Editorial. From nuchal translucency to intracranial translucency: towards the early detection of spina bifida. R. CHAOUI *and K. H.
|
|
|
- Sharleen Hines
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2010; 35: Published online in Wiley InterScience ( DOI: /uog.7552 Editorial From nuchal translucency to intracranial translucency: towards the early detection of spina bifida R. CHAOUI *and K. H. NICOLAIDES Prenatal Diagnosis and Human Genetics, Berlin, Germany and Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King s College Hospital and Department of Fetal Medicine, University College, London, UK *Correspondence ( chaoui@feindiagnostik.de) It is now clear that the vast majority of major fetal abnormalities can be diagnosed prenatally by ultrasound, that most of these abnormalities can be detected in the first trimester of pregnancy and that women want firsttrimester rather than later diagnosis. It is also clear that effective diagnosis of fetal abnormalities often necessitates the identification of easily recognizable markers which direct the attention of the sonographer to the specific abnormality. Good examples of such markers are the scalloping of the frontal bones (the lemon sign) and caudal displacement of the cerebellum (the banana sign), observed in the second trimester in most fetuses with open spina bifida, and increased nuchal translucency thickness (NT) which identifies in the first trimester the majority of fetuses with major aneuploidies, lethal skeletal dysplasias and a high proportion of major cardiac defects. It is now widely accepted that increased NT at weeks is the single most effective marker of trisomy 21 and all other major aneuploidies. First-trimester screening by a combination of maternal age, fetal NT, nasal bone, Doppler assessment of blood flow in the ductus venosus and across the tricuspid valve together with maternal serum free β-hcg and PAPP-A can identify more than 95% of all major aneuploidies for a screen-positive rate of less than 3%. A major remaining challenge in first-trimester ultrasonography has been the diagnosis of open spina bifida. This challenge, however, may now have been resolved by the realization that open spina bifida can be suspected by an easily detectable marker within the brain in the same mid-sagittal plane of the fetal face as for measurement of NT and assessment of the nasal bone. In normal fetuses the fourth cerebral ventricle presents as an intracranial translucency () parallel to the NT, while in fetuses with open spina bifida there may be absence of the 1. In almost all cases of open spina bifida there is an associated Arnold Chiari malformation, which is thought to be the consequence of leakage of cerebrospinal fluid into the amniotic cavity and hypotension in the subarachnoid spaces leading to caudal displacement of the brain and obstructive hydrocephalus. In the second trimester of pregnancy the manifestations of Arnold Chiari malformation are the lemon and banana signs and in the first trimester caudal displacement of the brain results in compression of the fourth ventricle and loss of the normal 1 4. MeasurementofissimilartothatofNT The two lines that define the are the posterior border of the brain stem anteriorly and the choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle posteriorly (Figure 1). Its measurement is similar to that of NT. The exact mid-sagittal plane of the fetal face should be obtained and the image should be magnified so that only the fetal head and upper thorax are included. The exact mid-sagittal plane of the fetal face is defined by the echogenic tip of the nose and rectangular shape of the palate anteriorly, the translucent thalamus in the center and the nuchal membrane posteriorly. Rotation of the head by about 10 away from the midline results in non-visibility of the tip of the nose and the appearance of the maxillary bone as an echogenic structure between the nasal bone above and the anterior part of the palate below. With further rotation, by about 15 from the midline, the nasal bone disappears and there is enlargement of the maxillary bone and coalescence with the palate. At weeks the brain stem appears hypoechogenic (dark gray) whereas the is anechoic (black) (Figure 1). Posterior to the is the future cisterna magna. In the mid-sagittal plane the has a slightly curved appearance and the widest anteroposterior diameter is in the middle part of the fourth ventricle. In measuring, as for NT, we recommend selecting the translucency with the widest Copyright 2010 ISUOG. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. E D ORIAL
2 134 Chaoui and Nicolaides Exact mid-sagittal and parasagittal planes Thalamus MB BS CM NT NB The exact mid-sagittal plane is ideal for measuring as it is for measuring NT and assessing the nasal bone. In this plane we can identify the fluid within the third ventricle between the right and left thalami and the aqueduct of Sylvius between the cerebral peduncles, although the thalami and peduncles themselves are not visible. The intracranial structures, including the thalamus, midbrain, brain stem, fourth ventricle and cisterna magna, can be identified easily in a slightly deviated parasagittal plane. Indeed, as shown in transverse view in Figure 2, the fourth ventricle remains wide on either side of the midline, therefore the effect of measuring the in planes that are slightly deviated from the exact mid-sagittal one should be minimal. Figure 1 Exact mid-sagittal plane of the fetal face at 13 weeks (crown rump length, 69 mm) showing the nasal bone (NB), nuchal translucency (NT), thalamus, midbrain (MB), brain stem (BS), cisterna magna (CM) and fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle appears as an intracranial translucent () area between two echogenic borders, the posterior border of the brain stem anteriorly and the choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle posteriorly. Measurement of the is achieved by placing the calipers on the anterior and posterior echogenic borders of the fourth ventricle. diameter and placing the calipers on the anterior and posterior echogenic borders. Gestational age for assessment of The optimal gestational age for measurement of fetal NT is to13+ 6 weeks. The reasons for selecting 11 weeks as the earliest gestation are: firstly, screening necessitates the availability of a diagnostic test and chorionic villus sampling before this gestation is associated with transverse limb reduction defects and secondly, many major fetal abnormalities can be diagnosed at the NT scan, provided the minimum gestation is 11 weeks. The reasons for selecting 13 weeks and 6 days as the upper limit are: firstly, to provide women with affected fetuses CP NT Figure 2 (a) Parasagittal plane of the fetal face at 13 weeks, with visible choroid plexus (CP). (b) The transverse view of the head at the level of the fourth ventricle obtained transvaginally demonstrates that mild deviations in insonation from the midline (solid line) have minimal effect on the measurement of intracranial translucency (). NT, nuchal translucency.
