? a. The stomach b. The lungs c. The esophagus d. The intestines 2. Where do arteries carry blood? a. From the heart to the body tissues b. From the lungs to the heart c. From the heart to the lungs d. Both a and c 3. The integumentary system has many functions. Its main function(s) is(are) to: a. Prevent infection b. Secrete hormones c. Produce white blood cells d. All of the above 4. In comparison with the chest, the neck is described as, whereas the abdomen is described as. a. Anterior, posterior b. Medial, lateral c. Superior, inferior d. Proximal, distal 5. The respiratory system and cardiovascular system work together to: a. Provide oxygen to the cells of the body b. Keep hormones distributed throughout the body c. Regenerate nervous tissue after injury d. Regulate blood flow to the digestive system 6. Which of the following is not in the pelvic cavity? a. Rectum b. Spleen c. Bladder d. Reproductive organs 7. Which of the following is one of the quadrants of the abdomen? a. Dorsal quadrant b. Superior quadrant c. Upper midline quadrant d. Right lower quadrant Emergency Care Workbook 19
18 Secondary Survey For Your Review Read Chapter 5 of Emergency Care, then complete the following activities. Key Terms Referring to Emergency Care, define the following terms: Blood pressure (BP): Brachial artery: Carotid artery: Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Glucometry: Golden Period: Head-tilt/chin-lift: Jaw thrust: Level of consciousness (LOC): Load-and-go emergency: Mechanism of injury (MOI): Primary survey: Pulse oximetry: Rapid body survey: Respiratory rate: Secondary survey: Secondary transport decision: Signs: Symptoms: Transport decision: Vital signs: Emergency Care Workbook 20
19 Do You Know 1. What are the three parts of the secondary survey? i. ii. iii. 2. If you need to call for further help, what are the seven pieces of information you will need to tell the dispatcher? i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. 3. If you are not transporting the patient yourself, you will need to obtain more advanced medical care in some cases. List five conditions in which you would do this. i. ii. iii. iv. v. 4. List the equipment you would ideally have to completely check vital signs. Fill in the Blanks 1. The Assessment Process Fill in the boxes to show the steps involved in assessment. 2. Label the pulse points in the diagram. Emergency Care Workbook 21
20 3. Commonly Used Assessment Mnemonics Complete the words or phrases represented by each mnemonic. ABC A B C SAMPLE S A M P L E AVPU A V P U OPQRST O P Q R S T APGAR (See Chapter 20 on childbirth.) A P G A R Some other assessment mnemonics you may hear in the field are: Why might a patient have an altered level of consciousness? Alcohol Epilepsy Insulin (diabetic) Overdose Uremia Trauma Infection Psychiatric/Poison Stroke (cardiovascular) When doing a secondary survey, remember to: Inspect for CLAPS Contusions Lacerations Abrasions Punctures/Penetrations Swelling/Subcutaneous emphysema and palpate for TICS Tenderness Instability Crepitus Swelling/Subcutaneous emphysema or DCAP and BLS Deformities Contusions Abrasions Punctures/Penetrations Burns Lacerations Swelling When doing a secondary survey, look for DOTS (signs of injury) Deformities Open wounds Tenderness Swelling Emergency Care Workbook 22
21 4. Vital Signs Fill in the name of the vital sign that corresponds to the number or observation written here. Observation Vital Sign 120/72 Alert and oriented Equal, round, and reactive to light 14, regular, and deep Dilated and fixed 93, weak, and irregular 130/P Pale, cool, and clammy GCS of 13 Red, hot, and dry 76, regular, and full Unresponsive 5. Assess Your Classmates Fill in the names of your classmates. Then take the following vital signs and fill in your findings for each classmate. Name Respirations Pulse Skin Characteristics Blood Pressure Pupils Emergency Care Workbook 23
22 What Would You Do? Read the following scenario and answer the questions below. You are called to the local park, where a child has collapsed in the sandbox. The child is not responsive. You confirm that the child is breathing and has a pulse. 1. What are the next three steps you should take? i. ii. iii. 2. You check the child s vital signs and find the following. Put an X next to the vital signs that are probably not normal for this child and a next to those that are probably normal. Vital Sign Level of consciousness: unresponsive Breathing: 10, shallow, and regular Pulse: 100, strong, and regular Skin: pale, cool, and clammy Blood pressure: 120/60 Pupils: equal, round, and reactive to light Normal vs. Not Normal 3. The child s babysitter is able to answer any questions you have regarding the child. Which of the following questions should you ask her? a. The child s sleeping patterns, eating times, and vaccination records b. The child s allergies, current medications, and the last time the child ate or drank anything c. The child s age, address, and where she goes to school d. The child s medical conditions, activities before the emergency, and normal breathing rate 4. After completing your secondary survey, you perform another vital signs check and observe the following. Put an X next to the vital signs that are probably not normal for this child and a next to those that are probably normal. Vital Sign Level of consciousness: reactive to verbal stimuli Breathing: 14, strong, and regular Pulse: 100, strong, and regular Skin: warm and pink Blood pressure: 110/60 Pupils: equal, round, and reactive to light Normal vs. Not Normal Test Your Knowledge Circle the best answer to each of the following questions. 