Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
|
|
|
- Phillip Baldwin
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal January 2000 Prepared by: Dr. J.F.R. Fleming Professor Emeritus, Division of Neurosurgery University of Toronto The Toronto Western Hospital Dr. J.F. Ross Fleming graduated from the University of Toronto Medical School in He did post-graduate training in neurosurgery at the University of Toronto, at the University of Michigan and at Oxford, England, from 1947 to He became a Fellow in neurosurgery in He holds the rank of Professor Emeritus in the Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, at the University of Toronto. His clinical and research interests were in neurosurgery. He has published widely in that area. He practiced at the Toronto Western Hospital as the Head of the Division of Neurosurgery from 1965 to 1984 and as staff in the Division of Neurosurgery from 1956 to Dr. Fleming was involved at the Tribunal as an assessor from 1988 to 1992, as a counsellor from 1993 to 1997 and as Chair of the medical counsellors group from 1998 to WSIAT literature search reviewed by Dr. D. Rowed in 2011, who is of the opinion that this paper still provides a balanced overview of the medical knowledge in this area. This medical discussion paper will be useful to those seeking general information about the medical issue involved. It is intended to provide a broad and general overview of a medical topic that is frequently considered in Tribunal appeals. Each medical discussion paper is written by a recognized expert in the field, who has been recommended by the Tribunal s medical counsellors. Each author is asked to present a balanced view of the current medical knowledge on the topic. Discussion papers are not peer reviewed. They are written to be understood by lay individuals.
2 Discussion papers do not necessarily represent the views of the Tribunal. A vice-chair or panel may consider and rely on the medical information provided in the discussion paper, but the Tribunal is not bound by an opinion expressed in a discussion paper in any particular case. Every Tribunal decision must be based on the facts of the particular appeal. Tribunal adjudicators recognize that it is always open to the parties to an appeal to rely on or to distinguish a medical discussion paper, and to challenge it with alternative evidence : see Kamara v. Ontario (Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal) [2009] O.J. No (Ont Div Court).
3 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The term thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) refers to symptoms caused by compression of nerves and/or blood vessels in the neck, in an area known as the thoracic outlet, through which the nerves and blood vessels travel to and from the arm. These symptoms may include arm pain, hand numbness, weakness and wasting of the hand muscles, and circulatory changes in the hand. The nerves that travel through the thoracic outlet are spinal nerves C-5,6,7,8 and T-1, which exit from the bony spinal column and travel together in a bundle called the brachial plexus to the axilla (arm pit), where they then divide into the major nerves of the arm (the ulnar, median and radial nerves). The blood vessels travelling through the thoracic outlet are the main artery and vein supplying the arm, the subclavian artery on its way from the aorta to the arm, and the subclavian vein which returns the blood from the arm to the heart. Anatomy of the thoracic outlet. The thoracic outlet is located at the side or base of the neck, above the first rib, behind the clavicle, and lateral to the bony spinal column. The nerves of the brachial plexus and the subclavian artery lie between a large muscle called the scalenus anterior (which forms the front of the thoracic outlet), and another muscle called the scalenus medius (which forms the back of the thoracic outlet), and they lie just above the first rib (which forms the bottom of the thoracic outlet). The subclavian vein lies in front of the scalenus anterior muscle, which separates it from the brachial plexus and subclavian artery. Although the thoracic outlet is a relatively confined space, it normally provides ample accomodation for its contained nerves and blood vessels. Congenital anomalies in the thoracic outlet. In some individuals there may be congenital anomalies in the thoracic outlet. These anomalies include: (1) the presence of an extra or cervical rib attached to the C-7 vertebra, and which may vary in length from a short rudimentary rib to an entire rib, and which tends to tent up the brachial plexus as it crosses this extra rib. (2) The presence of an abnormally long bony transverse process protruding from the C-7 vertebra, which tends to tent up the C-8 and T-1 nerves. The great majority of individuals who harbour these bony congenital anomalies have no symptoms. The brachial plexus and the subclavian artery adapt well to the particular configuration of the individual thoracic outlet. The presence of these bony anomalies in an individual with arm and hand symptoms does not necessarily mean that the anomalies are the cause of the symptoms. (3) The presence of an anomalous band of fibrous tissue in front of the brachial plexus. This fibrous band may compress the brachial plexus, and may sometimes be associated with symptoms. 1