3 Editorial 135 Figure 3 Intracranial translucency (calipers) in four fetuses scanned transabdominally at weeks. The fetal crown rump length was 48 mm in the fetus in (a), 63 mm in (b), 75 mm in (c) and 81 mm in (d). the option of first- rather than second-trimester termination, secondly, the incidence of abnormal accumulation of nuchal fluid in chromosomally abnormal fetuses decreases after 13 weeks and thirdly, the success rate for taking a measurement decreases after 13 weeks because the fetus becomes vertical, making it more difficult to obtain the appropriate image. At weeks it is possible to diagnose severe brain abnormalities, including holoprosencephaly, ventriculomegaly, acrania-exencephaly and encephalocele. Within the gestational age range of weeks the anteroposterior diameter of the increases with fetal crown rump length (CRL) from a median of 1.5 mm at a CRL of 45 mm to 2.5 mm at a CRL of 85 mm (Figure 3) 1. Extensive sonographic studies of the developing human brain have reported that the fourth ventricle is easily identified from 8 weeks as a hypoechoic structure 5 9. The extent to which the in fetuses with spina bifida is altered before 11 weeks remains to be determined. The fourth ventricle can also be identified easily after 13 weeks and the diameter increases with gestational age 10. However, from the 14 th week onwards open spina bifida can be unmasked easily by the lemon and banana signs and it is therefore unlikely that measurement of will be used for this purpose in the second trimester of pregnancy. Fetal position for assessment of At weeks the fetal nasal bone is considered to be absent in about 60% of fetuses with trisomy 21 compared with 1 3% of euploid fetuses and therefore assessment
4 136 Chaoui and Nicolaides 1 Figure 4 Visualization of the intracranial translucency () in three fetuses in a prone position at 12 weeks gestation (crown rump lengths, mm). There is shadowing of the brain by the occipital bone. Images (a) and (b) were obtained by transabdominal sonography and image (c) was obtained transvaginally. Figure 5 Transvaginal sonography (mid-sagittal plane) in two fetuses at 12 weeks. Although in both cases the resolution was high, in (a) the fourth ventricle and other structures of the brain are not visualized clearly and, although in (b) the intracranial translucency () is clearly visible, the contrast discrimination is poorer than that of mid-sagittal planes of the face obtained transabdominally (cf. Figures 1 3). of the nasal bone improves the performance of firsttrimester screening for aneuploidies. Although the nasal bone can be examined when the fetus is in the prone position the assessment is easier when the fetus is facing the transducer. As for the nasal bone, assessment of is preferable when the fetus is facing the transducer. Although the fourth ventricle may be visible when the fetus is in the prone position, adequate examination of the fetal brain is often hampered by shadowing from the fetal occipital bone (Figure 4). Transabdominal vs. transvaginal assessment of The exact mid-sagittal plane of the fetal face necessary for measurement of fetal NT and assessment of the nasal bone is obtained more easily by transabdominal than transvaginal sonography, because the latter allows
5 Editorial 137 Figure 6 Three-dimensional volume of the fetal head at 12 weeks acquired transvaginally and displayed in the orthogonal mode combined with static volume contrast imaging. The reference dot is placed in the center of the fourth ventricle (a) and the image is then adjusted to obtain a reconstructed mid-sagittal plane of the brain (b) for measurement of the intracranial translucency (). less transducer manipulation. However, the objective of the week scan is not restricted to screening for fetal aneuploidies but includes the early diagnosis of all major defects through a systematic examination of the whole fetal anatomy. Since the resolution of transvaginal sonography in the assessment of most fetal organs is superior to that of the transabdominal route, fetal medicine experts often use both approaches for detailed early fetal examination. The fourth cerebral ventricle can be visualized both transabdominally and transvaginally. However, as in the case of fetal NT and nasal bone, assessment and measurement of is best carried out in the midsagittal plane of the fetal face, which is easier to obtain transabdominally. Additionally, with transvaginal sonography even in the mid-sagittal plane of the fetal face the difference in contrast between the and surrounding brain is often poor (Figure 5). If the transvaginal route is chosen for assessment of the fourth ventricle it is preferable that the transducer is directed towards the posterior fossa (Figure 4c) rather than the face (Figure 5a). Three-dimensional ultrasound for assessment of Three-dimensional ultrasound is useful in assessing particularly when it is difficult to obtain the mid-sagittal plane directly by two-dimensional ultrasound. In such cases a transverse view of the fetal head at the level of the fourth ventricle is obtained. This is best achieved by tranvaginal sonography because the resolution is higher. A three-dimensional volume is then acquired and displayed in the orthogonal mode. The reference dot is placed in the center of the fourth ventricle and the image is then rotated to align the midline and obtain a mid-sagittal plane of the brain for measurement (Figure 6). This is similar to the approach used in the second-trimester scan for demonstration of other fetal intracerebral structures, such as the corpus callosum and vermis 11. To enhance image quality, a thin three-dimensional slice (volume contrast) instead of a simple plane can be used, for example by applying a static volume contrast imaging tool. Closing the loop in the week scan In the 1980s, the main method of screening for open spina bifida was by maternal serum α-fetoprotein at around 16 weeks and the method of diagnosis was amniocentesis and measurement of amniotic fluid α-fetoprotein and acetyl cholinesterase. Although it was possible to diagnose the condition by ultrasonographic examination of the spine, the sensitivity of this test was low 12,13. However, the observation that open spina bifida was associated with the lemon and banana signs has led to the replacement of biochemical assessment with second-trimester ultrasonography, both for screening and for diagnosis of this abnormality 2. In the 1970s, the main method of screening for trisomy 21 was by maternal age and in the 1980s it was by maternal serum biochemistry and detailed ultrasonographic examination in the second trimester. In the 1990s the emphasis shifted to the first trimester when it was realized that the great majority of trisomic fetuses have increased NT that can be detected easily in a mid-sagittal plane of the fetal face at weeks. Improved performance of screening was achieved subsequently with the observation that in the same mid-sagittal plane as for measurement of NT it was possible to examine the nasal bone, which is often absent in trisomic fetuses. It is now clear that in this same mid-sagittal plane the fourth cerebral ventricle is easily visible as an and that at least in some cases of open spina bifida, caudal displacement of the brain is evident from the first trimester,