1. If you check capillary refill and the nail bed does not return to normal colour after you release, what does this mean? a. The patient has insufficient circulation b. You pressed on the fingernail too hard c. You did not press on the fingernail hard enough d. The patient s heart is not beating 2. Which of the following should you treat before performing a secondary survey? a. A fracture/sprain of the elbow b. An impaled object through the right hand c. Severe bleeding from the left leg d. None of these should be treated until after the secondary survey 3. When doing a head-to-toe survey of an unconscious patient, you should: a. Look for medical insurance and check to see if anyone knows what happened b. Inspect the arms first as this can give you a good indication of injuries to the torso c. Ask the patient to take a deep breath in and then exhale d. Inspect the patient using sight and touch 4. When surveying the scene, which of the following should you NOT need to ask yourself? a. Is the scene safe? b. Can bystanders help? c. What might have happened? d. Do I have all the right equipment? Emergency Care Workbook 24
23 5. When forming a general impression, which of the following do you NOT need to determine? a. If the patient is ill or injured b. The patient s gender and approximate age c. If the patient takes any medications d. The patient s chief complaint 6. Which of the following would indicate a need for more advanced care? a. A 30-year-old woman who has a bruise on her leg from a soccer ball b. A 50-year-old man experiencing numbness and tingling on the right side of his body c. A 10-year-old girl who is crying because of a bee sting d. A 65-year-old man experiencing stiffness in his back after swimming 30 lengths of the pool 7. When assessing a child or baby, which of the following should you NOT do? a. Speak loudly and forcefully so she sees that you know what you are doing b. Use the child or baby s name and get down to her eye level c. Approach slowly and allow the child or baby time to get used to you d. Explain what you are doing and allow her to inspect equipment 8. What are the purposes of the primary and secondary surveys? a. Determine if the patient is in shock; identify if the patient is still in shock or if your treatment has helped b. Identify any hazards that are a threat to those at the scene; determine what else might be wrong with the patient c. Determine the initial vital signs to compare with during later monitoring; identify any allergies or medications the patient might have d. Identify conditions that are an immediate threat to life or could become an immediate threat to life; identify conditions that are not immediately life-threatening Emergency Care Workbook 25
24 Choking For Your Review Read Chapter 6 of Emergency Care, then complete the following activities. Key Terms Referring to Emergency Care, define the following terms: Airway obstruction: Finger sweep: Do You Know 1. What are the two types of airway obstruction? i. ii. What Would You Do? Read the following scenario and answer the questions below. You are called to a restaurant where someone is choking. More advanced care is also on the way. You arrive to find out the choking person has gone into the washroom to avoid embarrassment. The woman is visibly pregnant and quite far along. She is looking pale and anxious and is making high-pitched wheezing sounds. 1. After identifying yourself and explaining what you are going to do, you should: a. Get her to lie on the ground and begin chest compressions b. Stand behind the woman and begin abdominal thrusts c. Do nothing until she stops making sounds d. Stand behind the woman and alternate between five firm back blows and five chest thrusts 2. The woman goes unconscious. You protect her head and lower her to the ground. You open her airway using a head-tilt/chin-lift and check for breathing and a pulse. You find she is not breathing but has a pulse. You should: a. Attempt to give her a ventilation b. Check for a pulse c. Begin chest compressions d. Do a finger sweep of the mouth 3. At one point, your ventilation goes in and you see the chest just begin to rise. You should: a. Do 30 chest compressions b. Give another ventilation c. Roll her into the recovery position d. Recheck her ABCs 4. If you find that the woman is not breathing, but she still has signs of circulation (including a pulse), you should give her one ventilation every three to five seconds. T or F Test Your Knowledge Circle the best answer to each of the following questions. 1. You are giving care for someone who is unconscious and choking. If your FIRST breath does not go in, you should: a. Begin chest compressions b. Attempt another ventilation, with slightly more force c. Do a finger sweep of the mouth d. Re-tilt the head and attempt another ventilation 2. When performing back blows and chest thrusts on a conscious choking baby, how should you position the baby? a. On a flat surface such as a table b. Turned on her side for easy access to the back and chest c. Resting on your thigh with the head lower than the body d. Upside down so gravity has the most effect Emergency Care Workbook 26