4 Pathological conditions in the thoracic outlet. Whether or how much the thoracic outlet can be narrowed by swelling or overgrowth (hypertrophy) of the scalene muscles, or by swelling of adjacent ligaments or other tissues due to excessive wear and tear, repetitive awkward (e.g. overhead) movements, or by a sudden straining injury, remains speculative and controversial. The thoracic outlet may be narrowed by the presence of a tumour, such as a lung cancer involving the first rib, or by badly displaced bone fragments or excess callus formation from a fractured clavicle or a fractured first rib. The nerves in the thoracic outlet. The brachial plexus consists of both motor and sensory nerves, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibres. The motor nerves carry impulses from the brain to activate the arm and hand muscles. The sensory nerves carry touch, pain, temperature, vibration sense and joint position sense information from the fingers, hand and arm to the brain. The sympathetic nerve fibres carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord, which can constrict blood vessels and activate sweat glands in the arm and hand. Interruption or malfunction of motor or sensory nerves may result in muscle weakness and wasting, and/or impairment of sensation in the area of skin supplied by the affected nerve. Irritation of sensory nerves may result in tingling (paraesthesia) in the area supplied by that nerve. There may be an ache or a burning pain in the area supplied by the involved nerve. Only the lowest portion of the brachial plexus is affected by TOS. It consists of the C-8 and T-1 spinal nerve roots, which join together to form the lowest trunk and then the medial cord of the brachial plexus. Impaired conduction in the C-8 and T-1 nerves or the lower trunk of the brachial plexus results in weakness and wasting of the small (intrinsic) muscles of the hand, and numbness/tingling in the ring and little fingers and along the inner (ulnar) border of the palm and forearm. The extent to which the muscles are weakened and wasted, and the degree of sensory loss depends on the degree to which the nerves are impaired. Classification of TOS. TOS is not the name of a single entity, but rather a collective title for a number of conditions of variable validity (Wilbourn p.130 Muscle and Nerve Jan 99). When the signs and symptoms of TOS are due to compression of the brachial plexus nerves, the condition may be designated as neurogenic TOS (as opposed to vascular TOS). It is conceivable that a minimal degree of compression, or even irritation of the nerve fibres of the brachial plexus in the thoracic outlet, insufficient to cause any motor or sensory loss, might cause an ache, pain or discomfort in the arm, with or without a subjective feeling of tingling in the ring and little fingers. Thus, some authors have subdivided neurogenic TOS into true neurogenic TOS, in which 2
5 there is objective evidence of neurological abnormalities, and non-specific or disputed neurogenic TOS, in which there are no objective abnormal neurological findings. Disorders under the designation of true neurogenic TOS are universally accepted by the medical community; they occur very rarely, and have characteristic clinical pictures. Non-specific or disputed TOS is contentious; its proponents consider it to be very common, while skeptics believe that if it exists at all, it is exceedingly uncommon. Vascular TOS, with symptoms due to involvement of the subclavian artery, is extremely rare, and does not play a part in producing the symptoms of neurogenic TOS. Traditionally it has been believed that the subclavian artery may be compressed in the thoracic outlet in certain individuals when the shoulder and arm are being used a lot, and the thoracic outlet is presumed to become tighter due to this excess activity. In a few other individuals, the thoracic outlet was presumed to be excessively tight even at rest. Various socalled thoracic outlet compression tests * have been interpreted as confirming the presence of TOS. However, these tests are positive in as many as 50% of normal people, and are no longer considered reliable or valid in the diagnosis of TOS. It should be remembered that the flow of blood in any large artery is proportional to the fourth power of the diameter of that vessel. In other words, an extremely severe degree of narrowing of the subclavian artery would be required to cause a significant decrease in the amount of blood flowing to the arm and hand. In order to narrow the artery so severely, a marked degree of compression of the thoracic outlet would be required, and