III./9.4. Mononeuropathies tunnel syndromes
|
|
|
- Rachel Foster
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 III./9.4. Mononeuropathies tunnel syndromes Table 5 shows the possible causes of peripheral nerve damage. Mononeuropathy refers to the lesion of a single nerve. It is most often the consequence of a local lesion; the site of lesion along the course of the nerve can be well localized, however systemic disease (e.g. diabetes mellitus) may also lead to the lesion of a single nerve. In this case, exact localization of pathology on the given nerve is usually not possible due to diffuse damage. Table 5: Causes of peripheral nerve damage Compression of the nerve is one of the most common causes of focal nerve lesion. Compression may be of external origin or nerves may be compressed while traversing through narrow areas bounded by bones-connective tissue-muscles (entrapment sites). These latter are called tunnel syndromes or entrapment neuropathies. The focal nerve lesions most commonly encountered in clinical practice are discussed below. Median nerve The median nerve supplies with motor fibers the wrist and finger flexors, and most of the thenar eminence. Its sensory fibers innervate the radial palmar aspect of the hand, including the first three fingers and the radial surface of the fourth finger. (See a textbook of anatomy for further details.) Carpal tunnel syndrome: The tendons of flexor muscles and the median nerve pass from the forearm to the wrist through the carpal tunnel, which is an anatomical site bounded by the carpal bones and the transverse carpal ligament. The distal compression of the median nerve as a consequence of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is clearly the most common focal neuropathy. It is also the most common tunnel syndrome and a very common neurologic condition. The incidence of CTS is approximately /100,000 /year. CTS is three times more common in females than in males. Symptoms: CTS usually affects both hands, but generally symptoms of the dominant hand appear first. Initial, highly characteristic first symptom is painful numbness of the hand during the night, which may disrupt sleep. Patients often report of referred pain and numbness of the whole arm or forearm, and symptoms are not necessarily restricted to the median innervated first three fingers. Other characteristic signs include stiffness and feeling of swelling of the fingers. Later, symptoms are also experienced during the day, especially during certain activities such as kitchen work, bicycling or car driving. In a more advanced stage, the numbness-paresthesia becomes constant and sensory loss may develop on the fingers resulting in reduced manual dexterity, clumsiness of the hand. In late stage, motor fibers are also damaged and denervation of the thenar occurs (Fig. 8), which leads to further clumsiness of the hand; patients may be unable to perform simple, everyday tasks such as buttoning or closure of a zipper.
2 Causes: Fig. 8: Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome CTS is most often idiopathic, which probably reflects a constitutionally narrow tunnel. This affects mainly women of years of age. Furthermore, any condition that contributes to the narrowing of the tunnel or leads to changes in wrist anatomy or is associated with an overuse of the hand are risk factors of CTS: obesity edema (pl. pregnancy, lymphedema, hypothyroidism) old or recent wrist fracture arthrosis rheumatoid arthritis or other forms of arthritis diabetes mellitus (nerves already damaged by polyneuropathy are more sensitive to compression) occupations (e.g. carpenter, mason, locksmith) sports (e.g. bicycling) CTS can be usually diagnosed based on the highly characteristic symptoms. Symptoms may be provoked by the passive flexion of the wrist, which is called Phalen maneuver (Fig. 9). Tinel