Anatomy Viva Questions: Anatomy Unit 1: Anatomy Unit 2: Viva Questions. Viva Questions. Moore 6 th Edition. No Questions
|
|
|
- Emory Willis
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy : Moore 6 th Edition Anatomy Unit 1: No Questions Anatomy Unit 2: X-ray shoulder. Point out features (2/98, 2/98, 2/01) pg X-ray elbow. pg Features. Capsular and ligamentous attachments. (1/97, 2/03, 2/04) Vascular relations and ossification order. (2/04) X-ray hand and wrist. Identify bones. (2/05) pg X-ray hand and wrist. Features identify bones (1/97, 2/99, 2/03, 2/05) pg Blood supply of scaphoid. (2/99) pg 686 Ligamentous attachments. (2/03) Bone clavicle. Relations and muscular attachments. Surface anatomy of subclavian vein. (1/95, 2/02, 1/04, 1/09) pg Bone scapula. Attachments, rotator cuff. (1/98, 1/05, 2/06) pg 675 Bone humerus. Pg Features. (2/95, 2/98, 1/03, 2/07, 2/09) Common fracture sites and position of nerves relative to these SN, radial groove, supracondylar. (1/06) Bone radius. Features, extensor tendons at the wrist. (1/95, 1/00, 2/02, 1/04) pg Bone ulna. Features (proximal), stability (1/00, 2/00, 1/03) pg 678 Bone ulna and humerus: landmarks and articulation of elbow. (1/06) Bone articulated carpus. Features, positions and relations of the flexor retinaculum. (2/96, 1/05, 1/08, 2/09) pg 680 Photo upper limb. Venous structures and drainage of the upper limb. (1/10) pg Describe the lymphatic drainage of the upper limbs. (1/09) pg 692 Sensory innervation of the upper limb, including both dermatomal distribution and peripheral nerves. (2/04, 2/07, 2/08) pg
2 Anatomy Unit 3: Model shoulder. Discuss the insertion and actions of the muscles of the pectoral girdle. (1/04) pg Model arm. What muscles and nerves are involved in shoulder movement? (1/01, 1/02) pg Photo axilla. Demonstrate the boundaries and content of the axilla. (2/00) pg Point out the detail of the brachial plexus. (1/97, 1/99, 2/02, 2/04, 1/10) pg Tell me about the median nerve. (2/00) Describe the structure of the brachial plexus. The muscle groups supplied by the terminal branches of the brachial plexus to the upper limbs. (2/07) Anatomy Unit 4: Photo arm. Tell me about biceps. (1/00) pg 731 Radial nerve: pg 738 Describe a lesion. (2/04) Surface markings, course and branches in the upper arm (1/07) Model + Photo cubital fossa. Pg Name the boundaries and contents. (1/95, 2/96, 2/98, 1/06, 2/08) Surface anatomy of boundaries (1/08) Relations of the brachial artery (2/08) Median nerve relationships and course. (2/05) Describe the acromio-clavicular and coraco-clavicular joints. (1/97) pg 796 Model + X-ray shoulder. pg Tell me about the shoulder joint. (1/97, 2/01) Discuss movement and nerves involved. (2/01, 2/02) Capsular attachments, ligament and movements of the glenohumeral joint. (2/07) Point out features, describe the stabilising factors of the shoulder joint. (2/98, 2/98, 2/01) Model elbow. pg Tell me about the elbow joint, stability. (1/99)