would also compress the brachial plexus so much that the patient would be seeking medical attention with obvious signs of neurogenic TOS long before signs of impaired circulation develop. Severe subclavian artery compression usually only occurs when a bony abnormality such as a cervical rib is present. When severely compressed, the artery dilates distal (downstream) to the point of compression ( post-stenotic dilatation ). This dilatation predisposes to the deposition of thrombi (blood clots) inside the artery, and these clots may break off (emboli), travel down the artery and block the small arteries in the hand and fingers, causing ischemic changes such as necrosis or gangrene. *obliteration of the radial artery pulse at the wrist when the arm is abducted and the shoulder is externally rotated (Adson test), or the reproduction of the patient s symptoms when the arm is hyperabducted or when the shoulders are braced in the military position, or during the Elevated Arm Stress Test (EAST test). 3
6 Venous. Obstruction of the subclavian vein is exceedingly rare. The subclavian vein may become blocked by a thrombus (blood clot) after unusual and prolonged exertion ( effort thrombosis ), leading to a very swollen, tender, congested limb. This is not part of the thoracic outlet syndrome. Minor degrees of subclavian vein compression do not cause any symptoms. Clinical Picture True Neurogenic TOS. In true neurogenic TOS, there is weakness and wasting of the small muscles of the hand (the intrinsic hand muscles), especially those muscles in the palm near the base of the thumb (thenar muscles), but also those on the inner side of the palm (hypothenar muscles) and those within the hand between the metacarpal bones (interosseous muscles). There is often an intermittent aching along the inner (medial) aspect of the forearm and hand, with paraesthesiae (tingling, numbness) and decreased sensitivity to touch and pin prick testing in this area. The ache and paraesthesia may be exaggerated by certain limb positions such as carrying a heavy object in the hand. The tendon reflexes in the arm (biceps, triceps and brachio-radialis) remain normal, as the nerves supplying these reflexes are located in the mid and upper portions of the brachial plexus, and are not affected by TOS. Non-specific Neurogenic TOS. In non-specific or disputed neurogenic TOS, there are no abnormal motor findings (i.e. no true muscle weakness or wasting), and no sensory findings (i.e. no decreased sensitivity to testing with touch or pin prick). If muscle weakness is reported, it is usually described as subjective or voluntary or release weakness, but there is no muscle wasting, nor is there electro-diagnostic evidence of muscle denervation. The predominant complaints are pain and sometimes tingling and numbness (paresthesiae), often in a rather diffuse and non-specific distribution in the shoulder, arm, forearm and hand. These symptoms are sometimes worse with activity or when carrying a heavy object in the hand, and sometimes persist at rest. Sometimes it is claimed that manoeuvers that are presumed to tighten the thoracic outlet, such as arm hyperabduction, the elevated arm stress test (EAST test) or the Adson test will reproduce or aggravate the pain and/or paresthesiae. In non-specific TOS, there may also be a variety of symptoms that are completely unrelated to the thoracic outlet, such as headaches. 4
7 It is now known that compression of the subclavian artery does not play a significant role in neurogenic TOS, and hence tests designed to detect subtle degrees of decreased blood flow to the hand (doppler, finger plethysmography) or manoeuvers to attempt to reproduce the patient s symptoms by compressing the subclavian artery, are no longer considered to be valid or reliable in the diagnosis of neurogenic TOS. Tenderness on pressing over the thoracic outlet above the clavicle, production of pain or numbness in the arm and hand with supra-clavicular pressure, or tingling in the hand or fingers on tapping over the brachial plexus in this region have not been shown to have any consistent reliability or validity in the diagnosis of TOS. Differential Diagnosis Other conditions that may be mistaken for TOS. Weakness and wasting of hand muscles, sensory loss in fingers, tingling and numbness in the fingers, and aches and pains in the arm, forearm and hand may be caused by a variety of neurological disorders. Of these, carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common. Carpal tunnel syndrome may co-exist with TOS, but is not a part of TOS. (The controversial issue of double crush syndrome is considered at the end of this paper). Other conditions that must be considered in the differential diagnosis of neurogenic TOS include ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow (cubital tunnel syndrome) or in the hand in Guyon s canal*, and other peripheral nerve disorders in the arm. Cervical nerve root compression (cervical radiculopathy) or cervical spinal cord disorders such as syringomyelia may also present with symptoms somewhat similar to those of neurogenic TOS. It is essential to be certain that these conditions have been considered and excluded, usually by careful history taking and analysis of the symptoms, together with a detailed neurological examination. It may also be necessary to obtain electro-diagnostic studies and/or appropriate imaging of the cervical spine by x-rays, C.T. scan or M.R.I. to rule out some of these conditions. *Guyon s canal: the tunnel at the base of the hand, just below the wrist, through which the ulnar nerve travels 5