6 138 Chaoui and Nicolaides resulting in loss of the normal. It is certain that sonographers involved in first-trimester screening for aneuploidies will endeavour to obtain the exact mid-sagittal plane of the fetal face and as their eyes move from the NT to the nasal bone it is inevitable that they will also glance at the. If this is not visible the sonographers will be alerted to the possibility of an underlying open spina bifida and will undertake detailed examination of the fetal spine. Prospective large studies will determine the proportion of affected fetuses presenting with absent and the extent to which the week scan can provide an effective method for early diagnosis of open spina bifida. REFERENCES 1. Chaoui R, Benoit B, Mitkowska-Wozniak H, Heling KS, Nicolaides KH. Assessment of intracranial translucency () in the detection of spina bifida at the week scan. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009; 34: Nicolaides KH, Campbell S, Gabbe SG, Guidetti R. Ultrasound screening for spina bifida: cranial and cerebellar signs. Lancet 1986; 2: Van den Hof MC, Nicolaides KH, Campbell J, Campbell S. Evaluation of the lemon and banana signs in one hundred and thirty fetuses with open spina bifida. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990; 162: Ghi T, Pilu G, Falco P, Segata M, Carletti A, Cocchi G, Sanini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Prenatal diagnosis of open and closed spina bifida. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 28: Pilu G, Ghi T, Carletti A, Segata M, Perolo A, Rizzo N. Threedimensional ultrasound examination of the fetal central nervous system. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the hindbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995; 5: Timor-Tritsch IE, Monteagudo A, Santos R. Three-dimensional inversion rendering in the first- and early second-trimester fetal brain: its use in holoprosencephaly. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 32: Kim MS, Jeanty P, Turner C, Benoit B. Three-dimensional sonographic evaluations of embryonic brain development. J Ultrasound Med 2008; 27: Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH. Sonoembryology and early prenatal diagnosis of neural anomalies. Prenat Diagn 2009; 29: Goldstein I, Makhoul R, Tamir A, Rajamim BS, Nisman D. Ultrasonographic nomograms of the fetal fourth ventricle: additional tool for detecting abnormalities of the posterior fossa. J Ultrasound Med 2002; 21: Pilu G, Ghi T, Carletti A, Segata M, Perolo A, Rizzo N. Threedimensional ultrasound examination of the fetal central nervous system. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: Campbell S, Pryse-Davies J, Coltart TM, Seller MJ, Singer JD. Ultrasound in the diagnosis of spina bifida. Lancet 1975; 1: Roberts CJ, Evans KT, Hibbard BM, Laurence KM, Roberts EE, Robertson IB. Diagnostic effectiveness of ultrasound in detection of neural tube defect: the South Wales experience of 2509 scans ( ) in high-risk mothers. Lancet 1983; 2:
An introduction to fetal neurosonography using three-dimensional ultrasound
 An introduction to fetal neurosonography using three-dimensional ultrasound Taddei F, Fratelli N, Prefumo F, Franceshetti L, Signorelli M and Frusca T Maternal Fetal Medicine Unit, Department of Obstetrics
An introduction to fetal neurosonography using three-dimensional ultrasound Taddei F, Fratelli N, Prefumo F, Franceshetti L, Signorelli M and Frusca T Maternal Fetal Medicine Unit, Department of Obstetrics
Screening for trisomy 21 by fetal tricuspid regurgitation, nuchal translucency and maternal serum free β-hcg and PAPP-A at 11 + 0to13+ 6 weeks
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 27: 151 155 Published online 30 December 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2699 Screening for trisomy 21 by fetal tricuspid regurgitation,
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 27: 151 155 Published online 30 December 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2699 Screening for trisomy 21 by fetal tricuspid regurgitation,
Frontomaxillary and mandibulomaxillary facial angles at 11 + 0to13+ 6 weeks in fetuses with trisomy 18
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: 928 933 Published online 1 November 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.2/uog.5188 Frontomaxillary and mandibulomaxillary facial angles
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: 928 933 Published online 1 November 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.2/uog.5188 Frontomaxillary and mandibulomaxillary facial angles
Screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10 14 weeks: the role of ductus venosus blood flow
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12:380 384 Screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10 14 weeks: the role of ductus venosus blood flow A. Matias*, C. Gomes*, N. Flack*, N. Montenegro and K. H. Nicolaides*
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12:380 384 Screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10 14 weeks: the role of ductus venosus blood flow A. Matias*, C. Gomes*, N. Flack*, N. Montenegro and K. H. Nicolaides*
The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1
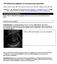 The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1 Werther Adrian Clavelli, MD 2, Silvia Susana Romaris de Clavelli, MD 2, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD 3 Adapted from The Ultrasound Detection of Chromosomal
The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1 Werther Adrian Clavelli, MD 2, Silvia Susana Romaris de Clavelli, MD 2, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD 3 Adapted from The Ultrasound Detection of Chromosomal
Patient information on soft markers
 Patient information on soft markers Before you read this section remember the following important points. The vast majority of babies with soft markers are normal. Soft markers are frequently seen in healthy
Patient information on soft markers Before you read this section remember the following important points. The vast majority of babies with soft markers are normal. Soft markers are frequently seen in healthy
The 11 13 +6 weeks scan
 The 11 13 +6 weeks scan Kypros H. Nicolaides The 11 13 +6 weeks scan Fetal Medicine Foundation, London 2004 Dedication to Herodotos & Despina Contents Introduction 1. First trimester diagnosis of chromosomal
The 11 13 +6 weeks scan Kypros H. Nicolaides The 11 13 +6 weeks scan Fetal Medicine Foundation, London 2004 Dedication to Herodotos & Despina Contents Introduction 1. First trimester diagnosis of chromosomal
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
 Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Fetal size and dating: charts recommended for clinical obstetric practice
 Fetal size and dating: charts recommended for clinical obstetric practice Pam Loughna 1, Lyn Chitty 2, Tony Evans 3 & Trish Chudleigh 4 1 Academic Division of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Nottingham University
Fetal size and dating: charts recommended for clinical obstetric practice Pam Loughna 1, Lyn Chitty 2, Tony Evans 3 & Trish Chudleigh 4 1 Academic Division of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Nottingham University
Sonographic screening for trisomy 13 at 11 to 13 D6 weeks of gestation
 American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (2006) 194, 397 401 www.ajog.org Sonographic screening for trisomy 13 at 11 to 13 D6 weeks of gestation Aris T. Papageorghiou, MD, a Kyriaki Avgidou, MD, a
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (2006) 194, 397 401 www.ajog.org Sonographic screening for trisomy 13 at 11 to 13 D6 weeks of gestation Aris T. Papageorghiou, MD, a Kyriaki Avgidou, MD, a
Clinical Studies Abstract Booklet
 Clinical Studies Abstract Booklet The Harmony Prenatal Test is a non-invasive prenatal test (NIPT) that assesses the risk of trisomies by analyzing cell-free DNA (cfdna) in maternal blood. Since January
Clinical Studies Abstract Booklet The Harmony Prenatal Test is a non-invasive prenatal test (NIPT) that assesses the risk of trisomies by analyzing cell-free DNA (cfdna) in maternal blood. Since January
Fetal Lateral Ventricular Width: What Should Be Its Upper Limit?