3 Discuss the mechanics of pronation and supination. (2/03) Name the features. Discuss flexion and extension. (1/01, 1/02, 2/04) Vascular relationships, order of ossification. ( 2/04) Anatomy Unit 5: Model forearm. Volar surface name muscles, flexor retinaculum, palmar muscles. (2/95, 2/97) pg Forearm flexors and distal insertions (2/06) pg Tell me about the muscles responsible for pronation and supination. (1/00, 2/03) pg 750, 756 Discuss extension of the forearm. (2/97, 1/00, 2/09) pg X-ray: elbow. Bony features of the joint. Extensor muscles of the forearm, origins, common extensor tendon (2/08) X-ray: wrist. Ligaments of the carpus and wrist (2/05) pg 754 X-ray hand and wrist. Boundaries and contents of snuff box. (2/04, 1/07) pg 757 Photo: wrist. Extensor retinaculum and the structures that run under it. (1/07, 1/09, 2/09) pg 754 Photo median nerve: position and distribution of median nerve distal to the elbow (2/05, 1/07, 1/08) pg 761 Photo dorsum hand. Extensor mechanism. (1/96) pg 755 Describe the flexor retinaculum and the structures bound by it (2/06) pg 753 Describe the venous drainage of the upper limb. (2/99, 1/03) pg 760 Anatomy Unit 6: Revision Week Anatomy Unit 7: Model forearm. Flexion of a finger, nerve supply of muscles involved. (1/01, 1/02, 1/05) pg 777
4 Photo wrist and hand. Name features, flexor tendons. (1/95, 1/96, 1/98, 2/99) pg 775 Attachments of flexor retinaculum, contents of carpal tunnel. (2/98) pg 791 Describe the palmar spaces and their relationships to the long flexor tendons (1/09) pg 773 Describe the innervation of the muscles of the thumb, and it s movements. (1/98, 2/99, 2/01, 1/05) pg Describe the actions of the interossei and the lumbricals, and their innervation. (2/03) pg 777 Demonstrate the surface anatomy of the carpal tunnel and anterior wrist. (1/99, 1/99, 2/02, 1/03, 1/04) pg Surface anatomy of the dorsum of the hand and wrist (1/07) pg 787 Describe the arterial supply of the hand. (2/03) pg 781 Describe the sensory innervation of the hand. (2/00, 2/02) pg Anatomy Unit 8: Bone/X-ray pelvis. Pg Hip joint, ligaments and pubis. (2/96, 2/98, 1/99, 1/08) Inguinal ligament and relations. (1/96, 1/98, 1/99, 2/02) Bony landmarks, path of ureters. (1/04, 2/05, 1/08, 1/10) Muscle attachments of movers of the hip (1/08, 1/10) Relationships of greater notch/sciatic nerve (2/05) Bone femur. Features, blood supply of head and neck, capsular attachments (1/95, 2/98, 1/05, 2/07, 1/10) pg Bone femur/tibia. Articulation and knee ligaments (1/06) Landmarks and capsular attachments. (1/06) Bone tibia/fibula. Pg Features, ligaments, capsular attachments of plateau (1/96, 2/08) Proximal tib-fib joint, relations of the proximal fibula (2/08) Model/X-ray ankle. Pg Bony structures (1/07, 2/07, 2/09) Relations of the medial malleolus (1/07, 2/07, 1/08) Bone articulated foot. Pg Tendon insertions of the muscles of the posterior and lateral compartments of the leg (1/97, 2/09)) Bones of the medial and longitudinal arches, factors contributing to stability of the arches. (1/09, 2/09) Superficial venous drainage of the lower limb (1/10) pg Surface markings of the great saphenous vein. (2/04) pg 534