8 Musculo-skeletal disorders in the arm, such as rotator cuff injury, tendonitis, bursitis, fibrositis and others, have to be considered as possible causes of arm pain. Careful history taking and physical examination should readily distinguish these conditions from true neurogenic TOS, but they may easily be mistaken for non-specific TOS. A variety of vascular conditions must be considered and ruled out before the diagnosis of vascular TOS can be made. These include vasospastic disorders, with inappropriate constriction of blood vessels, such as Raynaud s phenomenon, reflex sympathetic dystrophy, collagen vascular disease and arteritis. Diagnostic Tests There is no single laboratory test that can confirm the diagnosis of TOS. The diagnosis must be based on a combination of the patient s symptoms, the findings on physical and neurological examination, plus appropriate laboratory tests. Electro-diagnostic tests: Nerve Conduction Studies (NCV), Electromyography (EMG), F-Waves and Somato-Sensory Evoked Potentials (SEP). In true neurogenic TOS, there is usually decreased amplitude in the sensory and motor nerve action potentials in portions of the ulnar and median nerves, and also there is EMG evidence of denervation of hand muscles. It is not technically possible to measure nerve conduction across the brachial plexus because of its deep location in the neck. However, F-wave measurement is a technique that attempts to measure conduction across the plexus, by sending impulses anti-dromically (backwards) up the motor nerves and across the plexus; in true neurogenic TOS, the F-wave may show slowed conduction, but there is usually already sufficient clinical and EMG evidence to support the diagnosis, making this test superfluous. In non-specific TOS, there are no consistent or reliable electro-diagnostic abnormalities. Of course, electro-diagnostic tests are essential in ruling out other neurologic abnormalities in the arm, such as CTS or ulnar nerve entrapment. Somato-sensory evoked potentials (SEP) are measured by scalp electrodes when an electrical stimulus is applied to the skin over a nerve in the arm. SEP show delayed conduction or decreased amplitude when there is already clinical, NCV and EMG confirmation of true neurogenic TOS. SEP findings in non-specific neurogenic TOS have been inconsistent, and have not been shown to be reliable. 6
9 Imaging. Plain cervical spine x-rays and chest x-ray are useful in demonstrating the presence of a cervical rib or an unusually long C-7 bony transverse process, and also help to rule out a destructive tumor involving the first rib or other surprise pathology. CT scan and M.R.I. of the thoracic outlet have not been shown to have benefit in evaluating the size or shape of the thoracic outlet, nor the ability to consistently show the presence of a constricting fibrous band. CT and M.R.I of the cervical spine are helpful in evaluating the cervical spinal column and its contained nerve roots and spinal cord, where a potential lesion that is causing symptoms mimicking TOS might be found. Arterial doppler flow studies and plethysmographic studies have been advocated in the past by those who believed that TOS is due to compromise of the subclavian artery as well as the brachial plexus; as noted above, most experts today find these tests of little value. Arteriography (injection of radio-contrast material directly into the artery and then taking x-rays) is important in the diagnosis of vascular TOS as it clearly visualizes the condition of the subclavian artery. In the past, arteriography has been used in an attempt to demonstrate if narrowing of the artery at the thoracic outlet occurs when the arm is placed in hyperabduction. However, it is an invasive tests, and unnecessary in true neurogenic TOS, which can be diagnosed by simpler means. Venography (the injection of radio-contrast material into an arm vein, followed by x-rays) is only of value in the diagnosis of the very rare condition effort thrombosis of the subclavian vein, and not in the diagnosis of TOS. In the past, attempts were made to establish a diagnosis of TOS by performing venography with the arm placed in hyperabduction; constriction of the vein with the arm held in this position was presumed to indicate a narrow thoracic outlet and therefore confirm the diagnosis of TOS. However there is no reliable evidence to support this theory, and venography is no longer considered to be of any value in the diagnosis of TOS. The role of arteriography and venography in non-specific or disputed TOS is unproven, and their use in this context is probably unjustified. Management Neurogenic TOS, with wasting and weakness of hand muscles and/or sensory loss and/or severe pain, usually requires surgical treatment. Vascular TOS, with evidence of impaired circulation in the arm or hand, also requires surgery. In non-specific or disputed TOS, the very existence any organic basis in the thoracic outlet is unproven, and there is no reliable evidence to support a role for surgery for this condition. 7