 Article Fetal Lateral Ventricular Width: What Should Be Its Upper Limit? A Prospective Cohort Study and Reanalysis of the Current and Previous Data Benny Almog, MD, Ronni Gamzu, MD, PhD, Reuven Achiron,
Article Fetal Lateral Ventricular Width: What Should Be Its Upper Limit? A Prospective Cohort Study and Reanalysis of the Current and Previous Data Benny Almog, MD, Ronni Gamzu, MD, PhD, Reuven Achiron,
Fetal echocardiography at 11 13 weeks by transabdominal high-frequency ultrasound
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 296 301 Published online 10 February 2011 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8934 Fetal echocardiography at 11 13 weeks by transabdominal
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 296 301 Published online 10 February 2011 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8934 Fetal echocardiography at 11 13 weeks by transabdominal
Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system: guidelines for performing the basic examination and the fetal neurosonogram
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 29: 109 116 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.3909 GUIDELINES Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system:
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 29: 109 116 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.3909 GUIDELINES Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system:
Prenatal Testing Special tests for your baby during pregnancy
 English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Trisomy 18: Is It Practical in the Early Second Trimester?
 Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Trisomy 18: Is It Practical in the Early Second Trimester? Laurence E. Shields, MD, Leslie A. Carpenter, MS, CGC, Karin M. Smith, RDMS, Hanh V. Nghiem, MD The objective of
Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Trisomy 18: Is It Practical in the Early Second Trimester? Laurence E. Shields, MD, Leslie A. Carpenter, MS, CGC, Karin M. Smith, RDMS, Hanh V. Nghiem, MD The objective of
The First Trimester Anatomy Scan. John R. Allbert, MD Novant Maternal-Fetal Medicine Associates
 The First Trimester Anatomy Scan John R. Allbert, MD Novant Maternal-Fetal Medicine Associates Anatomic Survey Second trimester (18-22 week) scan remains the gold standard First trimester evaluation of
The First Trimester Anatomy Scan John R. Allbert, MD Novant Maternal-Fetal Medicine Associates Anatomic Survey Second trimester (18-22 week) scan remains the gold standard First trimester evaluation of
Maternal serum free b-hcg and PAPP-A in fetal sex chromosome defects in the rst trimester
 PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS Prenat Diagn 2000; 20: 390±394. Maternal serum free b-hcg and PAPP-A in fetal sex chromosome defects in the rst trimester Kevin Spencer 1 *, Natasha Tul 2 and Kypros H. Nicolaides 2
PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS Prenat Diagn 2000; 20: 390±394. Maternal serum free b-hcg and PAPP-A in fetal sex chromosome defects in the rst trimester Kevin Spencer 1 *, Natasha Tul 2 and Kypros H. Nicolaides 2
First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome
 First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome What is first trimester risk assessment for Down syndrome? First trimester screening for Down syndrome, also known as nuchal translucency screening, is a test
First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome What is first trimester risk assessment for Down syndrome? First trimester screening for Down syndrome, also known as nuchal translucency screening, is a test
Charts of fetal size: limb bones
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology August 2002, Vol. 109, pp. 919 929 Charts of fetal size: limb bones Lyn S. Chitty a, *, Douglas G. Altman b Objective To construct new size
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology August 2002, Vol. 109, pp. 919 929 Charts of fetal size: limb bones Lyn S. Chitty a, *, Douglas G. Altman b Objective To construct new size
Neural tube defects: open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica)
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Neural tube defects: open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica) Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Neural tube defects: open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica) Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version
fi АУ : fi apple Ав Ав АУ . apple, АУ fiав Ав. АК applefi АУ, АУАв Ав fi АУ apple fi Ав. А applefi АУ АУ АУ АсА» Ас Ам, длappleapple Ас...
 АВАВАКдлАмА дла длама АсАядлАмА АВА АсдлАя & MАядлдлАмАК TА. 4, T. 2, АВ. 113-118, 2005 fi АУ : Аяapplefi. fiapple АсА» Ас Ам, длappleapple Ас..., Ая: Аяapplefi. fiapple, АВАУ Ас, АсА» Ас Ам длappleapple
АВАВАКдлАмА дла длама АсАядлАмА АВА АсдлАя & MАядлдлАмАК TА. 4, T. 2, АВ. 113-118, 2005 fi АУ : Аяapplefi. fiapple АсА» Ас Ам, длappleapple Ас..., Ая: Аяapplefi. fiapple, АВАУ Ас, АсА» Ас Ам длappleapple
3D Ultrasound. Outline. What is 3D US? Volume Sonography. 3D Ultrasound in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential. Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
 in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential Outline What is 3D US? What are obvious advantages of 3D US? What is the future of 3D US? Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 2D US
in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential Outline What is 3D US? What are obvious advantages of 3D US? What is the future of 3D US? Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 2D US
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center
 Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
Trisomies 13 and 18. -Maternal age. (Patau and Edward s syndrome)
 Trisomies 13 and 18 (Patau and Edward s syndrome) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) is the commonest chromosomal disorder at birth, and has been considered in detail in previous annual reports 23. Other relatively
Trisomies 13 and 18 (Patau and Edward s syndrome) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) is the commonest chromosomal disorder at birth, and has been considered in detail in previous annual reports 23. Other relatively
Down s Syndrome: Ultrasound Screening
 October 2001 Down s Syndrome: Ultrasound Screening Hilary Hochberg Advanced Radiology Clerkship Dr. Gillian Lieberman Patient M.C. 32 year old female presents at 16 weeks gestational age with abnormal
October 2001 Down s Syndrome: Ultrasound Screening Hilary Hochberg Advanced Radiology Clerkship Dr. Gillian Lieberman Patient M.C. 32 year old female presents at 16 weeks gestational age with abnormal
Clinical Significance of First Trimester Umbilical Cord Cysts
 Clinical Significance of First Trimester Umbilical Cord Cysts Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Sergio Leible, MD, Angel Ulloa, MD, Milenko Ivankovic, MD, Carlos Schnapp, MD A cystic mass of the umbilical cord was
Clinical Significance of First Trimester Umbilical Cord Cysts Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Sergio Leible, MD, Angel Ulloa, MD, Milenko Ivankovic, MD, Carlos Schnapp, MD A cystic mass of the umbilical cord was
Intrauterine sonographic assessments of embryonic heart diameter
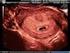 Human Reproduction vol.12 no.10 pp.2286 2291, 1997 Intrauterine sonographic assessments of embryonic heart diameter Toshiyuki Hata 1, Daisaku Senoh, Kohkichi Hata and Kohji Miyazaki Department of Obstetrics
Human Reproduction vol.12 no.10 pp.2286 2291, 1997 Intrauterine sonographic assessments of embryonic heart diameter Toshiyuki Hata 1, Daisaku Senoh, Kohkichi Hata and Kohji Miyazaki Department of Obstetrics
SOFT FETAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS
 SOFT FETAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Compiled by the Genetics Team at The Credit Valley Hospital Last updated February 2008 Page 2 This document refers to the ultrasound finding of a soft sign, as compared
SOFT FETAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Compiled by the Genetics Team at The Credit Valley Hospital Last updated February 2008 Page 2 This document refers to the ultrasound finding of a soft sign, as compared
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) Factsheet
 Introduction NIPT, which analyzes cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood, is a new option in the prenatal screening and testing paradigm for trisomy 21 and a few other fetal chromosomal aneuploidies.