25 Respiratory Emergencies For Your Review Read Chapter 6 of Emergency Care, then complete the following activities. Key Terms Referring to Emergency Care, define the following terms: Acute pulmonary edema: Anaphylaxis: Aspiration: Asthma: Breathing emergency: Bronchitis: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Cyanosis: Emphysema: Epinephrine: Hyperventilation: Metered-dose inhaler (MDI): Pneumonia: Pulmonary embolism: Rescue breathing: Respiratory arrest: Emergency Care Workbook 27
26 Do You Know 1. What are the signs and symptoms of a breathing emergency? 2. Respiratory Emergencies Fill in the type of emergency that corresponds to each description. Type of Emergency Description An obstruction in the airway A narrowing of the air passages 2. When is it appropriate to stop rescue breathing? A disease in which carbon dioxide/oxygen exchange is not effective Swelling of the air passages due to a reaction to an allergen A disease causing excessive mucous secretions and anti-inflammatory changes to the bronchi Breathing faster than normal Fill in the Blanks 1. Fill in the appropriate times below and indicate the significance of each time. Test Your Knowledge Circle the best answer to each of the following questions. 1. A person with anaphylaxis may carry a(n): a. Glucometer b. Epinephrine auto-injector c. Pulse oximeter d. Metered-dose inhaler 2. General care for any breathing emergency can include: a. Assisting the patient to take her prescribed medication; reassuring the patient b. Performing rescue breathing; giving high-flow oxygen c. Making the patient lie down; keeping the patient cool d. Ensuring the area is well ventilated; performing abdominal thrusts 3. After finding no breathing or a pulse and giving two one-second ventilations, what is the next step? a. Check for signs of circulation, including a pulse, for no more than 5 to 10 seconds b. Check for level of consciousness c. Continue rescue breathing d. Begin 30 chest compressions Emergency Care Workbook 28
27 4. If an unconscious patient vomits while you are performing rescue breathing, this is probably because: a. The smell of the mask is bothering the patient b. The head wasn t tilted back appropriately or you were ventilating too forcefully c. The patient had been poisoned and the ventilations caused the stomach to expel the poison d. The lungs are reacting to the positive pressure of the ventilations 5. If a patient is wearing dentures and you need to perform rescue breaths, you should: a. Always remove them; they are a choking hazard b. Always keep them in; if you take them out they will most likely get lost or broken c. Leave them in unless they have become loose; having them in will give you a better seal around the mouth d. Check the patient s wallet for a card that expresses what they want a rescuer to do with the dentures in case of emergency 6. Breathing emergencies can be life-threatening because: a. The airway is always blocked, not allowing oxygen to get to the lungs b. The process of oxygen getting into the lungs, exchanged into the blood, and getting to the body cells is disrupted c. The lungs are no longer working d. There are no treatments for breathing emergencies Emergency Care Workbook 29
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
404 Section 5 Shock and Resuscitation. Scene Size-up. Primary Assessment. History Taking
 404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation
 Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation Please do not write on this sheet. Indicate your answers on the answer sheet provided. 1. Medical control is the process by which a physician
Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation Please do not write on this sheet. Indicate your answers on the answer sheet provided. 1. Medical control is the process by which a physician
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
American Heart Association
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Technician Psychomotor Examination BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT
 BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT
 BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA
 PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
81 First Responder Respiratory
 81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPORT State Form 54407 (R / 5-13)
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough?
 IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer
 Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd. Ready Reference
 Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector
 OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK
 CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
National Registry Skill Sheets
 Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
TN Emergency Medical Services
 TN Emergency edical ODULES AND UNITS ES System ES Providers: ER and ET Safety and Wellness Body echanics System Communication Documentation Therapeutic Communication Legal and Ethical Issues Intro to Respiratory
TN Emergency edical ODULES AND UNITS ES System ES Providers: ER and ET Safety and Wellness Body echanics System Communication Documentation Therapeutic Communication Legal and Ethical Issues Intro to Respiratory
ADMINISTERING EMERGENCY OXYGEN
 FACT SHEET ADMINISTERING EMERGENCY OXYGEN Emergency oxygen can be given for many breathing and cardiac emergencies. It can help improve hypoxia (insufficient oxygen reaching the cells) and reduce pain
FACT SHEET ADMINISTERING EMERGENCY OXYGEN Emergency oxygen can be given for many breathing and cardiac emergencies. It can help improve hypoxia (insufficient oxygen reaching the cells) and reduce pain
Heart information. CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation
 Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES
 Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course
 Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
State of New Hampshire Department of Safety Division of Fire Standards and Training & Emergency Medical Services
 State of New Hampshire Department of Safety Division of Fire Standards and Training & Emergency Medical Services September 2013 PATIENT ASSESSMENT / MANAGEMENT - TRAUMA Time allowed: 10 minutes SCENARIO
State of New Hampshire Department of Safety Division of Fire Standards and Training & Emergency Medical Services September 2013 PATIENT ASSESSMENT / MANAGEMENT - TRAUMA Time allowed: 10 minutes SCENARIO
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
CHAPTER 21 QUIZ. Handout 21-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 21-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. A severe form of allergic reaction is called A. an allergen. C. epinephrine. B. anaphylaxis. D. an immune reaction. 2. Harmless
Handout 21-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. A severe form of allergic reaction is called A. an allergen. C. epinephrine. B. anaphylaxis. D. an immune reaction. 2. Harmless
2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE
 American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
3/24/2014. Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014. Why do we need a First Aid Program?
 Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
Get Trained. A Program for School Nurses to Train School Staff in Epinephrine Administration
 A Program for School Nurses to Train School Staff in Epinephrine Administration The Get Trained School Nursing Program was created through an unrestricted grant from Mylan Specialty. The Program is intended
A Program for School Nurses to Train School Staff in Epinephrine Administration The Get Trained School Nursing Program was created through an unrestricted grant from Mylan Specialty. The Program is intended
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Occupational Health and Safety. Bulletin. Quality Management Plan Requirements for First Aid Training in Alberta Workplaces
 Occupational Health and Safety Bulletin Quality Management Plan Requirements for First Aid Training in Alberta Workplaces FA010 First Aid 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Quality Management Plan (QMP)...
Occupational Health and Safety Bulletin Quality Management Plan Requirements for First Aid Training in Alberta Workplaces FA010 First Aid 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Quality Management Plan (QMP)...
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Southern Stone County Fire Protection District Emergency Medical Protocols
 TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
How To Treat A Pregnant Woman With A Miscarriage
 Special Patient Populations Obstetrics EMR Education Standard Recognizes and manages life threats based on simple assessment findings for a patient with special needs while awaiting additional emergency
Special Patient Populations Obstetrics EMR Education Standard Recognizes and manages life threats based on simple assessment findings for a patient with special needs while awaiting additional emergency
Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD)
 Goals: Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD) This program has been specifically designed to know how to use and be able to practice scenarios for Emergency Medical Dispatching. Objectives: Can explain how
Goals: Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD) This program has been specifically designed to know how to use and be able to practice scenarios for Emergency Medical Dispatching. Objectives: Can explain how
There is no cure for COPD Chronic Bronchitis Emphysema
 Live Well With COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or COPD is a lung disease. People with COPD have a hard time getting air in and out of their lungs. There is no cure for COPD. COPD is also commonly
Live Well With COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or COPD is a lung disease. People with COPD have a hard time getting air in and out of their lungs. There is no cure for COPD. COPD is also commonly
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
The administration of epinephrine for severe anaphylactic type allergic reactions. Training for Québec first aiders 2008
 The administration of epinephrine for severe anaphylactic type allergic reactions Training for Québec first aiders 2008 2 Acknowledgements AQAA St-John Ambulance Canadian Red Cross CSST Québec Heart and
The administration of epinephrine for severe anaphylactic type allergic reactions Training for Québec first aiders 2008 2 Acknowledgements AQAA St-John Ambulance Canadian Red Cross CSST Québec Heart and
What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma
 GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel
 Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
Patient Assessment/Management Trauma
 Patient Assessment/Management Trauma Date: / / Test Site Location: Station #: Takes or verbalizes standard precautions (BSI) if appropriate based on patient scenario SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the scene
Patient Assessment/Management Trauma Date: / / Test Site Location: Station #: Takes or verbalizes standard precautions (BSI) if appropriate based on patient scenario SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the scene
EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR
 I. GENERAL GUIDELINES EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR A. PURPOSE To counteract a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a foreign substance as prescribed by the licensed
I. GENERAL GUIDELINES EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR A. PURPOSE To counteract a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a foreign substance as prescribed by the licensed