10 Decompression of the brachial plexus in the thoracic outlet may be accomplished by a variety of surgical approaches. Removal of the first rib by approaching it through the axilla has been very popular in the past. However it is a major operation, and has a significantly high rate of complications, including damage to the brachial plexus, as well as a high incidence of failure to relieve symptoms. First rib removal is being performed much less often nowadays, as it is being recognized that the brachial plexus can be much better visualized and decompressed by a direct anterior neck approach, through which compressing fibrous bands or muscles can be directly seen and divided. The first rib itself probably does not contribute to brachial plexus compression, nor compromise the lower part of the plexus which happens to travel over it. Cervical ribs are removed by the anterior neck approach. The results of surgery for true neurologic TOS are generally good; the progression of muscle wasting and sensory loss is usually halted, and pain is usually relieved. The results of surgery for non-specific or disputed TOS are mixed, and quite often unfavorable, probably because different surgeons have different views on what does or what does not constitute TOS, and there are no clear diagnostic criteria or standards for this condition. Therefore patients in this category undergoing surgery represent a mixed group with a variety of pathologies, or possibly even no organic pathology, and good clinical studies of the surgical results cannot be done. Conservative management is preferable for non-specific or disputed TOS, except in extremely rare situations. 8
11 Figure 1 - Front view of neck showing brachial plexus traveling between scalene muscles and over first rib 9
12 Bibliography Dawson DM, Hallet M and Wilbourn AJ: Entrapment Neuropathies, 3rd edition. Lippincott - Raven, Philadelphia, Chapter 8, pages Kline DG and Hudson AR. Nerve Injuries, Operative Results for Major Nerve Injuries, Entrapments and Tumors, WB Saunders Company, Chapter 17, pages Leffert RD: Chapter 52 in Omer GE, Spinner M and Van Beek Al: Management of Peripheral Nerve Problems, 2nd edition, WB Saunders Company, 1998, pages Roos DB: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome is Underdiagnosed. Muscle and Nerve, January 1999, pages Wilbourn AJ: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome is Overdiagnosed. Muscle and Nerve, January 1999 pages Wilbourn AJ: Thoracic Outlet Syndromes. Neurological Clinics, Volume 17, August 1999, pages
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries
 1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES I. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME TOS is a compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, in the thoracic outlet region, which is the space between the collarbone
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES I. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME TOS is a compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, in the thoracic outlet region, which is the space between the collarbone
CONSTRUCTION WORK and CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS
 Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys
 Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain
 Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy. What to do with arm pain? Defining Arm Pain. Arm Pain
 Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual
 Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI
 CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION
 CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy
 Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
.org. Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Color Doppler and Duplex Sonography in 5 Patients With Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
 Case Series Color Doppler and Duplex Sonography in 5 Patients With Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Raju Wadhwani, DMRD, DNB, Nitin Chaubal, MD, Rajan Sukthankar, MD, Manu Shroff, MD, Sanjay Agarwala, MS Purpose.
Case Series Color Doppler and Duplex Sonography in 5 Patients With Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Raju Wadhwani, DMRD, DNB, Nitin Chaubal, MD, Rajan Sukthankar, MD, Manu Shroff, MD, Sanjay Agarwala, MS Purpose.