5 Discuss sensory innervation of the lower leg and foot, both peripheral nerve and dermatome. (2/02, 1/03, 1/05, 1/07) pg Reflex innervation of the lower limb. (2/99) pg 559,607,625 Myotomes of the lower limbs. (2/99, 2/00, 2/04, 1/05, 1/06) pg 539 Myotomes of inversion and eversion. (2/00) pg 539 Anatomy Unit 9: Model knee. Quadriceps (2/06) pg Model/Photo femoral triangle. Pg 551 Features, boundaries, contents. (2/96, 1/00, 1/08, 2/09) Features, inguinal ligament. (1/98) Origin, relations and distribution of the femoral nerve. (1/01, 1/02, 2/04) Origin and distribution of the femoral artery. (1/01, 1/02) Relationships and course of the femoral artery. (2/05, 1/06) Femoral nerve (1/06) pg 552 Photo adductor canal. Contents. (1/97) pg 556 Bone/Model/Photo hip joint. pg Articulation of the hip joint, factors that increase stability (2/07) Tell me about the hip joint. (1/96, 2/98) Stability and movement. (2/03) Relations. (2/98) Anatomy Unit 10: Photo posterior thigh. Pg 567 Identify the structures. (2/02, 1/06) Course and distributions of the sciatic nerve. (1/04, 1/07, 2/08) pg 574 Branches, relations of nerve. (1/97, 1/07, 2/08) pg 574 What are the surface markings of the sciatic nerve in the thigh? pg 580 Model/X-ray knee joint. Stability of the knee joint. (2/95, 2/97, 1/00, 2/04, 2/05, 1/08) pg Capsular attachments (1/06) pg 636 Features, origin and insertion of ligaments. (1/00, 1/03, 2/05, 1/06, 1/09) pg Movement and locking. (2/03, 2/04, 1/09) pg 642
6 Bursae locations and functions (1/09) pg Patellar stability (2/06) Anatomy Unit 11: Photo popliteal fossa. Features, boundaries, contents. (1/98, 2/99, 2/01, 2/08) pg Photo anterior compartment. Neurovascular. (1/99) pg Model/Photo lateral compartment. Neurovascular. (1/99) pg Fibularis muscles O+I, actions and nerve supply (1/09) pg 590 Muscles/nerves involved in inv/ev of the foot (2/00) pg 591, 595 Model/Photo posterior leg. Features. (1/97, 2/01) pg Attachment of Achilles tendon (2/05) pg Muscles, nerves and blood supply of the calf (2/00) Muscles/nerves involved in flex/ext of the foot. (2/00) 589/591/597 Describe a common fibular nerve lesion. (2/04) pg 605 Anatomy Unit 12: Photo dorsum of the foot. Features. (2/98) pg 614 Model leg. Pg Muscles involved in flexion and extension of the foot. (2/00) Muscles involved in inversion and eversion of the foot. (2/00) Sensory innervation of the foot (2/02, 2/03, 1/05) pg 618 Bone/Model/Photo/X-ray ankle Bony landmarks, nerves. (1/03, 1/05) pg 647 Medial features. (1/95, 2/96) pg 650 Lateral features, extensor tendons. (2/97, 2/98, 2/99) pg 649 Attachments of superior and inferior extensor retinaculum and the structures passing below them. (2/07) pg 590 Ligamentous stability and attachments. (1/01, 1/02, 2/03, 1/05, 1/06, 2/06) pg Neurovascular structures that pass over and around the joint. (2/07) Surface relations of structures around the ankle. (2/04) pg 623 X-ray foot. Features, mid-tarsal joint. (2/95, 2/99) pg 651
7 X-ray foot. Stability of the arch. (1/01, 1/02) pg 654 Anatomy Unit 13: Revision Week Anatomy Unit 14: Bone first rib. Features, relationships of nerves and vessels (2/05, 1/07) pg 76 Muscle attachments (1/07) pg 89 Layers passed through for a needle thoracostomy (1/07) pg 90, 121 Bone rib. Landmarks (1/97, 2/04) pg Rib articulations and joints (1/07) pg Chest wall Muscles of the anterior thoracic wall. (1/96, 1/08) pg 88 Tell me about the contents of a typical intercostal space. (1/96, 2/04) pg 90 Course and relationships of the neurovascular bundle (1/08) pg 92, 95, 97 Anatomy Unit 15: Lung features (hila) (1/97) pg Insertion of ICC landmarks (1/06) pg 121 Chest X-ray. Pleura and lung surface markings. (2/99, 1/05, 2/09) pg Features (1/95, 1/98, 1/99, 2/00, 2/02, 1/03, 1/05 1/07, 2/08) pg Anatomy Unit 16: Model heart. Chambers and valves (2/05, 2/08) pg