1. Dosing Schedule: your customized schedule of your weekly injections as provided by the center.
 Home Immunotherapy Raza Pasha, MD Congratulations. You are now on the path to better control of your allergies. The following is your instruction guide to allow you to become more familiar with proper
Home Immunotherapy Raza Pasha, MD Congratulations. You are now on the path to better control of your allergies. The following is your instruction guide to allow you to become more familiar with proper
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle?
 What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
Chapter Review Questions
 1 Chapter Review Questions Chapter 1 1. True or false: As an Emergency Medical Responder, your first priority when responding to any emergency scene is patient care. 2. True or false: The first step in
1 Chapter Review Questions Chapter 1 1. True or false: As an Emergency Medical Responder, your first priority when responding to any emergency scene is patient care. 2. True or false: The first step in
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC
 BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES
 T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
Skills Summaries. Legend. Wear personal protective equipment. Communicate with patient or other responders. Record/document findings
 Legend Wear personal protective equipment Communicate with patient or other responders Record/document findings Follow your local protocol Treat for shock Link to another skill Six Rights of Medication
Legend Wear personal protective equipment Communicate with patient or other responders Record/document findings Follow your local protocol Treat for shock Link to another skill Six Rights of Medication
Emergency Scenario. Chest Pain
 Emergency Scenario Chest Pain This emergency scenario reviews chest pain in a primary care patient, and is set up for roleplay and case review with your staff. 1) The person facilitating scenarios can
Emergency Scenario Chest Pain This emergency scenario reviews chest pain in a primary care patient, and is set up for roleplay and case review with your staff. 1) The person facilitating scenarios can
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION. Airway must be open so oxygen can enter the body.
 CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
CPR for the Professional Rescuer
 American Red Cross Video CPR for the Professional Rescuer As a professional rescuer, you are a key part of the emergency medical service (EMS) system. Whether you are paid or volunteer, in your position
American Red Cross Video CPR for the Professional Rescuer As a professional rescuer, you are a key part of the emergency medical service (EMS) system. Whether you are paid or volunteer, in your position
5420-R STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods
 STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
PARENT/GUARDIAN REQUEST: ADMINISTRATION OF EMERGENCY EPINEPHRINE, ANAPHYLAXIS CARE PLAN/ IHP & IEHP
 IEF Elementary School 105 Andrew Street, Green Brook, N.J. 08812 School Nurse: Mrs. Ostrander Office Phone: 732-9681052 ext. # 3 Fax: 732-968-0791 Green Brook Township Public Schools Green Brook Middle
IEF Elementary School 105 Andrew Street, Green Brook, N.J. 08812 School Nurse: Mrs. Ostrander Office Phone: 732-9681052 ext. # 3 Fax: 732-968-0791 Green Brook Township Public Schools Green Brook Middle
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Frontline First Aid EMR Scenario Examples
 Course Type: Start Date: Instructors initial scenarios as they are completed CPR-AED Scenarios CPR with Hypothermia Load and Go CPR with Obstructed Airway Continue CPR after airway clears with NO obvious
Course Type: Start Date: Instructors initial scenarios as they are completed CPR-AED Scenarios CPR with Hypothermia Load and Go CPR with Obstructed Airway Continue CPR after airway clears with NO obvious
Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff
 Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present. Emergency phone numbers Dial 111 for Fire/Police/Ambulance 1. Tell
Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present. Emergency phone numbers Dial 111 for Fire/Police/Ambulance 1. Tell
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