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options
 Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario
 Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy. Adam P. Smith, MD
 Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
APPENDIX F INTERJURISDICTIONAL RESEARCH
 Ontario Scheduled Presumption: Bursitis, listed in Schedule 3, of the Ontario Workers Compensation Act, entry number 18 Description of Disease Bursitis Process Any process involving constant or prolonged
Ontario Scheduled Presumption: Bursitis, listed in Schedule 3, of the Ontario Workers Compensation Act, entry number 18 Description of Disease Bursitis Process Any process involving constant or prolonged
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 286 17 TH JUNE 2013 Dr Sandeep Kusre, Dr Richard Telford Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital, United Kingdom Correspondence to skusre83@gmail.com QUESTIONS
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 286 17 TH JUNE 2013 Dr Sandeep Kusre, Dr Richard Telford Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital, United Kingdom Correspondence to skusre83@gmail.com QUESTIONS
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California.
 Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California. In this issue, we focus on a 23-year-old female patient referred by her
Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California. In this issue, we focus on a 23-year-old female patient referred by her
Carpal Tunnel Release. Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist
 Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation.
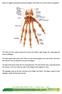 Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation. The hand and wrist contain twenty-seven bones and tendons, eight carpals, five metacarpals and fourteen
Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation. The hand and wrist contain twenty-seven bones and tendons, eight carpals, five metacarpals and fourteen
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1602/11
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1602/11 BEFORE: M. M. Cohen: Vice-Chair HEARING: August 16, 2011 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: August 23, 2011 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2011
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1602/11 BEFORE: M. M. Cohen: Vice-Chair HEARING: August 16, 2011 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: August 23, 2011 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2011
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders
 Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Cumulative trauma disorders can be classified as: What is CTD?
 #425 Lean-ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs, Part 2 of 2 Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Govid Bharwani, Ph.D, Biomedical Engineering Thursday,
#425 Lean-ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs, Part 2 of 2 Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Govid Bharwani, Ph.D, Biomedical Engineering Thursday,
The Central Nervous System
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Spinal strokes This fact sheet provides information on spinal strokes. Our fact sheets are designed as general introductions to each subject and are intended to be
A fact sheet for patients and carers Spinal strokes This fact sheet provides information on spinal strokes. Our fact sheets are designed as general introductions to each subject and are intended to be
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care. Table of Contents:
 Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Surgery for cervical disc prolapse or cervical osteophyte
 Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: paul@pauldurso.com
Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: paul@pauldurso.com
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG), NEEDLE, NERVE CONDUCTION STUDIES (NCS) AND QUANTITATIVE SENSORY TESTING (QST)
 AND QUANTITATIVE SENSORY TESTING (QST) Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
AND QUANTITATIVE SENSORY TESTING (QST) Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions *
 ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
CTS the Best EDX. Ernest W Johnson MD Emeritus Professor Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation The Ohio State University
 CTS the Best EDX Ernest W Johnson MD Emeritus Professor Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation The Ohio State University 1 Definition of CTS A syndrome 2d to dysfunction of median nerve in carpal tunnel resulting
CTS the Best EDX Ernest W Johnson MD Emeritus Professor Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation The Ohio State University 1 Definition of CTS A syndrome 2d to dysfunction of median nerve in carpal tunnel resulting
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist
 Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Electrodiagnostic Testing
 Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Significant nerve damage is uncommonly associated with a general anaesthetic
 Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 10: Nerve damage associated with an operation under general anaesthetic Section 10: Significant nerve damage is uncommonly associated with a general anaesthetic
Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 10: Nerve damage associated with an operation under general anaesthetic Section 10: Significant nerve damage is uncommonly associated with a general anaesthetic
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report
 Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)
 Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist
 http://www.pdratings.com/ AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist [L.C. 139.2 (J)-(2)&(3), (k)-(5), 4060(b)(1), 4062 (d)(2), 4068, 4620, 8 CCR WCAB 10606 & 8 CCR 9785] AMA Brachial