Introduction NIPT, which analyzes cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood, is a new option in the prenatal screening and testing paradigm for trisomy 21 and a few other fetal chromosomal aneuploidies.
Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas
 Case Series Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas Juliana Leite, MD, Pamela Ross, RDMS, RDCS, A. Cristina Rossi, MD, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD Objective. The aim of this study was to evaluate
Case Series Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas Juliana Leite, MD, Pamela Ross, RDMS, RDCS, A. Cristina Rossi, MD, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD Objective. The aim of this study was to evaluate
Neural Tube Defects - NTDs
 Neural Tube Defects - NTDs Introduction Neural tube defects are also known as NTDs. They happen when the spine and brain do not fully develop while the fetus is forming in the uterus. Worldwide, there
Neural Tube Defects - NTDs Introduction Neural tube defects are also known as NTDs. They happen when the spine and brain do not fully develop while the fetus is forming in the uterus. Worldwide, there
F. I. VOS*, E. A. P. DE JONG-PLEIJ, L. S. M. RIBBERT, E. TROMP and C. M. BILARDO*
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012; 39: 636 641 Published online 10 April 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10058 Three-dimensional ultrasound imaging and measurement
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012; 39: 636 641 Published online 10 April 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10058 Three-dimensional ultrasound imaging and measurement
Long-Term Prognosis of Pregnancies Complicated by Slow Embryonic Heart Rates in the Early First Trimester
 Long-Term Prognosis of Pregnancies Complicated by Slow Embryonic Heart Rates in the Early First Trimester Peter M. Doubilet, MD, PhD, Carol B. Benson, MD, Jeanne S. Chow, MD Slow embryonic heart rates
Long-Term Prognosis of Pregnancies Complicated by Slow Embryonic Heart Rates in the Early First Trimester Peter M. Doubilet, MD, PhD, Carol B. Benson, MD, Jeanne S. Chow, MD Slow embryonic heart rates
11 13 +6 Weeks Scan Project Newsletter
 USA FETAL MEDICINE FOUNDATION OF THE UNITED STATES OF A MERICA Non-profit Registration No.1635069 July 2007 11 13 +6 Weeks Scan Project Naomi Greene MPH RDMS RDCS 3940 Laurel Canyon Blvd. #838 Studio City,
USA FETAL MEDICINE FOUNDATION OF THE UNITED STATES OF A MERICA Non-profit Registration No.1635069 July 2007 11 13 +6 Weeks Scan Project Naomi Greene MPH RDMS RDCS 3940 Laurel Canyon Blvd. #838 Studio City,
cfdna in maternal plasma obtained from a population undergoing routine screening at 11-13 weeks gestation.
 Reports of Major Impact www.ajog.org Noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal trisomies in a routinely screened first-trimester population Kypros H. Nicolaides, MD; Argyro Syngelaki, RM; Ghalia Ashoor, MD;
Reports of Major Impact www.ajog.org Noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal trisomies in a routinely screened first-trimester population Kypros H. Nicolaides, MD; Argyro Syngelaki, RM; Ghalia Ashoor, MD;
Implementation of maternal blood cell-free DNA testing in early screening for aneuploidies
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 34 40 Published online 7 June 2013 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12504 Implementation of maternal blood cell-free DNA testing in
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 34 40 Published online 7 June 2013 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12504 Implementation of maternal blood cell-free DNA testing in
Ultrasound scans in pregnancy
 Ultrasound scans in pregnancy www.antenatalscreening.wales.nhs.uk Copyright 2016 Public Health Wales NHS Trust. All rights reserved. Not to be reproduced in whole or in part without the permission of the
Ultrasound scans in pregnancy www.antenatalscreening.wales.nhs.uk Copyright 2016 Public Health Wales NHS Trust. All rights reserved. Not to be reproduced in whole or in part without the permission of the
Development of the human fetal corpus callosum: a high-resolution, cross-sectional sonographic study
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1; 18: 33 37 Development of the human fetal corpus callosum: Blackwell Science Ltd a high-resolution, cross-sectional sonographic study R. ACHIRON and A. ACHIRON* Department of
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1; 18: 33 37 Development of the human fetal corpus callosum: Blackwell Science Ltd a high-resolution, cross-sectional sonographic study R. ACHIRON and A. ACHIRON* Department of
Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering
 Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
CAR Standard for Performing Diagnostic Obstetric Ultrasound Examinations
 CAR Standard for Performing Diagnostic Obstetric Ultrasound Examinations The standards of the Canadian Association of Radiologists (CAR) are not rules, but are guidelines that attempt to define principles
CAR Standard for Performing Diagnostic Obstetric Ultrasound Examinations The standards of the Canadian Association of Radiologists (CAR) are not rules, but are guidelines that attempt to define principles
A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing
 Patient Education Page 29 A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing This section describes prenatal tests that give information about your baby s health. It is your choice whether or not to have these tests
Patient Education Page 29 A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing This section describes prenatal tests that give information about your baby s health. It is your choice whether or not to have these tests
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES. Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD
 LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
The First Trimester Screening program
 The First Trimester Screening program The Fetal Medicine Foundation This guide has been designed to highlight the important clinical aspects of using the First Trimester Screening program. It is not intended
The First Trimester Screening program The Fetal Medicine Foundation This guide has been designed to highlight the important clinical aspects of using the First Trimester Screening program. It is not intended
GE Healthcare VOLUSON 730 PRO The Diamond Release
 GE Healthcare VOLUSON 730 PRO The Diamond Release imagination at work VOLUSON 730 PRO The Standard in Women's Healthcare 4D Dedication Dimensional Diagnostic Digital GE Healthcare continues to elevate
GE Healthcare VOLUSON 730 PRO The Diamond Release imagination at work VOLUSON 730 PRO The Standard in Women's Healthcare 4D Dedication Dimensional Diagnostic Digital GE Healthcare continues to elevate
Ultrasound evaluation of fetal gender at 12 14 weeks
 Ultrasound evaluation of fetal gender at 12 14 weeks Marek Lubusky a,b, Martina Studnickova a, Ales Skrivanek a, Katherine Vomackova c, Martin Prochazka a Aims. The aim of this study was to assess the
Ultrasound evaluation of fetal gender at 12 14 weeks Marek Lubusky a,b, Martina Studnickova a, Ales Skrivanek a, Katherine Vomackova c, Martin Prochazka a Aims. The aim of this study was to assess the
Gutenberg Center in MALAGA
 Introduction Gutenberg Center in MALAGA Gutenberg Center in Málaga opened in 1987 as a clinic to provide integral assisstance for women, divided into 6 Units, specialized in the different aspects of Obs
Introduction Gutenberg Center in MALAGA Gutenberg Center in Málaga opened in 1987 as a clinic to provide integral assisstance for women, divided into 6 Units, specialized in the different aspects of Obs
Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein
 Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Antonio Mackenna, MD, Jorge Sanchez, MD, Edgardo Corral, MD, Eduardo Carstens, MD To assess the clinical significance of varix
Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Antonio Mackenna, MD, Jorge Sanchez, MD, Edgardo Corral, MD, Eduardo Carstens, MD To assess the clinical significance of varix
Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
 In: Recent Advances in Equine Theriogenology, B.A. Ball (Ed.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org) Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
In: Recent Advances in Equine Theriogenology, B.A. Ball (Ed.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org) Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus
 LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis
 Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Neural tube defects (NTDs): open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica)
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Neural tube defects (NTDs): open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Neural tube defects (NTDs): open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version
your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing.