sign may be present (Fig. 10), which means that light pressure or tapping of the nerve at the site of lesion produces an electric sensation radiating along the course of the nerve. Fig. 9: Phalen s provocation maneuver in CTS Fig. 10: Tinel sign CTS can be confirmed by EMG, which first shows focal demyelination in the carpal tunnel followed by axonal lesion. In accordance with clinical symptoms, sensory fibers are earlier and more severely affected than motor fibers. It is also important to know that EMG may be normal in early stages of CTS (i.e. there is no nerve damage, only
3 irritation of the nerve causing positive sensory symptoms). Treatment: Symptomatic treatment of CTS includes splinting of the wrist during the night or local steroid injection. However, the final solution is surgical decompression of the nerve (release of the nerve by cutting the transverse carpal ligament). Proximal lesion of the median nerve is much less common (e.g. during sleep or compression due to a tumor or compartment syndrome). In addition to distal symptoms (sensory loss of the fingers and thenar atrophy and weakness), finger flexors are also weak leading to the sign of oath hand: in an attempt to make a fist, the first three fingers remain extended (Fig. 11). Ulnar nerve Fig. 11: Oath hand in proximal median nerve lesion The ulnar nerve supplies with motor fibers the adductor pollicis muscle of the thenar and all other small hand muscles, and the ulnar forearm flexors. Its sensory fibers supply the ulnar aspect of the hand, including the 4-5th finger. (See a textbook of anatomy for further details.) Ulnar nerve lesion at the elbow (UNE): The ulnar nerve is most often damaged at the elbow, either in the ulnar groove behind the medial epicondyle (retroepicondylar lesion), or less commonly in the cubital tunnel (directly below the elbow, in the tunnel formed by the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and the aponeurosis connecting them (Fig. 12). Fig.12: Anatomy of the ulnar nerve at the elbow Causes of retroepicondylar lesion: tardive ulnar nerve palsy: old elbow fractures or deformity arthrosis rheumatoid arthritis diabetes mellitus
4 external compression, often of iatrogenic origin (e.g. during surgeries) Causes of cubital tunnel syndrome: Symptoms: idiopathic frequent habitual elbow flexion As it is generally seen in compression neuropathies, sensory symptoms occur first: numbness, sensory loss on the 4-5th finger and the ulnar aspect of the hand. It is characteristic that initially only the fingertips are affected. Motor symptoms occur later or in more severe lesions: paresis and atrophy of the hypothenar, interosseus muscles and the adductor pollicis muscle of thenar muscle group. This results in ʽclaw hand (Fig. 13). The hand also has the appearance of a ʽskeleton hand due to the atrophy of small hand muscles. Interestingly, flexion power of the 4-5th finger is often preserved. Weakness of the adductor pollicis muscle can be demonstrated by Froment s sign (Fig. 14): loss of adduction power of the thumb is compensated by the long, median nerve innervated flexors. Another typical sign in ulnar nerve lesion is Wartenberg s sign (Fig. 15): due to the preferential involvement of the 3rd palmar interosseus muscle, the little finger stands apart from the other fingers. Fig. 13: Claw hand in ulnar nerve lesion Fig. 14: Froment s sign in ulnar nerve lesion Fig. 15: Wartenberg s sign in ulnar nerve lesion Ulnar nerve lesion can be confirmed by EMG (Fig. 16). Differential diagnosis includes C8 radicular lesion, where sensory symptoms are identical to those in ulnar nerve lesion, but other signs of cervical spondylosis may be seen and the distribution of motor symptoms respects the C8 myotome (not only the small hand muscles, but for example the radial nerve innervated extensor indicis muscle is also affected).