http://www.pdratings.com/ AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist [L.C. 139.2 (J)-(2)&(3), (k)-(5), 4060(b)(1), 4062 (d)(2), 4068, 4620, 8 CCR WCAB 10606 & 8 CCR 9785] AMA Brachial
How To Know If You Can Get A Carpal Tunnel Injury Compensation
 U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of BARBARA SNYDER and DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY, INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE, Germansville, PA Docket No. 03-1467; Submitted on
U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of BARBARA SNYDER and DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY, INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE, Germansville, PA Docket No. 03-1467; Submitted on
Medical Report Checklist: Upper Extremities Peripheral Nerve Disorders Impairments (PND)
 http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
Patient Information. Posterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician
 EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NUMBER F205928 DOUGLAS EUGENE WHIPKEY, EMPLOYEE CLAIMANT XPRESS BOATS, EMPLOYER RESPONDENT
 BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NUMBER F205928 DOUGLAS EUGENE WHIPKEY, EMPLOYEE CLAIMANT XPRESS BOATS, EMPLOYER RESPONDENT CONTINENTAL CASUALTY CO., INSURANCE CARRIER RESPONDENT
BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NUMBER F205928 DOUGLAS EUGENE WHIPKEY, EMPLOYEE CLAIMANT XPRESS BOATS, EMPLOYER RESPONDENT CONTINENTAL CASUALTY CO., INSURANCE CARRIER RESPONDENT
SHOULDER PAIN. Procedures: Subacromial, Glenohumeral and Acromioclavicular Injections Nonprocedural Treatments
 SHOULDER PAIN Anatomy Conditions: Muscular Spasm Pinched Nerve Rotator Cuff Tendonitis Procedures: Subacromial, Glenohumeral and Acromioclavicular Injections Nonprocedural Treatments Surgery: Rotator Cuff
SHOULDER PAIN Anatomy Conditions: Muscular Spasm Pinched Nerve Rotator Cuff Tendonitis Procedures: Subacromial, Glenohumeral and Acromioclavicular Injections Nonprocedural Treatments Surgery: Rotator Cuff
Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, The Cervical Spine. What is the Cervical Spine?
 Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness in the neck, shoulders, arms, and even hands. This patient
Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness in the neck, shoulders, arms, and even hands. This patient
Thoracic and Chest Pain Anatomy Risk Factors and Prevention Posture: Increased thoracic curve
 Thoracic and Chest Pain The thoracic spine is the region of the spine least likely to be injured in sport when compared to the cervical and lumbar region. However, this region can contribute to lumbar
Thoracic and Chest Pain The thoracic spine is the region of the spine least likely to be injured in sport when compared to the cervical and lumbar region. However, this region can contribute to lumbar
Elbow Examination. Haroon Majeed
 Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Traumatic injuries SPINAL CORD. Causes of Traumatic SCI SYMPTOMS. Spinal Cord trauma can be caused by:
 Traumatic injuries SPINAL CORD Jennie Trkulja RN, BScN, ENC (c) Causes of Traumatic SCI Spinal Cord trauma can be caused by: MVC (most injuries) Gunshots Falls Stabbings Assaults Industrial accidents Sports
Traumatic injuries SPINAL CORD Jennie Trkulja RN, BScN, ENC (c) Causes of Traumatic SCI Spinal Cord trauma can be caused by: MVC (most injuries) Gunshots Falls Stabbings Assaults Industrial accidents Sports
Get Rid of Elbow Pain
 Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Disclosure: I have nothing to disclose
 Disclosure: I have nothing to disclose Pectoralis Minor Syndrome Definition Hand and arm symptoms due to Compression of Axillary neurovascular bundle by Pec Minor Muscle Pectoralis Minor Syndrome Short
Disclosure: I have nothing to disclose Pectoralis Minor Syndrome Definition Hand and arm symptoms due to Compression of Axillary neurovascular bundle by Pec Minor Muscle Pectoralis Minor Syndrome Short
Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures
 Arcata Chiropractic Office Larry J. Kleefeld D.C. Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures Introduction Compression fractures are the most common type of fracture
Arcata Chiropractic Office Larry J. Kleefeld D.C. Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures Introduction Compression fractures are the most common type of fracture
Objectives. Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment. Level of Fracture. Neuro exam Muscle Grading
 Objectives Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment Johannes Bernbeck,, MD Review and apply the understanding of incidence and etiology of VCF. Examine conservative and operative management
Objectives Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment Johannes Bernbeck,, MD Review and apply the understanding of incidence and etiology of VCF. Examine conservative and operative management
Spinal Surgery 2. Teaching Aims. Common Spinal Pathologies. Disc Degeneration. Disc Degeneration. Causes of LBP 8/2/13. Common Spinal Conditions
 Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS Dr. Sahni B.S Dy. Chief Medical Officer, ONGC Hospital Panvel-410221,Navi Mumbai,India Introduction The cervical spine consists of the top 7 vertebrae of the spine. These are referred
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS Dr. Sahni B.S Dy. Chief Medical Officer, ONGC Hospital Panvel-410221,Navi Mumbai,India Introduction The cervical spine consists of the top 7 vertebrae of the spine. These are referred
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Ms. Jackson is the Manager of Health Finance and Reimbursement, Division of Health Policy and Practice Services, Washington, DC.