1st Responder to Emergency Medical Responder Transition Course
 1st Responder to Emergency Medical Responder Transition Course Mandatory Training July 5, 2011 Authored by: Eddie Manley, Education Coordinator OSDH - EMS 1 st Responder to EMR Recommended Transition Course
1st Responder to Emergency Medical Responder Transition Course Mandatory Training July 5, 2011 Authored by: Eddie Manley, Education Coordinator OSDH - EMS 1 st Responder to EMR Recommended Transition Course
Types of electrical injuries
 Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES
 FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES Liability Issues. Do the right thing State provides qualified immunity Chapter 258 C, Section 13. Good Samaritan Law: No person who, in good faith, provides or obtains, or
FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES Liability Issues. Do the right thing State provides qualified immunity Chapter 258 C, Section 13. Good Samaritan Law: No person who, in good faith, provides or obtains, or
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Adult Choking and CPR Manual
 Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
First Aid as a Life Skill. Training Requirements for Quality Provision of Unit Standard-based First Aid Training
 First Aid as a Life Skill Training Requirements for Quality Provision of Unit Standard-based First Aid Training New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2010 2 Index Introduction 3 Section One: Framework outline
First Aid as a Life Skill Training Requirements for Quality Provision of Unit Standard-based First Aid Training New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2010 2 Index Introduction 3 Section One: Framework outline
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
Accident Prevention. and Crisis Management. Learning Objectives
 13 1 1 Accident Prevention 2 and Crisis Management Learning Objectives How can you prevent accidents? What should you do when a food recall or food crisis occurs? What should you do if the establishment
13 1 1 Accident Prevention 2 and Crisis Management Learning Objectives How can you prevent accidents? What should you do when a food recall or food crisis occurs? What should you do if the establishment
American Red Cross First Aid EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
Undergoing an Oesophageal Endoscopic Resection (ER)
 Contact Information If you have an enquiry about your appointment time/date please contact the Booking Office on 0300 422 6350. For medication enquiries please call 0300 422 8232, this is an answer machine
Contact Information If you have an enquiry about your appointment time/date please contact the Booking Office on 0300 422 6350. For medication enquiries please call 0300 422 8232, this is an answer machine
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan
 Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
EMR EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Course Syllabus
 6111 E. Skelly Drive P. O. Box 477200 Tulsa, OK 74147-7200 EMR EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0009 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: 9373 Course Length: 66 Hours Career Cluster:
6111 E. Skelly Drive P. O. Box 477200 Tulsa, OK 74147-7200 EMR EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0009 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: 9373 Course Length: 66 Hours Career Cluster:
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPORT
 Reset Form EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street, Room E239 Indianapolis,
Reset Form EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street, Room E239 Indianapolis,
Emergency Medical Responder Safety and Wellness
 Chapter 2 Emergency Medical Responder Safety and Wellness OBJECTIVES DIRECTORY 1. Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 55-56 2. List indications of the potential for danger to yourself or others
Chapter 2 Emergency Medical Responder Safety and Wellness OBJECTIVES DIRECTORY 1. Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 55-56 2. List indications of the potential for danger to yourself or others
In case of an urgent concern or emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency department right away.
 Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
First Aid Multiple Choice Test
 First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
Immunologic Emergencies
 Immunologic Emergencies Part 1 You and your partner are dispatched to Pioneer Park, a local recreational area where residents frequently picnic and enjoy a variety of outdoor festivities, especially during
Immunologic Emergencies Part 1 You and your partner are dispatched to Pioneer Park, a local recreational area where residents frequently picnic and enjoy a variety of outdoor festivities, especially during
Emergency Medical Technician - Basic
 Washington State Specific Objectives for Emergency Medical Technician - Basic OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL AND TRAUMA PREVENTION September 1996 Emergency Medical Technician - Basic Definition: Emergency
Washington State Specific Objectives for Emergency Medical Technician - Basic OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL AND TRAUMA PREVENTION September 1996 Emergency Medical Technician - Basic Definition: Emergency
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
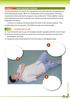 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
How To Treat A Heart Attack
 13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known
 Page 1 of 26 Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known Page 2 of 26 What s Inside Why Health Care Planning Is Important... 2 What You Can Do... 4 Work through the advance health care planning
Page 1 of 26 Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known Page 2 of 26 What s Inside Why Health Care Planning Is Important... 2 What You Can Do... 4 Work through the advance health care planning
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
Gunshot wounds. Warning: This presentation has extremely graphic pictures! Richard P. Kness, EMT- P
 Gunshot wounds Warning: This presentation has extremely graphic pictures! Richard P. Kness, EMT- P Objectives After this lesson the student will be able to: List scene safety issues Describe procedures
Gunshot wounds Warning: This presentation has extremely graphic pictures! Richard P. Kness, EMT- P Objectives After this lesson the student will be able to: List scene safety issues Describe procedures
12/5/2012. Introduction. Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries. Recognizing and Caring for Serious Head, Neck and Back Injuries
 Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector
 Lesson Guide Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 45 minutes Guidance for the Instructor To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Welcome participants and explain
Lesson Guide Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 45 minutes Guidance for the Instructor To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Welcome participants and explain
100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum
 100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum consist of not less than fifteen (15) hours in first aid and
100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum consist of not less than fifteen (15) hours in first aid and
EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR TRAINING POLICY ALLERGIC REACTION / ANAPHYLAXIS
 Page 1 of 1 EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR TRAINING POLICY ALLERGIC REACTION / ANAPHYLAXIS All members/employees of (service) affiliate number must complete DOH training module #004124 and be familiar with
Page 1 of 1 EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR TRAINING POLICY ALLERGIC REACTION / ANAPHYLAXIS All members/employees of (service) affiliate number must complete DOH training module #004124 and be familiar with
OFA 3 TO EMR BRIDGE COURSE STUDY GUIDE
 OFA 3 TO EMR BRIDGE COURSE STUDY GUIDE Frontline First Aid & Emergency Training 250-470-0205 training@frontlinefirstaid.ca www.frontlinefirstaid.ca Welcome to your Canadian Red Cross Emergency Medical
OFA 3 TO EMR BRIDGE COURSE STUDY GUIDE Frontline First Aid & Emergency Training 250-470-0205 training@frontlinefirstaid.ca www.frontlinefirstaid.ca Welcome to your Canadian Red Cross Emergency Medical
Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace
 A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
FIRST AID TEST. 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988. www.schoolbusing.com. Revised April 21, 2008 - 1 -
 FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History
 Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
IN CASE OF EMERGENCY. Emergency Telephone Number 112
 IN CASE OF EMERGENCY Emergency Telephone Number 112 Police, Fire, Ambulance Dial 112 in case of fire, medical emergency, serious or life threatening traffic or other accident. Tell the operator: What has
IN CASE OF EMERGENCY Emergency Telephone Number 112 Police, Fire, Ambulance Dial 112 in case of fire, medical emergency, serious or life threatening traffic or other accident. Tell the operator: What has
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins?
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Leader s Guide E4017. Bloodborne Pathogens: Always Protect Yourself
 E4017 Bloodborne Pathogens: Always Protect Yourself 1 Table of Contents Introduction 3 Video Overview.3 Video Outline.4 Preparing for and Conducting a Presentation. 7 Discussion Ideas..8 Quiz..9 Quiz Answers...11
E4017 Bloodborne Pathogens: Always Protect Yourself 1 Table of Contents Introduction 3 Video Overview.3 Video Outline.4 Preparing for and Conducting a Presentation. 7 Discussion Ideas..8 Quiz..9 Quiz Answers...11
KEY CAL/OSHA STANDARDS THAT APPLY TO MOST EMPLOYERS
 KEY CAL/OSHA STANDARDS THAT APPLY TO MOST EMPLOYERS FACTSHEET 1 Below are some key Cal/OSHA standards that apply to most employers: A. INJURY AND ILLNESS PREVENTION PROGRAM STANDARD (Title 8 California
KEY CAL/OSHA STANDARDS THAT APPLY TO MOST EMPLOYERS FACTSHEET 1 Below are some key Cal/OSHA standards that apply to most employers: A. INJURY AND ILLNESS PREVENTION PROGRAM STANDARD (Title 8 California
CHAPTER 32 QUIZ. Handout 32-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