 your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing. Accurate answers about your baby s health simply, safely, sooner. What is the verifi Prenatal
your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing. Accurate answers about your baby s health simply, safely, sooner. What is the verifi Prenatal
Contents. Introduction. 1 Standard views for examination of the fetus. 2 Central nervous system
 Contents Introduction 1 Standard views for examination of the fetus 2 Central nervous system Normal sonographic anatomy Neural tube defects Hydrocephalus and ventriculomegaly Holoprosencephaly Agenesis
Contents Introduction 1 Standard views for examination of the fetus 2 Central nervous system Normal sonographic anatomy Neural tube defects Hydrocephalus and ventriculomegaly Holoprosencephaly Agenesis
Clinical Policy: Ultrasound in Pregnancy Reference Number: CP.MP.38
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.38 Effective Date: 02/11 Last Review Date: 08/15 Revision Log Coding Implications See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.38 Effective Date: 02/11 Last Review Date: 08/15 Revision Log Coding Implications See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Embryonic Heart Rate as a Prognostic Factor for Chromosomal Abnormalities
 CME Article Embryonic Heart Rate as a Prognostic Factor for Chromosomal Abnormalities Deniz Oztekin, MD, Ozgur Oztekin, MD, Fatma I. Aydal, MD, Sivekar Tinar, MD, Zehra H. Adibelli, MD Objective. The purpose
CME Article Embryonic Heart Rate as a Prognostic Factor for Chromosomal Abnormalities Deniz Oztekin, MD, Ozgur Oztekin, MD, Fatma I. Aydal, MD, Sivekar Tinar, MD, Zehra H. Adibelli, MD Objective. The purpose
Ultrasonography of the Fetal Thyroid
 Article Ultrasonography of the Fetal Thyroid Nomograms Based on Biparietal Diameter and Gestational Age Angela C. Ranzini, MD, Cande V. Ananth, PhD, MPH, John C. Smulian, MD, MPH, Michelle Kung, Anita
Article Ultrasonography of the Fetal Thyroid Nomograms Based on Biparietal Diameter and Gestational Age Angela C. Ranzini, MD, Cande V. Ananth, PhD, MPH, John C. Smulian, MD, MPH, Michelle Kung, Anita
What is the diagnostic value of ultrasound for determining a viable intrauterine pregnancy?
 What is the diagnostic value of ultrasound for determining a viable intrauterine pregnancy? Full citation Sample size Tests Methods Results Limitations Steinkampf,M.P., Guzick,D.S., Hammond,K.R., Blackwell,R.E.,
What is the diagnostic value of ultrasound for determining a viable intrauterine pregnancy? Full citation Sample size Tests Methods Results Limitations Steinkampf,M.P., Guzick,D.S., Hammond,K.R., Blackwell,R.E.,
Inclusion of Early Fetal Deaths in a Birth Defects Surveillance System
 TERATOLOGY 64:S20 S25 (2001) Inclusion of Early Fetal Deaths in a Birth Defects Surveillance System MATHIAS B. FORRESTER AND RUTH D. MERZ* Hawaii Birth Defects Program, Honolulu, Hawaii 96817 ABSTRACT
TERATOLOGY 64:S20 S25 (2001) Inclusion of Early Fetal Deaths in a Birth Defects Surveillance System MATHIAS B. FORRESTER AND RUTH D. MERZ* Hawaii Birth Defects Program, Honolulu, Hawaii 96817 ABSTRACT
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners Testing and pregnancy
 Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners Testing and pregnancy Testing and pregnancy GP s role 3 Counselling before and during pregnancy 3 Collecting the family history
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners Testing and pregnancy Testing and pregnancy GP s role 3 Counselling before and during pregnancy 3 Collecting the family history
Increased fetal nuchal translucency at 11 14 weeks
 PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS Prenat Diagn 2002; 22: 308 315. Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/ pd.308 Increased fetal nuchal translucency at 11 14 weeks Kypros H.
PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS Prenat Diagn 2002; 22: 308 315. Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/ pd.308 Increased fetal nuchal translucency at 11 14 weeks Kypros H.
A test your patients can trust.