 Electrodiagnostic Testing with Same Day Evaluation Management By: Shane J. Burr, MD; Scott I. Horn, DO; Jenny J. Jackson, MPH, CPC; Joseph P. Purcell, DO Dr. Burr practices general inpatient and outpatient
Electrodiagnostic Testing with Same Day Evaluation Management By: Shane J. Burr, MD; Scott I. Horn, DO; Jenny J. Jackson, MPH, CPC; Joseph P. Purcell, DO Dr. Burr practices general inpatient and outpatient
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011
 Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Spine Injury and Back Pain in Sports
 Spine Injury and Back Pain in Sports DAVID W. GRAY, MD 1 Back Pain Increases with Age Girls>Boys in Teenage years Anywhere from 15 to 80% of children and adolescents have back pain depending on the studies
Spine Injury and Back Pain in Sports DAVID W. GRAY, MD 1 Back Pain Increases with Age Girls>Boys in Teenage years Anywhere from 15 to 80% of children and adolescents have back pain depending on the studies
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
GUIDANCE AND PROCEDURE FOR HAND ARM VIBRATION
 Department of Human Resources GUIDANCE AND PROCEDURE FOR HAND ARM VIBRATION 1.0 What is Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS)? Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS) is a widespread industrial disease. The Health
Department of Human Resources GUIDANCE AND PROCEDURE FOR HAND ARM VIBRATION 1.0 What is Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS)? Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS) is a widespread industrial disease. The Health
BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION
 BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION BARBARA SHEREE HUTSON ) Claimant ) ) VS. ) Docket No. 1,035,700 ) CUSTOM CAMPERS, INC. ) Self-Insured Respondent ) ORDER Claimant
BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION BARBARA SHEREE HUTSON ) Claimant ) ) VS. ) Docket No. 1,035,700 ) CUSTOM CAMPERS, INC. ) Self-Insured Respondent ) ORDER Claimant
Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions. Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789)
 Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789) Neck Pain Human Spine 25 bones Cervical (7) Thoracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Human Spine
Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789) Neck Pain Human Spine 25 bones Cervical (7) Thoracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Human Spine
Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds
 Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds Training conducted by: Michael Fishman and Sandrine Fisher 1 Objectives To become familiar with the application of the rating
Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds Training conducted by: Michael Fishman and Sandrine Fisher 1 Objectives To become familiar with the application of the rating
WORKCOVER DIVISION Case No. A12596889 --- S GARNETT LATROBE VALLEY REASONS FOR DECISION ---
 !Undefined Bookmark, I IN THE MAGISTRATES COURT OF VICTORIA AT LATROBE VALLEY WORKCOVER DIVISION Case No. A12596889 LEE ANNE SHEARS Plaintiff v STATE OF VICTORIA Defendant --- MAGISTRATE: S GARNETT WHERE
!Undefined Bookmark, I IN THE MAGISTRATES COURT OF VICTORIA AT LATROBE VALLEY WORKCOVER DIVISION Case No. A12596889 LEE ANNE SHEARS Plaintiff v STATE OF VICTORIA Defendant --- MAGISTRATE: S GARNETT WHERE
Basic Concepts. Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG. Pathophysiology. Median Nerve. A Clinical Approach
 Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