8 Structure, tell me about the coronary circulation. (1/97, 1/01, 1/02, 2/02, 1/04, 1/05, 1/07, 1/08, 1/10) pg Venous drainage (1/08) pg 148 Conducting system (2/08) pg Blood supply of the conducting system (1/06) pg 149 Anatomy Unit 17: Photo - arch of the aorta. Relations. (1/96, 2/96) pg Model heart. Pg 164 Great vessels, branches, ductus arteriosus. (2/04) Photo thoracic inlet. Pg , Features. (1/00, 2/07) Venous drainage of the head and upper limb. (2/01, 2/03) Arterial supply of the head and upper limb. (2/01, 2/04, 2/06) Thoracic aorta and its branches and area of supply (2/07) Vascular structures, branches of the subclavian artery (1/09, 2/09) Surface anatomy of the heart (2/08) pg Anatomy Unit 18: Revision Week Anatomy Unit 19: Photo anterior triangle of the neck. Pg 990 Boundaries and contents, carotid. (1/95, 2/99, 1/05, 1/07, 2/08) Sternomastoid relationships. (1/05) pg 989 Boundaries of posterior triangle (2/08) pg 990 Carotid sheath vessels and relationships (2/96) pg 1000 Photo neck. Relations, branches and supply of carotid artery (2/06, 2/08) pg Relationships of IJV (2/05) pg 1004 Surface anatomy of the neck: anterior triangle, thyroid gland, carotid bundle (1/09) pg 1005
9 Anatomy Unit 20: Model larynx. Features, movements (2/08, 1/10) pg 1023 Structure, compare adult with child. (2/04) pg 1024 Muscles of vocalization, nerve supply (1/08, 2/08, 1/10) pg 1025 Superficial neck muscles. (2/95, 1/98) pg 1027 Cartilages and intrinsic muscles. (2/99, 2/02, 2/08) pg Model neck. Tongue, palate, pharynx. (1/98) pg X-ray: lateral neck. Relationships of anterior cartilage structures to cervical levels (1/07) pg 1033 Soft tissue landmarks of pharynx, larynx and oesophagus (1/07) pg 1040 Anatomy Unit 21: Bone/X-ray mandible. Features. (2/97, 2/99, 2/01) pg 824, 827 Bone skull. Facial bones. (2/04) pg Bone base of skull. (2/95) pg Xray face. Features of zygomatic bone. (2/01) pg 823, 825 Features. (2/97, 1/98, 1/00, 2/04) pg 841 Photo side of the face. Muscles and innervation. (2/03) pg , 853 Sensory innervation of the face. (1/99, 1/00, 1/03, 1/05, 1/06) pg Infraorbital nerve. (1/00, 2/04, 2/05, 1/10) pg 851 Intra and extraorbital path of infraorbital nerve (2/08) pg 851 Distribution and relations of the facial nerve. (1/95, 2/96, 2/98, 2/98, 1/04, 2/05, 2/06) pg Demonstrate the blood supply of the face. (1/99, 2/00) pg Facial vein and venous drainage of the face (1/07) pg
10 Anatomy Unit 22: CT head Outline the structures of the cerebellum (1/09) pg 879 Trace the ventricular system of the brain (2/07) pg Describe visible intracranial structures (2/07, 2/09) pg 881 Area and functions supplied by middle cerebral artery (2/07) pg 885 Arteries of posterior circulation and areas supplied (1/09) pg 885 Secretion, circulation and absorption of CSF (2/07) pg Arterial circle of Willis and the areas of brain supplied (2/06, 2/08, 1/10) pg Bone/Xray face. Fissures (2/08) pg 889 Bones that form the