5 Treatment: avoiding elbow flexion, surgical release Fig. 16: Electrophysiological diagnosis of UNE Distal ulnar nerve lesion at the wrist is much less common than UNE. The area at the wrist where the ulnar nerve passes from the forearm to the hand is called Guyon tunnel. Real Guyon tunnel syndrome is however very rare and a questionable entity, and it is not the synonym of distal ulnar nerve lesion. In clinical practice, the distal, deep, purely motor branch in the palm is most often affected by compression (e.g. during bicycling, weight lifting, in certain occupations). This branch originates distally to the branch supplying the hypothenar and to the sensory branch, therefore weakness and atrophy of all small hand muscles are seen with the exception of the hypothenar, and there is no sensory loss. These symptoms are often erroneously attributed to motoneuron disease or cervical myelopathy. Radial nerve The radial nerve supplies with motor fibers the triceps muscle and the wrist and finger extensors. Its sensory fibers innervate the radial dorsal aspect of the hand. (See a textbook of anatomy for further details.) Compression of the radial nerve on the upper arm: The radial nerve is most often damaged at the level of the middle part of the humerus, where the nerve lies directly over the bone in the spiral groove. Compression palsy usually develops during sleep, as a result of the pressure exerted by the head of the patient or of the partner. This is more likely to occur when sleep is stuporous due to exhaustion or alcohol or drug consumption. Therefore, it is sometimes referred to as Saturday night s palsy. Symptoms: Wrist drop is seen due to the weakness of wrist and finger extensors (Fig. 17). Triceps muscle is spared, because the branch innervating the triceps muscle leaves the main trunk at the level of the axilla. Sensory loss affects the radial dorsal aspect of the hand. Fig. 17: Wrist drop in radial nerve lesion
6 Clinical symptoms alone usually allow diagnosis of radial nerve palsy. Weakness due to upper motoneuron lesion also results is distally pronounced weakness of the arm, resembling that of a wrist drop, however in this case finger flexion and small hand muscles are also weak. Treatment: In case of an external compression, spontaneous recovery is expected in a time frame depending on the severity of lesion (neurapraxia-axonotmesis). Radial nerve lesion on the forearm: The distal, pure motor branch of the radial nerve, the posterior interosseus nerve may be compressed at the level of the supinator muscle, which is penetrated by the nerve (supinator tunnel syndrome). It is usually caused by overuse, activities that involve frequent supination-pronation of the forearm. There is no sensory loss and only the finger extensors are weak (finger drop), wrist extension is largely spared. It is typical that weakness first affects the 4-5th finger. The distal, pure sensory branch of the radial nerve, the superficial radial nerve may be damaged in the distal third of the forearm where the nerve becomes superficial. Compression of the nerve may result from tight handcuffs, or it may be damaged by surgery of de Quervain s tenosynovitis. Common peroneal nerve The common peroneal nerve supplies with motor fibers the muscles performing dorsiflexion of the foot and toes, and the peroneal muscles. Its sensory fibers innervate the dorsum of the foot and the lateral aspect of the calf. (See a textbook of anatomy for further details.) Compression of the common peroneal nerve at the fibular head: The common peroneal nerve runs forward from the popliteal fossa passing around the fibular head on the outside where it lies directly over the bone covered only by skin. Therefore, the nerve is very vulnerable to compression at this site. Diabetes mellitus is risk factor for compression palsy. Causes: lying on the side for longer time (e.g. in a comatose state, bed-bound patients, during sleeping on a hard surface) leg crossing for longer time squatting for longer time (e.g. strawberry pickers, tilers) during operations (patients are fixed too tightly at the knees) cast The peroneal nerve passes through the peroneal tunnel formed by the head of the long peroneal muscle as it originates on the fibular head. Compression in this tunnel (real peroneal tunnel syndrome) is however very rare and may be suggested by slowly progressing symptoms. Symptoms: The typical symptom of peroneal nerve lesion is foot drop (Fig. 18) with resulting steppage gait (during walking, the patient lifts his/her leg higher on the affected side in order to avoid tripping). The patient is unable to stand on heel on the affected side. Sensory loss involves the lateral aspect of the calf and the dorsum of the foot. Differential diagnosis includes the common L5 radicular lesion, which may also cause a foot drop. However, in this case, other (non-peroneal nerve innervated ) muscles supplied by the L5 segment may also become weak, e.g. inversion of the foot (posterior tibial muscle) and abduction of the hip (gluteus medius muscle). Furthermore, other