 A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
Placenta, Cord, & Fluid
 , Cord, & Fluid Abruption Accreta/Increta/Percreta Chorioangioma Complete Partial Not generally Relevant to U/S Gestational Age (Weeks) Distance from 16-23.9 24 to Internal Os >20 mm No No 11-20 mm 0-10
, Cord, & Fluid Abruption Accreta/Increta/Percreta Chorioangioma Complete Partial Not generally Relevant to U/S Gestational Age (Weeks) Distance from 16-23.9 24 to Internal Os >20 mm No No 11-20 mm 0-10
Executive summary. Current prenatal screening
 Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. NIPT: dynamics and ethics of prenatal screening. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2013; publication no. 2013/34. In recent years, new tests
Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. NIPT: dynamics and ethics of prenatal screening. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2013; publication no. 2013/34. In recent years, new tests
Birth Defects and Prenatal Diognosis. Assoc. Prof. E. Elif Güzel, MD
 Birth Defects and Prenatal Diognosis Assoc. Prof. E. Elif Güzel, MD Birth Defects Structural, behavioral, functional, metabolic disorders present at birth Leading cause of infant mortality (%25) Importance
Birth Defects and Prenatal Diognosis Assoc. Prof. E. Elif Güzel, MD Birth Defects Structural, behavioral, functional, metabolic disorders present at birth Leading cause of infant mortality (%25) Importance
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Analytical goal setting in aneuploidy screening: within person biological variability of first trimester biochemical markers
 DOI: 10.1002/pd.4019 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analytical goal setting in aneuploidy screening: within person biological variability of first trimester biochemical markers Kevin Spencer* and Nicholas J. Cowans
DOI: 10.1002/pd.4019 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analytical goal setting in aneuploidy screening: within person biological variability of first trimester biochemical markers Kevin Spencer* and Nicholas J. Cowans
Fetal loss following ultrasound diagnosis of a live fetus at 6 10 weeks of gestation
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23; 22: 368 372 Published online 2 September 23 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.24 Fetal loss following ultrasound diagnosis of a live fetus
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23; 22: 368 372 Published online 2 September 23 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.24 Fetal loss following ultrasound diagnosis of a live fetus
First-Trimester Cesarean Scar Pregnancy Evolving Into Placenta Previa/Accreta at Term
 Case Report First-Trimester Cesarean Scar Pregnancy Evolving Into Placenta Previa/Accreta at Term Jara Ben Nagi, MD, Dede Ofili-Yebovi, MD, Mike Marsh, MD, Davor Jurkovic, MD Placenta accreta is a rare
Case Report First-Trimester Cesarean Scar Pregnancy Evolving Into Placenta Previa/Accreta at Term Jara Ben Nagi, MD, Dede Ofili-Yebovi, MD, Mike Marsh, MD, Davor Jurkovic, MD Placenta accreta is a rare
CONFIDENT CODING FOR OB/GYN CONFIDENT CODING FOR OB/GYN
 Arlene J. Smith, CPC AAPC National Advisory Board 2007-2009 1 So when exactly does the global period start? Unraveling the confusion in antepartum care coding Correct coding for multiple gestations! Vaginal
Arlene J. Smith, CPC AAPC National Advisory Board 2007-2009 1 So when exactly does the global period start? Unraveling the confusion in antepartum care coding Correct coding for multiple gestations! Vaginal
The first 3,000 Non-Invasive Prenatal Tests (NIPT) with the Harmony test in Belgium and the Netherlands
 FVV in ObGyn, 2014, 6 (1): 7-12 Preliminary report The first 3,000 Non-Invasive Prenatal Tests (NIPT) with the Harmony test in Belgium and the Netherlands P.J. Willems 1, H. Dierickx 1, ES. Vandenakker
FVV in ObGyn, 2014, 6 (1): 7-12 Preliminary report The first 3,000 Non-Invasive Prenatal Tests (NIPT) with the Harmony test in Belgium and the Netherlands P.J. Willems 1, H. Dierickx 1, ES. Vandenakker
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder. Chapter 14. Copyright 2008 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
Applications of Doppler Ultrasound in Fetal Growth Assessment. David Cole
 Applications of Doppler Ultrasound in Fetal Growth Assessment David Cole Aims The aim of this presentation is to consider the use of Doppler ultrasound to investigate and monitor those pregnancies at risk
Applications of Doppler Ultrasound in Fetal Growth Assessment David Cole Aims The aim of this presentation is to consider the use of Doppler ultrasound to investigate and monitor those pregnancies at risk
The California Prenatal Screening Program
 The California Prenatal Screening Program Quad Marker Screening One blood specimen drawn at 15 weeks - 20 weeks of pregnancy (second trimester) Serum Integrated Screening Prenatal Patient Booklet - English
The California Prenatal Screening Program Quad Marker Screening One blood specimen drawn at 15 weeks - 20 weeks of pregnancy (second trimester) Serum Integrated Screening Prenatal Patient Booklet - English
Chiari malformations
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
Human Embryology. Weeks 1-4
 Human Embryology Weeks 1-4 Week 1 Fertilisation to Implantation For this presentation embryonic age will be expressed as days or weeks from fertilisation. On this basis human pregnancy lasts about 266±3
Human Embryology Weeks 1-4 Week 1 Fertilisation to Implantation For this presentation embryonic age will be expressed as days or weeks from fertilisation. On this basis human pregnancy lasts about 266±3
Sequencing-based Tests to Determine Trisomy 21 from Maternal Plasma DNA
 Sequencing-based Tests to Determine Trisomy 21 from Maternal Plasma DNA Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.03.006 09/01/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 09/01/2013
Sequencing-based Tests to Determine Trisomy 21 from Maternal Plasma DNA Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.03.006 09/01/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 09/01/2013
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Kayseri Military Hospital, Kayseri, Turkey
 Orıgınal Article Obstetrics & Gynecology North Clin Istanbul 2015;2(2):92-100 doi: 10.14744/nci.2015.08370 A prospective study to assess the clinical impact of interobserver reliability of sonographic
Orıgınal Article Obstetrics & Gynecology North Clin Istanbul 2015;2(2):92-100 doi: 10.14744/nci.2015.08370 A prospective study to assess the clinical impact of interobserver reliability of sonographic
Obstetrical Ultrasound Policy
 Policy Number 2016R7112F Obstetrical Ultrasound Policy Annual Approval Date 1/27/2014 Approved By United HealthCare Community Plan Payment Policy Committee IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY
Policy Number 2016R7112F Obstetrical Ultrasound Policy Annual Approval Date 1/27/2014 Approved By United HealthCare Community Plan Payment Policy Committee IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY
TMMC&RC, Teerthanker Mahaveer University, Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh, India, 244001 Mobile No.: +91-9997605146, E Mail drnidhivarshney@gmail.
 SEXUAL DIMORPHISM IN CERVICAL VERTEBRAL CANAL MEASUREMENTS OF HUMAN FOETUSES Nidhi Sharma *, Farah Ghaus, Nafis Ahmad Faruqi, Raghuveer Singh Mandloi * Correspondence to: Dr. Nidhi Sharma, Assistant Professor,
SEXUAL DIMORPHISM IN CERVICAL VERTEBRAL CANAL MEASUREMENTS OF HUMAN FOETUSES Nidhi Sharma *, Farah Ghaus, Nafis Ahmad Faruqi, Raghuveer Singh Mandloi * Correspondence to: Dr. Nidhi Sharma, Assistant Professor,
An OB US protocol book is available in the reading room to help you learn what is needed for problem cases.
 HIGH RISK OBSTETRIC ULTRASOUND GUIDELINES Dolores H. Pretorius, M.D., Mary K. O Boyle M.D. and Lori Romine M.D. The obstetric ultrasound rotation is designed to emphasize an experience that relies on a
HIGH RISK OBSTETRIC ULTRASOUND GUIDELINES Dolores H. Pretorius, M.D., Mary K. O Boyle M.D. and Lori Romine M.D. The obstetric ultrasound rotation is designed to emphasize an experience that relies on a
M2 Pathology Course Phone: 312-996-1772 Lecture # 72 e-mail: tiborv@uic.edu Tuesday, February 11, 2003 9:30 10:20
 Tibor Valyi-Nagy, M.D., Ph.D. UIC College of Medicine Assistant Professor of Pathology, UIC M2 Pathology Course Phone: 312-996-1772 Lecture # 72 e-mail: tiborv@uic.edu Tuesday, February 11, 2003 9:30 10:20
Tibor Valyi-Nagy, M.D., Ph.D. UIC College of Medicine Assistant Professor of Pathology, UIC M2 Pathology Course Phone: 312-996-1772 Lecture # 72 e-mail: tiborv@uic.edu Tuesday, February 11, 2003 9:30 10:20
Prenatal Screening Policies in Europe
 Prenatal Screening Policies in Europe 2010 EUROCAT Central Registry Room 12L09, University of Ulster Newtownabbey, Co Antrim Northern Ireland, BT37 0QB Tel: +44 (0)28 90366639 Fax: +44 (0)28 90368341 Email:
Prenatal Screening Policies in Europe 2010 EUROCAT Central Registry Room 12L09, University of Ulster Newtownabbey, Co Antrim Northern Ireland, BT37 0QB Tel: +44 (0)28 90366639 Fax: +44 (0)28 90368341 Email:
The California Prenatal Screening Program
 The California Prenatal Screening Program Provider ook netic Disease Screening Program Quad Marker Screening Serum Integrated Screening Full Integrated Screening TABLE OF CONTENTS WELCOME to the California
The California Prenatal Screening Program Provider ook netic Disease Screening Program Quad Marker Screening Serum Integrated Screening Full Integrated Screening TABLE OF CONTENTS WELCOME to the California
BELIEVE MIDWIFERY SERVICES, LLC
 , LLC TITLE: ESTABLISHING the GESTATIONAL AGE & ROUTINE ULTRASOUND EFFECTIVE DATE: November 11th, 2013 POLICY STATEMENT Establishing accurate pregnancy dating impacts the management of normal and abnormal
, LLC TITLE: ESTABLISHING the GESTATIONAL AGE & ROUTINE ULTRASOUND EFFECTIVE DATE: November 11th, 2013 POLICY STATEMENT Establishing accurate pregnancy dating impacts the management of normal and abnormal
Birth defects. Report by the Secretariat
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
INTERGROWTH-21 st International Fetal and Newborn Growth Standards for the 21 st Century
 INTERGROWTH-21 st CRL standardization 1 INTERGROWTH-21 st International Fetal and Newborn Growth Standards for the 21 st Century The International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium Correct measurement
INTERGROWTH-21 st CRL standardization 1 INTERGROWTH-21 st International Fetal and Newborn Growth Standards for the 21 st Century The International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium Correct measurement
Doppler Ultrasound in the Management of Fetal Growth Restriction Chukwuma I. Onyeije, M.D. Atlanta Perinatal Associates
 Doppler Ultrasound in the Management of Fetal Growth Restriction Chukwuma I. Onyeije, M.D. Atlanta Perinatal Associates 1 For your convenience a copy of this lecture is available for review and download
Doppler Ultrasound in the Management of Fetal Growth Restriction Chukwuma I. Onyeije, M.D. Atlanta Perinatal Associates 1 For your convenience a copy of this lecture is available for review and download
Surface area measurement using rendered three-dimensional ultrasound imaging: an in-vitro phantom study
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 211; 38: 445 449 Published online 13 September 211 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.8984 Surface area measurement using rendered three-dimensional
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 211; 38: 445 449 Published online 13 September 211 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.8984 Surface area measurement using rendered three-dimensional
How To Use A Voluson Compact Ultrasound System
 Voluson i Extraordinary vision Compact series Extraordinary vision to care for your patients. Your needs shape the future of ultrasound. It s your feedback that drives every technological advancement that
Voluson i Extraordinary vision Compact series Extraordinary vision to care for your patients. Your needs shape the future of ultrasound. It s your feedback that drives every technological advancement that
isuog.org GUIDELINES ISUOG Practice Guidelines: performance of first-trimester fetal ultrasound scan
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 102 113 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12342 isuog.org GUIDELINES ISUOG Practice Guidelines: performance of first-trimester
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 102 113 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12342 isuog.org GUIDELINES ISUOG Practice Guidelines: performance of first-trimester
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, United States
 78 Four Dimensional Fetal Echocardiography, 2010, 78-83 CHAPTER 9 Automated Echocardiography Elena Sinkovskaya and Alfred Abuhamad Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Eastern Virginia Medical School,
78 Four Dimensional Fetal Echocardiography, 2010, 78-83 CHAPTER 9 Automated Echocardiography Elena Sinkovskaya and Alfred Abuhamad Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Eastern Virginia Medical School,
Cornual ruptured pregnancy with placenta increta CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE
 142 CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE Agarwal NR 1, Rani A 1 *, Batra S 1 1. Department of Obststetrics and Gynaecology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banares Hindu Univarsity.
142 CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE Agarwal NR 1, Rani A 1 *, Batra S 1 1. Department of Obststetrics and Gynaecology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banares Hindu Univarsity.
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
THE USE OF FIRST TRIMESTER ULTRASOUND
 SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES THE USE OF FIRST TRIMESTER ULTRASOUND This guideline has been reviewed by the Diagnostic Imaging Committee and approved by the Executive and Council of the Society of
SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES THE USE OF FIRST TRIMESTER ULTRASOUND This guideline has been reviewed by the Diagnostic Imaging Committee and approved by the Executive and Council of the Society of
Position Statement from the Aneuploidy Screening Committee on Behalf of the Board of the International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis, April 2013
 Position Statement from the Aneuploidy Screening Committee on Behalf of the Board of the International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis, April 2013 Peter Benn (Chair), Antoni Borell, Rossa Chiu, Howard Cuckle,
Position Statement from the Aneuploidy Screening Committee on Behalf of the Board of the International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis, April 2013 Peter Benn (Chair), Antoni Borell, Rossa Chiu, Howard Cuckle,
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chiari Malformation: An Overview
 Chiari Malformation: An Overview SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS LIVING WITH CHIARI TREATMENT Rick Labuda, Executive Director director@conquerchiari.org 724-940-0116 Disclaimer: This presentation is intended for informational
Chiari Malformation: An Overview SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS LIVING WITH CHIARI TREATMENT Rick Labuda, Executive Director director@conquerchiari.org 724-940-0116 Disclaimer: This presentation is intended for informational
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