orbit (2/05, 2/06, 2/08, 1/10) pg Model eye. Structures (1/05, 1/06) pg 890 Control of pupil, reflexes. (1/05, 2/06) pg 896, 911 Drainage of aqueous humour (1/06) pg 897 Extraocular muscles and eye movements. (2/01, 1/05, 2/07, 2/09) pg , 904 Anatomy Unit 23: Bone/Model/X-ray mandible. Movements, TMJ. (1/05) pg 916 Bony features (1/08) pg Attachments of muscles of mastication (2/00, 1/05, 1/08) pg 918 Face temporal region (1/95) pg 916 Upper airway tongue, palate (1/98) pg 938, 940 Model neck Muscles, blood supply, nerves and lymph drainage of the tongue (1/01, 1/02, 1/08) pg
11 Anatomy Unit 24: Revision Week Anatomy Unit 25: Photo ear. Sensory innervation. (1/00) Cranial nerve palsies. (1/05) pg 913 Anatomy Unit 26: Cervical spine X-ray features (1/96, 2/97, 2/02) pg Stability (2/99, 1/05) pg 446 Flexion, extension and rotation of the head (2/00) pg 467 PEG view (2/02, 1/06) pg 468 Components of the soft tissue shadow. (2/07) Bone C6 (2/99) pg 445 Articulation (2/04) pg 444 Bone C2 (2/97, 2/03, 2/09) pg 445 Ligaments (2/99, 2/07, 2/09) Movement with C1 and stability of joint (2/00, 2/03, 2/07) pg 446 Bone thoracic vertebra. (1/07, 1/09) pg 448 Stability and movement. (2/00, 2/03, 1/07) pg 470 Rib articulations. (2/03) pg 446 Posterior ligament attachments (1/09) Bone lumbar vertebra. Features, stability. (1/95, 1/96, 1/01, 1/02, 2/03, 2/05, 1/07) pg 450 Articulation. (2/98, 2/05) pg 451 X-ray lumbosacral spine. (2/98) pg 451 C+L-spine: bony features, highlight differences (1/09) Organisation of a spinal nerve. Pg 473, 498 Spinal cord/vertebral column layers passed through during LP (1/03, 1/06, 1/07, 1/09) pg 505
12 Anatomy Unit 27: Bones: Pelvis esp inguinal ligaments and relations (1/99) pg Anatomy Unit 28: Peritoneal folds and potential spaces for fluid collection (2/08) pg 217 Blood supply of the gut outline the major arteries (1/08) pg 228 X-ray abdomen. Position of solid organs (2/00, 2/08) General description. Bowel and other soft tissue structures. (2/05, 2/08) pg Anatomy Unit 29: Photo upper abdo. Spleen. (2/98) pg Liver. (2/97) pg Abdo CT Relations of the spleen (2/06) pg 263 The relations of the pancreas (1/09) pg Relations of the liver (2/06) pg 268 Identify the structures (1/09, 1/10) pg pg Anatomy Unit 30: Revision Week
13 Anatomy Unit 31: Viva Question X-ray abdomen. Solid organs, path of ureters. (2/96, 1/99, 2/00, 1/04, 1/07) pg 292 Photo retroperitoneum. Left kidney. Relations and blood supply (1/07) pg 292 Right kidney relations (1/10) pg 292 Kidneys, ureters. (2/95, 2/98, 1/03, 1/08, 1/09) pg Relations of the ureters. (2/00, 2/05) pg 294 Attachments and openings of the diaphragm, and structures passing though. (1/07, 1/09) pg 306, Diaphragm innervation and contribution to respiration. (1/09) pg 307, 309 Photo/X-ray abdo. Branches and distribution of aorta. (2/98, 2/02, 2/06, 2/07, 2/09) pg Course, relationships of the aorta. (2/02, 1/04) pg 313 Vasculature, venous drainage and relations. (2/03, 1/05, 2/07) pg 315 Anatomy Unit 32: Bone pelvis (1/96, 1/98, 1/99, 2/02) pg 329 X-ray pelvis (2/96, 2/98) pg 329 Iliac arteries, pelvic walls (2/06) pg 350 Anatomy Unit 33: No
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES. for Massage Therapists. Online!
 CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions *
 ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
Appendix A Partial Pick List of Injury and Sequelae Codes (ICD-10-CA)
 What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
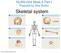 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology
 Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology by Visible Body contains 12 units. Below is a listing of each unit, the chapters within it, and the unit s associated learning objectives.
Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology by Visible Body contains 12 units. Below is a listing of each unit, the chapters within it, and the unit s associated learning objectives.
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List
 Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain
 Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Chiropractic ICD 9 Code List
 Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011
 Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Dermatomes and Myotomes
 Dermatomes and Myotomes C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 T1 Upper Cervical Flexion Upper Cervical Extension Cervical Lateral Flexion Shoulder Girdle Elevation Shoulder Abduction Elbow Flexion Elbow Extension Thumb
Dermatomes and Myotomes C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 T1 Upper Cervical Flexion Upper Cervical Extension Cervical Lateral Flexion Shoulder Girdle Elevation Shoulder Abduction Elbow Flexion Elbow Extension Thumb
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
MRI EXAM CPT CODE REFERENCE
 I EXAM REFERENCE Use this reference to quickly determine the correct exam for your patients based on the indications described herein and the for the order. Creatine levels should be obtained prior to
I EXAM REFERENCE Use this reference to quickly determine the correct exam for your patients based on the indications described herein and the for the order. Creatine levels should be obtained prior to
Structure & Function of the Knee. One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity.
 Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
MD 2016. Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy. A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience
 MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
Basic Concepts. Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG. Pathophysiology. Median Nerve. A Clinical Approach
 Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
A core syllabus in anatomy for medical students - Adding common sense to need to know
 Rev. from Eur J Anat, 11 (Supplement 1): 3-18 (2007) A core syllabus in anatomy for medical students - Adding common sense to need to know The Education Committee of the Anatomical Society of Great Britain
Rev. from Eur J Anat, 11 (Supplement 1): 3-18 (2007) A core syllabus in anatomy for medical students - Adding common sense to need to know The Education Committee of the Anatomical Society of Great Britain
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin
 by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more
 BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Upper Extremity Special Tests. Cervical Tests. TMJ Dysfunction
 Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb
 An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb Darren Kelly Artwork by Paddy Lennon Original photos courtesy of Mary Ferguson Students at University College Dublin, School of Veterinary Medicine. Video
An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb Darren Kelly Artwork by Paddy Lennon Original photos courtesy of Mary Ferguson Students at University College Dublin, School of Veterinary Medicine. Video
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
Vascular Access. Chapter 3
 Vascular Access Chapter 3 Vascular Access Introduction Obtaining vascular access in infants and children can be difficult even under optimal conditions. Attempting emergent access in a hypotensive, struggling
Vascular Access Chapter 3 Vascular Access Introduction Obtaining vascular access in infants and children can be difficult even under optimal conditions. Attempting emergent access in a hypotensive, struggling
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Atlas of Human Anatomy By Frank H. Netter, MD (5e to 6e)
 5e to 6e, see pages 1-13 Atlas of Human Anatomy By Frank H. Netter, MD (5e to 6e) 5e Plate # 6e Plate # Plate Title 1 1 Head and Neck: Surface Anatomy 2 2 Cutaneous Nerves of Head and Neck 3 3 Superficial
5e to 6e, see pages 1-13 Atlas of Human Anatomy By Frank H. Netter, MD (5e to 6e) 5e Plate # 6e Plate # Plate Title 1 1 Head and Neck: Surface Anatomy 2 2 Cutaneous Nerves of Head and Neck 3 3 Superficial
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Systems of the Human Body
 . s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
. s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys
 Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Structure and Function of the Hip
 Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Lower limb nerve blocks
 Lower limb nerve blocks Barry Nicholls is Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management at Musgrove Hospital, Taunton, UK. He qualified from Liverpool University and trained in Newcastle, UK, and Seattle,
Lower limb nerve blocks Barry Nicholls is Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management at Musgrove Hospital, Taunton, UK. He qualified from Liverpool University and trained in Newcastle, UK, and Seattle,
The Muscular System. Appendicular Musculature
 11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Extended Disability Income. Fixed cease age. Extended Disability Income. Whole Life UP TO 24 MONTHS. Pre-retirement.