7 signs of lumbar spondylosis may be present. Symptoms identical to common peroneal nerve lesion may be produced by more proximal lesions, e.g. sciatic nerve lesion or lumbosacral trunk lesion in the pelvis (see plexopathies). In the sciatic nerve, fibers eventually forming the common peroneal nerve run separately from tibial nerve fibers, thus they may be selectively affected. Fig. 18: Foot drop in common peroneal nerve lesion In addition to clinical symptoms, common peroneal nerve lesion at the fibular head may be well localized by EMG (Fig. 19). Furthermore, EMG has a major role in differentiating common peroneal nerve lesion from the other conditions mimicking peroneal nerve lesion, as mentioned above. Treatment: Fig. 19: Conduction block of the common peroneal nerve at the fibular head In case of an external compression, spontaneous recovery is expected in a time frame depending on the severity of lesion (neurapraxia-axonotmesis). In the rare peroneal tunnel syndrome, surgical release is recommended. Lateral cutaneus femoral nerve The lateral cutaneus femoral nerve is a pure sensory nerve, which innervates the skin on the lateral aspect of the thigh. The nerve exits the pelvis by penetrating the inguinal ligament close to the anterior superior iliac spine, where it is very often compressed or damaged. The condition is called meralgia paresthetica. Causes: idiopathic obesity pregnancy tight garments
8 Symptoms: diabetes mellitus crista biopsy Burning, tingling pain and hypesthesia on the lateral aspect of the thigh (Fig. 20). Symptoms are more pronounced in a standing position. The area of sensory loss has sharp borders, which helps in differentiating sensory loss of similar distribution due to the rare L2 radiculopathy. Fig. 20: Sensory innervation area of the lateral cutaneus femoral nerve Diagnosis is usually possible based on clinical symptoms. Treatment: Weight loss, loose garments. Rarely local steroid injection may be considered, but spontaneous remission is typical.
Basic Concepts. Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG. Pathophysiology. Median Nerve. A Clinical Approach
 Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy. Adam P. Smith, MD
 Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies
 Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies Barbara E. Shapiro, MD, PhD*, David C. Preston, MD KEYWORDS Entrapment neuropathy Compressive neuropathy Entrapment and compressive neuropathies of the upper and
Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies Barbara E. Shapiro, MD, PhD*, David C. Preston, MD KEYWORDS Entrapment neuropathy Compressive neuropathy Entrapment and compressive neuropathies of the upper and
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis. Disclosures: None
 Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Medical Report Checklist: Upper Extremities Peripheral Nerve Disorders Impairments (PND)
 http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
OVERVIEW. NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. WHAT IS THE MOST IMPORTANT PART OF THE PHYSICAL EXAM?
 NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. Neurological Surgery Bluegrass Orthopaedics and Hand Care OVERVIEW SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM PREVALENCE PATHOLOGY ANATOMIC CONSIDERATIONS ASSESSMENT
NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. Neurological Surgery Bluegrass Orthopaedics and Hand Care OVERVIEW SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM PREVALENCE PATHOLOGY ANATOMIC CONSIDERATIONS ASSESSMENT
Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis
 FPL FCR Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis Thenar motor branch Kaplan s cardinal line: distal TCL thenar branch Superficial palmar arch superficial arch Originates
FPL FCR Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis Thenar motor branch Kaplan s cardinal line: distal TCL thenar branch Superficial palmar arch superficial arch Originates
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy. What to do with arm pain? Defining Arm Pain. Arm Pain
 Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
The 10 Most Common Hand Pathologies In Adults. 1. Carpal Tunnel and Cubital Tunnel
 The 10 Most Common Hand Pathologies In Adults Bobbi Jacobsen PA C 1. Carpal Tunnel and Cubital Tunnel CARPAL TUNNEL (median nerve) ( ) Pain and numbness Distal, proximal radiating Sensory disturbance Distribution
The 10 Most Common Hand Pathologies In Adults Bobbi Jacobsen PA C 1. Carpal Tunnel and Cubital Tunnel CARPAL TUNNEL (median nerve) ( ) Pain and numbness Distal, proximal radiating Sensory disturbance Distribution
Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics
 from The Cleveland Clinic Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Jeffrey Lawton, MD Associate Staff, Department of Orthopaedic The Cleveland Clinic Appointments:
from The Cleveland Clinic Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Jeffrey Lawton, MD Associate Staff, Department of Orthopaedic The Cleveland Clinic Appointments:
How To Know If You Can Get A Carpal Tunnel Injury Compensation
 U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of BARBARA SNYDER and DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY, INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE, Germansville, PA Docket No. 03-1467; Submitted on
U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of BARBARA SNYDER and DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY, INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE, Germansville, PA Docket No. 03-1467; Submitted on
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy
 Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
9/11/12. EMG for OPAs. Amy Eswein, MSPT. Evaluation of Peripheral Nerve Injuries. Exam has two parts:! Nerve Conduction Study! Needle EMG!
 EMG for OPAs Amy Eswein, MSPT Evaluation of Peripheral Nerve Injuries Exam has two parts:! Nerve Conduction Study! Needle EMG! 1 Nerve Conduction Study Latency/NCV! State of the MYELIN Amplitude! State
EMG for OPAs Amy Eswein, MSPT Evaluation of Peripheral Nerve Injuries Exam has two parts:! Nerve Conduction Study! Needle EMG! 1 Nerve Conduction Study Latency/NCV! State of the MYELIN Amplitude! State
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
 TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS
 Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
by joe muscolino body mechanics
 by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
Compression Neuropathies. Andrew Martin DO, MBA, CAQSM OMED 2013
 Compression Neuropathies Andrew Martin DO, MBA, CAQSM OMED 2013 Compression Neuropathies Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Spinal Accessory Nerve Upper/Lower Trunk Plexopathy Long Thoracic
Compression Neuropathies Andrew Martin DO, MBA, CAQSM OMED 2013 Compression Neuropathies Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Spinal Accessory Nerve Upper/Lower Trunk Plexopathy Long Thoracic
WRIST EXAMINATION. Look. Feel. Move. Special Tests
 WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
Muscles of the Forearm and Hand
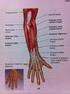 8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Work-related upper extremity disorders associated
 Nerve entrapments of the wrist Early treatment preserves function Nerve entrapment syndromes may affect as many as one in four office workers. Prompt diagnosis is critical to the selection of an appropriate
Nerve entrapments of the wrist Early treatment preserves function Nerve entrapment syndromes may affect as many as one in four office workers. Prompt diagnosis is critical to the selection of an appropriate
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
Electrodiagnostic Assessment: An Introduction to NCS and EMG
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment: An Introduction to NCS and EMG Barry Bernacki BSc MD FRCPC CSCN (EMG) Clinical Asst. Professor EMG Lab Director Saskatoon City Hospital Objectives Understand technique and
Electrodiagnostic Assessment: An Introduction to NCS and EMG Barry Bernacki BSc MD FRCPC CSCN (EMG) Clinical Asst. Professor EMG Lab Director Saskatoon City Hospital Objectives Understand technique and
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes
 A Quarterly Publication for Continuing Medical Education Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes Ann R. Stroink,
A Quarterly Publication for Continuing Medical Education Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes Ann R. Stroink,
The Numb Hand. James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics
 The Numb Hand James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation describes information to educate consumers on various
The Numb Hand James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation describes information to educate consumers on various
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI
 CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
LOW BACK PAIN EXAMINATION
 LOW BACK PAIN EXAMINATION John Petty, M.D. Medical Director Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Kettering Medical Center February 8, 2014 PRE-TEST QUESTION What part of the low back physical
LOW BACK PAIN EXAMINATION John Petty, M.D. Medical Director Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Kettering Medical Center February 8, 2014 PRE-TEST QUESTION What part of the low back physical
Dermatomes and Myotomes
 Dermatomes and Myotomes C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 T1 Upper Cervical Flexion Upper Cervical Extension Cervical Lateral Flexion Shoulder Girdle Elevation Shoulder Abduction Elbow Flexion Elbow Extension Thumb
Dermatomes and Myotomes C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 T1 Upper Cervical Flexion Upper Cervical Extension Cervical Lateral Flexion Shoulder Girdle Elevation Shoulder Abduction Elbow Flexion Elbow Extension Thumb
Chiropractic ICD 9 Code List
 Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation
 International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation Copyright 2010 by the Center for International Rehabilitation Research Information and Exchange (CIRRIE). All rights reserved. No part of this publication may
International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation Copyright 2010 by the Center for International Rehabilitation Research Information and Exchange (CIRRIE). All rights reserved. No part of this publication may
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION
 CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks
 The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks Nikki Strauss Schroeder, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 4, 2013 Outline Surface Anatomy Hand Anatomy Exam Management of
The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks Nikki Strauss Schroeder, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 4, 2013 Outline Surface Anatomy Hand Anatomy Exam Management of
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys
 Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
Orientation to Movement-Based Physical Therapy in the ED
 Orientation to Movement-Based Physical Therapy in the ED Physical Therapists in the ED PT consult icon available Debbie Fleming-McDonnell, PT, DPT flemingd@wusm.wustl.edu Pam Wendl, PT, DPT wendlp@wusm.wustl.edu
Orientation to Movement-Based Physical Therapy in the ED Physical Therapists in the ED PT consult icon available Debbie Fleming-McDonnell, PT, DPT flemingd@wusm.wustl.edu Pam Wendl, PT, DPT wendlp@wusm.wustl.edu
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Elbow Examination. Haroon Majeed
 Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Examination of the Elbow. Elbow Examination. Structures to Examine. Active Range of Motion. Active Range of Motion 8/22/2012
 Examination of the Elbow The elbow is a complex modified hinge joint The humero-ulnar joint is a hinge joint allowing flexion and extension The radio-ulnar joint allows for pronation and supination of
Examination of the Elbow The elbow is a complex modified hinge joint The humero-ulnar joint is a hinge joint allowing flexion and extension The radio-ulnar joint allows for pronation and supination of
Extremity Trauma. William Schecter, MD
 Extremity Trauma William Schecter, MD Approach to the Evaluation of the Patient with an Extremity Injury Blood Supply Skeleton Neurologic Function Risk for Compartment Syndrome? Coverage (Skin and Soft
Extremity Trauma William Schecter, MD Approach to the Evaluation of the Patient with an Extremity Injury Blood Supply Skeleton Neurologic Function Risk for Compartment Syndrome? Coverage (Skin and Soft
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS. Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain. Assessment & Treatment of. Low Back Pain. Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D.
 THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
WHEN TO ORDER; HOW TO INTERPRET
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AND 1 NERVE CONDUCTION TESTING: WHEN TO ORDER; HOW TO INTERPRET Ronald N. Kent, M.D., Ph.D. 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AND NERVE CONDUCTION TESTING EMG/NCS Testing is a component of a complete
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AND 1 NERVE CONDUCTION TESTING: WHEN TO ORDER; HOW TO INTERPRET Ronald N. Kent, M.D., Ph.D. 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AND NERVE CONDUCTION TESTING EMG/NCS Testing is a component of a complete
EMG AND NCS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO ELECTRODIAGNOSTICS
 EMG AND NCS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO ELECTRODIAGNOSTICS Dr. Harp Sangha, Dr. Tania R. Bruno Staff Physiatrists Toronto Rehab UHN Lecturers, Department of Medicine University of Toronto February 1, 2013
EMG AND NCS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO ELECTRODIAGNOSTICS Dr. Harp Sangha, Dr. Tania R. Bruno Staff Physiatrists Toronto Rehab UHN Lecturers, Department of Medicine University of Toronto February 1, 2013
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Median Nerve Injuries in, Fractures in the Region of the Wrist
 252 Median Nerve Injuries in, Fractures in the Region of the Wrist N. MEADOFF, M.D., Bakersfield SUMMARY Injuries of the median nerve in fractures in the region of the wrist are not uncommon. Median nerve
252 Median Nerve Injuries in, Fractures in the Region of the Wrist N. MEADOFF, M.D., Bakersfield SUMMARY Injuries of the median nerve in fractures in the region of the wrist are not uncommon. Median nerve
Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries
 1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
Laser Treatment Policy
 Laser Treatment Policy Pursuant to federal law 21 CFR 812.2(c)7 and 812.3(b), physician(s) at this pain center may advise and use unapproved laser s on patients under one or more of the following conditions:
Laser Treatment Policy Pursuant to federal law 21 CFR 812.2(c)7 and 812.3(b), physician(s) at this pain center may advise and use unapproved laser s on patients under one or more of the following conditions:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist
 http://www.pdratings.com/ AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist [L.C. 139.2 (J)-(2)&(3), (k)-(5), 4060(b)(1), 4062 (d)(2), 4068, 4620, 8 CCR WCAB 10606 & 8 CCR 9785] AMA Brachial
http://www.pdratings.com/ AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist [L.C. 139.2 (J)-(2)&(3), (k)-(5), 4060(b)(1), 4062 (d)(2), 4068, 4620, 8 CCR WCAB 10606 & 8 CCR 9785] AMA Brachial
Eric M. Kutz, D.O. Arlington Orthopedics Harrisburg, PA
 Eric M. Kutz, D.O. Arlington Orthopedics Harrisburg, PA 2 offices 805 Sir Thomas Court Harrisburg 3 Walnut Street Lemoyne Mechanism of injury Repetitive overhead activities Falls to the ground Falls with
Eric M. Kutz, D.O. Arlington Orthopedics Harrisburg, PA 2 offices 805 Sir Thomas Court Harrisburg 3 Walnut Street Lemoyne Mechanism of injury Repetitive overhead activities Falls to the ground Falls with
Background Š Compression neuropathy: Nerve compression resulting in nerve dysfunction. Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments
 Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments Compression Neuropathies: Pathophysiology Scott P. Olvey, MD 1 2 Goals Understand peripheral nerve histology Understand the pathophysiology of peripheral nerve compression
Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments Compression Neuropathies: Pathophysiology Scott P. Olvey, MD 1 2 Goals Understand peripheral nerve histology Understand the pathophysiology of peripheral nerve compression
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists
 Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual
 Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD
 Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD What is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy? Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) is a rare condition in which multiple motor nerves are attacked by
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD What is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy? Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) is a rare condition in which multiple motor nerves are attacked by
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care. Table of Contents:
 Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Carpal Tunnel Release. Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist
 Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Pain Management Top Diagnosis Codes (Crosswalk)
 Pain Management Top s (Crosswalk) 274.00 Gout arthropathy, M1000 Idiopathic gout, unspecified site unspecified M10011 Idiopathic gout, right shoulder M10012 Idiopathic gout, left shoulder M10019 Idiopathic
Pain Management Top s (Crosswalk) 274.00 Gout arthropathy, M1000 Idiopathic gout, unspecified site unspecified M10011 Idiopathic gout, right shoulder M10012 Idiopathic gout, left shoulder M10019 Idiopathic
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician
 EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Entrapment Neuropathies & Neuropathic Pain. Mazen M. Dimachkie, M.D.
 Entrapment Neuropathies & Neuropathic Pain Mazen M. Dimachkie, M.D. Disclosures Speaker Bureau Depomed, Merck, Pfizer Grants Pfizer, CSL-Behring Consultant Nufactor, Biomarin and Catalyst Case 1 A 39 yo
Entrapment Neuropathies & Neuropathic Pain Mazen M. Dimachkie, M.D. Disclosures Speaker Bureau Depomed, Merck, Pfizer Grants Pfizer, CSL-Behring Consultant Nufactor, Biomarin and Catalyst Case 1 A 39 yo
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Neuromuscular Medicine Fellowship Curriculum
 Neuromuscular Medicine Fellowship Curriculum General Review Goals and Objectives Attend weekly EMG sessions as assigned Take a Directed History and Exam of each EMG patient Attend every other week Muscle
Neuromuscular Medicine Fellowship Curriculum General Review Goals and Objectives Attend weekly EMG sessions as assigned Take a Directed History and Exam of each EMG patient Attend every other week Muscle
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List
 Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
10/15/2012. The Hand. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Hand (Bones) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related
 The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Knee Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) The Knee. The Knee Anatomy of the anteromedial aspect. The Knee
 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
BWC Diagnosis Determination Guidelines Quick Reference
 BWC Diagnosis Determination Guidelines Quick Reference Overview BWC relies on Managed Care Organizations to gather pertinent medical documentation from all treating providers to suppt the allowance determination.