 For intermediaries Sanlam Risk Cover January 2015 Temporary Disability Income benefit (OIT3) Primary Income Protector benefits Waiting period Sickness Temporary Disability Income Including fixed payment
For intermediaries Sanlam Risk Cover January 2015 Temporary Disability Income benefit (OIT3) Primary Income Protector benefits Waiting period Sickness Temporary Disability Income Including fixed payment
The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
 F10001-Ch02.qxd 4/7/06 9:04 AM Page 11 Spine 2 THE CERVICAL SPINE AND NECK The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
F10001-Ch02.qxd 4/7/06 9:04 AM Page 11 Spine 2 THE CERVICAL SPINE AND NECK The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
SPINE. Postural Malalignments 4/9/2015. Cervical Spine Evaluation. Thoracic Spine Evaluation. Observations. Assess position of head and neck
 SPINE Observations Body type Postural alignments and asymmetries should be observed from all views Assess height differences between anatomical landmarks Figure 25-9 Figure 25-10 Figure 25-11 & 12 Postural
SPINE Observations Body type Postural alignments and asymmetries should be observed from all views Assess height differences between anatomical landmarks Figure 25-9 Figure 25-10 Figure 25-11 & 12 Postural
Upper limb injuries. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Upper limb injuries Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Pain in the limbs: May be classified under 4 headings: 1. Joint pain 2. Soft tissue pain 3. Neurogenic pain 4. Orthopaedic causes (fractures,
Upper limb injuries Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Pain in the limbs: May be classified under 4 headings: 1. Joint pain 2. Soft tissue pain 3. Neurogenic pain 4. Orthopaedic causes (fractures,
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Body cavities. Body Planes
 Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
PRACTICE GUIDELINE TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-17-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL PURPOSE: To outline the indications and options for intravenous
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-17-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL PURPOSE: To outline the indications and options for intravenous
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
Manual Therapy for the Upper and Lower Quadrant: What Do I Need to Know? Objectives
 Manual Therapy for the Upper and Lower Quadrant: What Do I Need to Know? Objectives 1. Describe the current best evidence for manual therapy in the management of a variety of disorders. 2. Recognize subgroups
Manual Therapy for the Upper and Lower Quadrant: What Do I Need to Know? Objectives 1. Describe the current best evidence for manual therapy in the management of a variety of disorders. 2. Recognize subgroups
The Knee Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) The Knee. The Knee Anatomy of the anteromedial aspect. The Knee
 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Injury Prevention, Rehabilitation, and Compensation (Liability to Pay or Contribute to Cost. Amendment Regulations (No 2) 2004
 Amendment Regulations (No 2) 2004 Pursuant to section 324 of the and Compensation Act 2001, Her Excellency the Governor General, acting on the advice and with the consent of the Executive Council, makes
Amendment Regulations (No 2) 2004 Pursuant to section 324 of the and Compensation Act 2001, Her Excellency the Governor General, acting on the advice and with the consent of the Executive Council, makes
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Sports Massage & Athletic Training Specialist Certificate Program with Externship
 Office of Professional & Continuing Education 301 OD Smith Hall Auburn, AL 36849 http://www.auburn.edu/mycaa Contact: Shavon Williams 334-844-3108; szw0063@auburn.edu Auburn University is an equal opportunity
Office of Professional & Continuing Education 301 OD Smith Hall Auburn, AL 36849 http://www.auburn.edu/mycaa Contact: Shavon Williams 334-844-3108; szw0063@auburn.edu Auburn University is an equal opportunity
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