BWC Diagnosis Determination Guidelines Quick Reference Overview BWC relies on Managed Care Organizations to gather pertinent medical documentation from all treating providers to suppt the allowance determination.
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Chapter 35. Volar forearm fasciotomy incisions Hand/dorsal forearm fasciotomy incisions Finger fasciotomy incisions
 Chapter 35 HAND CRUSH INJURY AND COMPARTMENT SYNDROME KEY FIGURES: Volar forearm fasciotomy incisions Hand/dorsal forearm fasciotomy incisions Finger fasciotomy incisions The previous chapters about the
Chapter 35 HAND CRUSH INJURY AND COMPARTMENT SYNDROME KEY FIGURES: Volar forearm fasciotomy incisions Hand/dorsal forearm fasciotomy incisions Finger fasciotomy incisions The previous chapters about the
5/13/2013. Evaluation of Peripheral Nervous System Dysfunction. Disclosures. Peripheral Nervous System
 Evaluation of Peripheral Nervous System Dysfunction Christian M. Custodio, M.D. Cancer Rehabilitation Fellowship Director Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical
Evaluation of Peripheral Nervous System Dysfunction Christian M. Custodio, M.D. Cancer Rehabilitation Fellowship Director Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical
Upper Extremity Special Tests. Cervical Tests. TMJ Dysfunction
 Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
Diane M. Rowles, MS, ACNP, BC, CRRN
 Diane M. Rowles, MS, ACNP, BC, CRRN Nurse Practitioner, University Neurosurgery Rush University Medical Center Adjunct Assistant Professor, Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Disclosures
Diane M. Rowles, MS, ACNP, BC, CRRN Nurse Practitioner, University Neurosurgery Rush University Medical Center Adjunct Assistant Professor, Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Disclosures
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Injuries to Upper Limb
 Injuries to Upper Limb 1 The following is a list of common sporting conditions and injuries. The severity of each condition may lead to different treatment protocols and certainly varying levels of intervention.
Injuries to Upper Limb 1 The following is a list of common sporting conditions and injuries. The severity of each condition may lead to different treatment protocols and certainly varying levels of intervention.
3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing
 3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing Peter D. Donofrio, M.D. Professor of Neurology Vanderbilt University Medical Center
3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing Peter D. Donofrio, M.D. Professor of Neurology Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medical Treatment Guidelines Proposed by the State of New York Department of Insurance to the Workers Compensation Board
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medical Treatment Guidelines Proposed by the State of New York Department of Insurance to the Workers Compensation Board July 2011 Draft TABLE OF CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION 1 II. HISTORY
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medical Treatment Guidelines Proposed by the State of New York Department of Insurance to the Workers Compensation Board July 2011 Draft TABLE OF CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION 1 II. HISTORY
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Electrodiagnostic Testing
 Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease
 Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease Electrodiagnostic tests Electroencephalogram (EEG) Electromyography (NCV, EMG) Cerebral evoked potentials (CEP) Motor evoked potentials (MEP) Electronystagmogram
Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease Electrodiagnostic tests Electroencephalogram (EEG) Electromyography (NCV, EMG) Cerebral evoked potentials (CEP) Motor evoked potentials (MEP) Electronystagmogram
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion

 Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE  Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE